Abstract
This work proposes a modular learning framework (MIRA) for rehabilitation robots based on a new deep recurrent neural network (RNN) that achieves adaptive multi-joint motion imitation. The RNN is fed with the fundamental frequencies as well as the ranges of the joint trajectories, in order to predict the future joint trajectories of the robot. The proposed framework also uses a Segment Online Dynamic Time Warping (SODTW) algorithm to quantify the closeness between the robot and patient motion. The SODTW cost decides the amount of modification needed in the inputs to our deep RNN network, which in turn adapts the robot movements. By keeping the prediction mechanism (RNN) and adaptation mechanism (SODTW) separate, the framework achieves modularity, flexibility, and scalability. We tried both Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) RNN architectures within our proposed framework. Experiments involved a group of 15 human subjects performing a range of motion tasks in conjunction with our social robot, Zeno. Comparative analysis of the results demonstrated the superior performance of the LSTM RNN across multiple task variations, highlighting its enhanced capability for adaptive motion imitation.
1. Introduction
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation help patients recover from various conditions, including surgeries, injuries, and neurological issues [1]. In the last few decades, researchers have started exploring the use of robots and machine learning algorithms in patient rehabilitation [2]. The goal is to improve patients’ mobility, strength, and independence [3], while reducing the burden on the healthcare providers. In the recent past, few healthcare professionals have used social robots and AI-enabled solutions in their physiotherapy programs [4]. Some of these robot-assisted physiotherapy solutions have shown promise in areas like the treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). The use of social robots like Nao, Zeno, and Milo has been proved to help children with autism improve their social, physical, and communication skills [2,5]. The works presented in [6,7] discuss positive results for ASD treatments using social robots. However, some of the issues like technology integration, suitable training paradigms, high costs, and standardizing treatment protocols still need to be addressed.
Imitation learning is a type of machine learning method where robots learn by mimicking human/supervisor actions and has already shown significant potential in robot-assisted physiotherapy, especially for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Researchers have developed various imitation learning algorithms to enable robots to learn and replicate the movements essential for physiotherapy and rehabilitation sessions [8,9,10,11]. These robots, once trained, can then demonstrate the pre-learned movements to patients and record their responses for further assessment [12]. Notably, Zheng et al. [13] proposed a learning framework specifically for robot-assisted skill training tailored for children with ASD. Furthermore, techniques such as deterministic policy gradient, approximate dynamic programming, and recurrent neural networks have recently been utilized for imitation learning in social robots [14,15,16].
The authors of [17] developed a new shared control method using reinforcement learning (RL) to help people with walking difficulties. Another study by the same group [18] exploited a reinforcement learning-based master–slave robotics system for mirror therapy in patients with limb impairments. Bishe et al. [19] proposed and tested a novel adaptive ankle exoskeleton control that showed promise in improving the walking ability of patients. The use of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) in place of a standard RL has been useful in solving complex problems that traditional reinforcement learning struggles with. Taghavi et al. [20] used a DRL technique called Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) to help children with ASD learn movements through imitation. This DDPG-based method predicted the “shape” and “speed” of robot movements based on recorded joint motions, thereby adapting to the patient’s physical ability. However, this DDPG method could only be used in adaptive motion imitation (AMI) for single-joint movements and utilized batch training, which could make it difficult to generalize to more complex movements with multiple joints. Additionally, both RL and DRL methods can be computationally expensive and time-consuming because they need a fair amount of interaction with the environment to find the optimal/semi-optimal solutions [14,15,16]. Similarly, in wafer defect detection, an Incremental Learning (IL) approach has been shown to reduce training time by 60% and improve accuracy by 10% compared to traditional methods, demonstrating the potential benefits of advanced neural network techniques in complex tasks [21]. Hence, implementing these robot-enabled rehab techniques in many real-world settings is not straightforward as the resources and time are limited.
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have shown better performance than Reinforcement Learning (RL) in predicting sequences in tasks that change over time (trajectories and data with temporal component), like physiotherapy exercises [22,23]. The paper [24] used RNNs for imitation learning in social settings based on data from human interactions. Kim et al. [25] developed a new imitation learning method for robots to learn some specific tasks and transfer learned skills from force sensor and gaze data. Long Short-Term Memory RNN (LSTM-RNN) was used for exploiting the visual changes in the training images for imitation learning in [26]. Similarly, Johnson et al. [27] used an LSTM-RNN and a special objective function to predict the movement of pedestrians in a dynamic environment. A novel concept of parametric bias was proposed in [28] for RNN-based adaptive imitation learning, which enabled the robot to adjust its behavior according to task variations.
