Abstract
A large amount of soil was contaminated by radioactive cesium due to the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The adsorption behavior of cesium ions (Cs+) is strongly influenced by numerous factors, including the components, structure and weathering conditions of natural soil. The adsorption and ion exchange characteristics of Cs+ ions onto and from natural Japanese rocks with well-known components were studied. Cs+ adsorption onto volcanic rocks (0.9–5.3 mg/g) occurred more easily than that onto plutonic rocks (0.7–0.8 mg/g) due to differences in crystallinity. In addition, the adsorption quantity of cesium increased with increasing lattice water content and content of ion-exchangeable cations in the rock samples. The cesium adsorption ability of rock was inhibited by seawater and coexisting ions in the solution. Cesium adsorption quantities onto andosol, containing the corrosion products, increased approximately 2.7-fold with increasing pH from neutral to basic. Cesium desorption differed depending on the type of salt used, and the desorption rates were highest with ammonium salts. Cs+ desorption from regions such as the soil interlayer and the pores were inhibited by melting of the rock surface.
1. Introduction
The accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, which occurred as a consequence of the Great East Japan Earthquake on March 11, 2011, resulted in widespread contamination with radioactive materials [1,2,3]. A large amount of soil was contaminated by this accident. However, efficient and practical remediation of contamination caused by radioactive substances is difficult. Several reports have examined cesium adsorption/desorption onto zeolite, bentonite, and mica [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. The adsorption processes of exchangeable cations on the adsorption site of their minerals are different. For example, cesium ions (Cs+) are adsorbed in the interlayer of lamellar minerals and in the pores of zeolite [8,11,12]. However, the mechanism by which Cs+ adsorb onto and desorb from all minerals on the earth has not been fully elucidated. Natural soil is mixed with various kinds of rock [1,4,13]. Additionally, weathering processes, such as erosion, cause structural and chemical changes in natural minerals. The radioactive materials from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant have been incorporated into clay minerals—such as mica—in the natural soil in the surrounding environment. Cs+ ions are known to adsorb strongly onto the natural soil, such as biotite [7,14,15]. In particular, the half-time of Cs-137 is about 30 years [7,10]. Therefore, quick response to soil contamination is necessary.
Since the adsorption and desorption of Cs+ ions onto and from natural soil are strongly influenced by several factors, including the components, structure, and weathering conditions of the soil, the behavior on Cs in an actual environment has not yet been determined. The clear elucidation of the cesium adsorption and desorption mechanism is necessary. Therefore, in this study, the adsorption and ion exchange characteristics of Cs+ ions onto and from natural Japanese rocks with well-known components were studied.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Natural Japanese Rocks
Natural Japanese rocks were obtained from the Geological Survey of Japan in National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST). These natural Japanese rocks were ground into powder in a mortar and sieved with 0.149 mm sieves. Basic data, such as the sample components and collection locations, were previously reported [16]. Figure 1 shows that the reference samples were classified as igneous rock, sedimentary rock, metamorphic rock, and sediments. In this study, andesite (JA), basalt (JB), granodiorite (JG), gabbro (JGb), chert (JCh), slate (JSl), andosol (JSO), and stream sediment (JSd) were selected. “J” in these abbreviations denotes that these samples were collected in Japan. The silica oxide (SiO2) content and crystallinity of rock strongly influence Cs+ adsorption behavior. Igneous rock and the other rock groups were further divided into two categories: before weathering and after weathering.
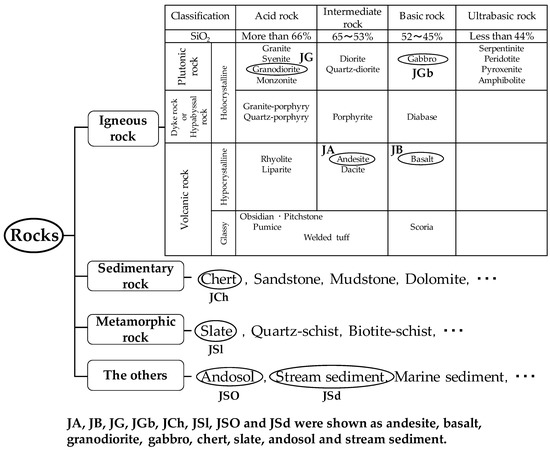
Figure 1.
