Allocation of Single and Multiple Multi-Type Distributed Generators in Radial Distribution Network Using Mountain Gazelle Optimizer
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Allotment of single and multiple DG units with unity, fixed, and optimal power factors.
- Research into the impact of DG power factors on RDN. Investigations reveal that utilizing the optimal power factor DGs improves RDN functionality.
- Both IEEE 33-bus and IEEE 69-bus RDNs are used to assess the MGO algorithm’s performance, and various recent and conventional algorithms are compared. The outcomes show that, in comparison to other algorithms, MGO offers better results.
- Economic evaluations of the DG types’ optimal allotment.
2. Problem Formulations
2.1. Objective Function
- A.
- Power Flow Equations
- B.
- Voltage Constraints
- C.
- Thermal Constraints
- D.
- DG Capacity Constraints
- E.
- Power Factor Constraints
- -
- In UPF DG, is taken as a value of
- -
- In FPF DG, is assumed to be
- -
- In OPF DG, the exact is determined by the MGO and ranges between the limits
- F.
- DG Penetration Limits
2.2. Technical and Economic Evaluations
- A.
- Voltage Profile Index
- B.
- Voltage Stability Index
- C.
- Power Loss Reduction
- D.
- Annual Cost
- i
- Cost of energy losses (CEL)
- ii
- Cost of DGs active and reactive power
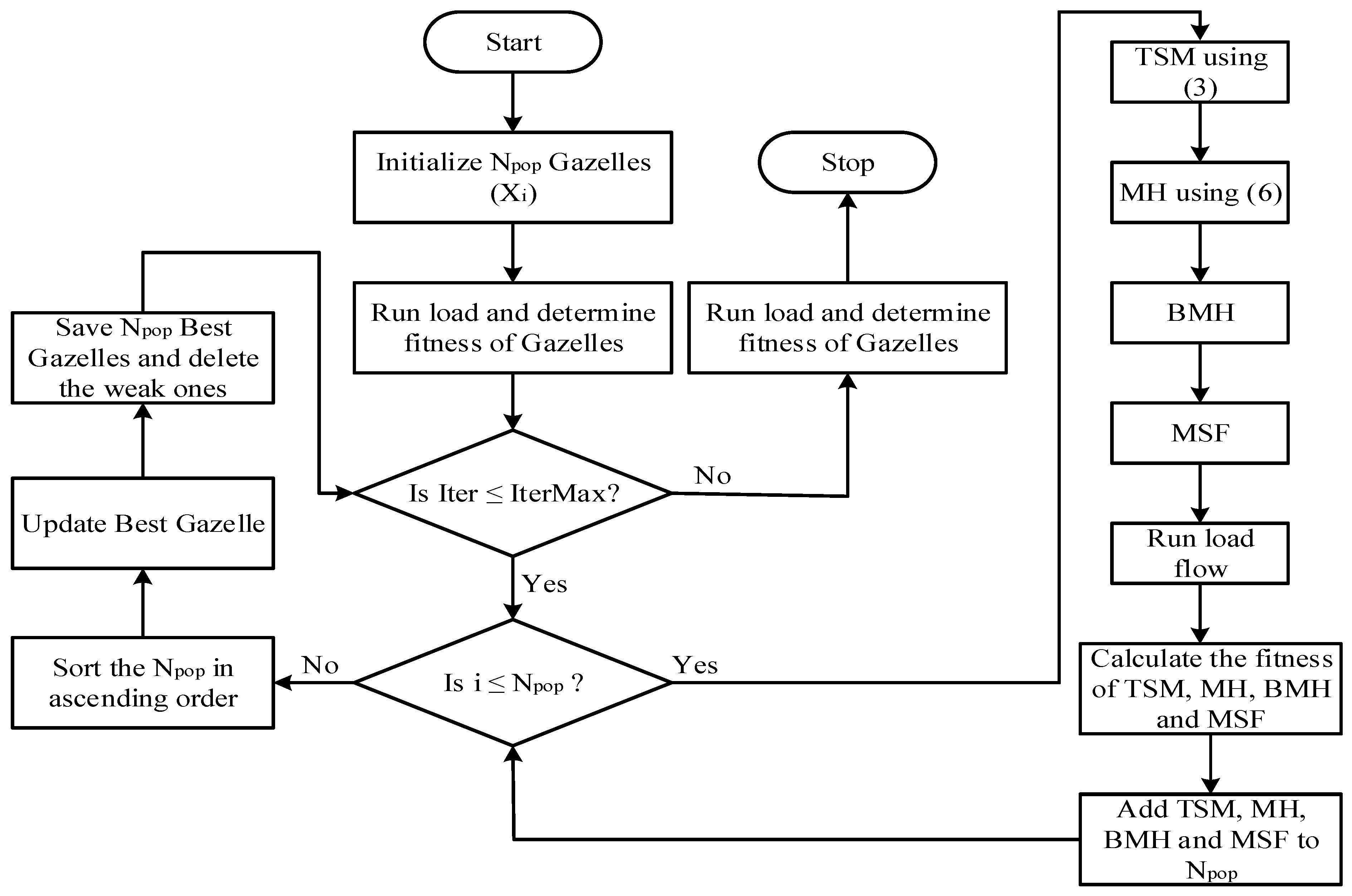
3. Solution Technique
3.1. Overview of Mountain Gazelle Optimizer (MGO)
3.1.1. Territorial Solitary Males
3.1.2. Maternity Herds
3.1.3. Bachelor Male Herds
3.1.4. Migration to Search for Food
3.2. Application of MGO for DG Allocation
- Step 1. Input the MGO parameters and distribution system line and load data
- Step 2. Initialize a random Npop population of Gazelles as given in Equation (32):
- Step 3. After selecting the DG type, perform load flow utilizing the Direct Load Flow (DLF) technique after modification of the line and load data for each initialized gazelle. Compute the fitness level and power loss of all the initialized gazelles as given in (37):
- Step 4. Set iter = 1
- Step 5. Utilize Equations (23), (28), (29) and (31) to determine TSM, MH, BMH, and MSF for each gazelle.