One of the practical issues in machine learning-inspired robot-assisted physiotherapy is the absence of a uniform standard or metric that can be used to quantify the efficiency of imitation. Most of the above-mentioned studies advocate diverse training methods, network architecture, and training methods which may lead to different results even for similar physiotherapy exercises. A simple yet effective way to quantify the similarities or differences between the robot and patient’s movements is to find the discrepancy between the joint trajectories. This measurement could then be used to train or adapt the neural networks which in turn drive the robot. The Segment Online Dynamic Time Warping (SODTW) algorithm [2] is a suitable option since it does not depend on the initial temporal variations (delay in the onset of proper imitation) of the joint trajectories. In robot-assisted physiotherapy, it is important to measure both the difference in movement size between the patient and robot, and the speed at which the patient repeats the movement. The SODTW algorithm can do both of these things, which could help standardize how we assess a patient’s physical ability. However, SODTW alone can not directly influence the robot movements, and a suitable neural network is needed to translate the information into proper meaningful robot movements.
To tackle the difficulties in multi-joint adaptive motion imitation, we propose a modular SODTW-based framework to predict the periodic physiotherapy movements of a robot using deep recurrent neural networks. The SODTW metric is exploited to adjust the network inputs, which in turn modify the robot’s movements based on the subject’s responses. This approach is different from our previous work with DDPG [20] because it reverses the input–output mapping. This helps maintain a comparatively smaller input space dimension even when the number of joints involved in physiotherapy exercise increases.
2. Proposed MIRA Framework
We introduce a new, modular framework (Figure 1) for Multi-Joint Imitation with Recurrent Adaptation (MIRA) in robot-assisted physiotherapy. This framework is unique because it allows the reference trajectory predictor (deep RNN layer) and the adaptation algorithm (SODTW module) to be changed independently for different types of physiotherapy sessions. This flexibility makes it easier to use our framework for complex movements with multiple joints and standardizes motion adaptation.
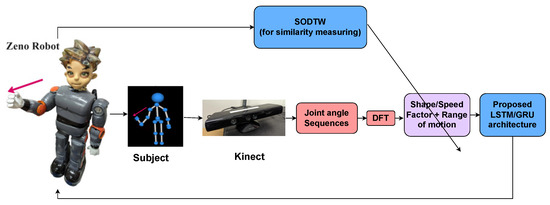
Figure 1.
Proposed MIRA framework.
We present an efficient way to train a deep RNN that can create reference trajectories for the robot based on the subject’s ability to imitate. The network is trained using only the basic frequency components (amplitude and frequency) and the range of periodic motion. After training, the RNN layer can create a suitable reference trajectory for the robot, which can adapt to different variations in shape and speed of the desired motion profile.
Our proposed framework is for the imitation of multi-joint adaptive motion comprising a series of synchronized tasks. To begin a robot-assisted physiotherapy session, a specific social robot, in this case, Zeno [29], shows a periodic upper-arm motion to human subjects. The subjects are then asked to replicate the robot’s upper-body motion as accurately as they can. The movements of the subjects are recorded using a Kinect camera, and the joint trajectories for both the human and Zeno are calculated. The periodic joint trajectories of the subject are subjected to a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) to generate fundamental components of amplitude (shape) and frequency (speed). Simultaneously, the multi-joint SODTW cost, which measures the similarity between the recorded human motion and the reference Zeno motion, is calculated. The fundamental DFT coefficients are later normalized to ensure consistent training across all ranges of motion. These coefficients, along with the range of motion, are then fed into our LSTM/GRU for training, enabling it to predict suitable reference joint trajectory commands for Zeno. The multi-joint SODTW cost is used as a metric to adjust the inputs (DFT coefficients) so that the trained network can modify the reference commands for Zeno proportionally.
To compare and align two time series sequences with variations in time and speed, the Segment Online Dynamic Time Warping (SODTW) algorithm, a variant of the Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) algorithm [30], is utilized. The SODTW algorithm computes the difference between the samples of the two signals using a dynamic error computation approach, given a reference signal of M samples and a measured signal of N samples. The mathematical representation of a single joint SODTW process involves the Euclidean norm of the difference between the ith sample of the reference trajectory and the jth sample of the measured trajectory is given by:
where is the Euclidean distance between x and y, i = 1, …, m, j = 1, …, n, and D(m, n) is the DTW cost. The SODTW algorithm recursively calculates the similarity cost between two samples based on the cost of previous samples, and the final cost for the entire motion sequences is given by . The multi-joint SODTW is a combination of single-joint SODTWs, mathematically represented as a convex combination of single-joint SODTWs for each joint in a specific motion.
where the value of a positive constant < 1 in the formula is decided by the weighting of a particular joint in the overall motion.
