Abstract
This paper aims to examine the determinants of financial stability in Jordanian commercial banks based on annual data for the period from 2011 to 2018. Based on the pooled effect model, this study shows that SME loans and capital adequacy positively and statistically affect the stability of Jordanian commercial banks, while financial inclusion, liquidity risk and credit risk negatively and statistically affect the stability of Jordanian commercial banks. The study recommends increasing the directing of bank loans towards small and medium enterprises, and the necessity for bank managers to commit to capital adequacy requirements because of their positive impact on banks’ stability. This study recommends that banks experiencing financial stability accelerate the increase in the rate of financial inclusion because financial inclusion ratios are very low in most of these stable banks. On the other hand, Jordanian commercial banks that have relatively high rates of financial inclusion should reduce the operating expenses resulting from financial inclusion. Bank managers also have to maintain sufficient liquidity in their banks and enhance credit standards by increasing collateral requirement from customers.
1. Introduction
The banking sector in Jordan plays the role of mediator and helps in the transfer of funds from surplus units to deficit units. It also facilitates the movement of payments from customers, merchants and stakeholders. The bank is considered a trust agent because all its business is based on trust between the client and the bank, and it also helps in the national economic development (Irfan et al. 2019). The continuity of the business of commercial banks is conditional on achieving profits, while the stability of banks, especially after the global financial crisis in 2008, has become a source of concern for banking regulatory authorities (Abedifar et al. 2013; Tan and Floros 2012). Therefore, the increasing risks facing banks, whether it is a funding risk, credit risk or liquidity risk, force banking supervisory authorities to pay attention to the bank capital adequacy and financial inclusion to protect commercial banks from the risks of bankruptcy and to increase its stability.
Financial stability is important in any economy because banks control and manage the financial system (Moyo et al. 2014). Banks are related to each other on the one hand, and to households and companies on the other. Therefore, if some banks are affected themselves, or between banks, families and individuals, this leads to banking instability (Ahamed and Mallick 2019). The market value of Jordanian commercial banks constitutes the largest share in the Amman Stock Exchange (ASE). Based on the annual financial stability report issued by the Central Bank of Jordan in 2021, the banking sector in Jordan constitutes more than 50% of the market value of companies listed on the ASE. Therefore, the stability of the banking sector is an important pillar at the level of the ASE and at the level of the Jordanian economy. In addition, looking at the study data related to the stability of Jordanian commercial banks, the average stability of these banks showed that they are clearly declining, especially after 2014. The average stability of Jordanian commercial banks was 6.54, 6.01, 5.72, 5.11, and 5.01 in 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, and 2018, respectively. This decline in the average stability of Jordanian commercial banks motivated us to examine the determinants of the stability of Jordanian commercial banks. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to examine the determinants of the stability of Jordanian commercial banks over the period from 2011 to 2018.
The motivation for this study comes from several important points. Firstly, the average value of stability for Jordanian commercial banks over the study period from 2011 to 2018 based on Z-Score, shows significant differences ranging from 0.07 to 15.22, with a standard deviation of 3.98%. Despite the stability of Jordanian commercial banks on average, the presence of these differences makes us wonder what the main factors that determine the stability of Jordanian commercial banks are. Therefore, this study attempts to fill this gap and examine the most important factors that affect financial stability in Jordanian commercial banks. Secondly, reviewing prior literature clearly shows that the focus of these studies was on very limited factors in terms of explaining stability in the financial sector. Moreover, the findings seem conflicting and inconsistent. For example, the focus of Männasoo and Mayes (2009) and Pessarossi et al. (2020) was on profitability, Lesmana (2021) on funding risk, Chai et al. (2022) on credit, liquidity and funding risk. The current study, however, includes six factors as determinants for stability in the banking sector. Part of these variables is rarely studied in the literature such as loans to SMEs. Thus, this study attempts to provide evidence that supports or contradicts previous studies and shows the direction and impact of these variables on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks.
The importance of this study stems from various aspects. First of all, the importance of this study lies in the importance of the banking sector in any country. In Jordan, the banking sector is one of the largest sectors that significantly contributes to national economic development. Thus, financial stability requires that banks have sound financial systems and leads to a healthy economy. Financial stability enhances confidence between banks and public savings. Thus, customers are assured that their money is not exposed to risks. Moreover, the issue of financial stability is one of the hot topics for decision makers and bank managers because financial stability contributes to improving the national economy. It is also a magnet for capital and investors. The issue of financial stability began to gain global attention in 1974, since the Basel 1 Accord. The number of research papers discussing the determinants of financial stability is increasing.
However, there are limited studies that discuss the determinants of financial stability in emerging countries, especially in Jordan. For example, Al Salamat and Al-Kharouf (2021) select the study period from 2007 to 2016 where this period includes the recent financial crisis, which might question the findings of their study; particularly the main point in the study is testing the stability in the Jordanian banking sector. Thus, testing this issue during the crisis period may not yield reasonable findings. Our paper, however, selects a different and up-to-date period to yield more consistent results and avoid biased findings. Therefore, this study is important because it sheds light on one of the emerging markets that lacks these studies and examines the determinants of financial stability in Jordanian commercial banks.
Secondly, the importance of the study also stems from the importance of the independent factors used in this study. Although there are studies in Jordan that discuss the relationship between financial stability and bank safety in Jordan, employing FMOLS methodology such as (Almahadin et al. 2020), and another study created an indicator of the financial stability consisting of basic factors such as capital adequacy, profitability and liquidity (Al-Rjoub 2021). In addition, the determinants of stability included in our paper are different from those papers, especially Al Salamat and Al-Kharouf (2021). The focus of our paper is on the micro variables (bank-specific variables). Our study includes several important determinants that the literature highlights as important factors that might affect stability such as financial inclusion, small and medium enterprise loans in addition to liquidity, funding, and credit risks, because all these variables provide important insights for policymakers and bank managers. In addition, all these variables are not included in Al Salamat and Al-Kharouf (2021). Moreover, Al Salamat and Al-Kharouf (2021) focus on the macro determinants such as GDP and inflation while ignoring other important factors as those mentioned above.