- Step 6. Determine the fitness and power loss of TSM, MH, BMH, and MSF by running load flow, then include them in the habitat.
- Step 7. Arrange the population as a whole in ascending order.
- Step 8. Adapt the fittest gazelle.
- Step 9. Store the N optimal gazelles in the maximum amount of populations
- Step 10. Increase Iter and go over Steps 5 to 9 if Iter is less than IterMax; if not, proceed to Step 11.
- Step 11. Present the optimal gazelle solution and compute the economic and technical assessments.
4. Results and Discussions
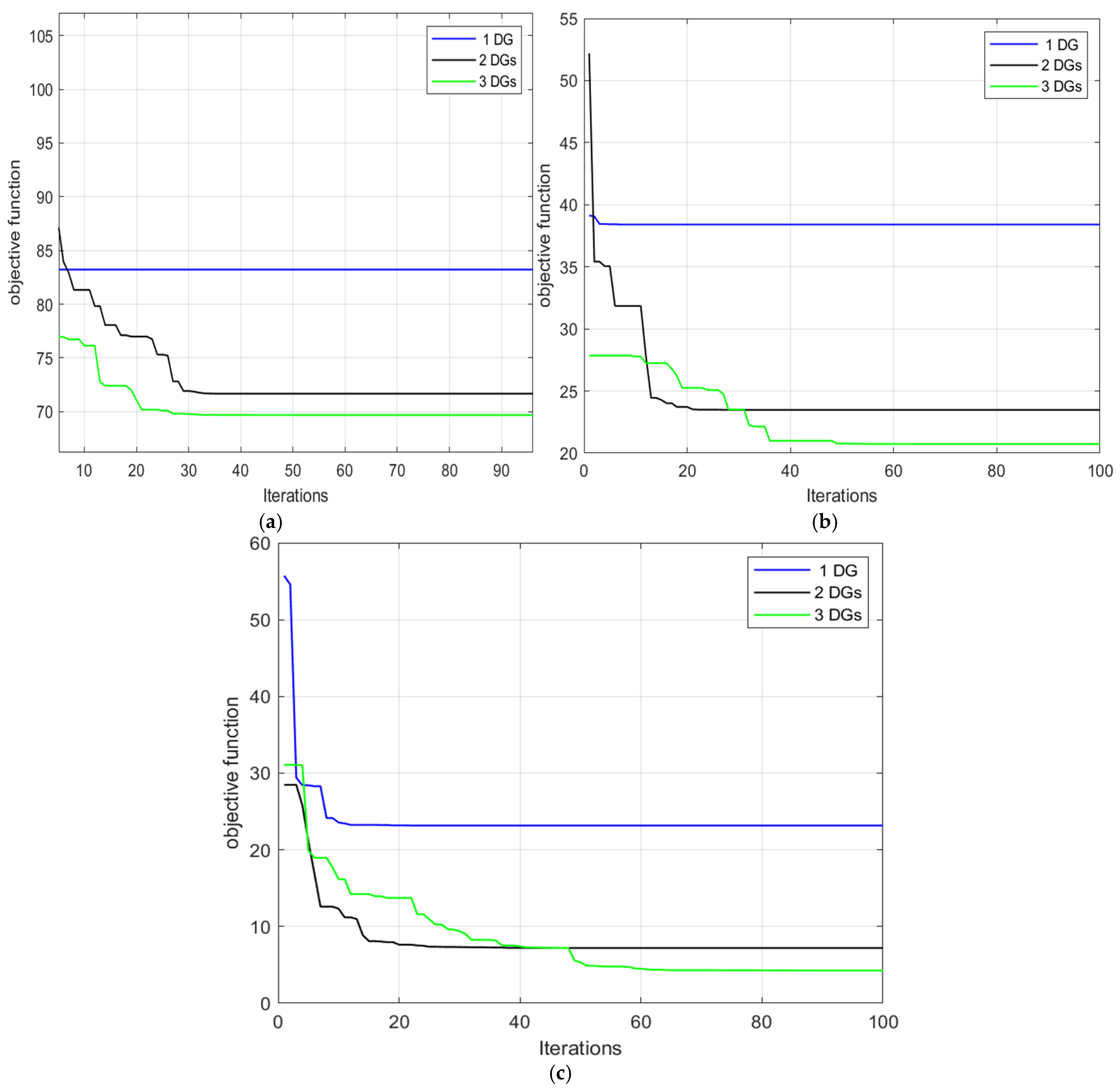
4.1. MGO Results for Standard 33-Bus RDN
4.1.1. Case One: Unity PF DGs
4.1.2. Fixed PF DGs
4.1.3. Variable PF DGs
4.1.4. Comparison of the Results Obtained from the Three Cases
4.2. MGO Results for Standard IEEE 69-Bus System
4.2.1. Unity PF DGs
4.2.2. Fixed PF DGs
4.2.3. Variable PF DGs
4.2.4. Comparison of the Results Obtained from the Three Test Cases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Parameters | |||
| Real power generated at th bus | Loss factor | ||
| Reactive power generated at th bus | Maximum complex power generation limits | ||
| magnitude of voltage at the bus | Maximum real power generation limits | ||
| voltage of voltage at the bus | young male herd coefficients vector | ||
| total number of branches | MaxIter | dandelion seed propagation’s best location | |
| injected power by DGs | Coefficient vectors | ||
| Real power demand | Xrand | coordinates of a randomly selected gazelle | |
| Current flow via distribution line | pop | population size | |
| total real power taken from the sub-station | Lower bound | ||
| total reactive power taken from the sub-station | Upper bound | ||
| Standard deviation of the bus voltage. | penalty factor | ||
| Voltage magnitude at bus i | |||
| Yearly cost demand for power loss | |||
| Annual cost of energy losses | |||
| Abbreviations | |||
| MGO | Mountain Gazelle Optimizer | QOTLBO | quasi-oppositional teaching learning-based optimization |
| RDN | radial distribution network | QOSIMBO-Q | Quasi-Oppositional Swine Influenza Model-Based Optimization with Quarantine |
| CP | constant power | BWO | Black Widow Optimizer |
| pf | Power factor | SFSA | Stochastic fractal search algorithm |
| DG | Distributed generation | TSO | Transient search optimizer |
| VPI | Voltage profile index | ALOA | Ant lion optimization algorithm |
| VSI | voltage stability index | SGA | Search group algorithm |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimization | ESGA | Enhanced search group algorithm |
| HHO | Harris Hawks Optimizer | CBOM | Coot Bird Optimization Method |
| IHHO | Improved Harris Hawks Optimizer | GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimizer | SIMBO-Q | Swine Influenza Model-Based Optimization with Quarantine |
| ESGA | Enhanced Search Group Algorithm | ARO | Artificial Rabbits Optimization |
| HM | Heuristic Method | AHA | Artificial Hummingbird Algorithm |
| ECOA | enhanced coyote optimization algorithm | ||
References
