Abstract
In recent years, the integration of smartphone technology with novel sensing technologies, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Deep Learning (DL) algorithms has revolutionized crop pest and disease surveillance. Efficient and accurate diagnosis is crucial to mitigate substantial economic losses in agriculture caused by diseases and pests. An innovative Apple® and Android™ mobile application for citizen science has been developed, to enable real-time detection and identification of plant leaf diseases and pests, minimizing their impact on horticulture, viticulture, and olive cultivation. Leveraging DL algorithms, this application facilitates efficient data collection on crop pests and diseases, supporting crop yield protection and cost reduction in alignment with the Green Deal goal for 2030 by reducing pesticide use. The proposed citizen science tool involves all Farm to Fork stakeholders and farm citizens in minimizing damage to plant health by insect and fungal diseases. It utilizes comprehensive datasets, including images of various diseases and insects, within a robust Decision Support System (DSS) where DL models operate. The DSS connects directly with users, allowing them to upload crop pest data via the mobile application, providing data-driven support and information. The application stands out for its scalability and interoperability, enabling the continuous integration of new data to enhance its capabilities. It supports AI-based imaging analysis of quarantine pests, invasive alien species, and emerging and native pests, thereby aiding post-border surveillance programs. The mobile application, developed using a Python-based REST API, PostgreSQL, and Keycloak, has been field-tested, demonstrating its effectiveness in real-world agriculture scenarios, such as detecting Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) infestation in tomato cultivations. The outcomes of this study in T. absoluta detection serve as a showcase scenario for the proposed citizen science tool’s applicability and usability, demonstrating a 70.2% accuracy (mAP50) utilizing advanced DL models. Notably, during field testing, the model achieved detection confidence levels of up to 87%, enhancing pest management practices.
1. Introduction
Plant diseases and insects are a major concern for agriculture, as the global economy suffers an estimated USD 220 billion loss annually due to plant diseases, while pests cause a loss of USD 70 billion each year [1]. The desired standard of pest and disease management is not met because of insufficiently precise diagnoses when needed. Around 40% of farming output is impacted by insects, pests, diseases, and weed invasions [2,3], leading to heavy reliance on pesticides. This reliance often results in economic and environmental issues caused by excessive and inappropriate pesticide usage. Plant diseases pose a significant threat to both crops and other cultivated plants; thus, it is crucial to identify plant diseases at an early stage to avert both immediate and long-term damage [4]. Early identification and diagnosis of these diseases and insects are essential for implementing preventive measures and reducing both economic and production damage [5]. Maintaining plant health and employing predictive measures are key to sustainable agriculture, as they play a crucial role in minimizing losses associated with the yield and quality of agricultural products [6]. Proactive management of plant health not only safeguards crops but also ensures the longevity and productivity of agricultural practices [7]. Traditional methods for diagnosing plant diseases often involve expert analysis, which can be time-consuming and subject to human error [8,9]. This reality presents a significant challenge in agriculture, where prompt and accurate disease identification is critical to implementing effective treatment strategies and mitigating potential losses. Additionally, a common method of insect surveillance involves identifying and counting them through adhesive traps positioned along agricultural fields. Typically, specialists undertake this monitoring by visually identifying and manually counting the trapped insects [10]. However, this process is highly time-consuming and prone to errors. This gap has necessitated the integration of advanced technological solutions to modernize and enhance the accuracy and efficiency of disease diagnosis in agriculture [11].
The advent of smartphones and their widespread adoption have paved the way for innovative solutions in this sector [12]. With over 4.41 million apps in the Google Play App Store and Apple App Store, there is an evident shift towards harnessing technology to tackle traditional agricultural issues [13]. These applications leverage advanced technologies such as image processing techniques, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. When combined with extensive databases containing images of numerous plant varieties and their diseases, these applications provide a more accurate and thorough method for diagnosing and managing plant diseases [26]. Moreover, this technological integration opens doors for citizen science in agriculture [27,28]. By enabling farmers, gardeners, and even hobbyists to contribute data and observations through these applications, a more extensive and diverse dataset is created. This collective participation enhances the precision of disease identification and nurtures a community-based approach toward the observation and management of plant health. A comprehensive review by Jafar et al. (2024) [29] highlights the critical role of AI in transforming plant disease detection, providing an in-depth analysis of various ML and DL methodologies and their applications in agriculture. Similarly, Toscano-Miranda et al. (2022) [30] conducted a systematic literature review on the use of AI and sensing techniques for managing diseases and insect pests in cotton, emphasizing the effectiveness of these technologies in classification, image segmentation, and feature extraction.
Several mobile applications have made strides in leveraging AI for plant and insect identification [31,32,33]. The use of cameras on mobile phones enables mobile applications to become useful citizen science tools. Picture Insect™ [34] uses AI to identify insects, aiding in pest management. PictureThis™ [35] applies AI for general gardening and plant care, assisting users in plant maintenance. Blossom™ [36] focuses on recognizing plant types and providing care tips, while Picture Mushroom™ [37] uses AI to identify mushroom species. Additionally, Mosquito Alert™ [38] tracks the movement of species like the tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) and the yellow fever mosquito (Aedes aegypti), contributing to the study of their spread. These applications demonstrate the potential of AI in addressing various aspects of plant and insect identification and care. In a study by Siddiqua et al. (2022) [33], an evaluation of various plant disease detection mobile applications, including “Plantix–your crop doctor”, demonstrated the current state of AI in agriculture. The study identified significant gaps in the quality and reliability of many applications, emphasizing the need for continued development and rigorous testing to achieve practical, field-ready solutions. Their findings indicated that despite the large number of applications available, only a few, like “Plantix”, showed promise in real-world scenarios, underscoring the importance of robust development and validation processes.
The integration of AI and DL in agriculture has significantly enhanced the detection of pests and diseases, providing critical tools for modern farming. Computer vision, a pivotal element in AI, has been instrumental in agriculture by aiding in farmland mapping, crop image segmentation, and the identification of pests and diseases. DL models, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have shown superior accuracy over traditional image processing methods for these tasks [26,39,40,41,42].
Recent advancements have demonstrated the effectiveness of DL models in early pest and disease detection. For instance, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been employed to detect Tuta absoluta infestations at early stages, significantly improving the efficiency and speed of detection [43].
In the study by Mdhaffar et al. (2022) [44], images from smart traps were used to create a dataset for detecting “Prays oleae” using YOLOv5 and YOLOv7 object detection models. These models achieved mean Average Precision (mAP) scores of 87% and 89%, respectively, demonstrating high accuracy in pest detection. Fuentes et al. (2017) [45] explored a DL-based approach to detect diseases and pests in tomato plants using various camera resolutions. They utilized Faster R-CNN, R-FCN, and SSD models with different backbones like VGG and ResNets, proving the effectiveness of these models in detecting tomato plant diseases and pests. The “PestNet” model was introduced as a region-based end-to-end approach for large-scale multi-class pest detection and classification [46]. Evaluated on the “Multi-class Pests Dataset 2018” (MPD2018), which includes 88,670 high-resolution images of 16 species and 582,170 bounding boxes, “PestNet” achieved a 75.46% mAP, outperforming state-of-the-art models like Faster R-CNN and SSD. Giakoumoglou et al. (2023) [47] enhanced T. absoluta detection on tomato plants using DL models and ensemble techniques. Applying the Weighted Boxes Fusion (WBF) ensemble technique improved mean Average Precision (mAP) scores by 20%, demonstrating significant advancements in agricultural pest detection accuracy.
In another study by Wang et al. (2021) [48], the “AgriPest” dataset was released as a domain-specific benchmark for recognizing and detecting small natural pests in real-world scenarios. It consists of 264,728 bounding boxes and 49,700 images, representing 14 species across four crops. Various object detection models, including SSD, RetinaNet, Faster R-CNN, FPN, and Cascade R-CNN pre-trained on ImageNet, were tested on this dataset, achieving an mAP of 70.83%. Giakoumoglou et al. (2024) [49] used multi-spectral imaging and DL to detect early B. cinerea symptoms on horticultural crops. The U-Net++ model with the MobileViT-S encoder achieved 90.1% accuracy, significantly advancing early crop disease diagnosis. Ilyas et al. (2021) [50] proposed a DL-based framework for identifying and classifying strawberry fruits, including diseased ones, achieving a 3% increase in mean intersection over union and 92.45% precision. Furthermore, Qasrawi et al. (2021) [51] applied ML models to classify tomato plant diseases using smartphone images, achieving 70% clustering accuracy and prediction accuracies of 70.3% and 68.9% with neural networks and logistic regression models, respectively. Furthermore, the issue of limited data for training AI models is addressed in the study by Rezaei et al. (2024) [52], which proposes a few-shot learning (FSL) approach. This approach is particularly useful in scenarios where data is scarce, utilizing as few as five images per class. Their method, which combines pre-training, meta-learning, and fine-tuning (PMF + FA), achieved an average accuracy of 90.12% in disease recognition, demonstrating the effectiveness of FSL in real-time disease detection with limited data.
Additionally, recent research by Zhang et al. [53] has introduced a dual-branch collaborative learning network (DBCLNet) for crop disease identification, addressing the inefficiencies of traditional monitoring methods. DBCLNet employs convolutional kernels of different scales to extract both global and local features from images, integrating a channel attention mechanism to refine these features further. Extensive experiments on the Plant Village dataset demonstrated the DBCLNet’s superior performance, achieving an accuracy of 99.89%, precision of 99.97%, recall of 99.67%, and F-score of 99.79% in identifying 38 categories of crop diseases. This method highlights the potential for using advanced deep-learning strategies to improve the precision and reliability of crop disease detection.
This paper presents a robust mobile application developed using the Ionic Framework designed for real-time detection of plant leaf diseases and pests through DL technology. Leveraging the smartphone’s camera, the application streamlines data collection while also utilizing georeferencing capabilities to facilitate location-based data that can be transmitted to a Decision Support System (DSS) or to a pan-European Early Warning System (EWS) for early decisions. This supports the urgent need to tackle invasions as outlined in the Communication ‘Towards an EU Strategy on Invasive Species’ [54] and the EU’s biodiversity strategy for 2030 [55]. This empowers farmers as well as importers (border inspections) with timely insights for proactive pest management and disease prevention strategies.
The application is built on the following key components:
- Development of an innovative Apple® and Android™ mobile application for citizen science, enabling real-time detection and identification of plant leaf diseases and pests.
- Leveraging DL algorithms for efficient and accurate data collection on crop pests and diseases, supporting crop yield protection and cost reduction while aligning with the Green Deal goal for 2030.
- Utilization of a robust data repository in DSS, enabling citizens to upload crop pest data via the AI-based mobile app and receive data-driven support and information.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 outlines the methodology, encompassing the design and development of the application, the dataset employed, and the DL model used. Section 3 details the results, focusing on the field testing of the mobile application and the evaluation of the model’s performance, as well as future research. The study concludes in Section 4.