Classification of rocks used in this study: igneous rock (JA, JB, JG, and JGb), sedimentary rock (JCh), metamorphic rock (JSl), and other rocks (JSO and JSd).
2.2. Cesium Adsorption Experiments
Cs+ aqueous solutions of 200 or 2000 mg/L were prepared from dissolving cesium chloride powder (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Osaka, Japan, Assay min. 99.0%) into deionized water. The particle diameter of all the mineral samples was less than 0.149 mm. The Cs+ adsorption saturation time of the minerals in this study was 5 min for zeolites and 30 min for the other minerals. A Cs+ solution of 50 mL and a mineral sample of 0.5 g were placed in a 200 mL polystyrene container and stirred for 2 h. Each sample solution was filtered through a 0.20-μm syringe filter, and the saturation quantities of adsorbed Cs+ were determined on the basis of the Cs+ concentration in the filtrates, as measured by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, ELAN-DRCII, Perkin Elmer, Yokohama, Japan).
The adsorption tests with seawater were carried out using the commercial product Tetra Marin® Salt Pro sea salt (Spectrum Brands Japan Co., Ltd., Yokohama, Japan). Cs+ was added at a concentration of 200 ppm to seawater adjusted to a predetermined concentration (specific gravity 1.020–1.023, 1 L water, and 33 g sea salt). Cs+ adsorption experiments on 0.5 g of the rocks were conducted with seawater using the procedure described in the cesium adsorption test using deionized water.
Solutions with coexisting ions, including potassium ions (K+), magnesium ions (Mg2+), calcium ions (Ca2+), and barium ions (Ba2+), with concentrations of 100 or 200 ppm, were prepared from potassium chloride, magnesium nitrate, calcium carbonate, and barium nitrate, respectively. The initial concentration of Cs+ used in these adsorption tests was 200 ppm. Cs+ adsorption experiments on 0.5 g of JB-1a and JSO-1 using solutions with coexisting ions were conducted using the procedure described in the cesium adsorption test, using deionized water.
The pH of the Cs+ solution (200 ppm) was adjusted to 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide solution. Cesium adsorption experiments were conducted on JB-1a and JSO-1 (0.5 g) under various pH conditions using the procedure described in the cesium adsorption test using deionized water.
2.3. Cesium Desorption Experiments
Hydrochloric acid (HCl), diammonium hydrogen phosphate ((NH4)2HPO4), ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), ammonium fluoride (NH4F), ammonium oxalate ((NH4)2C2O4), and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt dihydrate (EDTA-2Na·2H2O) were used in the desorption tests. First, 50 mL of 0.1 mol/L solution of each reagent was added to a JB-1a sample with Cs+ adsorbed at 2.01–2.94 mg/0.5 g, and the resultant solution was stirred for 2 h. Similar desorption tests were carried out after the adsorption tests.
Solutions with coexisting ions K+, Mg2+, Ca2+ and Ba2+ were prepared from potassium chloride, magnesium nitrate, calcium carbonate, and barium nitrate, respectively. Next, 50 mL of a solution with 200 ppm of each ion was added to JB-1a and JSO-1 samples with Cs+ adsorbed at 1.9–2.5 mg/0.5 g and 2.5–2.7 mg/0.5 g, respectively. The resultant mixtures were stirred for 2 h. Cs+ desorption experiments on 0.5 g of JB-1a and JSO-1 in the presence of the coexisting ions were conducted using the procedure described in cesium desorption test with ammonium salts.
2.4. Heat Treatment Experiments
The rock samples were calcined at 400, 600, 800, and 1000 °C, and Cs+ adsorption experiments were conducted with the calcined samples. In addition, a desorption experiment using 0.1 mol/L hydrochloric acid on the calcined rock samples was carried out. The rock and solution ratios and the procedure after stirring were similar to those used in the adsorption experiments.