- Prakash, K.; Lallu, A.; Islam, F.R.; Mamun, K.A. Review of Power System Distribution Network Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd Asia-Pacific World Congress on Computer Science and Engineering (APWC on CSE), Nadi, Fiji, 5–6 December 2016; pp. 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhu, B.; Lei, A.; Dong, X. Fault location for radial distribution network via topology and reclosure-generating traveling waves. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 6404–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duppala, D.; Nagaballi, S.; Kale, V.S. The Technical Impact of Increase in Penetration Level of DG Technologies on Power System. In Proceedings of the of 2019 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), Kolkata, India, 7–9 June 2019; pp. 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, P.; Patidar, N.P.; Nema, R.K. Planning of grid integrated distributed generators: A review of technology, objectives and techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, T.H.B.; Tran, T.; Van Tran, T.; Vo, D.N.; Nguyen, H.T.T. An improved metaheuristic method for simultaneous network reconfiguration and distributed generation allocation. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 8069–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimon, S.A.; Adepoju, G.A.; Adebayo, I.G.; Howlader, H.O.R.; Ayanlade, S.O.; Adewuyi, O.B. Impact of Distributed Generators Penetration Level on the Power Loss and Voltage Profile of Radial Distribution Networks. Energies 2023, 16, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalitha, M.P.; Reddy, V.C.V.; Reddy, N.S.; Reddy, V.U. DG Source Allocation by Fuzzy and Clonal Selection Algorithm for Minimum Loss in Distribution System. Distrib. Gener. Altern. Energy J. 2011, 26, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, D.Q.; Mithulananthan, N. Multiple Distributed Generator Placement in Primary Distribution Networks for Loss Reduction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fergany, A. Optimal allocation of multi-type distributed generators using backtracking search optimization algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 64, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.H.; Abedini, M. A novel method for optimal DG units capacity and location in Microgrids. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 75, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChithraDevi, S.A.; Lakshminarasimman, L.; Balamurugan, R. Stud Krill herd Algorithm for multiple DG placement and sizing in a radial distribution system. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, N.K.; Swarnkar, A.; Gupta, N.; Niazi, K.R. Multi-objective Taguchi approach for optimal DG integration in distribution systems. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 2418–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, A.; Kamel, S.; Jurado, F. Efficient optimization technique for multiple DG allocation in distribution networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 86, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, K.; Mukherjee, V. Optimal siting and sizing of distributed generation in radial distribution system using a novel student psychology-based optimization algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 15639–15667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.; Kamel, S.; Hassan, M.H.; Tostado-Véliz, M.; Zawbaa, H.M. An improved wild horse optimization algorithm for reliability based optimal DG planning of radial distribution networks. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 582–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, R.; Farooq, S.H.E.R.; Rafik, N.E.J.I. An improved MOPSO algorithm for optimal sizing & placement of distributed generation: A case study of the Tunisian offshore distribution network (ASHTART). Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 6960–6975. [Google Scholar]