2. Materials and Methods
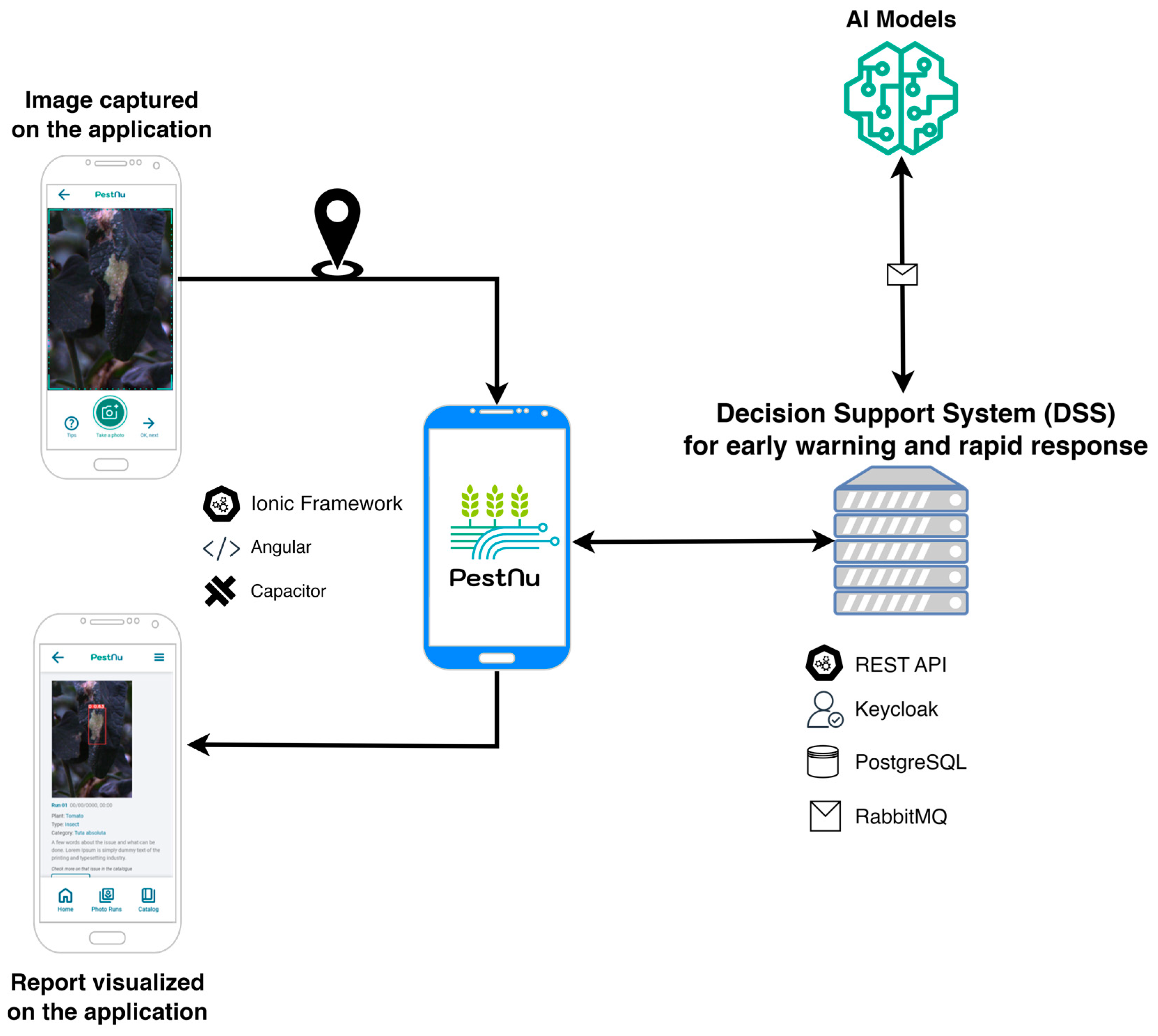
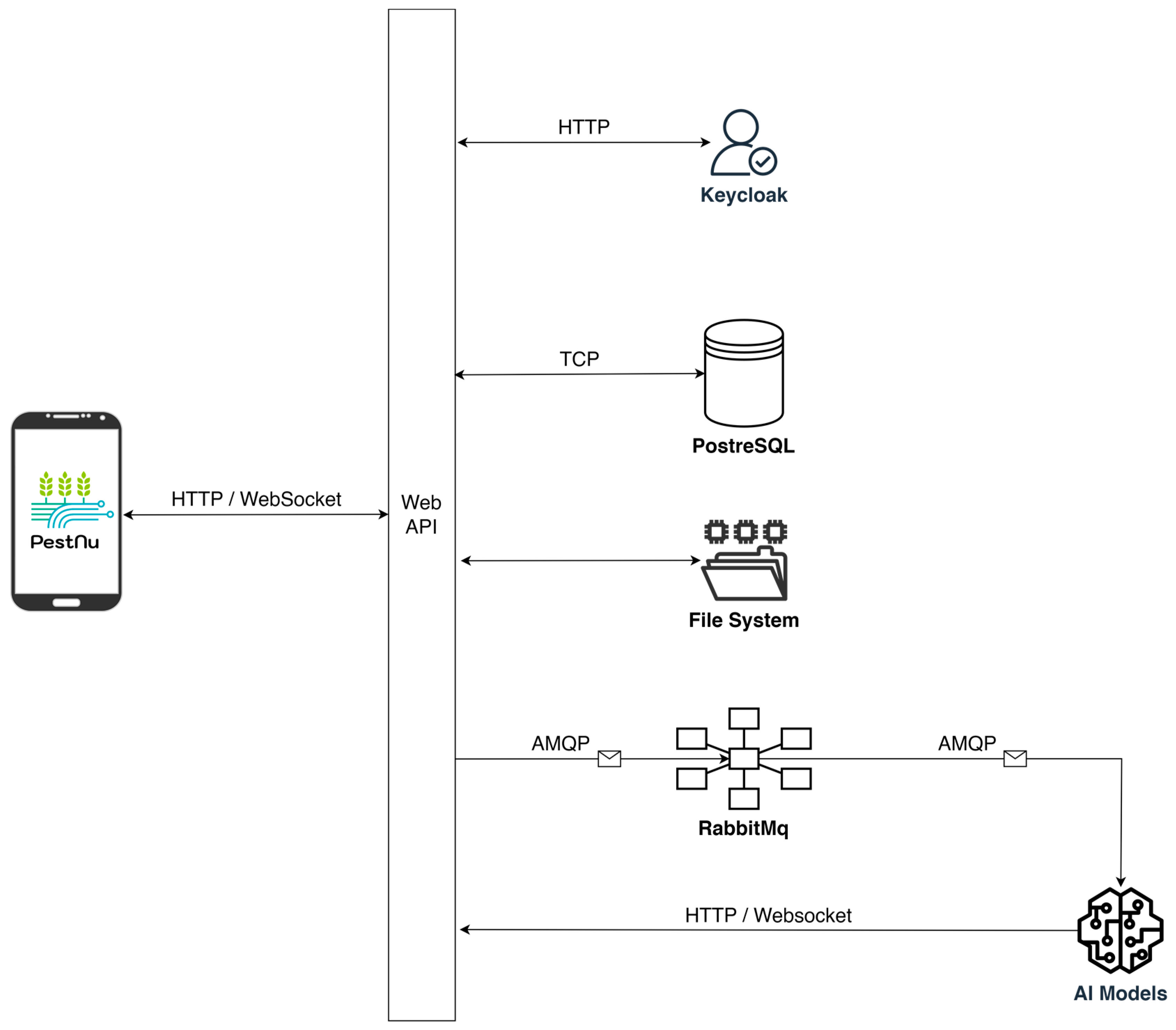
This section outlines the comprehensive methodology employed in this study, detailing the design and development processes of the mobile application, the specific dataset utilized, and the DL model implemented. It provides an in-depth look into each phase, from the initial design considerations and data collection techniques to the development and training of the DL model used. Figure 1 illustrates the conceptual architecture of the AI-based mobile application designed for real-time detection of plant leaf diseases and pests. The architecture emphasizes scalability, efficiency, and security. It utilizes the Ionic Framework with Capacitor for cross-platform compatibility and Angular for streamlined development. Interaction with server-side components is facilitated by a REST API in Python, while access control is managed by Keycloak. Additionally, RabbitMQ enables asynchronous communication between services. The user-captured image is initially transmitted to the back-end and processed by the DSS [56] along with the corresponding geospatial data. Subsequently, the DSS utilizes the appropriate AI model and returns a visual representation of the result along with the corresponding disease or insect detection report to the application.
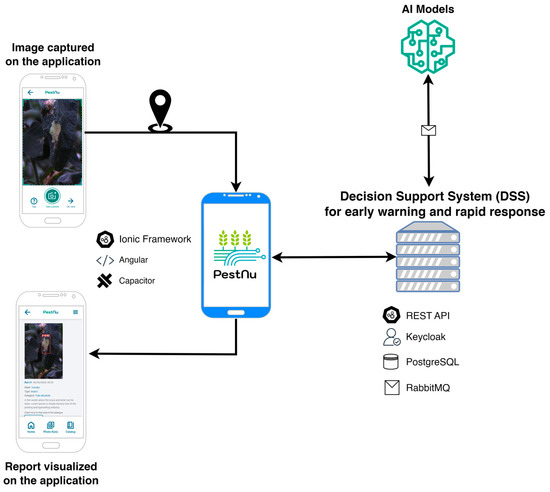
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the architecture for the Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based mobile application. The mobile application communicates with a DSS or an EWS to transmit the user-captured image and accompanying geospatial data. The DSS or EWS then utilizes the appropriate AI model to analyze the image and subsequently delivers the application with a visual representation of the findings along with a detailed report on the detected diseases or pests.
2.1. Design and Flow of the Mobile Application
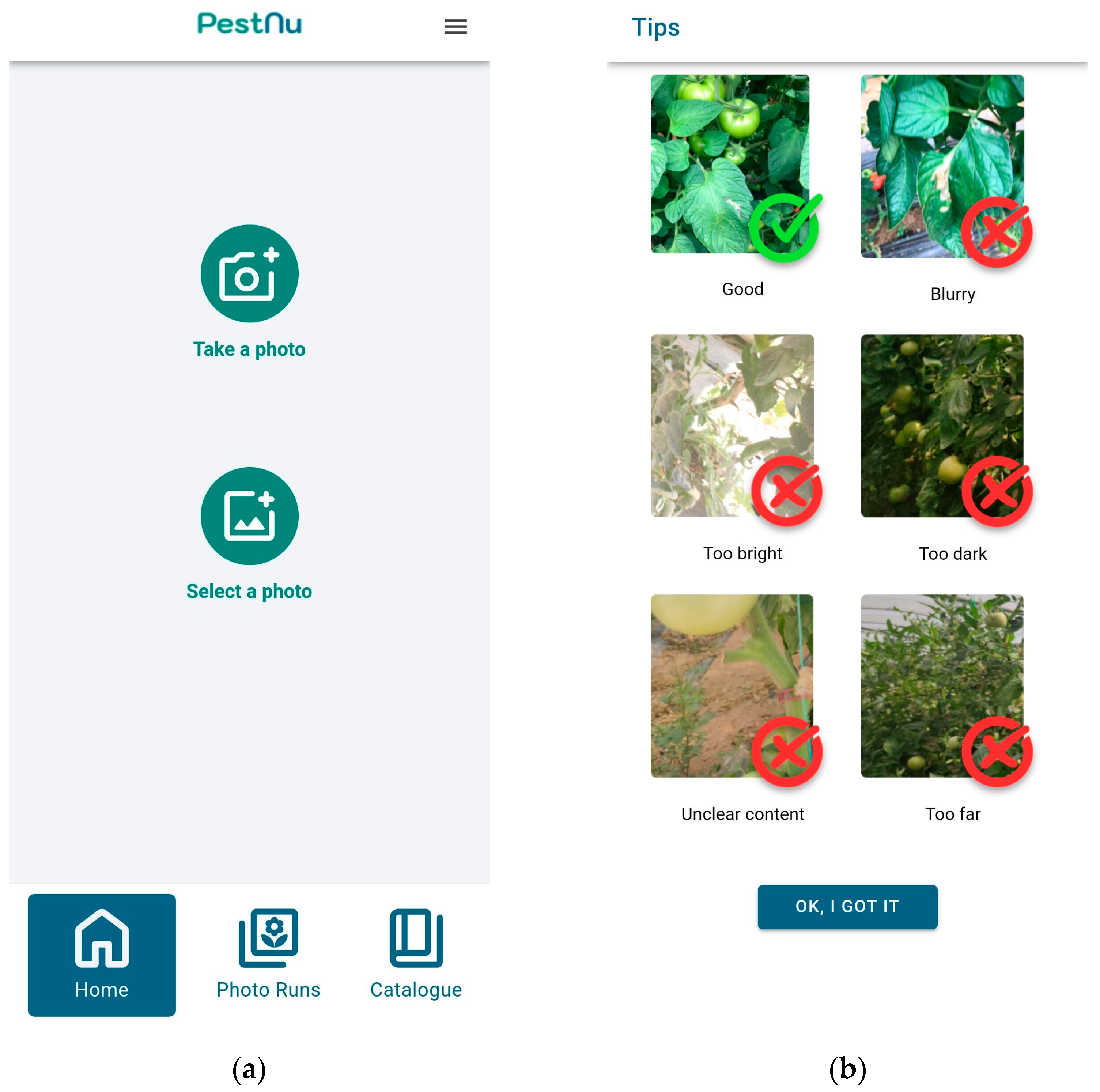
The mobile application was designed with user-friendliness as a top priority. It offers users the option to create a personalized account, complete with essential functions such as registration and login capabilities, ensuring seamless access to past interactions. To identify pests or diseases on their plants, users can either capture a photo in real-time or select a previously taken image on the Home Screen, as shown in Figure 2a. To ensure optimal results, users are provided with guidance on capturing photos effectively, as shown in Figure 2b.