Therefore, this study is the first to use various important independent variables to examine the financial stability in Jordanian commercial banks. For example, the impact of loans to SMEs in terms of their financial stability, especially because Jordan’s economy is emerging in this country in which SMEs play a major role in financial stability due to SMEs representing the largest portion of projects in Jordan. The study also discusses the impact of financial inclusion on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks. Financial inclusion is also an important topic in which all countries are concerned, because the more diverse groups are included in bank services, the more this leads to achieving justice and equality, as well as reducing the problems of unemployment and poverty. This study is also important because it discusses other important variables such as capital adequacy, funding risk, liquidity risk and credit risk. Thirdly, this study is important at the level of decision-makers and bank managers in any country in terms of recognizing the most important factors that play an important role in financial stability and enhance economic stability. Finally, there is no study that examined the impact of all these important previous factors together on financial stability. This study adds to the previous financial literature and discusses variables that did not attract researchers’ attention, such as small and medium loans and financial inclusion.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. Following the introduction, Section 2 reviews the related literature and develops the study hypotheses. Section 3 details the data and methodology employed in this paper. The study results and discussion are presented in Section 4. The last section concludes the paper.
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
2.1. Financial Inclusion (FI) and Banks’ Stability
Financial inclusion is an important aspect contributing to banking and economic stability and growth. Financial inclusion is the process of ensuring that all segments of society, including vulnerable groups like weaker sections and low-income groups in particular have access to the financial products and services they need in a fair and transparent manner, and at a reasonable cost (Chakrabarty 2010). Thus, having access to safe, simple and affordable sources of financing is recognized as a necessary condition for accelerating growth, creating equal opportunities, and reducing income disparities and poverty (Serrao et al. 2012). Theoretically, it is suggested that FI is clearly capable of minimizing agency issues and information asymmetries between creditors and debtors (Beck et al. 2014). Furthermore, FI can lead to higher stability since it is also capable of attracting deposits from a large customer base, thus reducing the volatility of bank funding. FI-led banks rely less on costly and riskier money market funds, which lowers return volatility (Kacperczyk and Schnabl 2013). However, FI may also increase agency problems because of the organization’s structure and wide range of products. When it becomes difficult for the bank’s headquarters to maintain proper monitoring of the activities of branches, it reduces a bank’s operating efficiency (Brickley et al. 2003).
The empirical evidence in this case is mixed. Ahamed and Mallick (2019) rely on a huge sample including 2913 banks from 87 countries. The study reports a positive link between FI and bank stability. In another cross-country study by Dienillah et al. (2018), the results demonstrate how financial inclusion improves the financial sustainability of higher, middle-income and lower-income countries. From Jordan, Al-Smadi (2018) employs macro-level data over the period from 2006 to 2017. The findings reveal a strong positive correlation between FI and inclusive financial growth and higher economic stability. However, Wang and Luo (2022) examine the relationship between FI and banks’ stability from 36 emerging countries, using data from 1500 banks over the period from 2004 to 2018. The findings reveal that FI inclusion negatively affects banks’ stability. Jungo et al. report no significant relationship between FI and banks’ stability using a sample from Latin American and Caribbean (LAC) and Sub-Saharan African (SSA) countries.
2.2. Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Loans and Banks’ Stability
The importance of SMEs is well documented, particularly, in emerging economies. For instance, in the MENA region, SME firms make up roughly 90% of all businesses and they employ around 30% of the labor force (Nasr and Pearce 2012). In these economies, SMEs significantly produce the majority of new jobs, hence, they play a critical role in reducing unemployment rates, growing the economy, and alleviating poverty (Wang and Shihadeh 2015; Kumar and Rao 2015). The economic theory of entrepreneurship (Casson 1982), argues that financial incentives are the primary drivers of entrepreneurship. These incentives include access to knowledge about market circumstances as well as taxation policies, industrial policies, sources of funding and raw materials, infrastructural accessibility, investments, and marketing opportunities. According to this idea, SME company growth is directly correlated with economic growth, which can only take place in an environment where the macroeconomic structure of the nation’s economy is favorable.
By offering financial services, technology, and business solutions, banks significantly contribute to the sustainability of SMEs. However, the literature documents that the main barrier to SME growth is access to financial resources. In this regard, banks viewed SMEs as a source of risk and as a threat to their stability. Since SMEs lack adequate collateral, there are no specific financial services designed for them, and they lack qualified management, advanced technology, and experienced personnel (Duygan-Bump et al. 2015; Shinozaki 2012; Beck and Demirguc-Kunt 2006). From another angle, Banks aim to reduce operational risks by balancing their income sources and loan portfolios, which entails offering services to consumers, SMEs, and businesses as well as making other types of investments, such as deposits with other bigger financial institutions or joint ventures with other businesses (Erdogan 2018). Empirically, Liang et al. (2017) examined the link between bank efficiency and lending to SMEs and discovered a negative correlation. They contend that this is because SMEs have more asymmetric information than their larger counterparts. However, positive association between credits to SMEs and bank stability is also found. Shihadeh et al. (2019) test the effect of banks’ credit to SMEs on credit risk using 15 Palestinian banks during the period from 2006 to 2016. The study reports the positive effects of granting credit and increasing loans to SMEs as these actions can promote the development and sustainability of these businesses.