- Subbaramaiah, K.; Sujatha, P. Optimal DG unit placement in distribution networks by multi-objective whale optimization algorithm & its techno-economic analysis. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 214, 108869. [Google Scholar]
- Gümüş, T.E.; Emiroglu, S.; Yalcin, M.A. Optimal DG allocation and sizing in distribution systems with Thevenin based impedance stability index. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 144, 108555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purlu, M.; Turkay, B.E. Optimal Allocation of Renewable Distributed Generations Using Heuristic Methods to Minimize Annual Energy Losses and Voltage Deviation Index. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 21455–21474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadman Abid, M.; Apon, H.J.; Morshed, K.A.; Ahmed, A. Optimal Planning of Multiple Renewable Energy-Integrated Distribution System with Uncertainties Using Artificial Hummingbird Algorithm. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 40716–40730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, A.; Kamel, S.; Alghamdi, A.S.; Jurado, F. Optimal placement of DGs in distribution system using an improved harris hawks optimizer based on single-and multi-objective approaches. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 52815–52829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Roy, P.K. Multi-objective quasi-oppositional teaching learning-based optimization for optimal location of distributed generator in radial distribution systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 63, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Quasi-Oppositional Swine Influenza Model Based Optimization with Quarantine for optimal allocation of DG in radial distribution network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 74, 348–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimon, S.A.; Adepoju, G.A.; Adebayo, I.G.; Adewuyi, O.B. Comparative assessment of techno-economic and environmental benefits in optimal allocation of distributed generators in distribution networks. Sci. Afr. 2023, 19, e01546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebiyi, O.W.; Okelola, M.O.; Salimon, S.A. Multi-objective Optimal Allocation of Renewable Energy Distributed Generations and Shunt Capacitors in Radial Distribution System using Corona Virus Herd Optimization. Majlesi J. Electr. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadoriya, J.S.; Gupta, A.R. A novel transient search optimization for optimal allocation of multiple distributed generator in the radial electrical distribution network. Int. J. Emerg. Electr. Power Syst. 2022, 23, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Vo, D.N. A novel stochastic fractal search algorithm for optimal allocation of distributed generators in radial distribution systems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 70, 773–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarzadeh, G.; Arabzadeh, M.; Keynia, F. A new optimal allocation of DGs in distribution networks by using coot bird optimization method. Energy Inform. 2023, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Nguyen, T.T.; Dinh, B.H. Find optimal capacity and location of distributed generation units in radial distribution networks by using enhanced coyote optimization algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 4343–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, T.H.B.; Vo, D.N.; Truong, K.H.; Van Tran, T. Optimal Distributed Generation Placement in Radial Distribution Networks using Enhanced Search Group Algorithm. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 103288–103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, M.Z.; Imran, K.; Akbar, M.I.; Ghafoor, S. Optimal distributed generators allocation with various load models under load growth using a meta-heuristic technique. Renew. Energy Focus 2024, 49, 100550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Naick, B.K. A Novel Artificial Rabbits Optimization Algorithm for Optimal Location and Sizing of Multiple Distributed Generation in Radial Distribution Systems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 6981–7012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahzadeh, B.; Gharehchopogh, F.S.; Khodadadi, N.; Mirjalili, S. Mountain gazelle optimizer: A new nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2022, 174, 103282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimon, S.A.; Adepoju, G.A.; Adebayo, I.G.; Ayanlade, S.O. Impact of shunt capacitor penetration level in radial distribution system considering techno-economic benefits. Niger. J. Technol. Dev. 2022, 19, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adepoju, G.A.; Salimon, S.A.; Adebayo, I.G.; Adewuyi, O.B. Impact of DSTATCOM penetration level on technical benefits in radial distribution network. e-Prime-Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2024, 7, 100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, M.; Kansal, S.; Verma, R. Sizing and allocation of DGs in a passive distribution network under various loading scenarios. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 209, 108046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, S.A.; Karimi, M.H. Optimal reconfiguration and DG allocation in balanced and unbalanced distribution systems. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2014, 5, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Tran, T.T.; Vo, D.N. Improved stochastic fractal search algorithm with chaos for optimal determination of location, size, and quantity of distributed generators in distribution systems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 7707–7732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, K.; Yorino, N.; Ahmed, A. Optimal distributed generation allocation in distribution systems for loss minimization. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 31, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, S.; Kumar, V.; Tyagi, B. Hybrid approach for optimal placement of multiple DGs of multiple types in distribution networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 75, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.S.; Abd Elazim, S.M.; Abdelaziz, A.Y. Ant Lion Optimization Algorithm for optimal location and sizing of renewable distributed generations. Renew. Energy 2017, 101, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Technique | Optimal DG | PL (kW) | %PL | VPI | V (p.u.) | Cost (USD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location (Bus) | Size (kW) | Pf (p.u.) | ||||||
| Base Case | 210.98 | 1.23 | 0.9038 (18) | CEL (USD) = 16,983.7877 | ||||
| Case One: One DG | ||||||||
| GA [28] | 2380 (6) | 132.64 | 34.56 | |||||
| SFS [38] | 2590 (6) | 111.02 | 47.38 | |||||
| CSFS3 [38] | 2590 (6) | 111.02 | 47.38 | |||||
| CBOM [28] | 2575 (6) | 111.03 | 47.38 | |||||
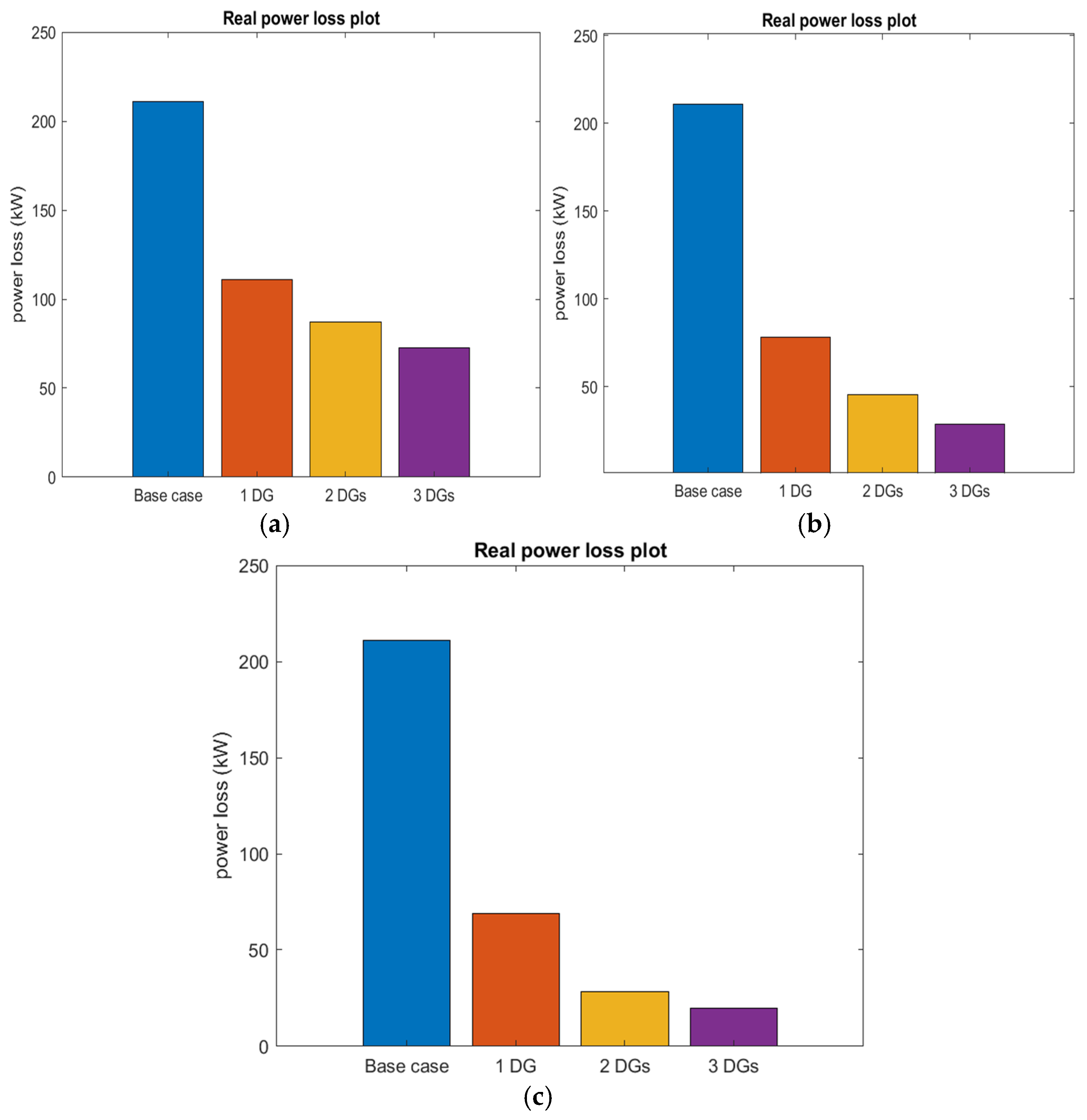
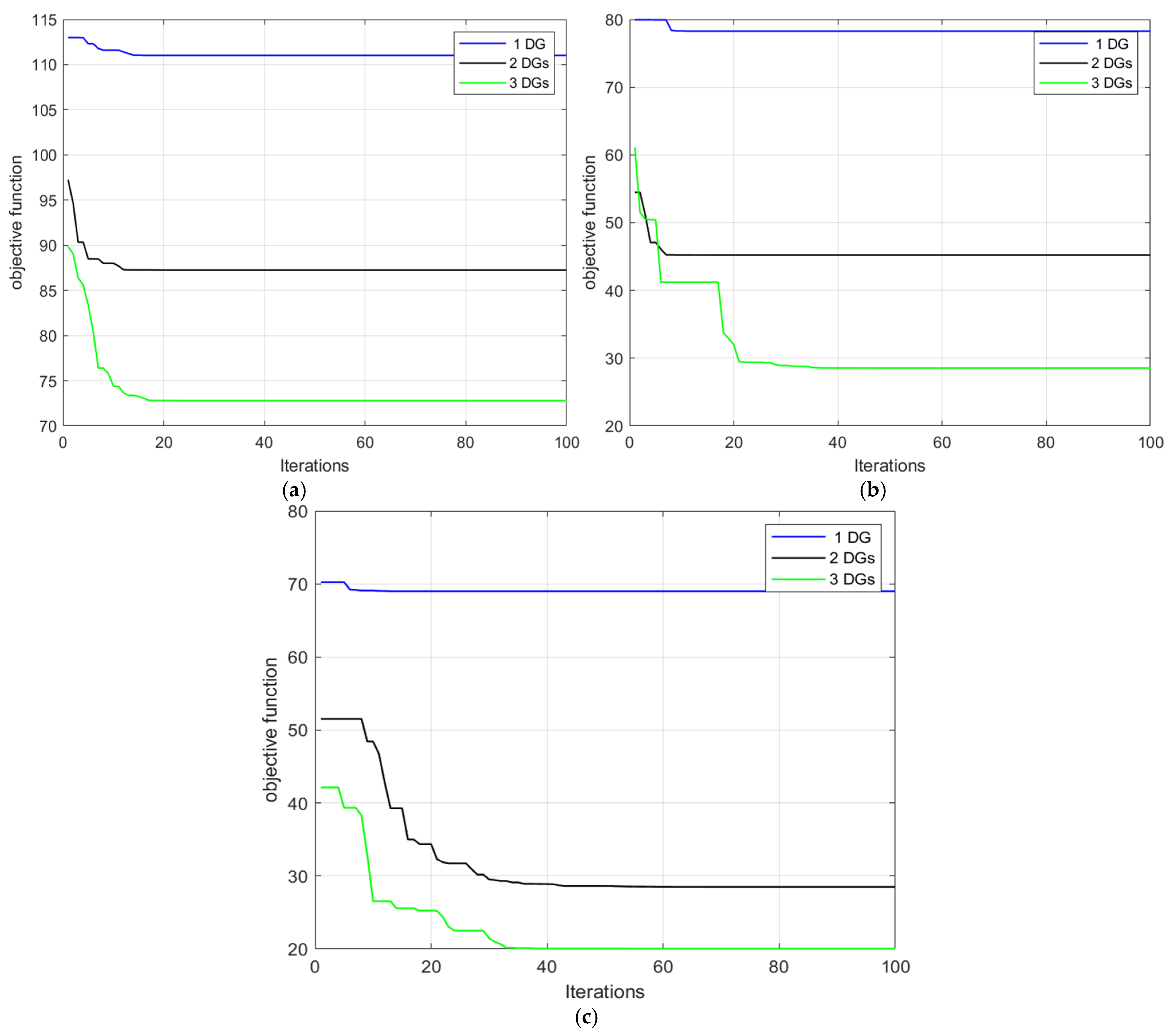
