Use of Twitter as an Educational Resource. Analysis of Concepts of Active and Trainee Teachers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Importance of Social Networks for Social Development
2.2. Approach to the Concept of Social Networks
2.3. Potential of Educational Social Networks.
- They offer interactive and effective tools for teaching and learning. In addition, the integration of tools and applications (blogs, chat, email, forums) by these services provides a very suitable scenario for the practice of most of the activities of working in online environments.
- They enable the teacher who uses these resources to teach his or her students to acquire skills to stand on their own feet, and to continue learning in a world undergoing an accelerated process of change and transformation.
- Not only do they enable the transmission of knowledge and collaboration between people. Moreover, they develop technological skills that are essential for operating in diverse and complex contexts.
- Enable students to develop skills and abilities such as socialization, teamwork, or the importance of sharing.
- They help teachers and students to become aware of the importance of digital identity and the social processes of participation, opinion formation, and decision-making that characterize an advanced and democratic society.
- They allow students to learn by doing things. Cognitive processes evolve through the transformation and manipulation of information. High-level cognitive skills are developed, such as reasoning, the ability to synthesize and analyze, and decision-making.
- From the teachers’ point of view, they constitute a magnificent opportunity for learning, permanent training, and professional development.
- They offer unparalleled opportunities for the dissemination of educational and institutional activity of schools.
2.4. The Teacher’s Role in Using Social Networks for Learning
2.5. The Student’s Role in Social Networks, Their Learning Styles, and Strategies
- To know the incidence of social networks as a teaching and learning strategy;
- To value the degree of importance of social networks for teachers;
- To know the different educational resources available in the social networks;
- To know what kind of training is acquired through social networks as an educational and training method.
3. Method
3.1. Subjects of the Research
- (a)
- Teachers:
- They teach in primary education.
- At least 5 years of service.
- They work in schools that carry out innovative activities and that the schools have innovation flows.
- (b)
- Future teachers:
- Last year of training.
- They were in their final training period.
3.2. Data Analysis
- 1.
- Pre-analysis;
- 2.
- Use of the material;
- 3.
- Treatment of results, inference, and interpretation.
4. Results
4.1. Knowledge of Social Networks as a Teaching and Learning Strategy
“The social networks I normally use are Twitter and Facebook. I think they’re two powerful tools for teacher communication.”(T3)
“I prefer to use Facebook because through group creation it is easier to be connected with other teachers.”(T14)
“I like Facebook and Twitter. I use them both to know what other teachers are doing and to learn from them.”(S12)
“I use Facebook too. There are many pages like Active Teaching, Innovative Teachers, Networking, Masters 25, etc. I actually use Twitter and Facebook to find out what other teachers are doing.”(S13)
“What I use a lot is Orientación Andújar. I follow him on Facebook and Twitter, and they have a lot of material.”(S15)
“I consider the use of social networks essential to my training.”(S2)
“[…] I can see through the social networks what I’ve been learning since the theory. It is a way of looking at educational practice.”(S8)
“I use it a lot for my professional development. We teachers have to keep moving forward.”(T9)
4.2. Importance of Social Networks for Teachers
“Social networks are very important to me because they help me to know what teachers are doing and I can maintain communication with them.”(S1)
“The use of social networks for teachers is very important because they can be in contact with each other, see what they are working on in the classroom, improve their content through feedback and be able to work as a team, even if that person is not in your same school. A great learning community is generated.”(S10)
“It is a good resource to have teachers because you can get experiences from other teachers about methodologies and resources that interest you, but you always have to know how to use it.”(S12)
“Social networks are a great resource to share educational experiences and see what other teachers are working on. It is a great opportunity to learn in an indirect way and to know how you do it and to be able to adapt those contents to your classroom reality.”(S1)
“From the new technologies there is a great variety of opportunities and there are teachers who are doing something new for example in Galicia may be sharing information with teachers in Andalusia. I do think that sharing methodologies through networks and ideas can bring positive things. I think it is very useful and powerful.”(S6)
“These are used for communication between professionals, but also for finding resources and tools. I consider that it improves my technological competence.”(S12)