Calcined rocks were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Ultima-IV, Rigaku, akishima, Japan), thermogravimetric and differential analysis (TG-DTA, 2000 SA, Bruker-AXS, Yokohama, Japan), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM, SU 8000, Hitachi, Minato, Japan).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption of Cs+ onto Natural Japanese Rocks
The components and crystallinity of natural minerals differ based on the formation process of the mineral with ground heat and pressure [16]. The results of the Cs+ adsorption tests indicate that Cs+ was adsorbed onto the JA and JB group rocks (volcanic rock: merocrystalline). In contrast, Cs+ was hardly adsorbed onto JG and JGb (plutonic rocks: holocrystalline). The adsorption quantities for Cs+ onto plutonic rocks, which are highly crystalline, were substantially lower than the adsorption quantities onto the JA and JB groups, which are poorly crystalline (Table 1 and Figure 2). Additionally, the high cesium adsorption ability of JSO was due to the corrosion product on the surface of JSO [1]. Cesium was adsorbed onto the adsorption sites on JSO and the surface hydroxyl groups of the corrosion product.

Table 1.
The major constituent of natural Japanese rocks.
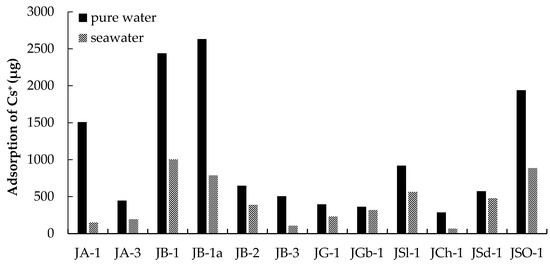
Figure 2.
Adsorption quantity of Cs+ onto the natural Japanese rocks (0.5 g) with pure water or seawater. Initial Cs+ concentration: 200 mg/L.
Water components in natural minerals are divided into H2O+ (water in the crystal lattice) and H2O− (moisture content) [17]. The adsorption quantity of Cs+ onto JA and JB groups differed with the collection location and the H2O+ content [16]. The evaporation temperature of H2O− and H2O+ range from room temperature to 105 °C and 105 to 950 °C, respectively [17]. Exchangeable cations are held between H2O+ and H2O+ in the soil layers. Therefore, the number of exchangeable cations increases with increasing H2O+ content in the rocks.
Figure 3 shows the variation in the ratio between the adsorbed quantity of Cs+ and the H2O+ content in the rock samples. The H2O+ content in the rock samples was proportional to the adsorbed quantity of Cs+ ions. However, the slopes of the two straight approximation lines differed according to the weathering condition of the rocks. This relationship is influenced by the leaching of cations as rocks weather in the natural environment [18]. In addition, Table 1 shows that the cation content ratios of Mg2+, Ca2+, Na+, and K+ in the igneous rocks were relatively lower than those in the other rock groups, such as JSl, JCh, JSd, and JSO. Those cations elute from rock as weathering progresses. Therefore, cesium adsorption quantity for weathered rocks were higher than for the unweathered rocks.
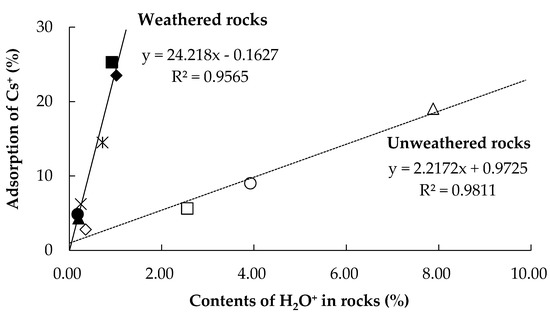
Figure 3.
The correlation between the adsorption quantity for Cs+ onto the natural Japanese rocks and the H2O+ of the samples. The solid and broken lines reveal the results for unweathered (igneous rocks) and weathered (others) rocks, respectively.
