1. Introduction
- Cassie:
- -and people are wanting to cross into the United States because they might…?
- Ari:
- Because they might be in danger.
- Cassie:
- Oh, they might live in a dangerous place.
- Ari:
- Yeah, so, basically I’m saying, keep walls down instead of up. ‘Cause, I hate the wall, ‘cause it’s not bringing immigrants, or anyone in. So, it’s not good. Donald Trump, boo! (laughs)
In the final week of the 2016–2017 academic year, Ari—a self-identified mixed-race (Black/Brown) girl dressed in a makeshift costume and carrying a box crafted as a backpack—summarized her argument against the GOP Administration’s proposed border wall with Mexico. Ari emphasized a very real reason individuals opt to make the treacherous journey toward the United States (U.S.)—many (im)migrants (including those in the now infamous “Caravan” that was tear-gassed in November 2018) are fleeing violence in their home countries. Yet, Ari both provided a rationale for why (im)migrants present themselves at the border and stated her opinion on the proposed border wall and the overseeing authority, GOP party leader Donald Trump. Here, and in the longer conversation we shared, Ari displayed a critical understanding of the issue at hand. Moreover, Ari and three other Black girls combined analog and digital materials in a recorded performance to critique contemporary (im)migration policies.
The snippet of the conversation Ari and I shared in early June 2017 in the opening of this article was part of the culminating activities of a persuasive writing unit within Ms. Honey’s third-grade class at Community School J, an urban public elementary school in the Midwestern U.S. Following the early actions of the GOP Administration to curb the number of (im)migrants entering the U.S. from Mexico (e.g., the proposed border wall) and from countries with large populations of Muslims with 2017’s 5th Executive Order (e.g., the #MuslimBan), Ms. Honey thought it imperative to cultivate her young students as civic agents. As such, she planned an extension to the shared grade-level persuasive writing unit [
1]. In my role as a co-player, co-teacher, and co-researcher with Ms. Honey and her students, I offered to aid her in the planning and execution of the extended unit.
Working together, we implemented a six-week integrated humanities unit that considered contemporary (im)migration issues and also afforded children the opportunity to ‘write’ using a diverse array of communicational tools. In this article, I detail how this work aligns with previous research focused on young children’s making and situate this inquiry in conversation with the Black Girls’ Literacies Collective, a collective of Black women scholars dedicated to amplifying the experiences of Black girls and women in connection to literacies and education. After sharing prior studies that informed my thinking about this project, I describe my methods before offering analytic snapshots of Ari and her friends’ making. Finally, I close by offering provocations for educational researchers and practitioners to consider as they facilitate school-based opportunities for making and civic action.
2. Literature Review and Framing
In the last decade, ‘making’ and ‘makerspaces’ have moved to the center of many discussions of formal and informal education [
2], particularly as the number of makerspaces in U.S. schools has increased [
3]. Situated within a community of practice (e.g., a makerspace), making is frequently understood as a set of hands-on activities a ‘maker’ does to design, build, transform, and/or produce various materials unto a new end. Often, this sort of remix is done through a process of tinkering [
4] as makers manipulate analog items like cardboard or perhaps play with digital components like audio through a process of trial-and-error.
While there has been an uptick in the prevalence of making in research, settler/colonial perspectives and those of white, upper-/middle-class men remain dominant while stories of historically marginalized groups, including racialized and Indigenous youth and children remain peripheral [
5,
6,
7]. Likewise, many of the studies about making are situated within upper-grade “STEM” classrooms (e.g., Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics). Few scholars yet focus on the possibilities of making for young learners or in literacies classrooms [
8]; fewer scholars still have considered the benefits of making for young Black girls in such spaces.
Generally, how children use non-digital technologies to (re)make artifacts and texts in literacies classrooms is framed as ‘maker literacies’ [
9] (p. 148). Although a relatively new concept, maker literacies emerges from the New London Group’s [
10] multiliteracies framework as maker literacies place “semiotic meaning-making at the centre of maker practice” [
8] (p. 5). Maker literacies are both about the end product and the making process
as well as the experiences occurring before, during, and after making. In many classrooms and the wider world, a similar argument has been made about writing, particularly because writers write to reflect on or document experiences.
2.1. On Writing/Making
Writers and makers both use a process of tinkering to devise a clear path forward in for their product. As Resnick and Rosenbaum describe, tinkering is a “playful, experimental, iterative style of engagement”; so too is it a “valid and valuable style of working” [
4] (p. 164). In print-based writing, writers revise the words before them on the page whereas makers often prototype their idea in one way before settling on a final method of production or product. Although writers/makers use different tools, the meta-level thought processes of revising and refining one’s work are remarkably similar; thus, as Cantrill and Oh have argued, “writing has always entailed making” [
11] (p. 107).
