Abstract
Given the high proportion of struggling readers in school and the long-term negative consequences of underachievement for those affected, the question of prevention options arises. The early identification of central indicators for reading literacy is a noteworthy starting point. In this context, curriculum-based measurements have established themselves as reliable and valid instruments for monitoring the progress of learning processes. This article is dedicated to the assessment of word recognition in silent reading as an indicator of adequate reading fluency. The process of developing an item pool is described, from which instruments for learning process diagnostics can be derived. A sample of 4268 students from grades 1–4 processed a subset of items. Each student template included anchor items, which all students processed. Using Item Response Theory, item statistics were estimated for the entire sample and all items. After eliminating unsuitable items (N = 206), a one-dimensional, homogeneous pool of items remained. In addition, there are high correlations with another established reading test. This provides the first evidence that the recording of word recognition skills for silent reading can be seen as an economic indicator for reading skills. Although the item pool forms an important basis for the extraction of curriculum-based measurements, further investigations to assess the diagnostic suitability (e.g., the measurement invariance over different test times) are still pending.
1. Introduction
Learning disabilities have numerous negative impacts on the educational progress of affected students. Not only is it assumed that school difficulties are consistent throughout the time of a student’s school career [1,2,3], but the problems can also be observed up to adulthood [1]. Against the background of these findings, the proportion of children with problems in learning in Germany is very worrisome. In a Germany-wide survey in 2016, the reading performance of almost 30,000 fourth graders was examined against the background of nationwide standards [4]. In the sample, more than 12% of the children did not reach the minimum standard. These children are therefore able to read simple texts and understand their meaning, but the information must be explicitly specified in the text. To ensure a successful transition to secondary education, intensive support for these children is necessary. Only about 10% achieved the optimum standard, which means that these children can cope with clearly demanding requirements. They can think independently about texts, grasp topics and motives that are not explicitly given in the text, and draw complex conclusions. About 65% of the tested children reached the minimum standard in reading. The results underline the need for specific support for those affected as early as possible, as spontaneous remission cannot be assumed [5].
Similar findings in the USA led to far-reaching legal reforms. With the No Child Left Behind Act in 2001, various standards were enacted to optimize the quality of teaching and support. These include universal screenings on identifying children at risk, better-trained teachers and support staff, and the use of evidence-based instruction and intervention. Moreover, high-stakes assessments have been developed to evaluate the quality of teaching. In this context, curriculum-based measurements (CBM, see below) have gained in meaning. In the context of a response-to-intervention model, CBM provide ongoing information on the learning progress during the school year. On this basis, data-based decisions as well as a formative evaluation of instruction and student support can be made to optimize the teaching-learning framework [6].
The situation in Germany varies considerably [7]. Although there are regular, nationwide tests, whose results are used to assess the effectiveness of the school system, there are no consequences for individual schools (in the sense of direct assumption of responsibility). The approval of financial and human resources to support children with learning problems in Germany requires an official diagnosis of disabilities (e.g., dyslexia). Only then will children have access to additional educational resources. Accordingly, diagnostic measures serve to determine the need for support and do not indicate the need for the adaptation of instruction. Data-based decision-making processes and formative evaluation of the instruction-based on standardized data are unusual [8]. This is because teachers cannot judge the idea behind them and the significance of their use [8]. In addition, the selection of suitable progress monitoring instruments such as CBM is still limited, but constantly growing [9,10]. Against the background of these aspects, this paper presents the construction and evaluation of an item pool from which economic CBM instruments for primary schools in German-speaking countries can be generated. We assume that the word recognition skills can serve as an indicator to screen for low reading fluency skills.
2. Reading Fluency
One of the most important goals of school attendance for all primary school students is the successful acquisition of reading skills. From the transition to secondary school onwards, it is assumed that students will be able to independently extract and understand information from texts [11]. Historically and currently, much importance is attached to reading fluency in connection with the acquisition of reading skills [12,13]. The literature reveals a multitude of attempts to define reading fluency [14,15,16]. Current attempts see fluency as the result of a successful interplay of different basic competencies [13,17]. The US-American National Reading Panel [16] published a frequently cited definition. They describe fluency as the ability “to read orally with speed, accuracy, and proper expression” [16] (p. 5). Accordingly, reading fluency is a process of appropriate recoding and decoding of what has been read, the quality of which depends on various aspects, such as reading accuracy and phonological, orthographic, and morphological abilities [12,13,17,18,19].
Reading fluency, however, is not only the outcome of a successful combination of different partial competences, but also often seen as a prerequisite for higher reading skills [20,21]. In this context, emphasis is placed on the speed of reading [12,22,23]. The basic assumption is that insufficient word reading skills (slow, stagnant, and erroneous decoding) is an obstacle to the contraction of individual information into larger units of meaning. This in turn complicates the processes of activating prior knowledge, integrating new information into existing knowledge structures, and metacognitive control processes [21]. Only when the word reading process is automated do resources become available for higher forms of information processing, i.e., more complex reading processes [16,24,25,26]. Especially in the first years of school, clear connections between the ability to quickly recognize and decode words and reading comprehension can be empirically depicted [27,28]. With increasing reading experience, the students’ mental lexicon expands, and frequent combinations of sounds, morphs, and words are stored and linked. Automated word recognition and rapid decoding thus form the basis for appropriate reading fluency at the sentence and text level, which is in turn necessary for the successful understanding of meaning [12,29].