3.2. Adsorption Behavior of Cs+ with Seawater
Figure 2 shows that the Cs+ adsorption quantities on all rock samples were lower when the adsorption was carried out in seawater than when the adsorption was carried out in pure water. The decrease in adsorption quantity for Cs+ onto JB-1, JB-1a, and JSO-1, which have large saturated adsorption quantities and high exchangeable cation content, exceeded approximately 50%. The influence of seawater on the Cs+ adsorption quantities varied with the type of rock, and the decrease in the Cs+ adsorption quantities ranged from 12% (minimum: JGb-1) to 90% (maximum: JA-1). Seawater contains high concentrations of cations, such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ [19]. The adsorption of Cs+ was inhibited by these cations. Based on these results, cesium adsorption in seawater was more difficult than in pure water.
3.3. Adsorption of Cs+ with Coexisting Ions
The adsorption quantity of Cs+ onto JB-1a was low when divalent ions coexisted. In addition, the Cs+ adsorption quantity decreased with increasing concentration of divalent ions (Figure 4). The surfaces of rocks are negatively charged by isomorphous replacement [20,21,22]. The adsorption affinity associated with the adsorption of divalent ions onto rock is higher than that associated with the adsorption of monovalent ions. Therefore, the observed inhibition of Cs+ adsorption onto rock increased in the sequence K+ < Ba2+ ≈ Mg2+ < Ca2+.
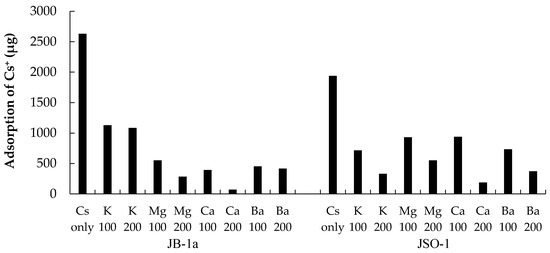
Figure 4.
Adsorption quantity for Cs+ in solutions with coexisting ions: K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, and Ba2+. The initial concentration of each coexisting ion was 100 or 200 mg/L.
In contrast, Cs+ adsorption onto JSO-1 was more affected by the concentration of coexisting ions than by their valence. Cs+ adsorption characteristics of JB-1a and JSO-1 differed according to the cation type and concentration. Cs+ adsorption in both JB-1a and JSO-1 was inhibited most effectively by Ca2+.
3.4. Adsorption Quantity of Cs+ for pH Change
The adsorption quantity of Cs+ onto JB-1a and JSO-1 increased with increasing pH (Figure 5). In particular, the adsorption of Cs+ onto JSO-1 increased approximately 2.7-fold as the conditions were adjusted from neutral to basic. The adsorption quantity of Cs+ onto JSO-1 fluctuated dramatically when large quantities of corrosion products were present. The corrosion products include soil organic materials that exhibit a negative surface charge under basic pH conditions in aqueous solution [23,24]. Therefore, the quantity of adsorbed Cs+ on JSO increased with increasing pH.
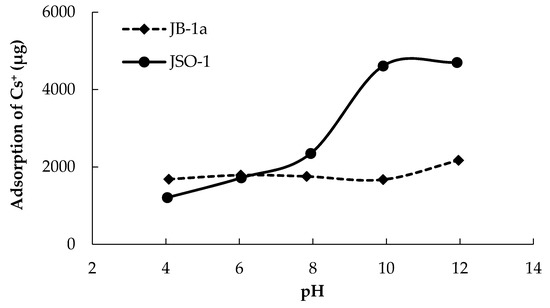
Figure 5.
Effect of pH on the adsorption quantity for Cs+ onto JB-1a and JSO-1 (0.5 g). Initial Cs+ concentration: 200 mg/L.