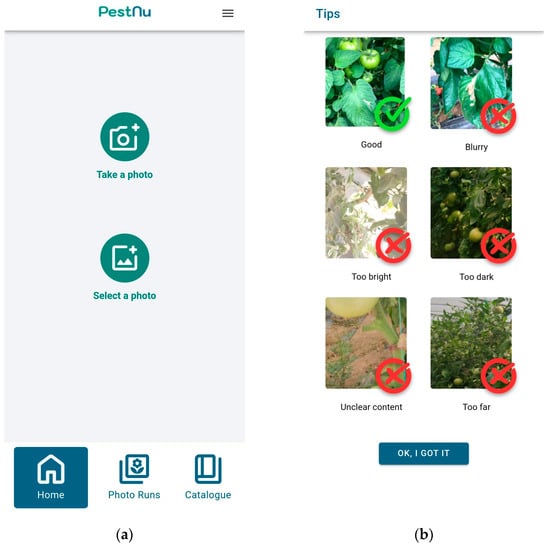
Figure 2.
Mobile application screens: (a) home screen of the application, where the user can either capture or select an existing photograph taken from his smartphone; (b) tips screen, where the user is guided on how to capture photographs effectively.
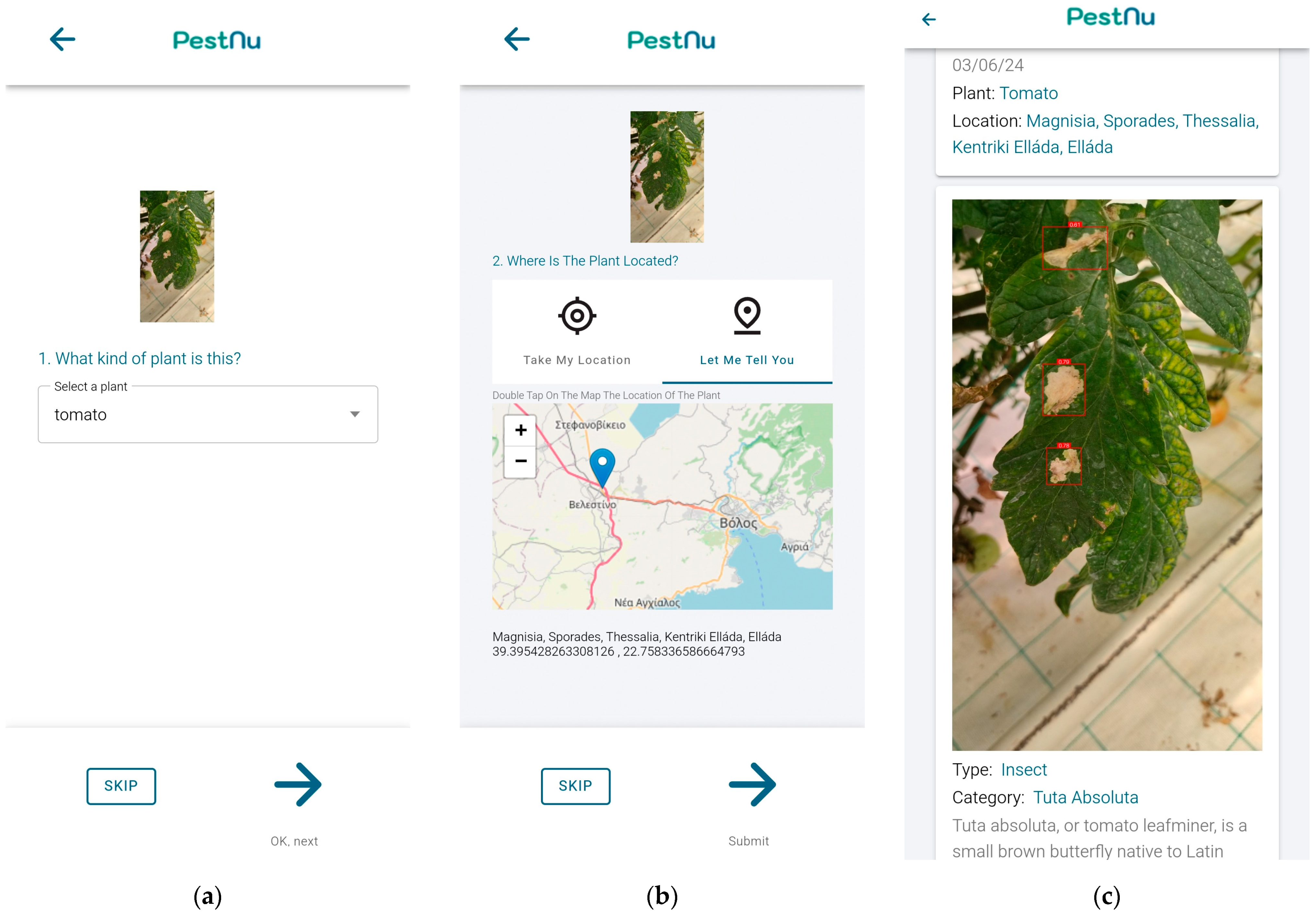
Upon uploading the photo, users have the choice to specify the plant species (Figure 3a) and optionally provide the location (Figure 3b), enabling the correlation of results with plant geography. The image is then transmitted to the back-end and processed by the DSS, utilizing the appropriate AI model. The application presents users with comprehensive results, including the user-captured image annotated with points of interest identified by the DL model. Additionally, it provides information on the detected category and type of pest or disease, along with its confidence level (Figure 3c), empowering users with the ability to zoom in on the image for closer examination.
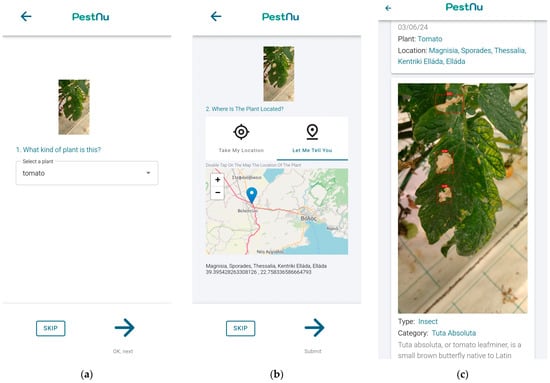
Figure 3.
Mobile application screens: (a) screen where the user can select what type of plant is photographed and transmitted to the DSS; (b) screen where the user can either give the location of the plant by accessing his precise location via GPS of the smartphone or select a location on the map; (c) detections screen in which the user can see the results of the AI model and the application’s recommendations for the specific problem they are facing.
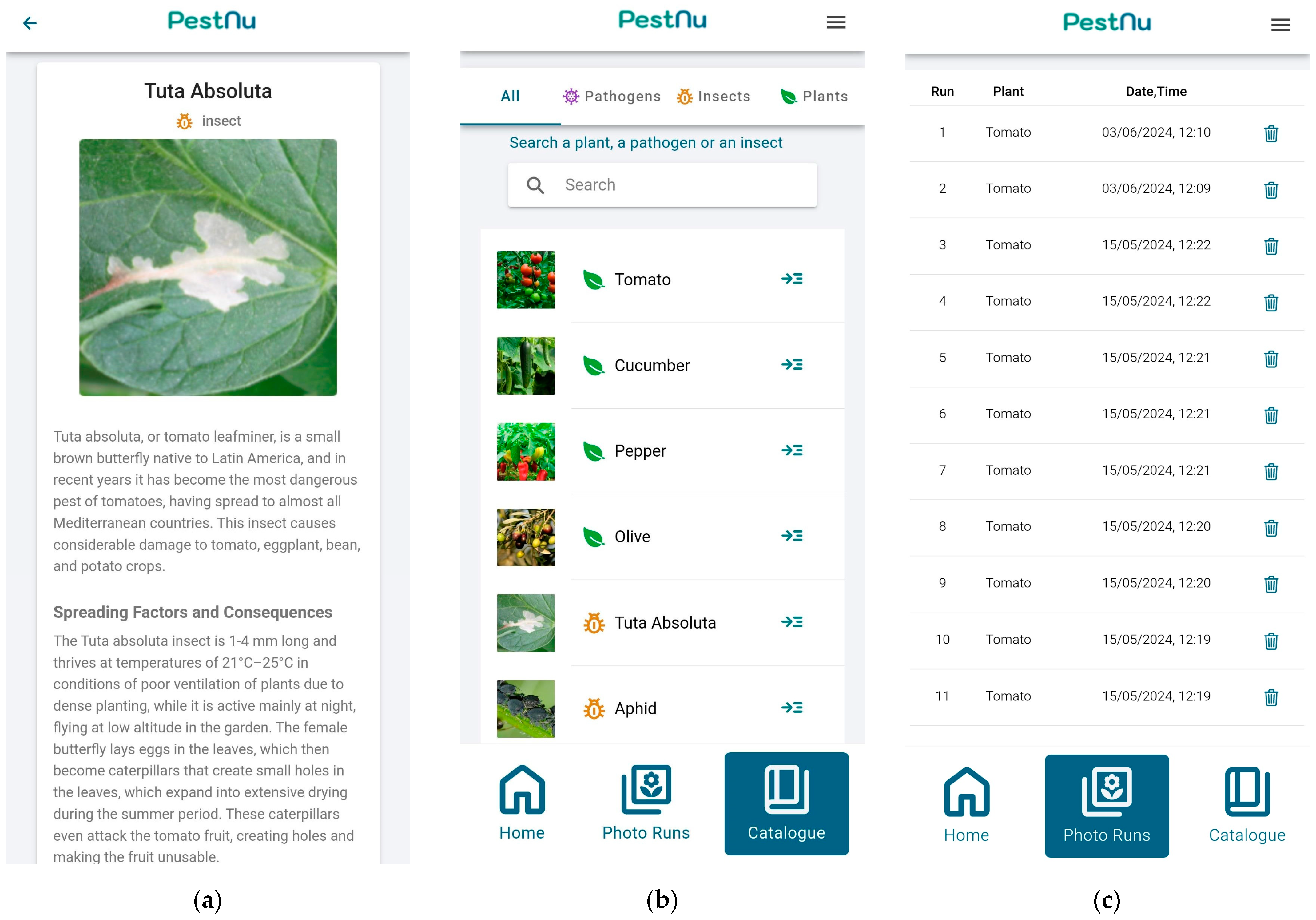
In each detection result, users can see a brief overview of the problem they are facing, or they can navigate directly to the catalog provided by the application to read more information about it (Figure 4a). Furthermore, users can explore the app’s full catalog, which offers detailed insights into managing the detected issues with various plants, insects, and pathogens they may encounter in the future, as shown in Figure 4b. Last but not least, since users are able to create an account, they can access their past results provided by the mobile application (Figure 4c).