2.3. Capital Adequacy and FI Banks’ Stability
By definition, capital adequacy is understood to be the amount of money that a financial institution needs and intends to keep in order to operate in a responsible and prudent manner (Kishore and Pandey 2005). It is suggested that adequate capital is the amount of capital that can successfully carry out the principal duty of preventing the failure of the banking industry by absorbing losses. Thus, it is viewed as a means of offering the highest level of protection against insolvency caused by the risk in the banking sector. Backed by the buffer theory that was developed by Calem and Rob (1996), there is a strong link between capital adequacy and bank stability. This theory argues that banks may choose to keep a “buffer” of additional capital to lessen the likelihood of falling below the legal capital requirements, particularly if their capital adequacy ratio is extremely volatile. Kamran et al. (2019), using a sample from Pakistan over the period from 2007 to 2016, found that the financial stability of commercial banks is increased by an increase in the capital adequacy ratio. However, too high of a capital adequacy ratio will have a detrimental effect on stability. Daoud and Kammoun (2020) used a sample across 22 countries and reported the positive effect of capital adequacy on banks’ stability.
2.4. Liquidity Risk, Credit Risk, Funding Risk and Banks’ Stability
Liquidity risk and credit risk are among the important determinants of banking sector stability. It is suggested that illiquidity of bank assets rises in response to an increase in banks’ credit risk. Our theoretical perspective is directed by the financial intermediation theory (Bryant 1980; Diamond and Dybvig 1983). Financial intermediaries play a crucial role in providing liquidity in the form of loan commitments. Banks influence the intermediation process by reducing the information asymmetry between lenders and borrowers, as well as through creating moral hazards and adverse selection (Holmström and Tirole 1998; Stiglitz and Weiss 1992). Liquidity risk is defined by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision as the risk of not being able to fund asset growth or fulfill depositor commitments as a result of a lack of liquid assets, while credit risk arises when a lender is susceptible to loss from a borrower, counterparty or obligor who does not honor their financial commitments as agreed (Colquitt 2007). The empirical findings seem to be mixed as to the effect of liquidity and credit risks on banks’ stability. Adusei (2015) found a significant negative effect of credit risk on the stability of the banking sector in Ghana, using quarterly data over 2009 to 2013. Ghenimi et al. (2017) employ a sample from 49 countries over the period from 2006 to 2013, and report that both liquidity and credit risks significantly lead to banks’ instability. Zaghdoudi (2019) provides evidence from the Tunisian conventional banking sector, that credit risk is found to negatively affect stability; however, liquidity risk has positive effect.
Another significant factor in determining bank stability is funding structure. Therefore, choosing the optimal combination of bank funding should be carefully considered. Theoretical considerations put forth by Calomiris and Kahn (1991) claim that a bank’s stability rises when proper monitoring of the bank’s funds and the best possible diversification of the funding structure both increase. To encourage bankers to perform adequate monitoring, it is advised that a portion of the bank’s funds be financed using equity. Meanwhile, the bank’s use of debt in the wholesale capital markets illustrates its creditworthiness and sends a clear message to its depositors. The “black side” of using non-deposit funding, involves cost and risk (Huang and Ratnovski 2011). On the other hand, the bank’s stability may be positively impacted by adding deposits in its funding structure. Customer deposits are regarded as a more reliable source of funds since they are safe and secure (Shleifer and Vishny 2010). Adusei (2015) investigates the relationship between funding risk and bank stability empirically using a sample from Ghana. According to the data employed, banks that depend more on deposit funding and have an effective deposit mobilization policy are more stable. Lesmana (2021) uses a sample of 141 conventional Indonesian banks from 2004 to 2018. According to the study, funding risk has a significant positive impact on banks’ stability. A recent paper by Chai et al. (2022) examines how different types of risks affect the stability of 15 Pakistani banks over the period from 2009 to 2020. The findings reveal that both credit risk and liquidity risk are negatively related to bank stability, whereas funding risk has no significant effect on stability.
Our hypotheses are based on the above discussion and six hypotheses as follows:
H1a.
There is a statistically significant effect of financial inclusion on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks.
H1b.
There is a statistically significant effect of SME loans on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks.
H1c.
There is a statistically significant effect of capital adequacy on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks.
H1d.
There is a statistically significant effect of liquidity risk on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks.
H1e.
There is a statistically significant effect of credit risk on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks.
H1f.
There is a statistically significant effect of funding risk on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks.
3. Data and Methodology
3.1. Data
To examine the impact of financial inclusion, loans to SMEs, capital adequacy, funding risk, liquidity risk and credit risk on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks, the study sample was selected to include all 13 Jordanian commercial banks listed on the Amman Stock Exchange. The sample was chosen to include all Jordanian commercial banks, while Islamic banks were excluded because Jordanian Islamic banks are few in number, equaling 3 banks, and because the nature of the work of Islamic banks is relatively different from the nature of the work of commercial banks. The study data was downloaded from the annual reports published on the website of the Central Bank of Jordan1, Security Depository Center2. This study is based on annual data and covers the time period from 2011 to 2018. The time period starting from 2011 was chosen to avoid the period of the global financial crisis in 2008, while the period through to and including 2018 was chosen to avoid the impact of the Coronavirus pandemic. Table 1 provides descriptive statistics of the variables used in this study, namely, stability as a dependent variable, while financial inclusion, loans to SMEs, capital adequacy, funding risk, liquidity risk and credit risk are independent variables.

Table 1.
Descriptive Statistics.
Table 1 presents the statistical description for the study variables. The first variable is BSTAB, which are measures that are used in the current study as a dependent variable to measure the stability of Jordanian commercial banks. Based on kurtosis result, the first measure has no outliers because it is less than 3. The average stability BSTAB is 5.78, which confirms the relative stability of Jordanian commercial banks because the standard deviation is 4.01.
The average financial inclusion (FI) in Jordanian commercial banks is relatively low at 0.13. Looking at the maximum and minimum values, there is a big difference between them at 0.32 and 0.026, respectively. This indicates that there are differences between Jordanian commercial banks in the levels of financial inclusion. Average loans to small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are also relatively low at 0.14. There are large differences in the maximum and minimum values in loans for small and medium enterprises at 0.53 and 0.00, respectively.