Against the background of the different understandings of reading fluency listed above, it becomes clear that early interventions are necessary to promote reading fluency in order to prevent reading problems [20,30,31]. Reading fluency should therefore be understood in a development-oriented way [20]. Attention should be paid to it even at the beginning of reading acquisition. At this point, this concerns aspects of phonemic segmentation, alphabetic understanding, phonics, and orthography [12,30], as well as word recognition [32]. As with reading fluency, word recognition skills can be seen as an outcome, as well as a predictor. As a result of the interplay of letter and sound knowledge, as well as decoding abilities, word recognition skills serve as an outcome variable [16,33].
According to the National Reading Panel [16], fluency is the direct result of successful word recognition. Overall, word recognition skills can be assumed to be a potential indicator of reading fluidity [12,13]. In this sense, the assessment of word recognition skills (amount of words read identified correctly within a limited time span) over time plays an important role in preventing reading difficulties. According to the study by Speece and Ritchey [34], word recognition skills develop at the same time as the first word recognition processes and are therefore already important in grade 1. At the end of grade 2, most students should have acquired fundamental word recognition skills [35], and by the middle of grade 4 at the latest [36]. The assessment of basic reading skills, such as the precise recoding and decoding of words, should be a goal of instruction in the first grades at school [33]. Based on this data, further pedagogical decisions can be made.
3. Assessing Reading Fluency with Curriculum-Based Measurements
Curriculum-based measurements (CBM) [37] are a very prominent approach for progress monitoring of academic skills. CBM were developed in the USA and already have a long research tradition there, especially in the fields of reading, writing, and mathematics [37,38,39]. The original aim of the use of CBM was to provide teachers working in special education with reliable and valid data for assessing the development of students, in order to support instructional decisions [37]. These short test procedures can be used regularly at short intervals. Within a time limit of only a few minutes, the children have to solve as many tasks of a test as possible. Due to the repeated application, the monitoring of academic progress can be derived [40]. On the one hand, CBM can be easily implemented in school routines. On the other hand, the instruments must correspond to the current standards of psychological tests, so that the results can be clearly interpreted.
Depending on the domain of use, CBM may refer to separate competencies that are curricularly identified for the area (e.g., CBM for addition tasks in the numerical range up to 20) or that can be regarded as an indicator of general outcome (e.g., reading aloud as an indicator of general reading skills). Alternatively, they may bundle different partial competences relevant to the domain in a single instrument (CBM with mixed tasks for calculating sizes, for factual tasks, etc.) [37,40,41,42,43].
The origin of CBM research lies in the field of reading. Accordingly, many methods have been published in this domain [43]. Reading fluency is often assessed by reading aloud individual syllables, words, or texts [44]. The working time is limited to one minute. The test leader documents the correctly read syllables or words.
A large number of research findings show, in particular, that measures of fluency are relevant with regard to students’ reading skills [45,46,47,48]. According to Fuchs et al. [44] and Reschly, Busch, Betts, Deno, and Long [49], oral reading fluency can be assumed to be a reliable indicator of overall reading competence.
While much attention has been paid to oral reading, there is a lack of research related to the silent reading of students [35,50]. One justification for this can be found in the conclusions of the National Reading Panel [16]. Accordingly, there is a lack of empirical research on the effectiveness of silent reading experiences [51]. Therefore, adequate time should rather be given to reading aloud in class [51,52,53]. In reality, however, silent reading is the most important form of reading from the first grade onwards [50]. Empirical findings indicate that there is a high correlation between oral reading and silent reading. This is particularly true for gifted readers and in higher grades [53,54,55].
4. Research Questions
Our research refers to the word recognition skills of elementary school students. In order to early identify struggling elementary school students, we want to generate CBM to assess their word recognition skills. To create different CBM instruments, we designed an item pool, from which items can be flexibly selected according to content-related but also psychometric aspects. The aim of the study presented here is to test the psychometric suitability of the item pool.
5. Methods
The psychometric suitability of the items from the item pool were tested using common item parameters (item difficulty, selectivity, and fit to the one-dimensional Rasch model). In addition, the coefficients of reliability and validity were determined.
5.1. Design
The items of the generated item pool were distributed and piloted within a multimatrix design [56]. Items were divided by grade level into eight different word lists each. Due to the multimatrix design, each list had a proportion of identical words (so-called anchor items) within one grade level and between grade levels. The tests were carried out by the teacher in the middle of the school year without a time limit, as is usually the case with CBM, in order to be able to calculate characteristic values for each item.
The multimatrix design of the test templates made it possible to generate a cross-linked data set. Analyses based on the item response theory (IRT) allowed the determination of psychometric parameters for all items based on the total sample. Since the present data matrix shows a binary coding in “correctly solved” or “incorrectly solved”, a dichotomous Rasch Model was estimated. The Rasch analyses were performed with the statistics program R [57] using the pairwise package [58]. The model fit of the items was judged by their estimated Infit values. Since the outfit statistics are clearly influenced by outlier values, whereas the Infit values are more sensitive in the range of medium ability values [59], the Infit statistics were primarily examined in the present study for deviations from the expected value 1 (0.70 ≤ Infit ≤ 1.30) [60]. For further analysis of the quality of the items, common item statistics (difficulty and selectivity) were calculated.
In order to check for differences in item difficulties between boys and girls (test fairness regarding gender), a graphical model test was carried out to assess the measurement invariance of the items.
To analyze the reliability, Cronbach’s α was reported. Based on a correlation of the items of the item pool with an external criterion (ELFE-II test), the construct validity could be tested.