Writing/Making is a relational matter. Writers/makers are always already in conversation with others—both those have come before them and those in the future that will be an audience for their work. Writing/Making is not necessarily done in solitude because writers/makers are informed by their experiences and encounters. Moreover, in writing/making, the “why” of one’s composing may have diverse rationale; it may be “practical, whimsical, or both” [
12] (p. 287). Importantly, in writing/making, the final product of a writer/maker is not always necessarily perfectly aligned with the writer/maker’s initial vision. “Good” writers/makers are those that are flexible, they adapt. Ultimately, writing/making should be judged on how well the writer/maker
progressed toward the goal towards which the activity was aimed [
12]. However, researchers and practitioners must also account for
who writers/makers are and
how their identities inform their writing/making, such as the Black girl writers/makers I describe in this paper.
2.2. On Black Girls’ Literacies
The Black Girls’ Literacies Collective (BGLC) and the associated Black Girls’ Literacies Framework
begins with the lived and felt experiences of Black girls and women [
13,
14,
15]. From this approach, the ways Black girls and women come to know, to be, and to be known in the world is valued first and foremost while the framework simultaneously seeks to “interrupt the violence, pedagogical injustices, and misrepresentations against Black girls in schools” [
14] (p. 294). Specifically, the Black Girls’ Literacies Framework emphasizes six components of Black girls’ literacies; their literacies are multiple, connected to identities, historical, collaborative, intellectual, and political/critical [
15] (see
Table 1 for full description of these tenets). Within and across each component, not only are the racial and gendered identities of Black girls foregrounded, but so too are the ways in which Black women and girls historically have used and continually practice literacies in collaborative ways to create social change.
While the BGLC necessitates a shift in pedagogical practice to take up and value the multiple identities and literacies of Black girls, others have made similar arguments. Crenshaw [
16], for instance, also contended that more attention in research must be placed on Black girls and women because they have been often grossly understudied and/or mis-/under-represented in scholarship. One of the reasons more research is needed is because Black girls and women are not a monolith, but carry diverse, intersectional identities [
17].
Importantly, the Black Girls’ Literacies Framework also resists deficit narratives of Black girls [
18] by illuminating how “Black girls’ literacies encompass layers of reading, writing, discussing, and performing. Black girls develop their individual and cultural identities through collaboration” [
19] (p. 5). In taking up a Black Girls’ Literacies approach, scholars reject “over-simplified, decontextualized, and reductionist views of the Black girl experience” while seeking to “center Black girls in caring and humanizing ways” [
20] (p. 437).
Additionally, the Black Girls’ Literacies Framework also illustrates how, historically and still today, Black girls’ literacies remain grounded in critical awareness and social action [
21]. Across studies that center Black girls’ literacies, scholars have demonstrated how Black girls consistently demonstrate confidence as they challenge dominant ‘norms’ of literacy and reimagine what it means to be a learner and community participant [
18,
21,
22,
23]. As noted by the BGLC, “Black girls create the roadmap for how education should be framed for all youth” [
13] (p. 386). In this way, the Black Girls’ Literacies Framework is useful for reimagining and advancing schooled literacies for all children and youth.
In my initial design of the larger study from which the data for this manuscript is drawn, I did not intentionally set out to use the Black Girls’ Literacies Framework. Rather, my larger project was an inquiry that examined children’s diverse communicative practices. I was attuned, however, to the growing body of Black women scholars engaged in developing and refining the aforementioned framework. In reading the work of the BGLC more closely, I came to see the practices of the young girls I described herein as closely aligned to the six components of the Black Girls’ Literacies Framework described by Muhammad and Haddix [
15]. That is to say, I came to see the ways in which the girls’ Blackness was embedded in their literacies. For instance, the four girls—a tight-knit friend group—created their own Black girl space by organizing themselves as a collaborative group of writers/makers. Their actions mirrored the sort of sacred kinship space Black girls and women have cultivated across history, as detailed across studies from the BGLC. Moreover, establishing this relational and physical space for themselves was itself a rich practice of Black girls’ literacies. Although the girls’ practices could be read as their engagement with literacies generally, I used the Black Girls’ Literacies Framework to illustrate the complexity of the girls’ practices in their child-led writing/making I describe in the latter part of this paper.
2.3. Research Questions
Bringing together the aforementioned bodies of scholarship, for this inquiry, I used a case study design and ethnographic methods [
24] to examine the following:
How did a collective of four Black girls collaboratively use writing/making to unpack their learning about (im)migration and to call for political/critical action on such issues?