“I use social networks as a teaching medium because I like to see what other people are working on and see if I can adapt it to my class. The truth is that a window to see what they do and to make known what you do in the classroom.”(T11)
“[…] also, as a teaching tool. I see this as a great opportunity to show and make known what we are working on in the centre and at the same time also to take ideas from other centres that are working on project-based methodology. The truth is that this type of network is particularly good for communication between teachers […]”(T4)
“What we do is make known what we are working on so that other teachers elsewhere can see it and whether it is useful for their classroom and be able to adapt it to that context […]”(T6)
“[…] It’s a continuous feedback because you can show how you do it and people are helping you.”(T11)
“I keep my own blog […] I share these tools so that other teachers can see them and adapt them to their needs and interests […]”(T5)
4.3. To Know What Type of Training is Acquired through Social Networks as an Educational and Training Route
“We try to always be in connection with the family and the children so that we can exchange knowledge. Then we have an internal chat at family level where I can communicate […]”(T4)
“We have a blog for each course from 3rd to 6th where each student has their own email and we are in constant contact with them and their families […]”(T2)
“I think so because it is a way to share what we all do, the ideas that each teacher has, because it can be through social networks. Not only talk to the teachers in the environment but see what they do elsewhere and that maybe I want to implement in the classroom.”(S11)
“It is a great opportunity to get to know what is being worked on in other contexts and in other classrooms and to see if you are really interested and to be able to adapt it to your classroom needs.”(T11)
“I find it very useful because it is good to be connected with other colleagues in other areas and see what they are working on and whether we can use it in our context.”(T14)
“Very much so. In fact, one of the internal training we have to do here involves the Google Drive and it is very easy to use and we plan to have teachers come in who do not handle it so that we can teach them how it works. We also have “sites” that are like a Gmail platform where students can hang up to see their work.”(T2)
“I’m not interested in social networks at all […] because it distracts me from what’s important. And most of the social networks is because teachers start to publish a lot because I think you want to have that degree of social recognition and show that you know certain things. I can understand that, but I don’t share that idea.”(T9)
4.4. To Know the Different Educational Resources Available on Social Networks
“The resources we select are essential for the correct learning of our students.”(T9)
“KARUBA. Card game and its possibilities.”(S8)
“Big Sun is a game to learn English from the Montessori methodology. The truth is that it is an especially important resource.”(T1)
“Having fun with DIXIT, a classic! You learn through fun and game-based learning.”(T6)
“The Club Lia platform gives a results screen with details of time, correct and incorrect attempts for the evaluation of the student.”(T5)
“The Club Lia platform includes video tutorials, internships and cross-cutting projects.”(T5)
“A selection of educational video games should be made they will serve to reinforce your students’ knowledge and even have fun learning.”(T2)
5. Discussion
6. Limitations and Future Works
7. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mancini, T.; Imperato, C. Can Social Networks Make Us More Sensitive to Social Discrimination? E-Contact, Identity Processes and Perception of Online Sexual Discrimination in a Sample of Facebook Users. Soc. Sci. 2020, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachos, G.; Paraskevopoulou-Kollia, E.-A.; Anagnostopoulos, I. Social media Uso in higher education: A review. Educ. Sci. 2018, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, C.C.S.C. La llegada de las nuevas tecnologías a la educación y sus implicaciones. Int. J. New Educ. 2019, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares Carmona, K.M.; Angulo Armenta, J.; Torres Gastelú, C.A.; Madrid García, E.M. Las TIC en educación: Metaanálisis sobre investigación y líneas emergentes en México. Apert. (Guadalaj. Jal.) 2016, 8, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, D.D.B.; Olivares, N.R.; Sandoval, J.R.G.; Cervantes, D.C. Tic-Innovación-Educación: Aportes, Estudios Y Reflexiones; Palibrio: Madrid, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, I.M.; Olivera-Smith, M. Learning in social networks: Rationale and ideas for its implementation in Higher education. Educ. Sci. 2013, 3, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, S.; Ranieri, M. Implicaciones de los sitios de redes sociales para la enseñanza y el aprendizaje. Dónde estamos y hacia dónde queremos ir. Educ. Y Tecnol. De La Inf. 2017, 22, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Díaz, V.; Sampedro-Requena, B.E.; Flores, J.F.F. ¿Inclusividad en las herramientas web 2.0? Educ. Soc. 2018, 39, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, I. Monográfico: Redes Sociales; Ministerio de Educación, Cultura y Deporte: Madrid, Spain, 2012; Available online: http://recursostic.educacion.es/observatorio/web/es/internet/web-20/1043-redes-sociales (accessed on 15 June 2019).
