Green Methodology for Producing Bioactive Nanocomposites of Mesoporous Silica Support for Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Against E. coli and S. aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
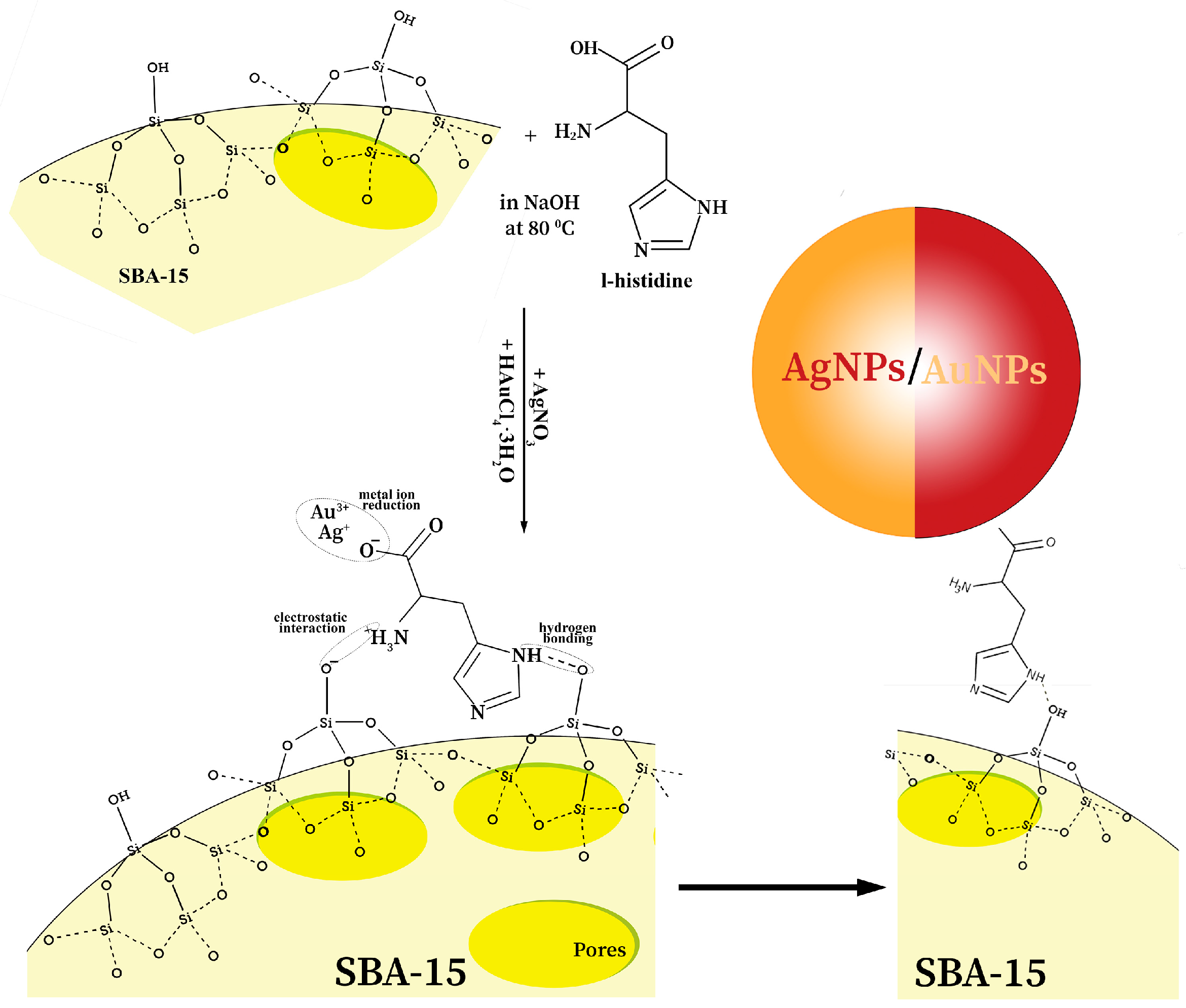
2.2. Preparation of SBA-15 and Nanocomposites
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Antibacterial Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
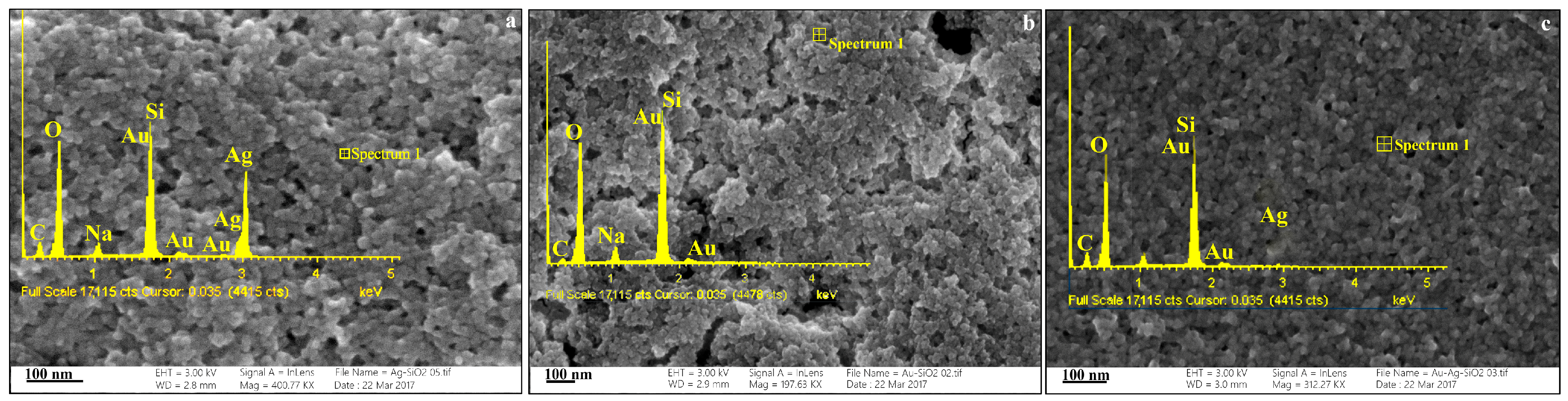
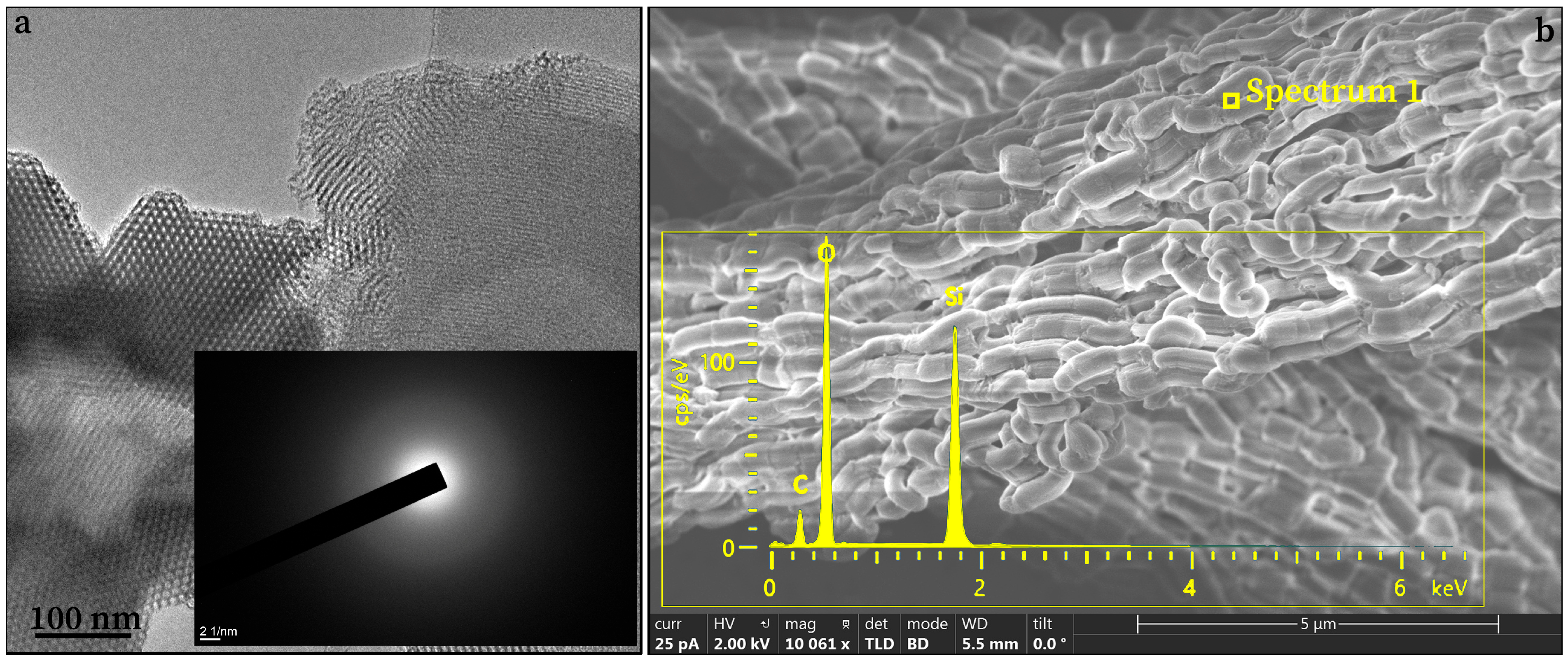
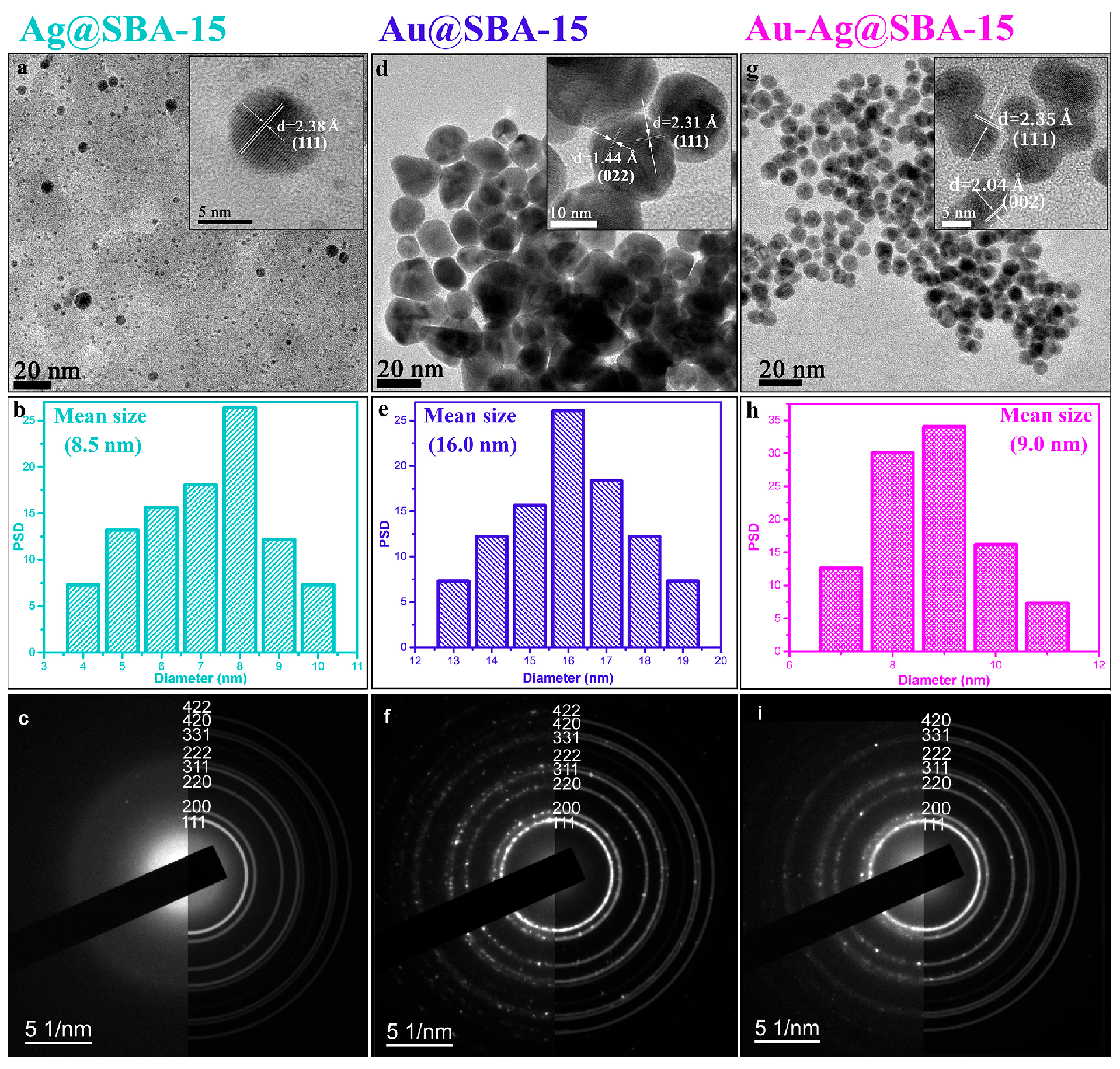
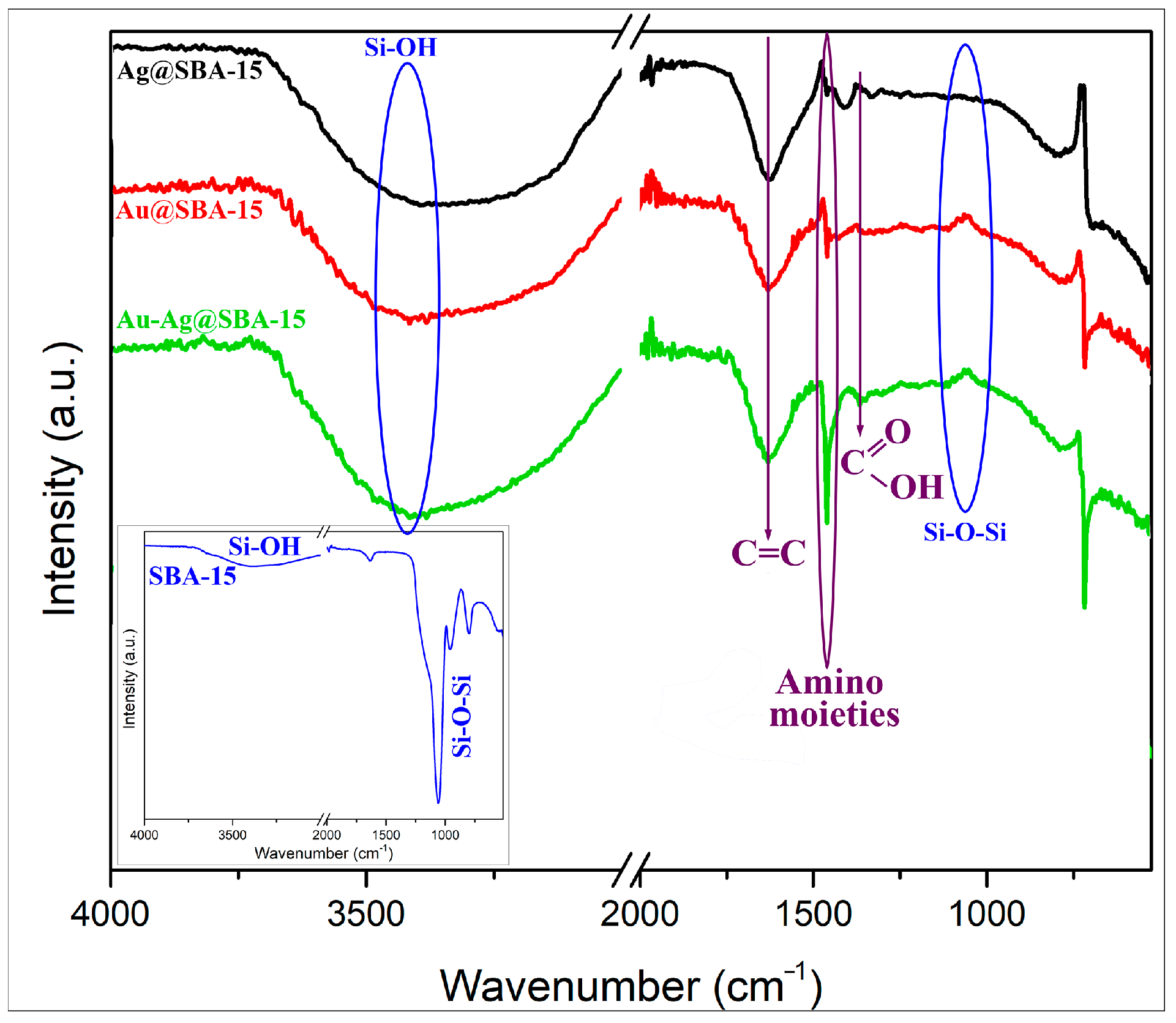
3.1. Characterizations
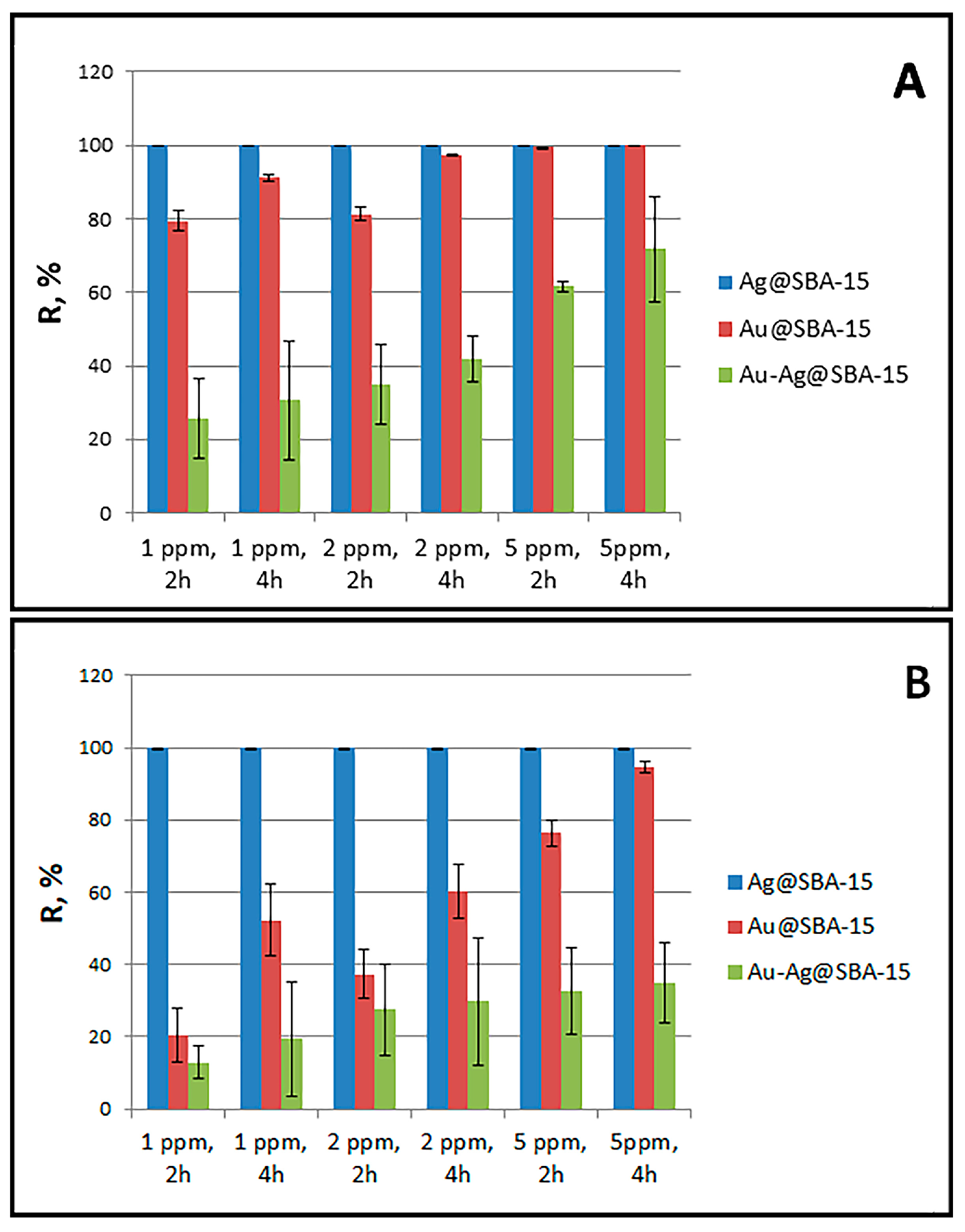
3.2. Antibacterial Efficacy of Nanocomposites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UV-Vis | Ultraviolet-Visible |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| HRTEM | High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| SAED | Selected Area Electron Diffraction |
| FESEM | Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared |
| XPS | X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| MSPs | Mesoporous Silica Particles |
| MetNPs | Metal Nanoparticles |
| TSB | Tryptone Soy Broth |
| LB | Luria–Bertani |
| CFUs | Colony Counting Units |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| fcc | Face-Centered Cubic |
| PSD | Particle Size Distribution |
References
- MacGowan, A.; Macnaughton, E. Antibiotic resistance. Medicine 2017, 45, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.A.; Sharma-Kuinkel, B.K.; Maskarinec, S.A.; Eichenberger, E.T.; Shah, P.P.; Carugati, M.M.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An overview of basic and clinical research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Bal, M.; Pati, S.; Rana, R.; Dixit, S.; Ranjit, M. Antibiotic resistance in toxigenic E. coli: A severe threat to global health. Discov. Med. 2024, 1, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.; Whittaker, A.; Lindgren, M.; Djerf-Pierre, M.; Manderson, L.; Flowers, P. Understanding media publics and the antimicrobial resistance crisis. Glob. Public Health 2018, 13, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Vodnik, V.; Stamenović, U.; Vukoje, I. Nanocomposites of metal nanoparticles and polymer as platform of alternative approach in combating antimicrobial resistance. In Nanotechnology Based Strategies for Combating Antimicrobial Resistance; Wani, I.A., Wani, M.Y., Rai, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; Chapter 18; pp. 489–510. [Google Scholar]