How did writing/making offer an alternative space for this collective of Black girls to thrive as literate beings in their early childhood classroom?
3. Materials and Methods
Stemming from a larger study examining children’s composing in two classrooms, for the purposes of this paper, I zoom in on a collective of four Black girls. In doing so, I examine their processes of writing/making and how they used writing/making to make a space for themselves in their classroom. Before detailing the findings, I describe the schooling context, the girls themselves, and my processes for data generation and analysis.
3.1. Context
Situated nearby the university where I was a doctoral student, Community School J (CSJ) was the focal site for my graduate research as I engaged critical perspectives to consider how classrooms might become more inclusive spaces for children’s multiple cultural, linguistic, and modal ways of knowing [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29]. Within my dissertation research, I took up this question within two third-grade classrooms across the 2016–2017 academic year—Ms. Honey’s classroom was one of these focal sites [
1,
30,
31].
Ms. Honey—a white 34-year-old, U.S.-born woman—taught one of four third grade classes at CSJ. Of the twenty-two children enrolled in her class during the 2016–2017 academic year, 6 children self-identified as white, 5 as Black/African American, 4 as mixed/bi-racial, 2 as Asian American, 1 as Asian, 1 as Latino, 1 as Mexican American, 1 as Mexican, and 1 as Muslim. The racial diversity of children in Ms. Honey’s class paralleled demographics of the wider school population noted in official reports; 48% of children were identified as children of Color (36% African American, 9% Asian American, 4% Hispanic, 1% Other) and 52% of children were identified as white. Thus, the make-up of the focal class and school mirrored national demographics of the U.S. and, I argue, made the school a critical site for study.
3.2. Child Participants
I focus on four focal children—Ari, Ciara, Rhianna, and Quarie; all self-identified as African American or Black girls and each self-selected their pseudonym. These four girls were selected for this analysis because they composed together and because of how they used writing/making to express civic concerns. In
Table 1, I provide additional details about the girls.
3.3. Researcher
As an early childhood educator-turned-researcher, I am committed to amplifying the voices of the young children I come to know through my research. However, given my positioning as a white, monolingual, cisgender, U.S.-born woman, I also find it important to highlight that, and as evidenced in recent U.S. elections, many white women continue to make choices that maintain systems of white supremacy. In turn, I acknowledge this has happened often in research as many white scholars often take up, profit from, and exploit the stories of Black people.
I also know that, for some individuals, the fact I am writing about young Black girls may be troubling as I write within/from the very tension I mentioned. Hence, I find it important to share why centering the experiences and knowledge of Black girls and other children of color remains central to my work. In part, my past work as a classroom teacher in New Orleans, Louisiana, U.S., informs what I feel is a moral imperative to amplify their stories. Not only did I teach a nearly all-Black population of students in my first years of teaching, but I was apprenticed into teaching by Black women that were my colleagues. Through these children, their families, and my colleagues, I came to understand the historical plight of Black persons, particularly in the Southern U.S., in new, more critical ways. My knowledge and understanding were further enriched in my graduate studies and, in turn, so was my commitment to dismantling systems of white supremacy in whatever ways I could through my work as a scholar and teacher educator.
My experiences living in New Orleans framed my perspective of the girls’ collaboration described in the findings insofar as my perception was that their literacies work was meaningful and deserving of its own inquiry. That is to say, my aforementioned lived experiences provided me with both a lens to notice the girls’ work as well as a grounding that the girls’ literacies were in and of themselves valuable. Paired with the readings and critical conversations I engaged in during my doctoral work, foregrounding Black communities’ contributions and literacies because they are historically and continually disregarded is a moral imperative for me. In this inquiry, I leveraged my knowledge of the historical plight of Black communities as a tool of analysis that could directly note how, still today, systems of white supremacy operate to disenfranchise Black children, especially Black girls.
As a white woman, I want to call attention to how my findings and discussion of the girls’ writing/making are my read of their stories. Likewise, then, the young girls’ writing/making should be read as their read of the lived experiences of others. Building from the asset-oriented Black Girls’ Literacies Framework, I encourage all readers to consider how this cadre of girls interrogated critical social issues in and through their writing/making and how their actions build upon the legacy of Black civic activists from across time.