Table 1 also shows that the average capital adequacy (CAR) of Jordanian commercial banks is 12.75%. This CAR is classified according to Basel A as being within excellent capital adequacy because it is higher than 12%. Standard deviation of CAR is 4.08%, which indicates that the fluctuation in capital adequacy is a little less than the average. Thus, Jordanian commercial banks have a stable, non-volatile significant capital adequacy. The kurtosis is 4.17, which indicates the presence of some extreme Jordanian commercial banks in the CAR. Maximum and minimum values confirm the existence of these extreme values through the minimum value of 3.36% and the maximum value of 27.83%. The average funding risk (FRISK), liquidity risk (LRISK), and credit risk (CRISK) are relatively low compared to the standard deviation of each factor, except for CRISK.
Figure 1 shows that most of the Jordanian commercial banks were relatively stable during the period from 2011 to 2018. All of these banks achieved a Z-score above 1. However, it is clearly noted that the stability of Jordanian commercial banks varies from one bank to another. For example, Invest Bank, Bank of Jordan, the Housing Bank and Arab Banking Cooperation achieved the highest average stability, while the Arab Bank, Jordan Ahli Bank, Capital Bank of Jordan and Jordan Commercial Bank were less stable than other banks. Therefore, differences exist between Jordanian banks and their levels of stability.
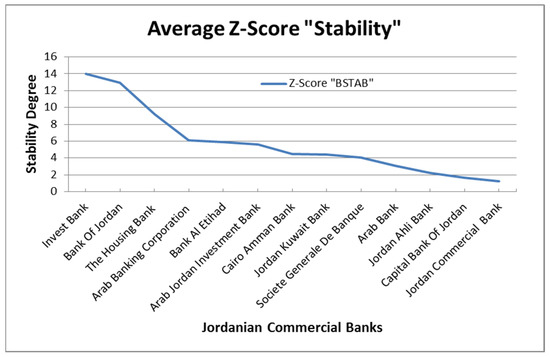
Figure 1.
Average Stability of Jordanian Commercial Banks from 2011 to 2018.
3.2. Methodology
This study uses stability as a dependent variable. In contrast, six independent variables are used, namely, financial inclusion, loans to small and medium enterprises, profitability, capital adequacy, funding risk, liquidity risk, and credit risk. These dependent and independent variables are explained in detail in the next section.
3.2.1. Stability (Z-Score)
The stability of Jordanian commercial banks is considered the main dependent variable used in this study. It was measured by Z-Score. This indicator, based on Demirgüç-Kunt and Huizinga (2010) takes into account profitability, leverage and volatility at the same time. Köhler (2015) indicated that the higher the Z-score, the more stable the bank would be and its low risk exposure to insolvency. The Z-score represents the bank’s ability to withstand losses, and the greater Z-score indicates greater bank stability and lower risks (Iannotta et al. 2007; Liu et al. 2013). The Z-Score indicator is used in this study because it is a commonly used measure in the financial literature, as it is easy to calculate, and its data is easy to obtain (Adusei 2015). It has been calculated as:
where:
- = Stability of bank i in time t,
- = Return on assets of bank i in time t,
- = Equity of bank i in time t,
- = Assets of bank i in time t,
- = Standard deviation of return on assets of bank i in full time period p.
3.2.2. Financial Inclusion (FI)
One of the main determinants used in this study is financial inclusion. The study followed the Sarma (2008) methodology, which uses the financial inclusion measure based on several measures that have many advantages. (1) The information used in the various dimensions of financial inclusion must be measurable. (2) This measure provides the ability to compare between states or between regions within countries during a certain period of time. (3) This indicator is useful in examining the academic issues related to financial inclusion that have been raised in the extensive financial literature (Sarma 2008). Financial inclusion was measured in this study through its development and reliance on three dimensions, and each dimension takes several aspects. Accessibility or penetration of banks, indicates the number of loan accounts per 1000 citizens. Banking usage refers to the ratio of credit and deposits to GDP, with the possibility and availability of banking services. The construction of the financial inclusion index was done using three dimensions based on the available data from the Jordanian commercial banks. The first dimension is related to bank availability that is measured by: a-Number of branch networks/100,000 adults b-Number of ATMs/100,000 adults. The second measure is related to bank accessibility that is measured by: a-Total number of loan accounts/1000 adults. The last dimension is related to bank usage that is measured by: a-Total banks credits/GDP (%) b-Total banks deposits/GDP (%). In our study we modify the model of Sarma (2008) to be applicable to our data i.e., the Jordanian banking sector.
The following equation was used to calculate each dimension:
where:
- Ai = Actual value of dimension i
- mi = Minimum value of dimension i
- Mi = Maximum value of dimension i
Equation (2) indicates that the value of each dimension is 0 ≤ di ≤ 1, zero is the worst, while 1 is the best in terms of achievement in this dimension. There are many dimensions including penetration, usage and availability. Therefore, this study uses (d1, d2, d3 … dn), with the same methodology of Sarma and Pais (2011) who use the lower and upper values of the dimensions. Each dimension has a weight assigned as follows: Availability Index 0.5, Usage Index 0.5, and Access Index 1. After giving the dimensional weights, the financial inclusion is calculated as follows:
where pi, ai and ui = The weighted dimension indices accessibility, availability and usage, respectively. Dimension information is counted between 0 and 1. In short, 0 indicates total financial exclusion, while 1 indicates total financial inclusion in the economy.