3.5. Desorption of Cs+ from Natural Japanese Rocks
Figure 6 shows that desorption of Cs+ varied with the type of salt and that the desorption ratio was highest in the case of ammonium salts. The ionic radius of exchangeable cations increases in the order Ca2+ < Na+ < K+ < NH4+ < Cs+ [25,26]. The experimental results are likely attributable to a strong chemical attraction among NH4+ ions, whose ionic radii are essentially equal to those of Cs+ ions. In addition, the desorption ratio of Cs+ in the presence of EDTA was approximately 80%, which is attributed to the ion-coordinating ability of EDTA and the ion-exchange ability of Na+. Structure components, such as Al3+ in JB-1a, can be dissolved by hydrochloric acid [10]. In this study, Cs+ was easily desorbed from rock samples in H2O (desorption ratio 30%) and in hydrochloric acid (desorption ratio 80%), due to the intentionally high concentrations of Cs+ adsorbed onto the rock samples.
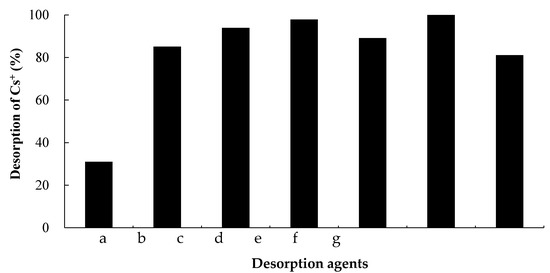
Figure 6.
Desorption ratio (%) of Cs+ from JB-1a (0.5 g) using 0.1 mol/L solutions of different salts. a: H2O, b: HCl, c: (NH4)2HPO, d: NH4Cl, e: NH4F, f: (NH4)2C2O4, and g: Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt, 2-hydrate. The desorption ratios were calculated based on the Cs+ adsorption quantities in Figure 2.
The desorption of Cs+ ions was reported to be difficult under conditions where the adsorbed quantity for Cs+ onto the substrate was low, as is true for natural soil [20,21]. In this work, however, we observed that high desorption ratios of Cs+ were due to the large adsorbed quantity of Cs+.
3.6. Desorption of Cs+ with Coexisting Ions
Figure 7 shows that the Cs+ desorption ratio in the presence of other coexisting ions differed depending on the type of rock. We confirmed that desorption of Cs+ from JB-1a using monovalent cations such as K+ was easier than the desorption using divalent cations. Desorption from JSO-1 was more strongly influenced by Ba2+ due to the ionic radius of Ba2+ being similar to that of cesium [27]. We confirmed that K+ most strongly promoted Cs+ desorption from JSO-1 and JB-1a, respectively, in the presence of coexisting cations.
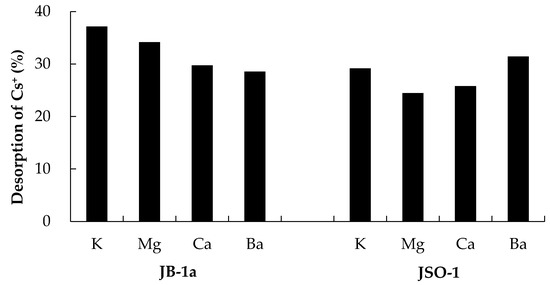
Figure 7.
Desorption ratio (%) of Cs+ from JB-1a and JSO-1 (0.5 g) in solutions with coexisting ions (initial concentration: 200 mg/L); the desorption ratios were calculated based on the Cs+ adsorption quantities in the absence of the coexisting ions (Figure 2).
3.7. Effect of the Heat Treatment of Rocks
Table 2 shows the influence of calcination temperature on the adsorption of Cs+ onto the rock samples. The adsorption quantity for Cs+ onto all rocks decreased with increasing calcination temperature. The adsorption quantity of Cs+ onto rocks calcined at 1000 °C was limited to approximately 20% or less of the saturated adsorbent quantities in the absence of calcination. The adsorption quantities of Cs+ onto all rocks calcined at 1100 °C were below the lower detection limit of the ICP-MS instrumentation.

Table 2.
Adsorption ratio (%) for Cs+ onto rocks (0.5 g) calcined at various temperatures, as calculated based on the Cs+ adsorption quantities without calcination (Figure 2).
Dehydration, oxidation decomposition, oxidation, and melting events for each rock sample were detected by TG-DTA (Figure 8). These results indicate that structural changes, such as melting and decomposition, occur during heating, leading to a reduction in the soil interlayer distance by dehydration.