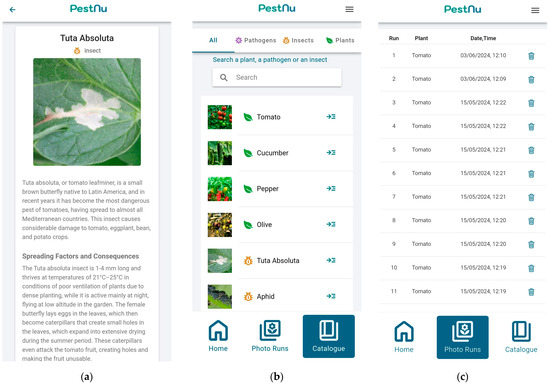
Figure 4.
Mobile application screens: (a) catalog screen navigated from detection screen where the user can see a brief overview of the problem they are facing; (b) full catalog of the mobile application, which allows users to read about several insects and pathogens, as well as plants; (c) past detections screen of the user account.
2.2. Development of the Mobile Application
2.2.1. Front-End
The mobile application’s front-end is developed using the Ionic Framework (https://ionicframework.com/docs (accessed on 26 April 2024)) in conjunction with Capacitor (https://capacitorjs.com/docs (accessed on 26 April 2024)). This combination provides a foundation for creating a cross-platform mobile application that is compatible with different native device functionalities. Ionic facilitates the development process because its library is adaptable to the design guidelines of both iOS and Android platforms.
The Ionic Framework is a tool that provides a robust UI toolkit for creating mobile interfaces with web technologies. It streamlines the creation of cross-platform applications by providing a set of pre-designed components and gestures that complement iOS and Android’s native design standards. Capacitor acts as an intermediary that allows web-based applications to access and use native device features through API calls. Normally, web applications operate in a browser and have restricted access to a device’s native capabilities. Capacitor overcomes these limits by allowing web code (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript) to interface with native code and access device functions such as cameras, GPS, and push notifications, critical for the application’s core features like taking photos and processing them for plant health diagnostics.
Furthermore, the application uses Angular (https://angular.io/docs (accessed on 26 April 2024)), which integrates easily with Ionic to organize and manage the app’s architecture, making development more efficient and scalable. Angular’s architecture is built around components, which is consistent with Ionic’s component-based design methodology. This combination enables an integration in which Angular technologies such as dependency injection, data binding, and routing improve Ionic’s ability to construct interactive and complex mobile UIs with efficiency.
The decision to implement the Ionic Framework and Capacitor was driven by the requirement for a high-performance, scalable solution that could provide a consistent experience while enabling easy access to device-specific functionality. These technologies were chosen because they allow for future enhancements without the need for significant redesign or reimplementation.
For storing and retrieving user history and general plant health information, the application leverages Capacitor’s native storage solutions, which offer secure and immediate access to data, ensuring that users can track their activity over time and access educational content efficiently.
2.2.2. Back-End—Decision Support System for Early Warning and Rapid Response
The back-end architecture of the mobile application consists of essential components: a data repository for storing application data; an API serving as the communication channel between the app and the server via standard protocols and methods; the business logic realizing the application’s functionality such as image processing and threat detection with the help of advanced AI algorithms; and an access management service for protecting system resources by controlling access to them.
The design philosophy prioritizes scalability, security, robustness, performance, and interoperability. Therefore, a REST [57] architectural model was adopted, offering fault tolerance through component decoupling and enhanced operation via statelessness and caching in order to reduce server load. Central to this design is the data repository, which comprises a relational database management system (DBMS) and a Linux file system. PostgreSQL (https://www.postgresql.org/docs/16/ (accessed on 9 May 2024)) was chosen as a robust, well-tested, and open-source DBMS for storing all system-generated data, excluding images, which are stored in the file system for optimized performance. A REST API was developed using the Python (https://www.python.org/doc/ (accessed on 9 May 2024)) programming language in order to facilitate interaction between the mobile application and the server-side components. Serving as the only access point for the system’s data, including images and the results of their analysis, clients can request data or functionality via HTTP [58] or WebSockets [59] protocols, enhancing the system’s interoperability. Access management, crucial for controlling access to system resources, is addressed using Keycloak (https://www.keycloak.org/documentation (accessed on 9 May 2024)), an open-source identity and access management solution facilitating single sign-on.
AI-powered image recognition and threat detection are performed by autonomous services integrated into the system using the publish-subscribe pattern. Upon a detection request for an uploaded image, a message is published on a broker for a specific topic as a task for an appropriate service to act upon. RabbitMQ (https://www.rabbitmq.com/docs (accessed on 9 May 2024)) was selected as the message broker, facilitating message routing, and therefore asynchronous communication between services via the AMQP [60] protocol. All server-side components are deployed using containerization technologies like Docker, ensuring a lightweight, portable, and consistent environment, promoting seamless scaling, optimized resource utilization, and swift deployment of updates. Figure 5 presents the system architecture and the integration of each component, as well as the communication protocols used.
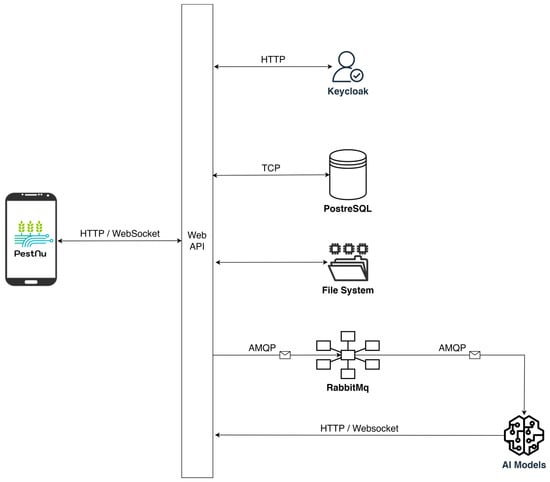
Figure 5.
Server architecture featuring each individual component and the communication protocols used for their integration into the system.
The architectural design of the server-side components facilitates an efficient and highly responsive DSS for information management by utilizing asynchronous communication between services and leveraging existing, proven software. This approach eliminates bottlenecks and ensures both speed and robustness. The Green Deal DSS of H2020 PestNu [56], integrated with a blockchain system for data integrity and AI model verification, as well as a cybersecurity platform to prevent cyber-attacks and IoT vulnerabilities, is utilized for this robust mobile application.
2.3. Deep Learning Integration
2.3.1. Dataset
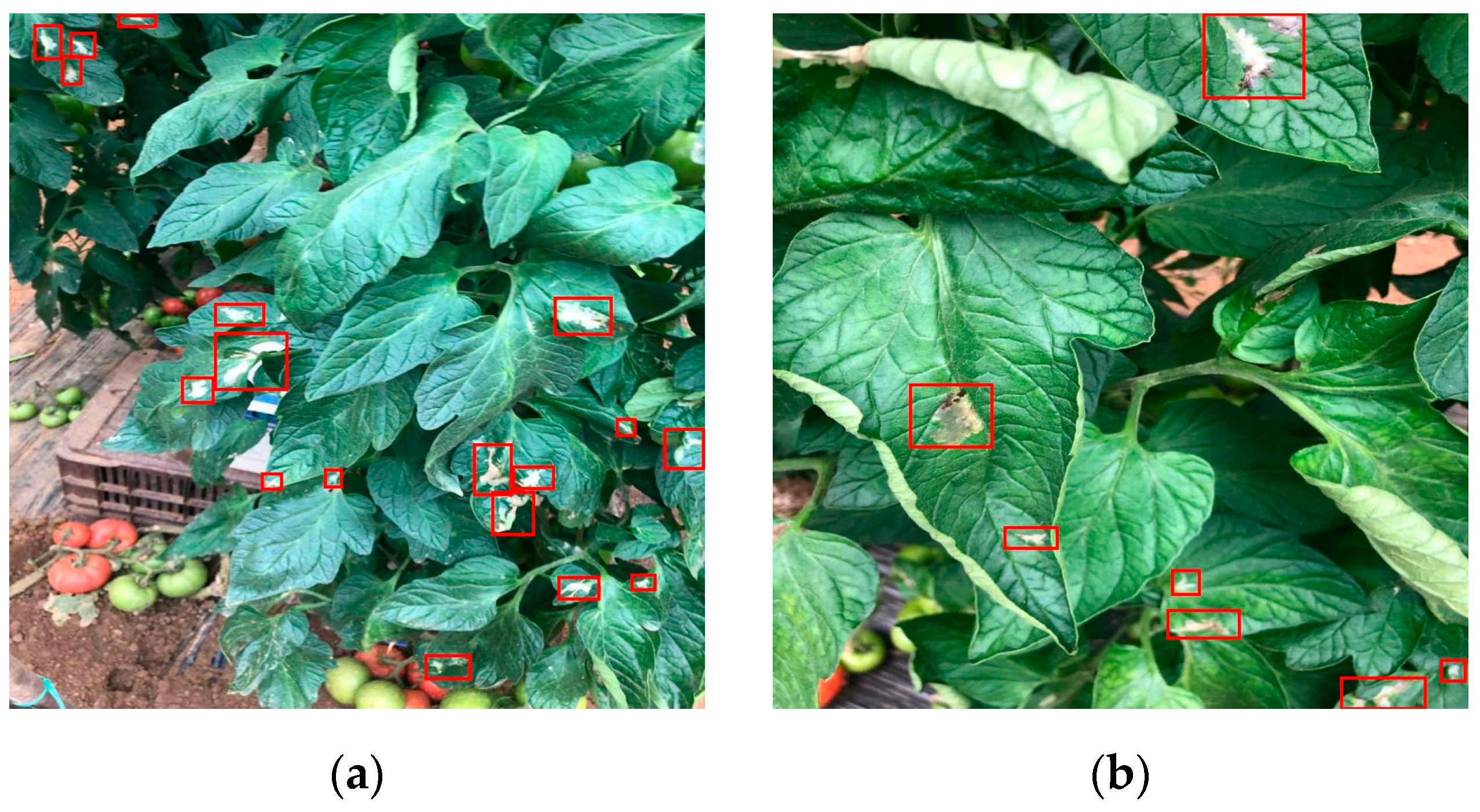
The mobile application currently uses a DL model trained on a dataset of RGB images collected in real-world settings in fields and greenhouses. These images depict the damage inflicted by T. absoluta on tomato plants. Farmers used mobile phones and other devices to gather images from different angles and lighting conditions. The dataset consists of 659 images, with 396 designated for training and 263 for validation. Expert agronomists annotated each image, marking bounding boxes around the damaged areas. The images and annotations were sourced from the EDEN Library (https://edenlibrary.ai/ (accessed on 8 March 2024)), comprising 5443 annotations in the training set and 3267 in the validation set, for a total of 8710 annotations. Figure 6 illustrates sample images that show the distinctive damage inflicted by T. absoluta on tomato leaves.

Figure 6.
Examples from the dataset: (a,b) images resized to 1024 × 1024 pixels, featuring bounding box annotations in red that highlight T. absoluta damage on tomato leaves. The annotations were generated using the Ultralytics framework [61]. Images and annotations are sourced from the EDEN Library.
2.3.2. Deep Learning Models and Training
YOLO (You Only Look Once) is an object detection algorithm first introduced by Redmon et al. [62] and is renowned for its speed and efficiency. It frames detection as a regression problem, which allows for real-time object detection. Since its introduction, several versions of YOLO have been developed. YOLO models are single-stage object detection systems, meaning they detect objects in one pass through the network. This end-to-end detection approach optimizes both detection tasks and inference speed, providing advantages over two-stage models, which first predict regions and then classify them.
