Playing with Complex Systems? The Potential to Gain Geographical System Competence through Digital Gaming
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Basis and Model Conception
2.1. State of Research: Games in Educational Contexts
Games and System Competence
2.2. Complex Systems and System Competence in Geography
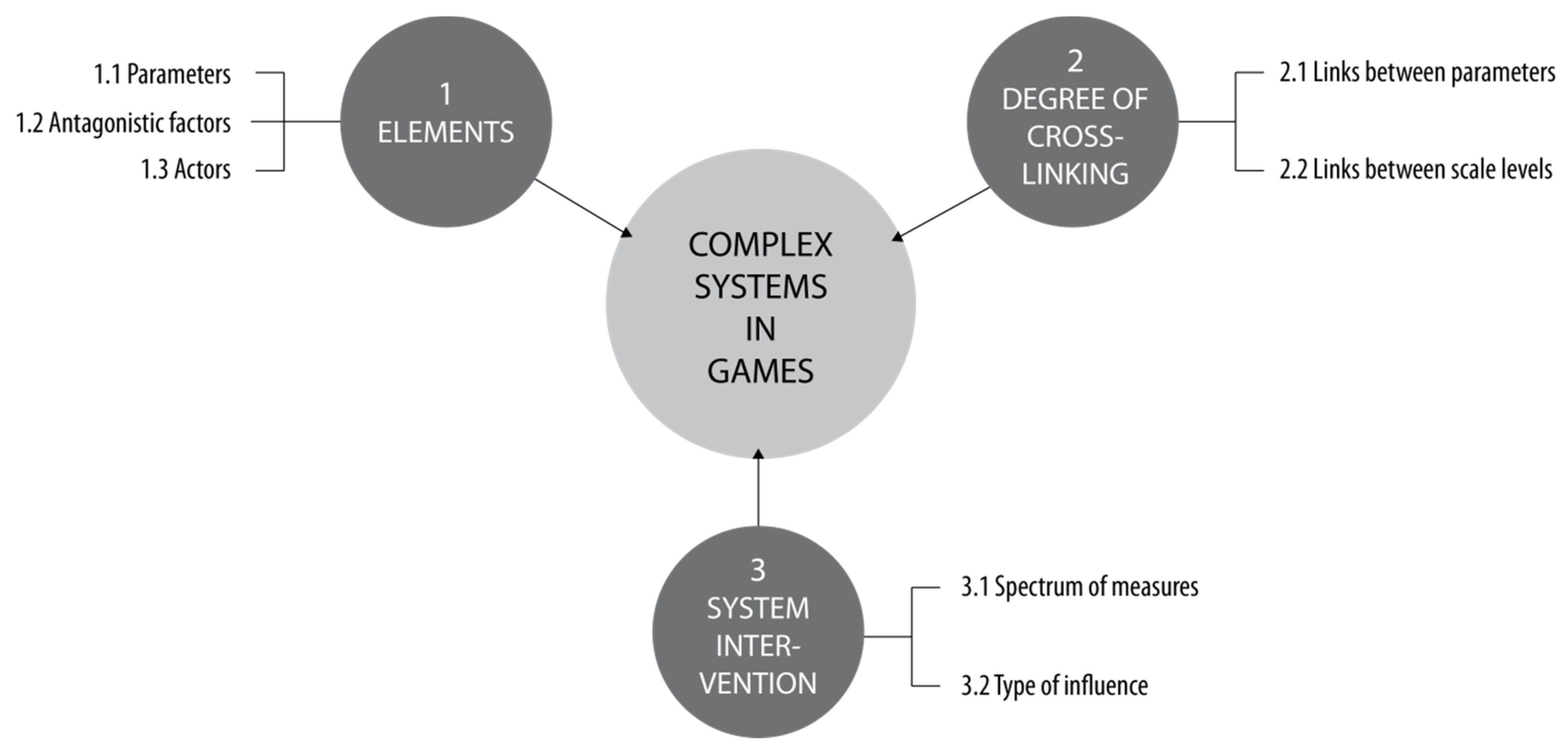
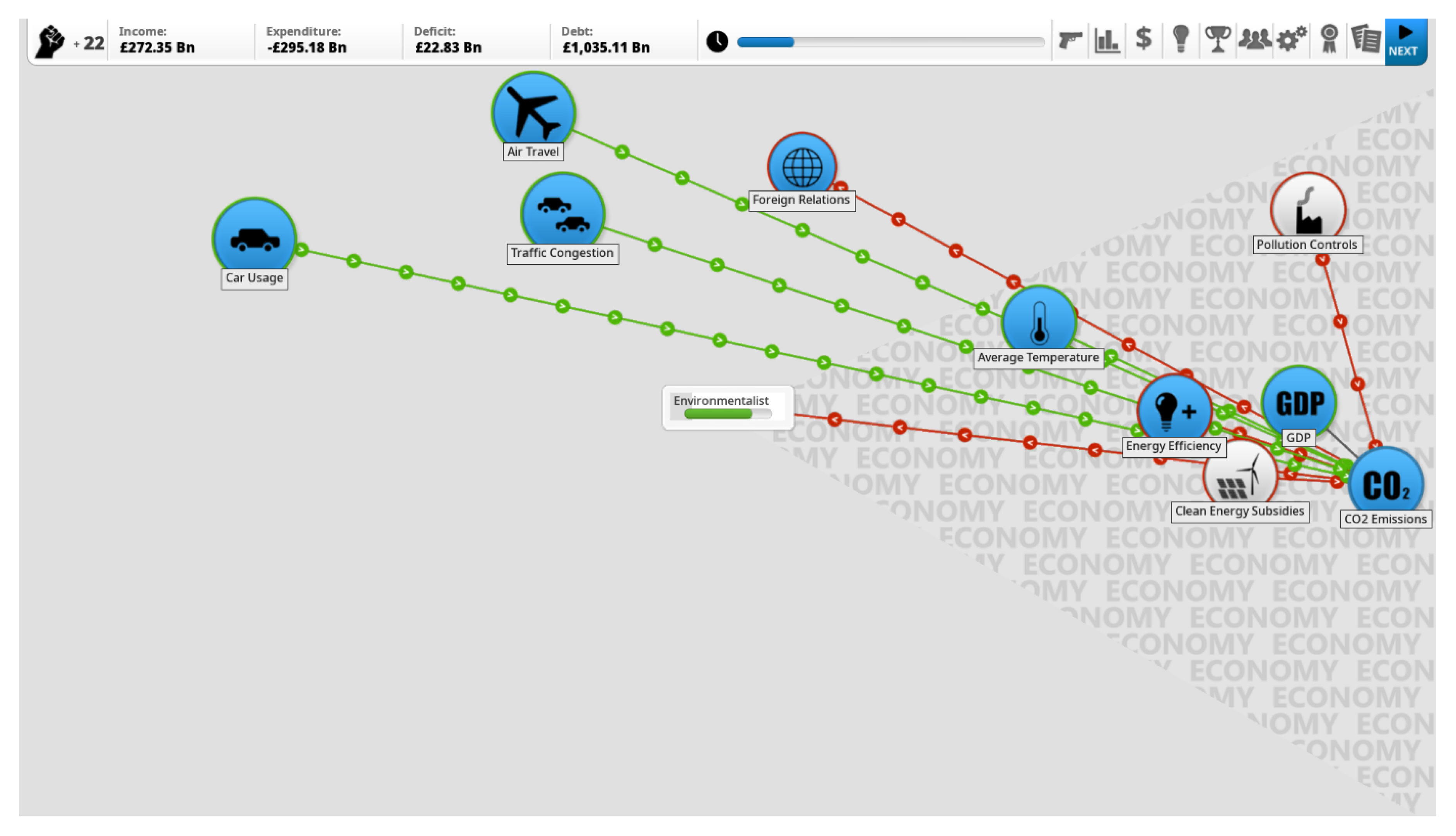
2.3. Framework for Assessing System Complexity in Digital Games
2.3.1. Elements
Parameters
Antagonistic Factors
Actors
2.3.2. Degree of Cross-Linking
Links between Parameters
Links between Scale Levels
2.3.3. System Intervention
Spectrum of Measures
Type of Influence
Non-Included System Characteristics
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Selection of Games
3.2. Application of the Analysis Framework in the Empirical Study
3.2.1. Elements
Parameters
Antagonistic Factors
Actors
3.2.2. Degree of Cross-Linking
Links between Parameters
Links between Scale Levels
3.2.3. System Intervention
Spectrum of Measures
Type of Influence
4. Results and Discussion
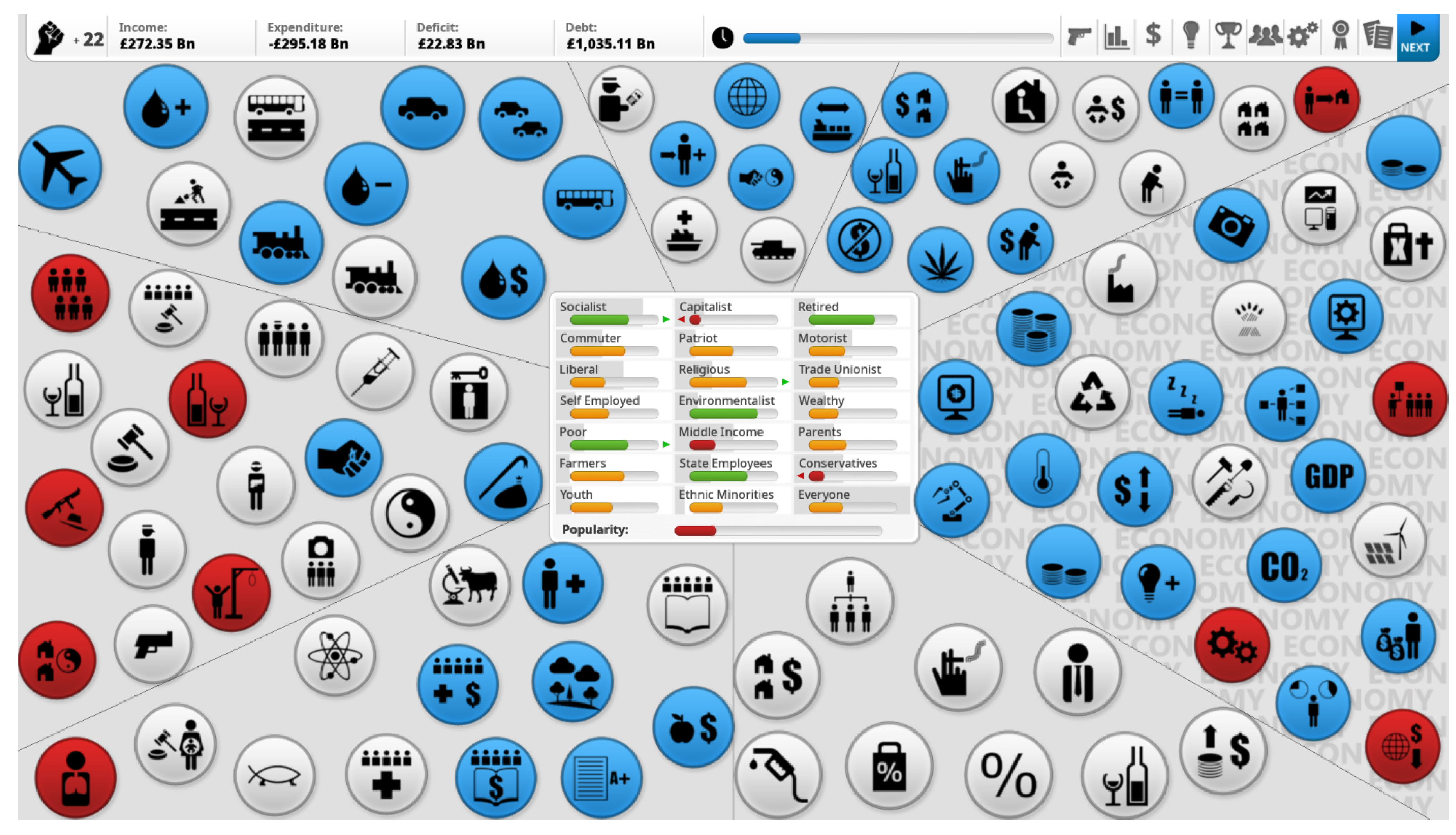
4.1. Elements
4.1.1. First Level Parameters
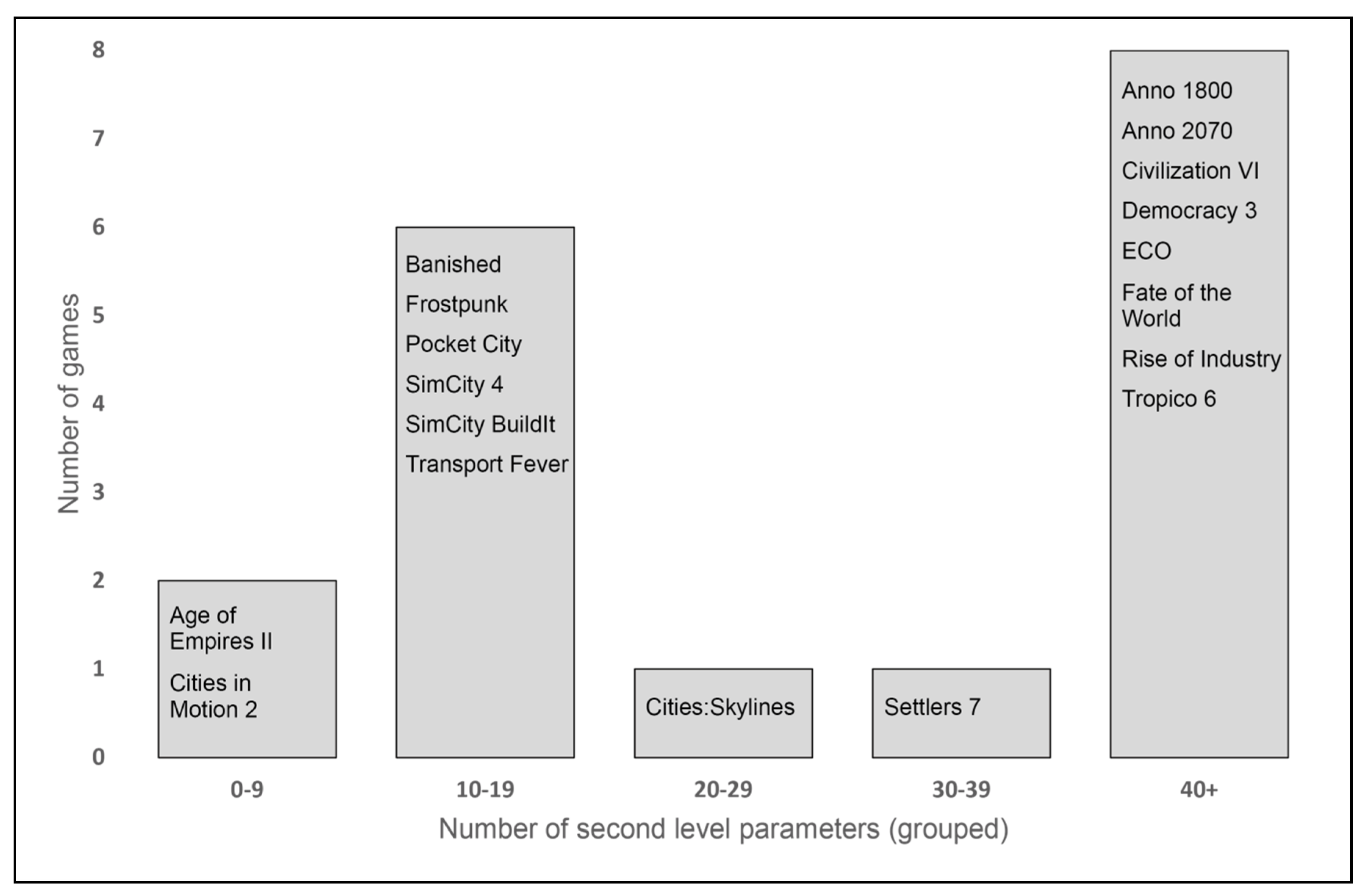
4.1.2. Second Level Parameters
4.1.3. Topics of Parameters
4.1.4. Antagonistic Factors
4.1.5. Actors
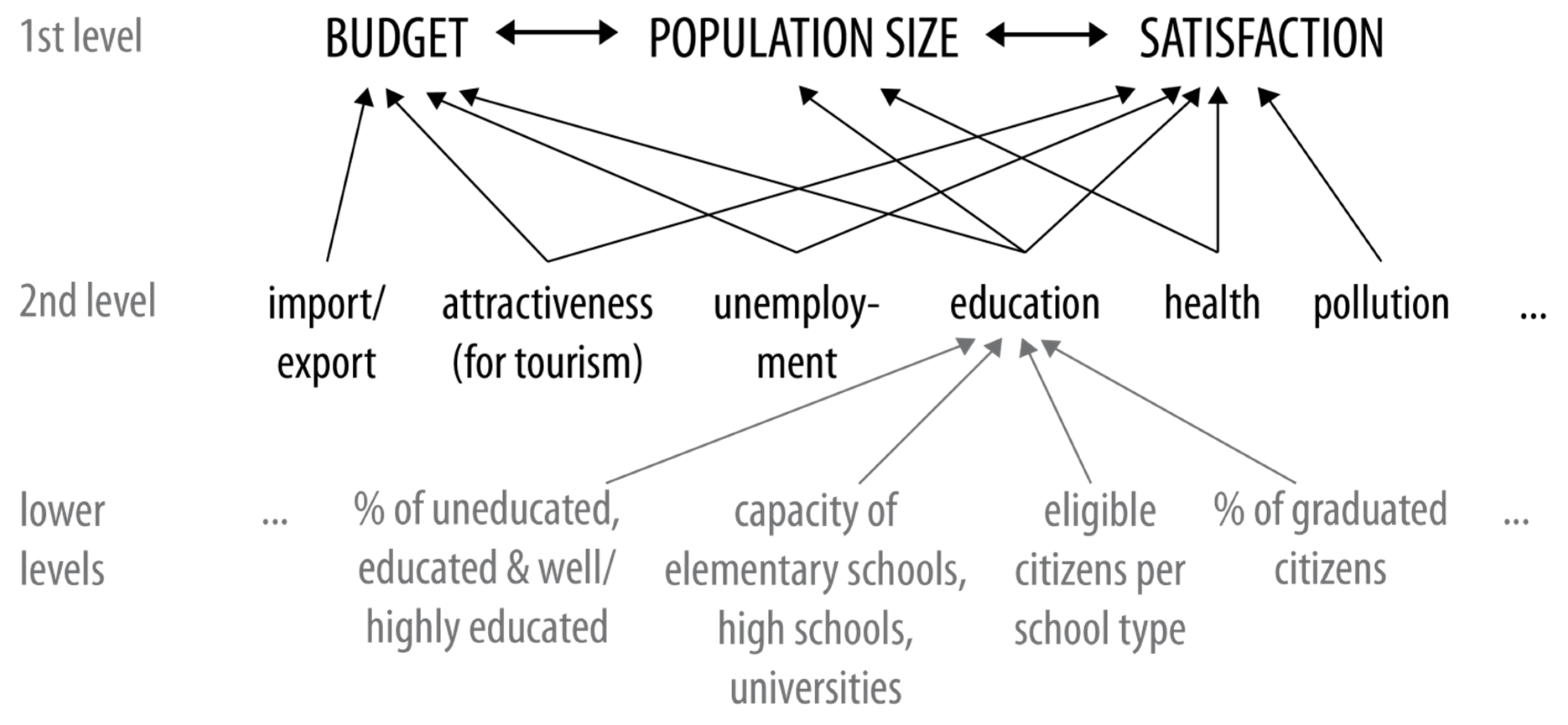
4.2. Degree of Cross-Linking
4.2.1. Links between Scale Levels
4.2.2. Links between Parameters
4.3. System Intervention
4.3.1. Spectrum of Measures
4.3.2. Type of Influence
5. Conclusions: Implications for Training System Thinking in Geography Education
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frischknecht-Tobler, U.; Kunz, P.; Nagel, U. Systemdenken-Begriffe, Konzepte und Definitionen. In Systemdenken. Wie Kinder und Jugendliche Komplexe Systeme Verstehen Lernen; Frischknecht-Tobler, U., Nagel, U., Seybold, H., Eds.; Pestalozzianum: Zürich, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 11–32. [Google Scholar]
- Rempfler, A.; Uphues, R. Systemkompetenz und ihre Förderung im Geographieunterricht. Geogr. Sch. 2011, 189, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, M.; Blackmore, C.; Ison, R.; Shah, R.; Wedlock, E. The Role of Systems Thinking in the Practice of Implementing Sustainable Development Goals. In Handbook of Sustainability Science and Research; World Sustainability Series; Leal Filho, W., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 677–698. [Google Scholar]
