Sodium Alginate-Pomegranate Peel Hydrogels for the Remediation of Heavy Metals from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation PPP and Synthesis of SA-PP-H
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.3.1. FTIR and SEM
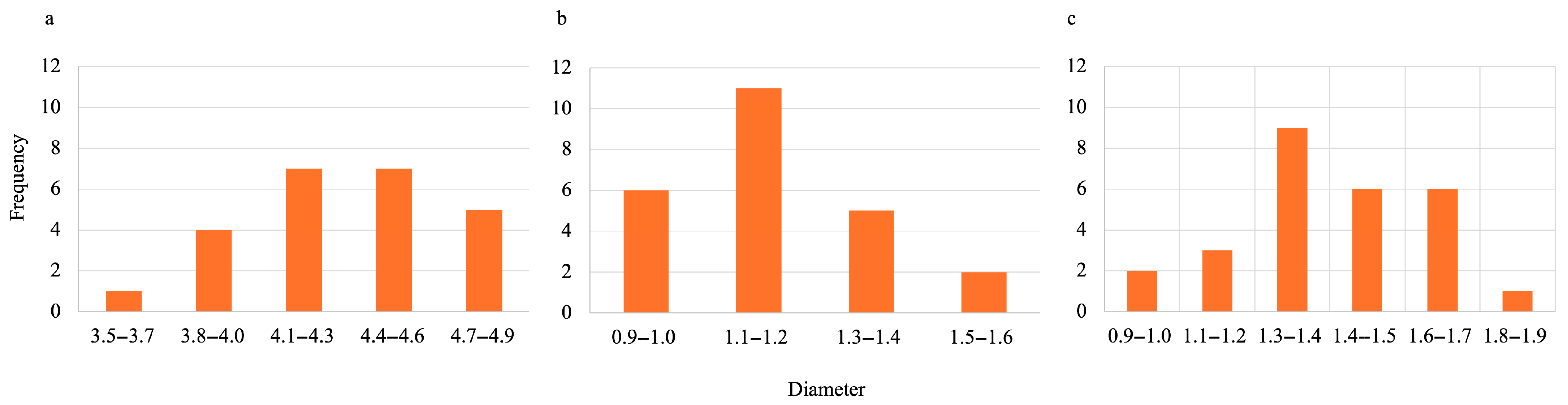
2.3.2. Diameter Size
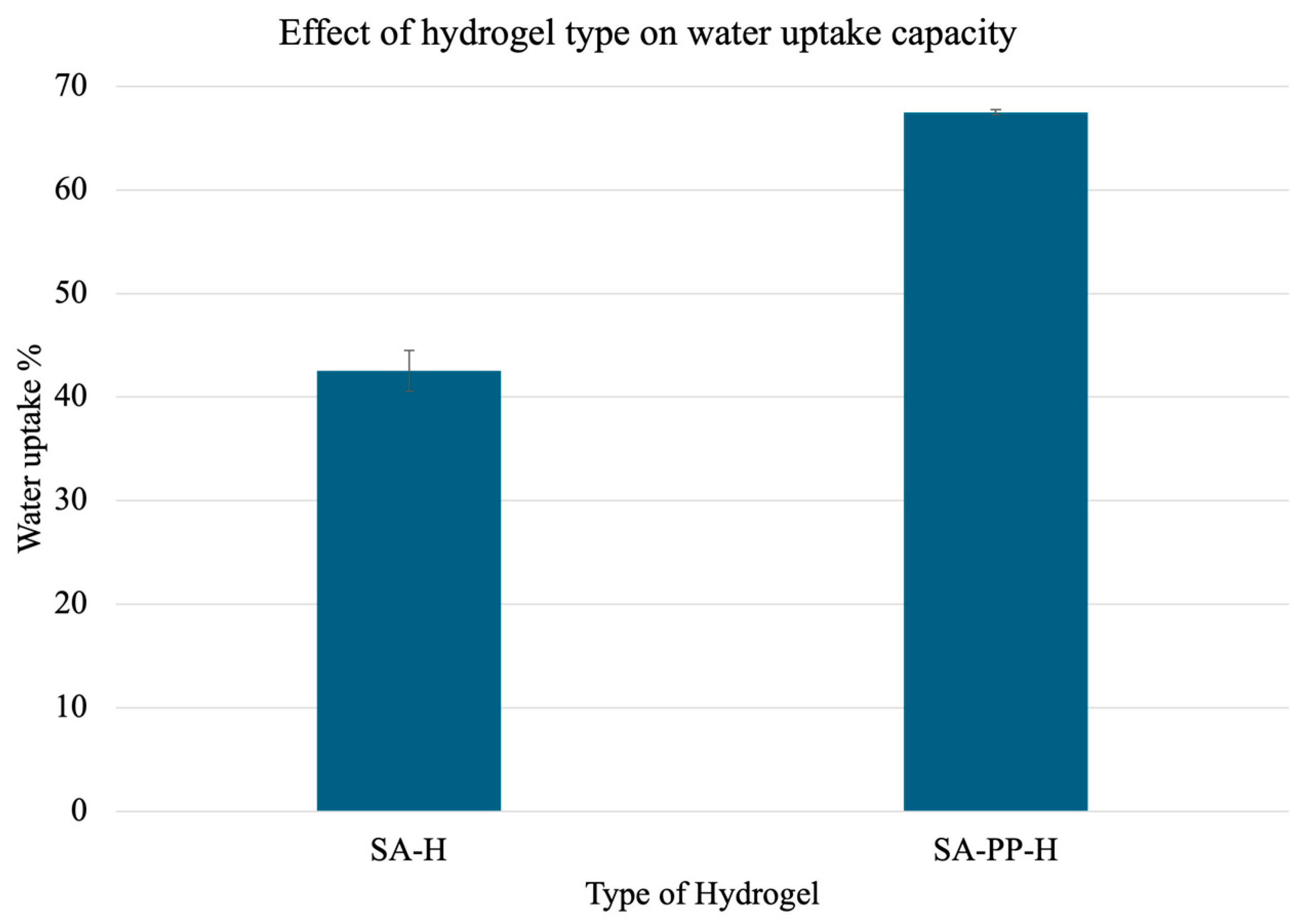
2.3.3. Water Uptake Capacity Tests
2.4. Batch Adsorption Tests
2.4.1. Effect of Contact Time
2.4.2. Effect of Initial pH
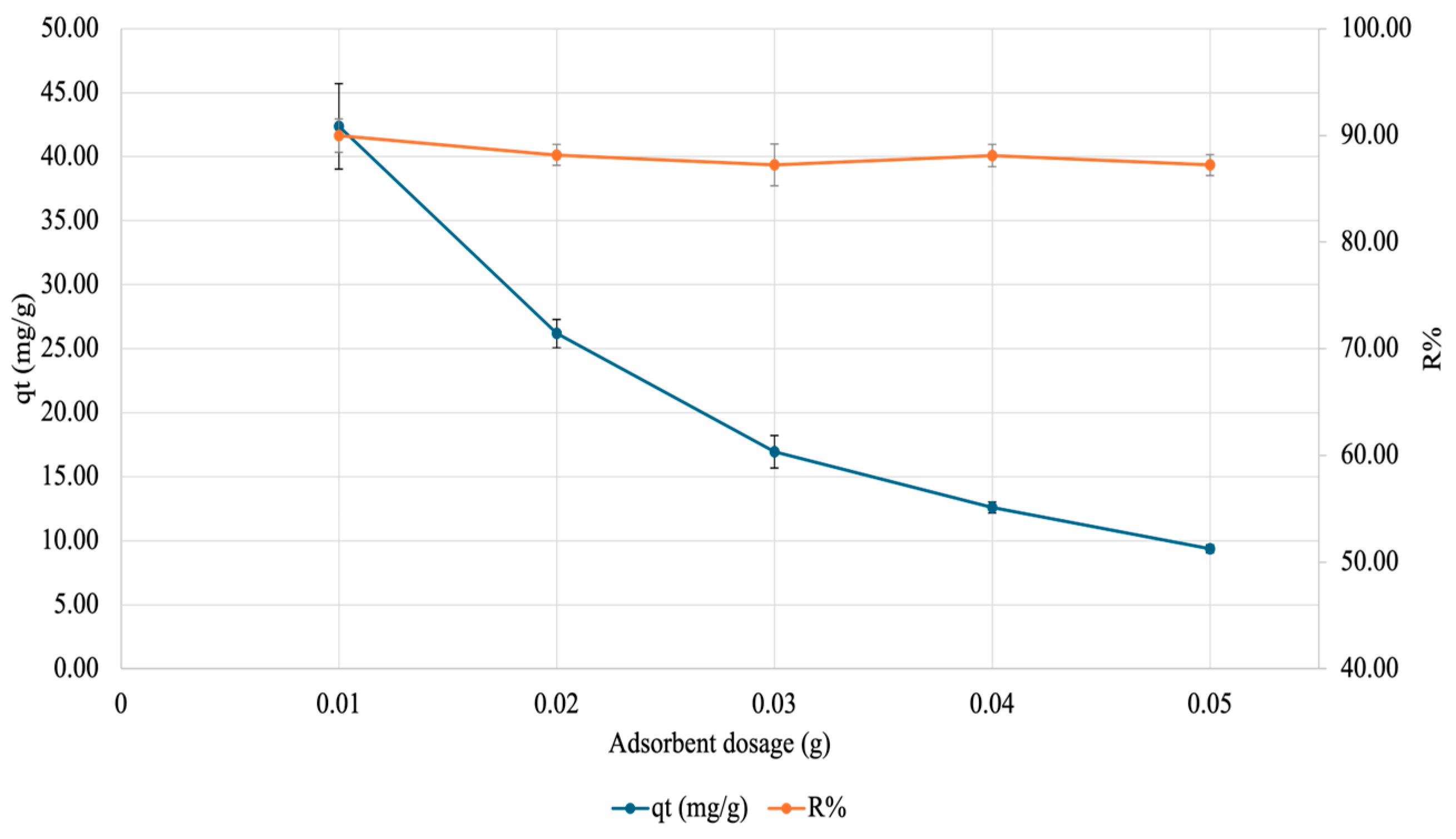
2.4.3. Effect of Gel Amount
3. Results
3.1. Structural and Functional Characterization
3.1.1. FTIR and SEM Analysis of SA-H and SA-PP-H
3.1.2. Diameter Size of SA-H vs. SA-PP-H
3.1.3. Effect of PPP Concentration and Hydrogel Type on Water Uptake Capacity
3.2. Batch Adsorption Tests for Copper and Nickel
3.2.1. Effect of Contact Time on Copper and Nickel Adsorption
3.2.2. Effect of pH on Adsorption of Copper onto SA-PP-H
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorbate Amount on Adsorption of Copper onto SA-PP-H
3.3. Comparison to Similar Adsorbents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Devi, P.I.; Manjula, M.; Bhavani, R.V. Agrochemicals, Environment, and Human Health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2022, 47, 399–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumudumali, R.G.I.; Jayawardana, J.M.C.K.; Piyathilake, I.D.U.H.; Randika, J.L.P.C.; Udayakumara, E.P.N.; Gunatilake, S.K.; Malavipathirana, S. What Drives the Pesticide User Practices among Farmers in Tropical Regions? A Case Study in Sri Lanka. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metals Toxicity and the Environment; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccarato, A.; Vommaro, M.L.; Amico, D.; Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Tagarelli, A.; Giglio, A. Triazine Herbicide and NPK Fertilizer Exposure: Accumulation of Heavy Metals and Rare Earth Elements, Effects on Cuticle Melanization, and Immunocompetence in the Model Species Tenebrio Molitor. Toxics 2023, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, G.; Spinelli, O.; Vismara, C.; Presutti, C.; Bolzacchini, E.; Orlandi, M.; Settimi, R. Evaluation of the Developmental Toxicity of the Pesticide Mcpa and Its Contaminants Phenol and Chlorocresol. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Chen, J.; Zhu, F.; Chai, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Y. Biological Toxicity of Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Natural Environments: From Microbes to Humans. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 920957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, F.C.; Squitti, R.; Ventriglia, M.; Cerchiaro, G.; Daher, J.P.; Rocha, J.G.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Moonen, A.-C. Agricultural Use of Copper and Its Link to Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, G.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Catalano, A. Nickel: Human Health and Environmental Toxicology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater: A Comprehensive and Critical Review. npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, S.; Patra, S. Innovations and Challenges in Adsorption-Based Wastewater Remediation: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wen, J. Study on the Harm of Waste Activated Carbon and Novel Regeneration Technology of It. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 769, 022047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Bae, J.; Fang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhao, F.; Yu, G. Hydrogels and Hydrogel-Derived Materials for Energy and Water Sustainability. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7642–7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaka, L.; Alsaka, L.; Altaee, A.; Zaidi, S.J.; Zhou, J.; Kazwini, T. A Review of Hydrogel Application in Wastewater Purification. Separations 2025, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, S.; Li, J. Water: The Soul of Hydrogels. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2025, 148, 101378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Guo, W.; He, S.; Liu, W. Alginate-Based Hydrogels Mediated Biomedical Applications: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djemaa, I.B.; Auguste, S.; Drenckhan-Andreatta, W.; Andrieux, S. Hydrogel Foams from Liquid Foam Templates: Properties and Optimisation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 294, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, X.; Li, D.; Lai, X.; Liu, Y. Development of Alginate-Based Hydrogels: Crosslinking Strategies and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Alcazar, R.; Bendix, S.; Groth, T.; Gallego Ferrer, G. Research Progress in Enzymatically Cross-Linked Hydrogels as Injectable Systems for Bioprinting and Tissue Engineering. Gels 2023, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaz, A.; Arris, S.; Viscusi, G.; Ayat, A.; Aissaoui, H.; Boumezough, Y. Adsorption of Safranin O Dye by Alginate/Pomegranate Peels Beads: Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Studies. Gels 2023, 9, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić Gajić, I.M.; Savić, I.M.; Svirčev, Z. Preparation and Characterization of Alginate Hydrogels with High Water-Retaining Capacity. Polymers 2023, 15, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwakeel, K.Z.; Ahmed, M.M.; Akhdhar, A.; Sulaiman, M.G.M.; Khan, Z.A. Recent Advances in Alginate-Based Adsorbents for Heavy Metal Retention from Water: A Review. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 272, 50–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakody, M.M.; Vanniarachchy, M.P.G.; Wijesekara, I. Composition Analysis of Selected Sri Lankan Seaweeds. J. Trop. For. Environ. 2019, 9, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.R.; Ale, D.S.; Aryal, R.L.; Ghimire, K.N.; Gautam, S.K.; Paudyal, H.; Pokhrel, M.R. Zirconium Modified Pomegranate Peel for Efficient Removal of Arsenite from Water. BIBECHANA 2022, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Ma, J.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zang, J. Pomegranate Peel as a Source of Bioactive Compounds: A Mini Review on Their Physiological Functions. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 887113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmat, F.; Safdar, M.; Ahmad, H.; Khan, M.R.J.; Abid, J.; Naseer, M.S.; Aggarwal, S.; Imran, A.; Khalid, U.; Zahra, S.M.; et al. Phytochemical Profile, Nutritional Composition of Pomegranate Peel and Peel Extract as a Potential Source of Nutraceutical: A Comprehensive Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Agricultural Waste Peels as Versatile Biomass for Water Purification—A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 244–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.I.; Oleiwi, J.K.; Mohamed, A.S. Investigation of Mechanical Properties of PMMA Composite Reinforced with Different Types of Natural Powders. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13, 8889–8900. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, A.; Aniagor, C.O.; Fikry, M.; Taha, G.M.; Badawy, S.M. Characterization and Adsorption of Raw Pomegranate Peel Powder for Lead (II) Ions Removal. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 2087–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ali, S. Application of Raw and Modified Pomegranate Peel for Wastewater Treatment: A Literature Overview and Analysis. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8840907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L. Preparation of Hydrogel Beads Based on Sodium Alginate and Aqueous Extract from Pomegranate Peel and Its Cyanobacteria Removal Performance. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2018, 44, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulska, E.; Ruszczyńska, A. Analytical Techniques for Trace Element Determination. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2017, 2, 20178002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.J.; Fisher, A.S. Atomic Absorption, Methods and Instrumentation. In Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry, 2nd ed.; Lindon, J.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, A.H.; Khalid, R.S.; Alaama, M.; Abdualkader, A.M.; Kasmuri, A.; Abbas, S.A. Comparative Study of Three Digestion Methods for Elemental Analysis in Traditional Medicine Products Using Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbar, B.; Alem, A.; Marcotte, S.; Pantet, A.; Ahfir, N.-D.; Bizet, L.; Duriatti, D. Experimental Investigation on Removal of Heavy Metals (Cu2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+) from Aqueous Solution by Flax Fibres. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 109, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Lopes, L.; Weber Macena, M.; Esteves, B.; Guiné, R. Ideal pH for the Adsorption of Metal Ions Cr6+, Ni2+, Pb2+ in Aqueous Solution with Different Adsorbent Materials. Open Agric. 2021, 6, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, L.A.; Blanchet, A.J.; Sombra, L.L.; Salonia, J.A.; Gasquez, J.A. Determination of the Total and Extractable Fraction of Ni in Lake Sediments and Natural Waters of San Luis (Argentina) by FAAS Using a Simple Solid Phase Extraction System. Microchem. J. 2014, 116, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherian, G.; Arab Chamjangali, M.; Shariati Evari, H.; Ashrafi, M. Determination of Copper(II) by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry after Its Perconcentration by a Highly Selective and Environmentally Friendly Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Technique. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. 3D Printed Zeolite-Y for Removing Heavy Metals from Water. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, O.; Thabet, W.M. Natural Zeolites and Zeolite Composites for Heavy Metal Removal from Contaminated Water and Their Applications in Aquaculture Systems: A Review. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2023, 49, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzukashvili, S.; Sommerville, R.; Rowson, N.A.; Waters, K.E. An Overview of Zeolites Synthesised from Coal Fly Ash and Their Potential for Extracting Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Can. Metall. Q. 2024, 63, 130–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Nong, S.; Zhao, Y.; Riaz, M.S.; Xiao, Y.; Molokeev, M.S.; Huang, F. Renewable P-Type Zeolite for Superior Absorption of Heavy Metals: Isotherms, Kinetics, and Mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferronato, C.; Vianello, G.; Antisari, L.V. Adsorption of Pathogenic Microorganisms, NH4+ and Heavy Metals from Wastewater by Clinoptilolite Using Bed Laminar Flow. Clay Miner. 