3.4. Unit Overview
In developing the extended unit, Ms. Honey and I knew it was imperative to offer information to children about who (im)migrants are, why they journey from their homes, and what challenges—including policies proposed by the current GOP Administration—they face in doing so. We did this through children’s literature, print and video news media, and a virtual conversation with Dr. Jason De León—a renowned anthropologist and archaeologist studying the clandestine migration between Mexico and the U.S. [
32]. During the conversation, he shared numerous examples of items individuals crossing the border left behind on their journey, including backpacks with messages of love, hope, or well wishes; remnants of food or drinks consumed; and personally-meaningful items like a teddy bear. Dr. De León told the children how, in his role as an anthropologist, he understood such items as part of a larger story—of individuals as well as of society. As is evident in the findings, Ari and her friends were quite taken by the work of Dr. De León and the stories he shared.
After setting the stage for the young children to be informed on issues of (im)migration, the unit culminated with an afternoon of writing/making. Some children made representational Lego border walls while others wrote/made informative three-dimensional books. Although many children used either analog or digital materials, Ari and her peers combined digital and non-digital technologies. While in the findings I provide an analytic snapshot of how the girls combined different materials, I first find it necessary to offer additional details about data generation and analysis.
3.5. Data Generation and Analysis
Alongside lesson artifacts or what the children produced, I also generated data in other ways. As a participant in the classroom, I wrote fieldnotes and also made audio- and/or video-recordings of daily classroom happenings. I used stationary recorders and video-cameras to capture whole-class movements and I used my smartphone when I engaged in more impromptu conversations. Similarly, I generated photos of children at work and play for informal interviews about their work. I supplemented this fieldwork with formal interviews with children. All subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Michigan State University (i048452).
Children also generated data themselves, as in the case of Ari and her peers; they used the digital technologies to record themselves or to document their peers at work. As much as possible, I tried to align child-produced videos with those generated by stationary cameras and my own recordings to gain a fuller picture of the ‘scene’ for my analysis. In this way, my analysis of children’s writing/making was one wherein I could look across children’s composing process (from beginning to end) and note instances when they ‘revised’ their work in ways similar to traditional print-based writing or shifts in how children discussed their stance on (im)migration and how peers perhaps informed their response.
In my review of the videos produced by Ari and her friends, I also noted how their writing/making aligned with the six tenets of the Black Girls’ Literacies Framework.
Table 2 provides descriptions of each of the six components of the framework, as well as examples of these tenets evident in the girls’ writing/making and talk.
3.6. A Caveat
In the findings, I detail how Ari and her peer group showcased their knowledge about issues of (im)migration through videoed skits. Across the series of videos they produced, the girls role-played as (im)migrants travelling from their homes toward the U.S, dressed in make-shift costumes they made themselves. For many readers, their skits may be quite troubling because of how they take up the stories of real people seeking refuge. The girls’ role-play does, to some extent, mirror the sorts of reenactment lessons some teachers encourage as a means for children to understand the history of enslaved persons in the U.S. In such lessons, the humanity of real people is often lost as they become nameless ‘characters’ in a one-off portrayal.
However, the girls’ skits were not produced with direct influence from their teacher or myself. The girls’ writing/making was a dramatic production of their own design. They collaboratively created the props they desired and then, together, acted out various scenes, taking turns to film one another. Their role-play became a vehicle for them to explore the complexity of (im)migrants’ lived experiences, as discussed in class. So too was their role-playing a means for them (as young children) to explain how they were constructing meaning of and about the larger world. This sort of child-initiated storytelling among friends is, according to early childhood expert Vivian Paley [
34], children’s work (and quite complicated work at that). While imagining scenarios related to real-world happenings may seem quite easy, in role-play children are constantly improvising based on the response and actions of their peers. In the case of the girls featured here, they also needed to include their perspective on issues of (im)migration (e.g., the task they were assigned) in a way that would be meaningful to an audience later (e.g., their teacher, classmates, and myself).
Thus, the stories I share in the findings are meant to highlight how the girls’ videoed role-play, as writing/making, was representative of their sense-making [
35,
36]. Simultaneously, I illustrate how their meaning-making was always already interwoven with their identities as political/critical and intellectual Black girls [
33]. In turn, I challenge adults to consider how the girls’ storytelling role-play evoked new provocations about how their bodies held stories of marginalization—of themselves and others—in complicated ways.
4. Findings
Throughout the time children engaged in writing/making, they were provided freedom to move about their classroom in uninhibited ways. Not only did they have free rein to use whatever available materials they desired, they could just as easily choose to engage their peers in a collaborative effort. Still, most children opted to use only analog or only digital technologies and many worked alone or perhaps with one other child. However, Ari and her friends took a different approach.