5.2. Sample
A total of 4268 elementary school students took part in the evaluation of the item pool. Table 1 gives an overview of the distribution of the children among the different grades. One part of these children (N = 178) solved the tasks of the item pool as well as a German reading comprehension test (“Ein Leseverständnistest für Erst- bis Siebtklässler—Version II”, ELFE II; see below).

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of the pilotage sample.
5.3. Instruments
5.3.1. The Item Pool
Against the theoretical background mentioned before, items for assessing word recognition skills were developed and compiled into a comprehensive item pool. In order to form a suitable item pool for assessing the word reading skills of children of primary school age, various considerations are necessary, which integrate verbal, literary, scientific, and curricular analyses. The formal design of the items was based on economic and pragmatic factors. Thus, they were to be feasible as group procedures in class. In connection with the previously described significance of silent reading experiences [35,50,51], it was therefore decided that the students should identify a real target word from a selection of pseudowords (e.g., “Maelr”–“Maler”–“Melar”–“Mlaer”; target word: “Maler” = painter).
To generate the item corpus used in this study, an analysis of various common textbooks was carried out. An intersection of the word material was created and compared with the available minimum vocabulary for the primary school sector in Germany. On this basis, 1277 words could be identified as relevant word material for primary schools. The words of the item pool were structured according to different aspects (word type, number of letters, number of syllables, and number of graphemes, as well as phonological, morphological, and orthographic peculiarities) and occurrences according to grade levels. For each word out of the item pool we designed pseudowords. Every distractor shows an optical proximity to the target word. For each item, pseudowords have been chosen that have a letter combination valid for Germany, as well as those that are unpronounceable in the German language.
Within the prepilot, a total of 533 children of the first to the fourth grade solved between 40 and 50 items according to the described task format, depending on the grade level. The distribution among the different grades is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics of the sample in the prepilot.
An analysis of the student outcomes (frequency of solutions) and interviews with the teachers and students (difficulty with tasks and possible remarks) indicate that the task format is understandable for students in elementary schools, that teachers consider it appropriate, and that there is a high variance of outcomes, i.e., it can differentiate between different achievement levels.
5.3.2. The ELFE-II Test
In addition to the items of the item pool, some of the children worked on an established instrument to assess the reading fluency, reading accuracy, and reading comprehension of German-speaking children at the word, sentence, and text level (ELFE-II) [61]. To test the reading comprehension at the word level, the children had to choose the correct word out of a list of four for a given picture within a limited time span. At the sentence level, the children had to separate the correct word from four given distractors, and at the text level, the children were asked to answer multiple-choice questions for short texts. The ELFE-II test can be used in an individual or group session from the end of the first grade to the beginning of the seventh grade. The reliability (split-half reliability: rtt = 96; retest reliability: rtt = 93; parallel reliability: rtt = 93) and concurrent validity (correlation to another reading test: r = 77; correlation to the teacher’s judgment: r = 70) of the instrument could be proven. Construct validity was determined using structural equation models. In addition, validity studies are available for children with diagnosed reading and spelling disorders and for children from different school types [61].
6. Results
Due to the scaling according to IRT, empirical characteristic values (difficulty, selectivity, and model fit statistics) considered during item selection are available for each item. The item difficulties σ result from the Thurston threshold values estimated in the Rasch Model (due to dichotomous response possibilities). The σ-values can be interpreted as z-values, so that a value of zero corresponds to an average difficulty. Values below zero indicate that the words were easier for the children to read, values above zero indicate more difficult items. The selectivity values were calculated as point biserial correlations of the raw scores with the respective total value of the test template. These values help to discriminate which items are separated between students with low and high levels of performance. A value close to one means that the item assesses the same aspect as the overall test. A value close to zero indicates that an item has little in common with the overall test. In this study a value of rpbis = 0.2 and above served as a minimum criterion.
Of the items analyzed, 206 showed too little selectivity (rpbis < 0.2) or an under or overfit in the Infit statistics (fit < 0.70 or fit > 1.30). These items were eliminated from the item pool for further analysis. The reduced item pool was then scaled again using a one-dimensional Rasch Model. The selectivity values were at least rpbis = 0.20, the maximum was rpbis = 0.66, and the average value was rpbis = 0.41. The item fit statistics (InfitMnSq) varied between min = 0.70 and max = 1.30. The mean InfitMnSq was 0.92. This indicates that there were no model violations and that all items meet the requirements of a one-dimensional Rasch model. All items thus form a one-dimensional scale, i.e., they measure the same construct.
The mean item difficulty was σ = 0.00, and the values scattered in a range between min = −2.99 and max = 3.68. The item pool thus covered a range of very easy to very difficult items. An analysis of the item difficulties separated by grade levels showed an increase in the mean values with constant standard deviation (see Table 3), i.e., the items became easier with the increasing grade level. Results show that there is a wide range of item difficulties in every grade level.

Table 3.
Mean, minimum, and maximum item difficulties, separated according to grade levels.
