Automated Segmentation of MS Lesions in MR Images Based on an Information Theoretic Clustering and Contrast Transformations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
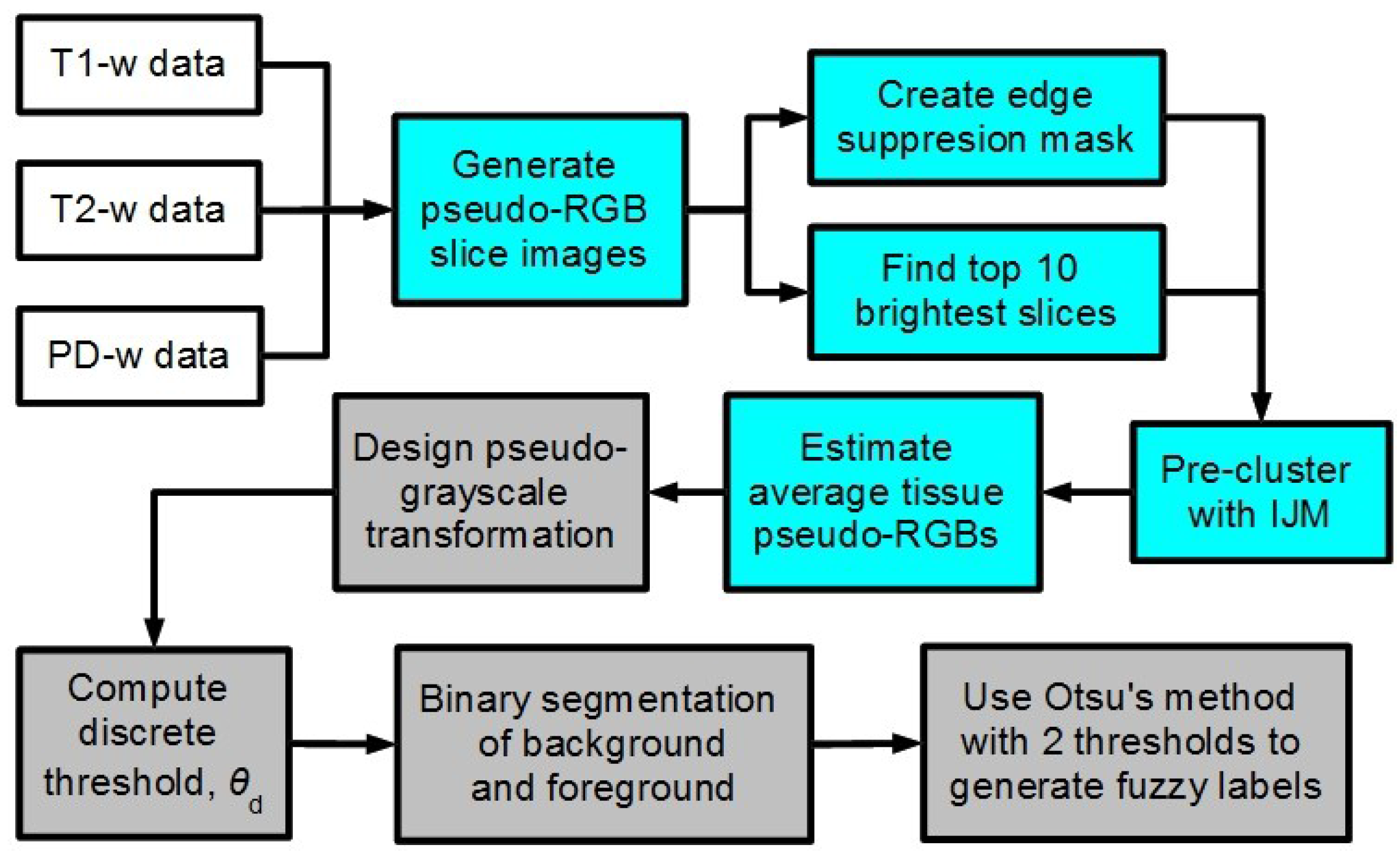
2. Methodology
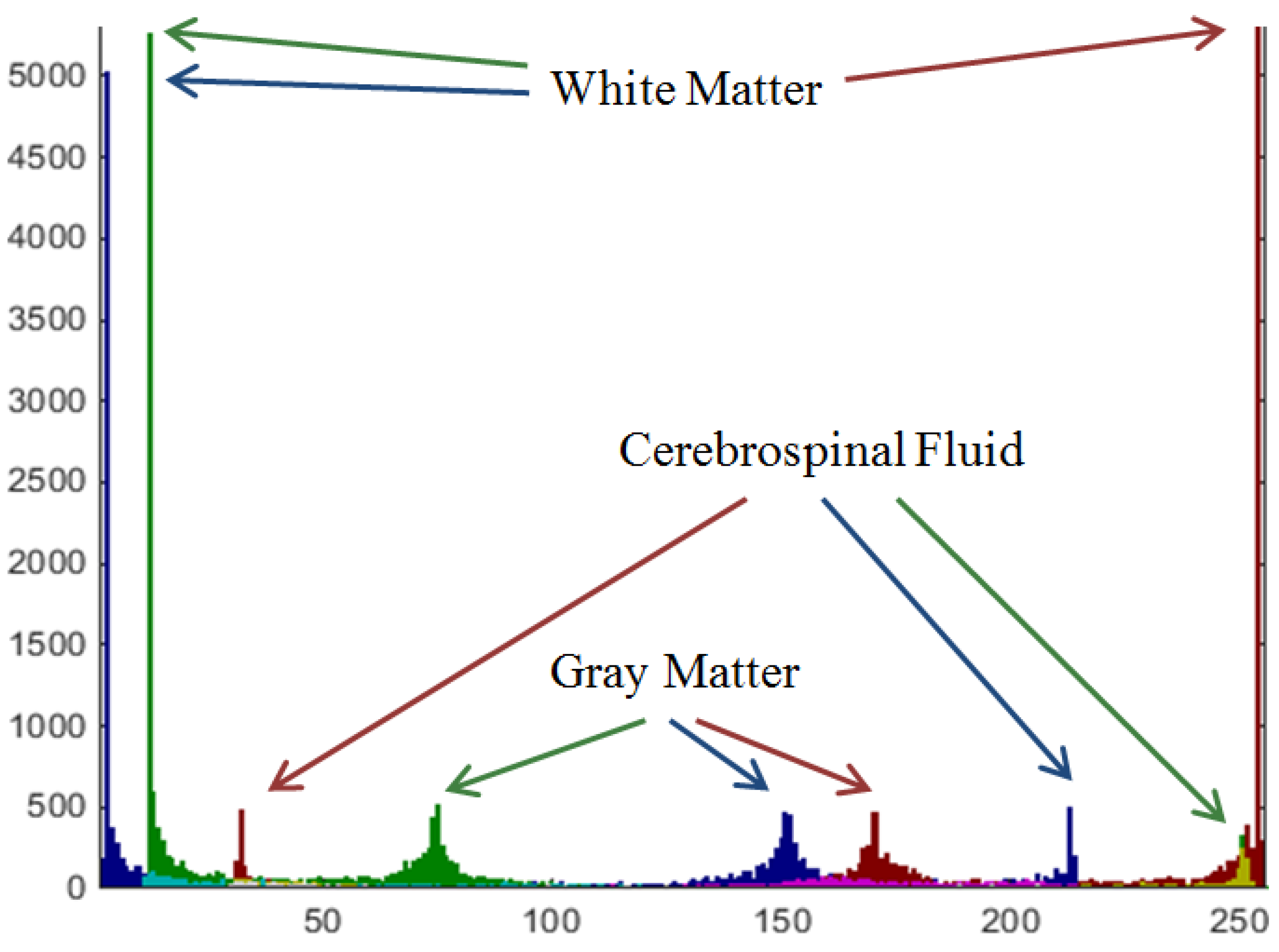
2.1. Preprocessing: A Pseudo-Color Image of MRI Data
2.2. Preliminary Segmentation: The Improved “Jump” Method
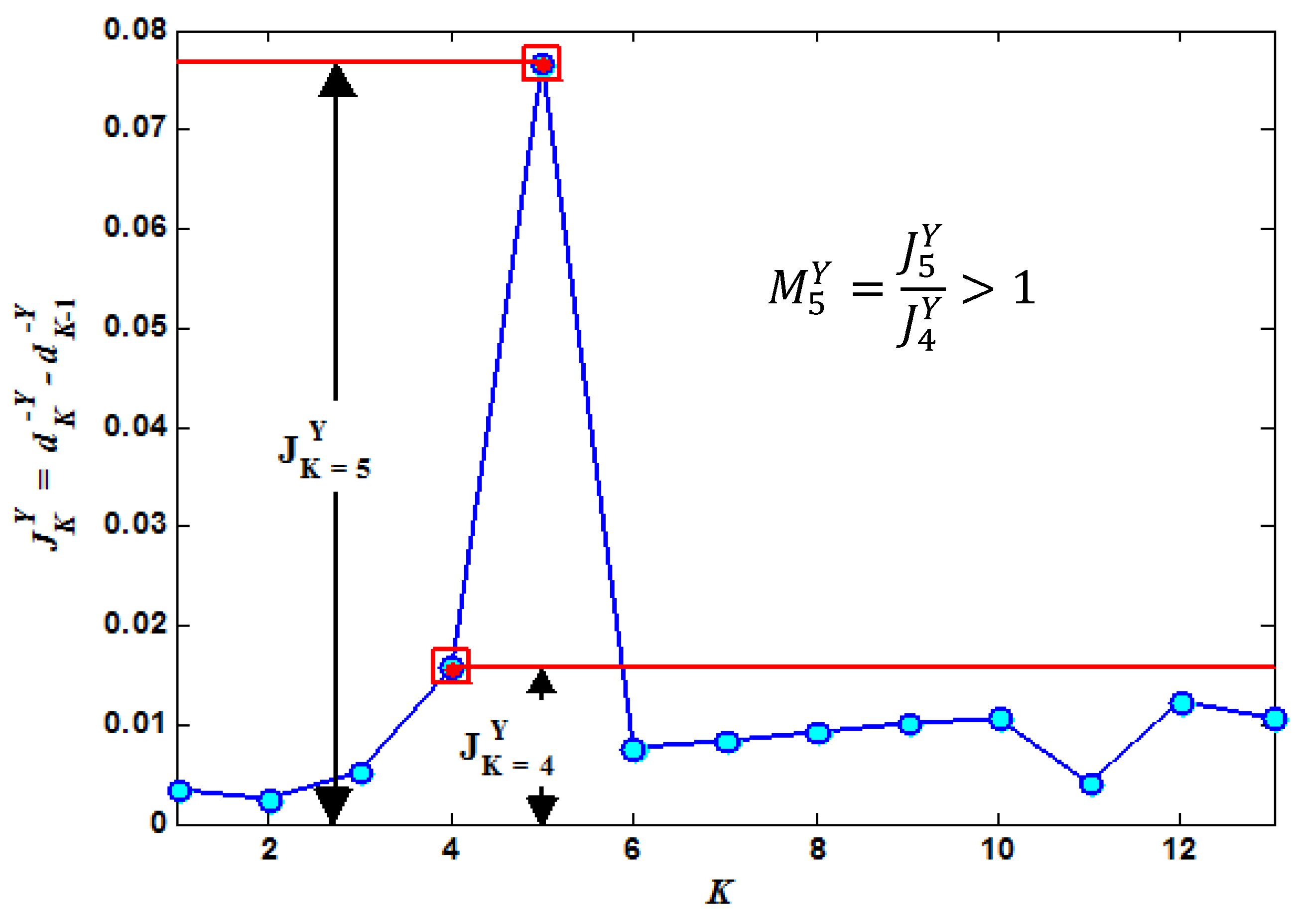
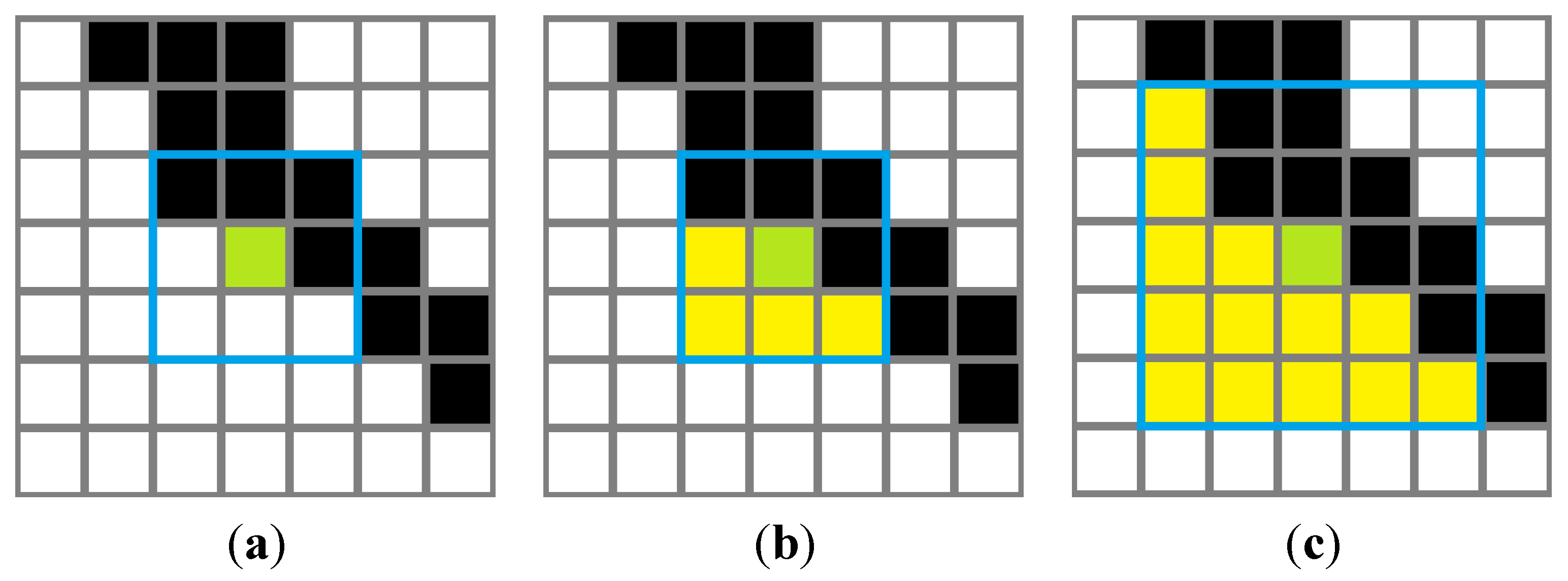
2.3. Edge Suppression and Adaptive Window Sampling
2.4. Post-Processing: Contrast Equalization and Enhancement via a Pseudo-Grayscale Conversion

3. Results and Discussion
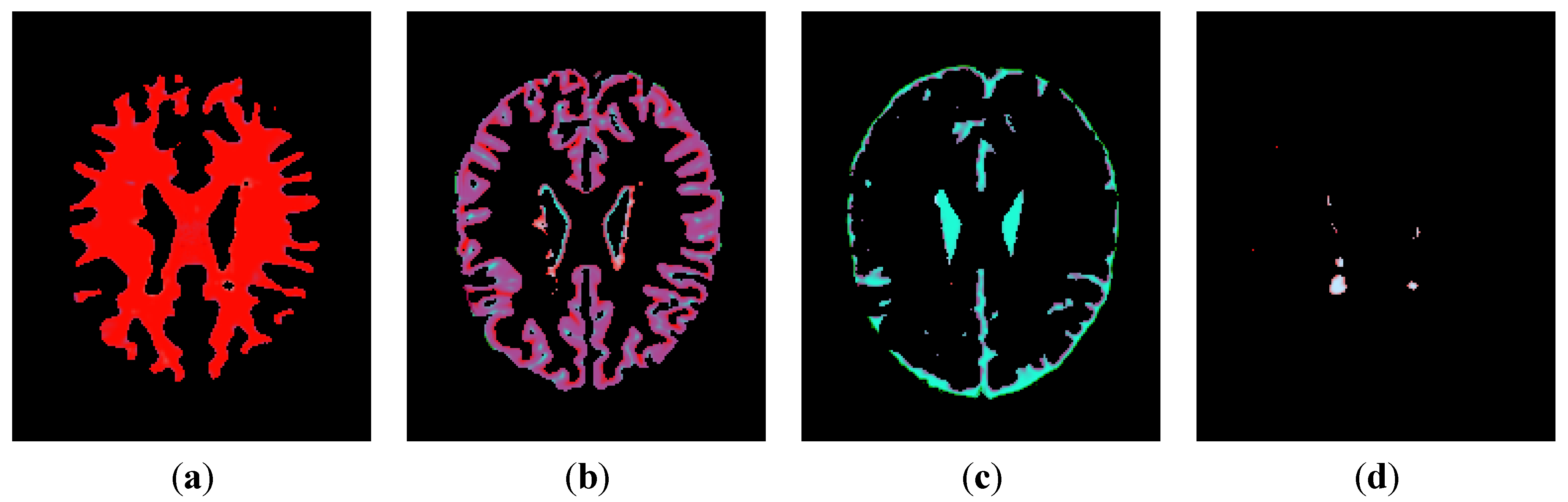
3.1. Segmentation of MS Lesions in a Slice
3.1.1. Estimation of Pseudo-Color Tissue Intensity Averages via IJM Image Segmentation
| Predicted/True | White Matter | Grey Matter | CSF | MS lesion | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segment 1 | 8564 | 240 | 0 | 1 | 97.26% |
| Segment 2 | 676 | 5789 | 312 | 59 | 82.58% |
| Segment 3 | 1 | 616 | 1920 | 9 | 75.41% |
| Segment 4 | 21 | 1 | 0 | 98 | 81.86% |
| Accuracy | 92.46% | 87.11% | 86.02% | 58.68% | - |
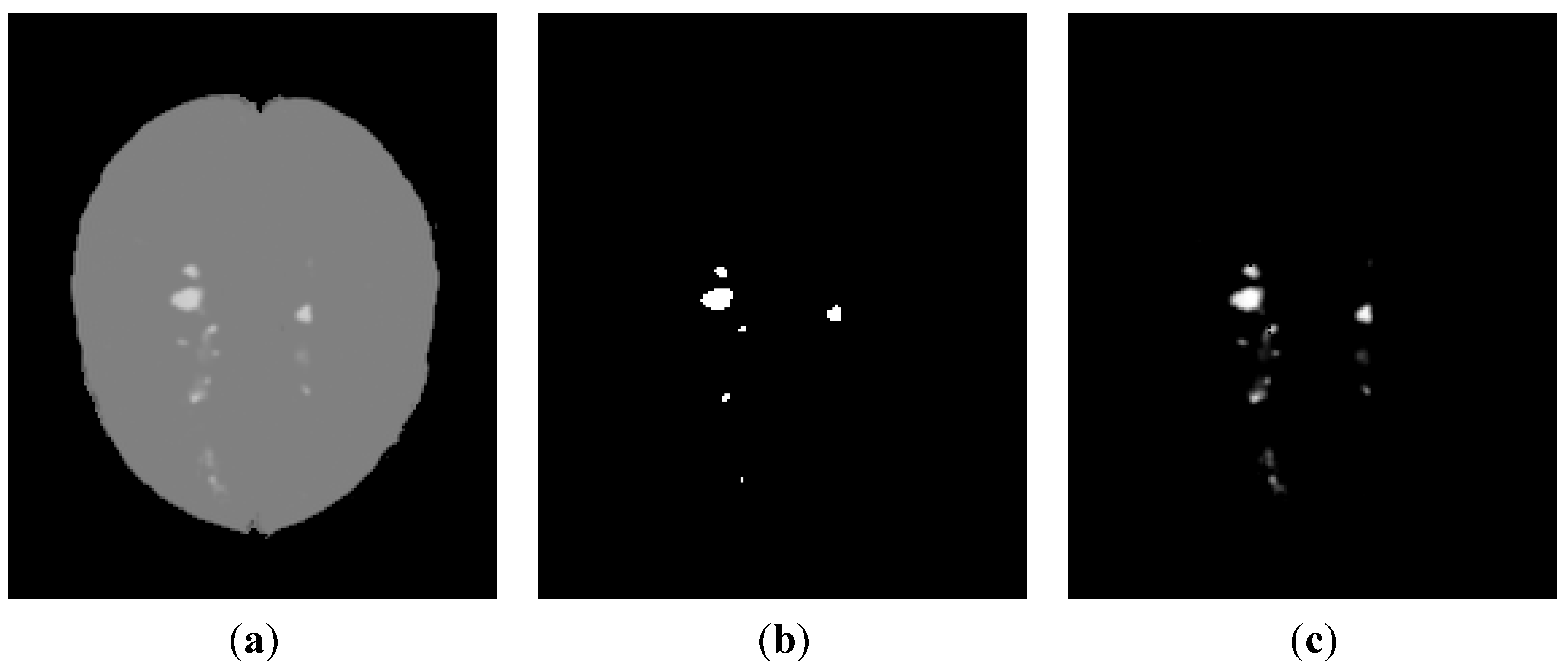
3.1.2. Contrast Equalization via a Pseudo-Grayscale Conversion
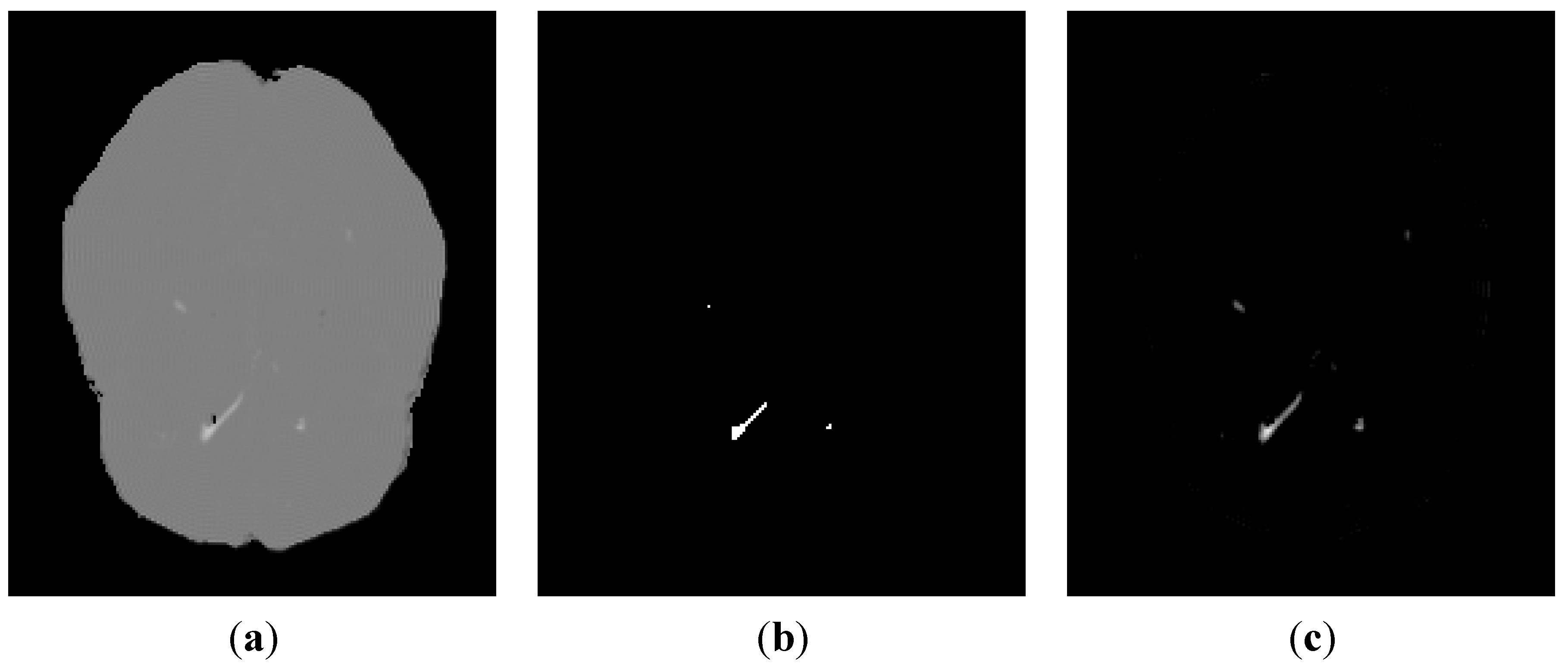
