Development of a Low-Cost Multi-Physiological Signal Simulation System for Multimodal Wearable Device Calibration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
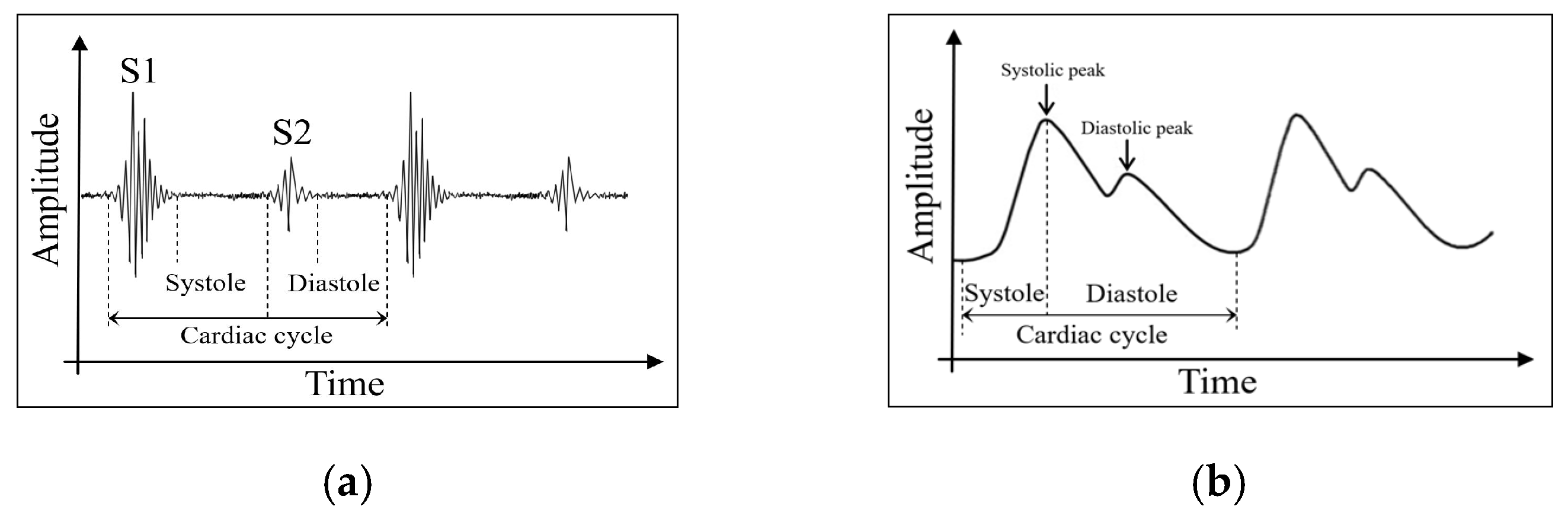
2.1. Cardiovascular Physiological Signals
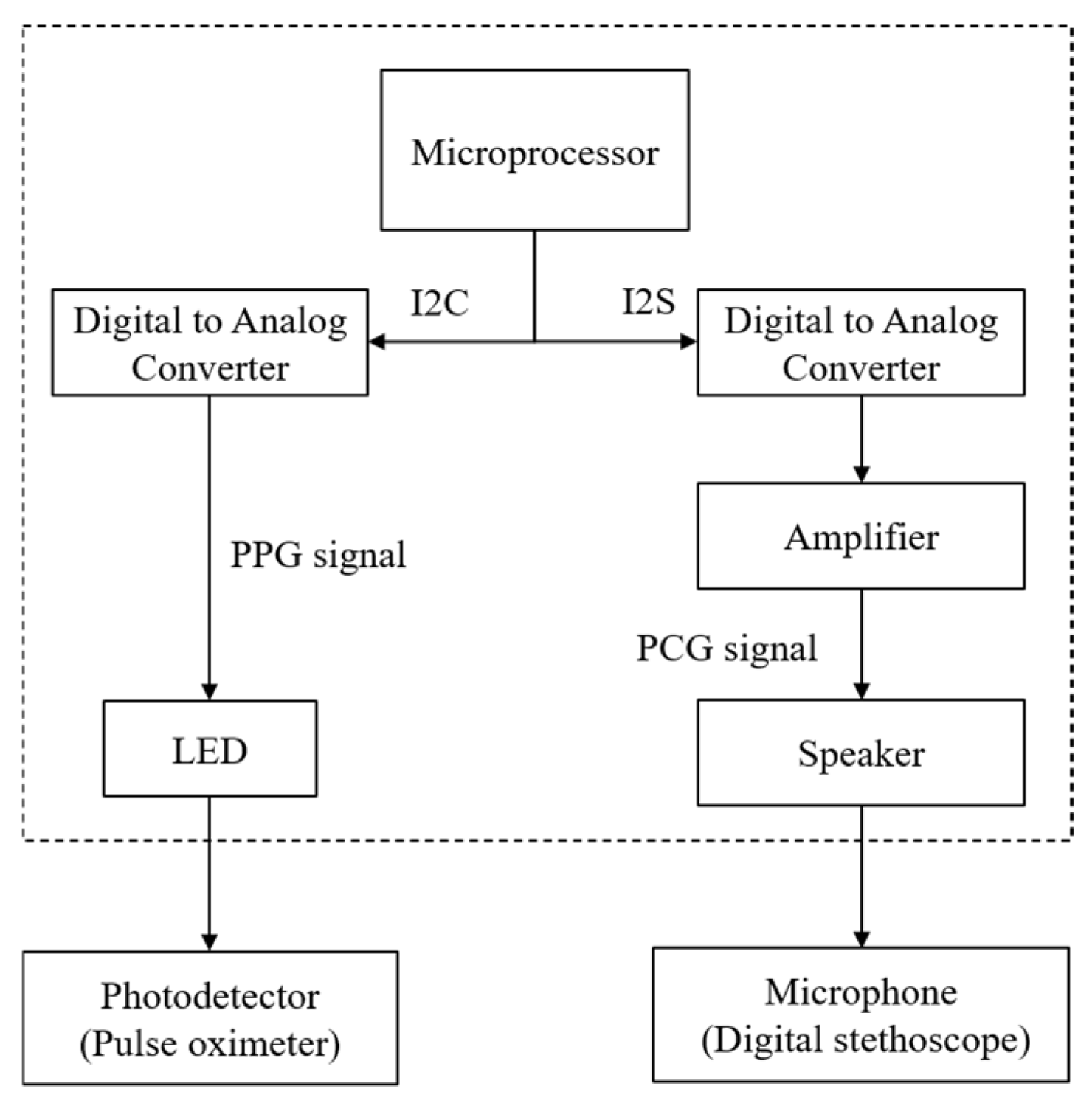
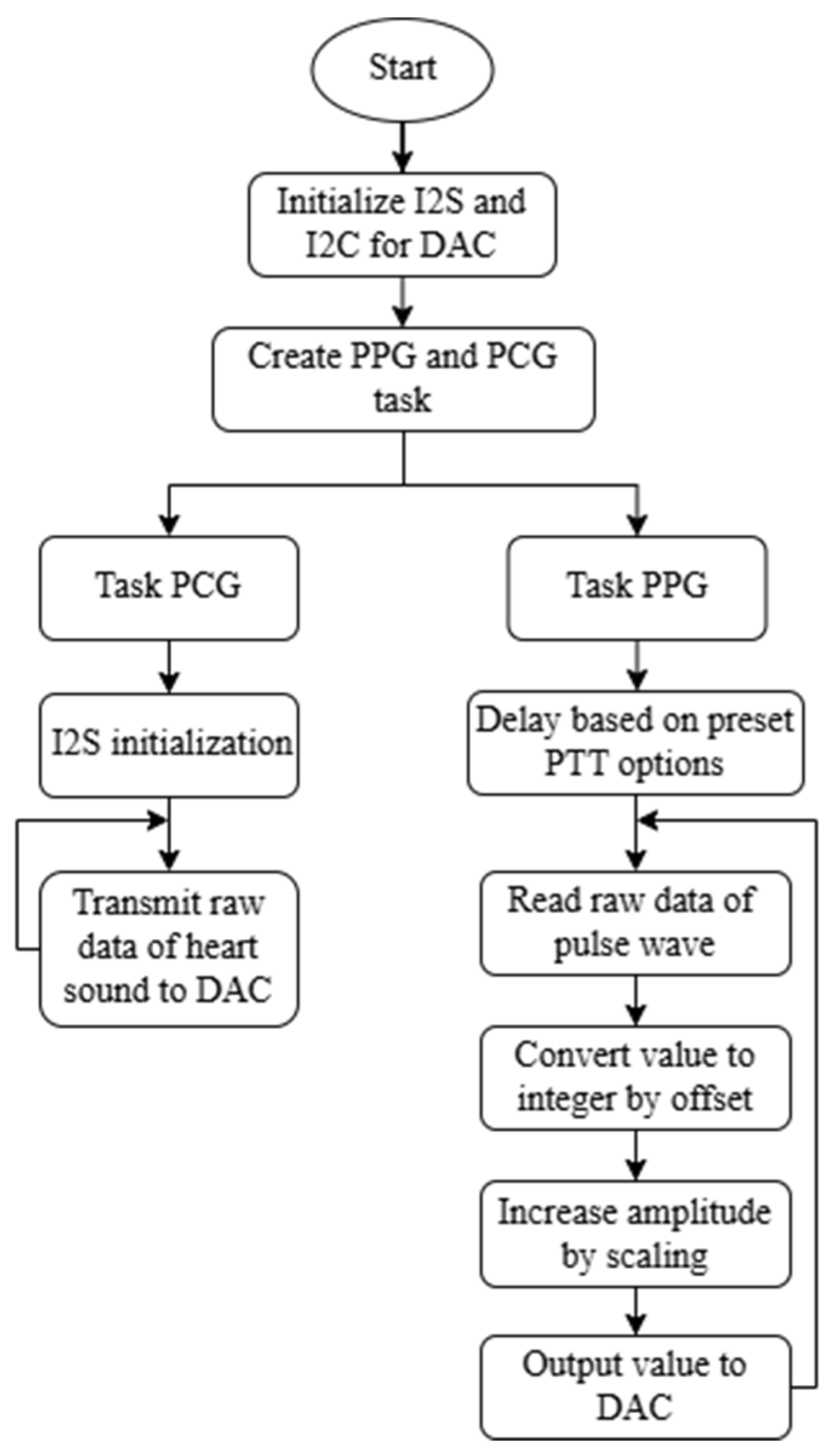
2.2. Proposed System Design and Principle
3. Materials and Experiment
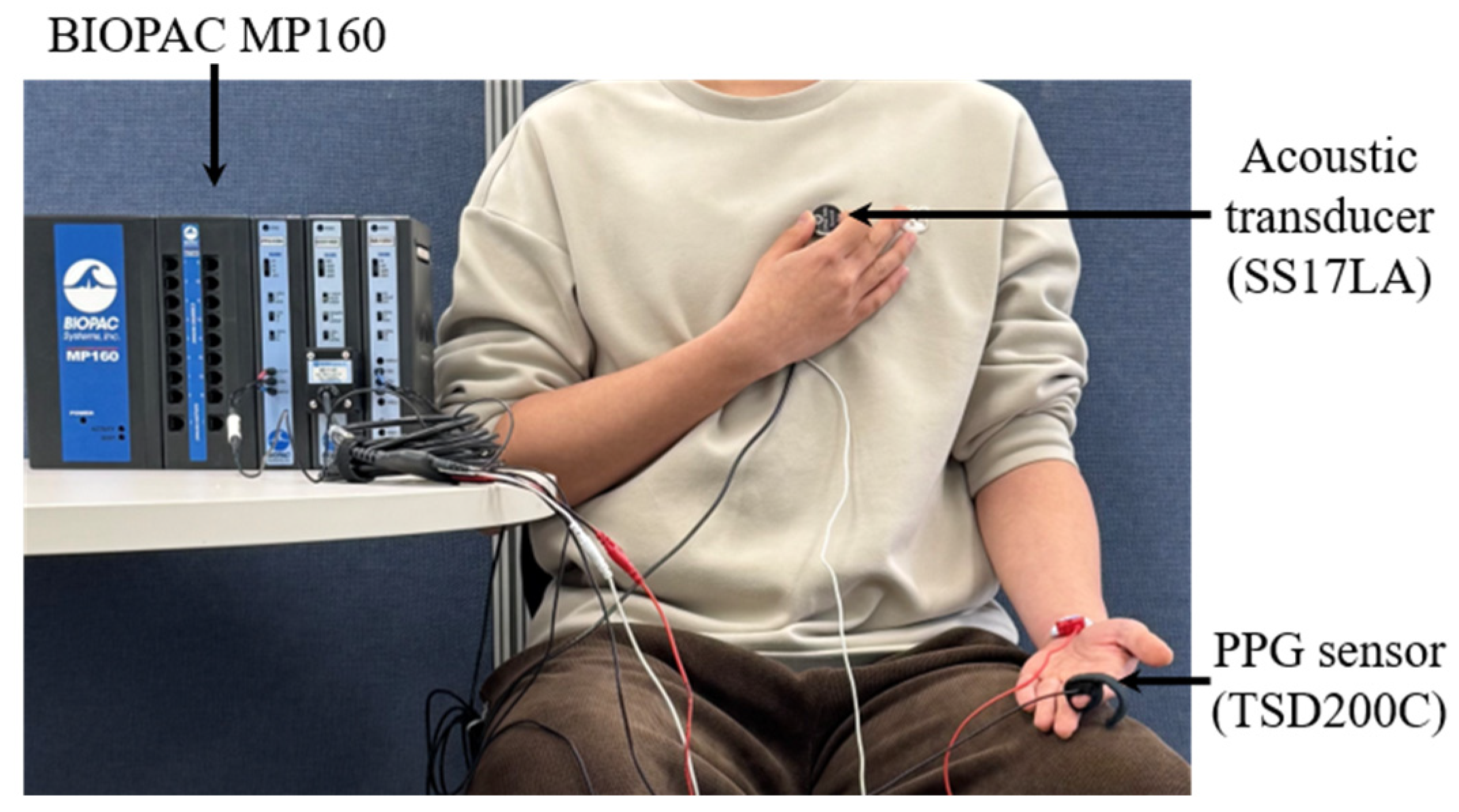
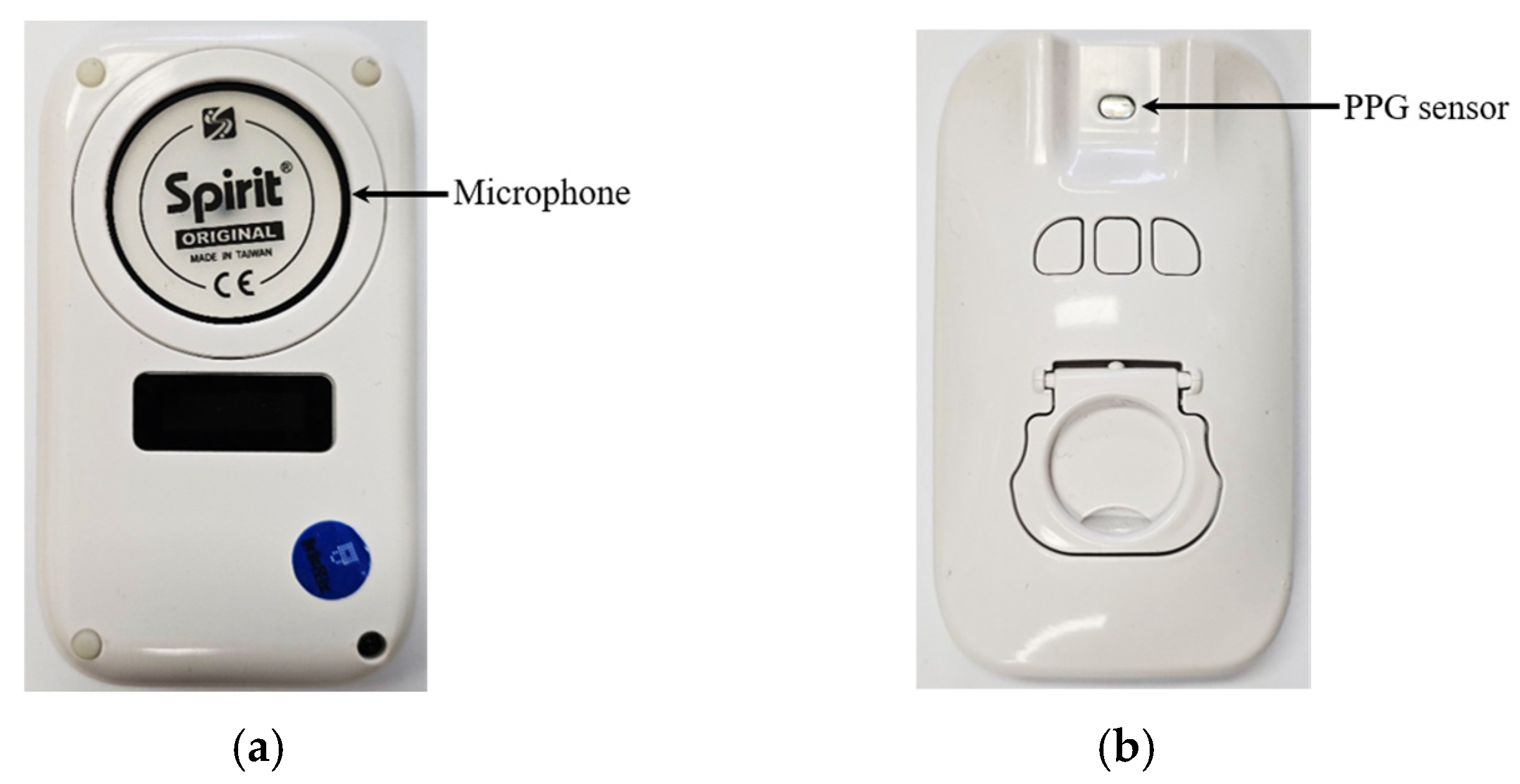
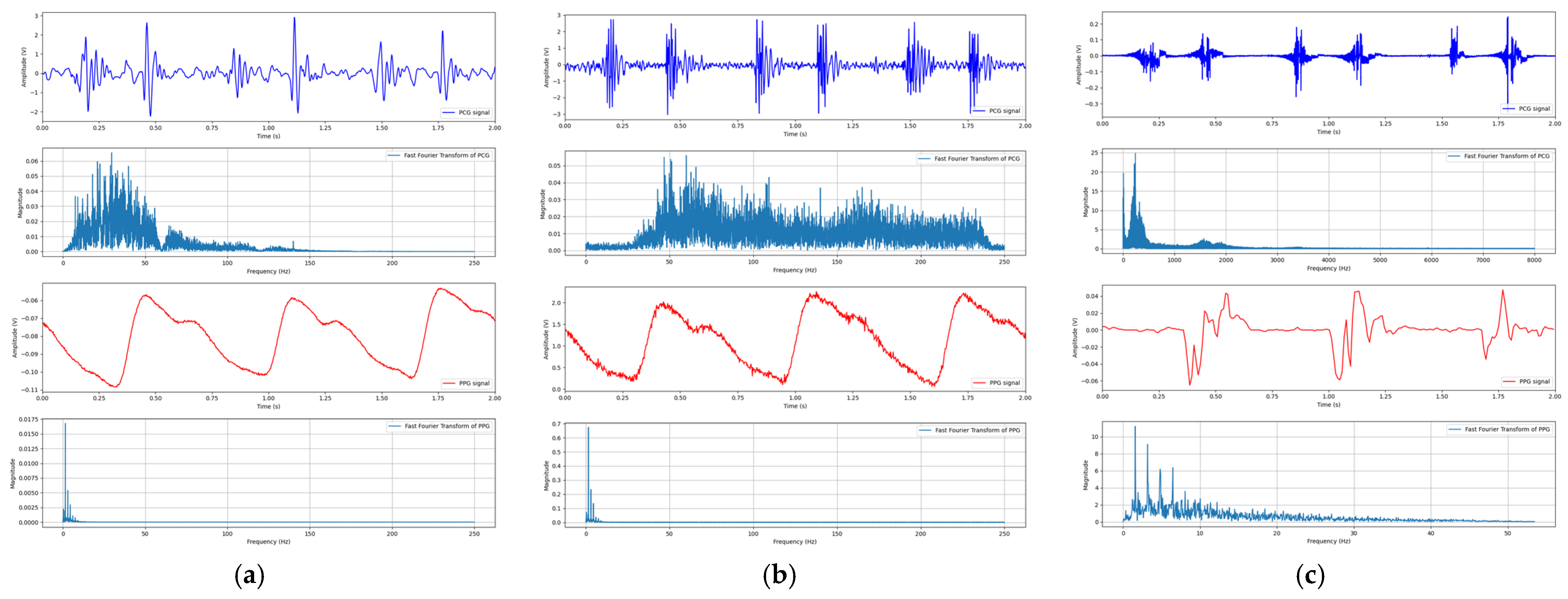
3.1. Prototype Manufacture
3.2. Signal Acquisition
3.2.1. Signal Recording
3.2.2. Signal Preprocessing
3.3. System Evaluation
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCG | Phonocardiography |
| PPG | Photoplethysmography |
| PTT | Pulse transit time |
| DAC | Digital-to-analog converter |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| MCU | Microcontroller unit |
| ECG | Electrocardiography |
| SCG | Seismocardiography |
| BCG | Ballistocardiography |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| I2C | Inter-Integrated circuit |
| I2S | Inter-Integrated circuit sound |
| S1 | First heart sound |
| S2 | Second heart sound |
References
- Temedie-Asogwa, T.; Atta, J.; Al Zoubi, M.; Amafah, J. Economic Impact of Early Detection Programs for Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Growth Eval. 2024, 5, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaysi, A.; Ali, S.; Mahmood, N.; Humaidi, A. Design of Ecg Monitoring System for Cardiovascular Patients Using Labview. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2024, 19, 1189–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, S.C.; Nedkoff, L.; Katzenellenbogen, J.; Hussain, M.A.; Sanfilippo, F. Challenges in Managing Acute Cardiovascular Diseases and Follow up Care in Rural Areas: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royo, M.F.C.; Mandi, A.J.C.; Maulana, A.E.; Sinsuat, S.E.B.; Usman, S.E.; Faller, E.M. Disparities in Rural Areas’ Availability of Health Care in South East Asia: A Review. Int. J. Res. Publ. Rev. 2023, 4, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Thompson, C.; Peterson, S.; Mandrola, J.; Beg, M.S. The Future of Wearable Technologies and Remote Monitoring in Health Care. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2019, 39, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, T.; Kotani, K.; Kitano, N.; Morimoto, J.; Emori, H.; Takahata, M.; Fujita, S.; Wada, T.; Ota, S.; Satogami, K.; et al. Telecardiology in Rural Practice: Global Trends. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Victoria-Castro, A.M.; Melchinger, H.; O’Connor, K.D.; Psotka, M.; Desai, N.R.; Ahmad, T.; Wilson, F.P. Wearables in Cardiovascular Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2023, 16, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshawrab, M.; Adda, M.; Bouzouane, A.; Ibrahim, H.; Raad, A. Smart