Ari and her three friends were the largest collaborative of writers/makers in Ms. Honey’s class; most other children that worked collaboratively only worked with one other peer. Together, the girls wrote/made a series of videos that displayed the multiplicity of their literacies as they combined analog and digital technologies. For example, the girls repurposed cardboard boxes as ‘backpacks’ by punching holes in the boxes and using string and pipe cleaners to make ‘straps’ so they could wear the backpacks. In turn, the girls used a digital camera to record themselves playing the role of (im)migrants wishing to cross the border. Additionally, Ari and her friends advocated for social action in innovative ways that differed from how their peers did, that is through performance. The backpacks the girls constructed supported the storytelling they recorded, while the final videos were intended to be stand-alone texts that could be read both by their classmates and wider audiences.
As I read across the girls’
collaborative writing/making—including the video shorts they recorded and the physical items they crafted—and the interviews I did with the girls, I did so through the lens of the Black Girls’ Literacies Framework. In particular, I read the girls’ use of diverse materials as representative of the
multiple literacies Muhammad and Haddix [
15] described. As the girls wove together many compositional modes, I noticed how they foregrounded their
intellectualism by making clear connections to class conversations about the
political/critical issue of (im)migration. Simultaneously, across the various videos they produced and in our post-writing/making conversations, I caught glimpses of how the girls connected their own
identities to contemporary women and girls, and those across
history. While space precludes me from sharing the numerous videos the girls produced or the many informal and formal conversations we had, across the analytic snapshots that follow, I showcase how this group of girls engaged in writing/making and to make sense of political/critical issues.
4.1. Snapshot 1: Collaborating on Politically/Critically Intellectual Messages
When Ari explained to me the underlying reasons why individuals may leave their home countries and journey to the U.S. (as in the opening vignette), she also told me about the materials she and her collaborators used to write/make. Ari explained how she and her friends used these analog items to write/make and as a starting point for their retelling of the stories shared by Dr. De León which they captured across several videos.
- Ari:
- It’s like, they’re walking on a journey, and it’s like, you know the story, I meant, you know when we, uh, talked to Devon Hearts? Kevin Hearts? Yeah, he had all these backpacks? So, this is one of the backpacks that represents-
- Cassie:
- Oh, Jason De León?
- Ari:
- Yeah.
- Cassie:
- Ohh…okay.
- Ari:
- (reading from box) “I love you.” “Good luck.” Yeah, we wrote that on the boxes, and we pretended that they [the boxes] were...Guys come here! (calling to other girls in group)...that they were, that they were backpacks. And we had like, kinds of food , and then like drinks. And then our, we had a video where our legs was tired. We fell on the ground because, because it was really hot. It started to hurt our legs from wa-walking all those journeys. Then, after that, we, we made a road, like a path, across the border. And I’m saying if, if that, if that, if you have a wall...refugees right now, they’re still stuck in places that they shouldn’t be right now. So I’m trying to represent refugees right now, for walking from that journey.
In this short video, Ari made explicit connections to the information that was shared in class and demonstrated the intellectualism of Black girls’ literacies. She both cited the source that informed her decision-making about the analog objects she created (e.g., De León’s backpacks) and she also provided details about common characteristics of (im)migrant stories discussed in class (e.g., long journeys with much walking and sometimes limited water). In turn, while she and her friends made use of print-based writing, they used this more traditional form of writing to reimagine the boxes in ways representative of the knowledge gained in the unit (e.g., messages written on the backpacks). In this way, through her writing/making, the box tied across Ari’s body as we talked was no longer a box. Instead, it was imagined as a backpack like the ones shown by Dr. De León in our virtual class conversation.
Backpacks, as Dr. De León shared in the discussion with Ari and her peers, were the primary way individuals crossing the border carried necessary supplies as well as mementos from the homes they left behind. Not only did the backpacks hold food items, but some travelers—particularly young ones—also carried small comforts such as teddy bears (another item Dr. De León showed children in the meeting) or notes from loved ones at home. As seen in the image of Ari’s backpack (
Figure 1), notes were often carried on the bag itself rather than a piece of paper.