- Bollmann-Zuberbühler, B.; Strauss, N.-C.; Kunz, P.; Frischknecht-Tobler, U. Systemdenken als Schlüsselkompetenz einer Bildung für nachhaltige Entwicklung–Eine explorative Studie zum Transfer in Schule und Unterricht. Beitr. Lehr. Lehr. 2016, 34, 368–383. [Google Scholar]
- Lantermann, E.D.; Döring-Seipel, E. Probleme im Umgang mit komplexen Umwelten. In Innovative Ansätze zum Schutz der Natur; Erdmann, K.H., Mager, T.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Stroh, D.P. Systems Thinking for Social Change: A Practical Guide to Solving Complex Problems, Avoiding Unintended Consequences and Achieving Lasting Results; Chelsea Green: White River Junction, VT, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Geographie (DGfG). Bildungsstandards im Fach Geographie für den Mittleren Schulabschluss mit Aufgabenbeispielen, 9th ed.; Self-Published: Bonn, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Viehrig, K.; Siegmund, A.; Funke, J.; Wüstenberg, S.; Greiff, S. The Heidelberg Inventory of Geographic System Competency Model. In Competence Assessment in Education. Methodology of Educational Measurement and Assessment; Leutner, D., Fleischer, J., Grünkorn, J., Klieme, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 31–53. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, V.; Budke, A. Politische Bildung durch Planungsaufgaben: Ein Vergleich deutscher und britischer Geographieschulbücher. In Politische Bildung im Geographieunterricht; Budke, A., Kuckuck, M., Eds.; Franz Steiner: Stuttgart, Germany, 2016; pp. 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Prensky, M. Teaching Digital natives: Partnering for Real Learning; Corwin: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Medienpädagogischer Forschungsverbund Südwest (MPFS). JIM-Studie 2018-Jugend, Information, Medien: Basisuntersuchung zum Medienumgang 12- bis 19-Jähriger; Self-Published: Stuttgart, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Prensky, M. Digital Game-Based Learning; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Squire, K. Changing the Game: What Happens When Video Games Enter the Classroom? Innov. J. Online Educ. 2005, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Akcaoglu, M. Using MMORPGs in Classrooms: Stories vs. Teachers as Sources of Motivation. In Cases on Digital Game-Based Learning: Methods, Models, and Strategies; Baek, Y., Whitton, N., Eds.; Information Science Reference (IGI Global): Hershey, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Dickey, M. Game design and learning: A conjectural analysis of how massively multiple online role-playing games (MMORPGs) foster intrinsic motivation. J. Educ. Psychol. 