When a subject is unable to satisfactorily mimic a specific motion demonstrated by the robot, the SODTW cost increases, signaling the need to simplify the physiotherapy until the subject achieves a satisfactory cost. Conversely, a low SODTW cost indicates that the subject has perfectly imitated the motion. In such instances, the complexity of the physiotherapy should be increased. Slower motions are generally observed to be more challenging to imitate compared to faster ones. Therefore, the reference trajectory of the Zeno robot is slowed down when the user has a lower SODTW cost and vice versa.
We tested our proposed framework with both LSTM- and GRU-based RNN. Our social robot, Zeno, was used to carry out the physiotherapy sessions involving 15 volunteers [31]. During training, we collected joint trajectory data from 15 subjects imitating an upper-body motion demonstrated by Zeno. We used data from 10 subjects to train the LSTM- and GRU-based RNNs. Then, we asked 5 subjects to intentionally change the motion and used these data to test our framework. The experiments showed that Zeno’s motion adapted well to all the variations in motion imitation from the test subjects.
3. Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) Architectures for Reference Generation
In the deep learning literature, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have had a prominent role in modeling sequences. Their role in modeling temporal patterns has seen remarkable developments through the 1990s [32]. RNNs are neural networks that sequentially process every input to generate outcomes. This is in contrast to simple feed-forward neural networks, where the temporal sequence of the data is not preserved. This advantage of RNNs over simple feed-forward neural networks has been leveraged for a multitude of activities like text generation [33], weather forecasting [34], time series forecasting [35], signal forecasting [36], etc. However, this sequential nature of RNNs creates limitations when processing longer data sequences. This has been characterized by the vanishing and exploding gradient problems in RNNs [37].
To address the limitations of RNNs, a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model was proposed by the milestone paper [38]. The structure of an LSTM network is complex when compared to a vanilla RNN. In contrast to an RNN unit, it comprises three gates: an input gate, a forget gate, and an output gate. This adds more parameters as compared to an RNN, but in turn diminishes the problem of vanishing gradients. The equations describing the LSTM model’s gates are given by the following equations [38]:
where represents the sigmoid activation function, represents the weight matrices that are used for transforming the input and the hidden state . represent the weight matrices that transform the input and the hidden state to the input gate, and do the same for the output gate, and , and are the bias terms. The notations used here have been adopted from the authors of [39]. The cell state and the hidden state can be calculated as follows [38,39]:
where and are the weight matrices, and is the bias term. A typical LSTM cell is shown in Figure 2.
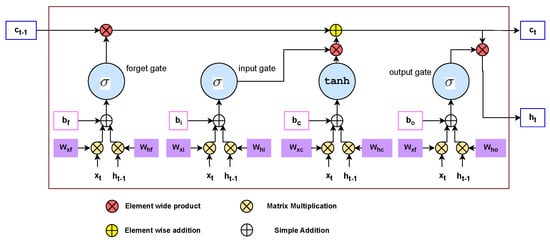
Figure 2.
Long Short−Term Memory cell.
GRUs, like LSTMs, have been structured to prevent the vanishing gradient problem of classical RNNs. As compared to LSTM models, GRUs have a much similar gating mechanism [39]. The equations governing GRUs can be represented by [39]:
In the equation above, is the reset gate, is the update gate, is the hidden unit for the current time step, , is the candidate hidden state, and are bias terms, and and are the weight matrices [39]. The reset gate is analogous to the forget gate in LSTM models. A GRU computational graph is shown in Figure 3.
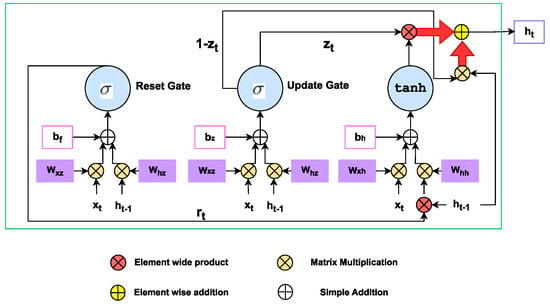
Figure 3.
Gated Recurrent Unit.