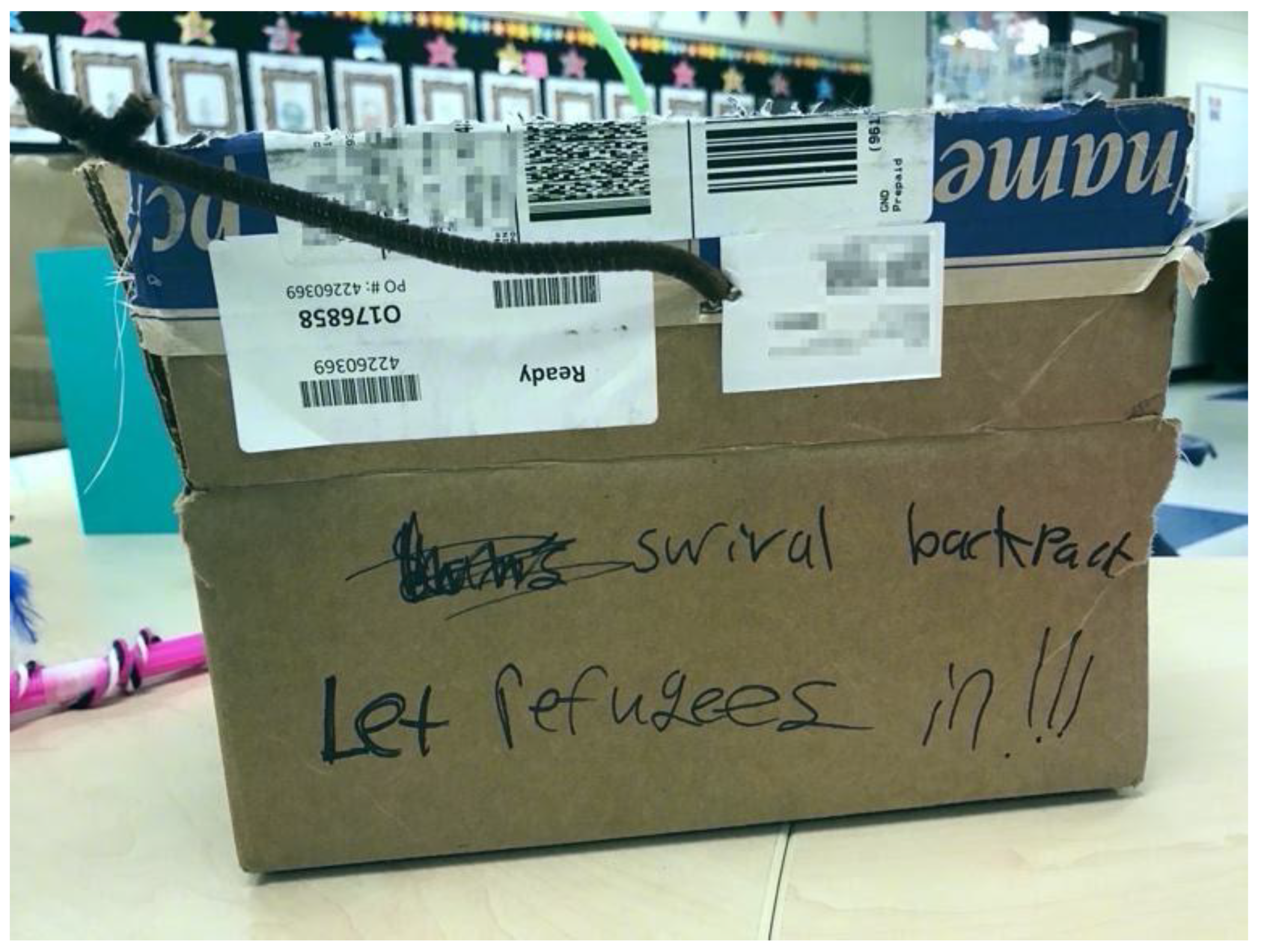
The words Ari wrote on her box, the same ones she read aloud to me, were significant in that they mirrored the messages of hope and love Dr. De León described in our virtual conversation. This was a common trend among the young girls that collaborated with her. Much like Ari, for example, her friend Ciara’s backpack (
Figure 2) carried important information about the purpose of the bag on the journey (e.g., “surival backpack”) and, at the same time, stated blatantly her desire for the U.S. government to “Let refugees in!!!” (Children often conflated refugees and (im)migrants in our discussions.) Ciara’s backpack served as another example of a text created by the girls within the group that was representative of their knowledge about the contentiousness of the issue of (im)migration. Simultaneously, the words Ciara wrote on her backpack demonstrated a political/critical stance as they described the purpose of the backpack (“surival”) and a critique of contemporary (im)migration policy. By declaring that refugees should be allowed in the U.S., Ciara noted a power differential existed and only social transformation might mediate this historical hierarchy.
Likely because the girls wrote/made their backpacks together, they shared exterior elements Dr. De León had mentioned. Additionally, the girls also included items within the boxes they knew were necessary for an (im)migrant’s journey. Each girls’ backpack had a handful of essential items such as food (e.g., empty food cartons and containers Ms. Honey and I brought in) and drinks (e.g., their own empty water bottles or another empty beverage container). Thus, the contents of their backpacks also illustrated the intellectualism of their writing/making and their recall of specific discussion points about an (im)migrant’s journey gathered from speaking with Dr. De León as well as class read alouds.
