Improvement of Sound-Absorbing Wool Material by Laminating Permeable Nonwoven Fabric Sheet and Nonpermeable Membrane
Abstract
1. Introduction
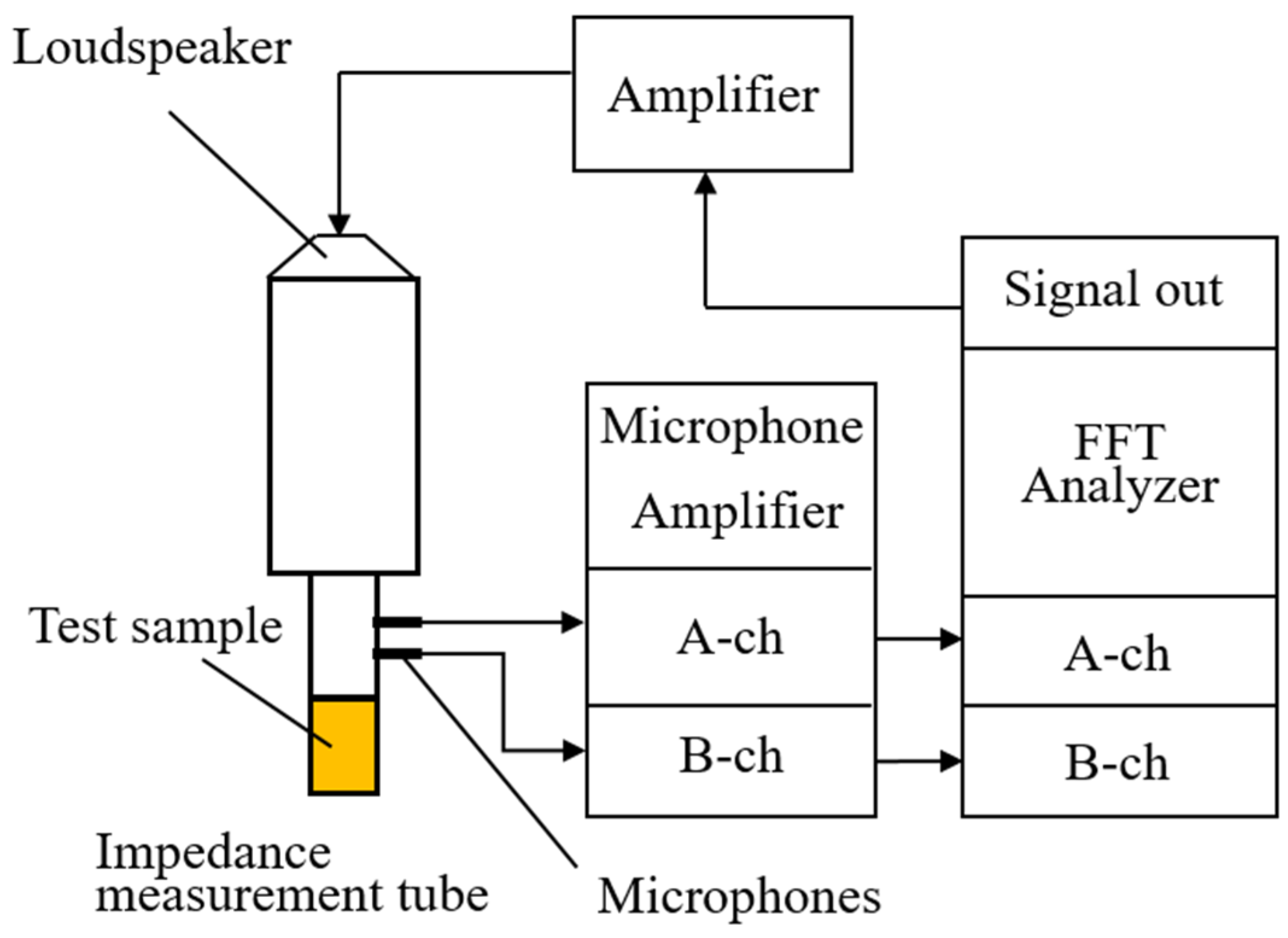
2. Measurement Equipment and Samples
2.1. Measuring Equipment