Wearables for the Detection of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumy, K.; Gaber, M.; Elshaafeey, A.; Mhaimeed, O.; Dineen, E.H.; Marvel, F.A.; Martin, S.S.; Muse, E.D.; Turakhia, M.P.; Tarakji, K.G.; et al. Smart wearable devices in cardiovascular care: Where we are and how to move forward. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wei, X.; Zhou, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, E.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, Z. Viscoelastic blood coagulation testing system enabled by a non-contact triboelectric angle sensor. Exploration 2024, 4, 20230073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qianming, L.; Wen, W.; Haotian, Y.; Kuangyi, Z.; Yiding, J.; Ye, Z. One-Dimensional Implantable Sensors for Accurately Monitoring Physiological and Biochemical Signals. Research 2024, 7, 0507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Z.; Guo, W.-T.; Chen, H.; Yin, Z.-X.; Tang, X.-G.; Sun, Q.-J. Recent Progress on Flexible Self-Powered Tactile Sensing Platforms for Health Monitoring and Robotics. Small 2024, 20, 2405520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.-T.; Lei, Y.; Zhao, X.-H.; Li, R.; Lai, Q.-T.; Liu, S.-Z.; Chen, H.; Fan, J.-C.; Xu, Y.; Tang, X.-G.; et al. Printed-scalable microstructure BaTiO3/ecoflex nanocomposite for high-performance triboelectric nanogenerators and self-powered human-machine interaction. Nano Energy 2024, 131, 110324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauserman, M.; Hailey, C.; Gado, J.; Lokangaka, A.; Williams, J.; Richards-Kortum, R.; Tshefu, A.; Bose, C. Determining the utility and durability of medical equipment donated to a rural clinic in a low-income country. Int. Health 2015, 7, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkire, B.C.; Peters, A.W.; Shrime, M.G.; Meara, J.G. The Economic Consequences of Mortality Amenable to High-Quality Health Care in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Health Aff. 2018, 37, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canali, S.; Schiaffonati, V.; Aliverti, A. Challenges and recommendations for wearable devices in digital health: Data quality, interoperability, health equity, fairness. PLoS Digit. Health 2022, 1, e0000104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Choudhary, R.; Archana; Yadav, N.; Jahangir, M. Calibration of Medical Devices: Method and Impact on Operation Quality. Int. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altayyar Saleh, S.; Mousa, M.; Alfaifi, A.M.; Negm, A.E.; Ali, M.O. The impact of calibration on medical devices performance and patient safety. Biomed. Res. 2018, 29, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Rowlands, A.; Trost, S.G. Calibration and validation of wearable monitors. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, S32–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabile, N.; Reynolds, K. Technological Review of Pulse Oximeter Simulators. J. Clin. Eng. 2002, 27, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hong, B.; Chen, J. Design of Pulse Oximeter Simulator Calibration Equipment. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Beijing, China, 26–31 May 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornberger, C.; Knoop, P.; Matz, H.; Dörries, F.; Konecny, E.; Gehring, H.; Otten, J.; Bonk, R.; Frankenberger, H.; Wouters, P.; et al. A Prototype Device for Standardized Calibration of Pulse Oximeters II. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2002, 17, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Gamboa, K.; Gonzalez-Vargas, A. Development of a Low-Cost Pulse Oximeter Simulator for Educational Purposes. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE ANDESCON, Santiago de Cali, Colombia, 22–24 August 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, M.E. Practical microcontroller-based simulator of graphical heart sounds with disorders. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Advanced Control Circuits Systems (ACCS) Systems & 2017 International Conference on New Paradigms in Electronics & Information Technology (PEIT), Alexandria, Egypt, 5–8 November 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Chaskar, U. Phonocardiography and Photoplethysmography Circuit for Integrated Physiological Signal Acquisition. In Proceedings of the 2023 World Conference on Communication & Computing (WCONF), Raipur, India, 14–16 July 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.A.; Ramkumar, B.; Manikandan, M.S. Automatic Identification of S1 and S2 Heart Sounds Using Simultaneous PCG and PPG Recordings. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 9430–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaili, A.; Kachuee, M.; Shabany, M. Nonlinear Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation of Healthy Subjects Using Pulse Transit Time and Arrival Time. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Research | Authors | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design of Pulse Oximeter Simulator Calibration Equipment | Zhang, P. et al. [21] |
|
|
| A Prototype Device for Standardized Calibration of Pulse Oximeters II | Hornberger, C. et al. [22] |
|
|
| Development of a Low-Cost Pulse Oximeter Simulator for Educational Purposes | Machado-Gamboa, K. et al. [23] |
|
|
| Practical microcontroller-based simulator of graphical heart sounds with disorders | Karar, M. E. [24] |
|
|
| This work: Development of a Low-Cost Multi-Physiological Signal Simulation System for Multimodal Wearable Device Calibration | Delgerkhaan, T. et al. |
|
|
| PCG | PPG | |
|---|---|---|
| Sampling rate | 500 Hz | 500 Hz |
| Resolution | 16 bit | 16 bit |
| Sensor technology | Electret condenser microphone | Light source and photodetector |