4. Results and Discussion
To assess the effectiveness of the proposed Multi-Joint Imitation with Recurrent Adaptation (MIRA) framework, we carried out experiments involving 15 human participants. These individuals were asked to replicate a series of hand movements demonstrated by our Zeno robot (see Figure 4). Each motion sequence was performed at three different speed settings—slow, normal, and fast—as well as three range settings (low, normal, high). The Kinect camera was used to capture the participants’ movements, and the collected data were analyzed to compute the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of the motion waveform and its Segment-based Online Dynamic Time Warping (SODTW) cost when compared to the robot’s motion.
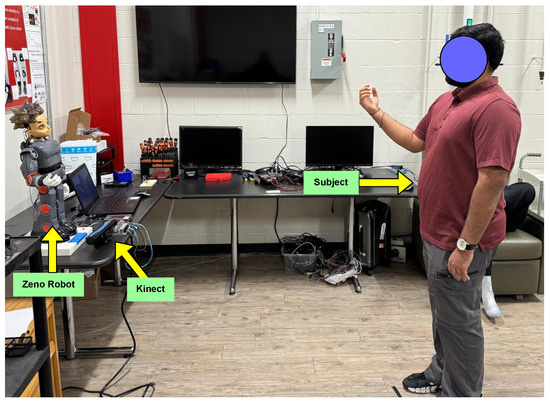

Figure 4.
Experiment setup.
The Zeno robot’s arm has four degrees of freedom (DoFs), specifically comprising the shoulder joints ( and ), and elbow joints ( and ) as illustrated in Figure 5. Depending on the arm motion, certain joints are more dominant than others. To assess the resilience of our framework, we selected a three-degree-of-freedom (DoF) arm motion: a diagonal arm lift with elbow bend. Initially, we calculated the contribution percentage of each joint in performing this motion. For the selected motion, the joint angles , , and had the most impact (Table 1), and therefore, the SODTW cost was calculated based on these angles exclusively.
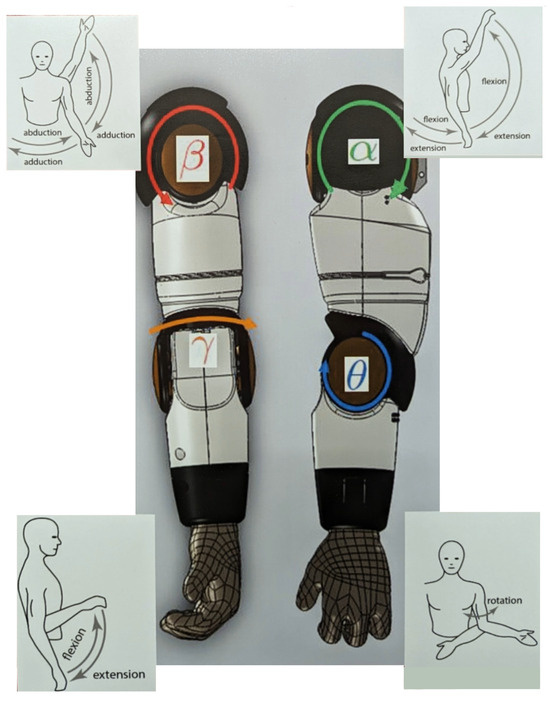

Figure 5.
Zeno’s arm with its four degrees of freedom [29].

Table 1.
Weight (in terms of range) of joint angle contribution during a diagonal arm motion with elbow bend.
The average SODTW cost was derived from the participants. Findings indicated that replicating fast motions was simpler, whereas slow motions presented more challenges for the participants. Regarding motion range, lower ranges were easier to imitate. Consequently, the magnitude was increased and frequency reduced to add complexity to the imitation, and vice versa. During the experiment, when the SODTW cost was high, it indicated that the subject had difficulty imitating the motion. Thus, we reduced the range or increased the speed of the reference motion (Zeno) to make it easier for the subject. Conversely, when the SODTW cost was low, it signaled that the subject was performing the motion efficiently. For this case, we either increased the range or decreased the speed, or both, to make it more challenging for the subjects.
In order to test the effectiveness of our proposed method for predicting future joint movements using Fourier coefficients, we first set up a baseline using a deep recurrent neural network (RNN). This RNN was given normalized and scaled previous joint angle data and was trained to forecast future joint movements. Each subject’s data were limited to a fixed number of samples (180) to ensure consistent processing. The training was conducted using data from 10 subjects, and testing was performed on data from a separate set of subjects. The cost function for this baseline network was determined as the root-mean-square (RMS) error between predicted and actual trajectories (Figure 6).