2015, 50, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O. Modification of Natural Zeolites and Their Applications for Heavy Metal Removal from Polluted Environments: Challenges, Recent Advances, and Perspectives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velarde, L.; Nabavi, M.S.; Escalera, E.; Antti, M.-L.; Akhtar, F. Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Natural Zeolites: A Review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sossou, K.; Prasad, S.B.; Agbotsou, K.E.; Souley, H.S. Evaluation of the Performance of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites in Removing Various Water Contaminants as Heavy Metals, Organic Pollutants, and Emerging Contaminants: A Review Evaluation of the Performance of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites in Removing Various Water Contaminants as Heavy Metals, Organic Pollutants, and Emerging Contaminants: A Review. Next Nanotechnol. 2024, 6, 100075. [Google Scholar]
- Eleraky, M.I.; Razek, T.M.A.; Hasani, I.W.; Fahim, Y.A. Adsorptive Removal of Lead, Copper, and Nickel Using Natural and Activated Egyptian Calcium Bentonite Clay. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Huang, L.; Su, C.; Yan, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Du, M.; Zhang, H. Application of Clay Minerals as Adsorbents for Removing Heavy Metals from the Environment. Green Smart Min. Eng. 2024, 1, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rando, G.; Scalone, E.; Sfameni, S.; Plutino, M.R. Functional Bio-Based Polymeric Hydrogels for Wastewater Treatment: From Remediation to Sensing Applications. Gels 2024, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyeue, C.; Garioud, T.; Lemestre, M.; Meyer, M.; Brégier, F.; Chaleix, V.; Sol, V.; Lebouvier, N. Biosorption of Nickel Ions Ni2+ by Natural and Modified Pinus Caribaea Morelet Sawdust. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, I.; Pelin, I.M.; Suflet, D.M.; Stanciu, M.C.; Constantin, M. Chitosan/Poly(Maleic Acid-Alt-Vinyl Acetate) Hydrogel Beads for the Removal of Cu2+ from Aqueous Solution. Gels 2024, 10, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamowska, M.; Kaniewska, K.; Muszyńska, M.; Romański, J.; Hyk, W.; Karbarz, M. Smart Hydrogel Based on Derivatives of Natural α-Amino Acids for Efficient Removal of Metal Ions from Wastewater. Gels 2024, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A.; Marin, L. Outstanding Sorption of Copper (II) Ions on Porous Phenothiazine-Imine-Chitosan Materials. Gels 2023, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noman, E.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Saphira Radin Mohamed, R.M.; Al-Sahari, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Naushad, M. Sustainable Approaches for Nickel Removal from Wastewater Using Bacterial Biomass and Nanocomposite Adsorbents: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 291 Pt 1, 132862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Bao, L.; Dong, T.; Xie, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Hao, C. Adsorption Properties of Cellulose/Guar Gum/Biochar Composite Hydrogel for Cu2+, Co2+ and Methylene Blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242 Pt 4, 125021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antić, K.; Onjia, A.; Vasiljević-Radović, D.; Veličković, Z.; Tomić, S.L. Removal of Nickel Ions from Aqueous Solutions by 2-Hydroxyethyl Acrylate/Itaconic Acid Hydrogels Optimized with Response Surface Methodology. Gels 2021, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque, L.M.; Fernández de Luis, R.; Fidalgo-Marijuan, A.; Infantes-Molina, A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Pérez, C.J.; Copello, G.J.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.M. Linear Polyethyleneimine-Based and Metal Organic Frameworks (DUT-67) Composite Hydrogels as Efficient Sorbents for the Removal of Methyl Orange, Copper Ions, and Penicillin V. Gels 2023, 9, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araque, L.M.; Infantes-Molina, A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Garro-Linck, Y.; Franzoni, B.; Pérez, C.J.; Copello, G.J.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.M. Ionic Crosslinking of Linear Polyethyleneimine Hydrogels with Tripolyphosphate. Gels 2024, 10, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayach, J.; El Malti, W.; Duma, L.; Lalevée, J.; Al Ajami, M.; Hamad, H.; Hijazi, A. Comparing Conventional and Advanced Approaches for Heavy Metal Removal in Wastewater Treatment: An In-Depth Review Emphasizing Filter-Based Strategies. Polymers 2024, 16, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.G.; Saleh, A.S.; Elsharma, E.M.; Metwally, E.; Siyam, T. Chitosan-g-maleic Acid for Effective Removal of Copper and Nickel Ions from Their Solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihsanullah; Abbas, A.; Al-Amer, A.M.; Laoui, T.; Al-Marri, M.J.; Nasser, M.S.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M.A. Heavy Metal Removal from Aqueous Solution by Advanced Carbon Nanotubes: Critical Review of Adsorption Applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, N.; Balakumar, S.; Shyamalagowri, S.; Manjunathan, J.; Pavithra, M.K.S.; Babu, P.S.; Kamaraj, M.; Govarthanan, M. Carbon-Based Adsorbents as Proficient Tools for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solution: A State of Art-Review Emphasizing Recent Progress and Prospects. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.; El Hanandeh, A. Insight into Copper and Nickel Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions onto Carbon-Coated-Sand: Isotherms, Kinetics, Mechanisms, and Cost Analysis. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, X.; Yu, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, B. Efficient Removal of Nickel from Wastewater Using Copper Sulfate–Ammonia Complex Modified Activated Carbon: Adsorption Performance and Mechanism. Molecules 2024, 29, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, D.; Alkhabbas, M.; Al-Ma’abreh, A.M. Adsorption of Pb, Cu, and Ni Ions on Activated Carbon Prepared from Oak Cupules: Kinetics and Thermodynamics Studies. Molecules 2024, 29, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdi Sabzehmeidani, M.; Mahnaee, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Heidari, H.; Roy, V.A.L. Carbon Based Materials: A Review of Adsorbents for Inorganic and Organic Compounds. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 598–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheraz, N.; Shah, A.; Haleem, A.; Jan Iftikhar, F. Comprehensive Assessment of Carbon-, Biomaterial- and Inorganic-Based Adsorbents for the Removal of the Most Hazardous Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 11284–11310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.; Sazali, N.