Importantly, the girls did not only create representational objects out of analog materials to showcase the knowledge gained in the unit. Rather, they also used the digital to capture what else they understood. As Ari noted in our conversations, the girls understood (im)migrants faced numerous challenges before, during, and after their journey. She shared with me that many (im)migrants must first decide whether the treacherous journey across the Mexico/U.S. border is worthwhile. (Im)Migrants must take stock of their situation and, in turn, prepare as much as possible for the journey. Not only must (im)migrants pack what Ciara termed a “surival backpack,” but they must say good-bye to loved ones and their homeland. In this way, the girls’ illustrated intellectualism as well as the political/critical tint they brought to their writing/making; they showcased their knowledge about the plight of (im)migrants seeking refuge in the U.S. and grounded their writing/making in critical thought and reflection about contemporary societal issues.
4.2. Snapshot 2: Writing/Making Multiple Literacies and Identities as a Collective
While the girls knew reasons why (im)migrants decided to make the trek north towards the border between Mexico and the U.S., they also understood many travelers would continue to face challenges. This was evidenced in one of the videos filmed and narrated by Ciara as the other three girls performed the role of journeyers.
- Ciara:
- (narrating) So, refugees are walking along…[off-camera, filming]
- Ms. Honey:
- What are you carrying with you on your journey?
- Rhianna:
- I’m carrying milk, I mean water, and a couple snacks and stuff.
- Ciara:
- (narrating) They’re carrying food and water so they can survive. They’re carrying a lot of stuff in their boxes, and they’re walking and they’re dragging their legs because they’re tired.
Like when Ari named the physical challenge (im)migrants face and voiced the feelings of exhaustion that accompany such a journey, so too did her peers display this in this excerpt of their collaborative skit. In Ari’s description of their role-play and in Ciara’s narration of the skit itself, the tiredness of (im)migrants’ legs that results from so many hours spent walking in the heat is emphasized. In my interpretation of their storytelling role-play, the girls both wanted to show the exhaustion of journeyers and to also try to feel the sense of tiredness described by Dr. De León, in class read alouds, and on the news at the time.
While this short video of the girls’ collaborative writing/making again contributes to their intellectualism and political/critical approach, so too does it more fully demonstrate their multiple literacies as the combined analog and digital technologies through their skit. The embodied and social nature of the storytelling also perhaps made more visible how their writing/making reflected literacies of Black girls and women across history. The girls used the loose structure of the classroom makerspace to address the issue of (im)migration and they did so by creating a space for themselves to express themselves through performance.
The initial videos the girls produced were of scenes representative of an (im)migrant’s journey, but the latter videos often included only one or two girls at a time. In these videos, the girls were no longer nameless (im)migrants. Rather, the girls role-played as mothers, daughters, and sisters journeying toward/across the Mexico/U.S. border, as in the following transcript from a video filmed by Rhianna.
- Rhianna:
- What’s your name? [off-camera, filming]
- Ciara:
- Ciara. I’m a refugee and I’m poor. They bombed our country, so we’re walking thousands of miles. I’ve only got one gallon of something to drink and I’m scared.
- Rhianna:
- How old are you?
- Ciara:
- Nine years old.
- Rhianna:
- Where’s your mom?
- Ciara:
- She’s out going to find some stuff.
- Rhianna:
- Um, do you know where you are right now?
- Ciara:
- No, I do not.
The girls also displayed their knowledge about issues facing (im)migrants while also playing a bit with their own identities in relation to the stories they had heard by and about (im)migrant children. As is clear in the transcript of Rhianna and Ciara’s question-and-answer, the girls understood that (im)migrants were not only adults; children could also carry this identity. Given that children often explore challenging experiences through play [
34,
35,
36,
37], the shifting identities of the girls across their skits is quite logical.
In many ways, I found myself unsurprised by the interaction between Rhianna and Ciara. Having come to know the girls across the course of the academic term, I also had met their caretakers and siblings. For some, like Ari, their mothers were quite present in the space of the school, often assisting in Ms. Honey’s class or wider community events. When Ari’s mother arrived in the classroom, all four girls often rushed to her and requested hugs; her mothering was not limited to Ari, but extended to Ari’s friends as well. Mothers also played an important role in many of the stories we had read as a class. (Im)Migrant children traversing across national borders was not uncommon in the picture books we shared. Thus, the girls’ storytelling aligned both to the ‘facts’ presented in class and to their own lives and relations to Black women.