- De Haro, J.J. Redes Sociales Para la Educación; Anaya: Madrid, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- García, M.C.; Seco, J.A.; Del Hoyo, M. La participación de los jóvenes en las redes sociales. Anàlisi: Quad. De Comun. I Cult. 2013, 48, 95–110. [Google Scholar]
- García, E.G.; Heredia, N.M. Redes sociales como factor incidente en el área social, personal y académica de alumnos de Educación Secundaria Obligatoria. Tendencias Pedagógicas 2018, 32, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, J.F.G.; Mira, Y.M.O. La globalización y la importancia de las TIC en el desarrollo social. Revista Reflexiones y Saberes 2019, 11, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, S.; Singh, T. Las redes sociales su impacto con aspectos positivos y negativos. Rev. Int. De Tecnol. E Investig. De Apl. Inf. 2016, 5, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Global Monitoring Report on Education. 2015. Available online: Es.unesco.org/gem-report/ (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Dafoulas, G.; Shokri, A. Investigating the educational value of social learning networks: A quantitative analysis. Interact. Technol. Smart Educ. 2016, 13, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, S.; Greenhow, C. Educational networking: A novel discipline for improved K-12 learning based on social networks. In Educational Networking; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–41. [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga, J. Las comunidades de aprendizaje y la evaluación formativa: Una experiencia significativa para transformar la práctica docente y el aprendizaje de los estudiantes desde el programa Todos a Aprender. Assensus 2018, 3, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, H.; Hernández, E. Redes sociales y educación. Sinectica 2012, 39. Available online: https://sinectica.iteso.mx/index.php/SINECTICA/article/view/75/67 (accessed on 25 March 2020).
- Mayor-Ruíz, C. El Asesoramiento Pedagógico Para la Formación Docente del Profesorado Universitario; Universidad de Sevilla: Sevilla, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mestres, L. Redes Sociales y Educación: Hacia la Innovación Didáctica. 2011; Available online: https://www.educaweb.com/noticia/2011/01/31/redes-sociales-educacion-innovacion-didactica-4583/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Santamaría, F. Posibilidades pedagógicas. Redes sociales y comunidades educativas. Telos Cuad. De Comun. E Innovación 2008, 76, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mero, K.; Merchán, E.; Mackenzie, A. Las redes sociales y su importancia en la educación superior. Opuntia Brava 2018, 9, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiro, B.E.; Montaño, P.F.; López, R.M. Del uso de las redes sociales: El caso de twitter como herramienta participativa para la intervención social. In Enfoques Y Exp. De Innovación Educ. Con Tic En Educ. Super; Allueva Pinilla and Alejandre Marco (cords.), Ed.; Prensas de la Universidad de Zaragoza: Zaragoza, Spain, 2019; pp. 299–317. [Google Scholar]
- Artero, B.N. Available online: http://www.educaweb.com/noticia/2011/01/31/interaccion-como-eje-aprendizaje-redes-sociales-14570.html (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Geijo, P.M. Estilos de enseñanza: Conceptualización e Investigación. (En función de los estilos de aprendizaje de Alonso, Gallego and Honey). Rev. De Estilos De Aprendiz. 2009, 2, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Garger, S.; Guild, P. Learning Styles: The Crucial Differences. Curric. Rev. 1984, 23, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Donolo, D. Estudiantes, Estrategias y Contextos de Aprendizaje Presenciales y Virtuales. In Proceedings of the Congreso Virtual Latinoamericano de Educación a Distancia, Río Cuarto, Argentina, 23 March–4 April 2004; Available online: https://isfd87-bue.infd.edu.ar/sitio/upload/Chiecher20Estudiar1_1.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Torres, F.V. SOMECE. 2004. Available online: http://www.somece.org.mx/simposio2004/memorias/ (accessed on 12 March 2020).
