A Suppression Method for Elution of F−, [B(OH)4]−, AsO43−, and CrO42− from Industrial Wastes Using Some Inhibitors and Crushed Stone Powder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Suppression of F Elution
3.2. Suppression of B Elution
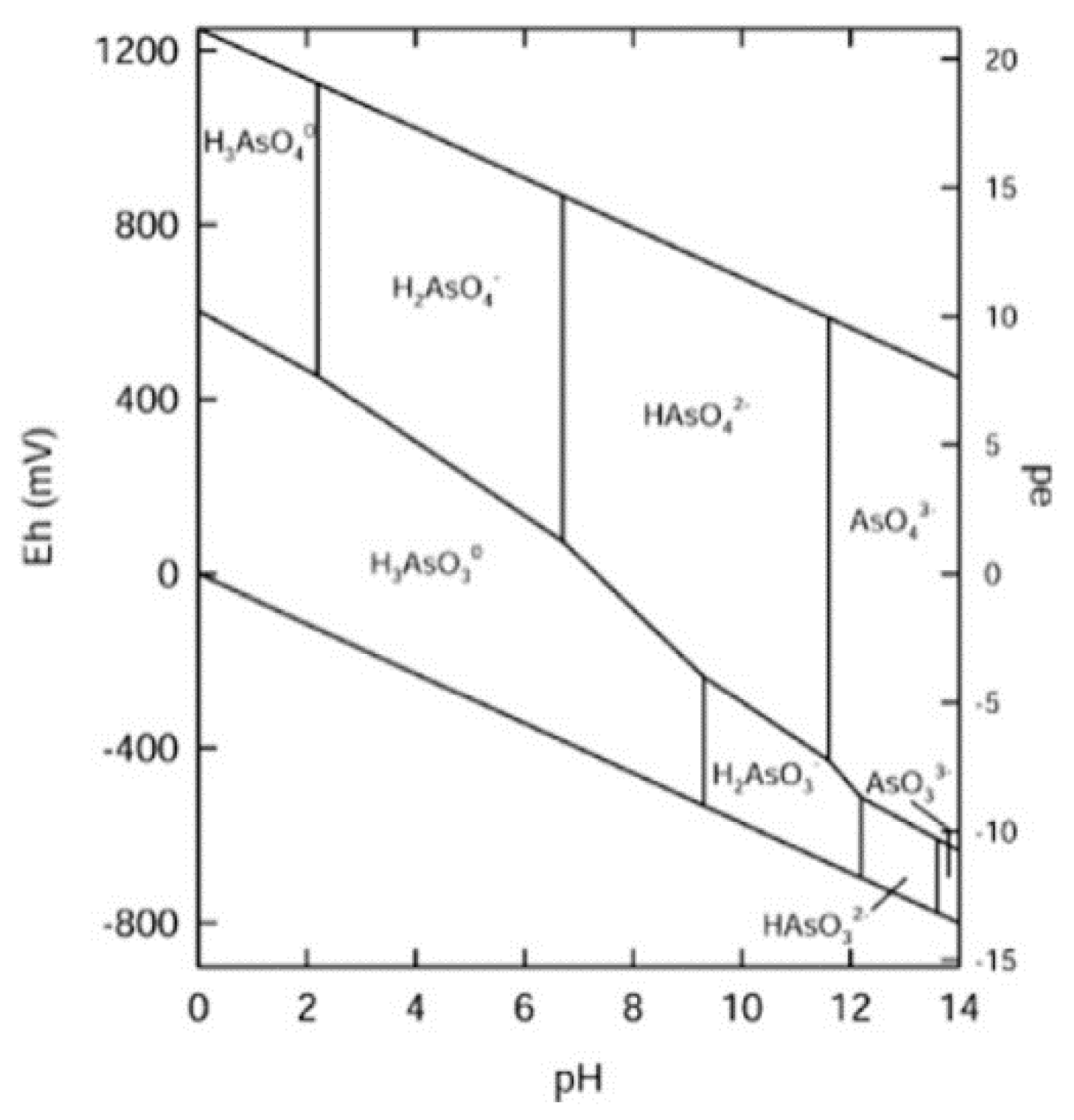
3.3. Suppression of As Elution
3.4. Suppression of Cr Elution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Environmental Quality Standards for Soil Pollution. Ministry of the Environment Government of Japan. Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/en/water/soil/sp.html (accessed on 18 August 2018).