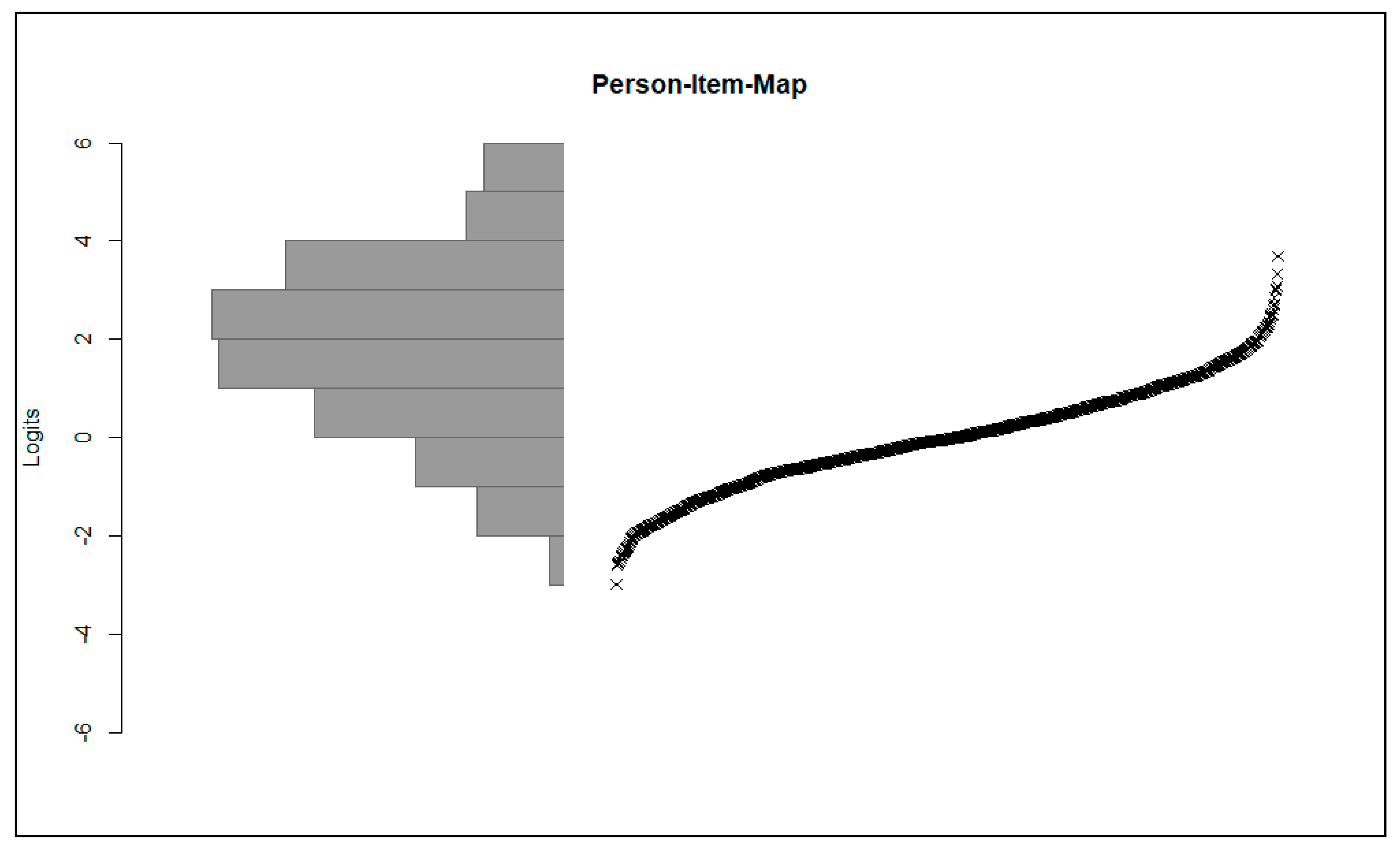
Due to the use of the Rasch model, it was also possible to map the item and person parameters on the same scale. The personal parameters WLE (Weighted-Maximum-Likelihood-Method) [62] were determined by a pairwise item comparison [63,64]. This method is particularly suitable for data sets with missing values [64,65]. The WLE can be used to assess the appropriateness of the degree of difficulty of the items. The person item map (see Figure 1) shows the person parameters as histograms, as well as the item difficulty. It becomes clear that the measurement range of the items essentially corresponds to the distribution of the person parameters. However, one can see that there is a lack of items for students with particularly high skills.
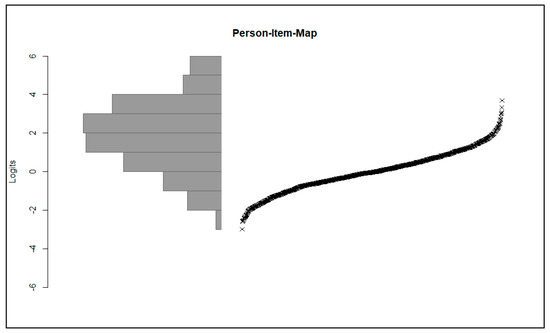
Figure 1.
A person–item map (distribution of a person’s abilities as a histogram on the left side; measuring range of the items ordered by item difficulty).