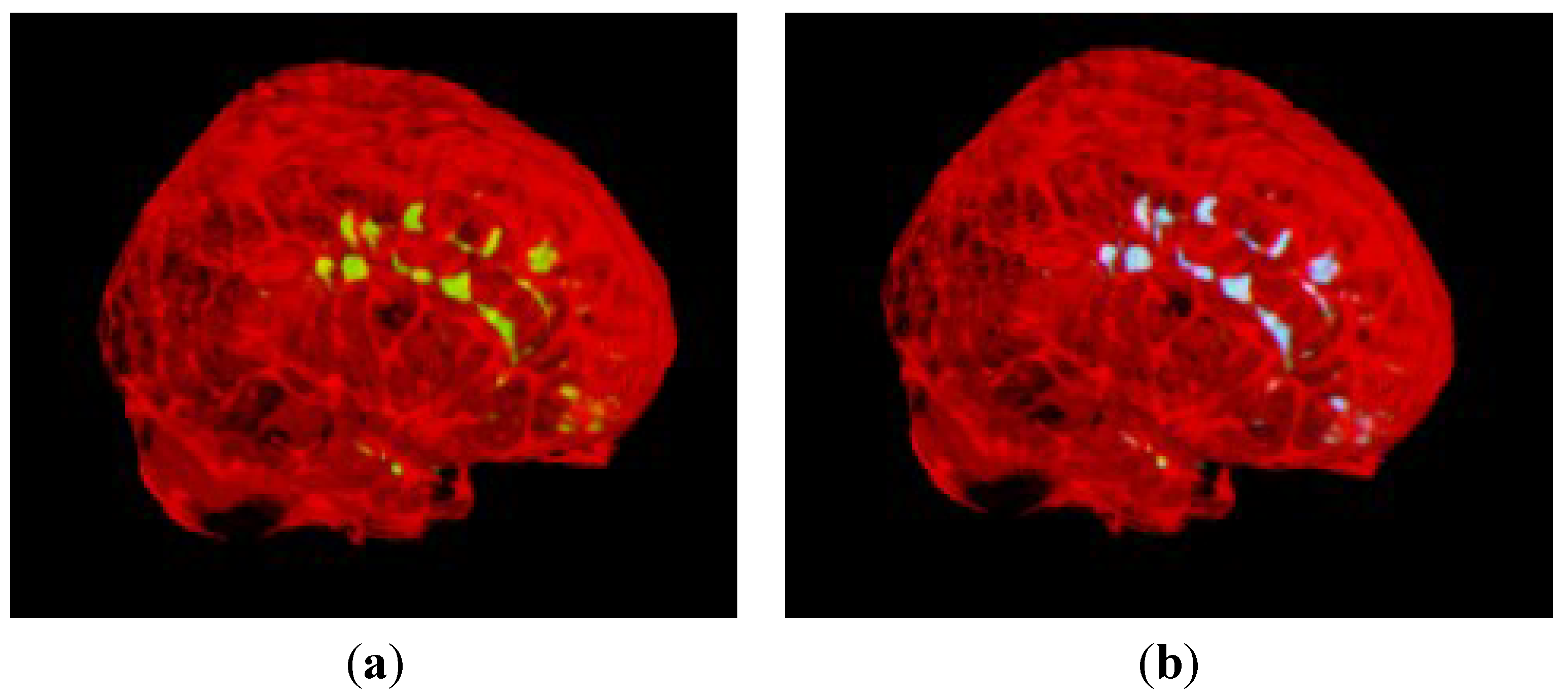
3.2. Segmentation of MS Lesions in a Whole Brain Volume
3.2.1. Brain Data with Mild MS Lesions
| True Positive (TP) | True Negative (TN) | False Positive (FP) | False Negative (FN) | Ground Truth (GT = TP + FP) | Sensitivity TP/GT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mild | 340 | 1954051 | 552 | 82 | 422 | 80.57% |
| moderate | 3383 | 1951234 | 347 | 129 | 3512 | 96.33% |
| severe | 9496 | 1941702 | 3375 | 608 | 10104 | 93.98% |
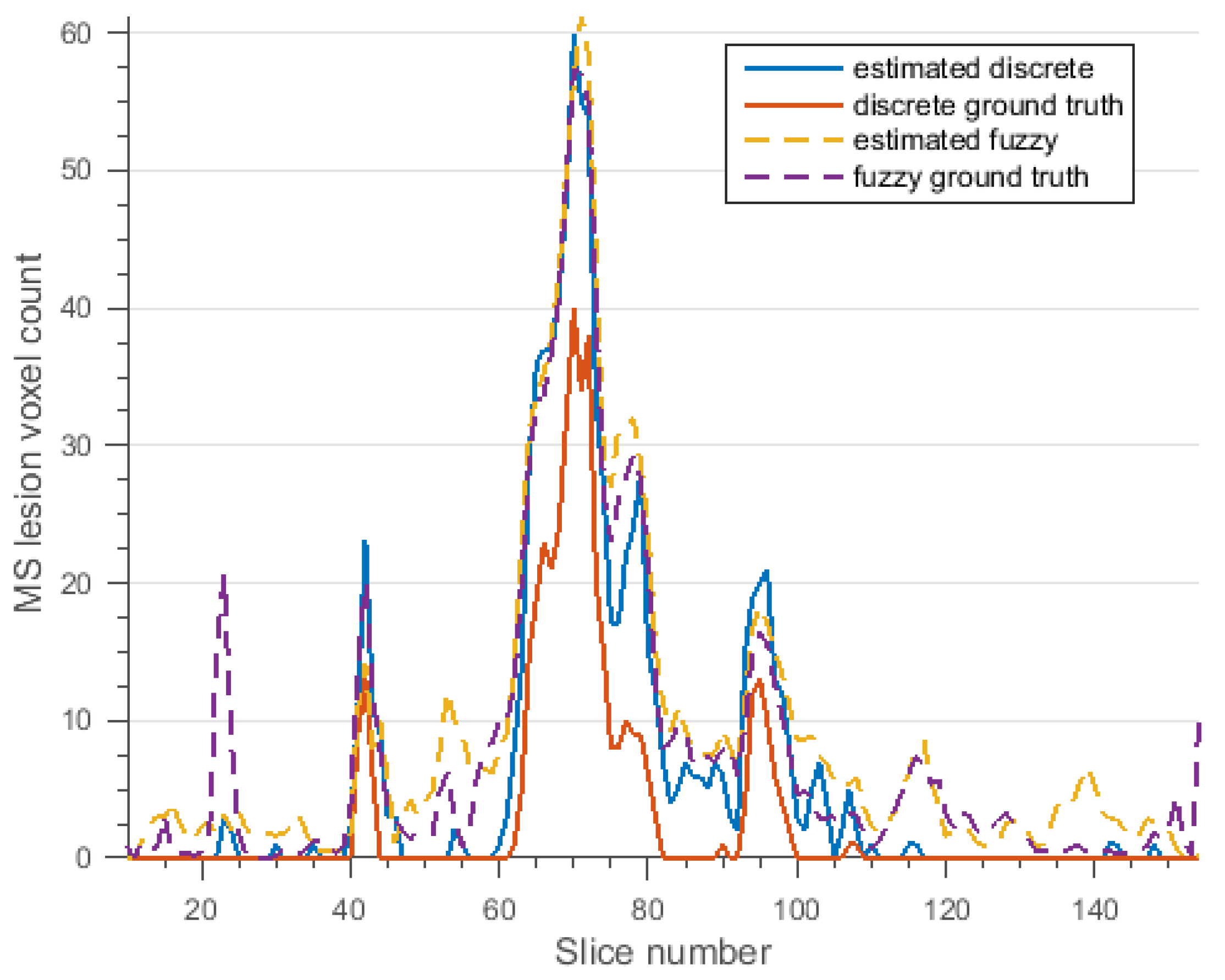

| Specificity TN/(TN+FP) | Reliability TP/(TP+FP) | Dice Similarity Coefficient 2TP/(2TP+FP+FN) | Under Estimation FN/(TN+FN) | Over Estimation FP/(TN+FN) | Average Fuzzy SSIM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mild | 99.97% | 47.31% | 0.5175 | 0.0042% | 0.0282% | 0.9029 |
| moderate | 99.96% | 90.70% | 0.8739 | 0.0066% | 0.0434% | 0.9468 |
| severe | 99.83% | 73.78% | 0.8266 | 0.0313% | 0.1700% | 0.9102 |
3.2.2. Brain Data with Moderate MS Lesions
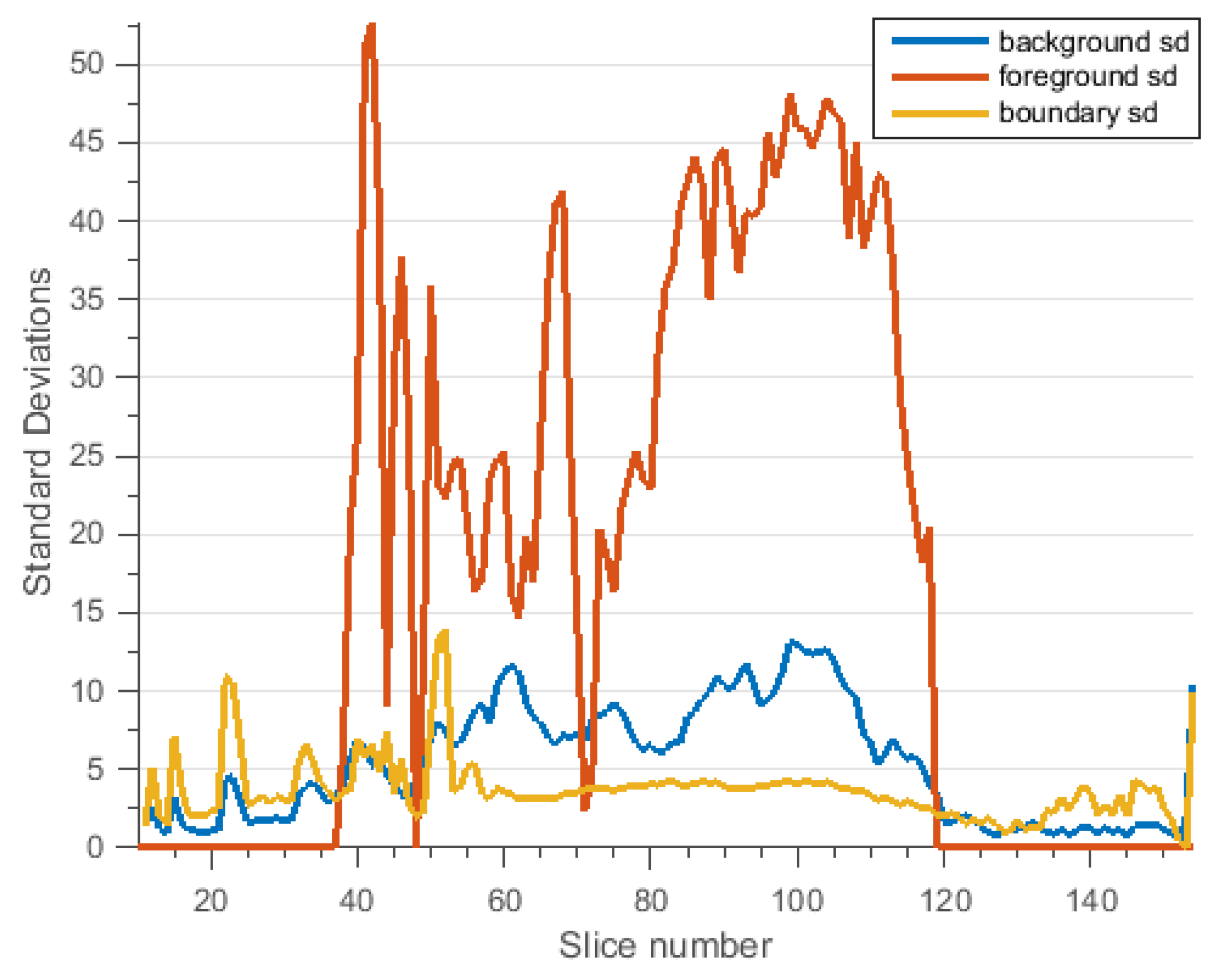

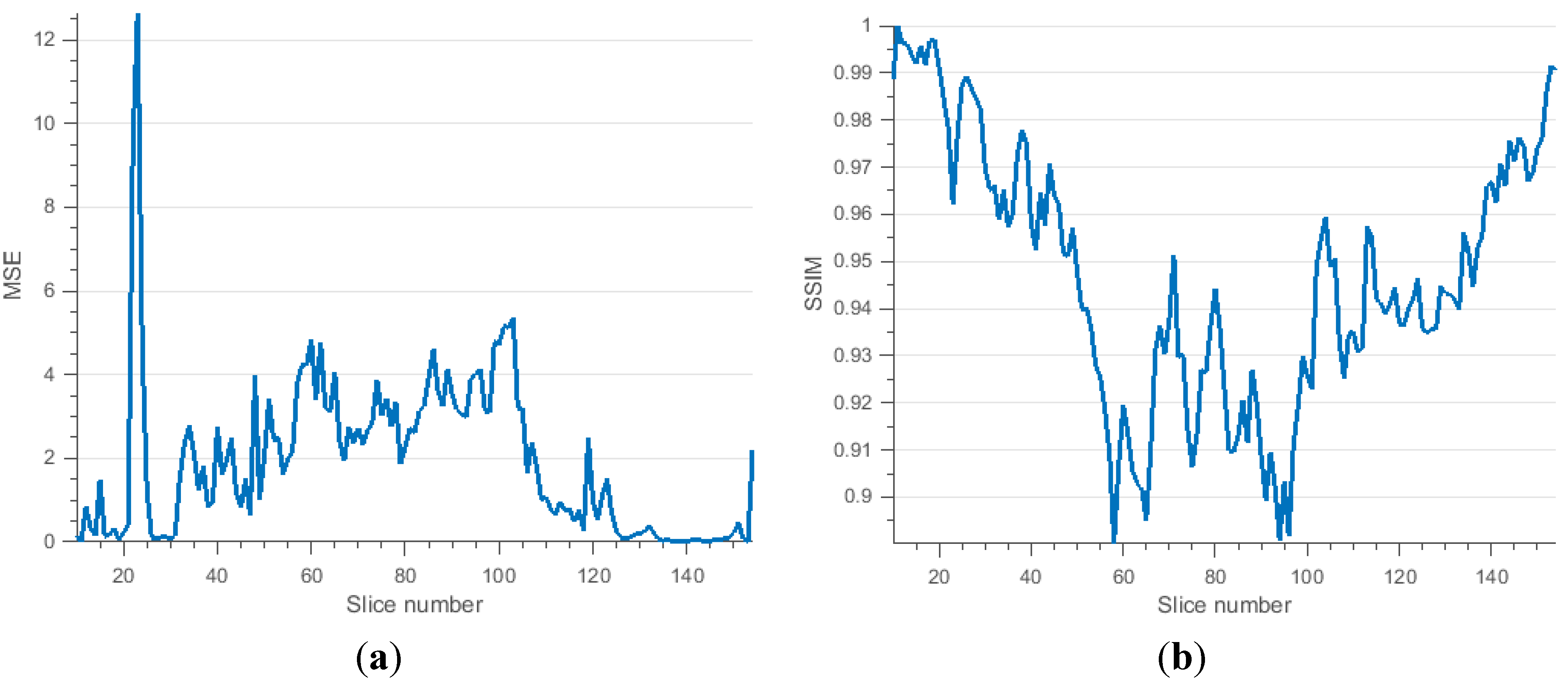
3.2.3. Brain Data with Severe MS Lesions
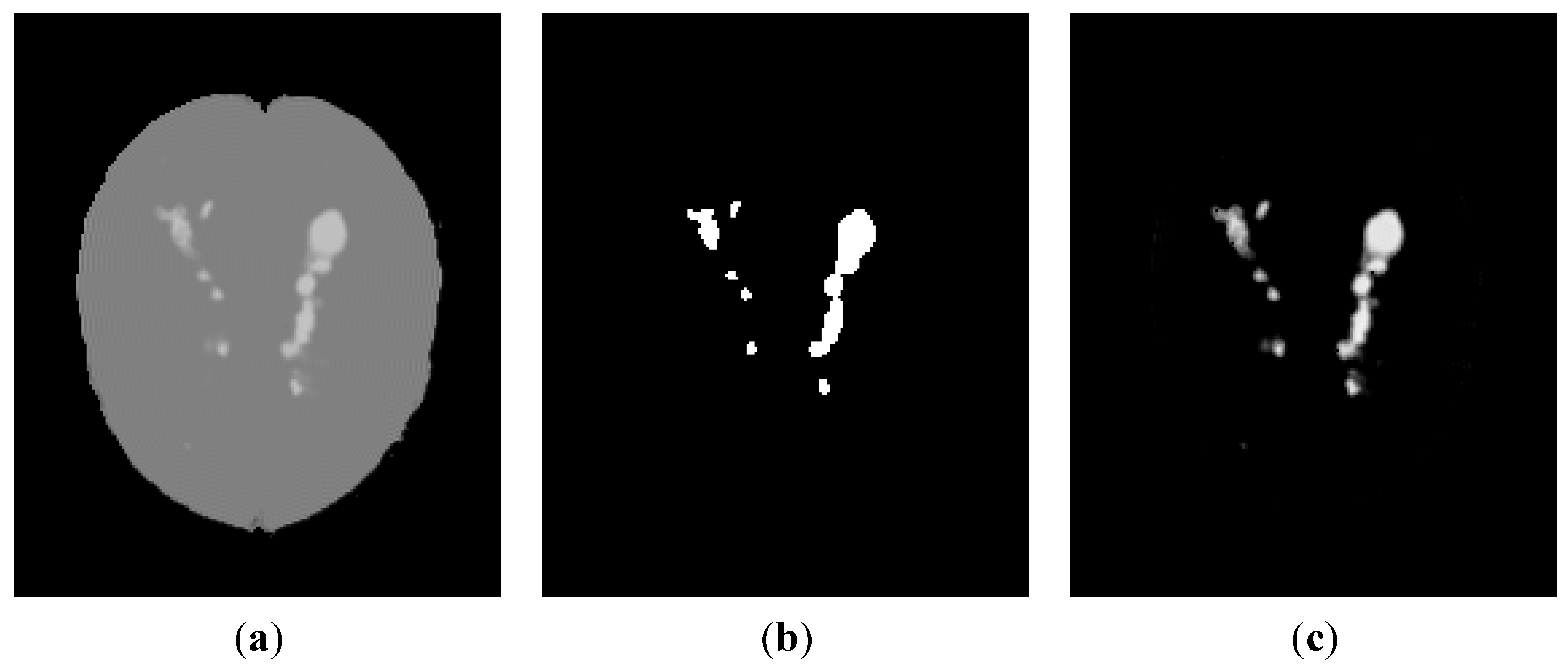

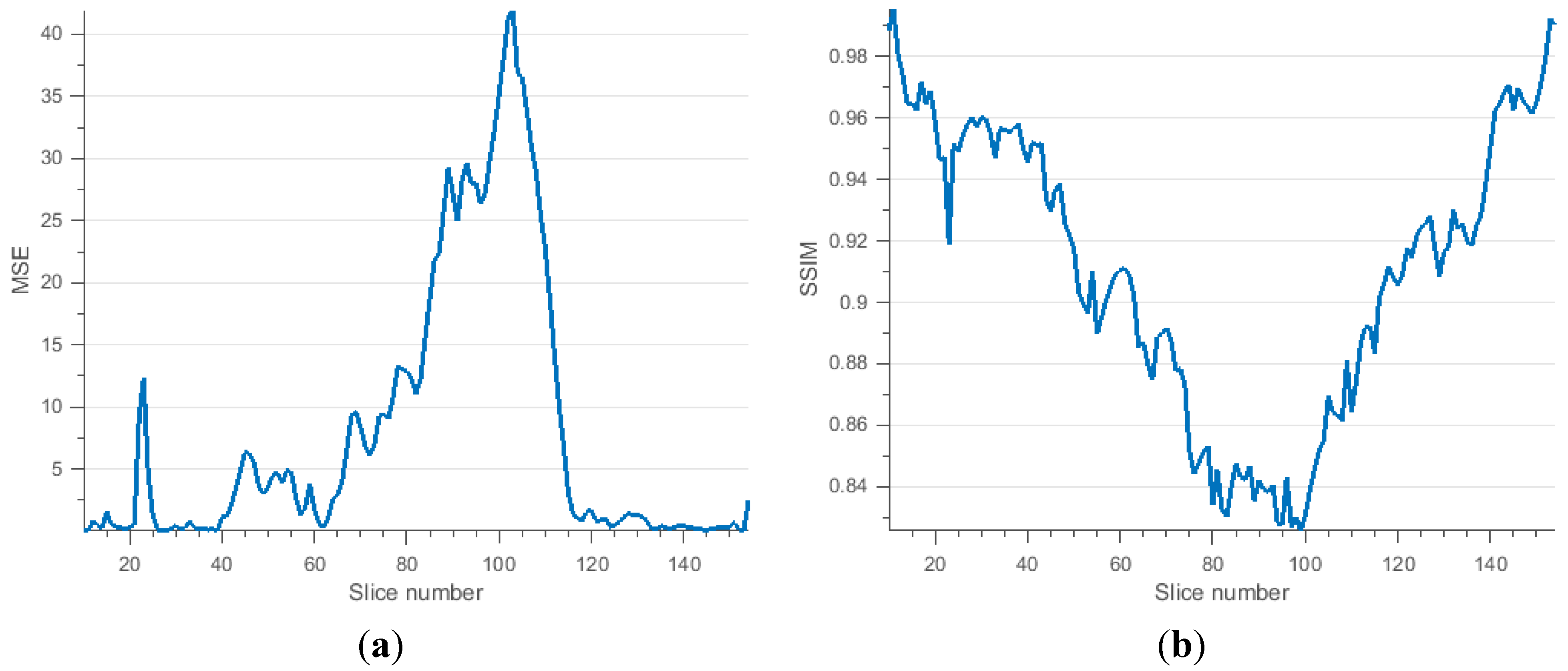