- Beyth, N.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Domb, A.; Khan, W.; Hazan, R. Alternative antimicrobial approach: Nano-antimicrobial materials. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 246012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Tang, H.; Jiang, X. Deploying gold nanomaterials in combating multi-drug-resistant bacteria. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 10066–10087. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardos, A.; Piacenza, E.; Sancenón, F.; Hamidi, M.; Maleki, A.; Turner, R.J.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Mesoporous silica-based materials with bactericidal properties. Small 2019, 15, e1900669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Gu, H.; Chai, Y.; Wang, Y. Silver nanoparticles-decorated and mesoporous silica coated single-walled carbon nanotubes with an enhanced antibacterial activity for killing drug-resistant bacteria. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Yue, R. Excellent antimicrobial properties of silver-loaded mesoporous silica SBA-15. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankala, R.K.; Lin, W.Z.; Lee, C.H. Combating antibiotic resistance through the synergistic effects of mesoporous silica-based hierarchical nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wei, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, D. Large-pore ordered mesoporous materials templated from non-Pluronic amphiphilic block copolymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Gun’ko, Y.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica materials as drug delivery: “The Nightmare” of bacterial infection. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen Karaman, D.; Manner, S.; Rosenholm, J.M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as diagnostic and therapeutic tools: How can they combat bacterial infection? Ther. Deliv. 2018, 9, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. In vivo bio-safety evaluations and diagnostic/therapeutic applications of chemically designed mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3144–3176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Han, N.; Bai, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Che, E.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, T.; et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liong, M.; Lu, J.; Kovochich, M.; Xia, T.; Ruehm, S.G.; Nel, A.E.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J.I. Multifunctional inorganic nanoparticles for imaging, targeting, and drug delivery. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanti, S.K.; Chaudhary, P.; Han, S.S. Environmentally sustainable route to SiO2@Au–Ag nanocomposites for biomedical and catalytic applications. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31311–31321. [Google Scholar]
- Tahmasbi, L.; Sedaghat, T.; Motamedi, H.; Kooti, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles supported copper(II) and nickel(II) Schiff base complexes: Synthesis, characterization, antibacterial activity and enzyme immobilization. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 258, 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Marcelo, G.A.; Duarte, M.P.; Oliveira, E. Gold@mesoporous silica nanocarriers for the effective delivery of antibiotics and by-passing of β-lactam resistance. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1354. [Google Scholar]