2007, 88, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, J.P. Why Video Games are Good for Your Soul: Pleasure and Learning; Common Ground Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, J.P. Good video games and good learning. Phi Kappa Phi Forum 2005, 85, 33–37. Available online: https://www.phikappaphi.org/docs/default-source/phi-kappa-phi-forum-documents/2005_summer.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Malone, T.W.; Lepper, M.R. Making learning fun: A taxonomy of intrinsic motivations for learning. In Aptitude, Learning, and Instruction; Snow, R.E., Farr, M.J., Eds.; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1987; Volume 3, pp. 223–254. [Google Scholar]
- Hébert, C.; Jenson, J.; Fong, K. Challenges with Measuring Learning through Digital Gameplay in K–12 Classrooms. Media Commun. 2018, 6, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, A.; Sparrowhawk, A.; Heald, Y. Report on the Educational Use of Games. An Exploration by TEEM of the Contribution Which Games Can Make to the Education Process; Teem: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Squire, K.; Jenkins, H. Harnessing the Power of Games in Education. Insight 2003, 3, 5–33. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, P.C. Teaching and Learning with SimCity 2000. J. Geogr. 1998, 97, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orim, R.E.; Ekwueme, C.O. The roles of games in teaching and learning of mathematics in junior secondary schools. Glob. J. Educ. Res. 2011, 10, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, T.C.S.; Falcao, T.P.; Tedesco, P.C.A.R. Exploring an approach based on digital games for teaching programming concepts to young children. Int. J. Child-Computer Interact. 2018, 16, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüzün, H.; Yılmaz-Soylu, M.; Karakuş, T.; İnal, Y.; Kızılkaya, G. The effects of computer games on primary school students’ achievement and motivation in geography learning. Comput. Educ. 2009, 52, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virvou, M.; Katsionis, G.; Manos, K. Combining software games with education: Evaluation of its educational effectiveness. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2005, 8, 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- DeVane, B.; Durga, S.; Squire, K. ‘Economists Who Think Like Ecologists’: Reframing systems thinking in games for learning. E-Learning Digit. Media 2010, 7, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, J. Simulating planning. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2007, 27, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endl, A.; Preisinger, A. Den Klimawandel spielbar machen–Diskursive Strategien der Darstellung von Umweltproblemen und Strategiespielen. Available online: http://www.paidia.de/den-klimawandel-spielbar-machen-diskursive-strategien-der-darstellung-von-umweltproblemen-in-strategiespielen/ (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Mehren, R.; Rempfler, A.; Ulrich-Riedhammer, E.M.; Buchholz, J.; Hartig, J. Systemkompetenz im Geographieunterricht: Ein theoretisch hergeleitetes und empirisch überprüftes Kompetenzstrukturmodell. Z. Didakt. Naturwissenschaften 2016, 22, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehren, R.; Rempfler, A.; Buchholz, J.; Hartig, J.; Ulrich-Riedhammer, E.M. System Competence Modeling: Theoretical Foundation and Empirical Validation of a Model Involving Natural, Social, and Human-Environment Systems. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2018, 55, 685–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, C. Mensch-Umwelt-Systeme in der Geographie: Zur metatheoretischen Möglichkeit einer grundlegenden Systemkompetenz. In Mensch: Umwelt:System–Theorethische Grundlagen und Praktische Beispiele für den Geographieunterricht; Gryl, I., Schlottmann, A., Kanwischer, D., Eds.; LIT: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Budke, A.; Müller, B. Nutzungskonflikte am Rhein als komplexe Mensch-Umwelt-Systeme mit Hilfe von Argumentationen erschließen. In Mensch:Umwelt:System—Theorethische Grundlagen und praktische Beispiele für den Geographieunterricht; Gryl, I., Schlottmann, A., Kanwischer, D., Eds.; LIT: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 177–189. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, B. Komplexe Mensch-Umwelt-Systeme im Geographieunterricht mit Hilfe von Argumentationen erschliessen am Beispiel der Trinkwasserproblematik in Guadalajara (Mexiko). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany, 6 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Weichhart, P. Physische Geographie und Humangeographie–eine schwierige Beziehung: Skeptische Anmerkungen zu einer Grundfrage der Geographie und zum Münchner Projekt einer “Integrativen Umweltwissenschaft”. In Integrative Ansätze in der Geographie–Vorbild oder Trugbild? Münchner Symposium zur Zukunft der Geographie, 28. April 2003, Münchener Geographische Hefte 85; Heinritz, G., Ed.; Universitätsverlag: Passau, Germany, 2003; pp. 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Page, S.E. Diversity and Complexity; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dörner, D.; Funke, J. Complex Problem Solving: What It Is and What It Is Not. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolte, J.P.; Hulse, D.W.; Gregory, S.V.; Smith, C. Modeling biocomplexity–actors, landscapes and alternative futures. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 22, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czauderna, A.; Budke, A. How Digital Strategy and Management Games Can Facilitate the Practice of Dynamic Decision-Making. Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Game | Year of Release | Included Topics | Copies Sold | User Critics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of Empires II HD | 2013 (remade 2019) | (a), (d) | 5,000,000–10,000,000 | (1) 65/100 (2) ‘overwhelmingly positive’ |
| Anno 1800 | 2019 | (a), (d) | no data yet | (1) 81/100 |
| Anno 2070 | 2011 | (a), (b), (d) | 500,000–1,000,000 | (1) 83/100 (2) ‘mixed’ |
| Banished | 2014 | (a), (c) | 1,000,000–2,000,000 | (1) 73/100 (2) ‘very positive’ |
| Cities in Motion 2 | 2013 | (a) | 500,000–1,000,000 | (1) 72/100 (2) ‘mixed’ |
| Cities: Skylines (incl. Add-Ons ‘Natural Disasters’ and ‘Green Cities’) | 2015 (N. D. 2016, G. C. 2017) | (a), (d) | 5,000,000–10,000,000 (base game; no data on Add-Ons) | (1) 85/100 (2) ‘very positive’ |
| Civilization VI (incl. Add-On ‘Gathering Storm’) | 2016 (G. S. 2019) | (a), (b), (d) | 2,000,000–5,000,000 (base game) | (1) 81/100 (2) ‘mostly positive’ |
| Democracy 3 | 2013 | (b), (c), (d) | 200,000–500,000 | (1) 70/100 (2) ‘mostly positive’ |
| ECO (Early Access) | Early Access | (a), (b), (d) | no data yet | no data yet |
| Fate of the World—Tipping Point | 2011 | (b), (c), (d) | 50,000–100,000 (base game; no data on ‘Tipping Point’) | (1) 70/100 (2) ‘mostly positive’ |
| Frostpunk | 2018 | (a), (b), (c), (d) | 2,000,000–5,000,000 | (1) 84/100 (2) ‘very positive’ |
| Pocket City (mobile game) | 2018 | (a), (d) | >1,000,000 (free version) >100,000 (paid version) | (3) 3.9/5 (free) 4.5/5 (paid) |