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Hasrul, N.; Ngadiman, A.; Fadil, N.A.; Harun, Z. Outlook on the Carbon-Based Materials for Heavy Metal Removal. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 12, 5303–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.; Lee, J.W.; Jeong, J.-W.; Kim, T.-S.; Lee, Y.; Gang, G.; Lee, S.G. Current Technologies for Heavy Metal Removal from Food and Environmental Resources. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, M.; Atasoy, M.; Arslan, Y.; Yildiz, D. Removal of Ni(II), Cu(II), Pb(II), and Cd(II) from Aqueous Phases by Silver Nanoparticles and Magnetic Nanoparticles/Nanocomposites. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 34834–34843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibiya, N.P.; Mahlangu, T.P.; Tetteh, E.K.; Rathilal, S. Review on Advancing Heavy Metals Removal: The Use of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Microalgae-Based Adsorbents. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2025, 11, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.E.D.; Al-Qahtani, K.M.; Alflaij, S.O.; Al-Qahtani, S.F.; Alsamhan, F.A. Green Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Lead, Nickel, and Cadmium Removal from Contaminated Water. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Das, S.; Biswas, G.; Haldar, P.K. Review on Some Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Effective Adsorbent in Wastewater Treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 3370–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawade, D.B.; Wada, O.Z.; Egbewole, B.I.; Fapohunda, O.; Ige, A.O.; Usman, S.O.; Ajisafe, O. Metal and Metal Oxide Nanomaterials for Heavy Metal Remediation: Novel Approaches for Selective, Regenerative, and Scalable Water Treatment. Front. Nanotechnol. 2024, 6, 1466721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, W.; Othman, M.; Souissi-Najar, S.; Ouederni, A. Copper Adsorption onto Pomegranate Peel Activated Carbon as a New Adsorbent. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2023, 57, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.U.; Su, X.; Zhao, M.; Liao, Y.; Wu, R.; Chen, D. Preparation of Hydroxypropyl-Cyclodextrin-Graphene/Fe3O4 and Its Adsorption Properties for Heavy Metals. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 16, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Aliwi, H.; Hazim Halboos, M. Nickel Ion Adsorption from Water by Nano Fe2O3/PP Prepared from Pomegranate Peel Residue and Treated Magnetically. BIO Web Conf. 2024, 139, 06032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shartooh, S.; Al-Azzawi, M.; Al-Hiyaly, S. Pomegranate Peels as Biosorbent Material to Remove Heavy Metal Ions from Industerial Wastewater. Iraqi J. Sci. 2013, 54, 823–831. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, Z.; Alikarami, M.; Homafar, A. Adsorption Study on Pomegranate Peel: Removal of Ni2+ and Co2+ from Aqueous Solution. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 8, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Nourmohammadi Dehbalaei, F.; Akbari, Z.; Abdi, M.S.; Naeeni, S.T.O. Green Walnut Husk and Pomegranate Peel for Nickel Removals from Industrial Wastewater by Absorption Process: Batch and Column Experiments. Appl. Water Sci. 2025, 15, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, M.; Mubarak, S.