Smart Cities and Healthcare: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
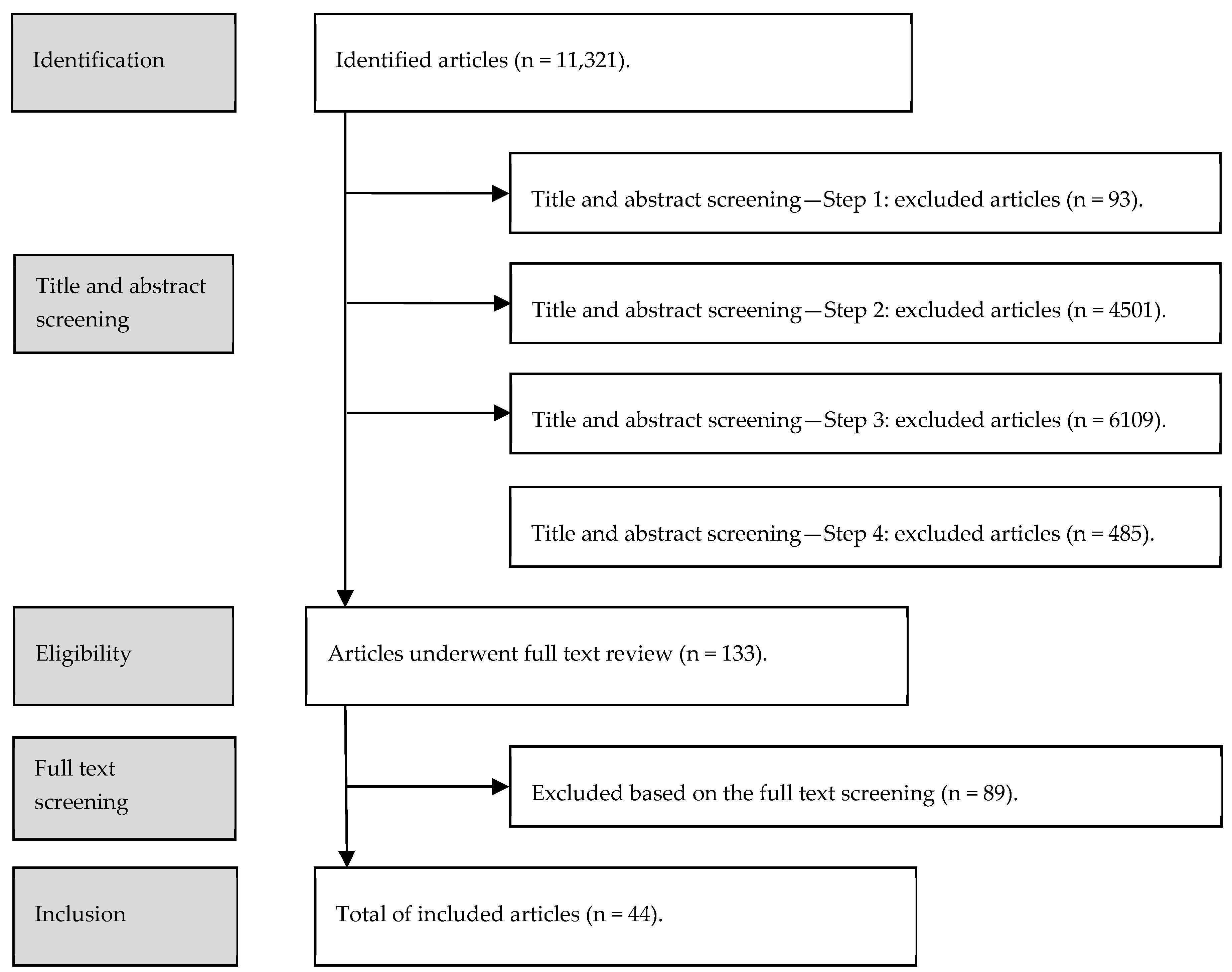
2. Materials and Methods
- RQ1: What are the most relevant application domains?