For the T. absoluta detection model, multiple versions of YOLOv8 [63] were explored, including YOLOv8n, YOLOv8s, YOLOv8m, YOLOv8l, and YOLOv8x. These variants differ in terms of network depth, which is determined by the number of layers, and network width, which is defined by the number of filters in those layers. As a cutting-edge, state-of-the-art model, YOLOv8 builds on the success of its predecessors by introducing new features and enhancements for improved performance, flexibility, and efficiency. YOLOv8 supports a wide range of vision AI tasks, including detection, segmentation, pose estimation, tracking, and classification, making it versatile for diverse applications and domains. Training was carried out using the Ultralytics framework [61] in PyTorch [64] for 100 epochs, with early stopping implemented after 15 epochs without improvement. The training used a batch size of 4 to 8 and an image resolution of 1024 × 1024 pixels. The optimizer used was SGD, with a learning rate of 0.01, a momentum of 0.9, and a weight decay of 0.0005.
The training process took place on a high-performance computing setup featuring an Intel® Core i9-13900F processor (Intel, Santa Clara, CA, USA), an RTX 4090 with 24 GB of VRAM (Nvidia, Santa Clara, CA, USA), and 128 GB of system RAM.
The results from the final trained model are detailed in Section 3, specifically in Table 1. These results highlight the model’s performance and accuracy in detecting T. absoluta infestations on tomato plants.

Table 1.
Performance evaluation (mAP50, recall, and precision) of YOLOv8 models.
2.3.3. Evaluation Metrics
To assess the performance of the models, we employed COCO detection metrics [65], which are recognized for their comprehensive evaluation of object detection, encompassing both localization and classification. A key metric of focus was mean Average Precision (mAP) at an Intersection over Union (IoU) threshold of 0.5, also known as mAP50, which provides a single measure of the model’s ability to accurately identify and locate objects across all classes. Furthermore, precision and recall metrics were also considered. Precision gauges the accuracy of positive predictions, while recall measures the model’s effectiveness in detecting all relevant instances.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Field Testing of the Mobile Application
The efficacy of the developed mobile application, designed for the detection of insect and fungal diseases in plants, was validated with the participation of 50 users, including 20 agronomists and 30 farmers, in the vicinity of Volos in Greece and the region of Murcia, Spain. The testing specifically targeted greenhouse crops, with a focus on tomato cultivation. The application’s capabilities were assessed in detecting T. absoluta infestations, utilizing advanced DL object detection models and more specifically the YOLOv8l model.
Agronomists contributed expert insights and conducted a technical assessment of the application’s effectiveness in detecting plant diseases and pests, leveraging their specialized knowledge and experience. Their feedback was critical for refining the AI models and improving detection accuracy. Farmers, as the primary end-users of the mobile application, provided important feedback on its usability and practicality in everyday agricultural scenarios. Their input was vital for making the application user-friendly and accessible to those without advanced Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) skills. These two stakeholder groups were chosen for the field testing and optimization of our mobile application because each offers distinct and valuable perspectives.
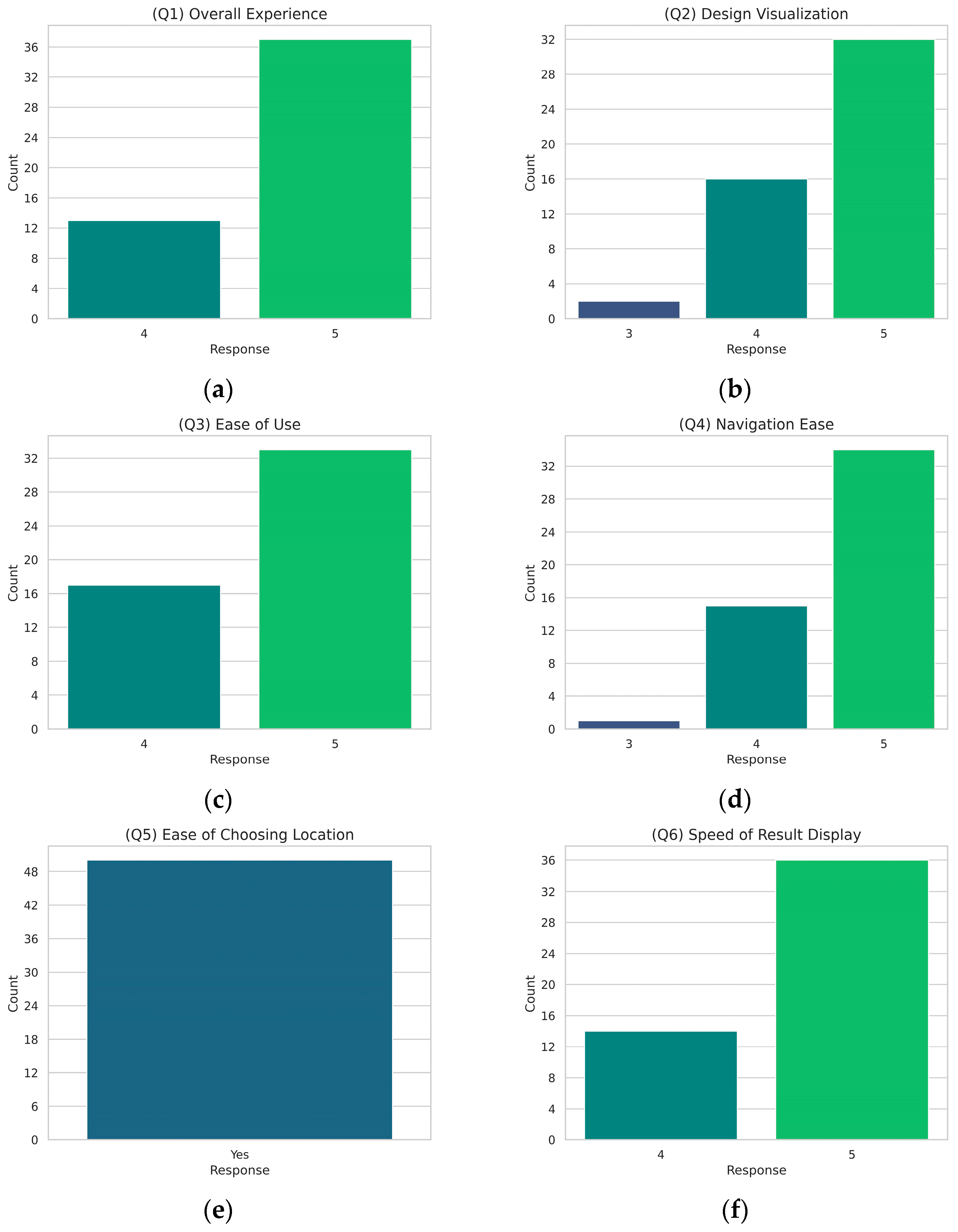
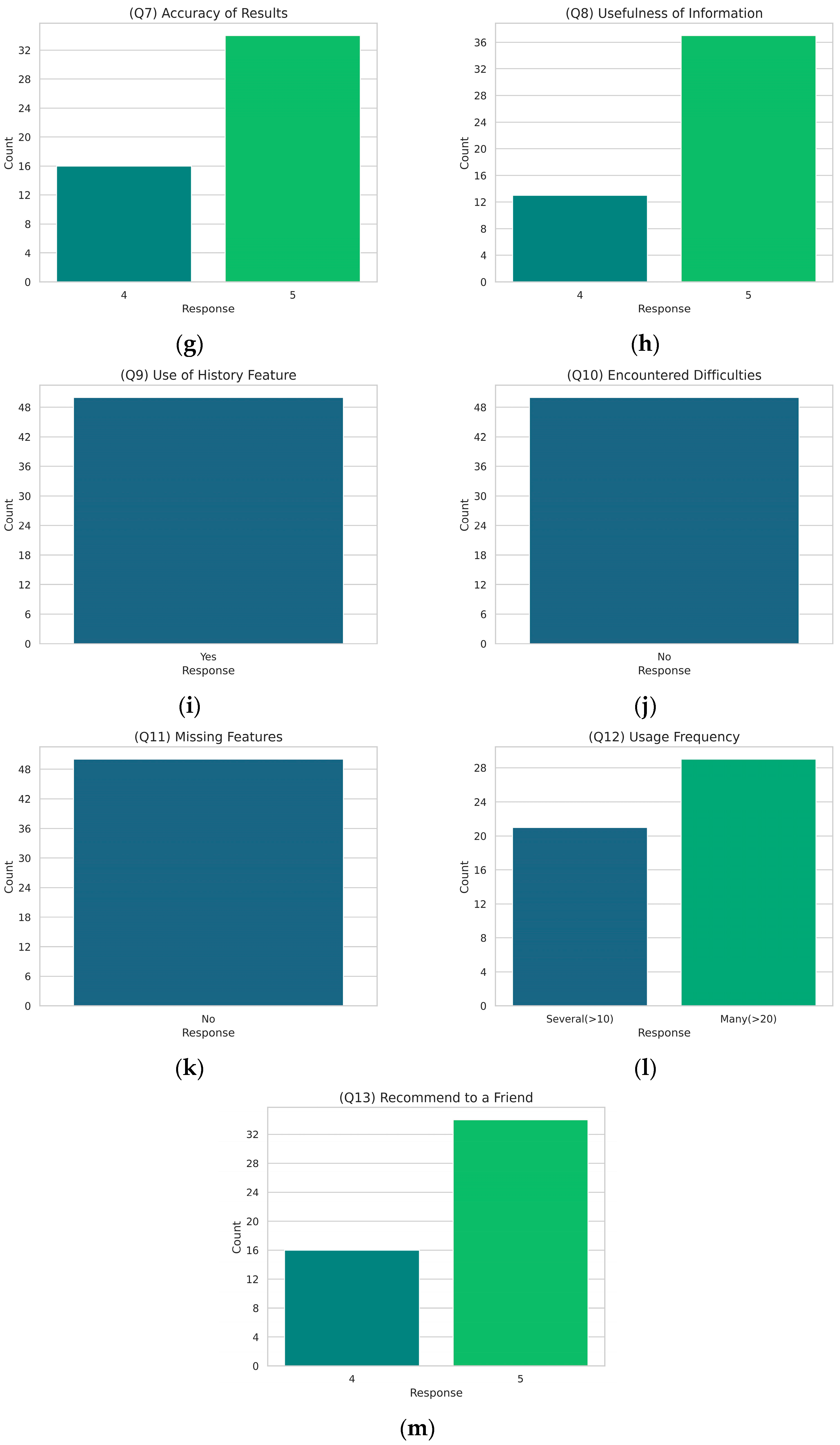
During the experimental phase, users tested the application by photographing various tomato plants and leaves in a greenhouse setting. The images captured by users varied in lighting conditions, shooting angles, and distances to comprehensively evaluate the AI detection model’s performance in real-world scenarios. At the end of the testing period, the 50 volunteers who used the application were asked to complete a questionnaire to assess the effectiveness and user experience of the developed mobile application. The precise content of the questionnaire is presented in Table A1 (Appendix A), along with visualizations extracted from the results in Figure A1 (Appendix A). The feedback from these tests and user responses indicates a high level of satisfaction with the mobile application.