Figure 2 shows the average financial inclusion for the period from 2011 to 2018. The banks are ranked in descending order in terms of the degree of stability, from most to least, to be consistent with Figure 1. There are important points shown in Figure 2 and they are as follows: First, although Jordanian commercial banks have a low rate of financial inclusion as it does not exceed 30% at best; there are significant differences between them. Second, the most stable banks such as Invest Bank and Bank of Jordan have the lowest financial inclusion ratios, while the least stable banks such as Arab Bank have relatively large financial inclusion. In summary, Figure 2 shows that Jordanian commercial banks have low percentages and differences in financial inclusion rates. In addition, more stable banks do not mean that they are more financially inclusive and vice versa.
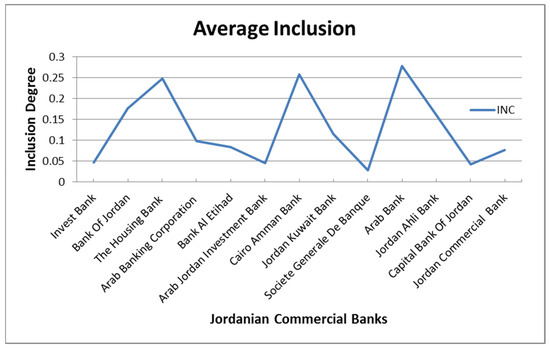
Figure 2.
Average Financial Inclusion in Jordanian Commercial Banks from 2011 to 2018.
3.2.3. Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Loans
Loans to small and medium-size enterprises as a percentage are divided by the total outstanding loans of commercial banks (Morgan and Pontines 2014). It can be calculated as:
where:
- = Loan to small and medium enterprises of bank i in time t,
- = Total loans of bank i in time t,
3.2.4. Capital Adequacy (CAR)
The capital adequacy ratio (CAR) is one of the important ratios that indicate the bank’s ability to run efficiently. It is a percentage that provides the bank with the ability to bear the risks of any risky financing or productive assets (Yudha et al. 2017). Therefore, increasing the capital adequacy ratio improves the bank’s performance (Pramudyani and Hartono 2018; Zulifiah and Susilowibowo 2014). The capital adequacy ratio can be formulated as follows:
where:
- = Total capital of bank i in time t,
- = Weighted average cost of capital of bank i in time t.
3.2.5. Funding Risk (FRISK)
This measure considers deposits and equity to the standard deviation of deposits over total assets. This variable is considered important because banks finance commercial activities, especially retail traders, with customer deposits (Köhler 2015). Thus, stability can be positively affected by funding risk. It is calculated as follows:
where:
- = Funding risk of bank i in time t,
- = Deposit of bank i in time t,
- = Equity of bank i in time t,
- = Total assets of bank i in time t,
- Standard deviation of the deposit of bank i in time t -to- total assets of bank i in full time period p.
3.2.6. Liquidity Risk (LRISK)
Liquidity risk is calculated by taking the total credit facilities divided by the total deposits. High liquidity risk in the bank leads to a decrease in the bank’s stability (Setiawati et al. 2017). It can be calculated as follows:
where:
- = Total credits of bank i in time t,
- = Total deposits of bank i in time t.
3.2.7. Credit Risk (CRISK)
The non-performing loans (NPL) mean credit risk. This ratio is measured by bad debt divided by total credit. This ratio measures the degree of credit risk facing the bank as a result of the volatility of the borrowers’ conditions (Yudha et al. 2017). An increase in this percentage indicates an increase in non-performing loans in the bank, and thus the bank may approach bankruptcy. It can be calculated as follows:
where:
- = Non-performing loans (NPL) or credit risk of bank i in time t,
- = Bad debt of bank i in time t,
- = Total credit of bank i in time t.
3.3. Method
In order to examine the determinants of stability of Jordanian commercial banks, panel data is used in the current study for the period from 2011 to 2018. Several pre-tests are conducted to check that the data fit the model used. The panel data based on the pooled effects model has been adopted to measure the determinants of stability of Jordanian commercial banks. The panel data is suitable for analyzing this data because it considers time series across a range of banks as follows:
where:
- = bank stability,
- = financial inclusion of bank i in time t,
- = small and medium enterprises loans of bank i in time t,
- = capital adequacy ratio of bank i in time t,
- = funding risk of bank i in time t,
- = liquidity risks of bank i in time t,
- = non-performing loans or credit risk of bank i in time t,
- = intercept,
- = the coefficients of explanatory variables,
- = the residual errors.
4. Results and Discussion
Before discussing and analyzing the results of this study, pre-tests were conducted such as unit root, correlation between independent variables, serial correlation test and Hausman test. This study then adopted the appropriate method for data analysis.
4.1. Unit Root Test
The Levin et al. (2002) test is usually used to examine panel data because it takes into account the time period across several companies or banks. This test examines the stationarity of time series. If the time series is not stationary on the level, then the differences are taken as the first difference or the second difference. Greene (2000) indicated that the alternative hypothesis is accepted if the time series are stationary. Table 2 shows that all variables are stable at the level and statistically significant. Therefore, this study adopts the level for these variables because the test in Table 2 showed that they are all stationary at the level and statistically significant. This study accepts the alternative hypothesis and indicates that the time series for the study variables are stationary at the level.

Table 2.
Unit Root Test result.
4.2. Correlation Test
To check that the independent variables do not influence each other, the correlation between the independent variables is tested. Based on Gujarati (2021), which indicates that the multi-collinearity occurs when the correlation between two variables is more than 80%. Looking at Table 3, the correlation between all the independent variables is very small. The highest correlation is between FI and FRISK at 0.75, which is less than 80%. Therefore, this study concludes that there is no multi-collinearity problem among the independent variables used in this study.

Table 3.
Correlation Matrix.
4.3. Discussion Results
Table 4 shows the impact of FI, SMEs, CAR, FRISK, LRISK, CRISK, on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks for the period from 2011 to 2018 using annual data. For the model used in this study, the results of the Lagrange multiplier (LM) tests showed that it is not statistically significant. Thus, this study adopts the pooled effects model. In addition, the heteroskedasticity test shows that it is statistically significant, and the problem of heterogeneity exists. Thus, the Panel EGLS (Cross-section) has been used to solve this problem. All variables have been regressed as either dependent or independent with log to solve the problem of autocorrelation.