| Rise of Industry | 2019 | (d) | 50,000–100,000 | (1) 80/100 (2) ‘very positive’ |
| Settlers 7 | 2010 (remade 2019) | (a), (d) | >150,000 (in Europe) | (1) 79/100 |
| SimCity 4 (Deluxe Edition) | 2003 | (a), (d) | 1,000,000–2,000,000 | (1) 84/100 (2) ‘very positive’ |
| SimCity BuildIt (mobile game) | 2014 | (a), (d) | >50,000,000 | (3) 4.5/5 |
| Transport Fever | 2016 | (a) | 200,000–500,000 | (1) 71/100 (2) ‘very positive’ |
| Tropico 6 | 2019 | (a), (c), (d) | 200,000–500,000 | (1) 78/100 (2) ‘very positive’ |
| Game | Finances | Population Size | Approval Parameters | Others | Sum (Param.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Civilization VI | x | Science, culture, faith, tourism, diplomatic favor, era score | 7 | ||
| Democracy 3 | x | GDP, health, education, unemployment, crime rate, poverty | 7 | ||
| Fate of the World | x | x | x | Emissions, GDP, temperature, atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases | 7 |
| Age of Empires II | x | x | Wood, stone, food | 5 | |
| Anno 1800 | x | x | x | Influence, city attractiveness | 5 |
| Settlers 7 | x | x | Winning points, prestige | 4 | |
| Anno 2070 | x | x | x | 3 | |
| Banished | x | x | Health | 3 | |
| Cities:Skylines | x | x | x | 3 | |
| Frostpunk | x | x (2x) | 3 | ||
| Pocket City | x | x | x | 3 | |
| SimCity 4 | x | x | x | 3 | |
| SimCity BuildIt | x | x | x | 3 | |
| Tropico 6 | x | x | x | 3 | |
| Cities in Motion 2 | x | x | 2 | ||
| ECO | Personal nutrient intake, skill points | 2 | |||
| Rise of Industry | x | x | 2 | ||
| Transport Fever | x | 1 | |||
| Sum (games) | 14 (78%) | 12 (67%) | 13 (72%) | 8 (44%) | Ø 3.7 parameters |
| Game | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democracy 3 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 11 | |
| Fate of the World | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 10 | ||
| Tropico 6 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 10 | ||
| Anno 2070 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 9 | |||
| Anno 1800 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 8 | ||||
| Cities: Skylines | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 8 | ||||
| Civilization VI | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 8 | ||||
| Pocket City | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 8 | ||||
| SimCity 4 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 8 | ||||
| SimCity BuildIt | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 7 | |||||