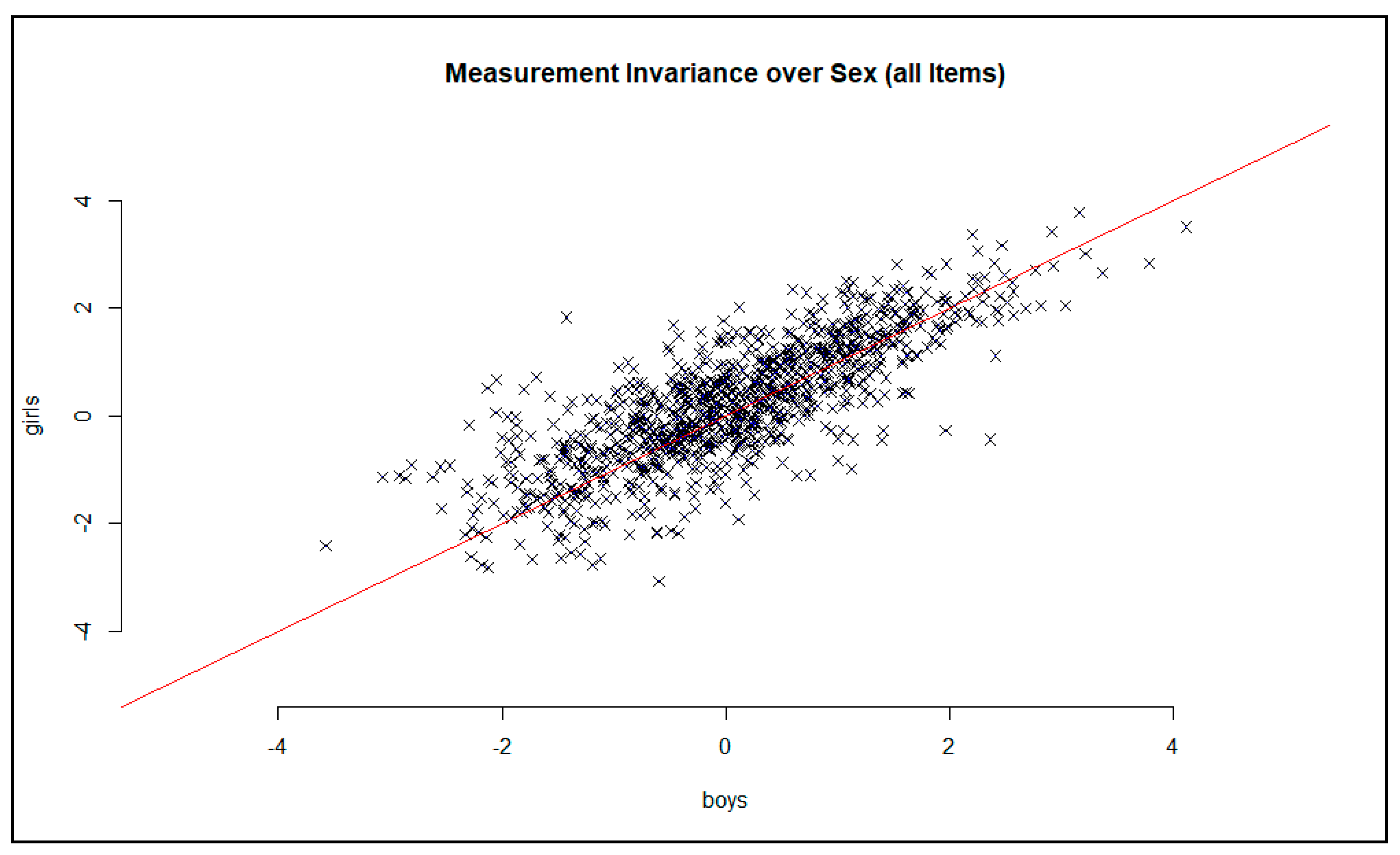
In order to analyze the differences in item difficulties between boys and girls, the results obtained were plotted separately by gender on the x- and y-axes (see Figure 2). If the parameters are constant across the sexes, they run along the bisectors of the angle. Here, there are differences in the item difficulties of individual items. A few items (N = 21) showed very large deviations from the bisecting line. A variance analysis showed a significant influence of sex (F(1, 4115) = 9.753, p < 05), but the effect was only small (η2 = 002 or d = 0.10).
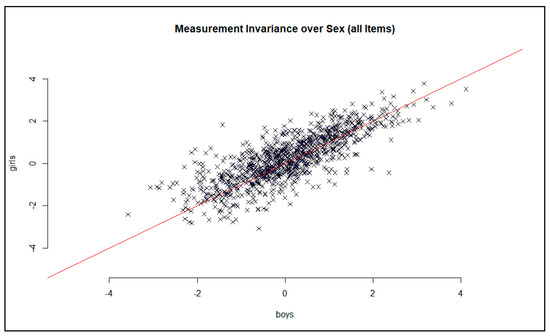
Figure 2.
Graphical model test for the assessment of the measurement invariance via gender. Note: a few items cannot be displayed here, as they show very large deviations from the bisecting line.
For the eight word lists from each grade level, we determined Cronbach’s α. The overall values varied between α = 74 and α = 97. On average, the values were high (grade 1: α = 95; grade 2: α = 89; grade 3: α = 89; and grade 4: α = 85).
According to Cohen [66], the correlation with the ELFE-II test is high: r = 64 (N = 178).
7. Discussion
The aim of the present study was to design an item pool to assess the word recognition skills of elementary school students. The importance of word recognition in the context of reading fluency was established. Overall, word recognition can be seen as a potential indicator for first reading skills [12,13]. To increase the assessment economy in school practice, the items were conceived as tasks for quiet reading. This enables an assessment of the whole class at a time. It is assumed that these results are largely related to oral reading skills [53,54].
Another aim of the study was to verify the psychometric suitability of these items. For this purpose, the items were distributed over different test templates, which were connected to each other by means of anchor items. Thus, not every child in the sample had to process all the items, but it was still possible to determine item and person estimators for each item and for all students using the item response theory. From the original 1277 items, a total of 1071 items corresponded to the previously set criteria. The other items were dropped due to unfavorable selectivity or an over- or underfit to the computed Rasch model. Overall, the reliability of the individual test templates is high (lowest average α = 85), which speaks for the homogeneity of the items. The correlation with other reading tests is also high (r = 64). This shows that word recognition skills are related to reading speed and reading comprehension.