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Kazi, A.A.; Hamid, A. Adsorption Studies of Pomegranate Peel Activated Charcoal for Nickel (II) Ion. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2015, 60, 2642–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A. Biosorption Optimization of Nickel Removal from Water Using Punica Granatum Peel Waste. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashtoukhy, E.-S.; Amin, N.K.; Abdelwahab, O. Removal of Lead (II) and Copper (II) from Aqueous Solution Using Pomegranate Peel as a New Adsorbent. Desalination 2008, 223, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenessova, A.K.; Seilkhanova, G.A.; Rakhym, A.B.; Mastai, Y. Composite Materials Based on Orange and Pomegranate Peels for Cu (II) and Zn (II) Ions Extraction. Int. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 13, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ali, S.; Jaouali, I.; Souissi-Najar, S.; Ouederni, A. Characterization and Adsorption Capacity of Raw Pomegranate Peel Biosorbent for Copper Removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142 Pt 4, 3809–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, A.M.; Ghaedi, M.; Vafaei, A.; Iravani, N.; Keshavarz, M.; Rad, M.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of Copper (II) Using Modified Activated Carbon Prepared from Pomegranate Wood: Optimization by Bee Algorithm and Response Surface Methodology. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 206, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.K.; Tayh, W. Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater Using Pomegranate Peel. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 881, 012187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, H.; Chaudhry, F.S.; Rehman, S.; Rashid, Z.; Ijaz, A.; Awan, J.A. Removal of Toxic Metallic Ions Cr(VI), Cu(II), Ni(II), Co(II) and Cd(II) from Waste Water Effluents of Tanneries by Using Punica Granatum (Pomgranate) Membrane. Iran. J. Energy Environ. 2016, 7, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Gardner, D.J.; Han, Y. Drying Cellulose Nanofibrils: In Search of a Suitable Method. Cellulose 2012, 19, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenea, A.-G.; Dinu, C.; Rus, P.A.; Ionescu, I.A.; Gheorghe, S.; Iancu, V.I.; Vasile, G.G.; Pascu, L.F.; Chiriac, F.L. Exploring Adsorption Dynamics of Heavy Metals onto Varied Commercial Microplastic Substrates: Isothermal Models and Kinetics Analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assegehegn, G.; Brito-de La Fuente, E.; Franco, J.M.; Gallegos, C. The Importance of Understanding the Freezing Step and Its Impact on Freeze-Drying Process Performance. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1378–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuppett, J.; Duncan, S.; Dietrich, A. Evaluation of Copper Speciation and Water Quality Factors That Affect Aqueous Copper Tasting Response. Chem. Senses 2006, 31, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, R.; Saikia, K.; Ponnusamy, S.K.; Rathankumar, A.K.; Rajendran, D.S.; Venkataraman, S.; Tannani, D.B.; Arvind, V.; Somanna, T.; Banerjee, K.; et al. Understanding the Factors Affecting Adsorption of Pharmaceuticals on Different Adsorbents—A Critical Literature Update. Chemosphere 2022, 287 Pt 1, 131958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
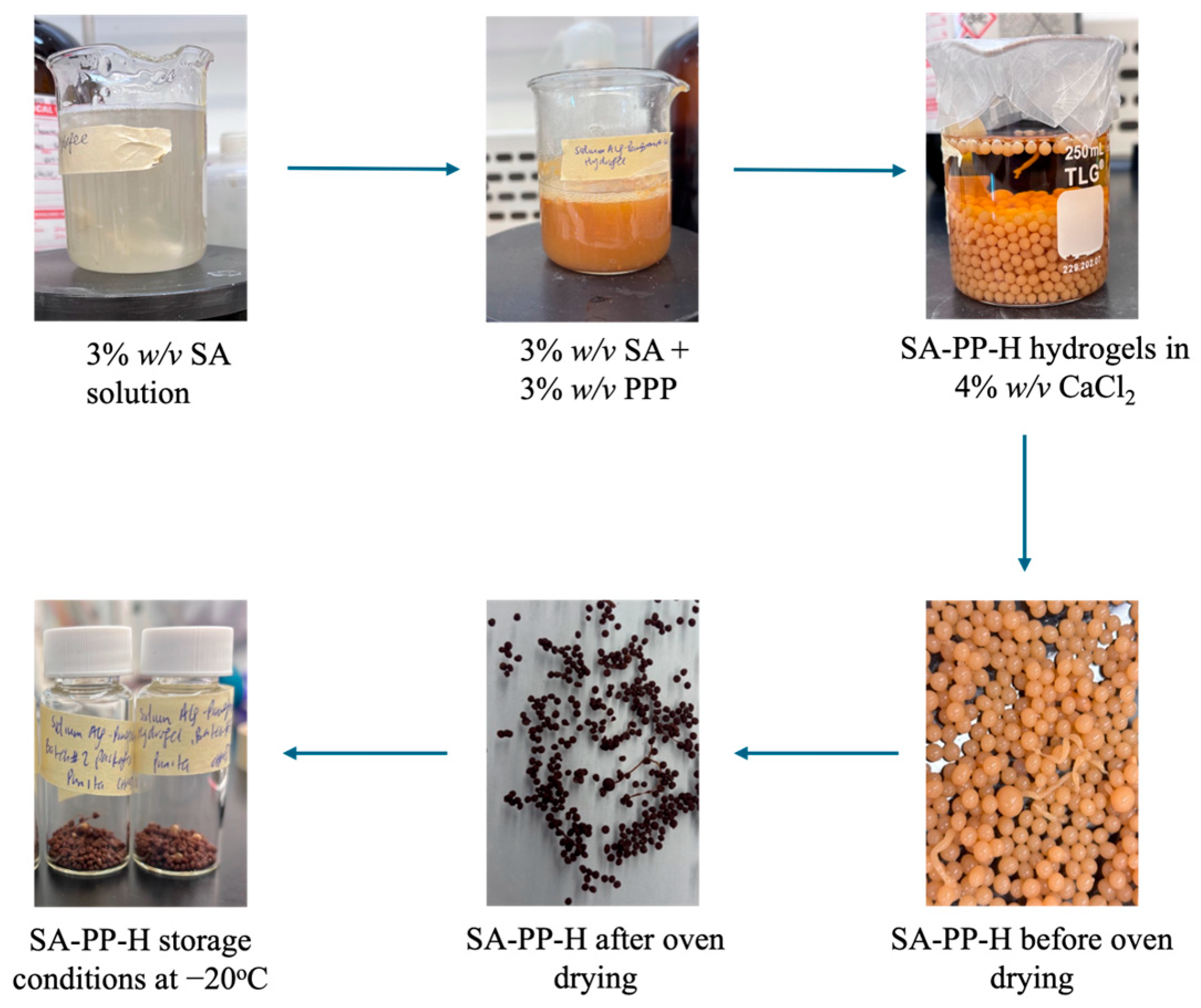