| Frostpunk | x | x | x | x | x | x | 6 | ||||||
| ECO | x | x | x | x | x | 5 | |||||||
| Settlers 7 | x | x | x | x | x | 5 | |||||||
| Age of Empires II | x | x | x | 3 | |||||||||
| Banished | x | x | x | 3 | |||||||||
| Cities in Motion 2 | x | x | x | 3 | |||||||||
| Rise of Industry | x | x | x | 3 | |||||||||
| Transport Fever | x | x | 2 | ||||||||||
| sum | 13 72% | 7 39% | 15 83% | 4 22% | 17 94% | 6 33% | 10 56% | 10 56% | 4 22% | 13 72% | 13 72% | 5 28% |
| Topic Diversity | 1–3 | 4–6 | 7–9 | 10–12 | Sum | |
| No. of Parameters | ||||||
| 0–9 | 2 Age of Empires II, Cities in Motion 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (11%) | |
| 10–19 | 2 Banished, Transport Fever | 1 Frostpunk | 3 Pocket City SimCity 4, SimCity BuildIt | 0 | 6 (33%) | |
| 20–29 | 0 | 0 | 1 Cities: Skylines | 0 | 1 (6%) | |
| 30–39 | 0 | 1 Settlers 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 (6%) | |
| 40+ | 1 Rise of Industry | 1 ECO | 4 Anno 1800, Anno 2070, Civilization VI, Tropico 6 | 2 Democracy 3, Fate of the World | 8 (44%) | |
| sum | 5 (28%) | 3 (17%) | 8 (44%) | 2 (11%) | 18 (100%) | |
| Game | Challenging Terrain/Map | Scarcity of Space | Depleting or Limited Resources | Fire | Diseases and Epidemics | Riots and Crime | Natural Disasters | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anno 2070 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 7 |
| Frostpunk | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 7 |
| Anno 1800 | x | x | x | x | x | x | 6 | |
| Banished | x | x | x | x | x | x | 6 | |
| Cities: Skylines | x | x | x | x | x | x | 6 | |
| Tropico 6 | x | x | x | x | x | x | 6 | |
| Fate of the World | x | x | x | x | x | 5 | ||
| Civilization VI | x | x | x | x | 4 | |||
| Pocket City | x | x | x | x | 4 | |||
| SimCity 4 | x | x | x | x | 4 | |||
| SimCity BuildIt | x | x | x | x | 4 | |||
| Democracy 3 | x | x | x | 3 | ||||
| ECO | x | x | x | 3 | ||||
| Settlers 7 | x | x | x | 3 | ||||
| Age of Empires II | x | x | 2 | |||||
| Cities in Motion 2 | x | x | 2 | |||||
| Rise of Industry | x | 1 | ||||||
| Transport Fever | x | 1 | ||||||
| Sum | 12 (67%) | 12 (67%) | 11 (61%) | 10 (56%) | 10 (56%) | 10 (56%) | 9 (50%) |
| Game | (Representatives of) Interest Groups or Factions | (Representatives of) Nations | NPC-Individuals | City Population (Mass) | Other Players | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tropico 6 | x | x | x | (x) | 3 (4) | |