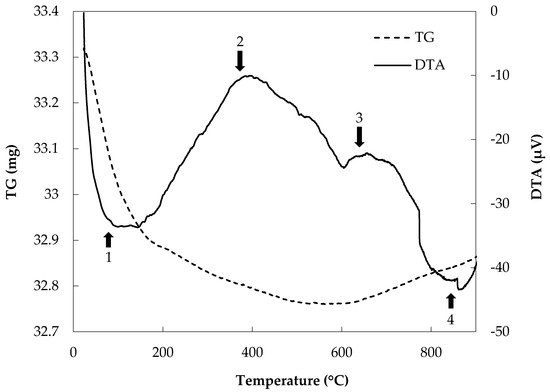
Figure 8.
Thermogravimetric and differential analysis (TG-DTA) patterns for JB-1a: 1. dehydration, 2. oxidation decomposition, 3. oxidation, and 4. melting.
In addition, Figure 9 shows the XRD patterns for rock samples calcined at different temperatures. The diffraction peaks of the rock samples decreased in intensity with increasing calcination temperature. These results indicate that the skeleton structure of the rocks was destroyed by heat.
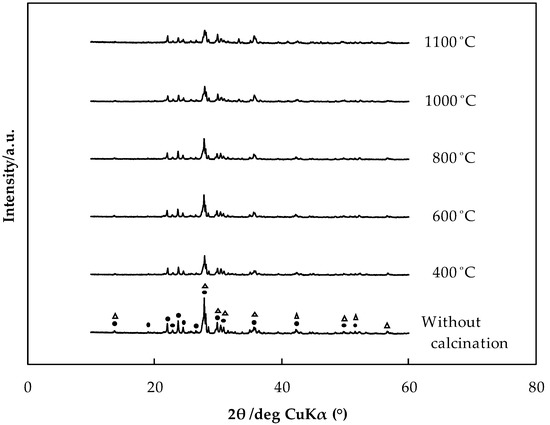
Figure 9.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of JB-1a calcined at various temperatures (●: albite calcian; △: augite; CuKα; scan rate: 10°/min; and step scan size: 0.02°).
The effects of melting of the surfaces of the rock samples were observed by SEM (Figure 10). The surfaces of rocks not subjected to calcination were uneven, as shown in Figure 10a,c. The surface structure of the rocks calcined at 1000 °C became smooth. All rock samples were changing state due to heat. Therefore, the adsorption of Cs+ onto the rocks was inhibited by a decrease in the number of adsorption sites upon heat treatment.
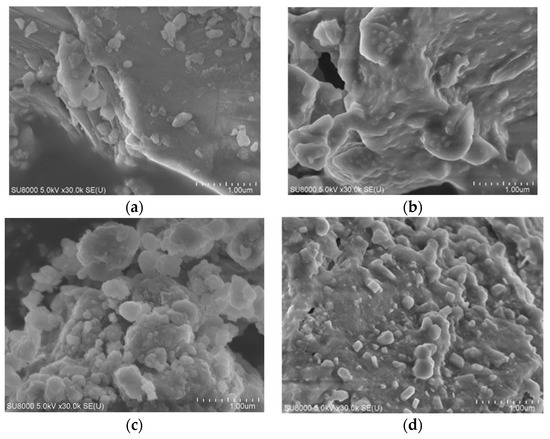
Figure 10.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of (a) JB-1a and (c) JSO-1 without calcination and (b) JB-1a and (d) JSO-1 after calcination at 1000 °C; magnification: 30,000×.
Table 3 shows that the desorption quantity of Cs+ from rocks tended to decrease with increasing calcination temperature. This result is related to changes in the skeletal structure and the Cs+ adsorption behavior. The desorption of Cs+ from, for example, soil interlayers and pores, would be inhibited by the melting rock surface. In particular, the inhibitory effect of Cs+ desorption was high in cases where the rock was calcined at temperatures greater than at 1000 °C. Nevertheless, Cs+ desorption from rock samples calcined at 400 and 600 °C occurred easily due to incomplete structural changes and because the cations were not trapped inside the rock. Consequently, heat treatments, similar to the calcination at 1000 °C described above, are expected to be used as the final disposal method for contaminated soil.