Although there are indications that some of the items are of different difficulty for girls and boys (in the sense of test fairness), these differences can be regarded as minor. No items measure in the upper performance range, which is another limitation of this study. However, it can be argued that although word recognition is highly correlated with other reading skills, such as passage comprehension throughout primary school [47], it is particularly important in the first years of primary school [34]. From the third grade onwards, it can be assumed that students have largely acquired word recognition skills [35,36]. In this respect, possible ceiling effects are to be expected in higher grades. The items of the item pool therefore differentiate particularly in the lower performance range. Against this background, however, they can be used for screening purposes. Overall, the targeting of the items appears to be adequate. Though word recognition skills seem to be a potential indicator of reading skills, they are not sufficient to diagnose higher reading skills. The use of further test instruments should be considered here.
Based on the item pool, CBM with parallel forms of the same structure were developed, which can be used every four weeks during a school year (10 parallel forms in each grade level). A proportion of easier (−2.5 ≤ σ < −1), medium (−1 ≤ σ < 0), and more difficult items (0 ≤ σ ≤ 1) was selected to map different areas of competence. In further investigations, the suitability of the developed CBM for progress monitoring will be investigated. In addition to classical quality criteria (objectivity, reliability, and validity), progress monitoring criteria must also be fulfilled (Fuchs, 2004). The study presented here only uses results from a cross-sectional study. Thus, no information can be derived on the suitability of the items for status diagnostic purposes. The scaling according to the item response theory, however, is to be seen as a meaningful addition to the classical test theory, which allows first statements about the suitability for progress monitoring (high reliability, unidimensionality of the measured construct, constant item difficulty, and high test fairness) [67,68,69]. In a further step, the measurement invariance over different test times should be investigated. In addition, the sensitivity to change as well as the applicability and effectiveness in the school context should be examined [42].
A calibrated item pool, as described in this study, provides many advantages. Different instruments can be flexibly developed from such a pool. It is also possible to realize adaptive test situations, whereby the item selection in the concrete test situation is dependent on the ability of the child, in order to enable more precise measurements at the ability level. In this context, the use of digital media appears to be particularly useful [35,70]. In addition, the time taken to process the items can be measured with the aid of a computer. This makes it possible to dispense with a time restriction on the processing time, which can lead to increased pressure on the students. A further advantage is the possible combination of diagnostic information and training material. Computer-aided training programs can react adaptively to the results of an upstream diagnosis. Digital technologies offer the potential to support struggling readers; however, little systematic research has focused on the effect of technology on reading skills [71]. In terms of quiet reading, the research situation has so far been even sparser.
Future research will concentrate on factors that influence the difficulty of the items of the word pool. Possible variables in this context are structural features of the words (word type, word length, number of syllables or graphemes in a word) and phonological, morphological, and orthographic characteristics and occurrences in textbooks according to grade level.
Author Contributions
The authors contributed equally to the conceptualization, writing, and revision of this article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania/Germany.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support of Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and Universität Rostock within the funding program Open Access Publishing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kohn, J.; Wyschkon, A.; Ballaschk, K.; Ihle, G.; Esser, G. Verlauf von Umschriebenen Entwicklungsstörungen: Eine 30-Monats-follow-up-Studie. Lernen und Lernstörungen 2013, 2, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, F.; Wyschkon, A.; Gallit, F.S.; Poltz, N.; Moraske, S.; Kucian, K.; von Aster, M.; Esser, G. Rechenprobleme von Grundschulkindern: Persistenz und Schulerfolg nach fünf Jahren. Lernen und Lernstörungen 2018, 7, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyschkon, A.; Schulz, F.; Gallit, F.; Poltz, N.; Kohn, J.; Moraske, S.; Bondü, R.; von Aster, M.; Esser, G. 5-Jahres-Verlauf der LRS: Stabilität, Geschlechtseffekte, Schriftsprachniveau und Schulerfolg. Zeitschrift für Kinder- und Jugendpsychiatrie und Psychotherapie 2017, 46, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanat, P.; Schipolowski, S.; Rjosk, C.; Weirich, S.; Haag, N. IQB-Bildungstrend 2016. Kompetenzen in den Fächern Deutsch und Mathematik am Ende der 4. Jahrgangsstufe im zweiten Ländervergleich; Waxmann: Münster, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselhorn, M.; Schuchardt, K. Lernstörungen. Eine kritische Skizze zur Epidemiologie. Kindheit und Entwicklung 2006, 15, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.M.; Coulter, W.A.; Reschly, D.J.; Vaughn, S. Alternative approaches to the definition and identification of learning disabilities: Some questions and answers. Ann. Dyslexia 2004, 54, 304–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, Y.; Voß, S.; Sikora, S.; Hartke, B. Selected findings of the first large-scale implementation of Response to Intervention in Germany. In Inclusive Mathematics Education. State-of-the-Art Research from Brazil and Germany; Kollosche, D., Marcone, R., Knigge, M., Penteado, M.G., Skovsmose, O., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 123–145. [Google Scholar]