Table 4.
The Stability Regression Results.
The value of adjusted R2 for the model is %84.03. This indicates that the independent variables used in this study are able to explain %84.03 of the variation in the dependent variable, which is stability. The F-test shows that it is statistically significant, indicating the appropriateness of the model used.
Table 4 shows that the coefficient of financial inclusion (FI) is negative and statistically significant in the model of stability. This result indicates that the relatively high stability of Jordanian commercial banks suffers from low financial inclusion ratios. On the other hand, the less stable Jordanian commercial banks have relatively high financial inclusion ratios. There is another explanation; financial inclusion may enhance agency problems arising from the organization’s structure and diversity of services. Consequently, it becomes difficult for the bank’s head office to efficiently monitor the activities of the branches, which negatively affects the efficiency of the bank’s operation. This result is consistent with the results of Wang and Luo (2022) who found that FI inclusion negatively affects banks stability using data comprised of 1500 banks from 36 emerging countries over the period from 2004 to 2018. Small and medium enterprise (SMEs) loans have a positive effect and statistical significance on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks in the bank stability model. This indicates that loans provided to small and medium enterprises achieve success and contribute to the stability of Jordanian commercial banks. This positive effect is not surprising since over 90% of all businesses in Jordan are small and medium-sized. Businesses operating in various economic sectors retain around 60% of the labor force and provide about 50% of the GDP. This illustrates the necessity of giving these institutions careful consideration and supporting efforts to remove obstacles to their growth so they can collectively serve as a major engine of growth in the diversification of the nation’s economy. This result is in line with the results of Shihadeh et al. (2019) who determined that development and sustainability of 15 Palestinian banks is positively affected by credit to SMEs during the period from 2006 to 2016.
The coefficient of capital adequacy ratio is positive and statistically significant at the 1% level in all models used in this study. Therefore, capital adequacy positively and statistically affects the stability of Jordanian commercial banks. This result is consistent with the buffer theory developed by Calem and Rob (1996). Capital adequacy helps absorb losses in the banking industry and protects against the risk of bankruptcy (Daoud and Kammoun 2020). This result is consistent with many studies such as Kamran et al. (2019).
Funding risks, liquidity risks, and credit risks negatively affect the stability of Jordanian commercial banks, but their coefficients are small and not statistically significant, except for credit risks, which are economically and statistically significant in the model. The model of stability indicates that there is a problem in Jordanian commercial banks on the side of loans in terms of increasing defaults of customers in repaying loans, or there are many withdrawals of deposits. This result related to credit risk is in agreement with previous studies such as Adusei (2015), Ghenimi et al. (2017) and Zaghdoudi (2019).
4.4. Robusness Checks
As a robustness check for the results in Table 4, we regressed the variables again to check the endogeneity problem by making the residual errors for each independent variable, along with the other independent variables in the equation in Table 5. In other words, residual errors were calculated for each variable by making the independent variable in the equation as follows FI C. Then we inputted the residual errors of the independent variable, instead of the independent variable, to know whether there is an effect of the errors of the independent variable on the dependent variable, which is the bank stability. The results in Table 5 confirmed that the model does not have endogeneity problem because the residual errors for each independent variable have no statistical significance.

Table 5.
A robustness Check for the Stability Regression Results.
5. Conclusions
The 2008–2009 global financial crisis redirected attention to the stability of the banking sector in all countries. The stability of the banking sector is very important because it provides countries with financial reserves and is reflected in macroeconomic stability. Preliminary descriptive statistics indicate that Jordanian commercial banks are relatively stable. Using panel data based on a pooled model, this study is conducted using all 13 Jordanian commercial banks for the period from 2011 to 2018. This paper aims to examine the determinants of the stability of Jordanian commercial banks.
The results of the study indicate that financial stability is negatively and positively affected by some factors. The factors that significantly affect the stability of Jordanian commercial banks positively and statistically include loans directed to small and medium enterprises and capital adequacy because it absorbs losses, thus increasing the stability of banks. On the other hand, the financial stability of Jordanian commercial banks is significantly affected negatively and statistically by several factors including financial inclusion, liquidity risks and credit risks.
To increase the stability of Jordanian commercial banks, requires that bank managers abide by the requirements of Basel II related to capital adequacy to ensure it is not less than 12%. There is also a need to direct more loans to small and medium enterprises because of their positive impact on the stability of banks. On the other hand, trying to adhere to sufficient liquidity ratios, and asking customers to provide more guarantees on the loans they take in order to reduce liquidity and credit risks and increase the stability of Jordanian commercial banks.
The negative impact of financial inclusion on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks can be explained by the relatively low rates of financial inclusion in Jordan and the high levels of stability in Jordanian commercial banks. In addition, some banks with relatively high financial stability have very low financial inclusion and vice versa. Therefore, the main recommendation of this study related to the negative impact of financial inclusion on the stability of Jordanian commercial banks is as follows: banks that enjoy financial stability such as Invest Bank, Bank of Jordan, Arab Banking Corporation, Bank Al Etihad and Arab Jordan Investment have very low financial inclusion rates and must accelerate the increase in the rate of financial inclusion. On the other hand, Jordanian commercial banks that have relatively high rates of financial inclusion, such as Arab Bank, must monitor and reduce the operating expenses and costs resulting from financial inclusion.
Limitations of the Study
- The study period continued until 2018 because some of the basic variables used in the study, such as financial inclusion are related to electronic services that became widely used in 2019 and during the Coronavirus pandemic. Therefore, the study was stopped until 2018 to avoid the bias in the results of the study.