- Montero-Oleas, A.; Ricci, M.L.M.; Ortiz, G.P.; Trens, P.; Roupioz, Y.; Kodjikian, S.; Marchi, M.C.; Cattoën, X.; Bilmes, S.A. One-pot synthesis of core–shell au@mSiO2 nanoparticles for photothermal applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2025, 8, 3631–3645. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Mao, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, L.; Wen, S. Silica coated upconversion nanoplatform for Ag-based chemo-/photodynamic therapy against drug-resistant bacteria. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 8685–8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanović, U.; Lazić, V.; Vodnik, V.; Budimir, M.; Marković, Z.; Dimitrijević, S. Copper nanoparticles with high antimicrobial activity. Mater. Lett. 2014, 128, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanović, U.; Vodnik, V.V.; Mitrić, M.; Dimitrijević, S.; Škapin, D.S.; Žunič, V.; Budimir, M.; Stoiljković, M. Nanomaterial with high antimicrobial efficacy—Copper/polyaniline nanocomposite. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1955–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukoje, I.; Lazić, V.; Vodnik, V.; Mitrić, M.; Jokić, B.; Ahrenkiel, S.P.; Nedeljković, J.M.; Radetić, M. The influence of triangular silver nanoplates on antimicrobial activity and color of cotton fabrics pretreated with chitosan. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 4453–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Nazam, N.; Rizvi, M.S.; Ahmad, K.; Baig, H.M.; Lee, J.E.; Choi, I. Mechanistic insights into the antimicrobial actions of metallic nanoparticles and their implications for multidrug resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert-Garzarán, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Influence of the surface functionalization on the fate and performance of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Effect of surface functionalization of MCM-41-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles on the endocytosis by human cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakannan, P.R.; Mantri, K.; Tardio, J.; Bhargava, S.K. High surface area Au–SBA-15 and Au–MCM-41 materials synthesis: Tryptophan amino acid mediated confinement of gold nanostructures within the mesoporous silica pore walls. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 394, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Saratale, R.G.; Kadam, A.A.; Saratale, G.D.; Syed, A.; Bahkali, A.H.; Ghodake, G.S. Histidine functionalized gold nanoparticles for screening aminoglycosides and nanomolar level detection of streptomycin in water, milk, and whey. Chemosensors 2021, 9, e358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumi, G.; Demissie, T.B.; Eswaramoorthy, R.; Bogale, R.F.; Kenasa, G.; Desalegn, T. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles functionalized with histidine and phenylalanine amino acids for potential antioxidant and antibacterial activities. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 24371–24386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, K.; He, C. Continuous Synthesis of Uniformly Dispersed Mesoporous SBA-15 Supported Silver Nanoparticles in a Coiled Flow Inverter Reactor. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 747105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoba, M.; Lim, K.S.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, S.K.; Alagar, M. Immobilization of human carbonic anhydrase on gold nanoparticles assembled onto amine/thiol-functionalized mesoporous SBA-15 for biomimetic sequestration of CO2. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6227–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, Z. Boosting antibacterial activity with mesoporous silica nanoparticles supported silver nanoclusters. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 555, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, M.; France, B.; Bradley, K.A.; Zink, J.I. Antimicrobial activity of silver nanocrystals encapsulated in mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1684–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joardar, S.; Adams, M.L.; Biswas, R.; Deodhar, G.V.; Metzger, K.E.; Deweese, K.; Davidson, M.; Richards, R.M.; Trewyn, B.G.; Biswas, P. Direct synthesis of silver nanoparticles modified spherical mesoporous silica as efficient antibacterial materials. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 313, 110824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodeiro, A.F.; Djafari, J.; Lodeiro, J.F.; Duarte, M.P.; Mauricio, E.M.; Martínez, J.L.C.; Lodeiro, C. Synthesis of mesoporous silica coated gold nanorods loaded with methylene blue and its potentials in antibacterial applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, X. Facile, One-pot synthesis, and antibacterial activity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles decorated with well-dispersed silver nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12038–12045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, A.; Laird, K.; Cross, R.B.M. Shape-dependent antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecium bacterium. App. Surf. Sci. 2017, 424, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameeda, S.; Wanga, Y.; Zhaoa, L.; Xiea, L.; Yinga, Y. Shape-dependent significant physical mutilation and antibacterial mechanisms of gold nanoparticles against foodborne bacterial pathogens (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus) at lower concentrations. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokunešoski, M.; Gulicovski, J.; Matović, B.; Logar, M.; Milonjić, S.K.; Babić, B. Synthesis and surface characterization of ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 124, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokunešoski, M.; Baščarević, Z.; Rakočević, Z.; Šaponjić, A.; Šaponjić, Đ.; Jordanov, D.; Babić, B. Influence of synthesis conditions on morphological features of the SBA-15 containing only elongated and rounded/spherical grains. Sci. Sinter. 2018, 50, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barret, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippens, B.C.; Linsen, B.G.; de Boer, J.H. Studies on pore systems in catalysts I. The adsorption of nitrogen; apparatus and calculation. J. Catalysis 1964, 3, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E2149-01; Standard Test Method for Determining the Antimicrobial Activity of Immobilized Antimicrobial Agents Under Dynamic Contact Conditions. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001. [CrossRef]
- Oszust, M.; Gdula, K.; Borowski, P.; Dąbrowski, A.; Barczak, M. Adsorption of L-histidine onto functionalized mesoporous SBA-15 organosilicas. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Rauwolf, S.; Suyetin, M.; Schwaminger, S.P.; Wenzel, W.; Berensmeier, S. Buffer Influence on the Amino Acid Silica Interaction. ChemPhysChem 2020, 21, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, N.; Golovkova, L. The adsorption of amino acids on the surface of highly dispersed silica. Colloid. J. 2004, 66, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Holland, G.P. Alanine Adsorption and Thermal Condensation at the Interface of Fumed Silica Nanoparticles: A Solid-State NMR Investigation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 25663–25672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iswarya, C.N.; Daniel, S.C.G.K.; Sivakumar, M. Studies on L-histidine capped Ag and Au nanoparticles for dopamine detection. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.M.; Jacob, J.; Philip, D. Green synthesis and applications of Au–Ag bimetallic nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A 2015, 137, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Zhang, L. Ambience-induced alternating change of optical absorption for the porous silica host loaded with silver nanometer particles. Appl. Phys. A 1998, 66, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerme, J.; Palpant, B.; Prevel, B.; Pellarin, M.; Treilleux, M.; Vialle, J.L.; Perez, A.; Broyer, M. Quenching of size effects in free and matrix-embedded silver clusters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 5105–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Mayer, B.; Xia, Y. Template-engaged replacement reaction: A one-step approach to the large-scale synthesis of metal nanostructures with hollow interiors. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, L.; Lu, X.; Xia, Y. A comparative study of galvanic replacement reactions involving Ag nanocubes and AuCl2− or AuCl4−. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2517–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, K.W.; Dyson, D.J.; Keown, S.R. Interpretation of Electron Diffraction Patterns; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, S.; Shields, J.E.; Thomas, M.A.; Thommes, M. Charactrization of Porous Solids and Powders: Surface Area, Pore Size and Density; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Niroumand, U.; Firouzabadi, N.; Goshtasbi, G.; Hassani, B.; Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. The effect of size, morphology and surface properties of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on pharmacokinetic aspects and potential toxicity concerns. REVIEW article. Front. Mater. Sec. Polym. Compos. Mater. 2023, 10, 1189463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhat, T.V.; Astam, K.P.; Dukjoon, K. Pore size and concentration effect of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on coefficient of thermal expansion and optical transparency of poly(ether sulfone) film. Phys. Chem. Chem. 2016, 19, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareen, S.; Mutreja, V.; Singha, S.; Pal, B. Highly dispersed Au, Ag and Cu nanoparticles in mesoporous SBA-15 for highly selective catalytic reduction of nitroaromatics. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.A.; Iqbal, J.; Nasir, J.A.; Zahra, S.A.; Shahbaz, A.; Uddin, S.; Hameed, S.; Gul, F.; Kanwal, S.; Mahmood, T. Environmentally friendly green approach for the fabrication of silver oxide nanoparticles: Characterization and diverse biomedical applications. Microsc. Res. Techn. 2020, 83, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, T.; Komiyama, H.; Tanaka, K. Gas-sensitive electrical-conduction and its mechanism in a Ag/insulator system with locally discontinuous structure. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 26, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Tan, M.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L. Reversible transition between transparency and opacity for porous silica host dispersed with silver nanometer particles within its pores. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 2980–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bail, A.; Duroy, H.; Fourquet, J.L. Ab-initio structure determination of LiSbWO6 by X-ray powder diffraction. Mater. Res. Bull. 1988, 23, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carvajal, J. Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1993, 192, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Baier, F.; Rosin, A.; Gerdes, T.; Schafföner, S. Structural characterization of the near-surface region of soda–lime–silica glass by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Int. J. Appl. Glass. Sci. 2023, 14, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.; Chaves, C.R.; Bargiela, P.; da Graça Carneiro da Rocha, M.; da Silva, A.F.; Chubaci, J.F.D.; Boström, M.; Persson, C.; Malta, M. Surface studies of the chemical environment in gold nanorods supported by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and ab initio calculations. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhendhi, A.; Prabakar, D.; Jacob, J.M.; Karuppusamy, I.; Saratale, R.G. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Gelidium amansii and its antimicrobial property against various pathogenic bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okkeh, M.; Bloise, N.; Restivo, E.; De Vita, L.; Pallavicini, P.; Visai, L. Gold Nanoparticles: Can They Be the Next Magic Bullet for Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria? Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skłodowski, K.; Chmielewska-Deptuła, S.J.; Piktel, E.; Wolak, P.; Wollny, T.; Bucki, R. Metallic Nanosystems in the Development of Antimicrobial Strategies with High Antimicrobial Activity and High Biocompatibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanović, U.; Dimitrijević, S.; Škapin, D.S.; Popović, M.; Rakočević, Z.; Leskovac, A.; Petrović, S.; Stoiljković, M.; Vodnik, V. Copper-polyaniline nanocomposite: Role of physicochemical properties on the antimicrobial activity and genotoxicity evaluation. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenović, U.; Davidović, S.; Petrović, S.; Leskovac, A.; Stoiljković, M.; Vodnik, V. Antimicrobial and biological effects of polyaniline/polyvinylpyrrolidone nanocomposites loaded silver nanospheres/triangles. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 12711–12720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makabenta, J.M.V.; Nabawy, A.; Li, C.H.; Malan, S.S.; Patel, R.; Rottello, V.M. Nanomaterial-based therapeutics for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseem, T.; Waseem, M. A comprehensive review on the role of some important nanocomposites for antimicrobial and wastewater applications. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 2221–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




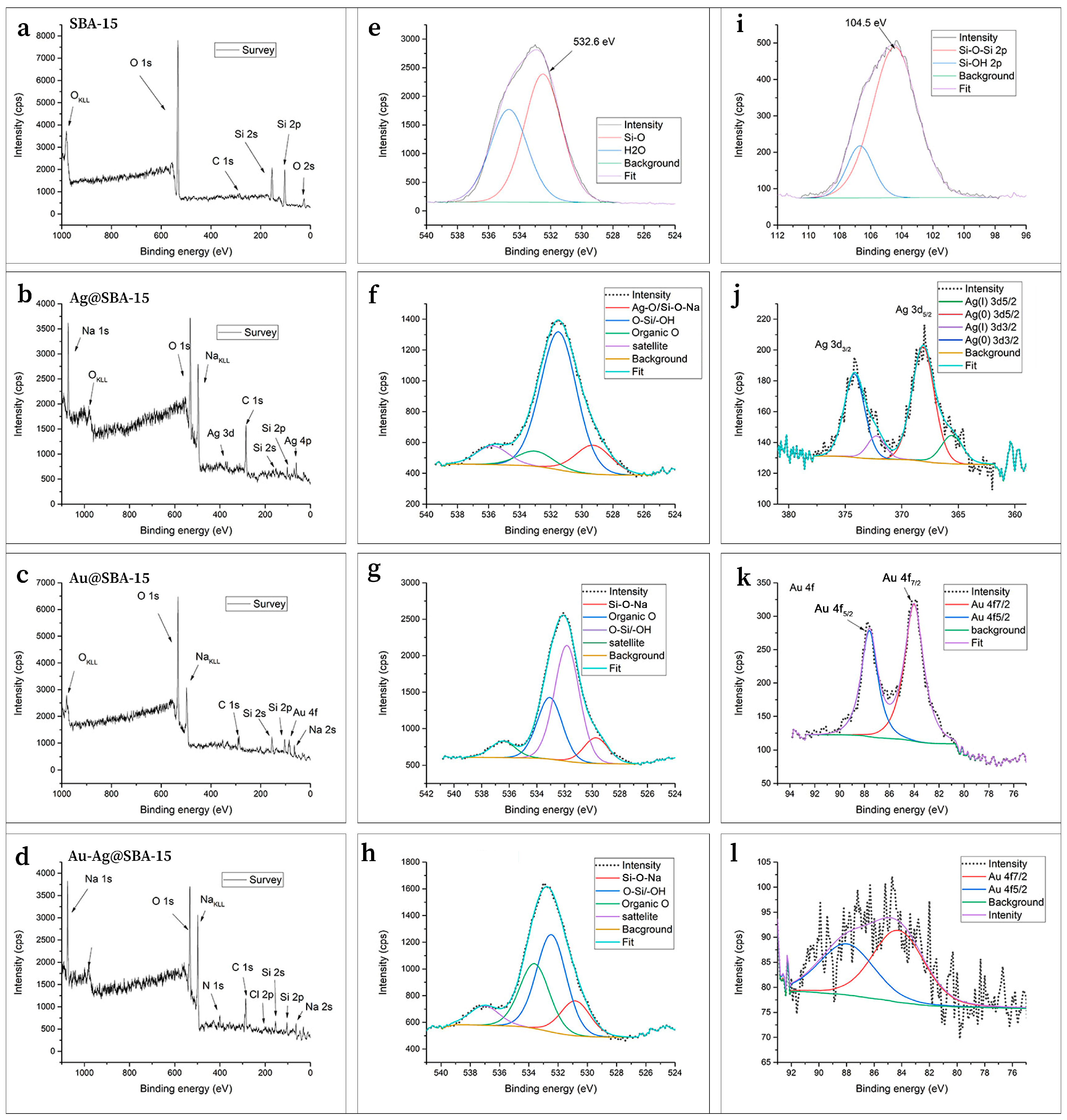
| Nanocomposites of Ag– or AuNPs—Mesoporous Silica | Preparation Method; Size (nm), Shape, and λmax of Ag or AuNPs | Ag or Au Concentration (µg/mL) | Strain | Microbial Reduction (R, %), Time of Incubation (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag–mesoporous silica | Prepared AgNPs (20 nm spheres, 425 nm) by boiling solution of Ag+, oleylamine, and toluene under nitrogen. These were used as the seed for the growth of silica. | 20–100 | E. coli | 100 µg/mL fully inhibited colonies [35]. |
| Ag–mesoporous silica | Prepared AgNPs (2 nm nanoclusters, 481 nm) by reduction of AgNO3 with NaBH4. These were used with Stober method to synthesize nanocomposite. | 5.0 | S. aureus | 99.99% after 12 h [34]. |