- RQ2: What are the types of technologies being used?
- RQ3: What are the maturity levels of the applications being reported?
- RQ4: What are the major barriers for the dissemination of the applications being reported?
- First, the authors assessed all titles and abstracts for relevance and those clearly outside the scope of applications related to smart cities (independently of being or not related to healthcare provision) were removed.
- Then, the abstracts of the retrieved articles were assessed to verify if they were related to smart living, which included health conditions. Articles reporting studies not related to smart living were excluded.
- Afterward, the abstracts of the remaining articles were assessed and those not reporting the use of applications with an impact in the provision of healthcare where excluded.
- Finally, the authors assessed the full text of the retrieved articles according to the outlined inclusion and exclusion criteria and classified them. This classification was performed by using a synthesis process based on the method proposed by Ghapanchi and Aurum [15] (i.e., terms and definitions used in the included articles were identified to create a primary list of application domains, which were later refined by further analyses).
3. Results
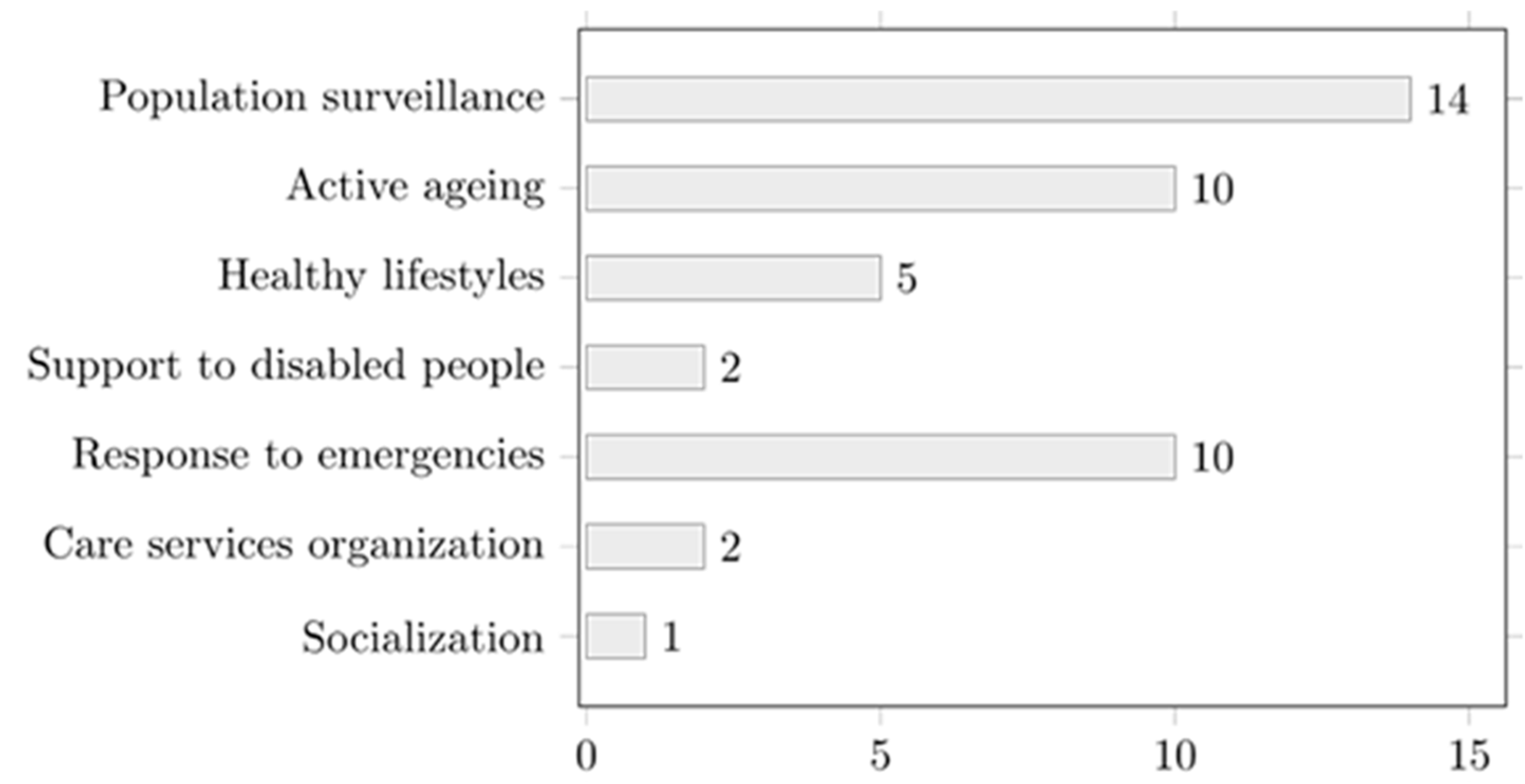
3.1. Application Domains
3.1.1. Population Surveillance
3.1.2. Active Ageing
3.1.3. Healthy Lifestyles
3.1.4. Support to Disabled People
3.1.5. Response to Emergencies
3.1.6. Care Services Organization
3.1.7. Socialization
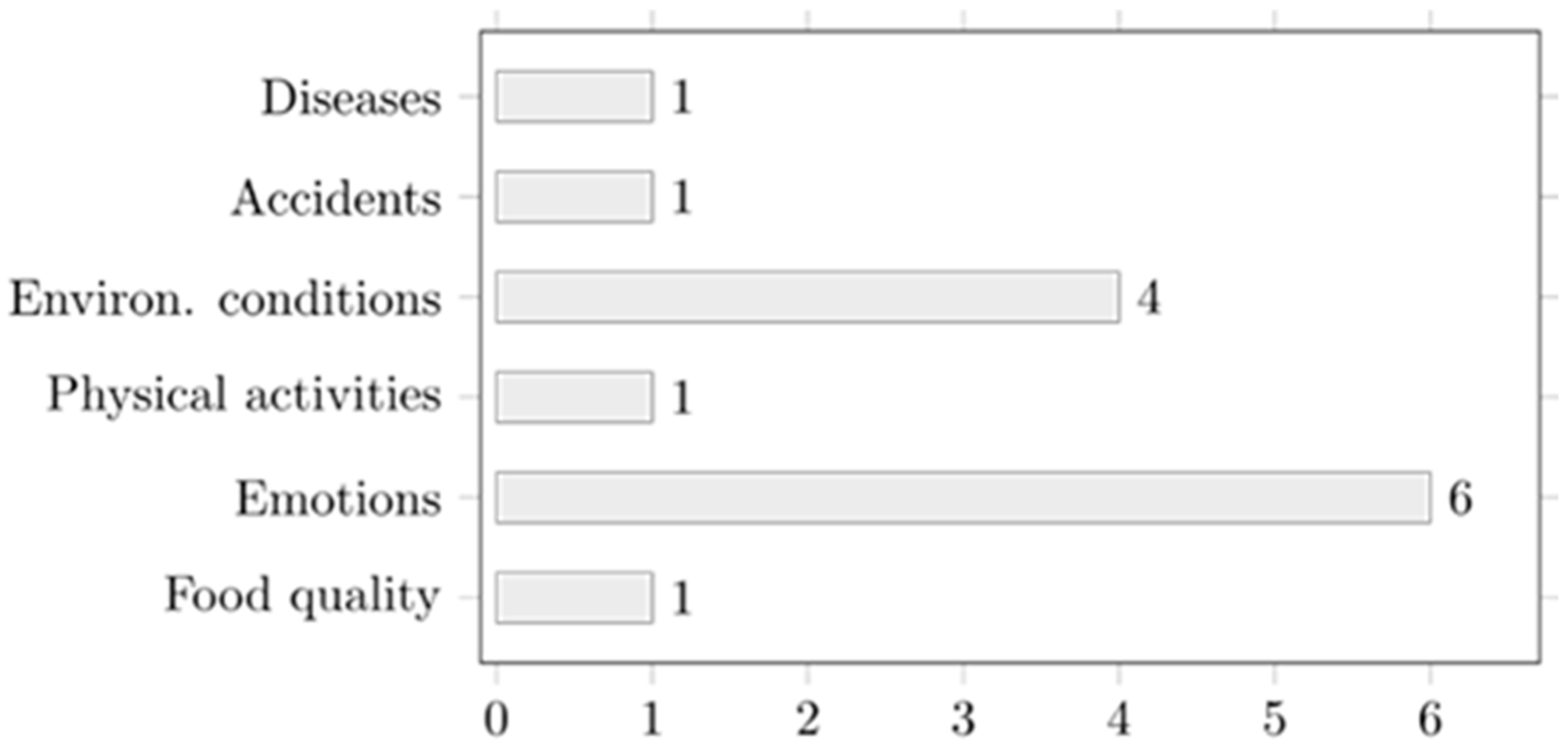
3.2. Technologies Being Used
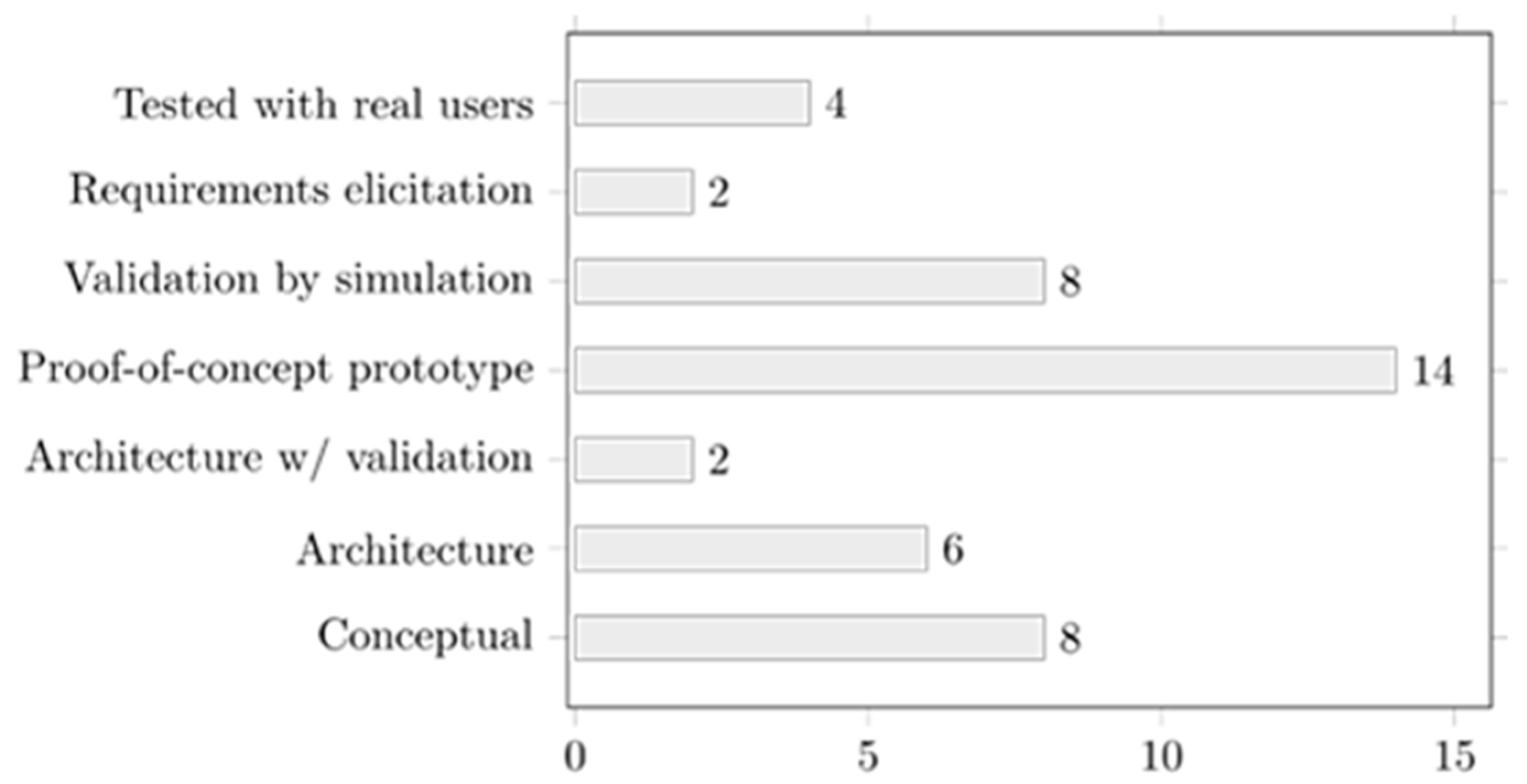
3.3. Maturity Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santinha, G.; Dias, A.; Rodrigues, M.; Queirós, A.; Rodrigues, C.; Rocha, N.P. How Do Smart Cities Impact on Sustainable Urban Growth and on Opportunities for Entrepreneurship? Evidence from Portugal: The Case of Águeda. In New Paths of Entrepreneurship Development; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 31–53. [Google Scholar]
- AlDairi, A. Cyber security attacks on smart cities and associated mobile technologies. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 109, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaroiu, G.C.; Roscia, M. Definition methodology for the smart cities model. Energy 2012, 47, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanolo, A. Smartmentality: The smart city as disciplinary strategy. Urban Stud. 2014, 51, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffinger, R.; Gudrun, H. Smart cities ranking: An effective instrument for the positioning of the cities? ACE Archit. City Environ. 2010, 4, 7–26. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos-Pablos, S.; García-Peñalvo, F.J. Technological ecosystems in care and assistance: A systematic literature review. Sensors 2019, 19, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlag, A.A.; Ghani, M.K.A.; Arunkumar, N.