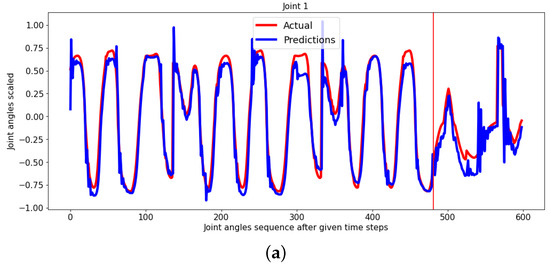
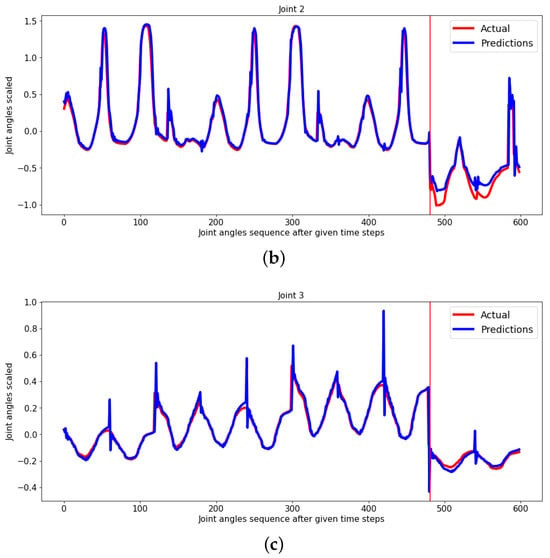
Figure 6.
RNN baseline output.
To further confirm the effectiveness of the proposed approach in predicting future joint trajectories based on Fourier coefficients, we used an identical dataset containing data from five subjects. Fourier coefficients and the motion range of each subject were utilized to train the neural network. Resampling techniques were applied to accommodate the varying shapes and speeds exhibited by subjects, adjusting Fourier coefficients accordingly (Figure 7).
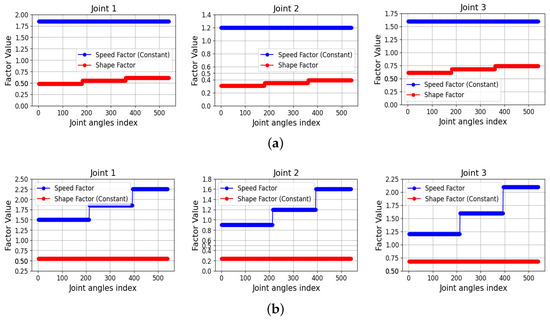
Figure 7.
Fourier coefficients (shape and speed factor). (a) Lower range, normal, and higher range motion of one subject data with fixed speed. (b) Oversampled (slower), normal, and undersampled (faster) version of one subject data with fixed range.
Our method utilized the two most significant amplitude components as the shape factor and frequency for the speed factor. The architecture of the deep network was optimized by varying the number of LSTM/GRU layers, dense layers, and learning rate, achieving the best results. The final architecture is presented in Figure 8.
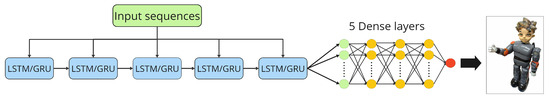
Figure 8.
Proposed five-layer GRU/LSTM architecture.
Each subject’s trajectory data were segmented into three cycles, with each cycle consisting of 60 samples. This fixed cycle length ensured uniform data processing. It is crucial to note that the inputs for each subject remained consistent across all output samples, including Fourier coefficients and the range of motion. The training of our network employed the Adam optimizer, which facilitated weight updates through backpropagation in time. The Adam optimizer is particularly suitable for optimizing convex and stochastic loss functions, using first-order gradient descent.
To assess the robustness of our framework, we instructed participants to deliberately deviate from Zeno’s motions in various ways, including moving slower, faster, or within a lower or higher range. For each of these four scenarios, we tested our network once with the LSTM and once with the GRU architecture. The reference trajectory, generated from the LSTM/GRU architecture, was then compared to the subject’s joint trajectory in each scenario (Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12), and corresponding RMSE values are summarized in Table 2. From Table 2, it can be concluded that the LSTM architecture performed better for out training dataset (it may not be same for all imitation learning tasks). The better expressiveness and prediction capability of LSTM may have stemmed from the presence of additional memory cells and output gates in the network.