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corona, E.; Hill, J.E.; Ao, J.; Nutter, B.; Mitra, S. An information theoretic approach to automated medical image segmentation. Proc. SPIE 2013, 8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.H.; Rudge, P.; Johnson, G.; Kendall, B.E.; Macmanus, D.G.; Moseley, I.F.; Barnes, D.; McDonald, W.I. Serial gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Brain 1988, 111, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsfield, M.A. Magnetic Resonance Image Post-Processing for Multiple Sclerosis Research. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2008, 18, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaud, J.; Lai, M.; Thorpe, J.; Adeleine, P.; Wang, L.; Barker, G.J.; Plummer, D.L.; Tofts, P.S.; McDonald, W.I.; Miller, D.H. Quantification of MRI lesion load in multiple sclerosis: A comparison of three computer-assisted techniques. Magn. Reson. Imag. 1996, 14, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikinis, R.; Shenton, M.E.; Gerig, G.; Martin, J.; Anderson, M.; Metcalf, D.; Guttmann, C.R.; McCarley, R.W.; Lorensen, W.; Cline, H.; et al. Routine quantitative analysis of brain and cerebrospinal fluid spaces with MR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imag. (JMRI) 1992, 2, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedell, B.J.; Narayana, P.A.; Wolinsky, J.S. A dual approach for minimizing false lesion classifications on magnetic resonance images. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 37, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijdenbos, A.; Forghani, R.; Evans, A. Automatic quantification of MS lesions in 3D MRI brain data sets: Validation of INSECT. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 1998, 1496, 439–448. [Google Scholar]
- Sajja, B.R.; Datta, S.; He, R.J.; Meghana, M.; Gupta, R.K.; Wolinsky, J.S.; Narayana, P.A. Unified approach for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation on brain MRI. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 442, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leemput, K.; Maes, F.; Vandermeulen, D.; Colchester, A.; Suetens, P. Automated segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions by model outlier detection. Medical Imag. 2001, 20, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbeek, P.; Vincken, K.L.; van Osch, M.J.; Bisschops, R.H.; van der Grond, J. Probabilistic segmentation of white lesions in MR imaging. Neuroimage 2004, 21, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warfield, S.; Dengler, J.; Zaers, J.; Guttmann, C.R.G.; Wells, W.M., 3rd; Ettinger, G.J.; Hiller, J.; Kikinis, R. Automatic identification of gray matter structures from MRI to improve the segmentation of white matter lesions. J. Image Guid. Surg. 1995, 1, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, J.K.; Wei, L.; Samarasekera, S.; Miki, Y.; van Buchem, M.A.; Grossman, R.I. Multiple sclerosis lesion quantification using fuzzy-connectedness principles. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 1997, 16, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Admasu, F.; Al-Zubi, S.; Toennies, K.D.; Bodammer, N.; Hinrichs, H. Segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions from MR brain images using the principles of fuzzy-connectedness and artificial neuron networks. In Proceedings of the 2003 International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP 2003, Barcelona, Spain, 14–17 September 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1081–1084.
- Yoo, Y.J.; Brosch, T.; Traboulsee, A.; Li, D.K.B.; Tam, R. Deep Learning of Image Features from Unlabeled Data for Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop, Machine Learning in Medical Imaging 2014 (MLMI14), Boston, MA, USA, 14 September 2014; Volume 8679, Lecture Notes in Computer Science. pp. 117–124.