| MGO | 2590 (6) | 111.02 | 47.38 | 1.54 | 0.9424 (18) | CEL (USD) = 8936.6326 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 52.0500 | ||
| Case Two: Two DGs | ||||||||
| EA [39] | 844 (13) 1149 (30) | 87.17 | 58.68 | |||||
| EA-OPF [39] | 852 (13) 1158 (30) | 87.17 | 58.69 | |||||
| AM-PSO [40] | 830 (13) 1110 (30) | 87.28 | 58.64 | |||||
| SFS [38] | 852 (13) 1158 (30) | 87.17 | 58.69 | |||||
| CBOM [28] | 852 (13) 1158 (30) | 87.17 | 58.69 | |||||
| MGO | 852 (13) 1157 (30) | 87.17 | 58.69 | 1.68 | 0.9685 (33) | CEL (USD) = 7016.8101 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 40.4300 | ||
| Case Three: Three DGs | ||||||||
| BFOA [26] | 779 (14) 880 (25) 1083 (30) | 73.53 | 65.14 | |||||
| QOSIMBO-Q [22] | 771 (14) 1097 (24) 1096 (30) | 72.79 | 65.49 | |||||
| SIMBO-Q [22] | 764 (14) 1042 (24) 1135(29) | 73.4 | 65.21 | |||||
| HHO [20] | 746 (14) 1023 (24) 1136 (30) | 72.98 | 65.40 | |||||
| IHHO [20] | 776 (14) 1081 (24) 1067(30) | 72.79 | 65.50 | |||||
| TSO [26] | 772 (14) 1104 (24) 1065 (30) | 72.79 | 65.50 | |||||
| SGA [30] | 802 (13) 913 (24) 1054 (30) | 72.79 | 65.50 | |||||
| ESGA [30] | 771 (14) 1097 (24) 1066 (30) | 72.79 | 65.50 | |||||
| ARO [32] | 804 (13) 1094 (24) 1057 (30) | 72.78 | 65.50 | |||||
| MGO | 771 (14) 1097 (24) 1066 (30) | 72.79 | 65.50 | 1.72 | 0.9687 (33) | CEL (USD) = 5859.2820 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 58.9300 | ||
| Technique | Optimal DG | PL (kW) | %PL | VPI | V (p.u.) | Cost (USD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location (Bus) | Size (kW) | Pf (p.u.) | ||||||
| Base Case | 210.98 | CEL (USD) = 16,983.7877 | ||||||
| Case One: One DG | ||||||||
| MGO | 2670 (6) | 0.95 | 78.27 | 62.90 | 1.66 | 0.9547 (18) | CEL (USD) = 6300.3984 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 53.6500 QG Cost ($/MVArh) = 2.5434 | |
| Case Two: Two DGs | ||||||||
| MGO | 13 30 | 840 1284 | 0.95 0.95 | 45.23 | 78.56 | 1.95 | 0.9798 (25) | CEL (USD) = 3640.8205 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 42.7300 QG Cost ($/MVArh) = 2.0233 |
| Case Three: Three DGs | ||||||||
| QOSIMBO-Q [22] | 13 24 30 | 830 1124 1240 | 0.95 | 28 | 86.49 | |||
| SIMBO-Q [22] | 13 24 30 | 888 1085 1309 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 29 | 86.26 | |||
| HHO [20] | 13 24 30 | 871 1327 1076 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 29.71 | 85.92 | |||
| IHHO [20] | 14 24 30 | 794 1132 1258 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 28.95 | 86.49 | |||
| TSO [26] | 13 24 30 | 833 1083 1250 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 28.50 | 86.49 | |||
| ARO [32] | 13 24 30 | 840 1138 1254 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 28.53 | 86.48 | |||
| MGO | 14 24 30 | 812 1080 1258 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 28.29 | 86.59 | 2.03 | 0.9880 (33) | CEL (USD) = 2296.5423 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 60.9700 QG Cost ($/MVArh) = 2.8921 |
| Technique | Optimal DG | PL (kW) | %PL | VPI | Vmin (p.u.) | Cost (USD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location (Bus) | Size (kW) | PF (p.u.) | ||||||
| Base Case | 210.98 | 1.23 | 0.9038 (18) | CEL (USD) = 16,983.7877 | ||||
| Case One: One DG | ||||||||
| CBOM [28] | 26 | 2410 | 62.4 | 70.38 | ||||
| MGO | 6 | 2423 | 0.82 | 60.03 | 72.28 | CEL (USD) = 5556.6182 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 39.9700 QGCost ($/MVArh) = 7.7812 | ||
| Case Two: Two DGs | ||||||||
| CBOM [28] | 13 30 | 820 1243 | 0.8845 0.80 | 29.31 | 86.10 | |||