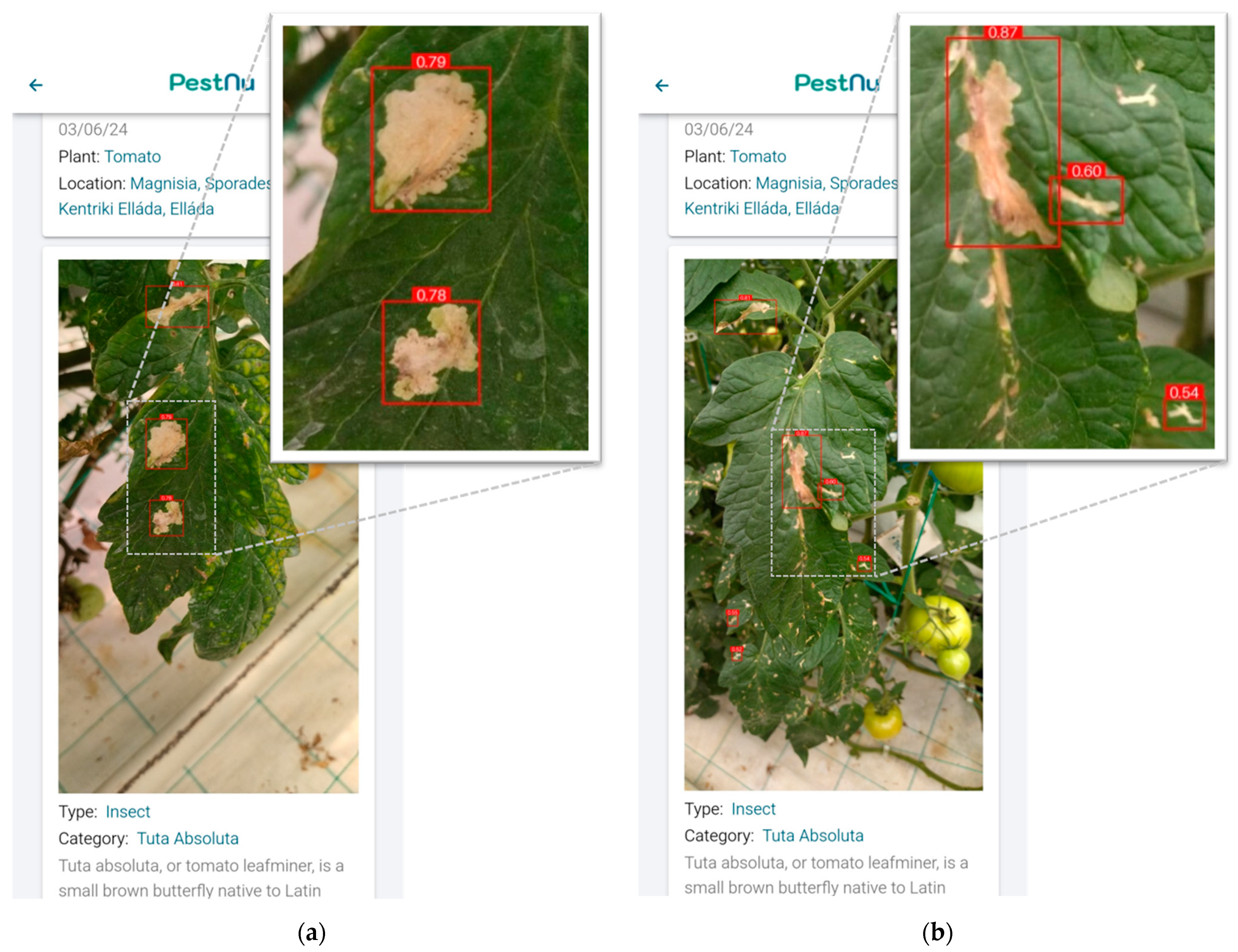
Figure 7 illustrates the developed mobile application in use on a smartphone. Figure 7a displays the home screen, which provides users with options to either take a photo or select one from their gallery. Figure 7b shows the detection details screen, featuring an image of tomato leaves captured by the user. The screen highlights detections made by the DL model, showcasing its ability to identify areas of infestation. Figure 7b presents close-up screenshots from the mobile application displaying the detection results of T. absoluta infestations on tomato leaves that were captured during the experimental session. More specifically, in Figure 8a, the application displays an image where the model detects infested areas on tomato leaves with a confidence level of up to 79%. The bounding boxes in red indicate the specific regions identified by the model as affected by T. absoluta. Similarly, Figure 8b showcases another image with the model identifying infested areas with a higher confidence level, reaching up to 87%. These annotated images effectively illustrate the model’s capability to accurately pinpoint infested regions in real-life settings, providing fast and valuable insights for users.

Figure 7.
Images from the developed AI-based mobile application: (a) home screen of the mobile app; (b) detection details screen showing model detections of T. absoluta infested areas.
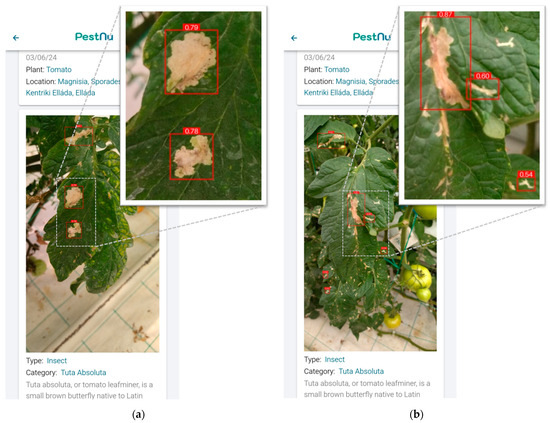

Figure 8.
Mobile application results screens: (a) image depicting tomato leaves where the model identifies areas infested by T. absoluta with a confidence level of up to 79%, highlighted by red bounding boxes; (b) image showing tomato leaves with the model identifying areas infested by T. absoluta with a confidence level up to 87%, highlighted by red bounding boxes.
The results of the user questionnaire, as presented in Figure A1 (Appendix A), reveal a high level of satisfaction among the participants regarding the application’s performance and user experience. The positive feedback underscores the application’s robustness and its practical utility in real-world agricultural settings. The development of the mobile application was thoroughly designed with scalability in mind, ensuring that it can accommodate additional AI models in the future. This forward-thinking approach allows for the seamless integration of new functionalities, thereby enhancing the application’s versatility and its potential impact on agricultural practices.
Future development efforts should focus on expanding the application’s capabilities to detect a broader range of plant diseases and pests. For instance, developing and integrating models for the detection of diseases such as B. cinerea and pests like whiteflies, aphids, and the olive fruit fly (Bactrocera oleae) would be a significant advancement. Future models incorporated into the application should be derived from comprehensive datasets that accurately reflect real-world conditions, capturing the variability of plant health and disease progression across diverse environments. The successful integration of these new models would extend the application’s utility beyond its current scope, providing farmers and agronomists with a more powerful tool for managing crop health. Additionally, future testing will involve diverse geographical locations, as well as various crop types and environments (greenhouses and open-field cultivations), to ensure the broad applicability and effectiveness of the mobile application.
3.2. Deep Learning Model Performance Evaluation
The performance evaluation, as detailed in Table 1, demonstrated varying levels of effectiveness across the different object detection models, with metrics including mAP50, recall, and precision. The YOLOv8n model achieved an mAP50 score of 65.6%, highlighting its basic capability in detecting T. absoluta infestations. The YOLOv8s model performed better, reaching an mAP50 of 68.1%, indicating improved accuracy. The medium-sized YOLOv8 variant showed worse detection performance, achieving an mAP50 of 67.8%, a precision of 0.715, and a recall of 0.653. The best results were obtained from the larger models, YOLOv8l and YOLOv8x, both of which achieved higher mAP50 scores, with YOLOv8l attaining a score of 70.2% and YOLOv8x also scoring 69.6%. Specifically, the YOLOv8l model demonstrated superior performance with a precision score of 0.691 and a recall score of 0.694.
These findings underscore the effective performance of the YOLOv8 series models in detecting T. absoluta infestations on tomato plants, confirming their suitability for practical application in agricultural pest detection. Notably, the model’s capability was highlighted during the experimental session, where it achieved detection confidence levels of up to 87%, as detailed in Section 3.1.
3.3. Comparative Analysis with Similar Applications
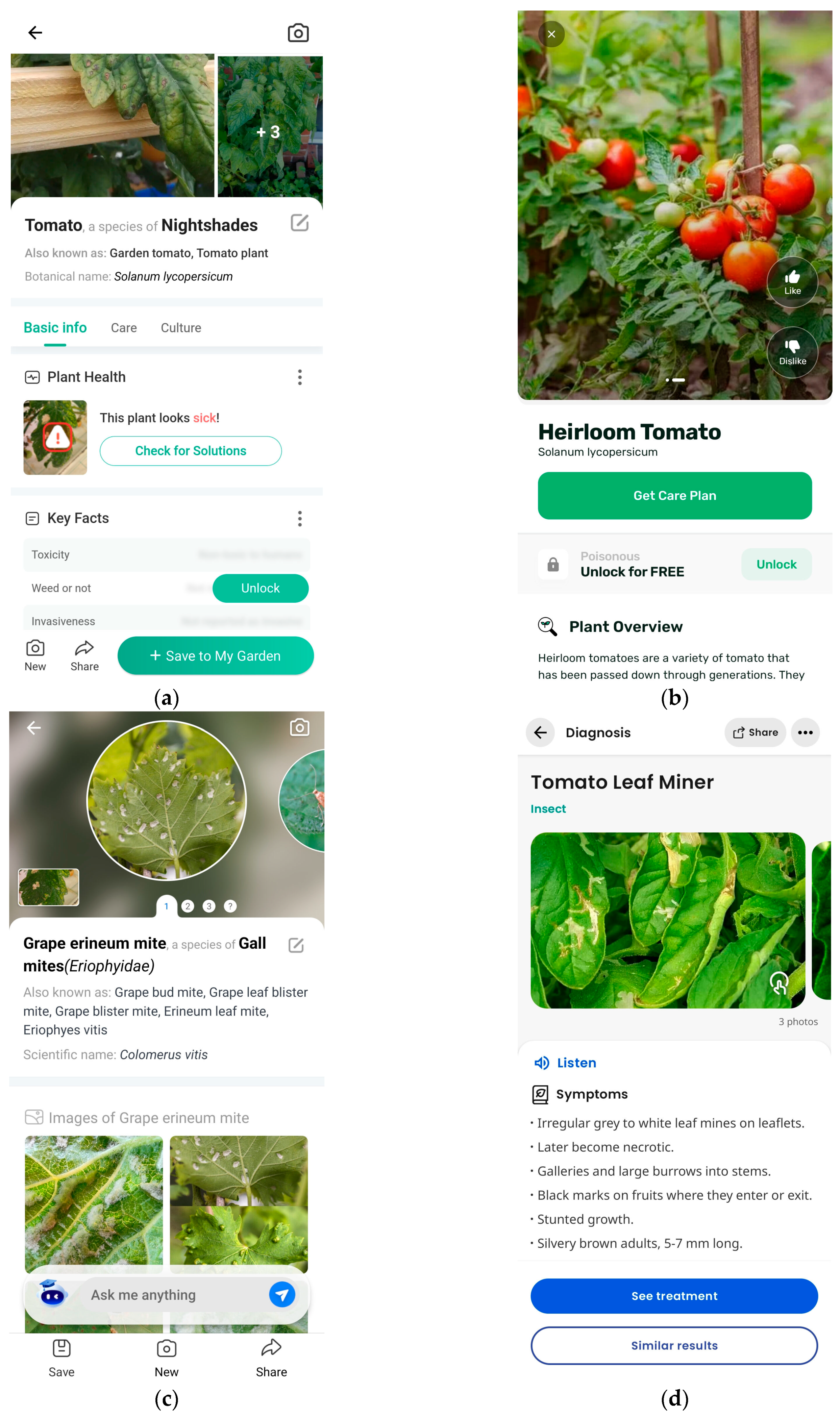
To contextualize the performance of our developed mobile application, a comparative analysis with existing similar applications was conducted. This comparison aims to highlight the unique features and advantages of our application in detecting plant diseases and pests, particularly T. absoluta infestations, as well as to acknowledge areas for potential improvement. The comparison includes Plantix™, PictureThis™, Picture Insect™, and PlantApp™. These applications are well-known for plant disease and pest detection. The analysis focuses on four main aspects: detection capability, user interface usability, processing time, and geospatial data utilization.