- The sample size of the study is small, because the number of Jordanian commercial banks is only 13.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.K. and O.K.G.; methodology, B.K. and O.K.G.; software, B.K. and O.K.G.; validation, B.K., O.K.G.; formal analysis, B.K. and O.K.G.; investigation, B.K. and O.K.G.; resources, B.K. and O.K.G.; data curation, B.K. and O.K.G.; writing—original draft preparation, B.K.; writing—review and editing, B.K.; visualization, B.K. and O.K.G.; supervision, B.K. and O.K.G.; project administration, B.K. and O.K.G.; funding acquisition, No fund for this article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No data are reported.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Notes
| 1 | https://www.cbj.gov.jo/ (accessed on 14 August 2022). |
| 2 | https://www.sdc.com.jo/arabic/index.php (accessed on 27 August 2022). |
References
- Abedifar, Pejman, Philip Molyneux, and Amine Tarazi. 2013. Risk in Islamic banking. Review of Finance 17: 2035–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusei, Michael. 2015. The impact of bank size and funding risk on bank stability. Cogent Economics & Finance 3: 1111489. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed, M. Mostak, and Sushanta K. Mallick. 2019. Is financial inclusion good for bank stability? International evidence. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization 157: 403–27. [Google Scholar]
- Al Salamat, Wasfi, and Shaker Al-Kharouf. 2021. The Determinants of Financial Stability: Evidence from Jordan. International Journal of Business and Social Science 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahadin, Hamed Ahmad, Thair Kaddumi, and AL-Kilani Qais. 2020. Banking soundness financial stability nexus: Emprical evidence from Jordan. Banks and Bank Systems 15: 218–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rjoub, Samer A. 2021. A financial Stability Index for Jordan. Journal of Central Banking Theory and Practice 2: 157–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Smadi, Mohammad. 2018. The Role of Financial Inclusion in Financial Stability: Lesson from Jordan. Banks and Bank Systems 13: 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, Thorsten, and Asli Demirguc-Kunt. 2006. Small and medium-size enterprises: Access to finance as a growth constraint. Journal of Banking & Finance 30: 2931–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, Thorsten, Chen Lin, and Yue Ma. 2014. Why Do Firms Evade Taxes? The Role of Information Sharing and Financial Sector Outreach. The Journal of Finance 69: 763–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickley, James A., James S. Linck, and Clifford W. Smith, Jr. 2003. Boundaries of the Firm: Evidence from the Banking Industry. Journal of Financial Economics 70: 351–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, John. 1980. A model of reserves, bank runs and deposit insurance. Journal of Banking & Finance 4: 335–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calem, Paul S., and Rafael Rob. 1996. The Impact of Capital-Based Regulation on Bank Risk-Taking: A Dynamic Model. Washington, DC: Federal Reserve Board, pp. 96–107. [Google Scholar]
- Calomiris, Charles W., and Charles M. Kahn. 1991. The role of demandable debt in structuring optimal banking arrangements. American Economic Review 81: 497–513. [Google Scholar]
- Casson, Mark. 1982. The Entrepreneur: An Economic Theory. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Zhengmeng, Muhammad Nauman Sadiq, Najabat Ali, Muhammad Malik, and Syed Ali Raza Hamid. 2022. Bank Specific Risks and Financial Stability Nexus: Evidence From Pakistan. Frontiers in Psychology 13: 909141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, K. C. 2010. Financial Inclusion and Banks: Issues and Perspectives. New Delhi: Reserve Bank of India. [Google Scholar]
- Colquitt, Joetta. 2007. Credit Risk Management: How to Avoid Lending Disasters and Maximize Earnings. New York: McGraw Hill Professional. [Google Scholar]
- Daoud, Yomna, and Aida Kammoun. 2020. Financial Stability and Bank Capital: The Case of Islamic Banks. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues 10: 361–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirgüç-Kunt, Asli, and Harry Huizinga. 2010. Bank activity and funding strategies: The impact on risk and returns. Journal of Financial Economics 98: 626–50. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, Douglas W., and Philip H. Dybvig. 1983. Bank runs, deposit insurance, and liquidity. Journal of Political Economy 91: 401–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienillah, Azka Azifah, Lukytawati Anggraeni, and Sahara Sahara. 2018. Impact of Financial Inclusion on Financial Stability based on Income Group Countries. Buletin Ekonomi Moneter dan Perbankan 20: 429–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duygan-Bump, Burcu, Alexey Levkov, and Judit Montoriol-Garriga. 2015. Financing constraints and unemployment: Evidence from the great recession. Journal of Monetary Economics 75: 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, Aysa Ipek. 2018. Factors affecting SME access to bank financing: An interview study with Turkish bankers. Small Enterprise Research 25: 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghenimi, Ameni, Hasna Chaibi, and Mohamed Ali Brahim Omri. 2017. The effects of liquidity risk and credit risk on bank stability: Evidence from the MENA region. Borsa Istanbul Review 17: 238–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, William. 2000. Econometric Analysis, 4th ed. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Gujarati, Damodar N. 2021. Essentials of Econometrics. London: SAGE Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Holmström, Bengt, and Jean Tirole. 1998. Private and public supply of liquidity. Journal of Political Economy 106: 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Rocco, and Lev Ratnovski. 2011. The dark side of bank wholesale funding. Journal of Financial Intermediation 20: 248–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannotta, Giuliano, Giacomo Nocera, and Andrea Sironi. 2007. Ownership structure, risk and performance in the European banking industry. Journal of Banking & Finance 31: 2127–49. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, Moch, I. Wayan Suwendra, and I. Nyoman Sujana. 2019. Pengaruh Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR), Loan To Deposit Ratio (LDR), Dan Net Interest Margin (NIM) Terhadap Return on Assets (ROA) Pada Bank Umum Swasta Nasional Devisa Yang Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Indonesia Tahun 2015–2017. Jurnal Pendidikan Ekonomi Undiksha 11: 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacperczyk, Marcin, and Philipp Schnabl. 