| MGO | 13 30 | 761 830 | 0.90 0.73 | 28.50 | 86.49 | 1.85 | 0.9803 (25) | CEL (USD) = 2294.1274 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 32.3200 QG Cost ($/MVArh) = 6.9367 |
| Case Three: Three DGs | ||||||||
| HHO [20] | 12 24 30 | 913 883 1079 | 0.85 0.82 0.83 | 14.94 | 92.92 | |||
| IHHO [20] | 14 24 30 | 762 1141 1014 | 0.90 0.91 0.71 | 11.83 | 93.39 | |||
| TSO [26] | 14 24 30 | 754 1143 1048 | 0.88 0.93 0.73 | 12.03 | 94.29 | |||
| ARO [32] | 13 24 30 | 807 1079 1031 | 0.91 0.91 0.72 | 11.74 | 94.44 | |||
| SGA [30] | 14 25 30 | 873 899 1459 | 0.903 0.939 0.6790 | 12.97 | 93.85 | |||
| ESGA [30] | 14 24 30 | 877 1188 1443 | 0.9050 0.9005 0.7133 | 11.74 | 94.44 | |||
| MGO | 13 24 30 | 385 492 994 | 0.8984 0.9100 0.7199 | 11.74 | 94.44 | 1.92 | 0.9825 (25) | CEL (USD) = 1613.1338 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 41.2500 QGCost ($/MVArh) = 7.6870 |
| Technique | Optimal DG | PL (kW) | %PL | VPI | V (p.u.) | Cost (USD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location (Bus) | Size (kW) | pf (p.u.) | ||||||
| Base Case | 210.98 | 1.23 | 0.9038 (18) | CEL (USD) = 18 110.7270 | ||||
| Case One: One DG | ||||||||
| SFS [38] | 1873 (61) | 83.22 | 63.01 | |||||
| CSFS3 [38] | 1873 (61) | 83.22 | 63.01 | |||||
| CBOM [28] | 1873 (61) | 83.22 | 63.01 | |||||
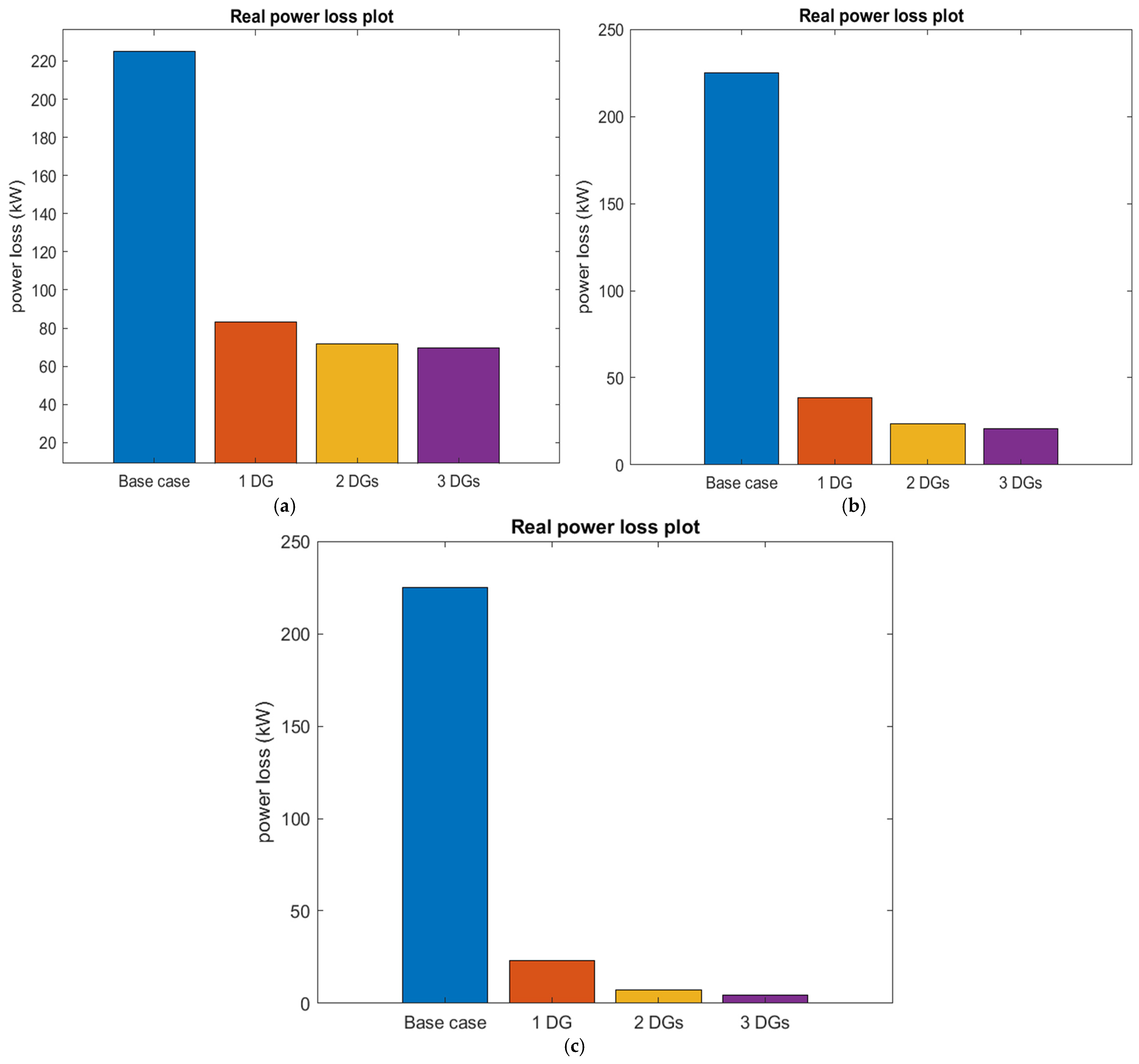
| MGO | 1873 (61) | 83.22 | 63.01 | 1.89 | 0.9682 (27) | CEL (USD) = 6698.8521 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 37.7100 | ||
| Case Two: Two DGs | ||||||||
| AGA [28] | 389 (18) 1848 (61) | 72.76 | 67.66 | |||||
| SFS [38] | 531 (17) 1781 (61) | 71.68 | 68.14 | |||||
| CSF3 [38] | 531 (17) 1781 (61) | 71.68 | 68.14 | |||||
| CBOM [28] | 531 (17) 1781 (61) | 71.68 | 68.14 | |||||
| MGO | 532 (17) 1781 (61) | 71.67 | 68.14 | 2.14 | 0.9789 (65) | CEL (USD) = 5769.1268 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 46.5100 | ||
| Case Three: Three DGs | ||||||||
| TSO [26] | 825 (9) 405 (22) 1650 (61) | 70.25 | 68.77 | |||||
| QOSIMBO-Q [22] | 834 (9) 480 (17) 1500 (61) | 71.0 | 68.44 | |||||
| SIMBO-Q [22] | 619 (9) 530 (17) 1500 (61) | 71.3 | 68.31 | |||||
| HHO [20] | 378 (11) 480 (17) 1706 (61) | 69.73 | 69.00 | |||||
| IHHO [20] | 527 (11) 382 (17) 1719 (61) | 69.41 | 69.15 | |||||
| SGA [30] | 467 (17) 1685 (54) 547 (53) | 70.17 | 68.81 | |||||
| ABC [30] | 576 (8) 1743 (61) 411 (17) | 70.16 | 68.82 | |||||
| GA [30] | 720 (50) 531 (17) 1781 (61) | 70.16 | 68.82 | |||||
| MGO | 1727 (18) 400 (18) 459 (66) | 69.69 | 69.02 | 2.18 | 0.9790 (65) | CEL (USD) = 5609.7453 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 51.9700 | ||
| Technique | Optimal DG | PL (kW) | %PL | VPI | V (p.u.) | Cost (USD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location (Bus) | Size (kW) | Pf (p.u.) | ||||||
| Base Case | 210.98 | 1.56 | 0.9092 (65) | CEL (USD) = 18,110.7270 | ||||
| Case One: One DG | ||||||||
| MGO | 61 | 1947 | 0.95 | 38.41 | 82.93 | 2.00 | 0.9717 (27) | CEL (USD) = 3091.8398 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 39.1900 QGCost ($/MVArh) = 1.8547 |
| Case Two: Two DGs | ||||||||
| MGO | 61 17 | 1849 550 | 0.95 0.95 | 23.48 | 89.56 | 2.44 | 0.9934 (69) | CEL (USD) = 1890.0390 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 48.2300 QGCost ($/MVArh) = 2.2853 |
| Case Three: Three DGs | ||||||||
| TSO [26] | 11 18 61 | 352 501 1878 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 21.13 | 90.61 | |||