To evaluate detection capability, the same image (Figure 8a) was input into all four applications. PictureThis™ and PlantApp™ only identified the category of the plant (tomato) and provided basic information for it, as shown in Figure 9a and Figure 9b, respectively. For detailed health information and care advice against specific diseases or pests, users need to pay a fee per year for PictureThis™ and a fee per week or a one-time lifetime access fee for PlantApp™. Picture Insect™ could not detect T. absoluta infestation without the bug being visible, leading to false detection (Figure 9c). This app charges a fee per year for full access. In contrast, Plantix™ correctly diagnosed the T. absoluta infestation but did not specify the exact location of the infestation on the image, merely providing the name of the diagnosis along with similar pictures and relevant information (Figure 9d).
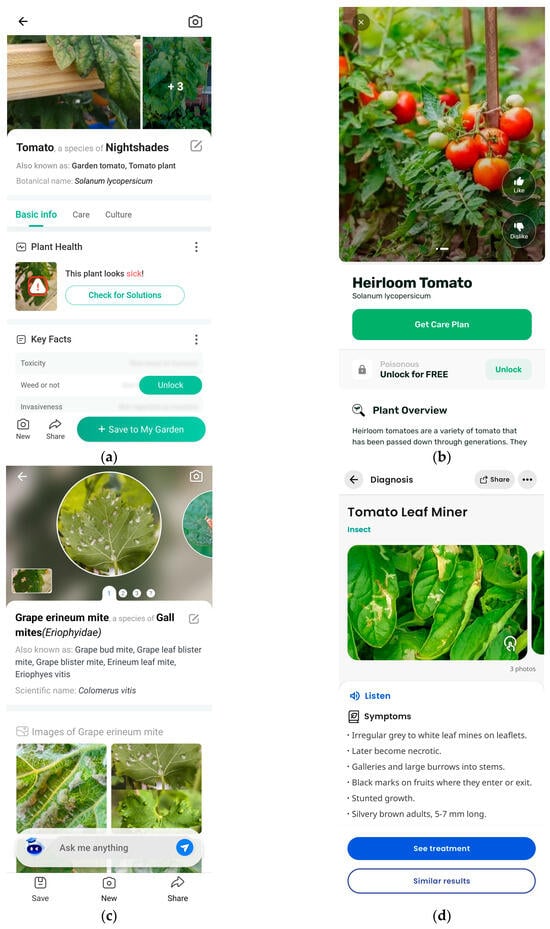
Figure 9.
Screenshots from existing similar applications diagnosis for comparative analysis: (a) PictureThis™ application; (b) PlantApp™ application; (c) Picture Insect™ application; (d) Plantix™ application.
The proposed citizen science mobile application not only correctly identifies T. absoluta but also specifies the exact location of the infestation within the user’s image (Figure 8a) and provides confidence levels for the detections, offering users valuable insight into the model’s certainty.
All applications, including ours, feature user-friendly interfaces that allow users to easily take a new picture or select one from their album and navigate through the app. The ease of use was comparable across all applications. The speed of image processing and result generation was satisfactory across all applications, with each providing detection results within 4–5 s, similar to the proposed application. Regarding geospatial data utilization, Plantix™ requests the user’s location but does not link it to the diagnosis. PictureThis™ and Picture Insect™ allow users to enter or allow access to their location but do not display the recorded geospatial data of the diagnosed plant. PlantApp™ does not offer location-saving capabilities. In contrast, our application records and displays the location of each diagnosis, enhancing traceability. Additionally, all apps allow users to view their diagnosis history, but PictureThis™ charges a fee per year for this feature.
Unlike the other applications reviewed, the proposed AI-based mobile application is offered free of charge. It is capable of providing detailed information on pest and disease detection, including exact infestation locations and confidence levels, and fully utilizes geospatial data to link diagnoses to specific locations. These features make our application a comprehensive and cost-effective citizen science tool for users, farmers, and agronomists, promoting proactive pest management and disease prevention without any associated costs.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, the developed mobile application has demonstrated significant potential in the detection of T. absoluta infestations on tomato plants, utilizing a robust dataset and an advanced DL model. The application’s design emphasizes flexibility and scalability, ensuring it can adapt to future needs by incorporating additional data and new models for a wider range of plant diseases and pests. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining the application as a cutting-edge tool in the ongoing battle against agricultural pests and diseases.
The application’s ability to provide real-time, accurate diagnostics represents a significant advancement in sustainable farming and effective crop management, as well as being applied to border inspections. The evaluation of the YOLOv8l DL model using the dataset resulted in an accuracy of 70.2% (mAP50). During the field-testing sessions, the model utilized within the mobile application demonstrated the capability of detecting T. absoluta infestations with confidence levels of up to 87%. By enabling the detection and precise identification of pest infestations and possible diseases, the application can help farmers take timely and targeted actions, thereby minimizing crop losses and reducing their reliance on chemical treatments. This not only supports crop yield protection and cost reduction but also aligns with broader goals, such as the Green Deal and Biodiversity Agenda for 2030, which aim to reduce pesticide use, promote sustainable agricultural practices, and secure biodiversity through digital developments in the underlying technologies for surveillance and modeling procedures. Furthermore, the positive feedback from the experimental session underscores the application’s practical utility and user satisfaction in real-world agricultural settings. The successful field testing and high levels of user satisfaction indicate that the application is both effective and user-friendly, making it a valuable tool for farmers and agronomists.
Looking ahead, the development efforts should continue to focus on expanding the application’s capabilities. Future models should be derived from comprehensive datasets that accurately reflect real-world conditions, capturing the variability of plant health and disease progression across diverse environments. Moreover, upcoming testing will encompass a range of geographical regions, different crop species, and settings (both greenhouses and open-field cultivations) to verify the wide-ranging applicability and efficacy of the mobile application. This will ensure that the application can address a broader spectrum of plant health issues and biodiversity loss, further enhancing its utility and impact.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M.P.; methodology, P.C. and E.M.P.; software, P.C., G.P., N.K. and G.M.; validation, D.I.; formal analysis, P.C.; investigation, P.C.; resources, E.M.P. and D.I.; data curation, N.K. and P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, P.C., G.P., N.K. and G.M.; writing—review and editing, E.M.P., D.I. and D.T.; visualization, G.M. and P.C.; supervision, E.M.P.; project administration, D.T.; funding acquisition, E.M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Green Deal PestNu project, funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No. 101037128.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank S. Faliagka and N. Katsoulas from the Department of Agriculture Crop Production and Rural Environment, University of Thessaly, for providing their resources and their network for volunteering in the field testing and assessment of the mobile application.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
This appendix includes Table A1, which presents the questionnaire administered to users following the application’s testing phase. The purpose of this survey was to gather a statistical sample to assess user satisfaction with the application.

Table A1.
Content of the questionnaire distributed to users after testing the mobile application.
Table A1.
Content of the questionnaire distributed to users after testing the mobile application.
| Q1. How would you rate your overall experience using the app? | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Negative |  |  |  |  |  | Positive |
| Q2. How would you rate the design of the app in terms of visualization? | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Negative |  |  |  |  |  | Positive |
| Q3. How would you rate the app in terms of ease of use? | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Negative |  |  |  |  |  | Positive |
| Q4. How difficult or easy was it to navigate through the app? | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Very Difficult |  |  |  |  |  | Very Easy |
| Q5. Was it easy to choose a location using the map? | ||||||
| No | Yes | |||||
 |  | |||||
| Q6. How satisfied are you with the speed of displaying the detection result? | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Not at all |  |  |  |  |  | Very Much |
| Q7. How satisfied are you with the accuracy of the results? | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Not at all |  |  |  |  |  | Very Much |
| Q8. How useful did you find the information about the plants-insects-pathogens contained in the catalog of the application? | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Not at all |  |  |  |  |  | Very Much |
| Q9. Did you make use of the history of past diagnoses provided by the app? | ||||||
| No | Yes | |||||
 |  | |||||
| Q10. Did you encounter any difficulties or problems when using the application? If so, what were they? | ||||||
| No | Yes | |||||
 |  | |||||
| Q11. Is there any feature that you think is missing from the application? If so, which one? | ||||||
| No | Yes | |||||
 |  | |||||
| Q12. How many times did you use the application during the testing period? | ||||||
| Very Few (<5) | Few (<10) | Several (>10) | Many (>20) | |||
 |  |  |  | |||
| Q13. Would you recommend the app to a friend or colleague? | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Very Difficult |  |  |  |  |  | Very Easy |
| Q14. Is there anything else you would like to share with us about the app? | ||||||
Figure A1 presents the results from the user experience questionnaire conducted after the experimental session of the mobile application testing phase. The subfigures (a) to (m) depict the distribution of user responses, providing insights into the overall user satisfaction and the effectiveness of the mobile application. The responses are generally positive, with higher ratings indicating user satisfaction and the application’s usability.
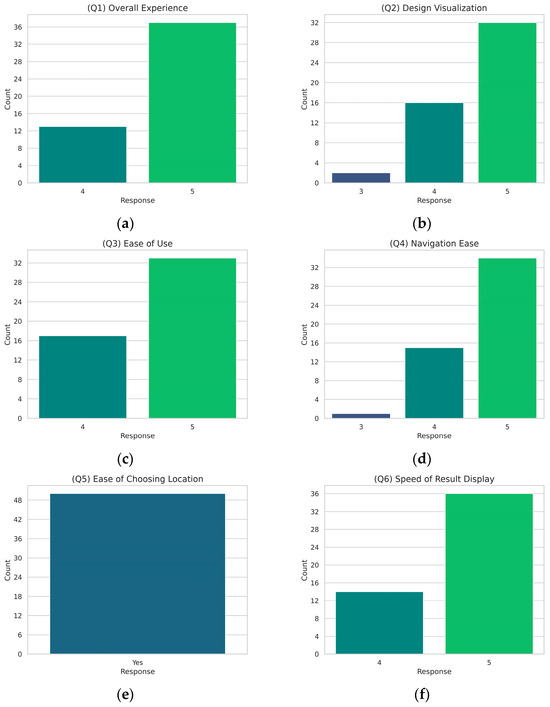
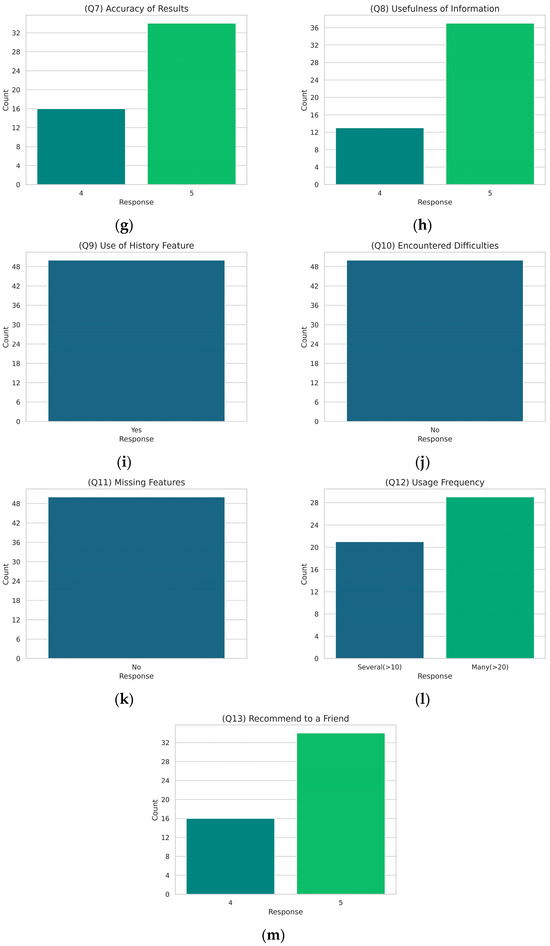
Figure A1.