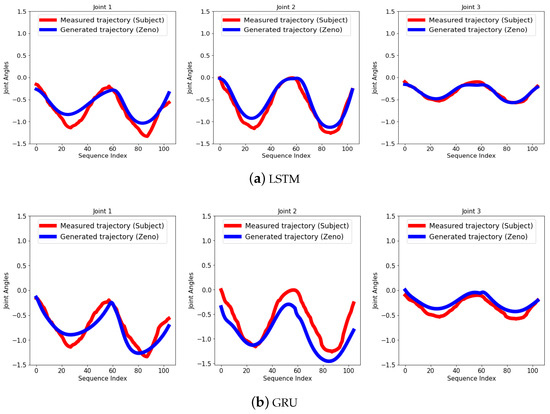
Figure 9.
Generated sequence after training for a subject performing a motion with a lower range.
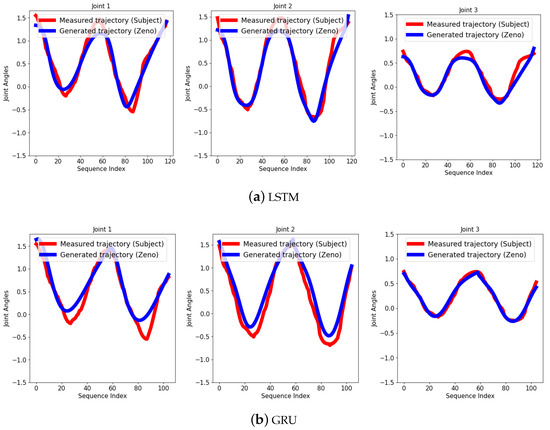
Figure 10.
Generated sequence after training for a subject performing a motion with a higher range.
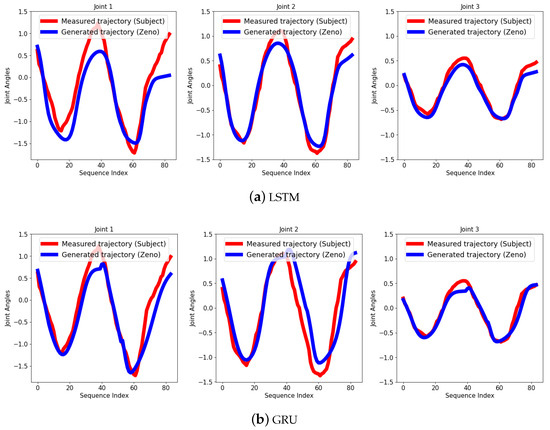
Figure 11.
Generated sequence after training for a subject performing a motion with a faster speed.
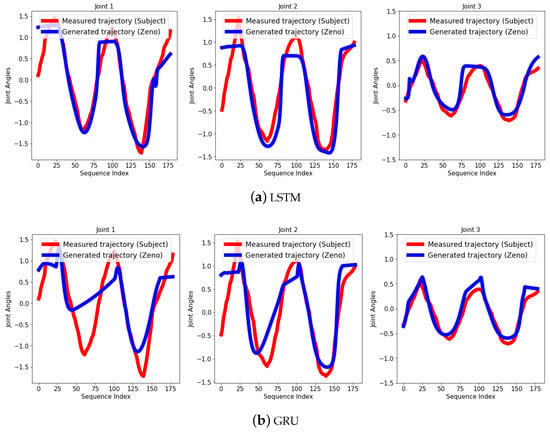
Figure 12.
Generated sequence after training for a subject performing a motion with a slower speed.

Table 2.
Comparison of average RMSE for different task variations.
The training of our algorithm was carried out on Google Colab, utilizing an NVIDIA T4 GPU. This NVIDIA T4 GPU is optimized for high-performance computing and AI workloads, featuring 16 GB of GDDR6 memory and Tensor Cores designed for efficient deep learning tasks. The training duration typically varied from 11 to 13 min for all joint sequences and epochs. Additionally, widely used Python libraries such as TensorFlow and Keras were utilized for developing the deep neural networks.
In one scenario, to assess the robustness of our framework, we instructed a specific test subject to deliberately perform a motion with varying speed and shape simultaneously. Given the LSTM’s superior performance in previous tasks, we opted to exclusively utilize the LSTM network rather than the GRU for this scenario. As depicted in Figure 13, our framework adeptly adjusted to these variations. The root-mean-square error (RMSE) for the LSTM network was determined to be 0.052.