- Voß, S.; Blumenthal, Y. Data-Based Decision-Making. In Zum Konstrukt und Verständnis datenbasierter Förderentscheidungsprozesse im Unterricht. In Proceedings of the Arbeitsgruppe Empirische Sonderpädagogische Forschung (AESF), Siegen, Germany, 22–23 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselhorn, M.; Schneider, W.; Trautwein, U. Lernverlaufsdiagnostik; Hogrefe: Göttingen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Voß, S.; Gebhardt, M. Schwerpunktthema: Verlaufsdiagnostik in der Schule. Empirische Sonderpädagogik 2017, 2, 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Scheerer-Neumann, G. Lese-Rechtschreib-Schwäche und Legasthenie. Grundlagen, Diagnostik und Förderun; Kohlhammer: Stuttgart, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, M.; Katzir-Cohen, T. Reading Fluency and Its Intervention. Sci. Stud. Read. 2001, 5, 211–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasinski, T.V.; Reutzel, C.R.; Chard, D.; Linan-Thompson, S. Reading Fluency. In Handbook of Reading Research; Kamil, M.L., Pearson, P.D., Moje, B., Afflerbach, P., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 4, pp. 286–319. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, R.F.; Lane, H.B.; Pullen, P.C.; Torgesen, J.K. The complex nature of reading fluency: A multidimensional view. Read. Writ. Q. 2009, 25, 4–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn, M.R.; Good, R.H.; Knutson, N.; Tilly, W.D.; Collins, V.L. Curriculum based measurement of oral reading fluency: A confirmatory analysis of its relation to reading. Sch. Psychol. Rev. 1992, 21, 459–479. [Google Scholar]
- National Reading Panel. Teaching Children to Read: An Evidencebased Assessment of the Scientific Research Literature on Reading and Its Implications for Reading Instruction; National Institute of Child Health and Human Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Leppänen, U.; Aunola, K.; Niemi, P.; Nurmi, J.E. Letter knowledge predicts fourth grade reading fluency and reading comprehension. Learn. Instr. 2008, 18, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, V.W.; Abbott, R.D.; Billingsley, F.; Nagy, W. Processing underlying timing and fluency of reading: Efficiency, automaticity, coordination, and morphological awareness. In Dyslexia, Fluency and the Brain; Wolf, M., Ed.; York Press: Timonium, MD, USA, 2001; pp. 383–414. [Google Scholar]
- Rosebrock, C.; Nix, D. Grundlagen der Lesedidaktik: Und der systematischen schulischen Leseförderung, 8th ed.; Schneider: Hohengehren, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kame’enui, E.J.; Simmons, D.C.; Good, R.H.; Harn, B.A. The use of fluency-based measures in early identification and evaluation of intervention efficacy in schools. In Dyslexia, Fluency and the Brain; Wolf, M., Ed.; York Press: Timonium, MD, USA, 2001; pp. 308–331. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, J. LDL—Lernfortschrittsdiagnostik Lesen; Hogrefe: Göttingen, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, W.P.; Rupley, W.H.; Rasinski, T. Fluency in learning to read for meaning: Going beyond repeated readings. Lit. Res. Instr. 2009, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasinski, T.V. Reading fluency instruction: Moving beyond accuracy, automaticity, and prosody. Read. Teach. 2006, 59, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.; Dunphy, E.; Dwyer, B.; Hayes, G.; McPhillips, T.; Marsh, J.; O’Connor, M.; Shiel, G. Literacy in Early Childhood and Primary Education (3–8 years); Research Report No 15; NCCA: Sheffield, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Perfetti, C.A.; Landi, N.; Oakhill, J. The acquisition of reading comprehension skill. In The Science of Reading: A Handbook; Snowling, M.J., Hulme, C., Eds.; Basil Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 227–247. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.R. Methods for detecting and evaluating cultural bias in neuropsychological tests. In Handbook of Cross-Cultural Neuropsychology; Fletcher-Janzen, E., Strickland, T.L., Reynolds, C.R., Eds.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rupley, W.H.; Willson, V.L.; Nichols, W.D. Exploration of the developmental components contributing to elementary school children’s reading comprehension. Sci. Stud. Read. 1998, 2, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willson, V.L.; Rupley, W.H. A structural equation model for reading comprehension based on background, phonemic, and strategy knowledge. Sci. Stud. Read. 1997, 1, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.S.; Hook, P.E. Fluency: A Key Link between Word Identification and Comprehension. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2009, 40, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzir, T.; Kim, Y.; Wolf, M.; O’Brien, B.; Kennedy, B.; Lovett, M.; Morris, R. Reading fluency: The whole is more than the parts. Ann. Dyslexia 2006, 56, 51–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgesen, J.K.; Rashotte, C.A.; Alexander, A.W. Principles of fluency instruction in reading: Relationships with established empirical outcomes. In Dyslexia, Fluency and the Brain; Wolf, M., Ed.; York Press: Timonium, MD, USA, 2001; pp. 332–355. [Google Scholar]
- Coltheart, M.; Rastle, K.; Perry, C.; Langdon, R.; Ziegler, R. DRC: A dual route cascaded model of visual word recognition and reading aloud. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 108, 204–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamhi, A.G. The Case for the Narrow View of Reading. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2009, 40, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speece, D.L.; Ritchey, K.D. A longitudinal study of the development of oral reading fluency in young children at risk for reading failure. J. Learn. Disabil. 2005, 38, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiebert, E.H.; Wilson, K.M.; Trainin, G. Are students really reading in independent reading contexts? An examination of comprehension-based silent reading rate. In Revisiting Silent Reading: New Directions for Teachers and Researchers; Hiebert, E.H., Reutzel, D.R., Eds.; International Reading Association: Newark, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 151–167. [Google Scholar]