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Mohd, O. Enabling technologies for fog computing in healthcare IoT systems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 90, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarlatidou, A.; Hamilton, A.; Vitos, M.; Haklay, M. What do volunteers want from citizen science technologies? A systematic literature review and best practice guidelines. JCOM J. Sci. Commun. 2019, 18, A02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, G.; Lanzarotti, R.; Napoletano, P.; Noceti, N.; Odone, F. Positive technology for elderly well-being: A review. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, A.; Alvarelhão, J.; Cerqueira, M.; Silva, A.; Santos, M.; Rocha, N.P. Remote care technology: A systematic review of reviews and meta-analyses. Technologies 2018, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Agarwal, N.; Kar, A.K. Addressing big data challenges in smart cities: A systematic literature review. Info 2016, 18, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M. A Systematic Review of Information Security Frameworks in the Internet of Things (iot). In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 14th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 2nd International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), Sydney, Australia, 12–14 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Purnomo, F.; Prabowo, H. Smart city indicators: A systematic literature review. J. Telecommun. Electron. Comput. Eng. (JTEC) 2016, 8, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghapanchi, A.; Aurum, A. Antecedents to IT personnel’s intentions to leave: A systematic literature review. J. Syst. Softw. 2011, 84, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Bernabeu, J.M.; Berna-Martinez, J.V.; Maciá Pérez, F. Smart sentinel: Monitoring and prevention system in the smart cities. Int. Rev. Comput. Softw. (IRECOS) 2014, 9, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.; Peoples, C. A Web-Based Portal for Assessing Citizen Well-Being. IT Prof. 2017, 19, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschippig, C.; Kluss, T. Gardening in ambient assisted living. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 15, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casino, F.; Patsakis, C.; Batista, E.; Borràs, F.; Martínez-Ballesté, A. Healthy routes in the smart city: A context-aware mobile recommender. IEEE Softw. 2017, 34, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trencher, G.; Karvonen, A. Stretching “smart”: Advancing health and well-being through the smart city agenda. Local Environ. 