- Sandin, M.P. Investigación Cualitativa en Educación. In Fundamentos y Tradiciones; Mc Graw Hill: Madrid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Flick, U. El Diseño de Investigación Cualitativa; Morata: Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Denzin, N.K.; Lincoln, Y.S. The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research; SAGE: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Flick, U. Introducción a la Investigación Cualitativa, 3rd ed.; Morata: Madrid, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bardin, L. Análisis de Contenido; Akal: Madrid, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tójar, J.C. Investigación Cualitativa. Comprender y Actuar; La Muralla: Madrid, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Krippendorff, K. Metodología de Análisis de Contenido. Teoría y Práctica; Paidós: Barcelona, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- McMillan, J.H.; Schumacher, S. Investigación Educativa. In Una Introducción Conceptual, 5th ed.; Pearson Educación: Madrid, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar, N.M. A social network perspective on teacher collaboration in schools: Theory, methodology, and applications. Am. J. Educ. 2012, 119, 7–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.; Dawley, L. Social network knowledge construction: Emerging virtual world pedagogy. Horizen 2009, 17, 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, L.J.; Hall, C.M. A survey of K-12 teachers’ utilization of social networks as a professional resource. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2018, 23, 633–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, B.; McKenzie, B. Social networking tools for teacher education. In Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference; Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE): Waynesville, NC, USA, 2008; pp. 2772–2776. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal, C.E.; Martínez, J.G.; Fortuño, M.L.; Cervera, M.G. Actitudes y expectativas del uso educativo de las redes sociales en los alumnos universitarios. RUSC Univ. Knowl. Soc. J. 2011, 8, 171–185. [Google Scholar]
- Higueras-Rodríguez, L.; Martín-Romera, A.; Molina, E. Las redes sociales como vía para la formación docente en el uso de herramientas lúdico/didácticas. In Experiencias Pedagógicas e Innovación Educativa. Aportaciones Desde la Praxis Docente e Investigadora; Eloy, L.M., David, C.S., Antonio, H.M.P., Laura, M.G., Alicia, J.M., Eds.; Octaedro: Barcelona, Spain, 2018; pp. 2943–2951. [Google Scholar]