| Gel Type | Appearance | |
|---|---|---|
| Color (wet, dry, lyophilized) | Shape | |
| SA-H | White, off-white, off-white | Circular |
| SA-PP-H | Light brown, light brown, light brown | Circular |
| Adsorbent Type | Examples | Max Adsorption Capacity (qmax) (mg/g) | Max Removal Percent | Advantage(s) | Limitation(s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Adsorbents | zeolite, bentonite, and kaolinite | Cu2+ 189.03–267.94 | Cu2+ >90% | Selective, high adsorption capacity | Some may require modification for high efficiency | [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] |
| Ni2+ 15.6 | Ni2+ 40–96% | |||||
| Biopolymers | chitin, cellulose, amino acid, alginic acid, polysaccharide, starch | Cu2+ 805.45 | Cu2+ >99% | Ecofriendly, biocompatible, biodegradable, adaptable, selective | Low mechanical strength, low chemical stability, expensive to produce | [48,49,50,51,52,53,54] |
| Ni2+ 5.7–556 | Ni2+ >99% | |||||
| Synthetic Polymers | poly (vinyl alcohol), poly (acrylic acid), polyacrylamide, poly (ethylene glycol) | Cu2+ 312.4 | Cu2+ 78–90% | High efficiency | High energy consumption | [55,56,57,58,59] |
| Ni2+ 70.1 | Ni2+ 85% | |||||
| Carbon-Based Materials | activated carbon, biochar, graphene oxide (GO) | Cu2+ 3.464–345 | Cu2+ 80–95.5% | Chemical stability, cost-effective | Low recovery and reusability | [60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69] |
| Ni2+ 3.254–149.25 | Ni2+ 41–78.12% | |||||
| Metal Oxides | Fe3O4, Al2O3, MnO2 | Cu2+ 18.57–543.3 | Cu2+ 75.52% | Cost-effective, eco-friendly | Low stability | [69,70,71,72,73,74,75] |
| Ni2+ 8.71–33.33 | Ni2+ 42.75–90.1% | |||||
| Pomegranate Peel-Based Adsorbents | activated carbon from pomegranate peel, raw pomegranate peel, pomegranate peel composites | Cu2+ 1.31–30.12 | Cu2+ 62–99.82% | Eco-friendly, cost-effective, renewable, readily available | Limited adsorption capacity, pre-treatment requirements | [29,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87] |
| Ni2+ 7.54–52 | Ni2+ 99.615% | |||||
| SA-PP-H * | Cu2+ 42.37 ± 3.35; pH 5.5, 50 mg/L Cu(NO3)2·3H2O, 0.01 g hydrogel, 60 min contact time | Cu2+ 89.98 ± 1.55%; pH 5.5, 50 mg/L Cu(NO3)2·3H2O, 0.01 g hydrogel, 60 min contact time | Cost-effective, simple preparation method with mild conditions, eco-friendly | Low adsorption capacity | This study | |
| Ni2+ 39.52 ± 7.49, pH 5, 50 mg/L Ni(NO3)2·6H2O, 0.07 g hydrogel, 5 min contact time | Ni2+ 82.25 ± 0.48%; pH 5, 50 mg/L Ni(NO3)2·6H2O, 0.07 g hydrogel, 5 min contact time |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lalchand, P.; Thavarajah, N.; Fernando, X. Sodium Alginate-Pomegranate Peel Hydrogels for the Remediation of Heavy Metals from Water. Technologies 2025, 13, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13080351
Lalchand P, Thavarajah N, Fernando X. Sodium Alginate-Pomegranate Peel Hydrogels for the Remediation of Heavy Metals from Water. Technologies. 2025; 13(8):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13080351
Chicago/Turabian StyleLalchand, Punita, Nirusha Thavarajah, and Xavier Fernando. 2025. "Sodium Alginate-Pomegranate Peel Hydrogels for the Remediation of Heavy Metals from Water" Technologies 13, no. 8: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13080351
APA StyleLalchand, P., Thavarajah, N., & Fernando, X. (2025). Sodium Alginate-Pomegranate Peel Hydrogels for the Remediation of Heavy Metals from Water. Technologies, 13(8), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13080351