- Japan Industrial Waste Information Center. Available online: http://www.jwnet.or.jp/waste/knowledge/genjou.html (accessed on 18 August 2018).
- Chrysochoou, M.; Dermatas, D. Evaluation of ettringite and hydrocalumite formation for heavy metal immobilization: Literature review and experimental study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montañés, M.T.; Sánchez-Tovar, R.; Roux, M.S. The effectiveness of the stabilization/solidification process on the leachability and toxicity of the tannery sludge chromium. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 143, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.T.; Lee, T.G. A simultaneous stabilization and solidification of the top five most toxic heavy metals (Hg, Pb, As, Cr, and Cd). Chemosphere 2017, 178, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.W.; Choi, A.E.S.; Park, H.S. Solidification/stabilization of ASR fly ash using Thiomer material: Optimization of compressive strength and heavy metals leaching. Waste Manag. 2017, 70, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.J.; Jiang, J.Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.P.; Ding, H. Assessment of water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde (WTF) resin for stabilization/solidification (S/S) of heavy metal contaminated soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 346, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mashqbeh, A.; Abuali, S.; El-Eswed, B.; Khalili, F.I. Immobilization of toxic inorganic anions (Cr2O72−, MnO4− and Fe(CN)63−) in metakaolin based geopolymers: A preliminary study. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 5613–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.H.; Kim, E.I.; Park, J.Y. Fluoride removal capacity of cement paste. Desalination 2007, 202, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Byun, H.J.; Choi, W.H.; Kang, W.H. Cement paste column for simultaneous removal of fluoride, phosphate, and nitrate in acidic wastewater. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunashima, Y.; Iizuka, A.; Akimoto, J.; Hongo, T.; Yamasaki, A. Preparation of sorbents containing ettringite phase from concrete sludge and their performance in removing borate and fluoride ions from waste water. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200–202, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Reardon, E.J. Removal of B, Cr, Mo, and Se from wastewater by incorporation into hydrocalumite and ettringite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2947–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraga, Y.; Shigemoto, N. Boron uptake behavior during ettringite synthesis in the presence of H3BO3 and in a suspension of ettringite in H3BO3. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2010, 43, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, T.; Tsunashima, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Iizuka, A.; Yamasaki, A. A comparative borate adsorption study of ettringite and metaettringite. Chem. Lett. 2011, 40, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Sakai, Y.; Hongo, T.; Iizuka, A.; Yamasaki, A. Preparation of a solid adsorbent derived from concrete sludge and its boron removal performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 5813–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, S.C.B.; Traina, S.J.; Logan, T.J.; Waychunas, G.A. Oxyanion behavior in alkaline environments: Sorption and desorption of arsenate in ettringite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolonen, E.T.; Hu, T.