- Pinnell, G.S.; Pikulski, J.J.; Wixson, K.K.; Campbell, J.R.; Gough, P.B.; Beatty, A.S. Listening to Children Read aloud; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Deno, S.L. Curriculum-based measurement: The emerging alternative. Except. Child. 1985, 52, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deno, S.L.; Fuchs, L.S. Developing curriculum-based measurement systems for data-based special education problem solving. Focus Except. Child. 1987, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deno, S.L.; Mirkin, P.K. Data Based Program Modification: A Manual; Council for Exceptional Children: Reston, VA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Hosp, M.K.; Hosp, J.L.; Howell, K.W. The ABCs of CBM: A Practical Guide to Curriculum-Based Measurement; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, L.S.; Deno, S.L. Curriculum-based measurement: Current applications and future directions. Except. Child. 1991, 57, 466–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, L.S. The Past, Present, and Future of Curriculum-Based Measurement Research. Sch. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 33, 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wayman, M.M.; Wallace, T.; Wiley, H.I.; Tichá, R.; Espin, C.A. Literature Synthesis on Curriculum-Based Measurement in Reading. J. Spec. Educ. 2007, 41, 85–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, L.S.; Fuchs, D.; Hosp, M.K.; Jenkins, J.R. Oral reading fluency as an indicator of reading competence: A theoretical, empirical, and historical analysis. Sci. Stud. Read. 2001, 5, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, T.J.; Zopluoglu, C.; Long, J.; Monaghen, B. Curriculum-based measurement of oral reading: Quality of progress monitoring outcomes. Except. Child. 2012, 78, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, R.H.; Simmons, D.C.; Kame’enui, E.J. The Importance and Decision-Making Utility of a Continuum of Fluency-Based Indicators of Foundational Reading Skills for Third-Grade High-Stakes Outcomes. Sci. Stud. Read. 2009, 5, 257–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosp, M.K.; Fuchs, L.S. Using CBM as an indicator of decoding, word reading, and comprehension: Do the relations change with grade? Sch. Psychol. Rev. 2005, 34, 9–26. [Google Scholar]
- Stecker, P.M.; Lembke, E.S.; Foegen, A. Using progress-monitoring data to improve instructional decision making. Prev. Sch. Fail. 2008, 52, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reschly, A.L.; Busch, T.W.; Betts, J.; Deno, S.L.; Long, J.D. Curriculum-based measurement oral reading as an indicator of reading achievement: A meta-analysis of the correlational evidence. J. Sch. Psychol. 2009, 47, 427–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Wagner, R.K.; Lopez, D. Developmental relations between reading fluency and reading comprehension: A longitudinal study from grade one to two. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2012, 113, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.; Hiebert, E.H.; Tompkins, R. How much and what are third graders reading? Reading in core programs. In Reading More, Reading Better; Hiebert, E.H., Ed.; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 118–140. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, D.; Hiebert, E.H. If I follow the teachers’ editions, isn’t that enough? Analyzing reading volume in six core reading programs. Elem. Sch. J. 2010, 110, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.R.; Jewell, M. Examining the validity of two measures for formative teaching: Reading aloud and maze. Except. Child. 1993, 59, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Wagner, R.K.; Foster, E. Relations among Oral Reading Fluency, Silent Reading Fluency, and Reading Comprehension: A Latent Variable Study of First-Grade Readers. Sci. Stud. Read. 2011, 15, 338–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasinski, T.; Rikli, A.; Johnston, S. Reading Fluency: More than Automaticity? More Than a Concern for the Primary Grades? Lit. Res. Instr. 2009, 48, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mislevy, R.J.; Beaton, A.E.; Kaplan, B.; Sheehan, K.M. Estimating population characteristics from sparse matrix samples of item responses. J. Educ. Meas. 1992, 29, 133–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing [Computer software]. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/mirrors.html (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Pairwise: Rasch Model Parameters by Pairwise Algorithm (R package version 0.5.1) [Computer software]. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pairwise/index.html (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Linacre, J.M. What do Infit and Outfit, Mean-square and Standardized mean? Rasch Meas. Trans. 2002, 16, 878. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, T.G.; Fox, C.M. Applying the Rasch Model: Fundamental Measurement in the Human Sciences, 3rd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard, W.; Lenhard, A.; Schneider, W. Ein Leseverständnistest für Erst- bis Siebtklässler—Version II; Hogrefe: Göttingen, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Warm, T.A. Weighted Likelihood Estimation of Ability in Item Response Theory. Psychometrika 1989, 54, 427–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choppin, B. Item Bank using Sample-free Calibration. Nature 1968, 219, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, B.D.; Masters, G.N. Rating Scale Analysis; MESA Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Heine, J.-H.; Tarnai, C. Pairwise Rasch Model Item Parameter Recovery under Sparse Data Conditions. Psychol. Test Assess. Modeling 2015, 57, 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Rost, J. Lehrbuch der Testtheorie—Testkonstruktion, 2nd ed.; Hans Huber: Bern, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Klauer, K.J. Lernverlaufsdiagnostik—Konzept, Schwierigkeiten und Möglichkeiten. Empirische Sonderpädagogik 2011, 3, 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wilbert, J.; Linnemann, M. Kriterien zur Analyse eines Tests zur Lernverlaufsdiagnostik. Empirische Sonderpädagogik 2011, 3, 225–242. [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert, E.H.; Menon, S.; Martin, L.A.; Bach, K.E. Online Scaffolds that Support Ado1escents’ Comprehension; Apex Learning: Seattle, WA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, J.; Ferdig, R.E.; Pearson, P.D.; Wardrop, J.; Blomeyer, R.L., Jr. Technology and reading performance in the middle-school grades: A metaanalysis with recommendations for policy and practice. J. Lit. Res. 2008, 40, 6–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).