| SIMBO-Q [22] | 19 61 64 | 566 1500 422 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 23.1 | 89.73 | |||
| QOSIMBO-Q [22] | 17 61 64 | 583 1500 427 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 22.80 | 89.87 | |||
| HHO [20] | 16 50 61 | 703 287 1891 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 22.85 | 89.80 | |||
| IHHO [20] | 11 18 61 | 5533 420 1879 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 20.71 | 90.80 | |||
| MGO | 21 61 11 | 361 178 567 | 0.95 0.95 0.95 | 20.73 | 90.79 | 2.56 | 0.9942 (50) | CEL (USD) = 1668.6758 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 54.4700 QG-Cost ($/MVArh) = 2.5825 |
| Technique | Optimal DG | PL (kW) | %PL | VPI | V (p.u.) | Cost (USD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location (Bus) | Size (kW) | Pf (p.u.) | ||||||
| Base Case | 210.98 | 1.56 | 0.9092 (65) | CEL (USD) = 18,110.7270 | ||||
| Case One: One DG | ||||||||
| BB-BC [28] | 61 | 1801 | 0.81 | 23.17 | 89.69 | |||
| ALOA [41] | 61 | 1827 | 0.82 | 23.19 | 89.69 | |||
| CBOM [28] | 61 | 1828 | 0.81 | 23.17 | 89.70 | |||
| MGO | 61 | 1849 | 0.81 | 23.17 | 89.70 | 1.93 | 0.9725 (27) | CEL (USD) = 1865.0854 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 30.0300 QGCost ($/MVArh) = 6.2264 |
| Case Two: Two DGs | ||||||||
| ALOA [41] | 17 61 | 603 1200 | 0.83 0.80 | 20.93 | 90.69 | |||
| CBOM [28] | 17 61 | 522 1735 | 0.83 0.81 | 7.20 | 96.79 | |||
| MGO | 61 17 | 1412 432 | 0.81 0.83 | 7.20 | 96.80 | 2.21 | 0.9943 (50) | CEL (USD) = 579.5690 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 37.3800 QGCost ($/MVArh) = 7.4856 |
| Case Three: Three DGs | ||||||||
| TSO [26] | 12 59 61 | 697 846 1064 | 0.80 0.91 0.81 | 11.89 | 94.71 | |||
| HHO [20] | 17 61 66 | 271 1541 697 | 0.57 0.76 0.97 | 6.58 | 97.10 | |||
| IHHO [20] | 11 18 61 | 456 389 1715 | 0.85 0.82 0.83 | 4.44 | 98.00 | |||
| ESGA [30] | 18 61 11 | 378 1672 494 | 0.83 0.81 0.81 | 4.27 | 98.10 | |||
| SGA [30] | 61 19 11 | 1681 386 439 | 0.82 0.87 0.71 | 4.36 | 98.06 | |||
| ABC [30] | 61 18 66 | 1791 323 417 | 0.81 0.87 0.71 | 4.98 | 97.79 | |||
| MGO | 18 11 61 | 320 391 1365 | 0.84 0.80 0.81 | 4.27 | 98.10 | 2.27 | 0.9943 (50) | CEL (USD) = 343.7166 PG-Cost ($/MWh) = 42.2700 QGCost ($/MVArh) = 8.5387 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salimon, S.A.; Fajinmi, I.O.; Onatoyinbo, O.O.; Alimi, O.A. Allocation of Single and Multiple Multi-Type Distributed Generators in Radial Distribution Network Using Mountain Gazelle Optimizer. Technologies 2025, 13, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13070265
Salimon SA, Fajinmi IO, Onatoyinbo OO, Alimi OA. Allocation of Single and Multiple Multi-Type Distributed Generators in Radial Distribution Network Using Mountain Gazelle Optimizer. Technologies. 2025; 13(7):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13070265
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalimon, Sunday Adeleke, Ifeoluwa Olajide Fajinmi, Olubunmi Onadayo Onatoyinbo, and Oyeniyi Akeem Alimi. 2025. "Allocation of Single and Multiple Multi-Type Distributed Generators in Radial Distribution Network Using Mountain Gazelle Optimizer" Technologies 13, no. 7: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13070265
APA StyleSalimon, S. A., Fajinmi, I. O., Onatoyinbo, O. O., & Alimi, O. A. (2025). Allocation of Single and Multiple Multi-Type Distributed Generators in Radial Distribution Network Using Mountain Gazelle Optimizer. Technologies, 13(7), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13070265