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. The removal of sulphate from mine water by precipitation as ettringite and the utilisation of the precipitate as a sorbent for arsenate removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamalidis, A.K.; Voudrias, E.A. Release of Zn, Ni Cu, SO42− and CrO42− as a function of pH fromcement-based stabilized/solidified refinery oily sludge and ash from incineration of oily sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyronnard, O.; Benzaazoua, M.; Blanc, D.; Moszkowicz, P. Study of mineralogy and leaching behavior of stabilized/solidified sludge using differential acid neutralization analysis, Part I: Experimental study. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisinger, S.M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Lothenbach, B.; Johnson, C.A. Solubility of chromate in a hydrated OPC. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 48, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, C.; Zhao, M.; Yu, L.; Yang, K.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, X. Immobilization of Cr(VI) by hydrated Portland cement pastes with and without calcium sulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, X.; Sasaki, A.; Endo, M. The inhibition of fluoride elution from industrial wastes with Portland cement, calcium and magnesium salts in alkaline region. J. Ion Exc. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Sasaki, A.; Endo, M. Solidification/stabilization of arsenic in red mud upon addition of Fe(III) or Fe(III) and Al(III) dissolved in H2SO4. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2018, 16, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Sasaki, A.; Endo, M. Reclamation of a waste arsenic-bearing gypsum as a soil conditioner via acid treatment and subsequent Fe(II)-As stabilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, D.; Mahoney, J.; Rowson, J. Solubility products of amorphous ferric arsenate and crystalline scorodite (FeAsO4·2H2O) and their application to arsenic behavior in buried mine tailings. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 2942–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluteau, M.C.; Demopoulos, G.P. The incongruent dissolution of scorodite–solubility, kinetics and mechanism. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 87, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daenzer, R.; Xu, L.; Doerfelt, C.; Jia, Y.; Demopoulos, G.P. Precipitation behaviour of As(V) during neutralization of acidic Fe(II)−As(V) solutions in batch and continuous modes. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 146, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Wang, K.; Song, Y.; Xiao, F.; Jia, Y. Effect of hydroquinone-induced iron reduction on the stability of scorodite and arsenic mobilization. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Saeki, T.; Inoshita, I. Characteristics of crushed stone sludge collected as admixture by wet process method. P. Jpn. Concr. Inst. 2002, 24, 1335–1340. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyama, T.; Fumoto, T.; Ishino, R.; Yamada, M. Study on the utilization of crushed stone powder as admixture for high fluidity concrete. Jpn. Concr. Inst. 2003, 25, 982–997. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Zichella, L.; Bellopede, R.; Spriano, S.; Marini, P. Preliminary investigations on stone cutting sludge processing for a future recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, M.Y.; Sabah, E. Geological and technical characterisation of Iscehisar (Afyon-Turkey) marble deposits and the impact of marble waste on environmental pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Kalla, P.; Verma, H.K.; Mohnot, J.K. Recycling of dimensional stone waste in concrete: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 312–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.C.; Lee, M.Y.; Lo, S.L.; Lin, J.D. Artificial aggregate made from waste stone sludge and waste silt. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De’Gennaro, R.; Graziano, S.F.; Cappelletti, P.; Colella, A.; Dondi, M.; Langella, A. Structural concretes with waste-based lightweight aggregates: From landfill to engineered materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7123–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zboon, K.; Tahat, M.; Abu-Hamatteh, Z.S.; Al-Harahsheh, M.S. Recycling of stone cutting sludge in formulations of bricks and terrazzo tiles. Waste Manag. Res. 2010, 28, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, B. Recycling of crushed stone powder as a partial replacement for silica powder in extruded cement panels. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 52, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Jeong, Y.; Jun, Y.; Oh, J.E. Production of price-competitive bricks using a high volume of stone powder sludge waste and blast furnace slag through cementless CaO activation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davraz, M.; Ceylan, H.; Topçu, İ.B.; Uygunoğlu, T. Pozzolanic effect of andesite waste powder on mechanical properties of high strength concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese Industrial Standard, Japanese Standards Association. JIS K0102: 2016 Testing Methods for Industrial Wastewater. Available online: https://webdesk.jsa.or.jp/books/W11M0090/?bunsyo_id=JIS%20K%200102:2016 (accessed on 18 August 2018).
- Goto, I.O.; Muramoto, J.J.; Ninaki, M. Application of inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) to soil analysis, 3: Total analysis of major elements in soils by lithium metaborate fusion ICP-AES. Jpn. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1991, 62, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Luukkonen, T.; Runtti, H.; Niskanen, M.; Tolonen, E.T.; Sarkkinen, M.; Kemppainen, K.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Simultaneous removal of Ni(II), As(III), and Sb(III) from spiked mine effluent with metakaolin and blast-furnace-slag geopolymers. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Lin, J.; Zhang, P.; Fang, L.; Ma, R.; Quan, Z.; Song, X. Geopolymer synthetized from sludge residue pretreated by thewet alkalinizing method: Compressive strength and immobilization efficiency of heavy metal. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 170, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masonnave, J.M.C. Immobilization of borates and phosphates with saturated lime solutions. Solid State Ion. 1993, 56, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, S.; Guerrero, A.; Gonñi, S. Leaching of borate waste cement matrices: Pore solution and solid phase characterization. Adv. Cem. Res. 2000, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumes, C.C.D.; Dhoury, M.; Champenois, J.B.; Mercier, C.; Damidot, D. Combined effects of lithium and borate ions on the hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 97, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Shimizu, K.; Kuroda, Y.; Higuchi, M. Advanced wastewater treatment of tetrafluoroboric acid-hexavalent chromium containing effluent using the ettringite. J. Surf. Finish. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 67, 111–117. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Dependence of solubility and stability of calcium arsenates on pH value. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2005, 25, 1652–1660. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, T.; Iizuka, A.; Watanabe, M.; Hongo, T.; Yamasaki, A. Preparation and performance of arsenate (V) adsorbents derived from concrete wastes. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1829–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Peng, B.; Min, X.; Liang, Y.; You, Y.; Chai, L. Modeling and optimization of lime-based stabilization in high alkaline arsenic-bearing sludges with a central composite design. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2017, 52, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Peng, B.; Liang, Y.; Min, X.; Chai, L.; Ke, Y.; You, Y. Effects of anions on calcium arsenate crystalline structure and arsenic stability. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 177, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L. Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Vipulanandan, C. Solidification/stabilization of Cr(VI) with cement Leachability and XRD analyses. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Garg, M. Effect of Cr(VI) on the hydration behavior of marble dust blended cement: Solidification, leachability and XRD analyses. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1851–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasheras-Zubiate, M.; Navarro-Blasco, I.; Fernández, J.M.; Álvarez, J.I. Encapsulation, solid-phases identification and leaching of toxic metals in cement systems modified by natural biodegradable polymers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 233–234, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omotoso, O.E.; Ivey, D.G.; Mikula, R. Characterization of chromium doped tricalcium silicate using SEM/EDS, XRD and FTIR. J. Hazard. Mater. 1995, 42, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Suito, H. Immobilization of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solution through the formation of 3CaO·(Al, Fe)2O3·Ca(OH)2·xH2O phase, ettringite and C–S–H gel. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.P.; Singer, P.C. Effect of Mg2+ on the kinetics of calcite crystal growth. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 312, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Xu, J.; Teng, H.H. Evolution of calcite growth morphology in the presence of magnesium: Implications for the dolomite problem. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 172, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Spooren, J.; Broos, K.; Nielsen, P.; Horckmans, L.; Vrancken, K.C.; Quaghebeur, M. New method for selective Cr recovery from stainless steel slag by NaOCl assisted alkaline leaching and consecutive BaCrO4 precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 295, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Q.; Cheng, G.; Wang, D.; Liang, Y.; Lu, J. Solubility and stability of barium arsenate and barium hydrogen arsenate at 25 °C. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 120, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Yuan, Y.; Christensen, T.H. Reductive effect of ferrous iron on chromate in alkaline system and its application to controlling chromium leaching from incineration fly ashes. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2005, 25, 1202–1210. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Utton, C.A.; Gallucci, E.; Hill, J.; Milestone, N.B. Interaction between BaCO3 and OPC/BFS composite cements at 20 °C and 60 °C. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezulová, A.; Staněk, T.; Opravil, T. The influence of barium sulphate and barium carbonate on the Portland cement. Procedia Eng. 2016, 151, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
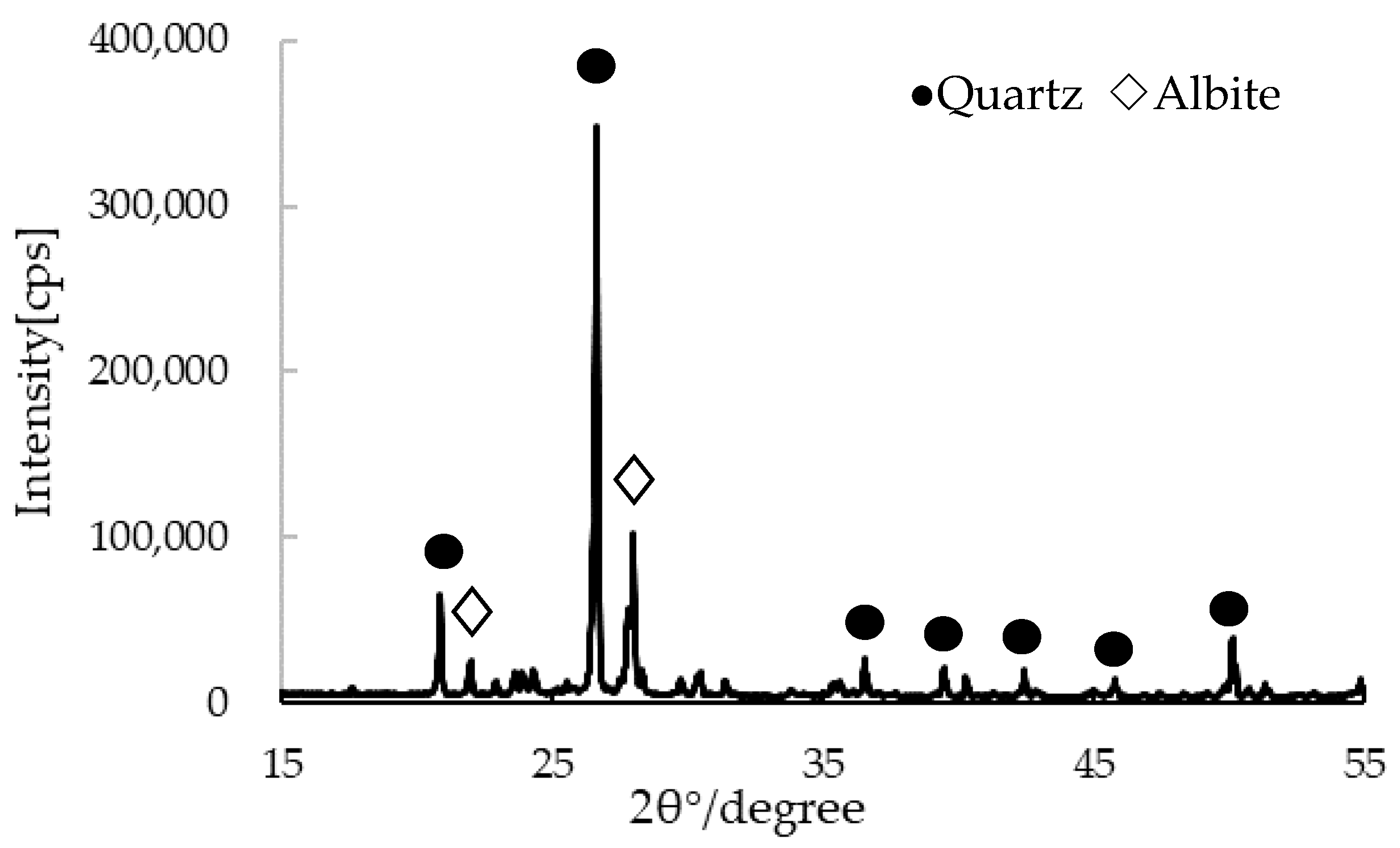

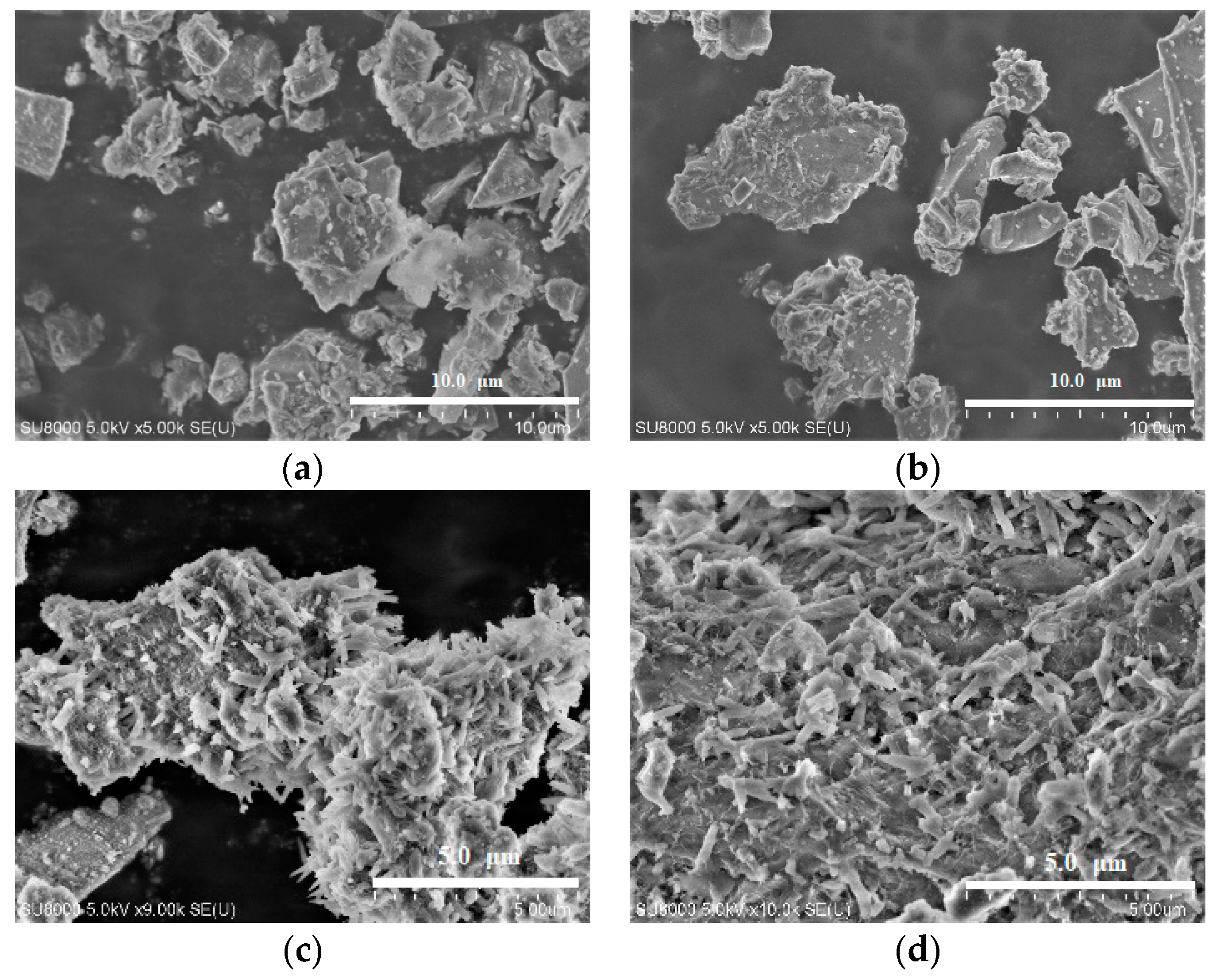

| Sample No. | 200 mg/L of Hazardous Ions Solution (mL) | CSP (g) | OPC (g) | Weight Ratio of OPC (wt.%) | Elution Conc. (mg/L) | pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | B | As | Cr | ||||||
| 1 | 4.00 | 8.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 7.15 | 8.60 | 2.75 | 4.46 | 8.6 |
| 2 | 1.00 | - | 2.00 | - | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 4.76 | 12.4 |
| 3 | 1.72 | - | 3.43 | - | 0.65 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 6.29 | 12.5 |
| 4 | 4.00 | - | 8.00 | - | 0.70 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 5.80 | 12.6 |
| 5 | 5.00 | 8.00 | 2.00 | 20 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 3.78 | 12.2 |
| 6 | 5.72 | 8.00 | 3.43 | 30 | 0.47 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.41 | 12.4 |
| 7 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 50 | 0.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 4.20 | 12.4 |
| Type of Material | Chemical Compositions (wt %) | Elution Conc. (μg/L) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | MgO | K2O | CaO | Other | F | B | As | Cr | |
| CSP | 52.9 | 14.4 | 2.1 | 3.2 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 2.9 | 22.6 | 82.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 2.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuang, X.; Sentoku, A.; Sasaki, A.; Endo, M. A Suppression Method for Elution of F−, [B(OH)4]−, AsO43−, and CrO42− from Industrial Wastes Using Some Inhibitors and Crushed Stone Powder. Technologies 2018, 6, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies6030079
Kuang X, Sentoku A, Sasaki A, Endo M. A Suppression Method for Elution of F−, [B(OH)4]−, AsO43−, and CrO42− from Industrial Wastes Using Some Inhibitors and Crushed Stone Powder. Technologies. 2018; 6(3):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies6030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuang, Xiaoxu, Atsuki Sentoku, Atsushi Sasaki, and Masatoshi Endo. 2018. "A Suppression Method for Elution of F−, [B(OH)4]−, AsO43−, and CrO42− from Industrial Wastes Using Some Inhibitors and Crushed Stone Powder" Technologies 6, no. 3: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies6030079
APA StyleKuang, X., Sentoku, A., Sasaki, A., & Endo, M. (2018). A Suppression Method for Elution of F−, [B(OH)4]−, AsO43−, and CrO42− from Industrial Wastes Using Some Inhibitors and Crushed Stone Powder. Technologies, 6(3), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies6030079