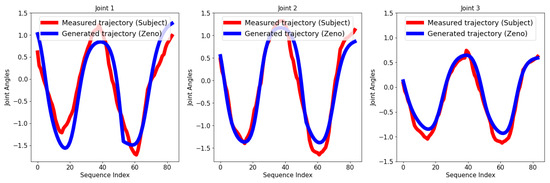
Figure 13.
Generated sequence after training for a subject performing a motion with a higher range and faster speed.
5. Conclusions
This study presented a novel modular framework, called MIRA, for robot-assisted physiotherapy. The framework utilized a deep recurrent neural network (RNN) for prediction, with the LSTM RNN architecture proving to be superior in relation to a GRU in our experimental evaluations, where our social robot Zeno had to adapt according to the ability of human subjects. Segment Online Dynamic Time Warping (SODTW) was used for quantifying the discrepancies between robot and human movements, enabling adaptive and personalized motion imitation. MIRA was designed to help individuals with movement deficiencies train and improve their efficiency through personalized robotic exercises that mimic human movements. We trained the framework with a cohort of 10 adult participants to create these personalized exercises and further validated its effectiveness with a separate cohort of 5 adult participants. Our experiments demonstrated that this approach improved the accuracy of the robot’s movement prediction by an average of 15.8% across all of our 15 subjects’ data compared to previous methods, and it holds promise for personalized therapy, particularly for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). As this framework is flexible and can handle complex motions, we plan to expand it to handle non-periodic movements as well as imitating full-body movements in the future. To achieve this, we intend to enhance our LSTM/RNN approach by incorporating advanced techniques such as attention mechanisms and transformer models to better capture and replicate the complexity and variability of full-body and non-periodic movements.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.; methodology, A.A. and M.M.R.; software, A.A.; validation, A.A. and M.M.R.; formal analysis, A.A. and M.M.R.; investigation, A.A.; resources, M.M.R. and A.A.; data curation, A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A., M.M.R., and R.M.; writing—review and editing, M.M.R. and D.O.P.; visualization, R.M.; supervision, M.M.R. and D.O.P.; project administration, M.M.R. and D.O.P.; funding acquisition, D.O.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by NSF grant numbers #1838808 and #1849213.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the UofL Institutional Review Boards (IRB number: 18.0726, IRB approval date: 18 July 2024). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data cannot be shared due to subjects’ privacy.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Namrata Balakrishnan for providing the data used in this research. The data from their paper were invaluable to our study, and we appreciate their efforts in sharing this information. This research would not have been possible without their contribution.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Andrade, R.M.; Ulhoa, P.H.F.; Vimieiro, C.B.S. Designing a Highly Backdrivable and Kinematic Compatible Magneto-Rheological Knee Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 5724–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzi, E.; Canzi, E.; Piga, G.; Galassi, A.; Lippi, G.; Benassi, G. Segment Online DTW for Smart Rehabilitation of ASD Children: A Preliminary Study. In Proceedings of the 4th EAI International Conference on Smart Objects and Technologies for Social Good (GOODTECHS), Rome, Italy, 26 October 2015; pp. 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Frolov, A.; Kozlovskaya, I.; Biryukova, E.; Bobrov, P. Use of robotic devices in post-stroke rehabilitation. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2018, 48, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, T.; Hussain, S.; Martinez-Marroquin, E.; Brown, N.A.T.; Jamwal, P.K. Stiffness-Observer-Based Adaptive Control of an Intrinsically Compliant Parallel Wrist Rehabilitation Robot. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2023, 53, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtay, M.; Chevalère, J.; Lazarides, R.; Hafner, V.V. Learning in Social Interaction: Perspectives from Psychology and Robotics. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Development and Learning (ICDL), Beijing, China, 23–26 August 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayasinghe, I.B.; Ranatunga, I.; Balakrishnan, N.; Bugnariu, N.; Popa, D.O. Human–Robot Gesture Analysis for Objective Assessment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2016, 8, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, H.; Akgun, S.A.; Saleh, S.; Dautenhahn, K. A survey on the design and evolution of social robots—Past, present and future. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2022, 156, 104193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbeel, P.; Ng, A.Y. Apprenticeship Learning via Inverse Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Machine Learning, Banff, AB, Canada, 4–8 July 2004; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Argall, B.D.; Chernova, S.; Veloso, M.; Browning, B. A Survey of Robot Learning from Demonstration. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2009, 57, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashary, A.; Rayguru, M.M.; Dowdy, J.; Taghavi, N.; Popa, D.O. Adaptive Motion Imitation for Robot Assisted Physiotherapy Using Dynamic Time Warping and Recurrent Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environme, Crete Greece, 26–28 June 2024; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashary, A.; Rayguru, M.M.; SharafianArdakani, P.; Kondaurova, I.; Popa, D.O. Multi-Joint Adaptive Motion Imitation in Robot-Assisted Physiotherapy with Dynamic Time Warping and Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the SoutheastCon 2024, Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–24 March 2024; pp. 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.; Gaber, M.M.; Elyan, E. Imitation Learning: A Survey of Learning Methods. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2017, 48, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Young, E.M.; Swanson, A.R.; Weitlauf, A.S.; Warren, Z.E.; Sarkar, N. Robot-Mediated Imitation Skill Training for Children With Autism. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Peng, L.; Cao, J.; Fu, X.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Yang, J. Ensemble Bootstrapped Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient for Vision-Based Robotic Grasping. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19916–19925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarnoja, T.; Zhou, A.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Soft Actor-Critic: Off-Policy Maximum Entropy Deep Reinforcement Learning with a Stochastic Actor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1856–1865. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S. Direct Demonstration-Based Imitation Learning and Control for Writing Task of Robot Manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–8 January 2023; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tao, C.; Cheng, L. Reinforcement learning based shared control for walking aid robot and its experimental verification. Adv. Robot. 2015, 29, 1463–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Cheng, G.; Shi, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, S. A multi-channel reinforcement learning framework for robotic mirror therapy. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 5385–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishe, S.S.P.A.; Nguyen, T.; Fang, Y.; Lerner, Z.F. Adaptive ankle exoskeleton control: Validation across diverse walking conditions. IEEE Trans. Med Robot. Bionics 2021, 3, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, N.; Alqatamin, M.H.A.; Popa, D.O. AMI: Adaptive Motion Imitation Algorithm Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Tao, Q.; Li, A.; Chen, Y. An unknown wafer surface defect detection approach based on Incremental Learning for reliability analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 244, 109966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, Z.C.; Berkowitz, J.; Elkan, C. A Critical Review of Recurrent Neural Networks for Sequence Learning. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.00019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Song, R.; Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Watch and Act: Learning Robotic Manipulation From Visual Demonstration. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2023, 53, 4404–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doering, M.; Glas, D.F.; Ishiguro, H. Modeling interaction structure for robot imitation learning of human social behavior. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2019, 49, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Ohmura, Y.; Nagakubo, A.; Kuniyoshi, Y. Training robots without robots: Deep imitation learning for master-to-robot policy transfer. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 2906–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Song, R.; Lu, W.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Explicit-to-Implicit Robot Imitation Learning by Exploring Visual Content Change. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2022, 27, 4920–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Vasudevan, R.; Johnson-Roberson, M. Bio-LSTM: A biomechanically inspired recurrent neural network for 3-d pedestrian pose and gait prediction IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett 2019, 4, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaharazuka, K.; Kawamura, Y.; Okada, K.; Inaba, M. Imitation learning with additional constraints on motion style using parametric bias. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 5897–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, N.A.; Clark, N.; Ranatunga, I.; Popa, D. Implementation of interactive arm playback behaviors of social robot Zeno for autism spectrum disorder therapy. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Crete, Greece, 6–8 June 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Taghavi, N.; Berdichevsky, J.; Balakrishnan, N.; Welch, K.C.; Das, S.K.; Popa, D.O. Online Dynamic Time Warping Algorithm for Human-Robot Imitation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 3843–3849. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, N. Motion Learning and Control For Social Robots In Human-Robot Interaction. Master’s Thesis, The University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Medsker, L.R.; Jain, L. Recurrent Neural Networks: Design and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; Volume 5, p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sutskever, I.; Martens, J.; Hinton, G.E. Generating text with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-11), Bellevue, WA, USA, 28 June–2 July 2011; pp. 1017–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Balluff, S.; Bendfeld, J.; Krauter, S. Meteorological data forecast using RNN. Int. J. Grid High Perform. Comput. 2017, 9, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewamalage, H.; Bergmeir, C.; Bandara, K. Recurrent neural networks for time series forecasting: Current status and future directions. Int. J. Forecast. 2021, 37, 388–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Welch, K.C. Towards Forecasting Engagement in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder using Social Robots and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the SoutheastCon, Orlando, FL, USA, 1–16 April 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 838–843. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsantekidis, A.; Passalis, N.; Tefas, A. Chapter 5—Recurrent neural networks. In Deep Learning for Robot Perception and Cognition; Iosifidis, A., Tefas, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).