- Moghavvemi, S.; Sulaiman, A.; Jaafar, N.I.; Kasem, N. Las redes sociales como una herramienta de aprendizaje complementaria para la enseñanza y el aprendizaje: El caso de youtube. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2018, 16, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, J. Redes Sociales y Educación; Universidad de Málaga: Málaga, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Çam, E.; Isbulan, O. A new addiction for teacher candidates: Social networks. Turk. Online J. Educ. Technol. -Tojet 2012, 11, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ranieri, M.; Manca, S.; Fini, A. Why (and how) do teachers engage in social networks? An exploratory study of professional use of F acebook and its implications for lifelong learning. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2012, 43, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, V.; Cabero, J. Las redes sociales en educación: Desde la innovación a la investigación educativa. Ried. Rev. Iboeroamericana De Educ. A Distancia 2019, 22, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, L.J.; Hall, C.M. Una encuesta sobre la utilización de las redes sociales por parte de los maestros de K-12 como recurso profesional. Educ. Y Tecnol. De La Inf. 2018, 23, 633–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestridge, S. Categorizar el uso que los docentes hacen de las redes sociales para su aprendizaje profesional: Un paradigma de aprendizaje profesional autogenerado. Comput. Y Educ. 2019, 129, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
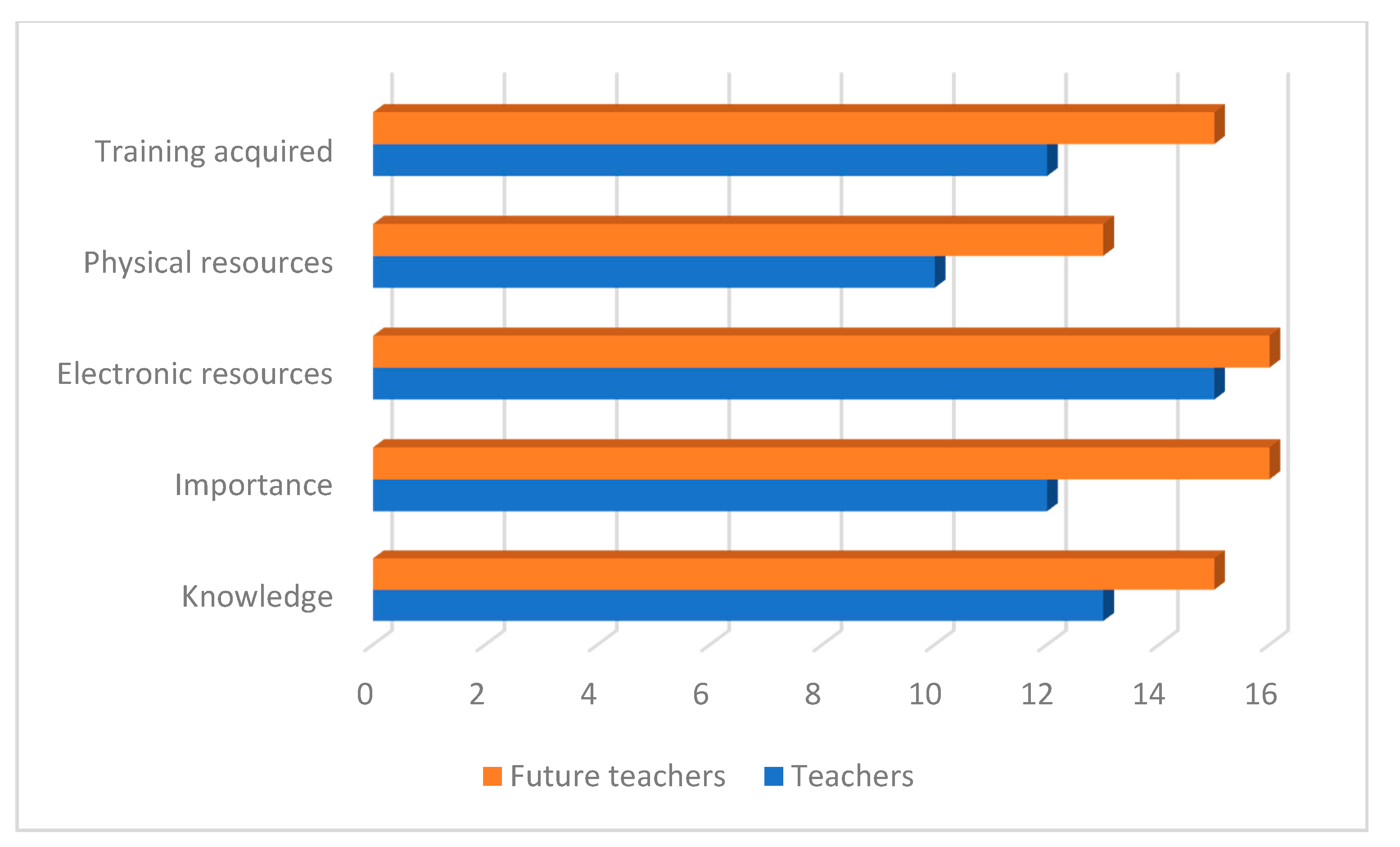
|
| Category and Code | Definition |
|---|---|
| Knowledge KN | Teachers’ knowledge of social networks as a training tool |
| Importance IM | Level of involvement of social networks in the teaching and learning process |
| Electronic Resources ER | Possible educational resources. Electronic resources that can be used in the classroom |
| Physical Resources PR | Possible educational resources. Resources that are physically available to work in the classroom |
| Training Acquired TA | Training aspects related to the use of social networks in education |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Higueras-Rodríguez, L.; Medina-García, M.; Pegalajar-Palomino, M.d.C. Use of Twitter as an Educational Resource. Analysis of Concepts of Active and Trainee Teachers. Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10080200
Higueras-Rodríguez L, Medina-García M, Pegalajar-Palomino MdC. Use of Twitter as an Educational Resource. Analysis of Concepts of Active and Trainee Teachers. Education Sciences. 2020; 10(8):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10080200
Chicago/Turabian StyleHigueras-Rodríguez, Lina, Marta Medina-García, and Mª del Carmen Pegalajar-Palomino. 2020. "Use of Twitter as an Educational Resource. Analysis of Concepts of Active and Trainee Teachers" Education Sciences 10, no. 8: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10080200
APA StyleHigueras-Rodríguez, L., Medina-García, M., & Pegalajar-Palomino, M. d. C. (2020). Use of Twitter as an Educational Resource. Analysis of Concepts of Active and Trainee Teachers. Education Sciences, 10(8), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10080200