| Anno 2070 | x | x | x | (x) | 3 (3) | |
| Age of Empires II | x | x | (x) | 2 (3) | ||
| Anno 1800 | x | x | (x) | 2 (3) | ||
| Settlers 7 | x | x | (x) | 2 (3) | ||
| Cities in Motion 2 | x | (x) | 1 (2) | |||
| Civilization VI | x | (x) | 1 (2) | |||
| Banished | x | 1 | ||||
| Cities Skylines | x | 1 | ||||
| Democracy 3 | x | 1 | ||||
| ECO | x | 1 | ||||
| Fate of the World | x | 1 | ||||
| Frostpunk | x | 1 | ||||
| Pocket City | x | 1 | ||||
| SimCity 4 | x | 1 | ||||
| SimCity BuildIt | x | 1 | ||||
| Transport Fever | x | 1 | ||||
| Rise of Industry | 0 | |||||
| Sum | 3 (17%) | 4 (22%) | 3 (17%) | 13 (72%) | 1 (6%) (8 [44%]) |
| Game | Local | Regional | Interregional | National | International | Global | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Civilization VI | x | x | x | x | x | x | 6 |
| ECO | x | x | x | x | x | x | 6 |
| Anno 2070 | x | x | x | x | 4 | ||
| Tropico 6 | x | x | x | x | 4 | ||
| Anno 1800 | x | x | x | 3 | |||
| Fate of the World | x | x | x | 3 | |||
| Settlers 7 | x | x | x | 3 | |||
| Transport Fever | x | x | x | 3 | |||
| Age of Empires II | x | x | 2 | ||||
| Rise of Industry | x | x | 2 | ||||
| Banished | x | 1 | |||||
| Cities in Motion 2 | x | 1 | |||||
| Cities: Skylines | x | 1 | |||||
| Democracy 3 | x | 1 | |||||
| Frostpunk | x | 1 | |||||
| Pocket City | x | 1 | |||||
| SimCity 4 | x | 1 | |||||
| SimCity BuildIt | x | 1 | |||||
| sum | 15 (83%) | 9 (50%) | 8 (44%) | 4 (22%) | 4 (22%) | 4 (22%) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lux, J.-D.; Budke, A. Playing with Complex Systems? The Potential to Gain Geographical System Competence through Digital Gaming. Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10050130
Lux J-D, Budke A. Playing with Complex Systems? The Potential to Gain Geographical System Competence through Digital Gaming. Education Sciences. 2020; 10(5):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10050130
Chicago/Turabian StyleLux, Joelle-Denise, and Alexandra Budke. 2020. "Playing with Complex Systems? The Potential to Gain Geographical System Competence through Digital Gaming" Education Sciences 10, no. 5: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10050130
APA StyleLux, J.-D., & Budke, A. (2020). Playing with Complex Systems? The Potential to Gain Geographical System Competence through Digital Gaming. Education Sciences, 10(5), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10050130