| Ag–mesoporous silica | In situ synthesis of AgNPs (15–18 nm in size) and silica particles by cetyltrimethylammonium perchlorate and TEOS. | 6.1 | 95% after 24 h [36]. | |
| Au–mesoporous silica | Synthesis of Au nanorods (length 42.4 ± 9.0 nm, width 19.2 ± 3.8 nm, 518 and 656 nm) coated with a mesoporous silica shell and conjugated with methylene blue. | 1.0 × 103 | E. coli, S. aureus | ~8 log10 unit reduction against both strains after laser irradiation during a short time period [37]. |
| Ag–mesoporous silica | In situ synthesis silica and AgNPs (2–10 nm spheres) by co-condensation method in dilute sodium hydroxide solution (Cai reaction). | 3.36 13.44 | E. coli,
S. aureus | 99.99% of E. coli was killed by the first 2 h; 99.99% of S. aureus was killed in the first 2 h [38]. |
| Ag–mesoporous silica, Au–mesoporous silica | In situ synthesis of AgNPs (8.5 nm spheres, 432 nm) and AuNPs (16 nm spheres, 527 nm) in the prepared silica solution by Pluronic P123 and TEOS. | 1 5 | E. coli, S. aureus | 99.99% reduction in both strains after 2 h; 99.98% E. coli and 94.71 % S. aureus, after 4 h [This study]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stamenović, U.; Mašojević, D.; Kokunešoski, M.; Otoničar, M.; Davidović, S.; Škapin, S.; Barudžija, T.; Pjević, D.; Arsić, T.M.; Vodnik, V. Green Methodology for Producing Bioactive Nanocomposites of Mesoporous Silica Support for Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Against E. coli and S. aureus. Technologies 2025, 13, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13100458
Stamenović U, Mašojević D, Kokunešoski M, Otoničar M, Davidović S, Škapin S, Barudžija T, Pjević D, Arsić TM, Vodnik V. Green Methodology for Producing Bioactive Nanocomposites of Mesoporous Silica Support for Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Against E. coli and S. aureus. Technologies. 2025; 13(10):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13100458
Chicago/Turabian StyleStamenović, Una, Dijana Mašojević, Maja Kokunešoski, Mojca Otoničar, Slađana Davidović, Srečo Škapin, Tanja Barudžija, Dejan Pjević, Tamara Minović Arsić, and Vesna Vodnik. 2025. "Green Methodology for Producing Bioactive Nanocomposites of Mesoporous Silica Support for Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Against E. coli and S. aureus" Technologies 13, no. 10: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13100458
APA StyleStamenović, U., Mašojević, D., Kokunešoski, M., Otoničar, M., Davidović, S., Škapin, S., Barudžija, T., Pjević, D., Arsić, T. M., & Vodnik, V. (2025). Green Methodology for Producing Bioactive Nanocomposites of Mesoporous Silica Support for Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Against E. coli and S. aureus. Technologies, 13(10), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13100458