Interestingly, the girls frequently had several ‘takes’ of their videos, while in other circumstances the girls shifted directions completely. For example, in the video just described, neither Ciara’s “sister” or “mother” was near-enough by to enter the scene as documented on a stationary camera in the classroom. However, in the moments that followed, Ciara and Rhianna called and motioned for the other two girls to join them in the corner where they were filming. Once the group was reunited, Rhianna continued filming Ciara.
- Ciara:
- I’m back, and my water is gone, I don’t have nothing to drink, I’m starving, and I just hope we get to the country United States. They never let us come, so I’m really, really sad, that like, my whole family is gone, and I don’t know where they are so…
- Rhianna:
- Her sister is coming in now. [Whispering for Quarie to enter] Your sister is coming in a minute, so she will make you feel better. And your mother.
- Ciara:
- And I hope that we all present ourselves as the U.S.A. of America, and I hope that Donald Trump really helps us, and here come my sister [Quarie enters], my sister, and like, we don’t have nothing for ourselves.
Throughout their writing/making—from the analog backpacks to the final scenes of their videoed skits—the girls held strong to their stance that contemporary (im)migration policies implemented by the GOP Administration under the direction of the party’s leader, Donald Trump, were unjust. While Quarie did not initially articulate an explicit stance like Ari and Ciara, in a final video where Rhianna was filming, Quarie did, stating, “These are all the people that need help. Please help us Donald Trump, don’t make anything else bad and difficult for us. Thank you, please help us.” In my read of the four girls’ comments alongside their storytelling, I read them as having grasped the inhumanity of turning persons seeking refuge away at the border. Further, the girls understood the injustice of calling for blockades or teargas to prevent the entry of (im)migrants, particularly given the physical toll such a journey has on (im)migrants’ bodies.
5. Discussion
Despite that the girls used “materials that aren’t typically associated with writing” a close analysis of their composing made clear for me several ways in which they engaged as writer/makers [
11] (p. 119). The make-shift makerspace that we transformed Ms. Honey’s classroom into afforded the girls the opportunity to blend “digital and physical technologies to explore ideas, learn technical skills, and create new products” [
38] (p. 505). Put simply, the girls could be self-determinant [
39] while collectively forging a space for themselves within the classroom [
19]. This is critically important insofar as Black girl spaces are frequently not given specific support within school spaces, even though collectivism is often desired by Black girls themselves [
40]. Historically, as noted by the BGLC, Black girls have had to create spaces for themselves to resist oppression [
15,
40]. In the videos Ari and her friends wrote/made, they did just that.
Many schools and classrooms still have a tendency “to privilege spoken and written language over other communicative modes such as silence, visual image, laughter, gesture, music, etc.” [
41]. In this paper I have presented how writing/making has the possibility of transforming learning spaces to be more fertile grounds for Black girls’ literacies—their intellectualism and criticality—and their ways of being to be supported. The girls collaboratively used reading, writing, listening, viewing, and speaking to collectively reimagine more just social futures [
10]. Yet, in many ways, the young girls were reclaiming not only literacies through their writing/making, but also their future. Their video-recorded play, as writing/making, offers new possibilities and practicalities for children to interrogate and innovate issues of equity and justice.
Importantly, Black girls are not a monolith and the Black Girls’ Literacies Framework should not be read as a checklist of instructional strategies for teachers or as a checklist of opportunities to be provided to young Black girls. Rather, the framework should be conceptualized in a similar way to critical literacies—as “a lens, frame or perspective for teaching throughout the day” [
42] (p. 306). Black girls’ literacies are not a separate lesson on the daily agenda, but they are entangled with Black girls’ bodily and intellectual encounters in the world, as demonstrated in the stories of Ari and her friends.
As I previously noted, the storytelling role-plays the girls engaged in, as described in this article, were not planned by Ms. Honey or myself. The girls’ writing/making was instead child-led. Reflecting back on their writing/making now and the roles Ms. Honey and I held in the space of the classroom, I do think it is critical to again note that, like the re-enactments of enslaved individuals in the U.S., teacher-directed role-play of historically and continually marginalized communities is not best practice or something to be encouraged. I do so with the risk of minimizing what the girls did as writers/makers. I do not want to overlook or minimize that real people are encountering real challenges in their attempts to enter the U.S. Thus, I find it necessary to reiterate that using role-play in the ways the girls did can have complicated consequences. To clarify then, I do not want to dismiss their writing/making, but caution adults for implementing such role-play in their classrooms.