| Measurement point | Pulmonic area of chest | Fingertip |
| Duration | 21,676 milliseconds | 21,676 milliseconds |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delgerkhaan, T.; Wei, Q.; Jung, J.; Lee, S.; Na, G.; Kim, B.; Kim, I.-C.; Park, H. Development of a Low-Cost Multi-Physiological Signal Simulation System for Multimodal Wearable Device Calibration. Technologies 2025, 13, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13060239
Delgerkhaan T, Wei Q, Jung J, Lee S, Na G, Kim B, Kim I-C, Park H. Development of a Low-Cost Multi-Physiological Signal Simulation System for Multimodal Wearable Device Calibration. Technologies. 2025; 13(6):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13060239
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelgerkhaan, Tumenkhuslen, Qun Wei, Jiwoo Jung, Sangwon Lee, Gangoh Na, Bongjo Kim, In-Cheol Kim, and Heejoon Park. 2025. "Development of a Low-Cost Multi-Physiological Signal Simulation System for Multimodal Wearable Device Calibration" Technologies 13, no. 6: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13060239
APA StyleDelgerkhaan, T., Wei, Q., Jung, J., Lee, S., Na, G., Kim, B., Kim, I.-C., & Park, H. (2025). Development of a Low-Cost Multi-Physiological Signal Simulation System for Multimodal Wearable Device Calibration. Technologies, 13(6), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13060239