Responses to the user experience questionnaire: (a) overall experience; (b) design visualization; (c) ease of use; (d) navigation ease; (e) ease of choosing location; (f) speed of result display; (g) accuracy of results; (h) usefulness of information; (i) use of history feature; (j) encountered difficulties; (k) missing features; (l) usage frequency; (m) recommend to a friend. Each subfigure illustrates the distribution of responses for a specific question, highlighting user satisfaction and feedback on various aspects of the mobile application.
Figure A1.
Responses to the user experience questionnaire: (a) overall experience; (b) design visualization; (c) ease of use; (d) navigation ease; (e) ease of choosing location; (f) speed of result display; (g) accuracy of results; (h) usefulness of information; (i) use of history feature; (j) encountered difficulties; (k) missing features; (l) usage frequency; (m) recommend to a friend. Each subfigure illustrates the distribution of responses for a specific question, highlighting user satisfaction and feedback on various aspects of the mobile application.
References
- FAO. News Article: New Standards to Curb the Global Spread of Plant Pests and Diseases. 2018. Available online: https://www.fao.org/news/story/en/item/1187738/icode/ (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Carvajal-Yepes, M.; Cardwell, K.; Nelson, A.; Garrett, K.A.; Giovani, B.; Saunders, D.G.O.; Kamoun, S.; Legg, J.P.; Verdier, V.; Lessel, J.; et al. A global surveillance system for crop diseases. Science 2019, 364, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boedeker, W.; Watts, M.; Clausing, P.; Marquez, E. The global distribution of acute unintentional pesticide poisoning: Estimations based on a systematic review. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hiary, H.; Bani-Ahmad, S.; Reyalat, M.; Braik, M.; Alrahamneh, Z. Fast and accurate detection and classification of plant diseases. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 17, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Dinh, A.; Wahid, K.; Bhowmik, P. Detection of potato diseases using image segmentation and multiclass support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Windsor, ON, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Khirade, S.D.; Patil, A. Plant disease detection using image processing. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation, Pune, India, 26–27 February 2015; pp. 768–771. [Google Scholar]
- Butterfield, J.; Bingham, S.; Savory, A. Keeping Management Proactive. In Holistic Management Handbook; Island Press/Center for Resource Economics: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 129–175. ISBN 978-1-64283-064-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ramcharan, A.; McCloskey, P.; Baranowski, K.; Mbilinyi, N.; Mrisho, L.; Ndalahwa, M.; Legg, J.; Hughes, D.P. A mobile-based deep learning model for cassava disease diagnosis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 425916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutot, M.; Nelson, L.; Tyson, R. Predicting the spread of postharvest disease in stored fruit, with application to apples. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 85, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zheng, T.; Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Sun, C.; Yang, X. Classification and detection of insects from field images using deep learning for smart pest management: A systematic review. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 66, 101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrellis, N. Mobile application for plant disease classification based on symptom signatures. In Proceedings of the 21st Pan-Hellenic Conference on Informatics, Larissa, Greece, 28–30 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Aletdinova, A. Popular Mobile Applications for Crop Production. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 666, 032036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, J. Number of Apps in Leading App Stores. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/276623/number-of-apps-available-in-leading-app-stores/ (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Singh, A.K.; Ganapathysubramanian, B.; Sarkar, S.; Singh, A. Deep learning for plant stress phenotyping: Trends and future perspectives. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B. Plant disease detection and classification by deep learning—A review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 56683–56698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrellis, N. Plant disease diagnosis for smart phone applications with extensible set of diseases. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, S.; Kishore, G.; Rajesh, V.; Suchitra, S.; Sophia, S.G.; Pavithra, B. Tomato leaf disease detection using deep learning techniques. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 10–12 June 2020; pp. 979–983. [Google Scholar]
- Al Bashish, D.; Braik, M.; Bani-Ahmad, S. A framework for detection and classification of plant leaf and stem diseases. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, Chennai, India, 15–17 December 2010; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Arsenovic, M.; Karanovic, M.; Sladojevic, S.; Anderla, A.; Stefanovic, D. Solving current limitations of deep learning based approaches for plant disease detection. Symmetry 2019, 11, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchi, H.; Sadik, M.; Khaldoun, M. On using artificial intelligence and the internet of things for crop disease detection: A contemporary survey. Agriculture 2021, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picon, A.; Alvarez-Gila, A.; Seitz, M.; Ortiz-Barredo, A.; Echazarra, J.; Johannes, A. Deep convolutional neural networks for mobile capture device-based crop disease classification in the wild. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 161, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, H.; Li, L. Advanced agricultural disease image recognition technologies: A review. Inf. Process. Agric. 2022, 9, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Yang, Y.; Yue, Y.; Ye, C.; Hassan, M.; Cheng, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Deep Learning Based Detector YOLOv5 for Identifying Insect Pests. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, T.; Li, X.; Dong, J.; Liu, J. Recommending Advanced Deep Learning Models for Efficient Insect Pest Detection. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Chen, P.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Xie, C. Insect Detection and Classification Based on an Improved Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumoglou, N.; Pechlivani, E.M.; Tzovaras, D. Generate-Paste-Blend-Detect: Synthetic dataset for object detection in the agriculture domain. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.; Adamson, N.; Aktipis, A.; Andersen, L.; Austin, R.; Barnes, L.; Beasley, M.; Bedell, K.; Briggs, S.; Chapman, B. The role of citizen science in addressing grand challenges in food and agriculture research. Proc. R. Soc. B 2018, 285, 20181977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebitu, L.; Avery, H.; Mourad, K.A.; Enyetu, J. Citizen science for sustainable agriculture–A systematic literature review. Land Use Policy 2021, 103, 105326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar, A.; Bibi, N.; Naqvi, R.A.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Jeong, D. Revolutionizing agriculture with artificial intelligence: Plant disease detection methods, applications, and their limitations. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1356260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscano-Miranda, R.; Toro, M.; Aguilar, J.; Caro, M.; Marulanda, A.; Trebilcok, A. Artificial-intelligence and sensing techniques for the management of insect pests and diseases in cotton: A systematic literature review. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 160, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, B.K.; Iyawa, G.E.; Gamundani, A.M. Systematic Review of Plant Pest and Disease Identification Strategies and Techniques in Mobile Apps. In Trends and Applications in Information Systems and Technologies; Rocha, Á., Adeli, H., Dzemyda, G., Moreira, F., Ramalho Correia, A.M., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1366, pp. 491–502. ISBN 978-3-030-72650-8. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R.; Casario, B.; Zipse, P.; Grabosky, J. An Analysis of the Accuracy of Photo-Based Plant Identification Applications on Fifty-Five Tree Species. AUF 2022, 48, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqua, A.; Kabir, M.A.; Ferdous, T.; Ali, I.B.; Weston, L.A. Evaluating Plant Disease Detection Mobile Applications: Quality and Limitations. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Next Vision Limited. Picture Insect: Bug Identifier. 2019. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.glority.pictureinsect&hl=en (accessed on 6 December 2023).
- Glority Global Group Ltd. PictureThis—Plant Identifier. 2017. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=cn.danatech.xingseus&hl=en (accessed on 6 December 2023).
- Mobile Heroes. Blossom—Plant Identifier. 2021. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.conceptivapps.blossom&hl=en (accessed on 6 December 2023).
- Next Vision Limited. Picture Mushroom—Mushroom ID. 2019. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.glority.picturemushroom&hl=el (accessed on 6 December 2023).
- Movement Ecology Lab. Mosquito Alert. 2014. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=ceab.movelab.tigatrapp&hl=en (accessed on 6 December 2023).
- Chen, C.-J.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.-M. Identification of Fruit Tree Pests with Deep Learning on Embedded Drone to Achieve Accurate Pesticide Spraying. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 21986–21997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumoglou, N.; Pechlivani, E.M.; Katsoulas, N.; Tzovaras, D. White Flies and Black Aphids Detection in Field Vegetable Crops using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Conference on Image Processing Applications and Systems (IPAS), Genova, Italy, 5–7 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Giakoumoglou, N.; Pechlivani, E.M.; Sakelliou, A.; Klaridopoulos, C.; Frangakis, N.; Tzovaras, D. Deep learning-based multi-spectral identification of grey mould. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 4, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X. Deep learning in agriculture: A survey. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 147, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ganapathysubramanian, B.; Singh, A.K.; Sarkar, S. Machine Learning for High-Throughput Stress Phenotyping in Plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mdhaffar, A.; Zalila, B.; Moalla, R.; Kharrat, A.; Rebai, O.; Hsairi, M.M.; Sallemi, A.; Kobbi, H.; Kolsi, A.; Chatti, D.; et al. A Smart Trap for Counting Olive Moths Based on the Internet of Things and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/ACS 19th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 5–8 December 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, A.; Yoon, S.; Kim, S.C.; Park, D.S. A Robust Deep-Learning-Based Detector for Real-Time Tomato Plant Diseases and Pests Recognition. Sensors 2017, 17, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Xie, C.; Yang, P.; Wang, F.; Sudirman, S.; Liu, W. PestNet: An End-to-End Deep Learning Approach for Large-Scale Multi-Class Pest Detection and Classification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 45301–45312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumoglou, N.; Pechlivani, E.-M.; Frangakis, N.; Tzovaras, D. Enhancing Tuta absoluta Detection on Tomato Plants: Ensemble Techniques and Deep Learning. AI 2023, 4, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, L.; Xie, C.; Yang, P.; Li, R.; Zhou, M. AgriPest: A Large-Scale Domain-Specific Benchmark Dataset for Practical Agricultural Pest Detection in the Wild. Sensors 2021, 21, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giakoumoglou, N.; Kalogeropoulou, E.; Klaridopoulos, C.; Pechlivani, E.M.; Christakakis, P.; Markellou, E.; Frangakis, N.; Tzovaras, D. Early detection of Botrytis cinerea symptoms using deep learning multi-spectral image segmentation. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, T.; Khan, A.; Umraiz, M.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, H. Multi-Scale Context Aggregation for Strawberry Fruit Recognition and Disease Phenotyping. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 124491–124504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasrawi, R.; Amro, M.; Zaghal, R.; Sawafteh, M.; Polo, S.V. Machine Learning Techniques for Tomato Plant Diseases Clustering, Prediction and Classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Promising Electronic Technologies (ICPET), Deir El-Balah, Palestine, 17–18 November 2021; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, M.; Diepeveen, D.; Laga, H.; Jones, M.G.K.; Sohel, F. Plant disease recognition in a low data scenario using few-shot learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 219, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Zhou, L.; Xie, X.; Zhao, W.; Liang, Z.; Zhuang, P. Dual-branch collaborative learning network for crop disease identification. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1117478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Environment Agency. Towards an Early Warning and Information System for Invasive Alien Species (IAS) Threatening Biodiversity in Europe; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2010; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2800/4167 (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Biodiversity Strategy for 2030—European Commission. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/strategy/biodiversity-strategy-2030_en (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Pechlivani, E.M.; Gkogkos, G.; Giakoumoglou, N.; Hadjigeorgiou, I.; Tzovaras, D. Towards Sustainable Farming: A Robust Decision Support System’s Architecture for Agriculture 4.0. In Proceedings of the 2023 24th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), Rhodes (Rodos), Greece, 11–13 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fielding, R.T. Architectural Styles and the Design of Network-Based Software Architectures. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Irvine, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fielding, R.; Nottingham, M.; Reschke, J. RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics; RFC Editor: Marina del Rey, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fette, I.; Melnikov, A. RFC 6455: The WebSocket Protocol; RFC Editor: Marina del Rey, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara, J. Toward a Commodity Enterprise Middleware: Can AMQP enable a new era in messaging middleware? A look inside standards-based messaging with AMQP. Queue 2007, 5, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; NanoCode012; Kwon, Y.; Michael, K.; Xie, T.; Fang, J.; Imyhxy; et al. ultralytics/yolov5: v7.0—YOLOv5 SOTA Realtime Instance Segmentation. Zenodo 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. arXiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLO. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Bourdev, L.; Girshick, R.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Dollár, P. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. arXiv 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).