Table 3.
Desorption ratio (wt %) of Cs+ from the rocks (0.5 g) calcined at various temperatures, as calculated based on the Cs+ adsorption quantities t without calcination (Figure 2).
4. Conclusions
We confirmed that Cs+ adsorption onto volcanic rocks (0.9–5.3 mg/g) occurred more easily than that onto plutonic rocks (0.7–0.8 mg/g). Adsorption quantity of Cs+ onto rock samples increased with increasing exchangeable cation quantity in the solution and decreasing rock crystallinity. Cesium adsorption quantities for the before weathering rocks were higher than for the after weathering rocks. The adsorption quantity for Cs+ onto all the rock samples decreased when seawater was used. The adsorption of Cs+ was inhibited under adsorption experiments conducted with Ca2+ ions coexisting in the solution. In addition, the adsorption quantity of Cs+ onto JSO increased approximately 2.7-fold when the solution pH was changed from acidic to basic. We determined that the adsorption behavior in the case of JSO-1 was influenced by the pH-dependency of the corrosion product.
The desorption ratio of Cs+ in the case of ion exchange with NH4+ salts was relativity high. The ionic radius of exchangeable cations occurs in the increasing order: Ca2+ < Na+ < K+ < NH4+ < Cs+. Cesium desorption behavior with ammonium salts was attributable to a strong chemical attraction among NH4+, whose ionic radius is substantially equal to that of a Cs+ ion. Desorption behavior with coexisting ions was related to the valence and radius of the ions.
The quantity of Cs+ adsorbed onto and desorbed from all the rock samples decreased with increasing rock calcination temperature. The results were influenced by the melting of the rock surface, which decreased the number of available adsorption sites.
In this study, we confirmed that the cesium adsorption and desorption characteristics were changed by the major constituent elements in the natural Japanese rocks and the condition of the reaction solution (seawater, coexisting ions, and pH). These characteristics of rock in natural environments are influenced by many factors, such as structure, weathering condition, exchangeable cations, and pH. This research result, using natural Japanese rocks with well-known components, is expected to help elucidate and simplify the cesium adsorption/desorption characteristics for contaminated soil. Additionally, we were able to control the cesium adsorption and desorption with the calcination of rocks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.M.; M.E.; Data Curation, T.M.; A.S.; M.E.; Formal Analysis, T.M.; A.S.; M.E.; Investigation, T.M.; Methodology, T.M.; A.S.; M.E.; Project Administration, T.M.; M.E; Supervision, M.E.; Validation, A.S.; M.E.; Writing Original Draft Preparation, T.M.; Writing Review and Editing, A.S.; M.E; All authors have read and approved the final manuscript. Atsushi Sasaki is my adviser for the experiment and writing article. Masatoshi Endo is my PhD supervisor.