2017, 24, 610–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilart-Iglesias, V.; Mora, H.; Pérez-delHoyo, R.; García-Mayor, C. A computational method based on radio frequency technologies for the analysis of accessibility of disabled people in sustainable cities. Sustainability 2015, 7, 14935–14963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, H.; Zhu, R. Robotic automated external defibrillator ambulance for emergency medical service in smart cities. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, S.; Delavar, M.R.; Rajabifard, A. Multi-Agent Simulation of Allocating and Routing Ambulances under Condition of Street Blockage after Natural Disaster. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 42, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, F.; Ficco, M.; Pardi, S.; Castiglione, A. A cloud-based architecture for emergency management and first responders localization in smart city environments. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2016, 56, 810–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, A.; Olstad, D.L.; Minaker, L.M. Smart prevention: A new approach to primary and secondary cancer prevention in smart and connected communities. Cities 2018, 79, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, S.B.; Berkelman, R.L. Public health surveillance in the United States. Epidemiol. Rev. 1988, 10, 164–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsakis, C.; Clear, M.; Laird, P.; Zigomitros, A.; Bouroche, M. Privacy-aware Large-Scale Virologic and Epidemiological Data Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 27th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, New York, NY, USA, 27–29 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shikhar, A.; Naveen, J.S.; Sowmya, B.J.; Srinivas, K.G. Data Analytics on Accident Data for Smarter Cities and Safer Lives. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Computation System and Information Technology for Sustainable Solutions (CSITSS), Bangalore, India, 6–8 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Federico, W.; Ceballos, G.R.; Rivera, H.M.; Larios, V.M.; Beltran, N.E.; Beltran, R.; Ascencio, J.A. Smart Genetics for Smarter Health-an Innovation Proposal to Improve Wellness and Health Care in the Cities of the Future. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Wuxi, China, 14–17 September 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Al Shami, A.; Wang, Y. Ubiquitous Monitoring of Human Sunlight Exposure in cities. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE First International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Guadalajara, Mexico, 25–28 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, A.; Steele, R. How Personal Fitness Data can be Re-used by Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Seventh International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing, Adelaide, SA, Australia, 6–9 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guthier, B.; Abaalkhail, R.; Alharthi, R.; El Saddik, A. The Affect-Aware City. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Guadalajara, Mexico, 25–28 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Roza, V.C.C.; Postolache, O.A. Citizen Emotion Analysis in Smart City. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 7th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA), Chalkidiki, Greece, 13–15 July 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Gupta, N.; Pogrebna, G.; Jarvis, S. Understanding Happiness in Cities Using Twitter: Jobs, Children, and Transport. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Trento, Italy, 12–15 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jianqiang, Z. Pre-processing Boosting Twitter Sentiment Analysis? In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Smart City/SocialCom/SustainCom (SmartCity), Chengdu, China, 19–21 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, T.H.M.; Painho, M. Emotion & Stress Mapping: Assembling an Ambient Geographic Information-based Methodology in Order to Understand Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 10th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Aveiro, Portuga, 17–20 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.A.; Ramaiah, C.S.; Prasad, M.G.; Hussain, S.M. Milk Products Monitoring System with Arm Processor for Early Detection of Microbial Activity. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 3rd MEC International Conference on Big Data and Smart City (ICBDSC), Muscat, Oman, 15–16 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Righi, V.; Sayago, S.; Blat, J. Urban Ageing: Technology, Agency and Community in Smarter Cities for Older People. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Communities and Technologies, Limerick, Ireland, 27–30 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, C.A.; Araújo, L.; Figueiredo, M.; Morais, N.; Pereira, J.; Rito, P.; Gouveia, T. VIAS|Viseu InterAge stories: Developing an App to Foster Social Inclusion and Healthy Lifestyles. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2017 International Symposium on Computers in Education (SIIE), Lisbon, Portugal, 9–11 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, F. Construction and Value Study of IT-based Smart Senior Citizens’ Communities. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Sixth International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation, Zhangjiajie, China, 10–11 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bryant, N.; Spencer, N.; King, A.; Crooks, P.; Deakin, J.; Young, S. IoT and Smart City Services to Support Independence and Wellbeing of Older People. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 25th International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks (SoftCOM), Split, Croatia, 21–23 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mulero, R.; Almeida, A.; Azkune, G.; Mainetti, L.; Mighali, V.; Patrono, L.; Sergi, I. An AAL System Based on IoT Technologies and Linked Open Data for elderly monitoring in Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd International Multidisciplinary Conference on Computer and Energy Science (SpliTech), Split, Croatia, 12–14 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Villarrubia, G.; De Paz, J.F.; de la Prieta, F.; Sánchez, A.J. Wireless Sensor Networks to Monitoring Elderly People in Rural Areas. In Ambient Intelligence-Software and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Liouane, Z.; Lemlouma, T.; Roose, P.; Weis, F.; Messaoud, H. A Genetic-based Localization Algorithm for Elderly People in Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Symposium on Mobility Management and Wireless Access, Malta, Malta, November 13–17 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liming, B.A.I.; Gavino, A.I.; Lee, P.; Jungyoon, K.; Na, L.; Pi, T.H.P.; Jia, E.Y. SHINESeniors: Personalized Services for Active Ageing-in-place. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE First International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Guadalajara, Mexico, 25–28 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kötteritzsch, A.; Koch, M.; Wallrafen, S. Expand your comfort zone! Smart Urban Objects to Promote Safety in Public Spaces for Older Adults. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing: Adjunct, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–16 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Stibe, A.; Larson, K. Persuasive Cities for Sustainable Wellbeing: Quantified Communities. In International Conference on Mobile Web and Information Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Queirós, A.; Silva, A.G.; Simões, P.; Santos, C.; Martins, C.; da Rocha, N.P.; Rodrigues, M. SmartWalk: Personas and Scenarios Definition and Functional Requirements. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Technology and Innovation in Sports, Health and Wellbeing (TISHW), Thessaloniki, Greece, 20–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, M.; Santos, R.; Queirós, A.; Silva, A.G.; Amaral, J.; Gonçalves, L.J.; da Rocha, N.P. Meet SmartWalk, Smart Cities for Active Seniors. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Technology and Innovation in Sports, Health and Wellbeing (TISHW), Thessaloniki, Greece, 20–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Montanha, A.; Escalon, M.J.; Dominguez-Mayo, F.J.; Polidorio, A.M. A Technological Innovation to Safely Aid in the Spatial Orientation of Blind People in a Complex Urban Environment. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Portsmouth, UK, 3–5 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Ghazal, M. Real-time Heart Attack Mobile Detection Service (RHAMDS): An IoT Use Case for Software Defined Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Windsor, ON, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, P.S.; Tiwari, A.; Sinha, P.R. Adaptive and optimized emergency vehicle dispatching algorithm for intelligent traffic management system. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 57, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulton, M.; Roussos, G. Towards Smarter Metropolitan Emergency Response. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 24th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), London, UK, 8–11 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Nicola, A.; Melchiori, M.; Villani, M.L. A lateral thinking framework for semantic modelling of emergencies in smart cities. In International Conference on Database and Expert Systems Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lohokare, J.; Dani, R.; Sontakke, S.; Apte, A.; Sahni, R. Emergency Services Platform for Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), Cochin, India, 14–16 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Elkheir, M.; Hassanein, H.S.; Oteafy, S.M. Enhancing emergency response systems through leveraging crowdsensing and heterogeneous data. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Paphos, Cyprus, 5–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, R.; Mohan, A.; Srinivasan, P. Privacy Conscious Architecture for Improving Emergency Response in Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2016 Smart City Security and Privacy Workshop (SCSP-W). IEEE, Vienna, Austria, 11 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, C.; Hansen, C.; Alstrup, S.; Lioma, C. Smart City Analytics: Ensemble-Learned Prediction of Citizen Home Care. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, ACM, Singapore, 6–10 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Gavino, A.; Purao, S. A Method for Designing Value-infused Citizen Services in Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research, ACM, Aguascalientes, Mexico, 18–21 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, J.Y.; Yoo, J.S.; Lee, J.; Kwon, H. Breadcrumb SNS: Asynchronous Empathy Chat for Smart City Residents. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Eighth International Conference on Mobile Computing and Ubiquitous Networking (ICMU), Hakodate, Japan, 20–22 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.; Morgan, A.; Bonnefoy, J.; Butt, J.; Bergman, V.; Mackenbach, J.P. The Social Determinants of Health: Developing an Evidence Base for Political Action; National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. European Action Plan for Strengthening Public Health Capacities and Services; Regional Committee for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. A Glossary of Terms for Community Health Care and Services for Older Persons; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cosco, T.D.; Prina, A.M.; Perales, J.; Stephan, B.C.; Brayne, C. Operational definitions of successful aging: A systematic review. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2014, 26, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annear, M.; Keeling, S.; Wilkinson, T.I.M.; Cushman, G.; Gidlow, B.O.B.; Hopkins, H. Environmental influences on healthy and active ageing: A systematic review. Ageing Soc. 2014, 34, 590–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, P.J.; Coleman, R. History of Inclusive Design in the UK. Appl. Ergon. 2015, 46, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Health and Aging; US National Institute of Aging: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2011.
- Holt-Lunstad, J.; Smith, T.B.; Layton, J.B. Social relationships and mortality risk: A meta-analytic review. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Types of Data | References |
|---|---|
| Data from smart city infrastructure | [16,19,25,29,30,31,48,49,52] |
| Data provided by sensors inside vehicles | [28,51] |
| Data provided by video cameras | [50,56] |
| Data provided by gas sensors | [37] |
| Geo-tagged social media data | [34,35,36,56] |
| Data collected by online questionnaire | [17,33] |
| Data provided by lifestyle monitoring devices: | |
| Location | [16,21,30,31,39,40,43,45,48,49,50,55] |
| Activity | [18,20,24,31,41,42,48,49] |
| Motion | [24] |
| Steps | [20,48,49] |
| Cycling cadence | [31] |
| Swim distance | [31] |
| Weight, body mass index, and body fat percentage | [20] |
| Heart rate and heart rate variability | [18,31,32,44] |
| Level of glucose | [44] |
| Temperature of the body | [44] |
| Electroencephalogram | [33] |
| Galvanic skin response | [32,33] |
| Social interactions | [46] |
| Crowd behaviors | [47] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pacheco Rocha, N.; Dias, A.; Santinha, G.; Rodrigues, M.; Queirós, A.; Rodrigues, C. Smart Cities and Healthcare: A Systematic Review. Technologies 2019, 7, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies7030058
Pacheco Rocha N, Dias A, Santinha G, Rodrigues M, Queirós A, Rodrigues C. Smart Cities and Healthcare: A Systematic Review. Technologies. 2019; 7(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies7030058
Chicago/Turabian StylePacheco Rocha, Nelson, Ana Dias, Gonçalo Santinha, Mário Rodrigues, Alexandra Queirós, and Carlos Rodrigues. 2019. "Smart Cities and Healthcare: A Systematic Review" Technologies 7, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies7030058
APA StylePacheco Rocha, N., Dias, A., Santinha, G., Rodrigues, M., Queirós, A., & Rodrigues, C. (2019). Smart Cities and Healthcare: A Systematic Review. Technologies, 7(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies7030058