2013. How safe are Money Market Funds? The Quarterly Journal of Economics 128: 1073–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, Hafiz Waqas, Abdelnaser Omran, and Shamsul Bahrain Mohamed-Arshad. 2019. Risk Management, Capital Adequacy and Audit Quality for Financial Stability: Assessment from Commercial Banks of Pakistan. Asian Economic and Financial Review 9: 654–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, and I. M. Pandey. 2005. Financial Management. New Dehi: Vikas Publishing House Ltd., pp. 517–55. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, Matthias. 2015. Which banks are more risky? The impact of business models on bank stability. Journal of Financial Stability 16: 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Satish, and Purnima Rao. 2015. A conceptual framework for identifying financing preferences of SMEs. Small Enterprise Research 22: 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesmana, Dadang. 2021. Funding Risk and Bank Stability: Evidence in Indonesia Banking. IAR Journal of Business Management 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, Andrew, Chien-Fu Lin, and Chia-Shang James Chu. 2002. Unit root tests in panel data: Asymptotic and finite-sample properties. Journal of Econometrics 108: 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Lien-Wen, Bor-Yi Huang, Chih-Feng Liao, and Yu-Ting Gao. 2017. The impact of SMEs’ lending and credit guarantee on bank efficiency in South Korea. Review of Development Finance 7: 134–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Hong, Phil Molyneux, and John O. S. Wilson. 2013. Competition and stability in European banking: A regional analysis. The Manchester School 81: 176–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Männasoo, Kadri, and David G. Mayes. 2009. Explaining Bank Distress in Eastern European Transition Economies. Journal of Banking and Finance 33: 244–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, Peter, and Victor Pontines. 2014. Financial Stability and Financial Inclusion: ADBI Working Paper 1–16. Available online: https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/156343/adbi-wp488.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Moyo, Jennifer, Boaz Nandwa, Dubai Economic Council, Jacob Oduor, and Anthony Simpasa. 2014. Financial sector reforms, competition and banking system stability in Sub-Saharan Africa. New perspectives 14: 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Nasr, Sahar, and Douglas Pearce. 2012. Middle East and North Africa Region—SMEs for Job Creation in the Arab World: SME Access to Financial Services. Washington, DC: World Bank. Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/687631468110059492/Middle-East-and-North-Africa-Region (accessed on 17 July 2022).
- Pessarossi, Pierre, Jean-Luc Thevenon, and Laurent Weill. 2020. Does high profitability improve stability for European banks? Research in International Business and Finance 53: 101220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramudyani, Dita Ayusnia, and Ulil Hartono. 2018. Pengaruh CAR, BOPO, LDR, Dan Inflasi Terhadap Profitabilitas Pada Bank BUSN Non Devisa Yang Terdaftar Di Indonesia Periode 2012–2016. Sinergitas Quadruple Helix: e-Business dan Fintech sebagai Daya Dorong Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Lokal, 535–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, Mandira. 2008. Financial Inclusion and Development: A Cross Country Analysis. New Delhi: Annual Conference of the Human Development and Capability Association. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, Mandira, and Jesim Pais. 2011. Financial inclusion and development. Journal of International Development 23: 613–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrao, Manohar Vincent, A. H. Sequeira, and Basil Hans. 2012. Designing a methodology to investigate accessibility and impact of financial inclusion. SSRN Electronic Journal. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawati, Erma, Dimas Ilham Nur Rois, and Indah Nur Aini. 2017. Pengaruh kecukupan modal, risiko pembiayaan, efisieni operasional dan likuiditas terhadap profitabilitas (studi pada Bank Syariah dan Bank Konvensional di Indonesia). Riset Akuntansi Dan Keuangan Indonesia 2: 109–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shihadeh, Fadi, Sisira Kumara Naradda Gamage, and Azzam Hannoon. 2019. The causal relationship between SME sustainability and banks’ risk. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja 32: 2743–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, Shigehiro. 2012. A New Regime of SME Finance in Emerging Asia: Empowering Growth-Oriented SMEs to Build Resilient National Economies. ADB Working Paper Series on Regional Economic Integration. pp. 1–37. Available online: https://www.econstor.eu/handle/10419/109602 (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Shleifer, Andrei, and Robert W. Vishny. 2010. Unstable banking. Journal of Financial Economics 97: 306–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglitz, Joseph E., and Andrew Weiss. 1992. Asymmetric information in credit markets and its implications for macro-economics. Oxford Economic Papers 44: 694–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Yong, and Christos Floros. 2012. Bank profitability and inflation: The case of China. Journal of Economic Studies 39: 675–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Rui, and Hang Robin Luo. 2022. How does financial inclusion affect bank stability in emerging economies? Emerging Markets Review 51: 100876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Xiuhua, and Fadi Shihadeh. 2015. Financial inclusion: Policies, status, and challenges in Palestine. International Journal of Economics and Finance 7: 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudha, Aji, Mochammad Chabachib, and Irene Rini Demi Pangestuti. 2017. Analysis of the effect of NPL, NIM, Non Interest Income, and LDR toward ROA with size as control variables (differences study on domestic and foreign banks listed on BEI period 2010–2015). Jurnal Bisnis Strategi 26: 100–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zaghdoudi, Khemais. 2019. The effects of risks on the stability of Tunisian conventional banks. Asian Economic and Financial Review 9: 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulifiah, Fitri, and Joni Susilowibowo. 2014. Pengaruh inflasi, BI rate, capital adequacy ratio (car), non performing finance (npf), biaya operasional dan pendapatan operasional (bopo) terhadap profitabilitas bank umum syariah periode 2008–12. Jurnal Ilmu Manajemen 2: 759–70. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).