Funding
This research received the funding from Japan Society of Ion Exchange.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fujii, K.; Ikeda, S.; Akama, A.; Komatsu, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kaneko, S. Vertical migration of radiocesium and clay mineral composition in five forest soils contaminated by the Fukushima nuclear accident. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 60, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, D.; Takahashi, A.; Tanaka, H.; Sato, M.; Fukuda, S.; Kamimura, R.; Kawamoto, T. Variation in available cesium concentration with parameters during temperature induced extraction of cesium from soil. J. Environ. Radioact. 2015, 140, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, H.; Hirose, A.; Motai, S.; Kikuchi, R.; Tanoi, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Yaita, T.; Kogure, T. Cesium adsorption/desorption behavior of clay minerals considering actual contamination conditions in Fukushima. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogure, T.; Morimoto, K.; Tamura, K.; Sato, H.; Yamagishi, A. XRD and HRTEM Evidence for Fixation of Cesium Ions in Vermiculite Clay. Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedicto, A.; Missana, T.; Fernández, A.M. Interlayer collapse affects on cesium adsorption onto illite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4909–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaunbrecher, L.K.; Cygan, R.T.; Elliott, W.C. Molecular models of cesium and rubidium adsorption on weathered micaceous minerals. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 5691–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, A.J.; Shaw, S.; Peacock, C.L.; Trivedi, D.; Small, J.S.; Abrahamsen, L.G.; Burke, I.T. Ionic strength and pH dependent multi-site sorption of Cs onto a micaceous aquifer sediment. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 40, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Yoshikawa, E.; Muramatsu, N.; Takizawa, N.; Kawai, T.; Unuma, H.; Sasaki, A.; Masano, A.; Takeyama, Y.; Kahara, T. The removal of cesium ion with natural Itaya zeolite and the ion exchange characteristics. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, P.N.; Wang, M.K.; Huang, P.M.; Wang, J.J. Effects of low molecular weight organic acids on (137) Cs release from contaminated soils. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, T.; Takizawa, N.; Togashi, K.; Sasaki, A.; Endo, M. Adsorption/Desorption Characteristics of Cesium Ions on Natural and Synthetic Minerals. J. Ion Exch. 2018, 29, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna, F.J.; Cota, A.; Pavón, E.; Pazos, M.C.; Alba, M.D. Cesium adsorption isotherm on swelling high-charged micas from aqueous solutions: Effect of temperature. Am. Mineral. 2018, 103, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, C.B.; Begg, J.D.; Kersting, A.B.; Zavarin, M. Cesium sorption reversibility and kinetics on illite, montmorillonite, and kaolinite. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.Q.; Jin, X.Y.; Lu, X.Q.; Chen, Z.L. Adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) onto natural kaolinite clay. Desalination 2010, 252, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostick, B.C.; Vairavamurthy, M.A.; Karthikeyan, K.G.; Chorover, J. Cesium adsorption on clay minerals: An EXAFS spectroscopic investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, A.; Thiry, Y.; Funakawa, S.; Kosaki, T. Characterization of the frayed edge site of micaceous minerals in soil clays influenced by different pedogenetic conditions in Japan and northern Thailand. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2008, 54, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSJ Geochemical Reference Samples Data Base. Available online: https://gbank.gsj.jp/geostandards/welcome.html (accessed on 14 June 2018).
- Johnson, W.M.; Maxwell, J.A. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1981; ISBN 13 9780471027430. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, K. Weathering during late Pliocene of Gotsu plutonic rocks. J. Jpn. Soc. Eng. Geol. 1973, 14, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onikata, M.; Kondo, M.; Hayashi, N.; Yamanaka, S. Complex formation of cation-exchanged montmorillo-nites with propylene carbonate: Osmotic swelling in aqueous electrolyte solutions. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, K.; Kogure, K.; Tamura, K.; Tomofuji, T.; Yamagishi, A.; Sato, H. Desorption of Cs+ Ions Intercalated in Vermiculite Clay through Cation Exchange with Mg2+ Ions. Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 1715–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Sato, H.; Yamagishi, A. Desorption of Cs+ ions from a vermiculite by exchanging with Mg2+ ions: Effects of Cs+-capturing ligand. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2015, 303, 2205–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzene, L.; Tertre, E.; Hubert, F.; Ferrage, E. Nature of the sites involved in the process of cesium desorption from vermiculite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 455, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komy, Z.R.; Shaker, A.M.; Heggy, S.E.M.; El-Sayed, M.E.A. Kinetic study for copper adsorption onto soil minerals in the absence and presence of humic acid. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumat, C.; Stauton, S. Reduced adsorption of caesium on clay minerals caused by various humic substances. J. Environ. Radioact. 1999, 46, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, E.; Baeyens, B.; Maes, A.; Cremers, A. Cesium and rubidium ion equilibriums in illite clay. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staunton, S.; Roubaud, M. Adsorption of 137Cs on montmorillonite and illite: Effect of charge compensating cation, ionic strength, concentration of Cs, K, and fluvic acid. Clays Clay Miner. 1997, 45, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Chemistry.com. Available online: https://environmentalchemistry.com/yogi/periodic/ioni-cradius.html (accessed on 14 June 2018).
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).