- Cabezas-Grebol, M. Altas-Based Segmentation of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Girona, Girona, Spain, 16 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, J.E.; Nutter, B.; Mitra, S. An Information Theoretic Approach via IJM to Segmenting MR images with MS lesions. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 27th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), New York, NY, USA, 27–29 May 2014; pp. 180–192.
- Corona, E. Unsupervised Learning Methods: An Efficient Clustering Framework with Integrated Model Selection. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX, USA, August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Corona, E.; Hill, J.E.; Ao, J.; Nutter, B.; Mitra, S. A novel unsupervised learning model for automated detection of precancerous abnormalities in uterine cervix with unified analysis of cervical cells and digital uterine cervix images. In Proceedings of the First IEEE Healthcare Technology Conference: Translational Engineering in Health & Medicine, Houston, TX, USA, 7–9 November 2012.
- BrainWeb: Simulated Brain Database. Available online: http://brainweb.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/brainweb/ (accessed on 28 May 2015).
- Lecoeur, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, L.M.; Li, R.; Aviso, M.; Dawant, B. Sub-millimeter Coregistration of Functional Maps across Imaging Sessions. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Meeting of The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), Montréal, QC, Canada, 7–13 May 2011.
- Sugar, C.A.; James, G.M. Finding the number of clusters in a dataset: An information-theoretic approach. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2003, 98, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.; Corona, E.; Ao, J.; Mitra, S.; Nutter, B. Information theoretic clustering for medical image segmentation. In Advanced Computational Approaches to Biomedical Engineering; Saha, P.K., Maulik, U., Basu, S., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 47–70. [Google Scholar]
- Alzate, C.; Suykens, J.A.K. Multiway spectral clustering with out-of-sample extensions through weighted kernel PCA. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, I.S.; Modha, D.M. Concept decompositions for large sparse text data using clustering. Mach. Learn. 2001, 42, 143–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowlkes, C.; Belongie, S.; Chung, F.; Malik, J. Spectral grouping using the Nystrom method. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, C.; Arnold, D.L.; Collins, D.L. Temporally Consistent Probabilistic Detection of New Multiple Sclerosis Lesions in Brain MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2013, 32, 1490–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MathWorks. Available online: http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/21993-viewer3d (accessed on 28 May 2015).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hill, J.; Matlock, K.; Nutter, B.; Mitra, S. Automated Segmentation of MS Lesions in MR Images Based on an Information Theoretic Clustering and Contrast Transformations. Technologies 2015, 3, 142-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies3020142
Hill J, Matlock K, Nutter B, Mitra S. Automated Segmentation of MS Lesions in MR Images Based on an Information Theoretic Clustering and Contrast Transformations. Technologies. 2015; 3(2):142-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies3020142
Chicago/Turabian StyleHill, Jason, Kevin Matlock, Brian Nutter, and Sunanda Mitra. 2015. "Automated Segmentation of MS Lesions in MR Images Based on an Information Theoretic Clustering and Contrast Transformations" Technologies 3, no. 2: 142-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies3020142
APA StyleHill, J., Matlock, K., Nutter, B., & Mitra, S. (2015). Automated Segmentation of MS Lesions in MR Images Based on an Information Theoretic Clustering and Contrast Transformations. Technologies, 3(2), 142-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies3020142