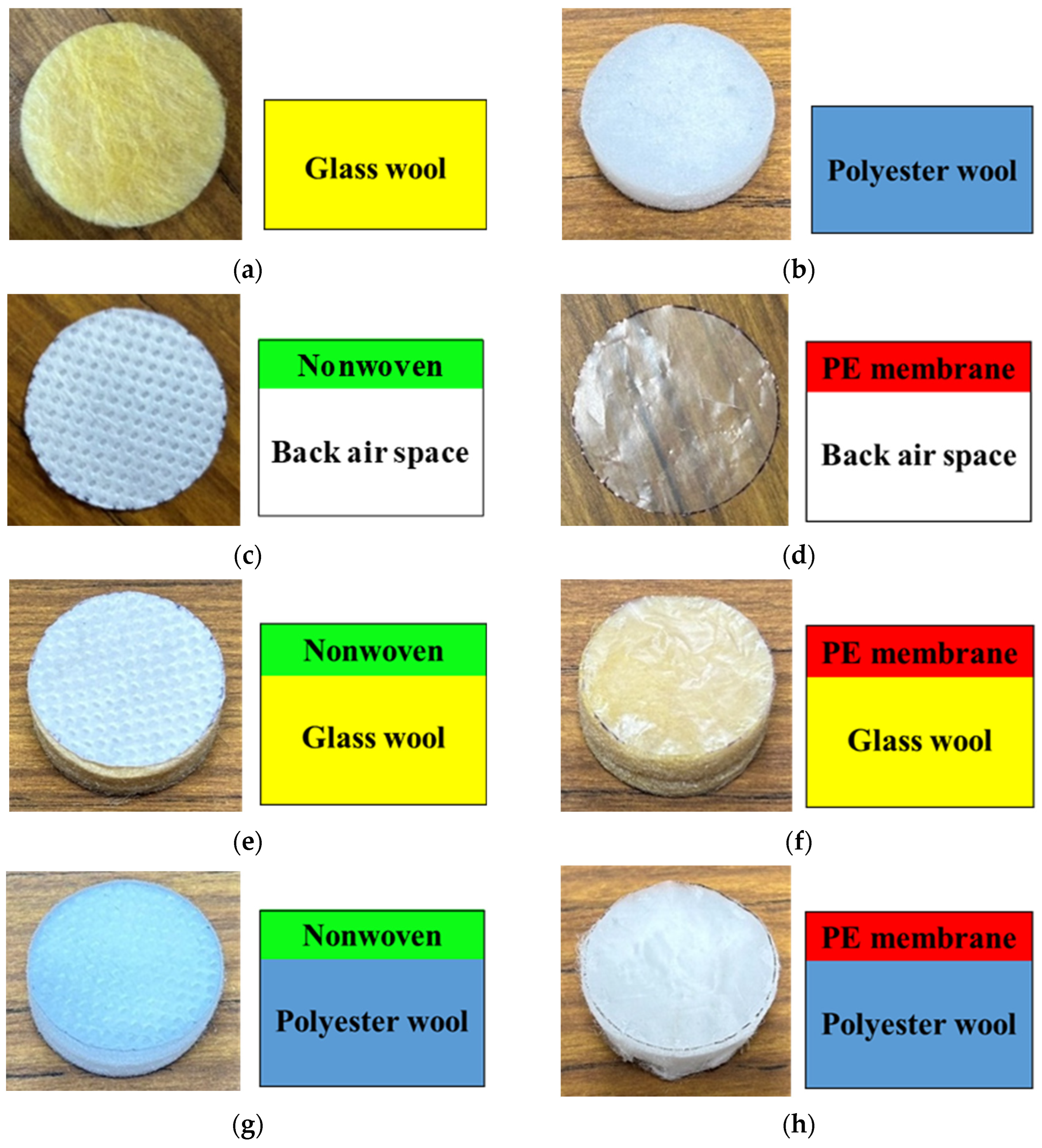
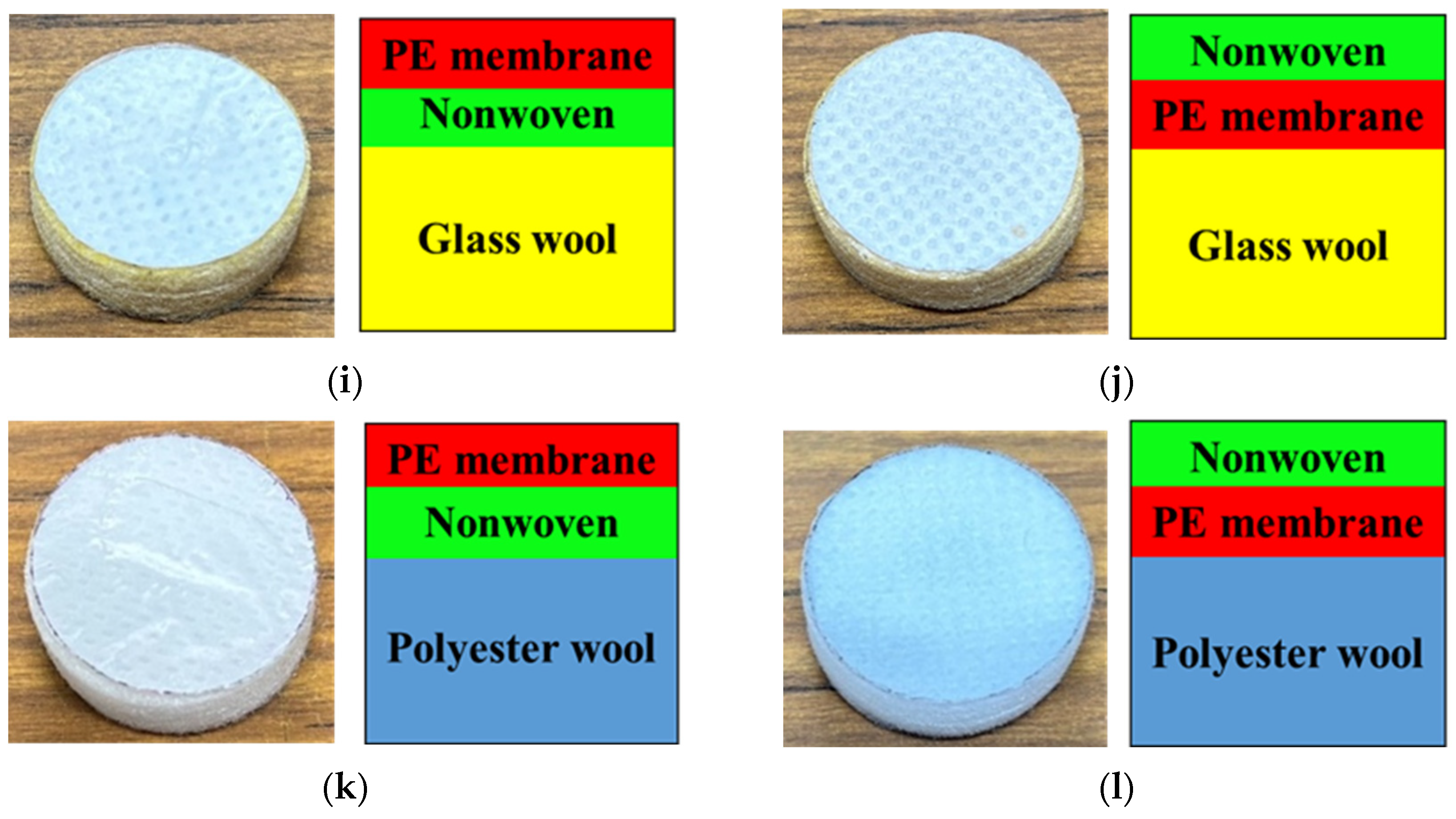
2.2. Measurement Samples
2.3. Sample Holder
3. Theoretical Analysis
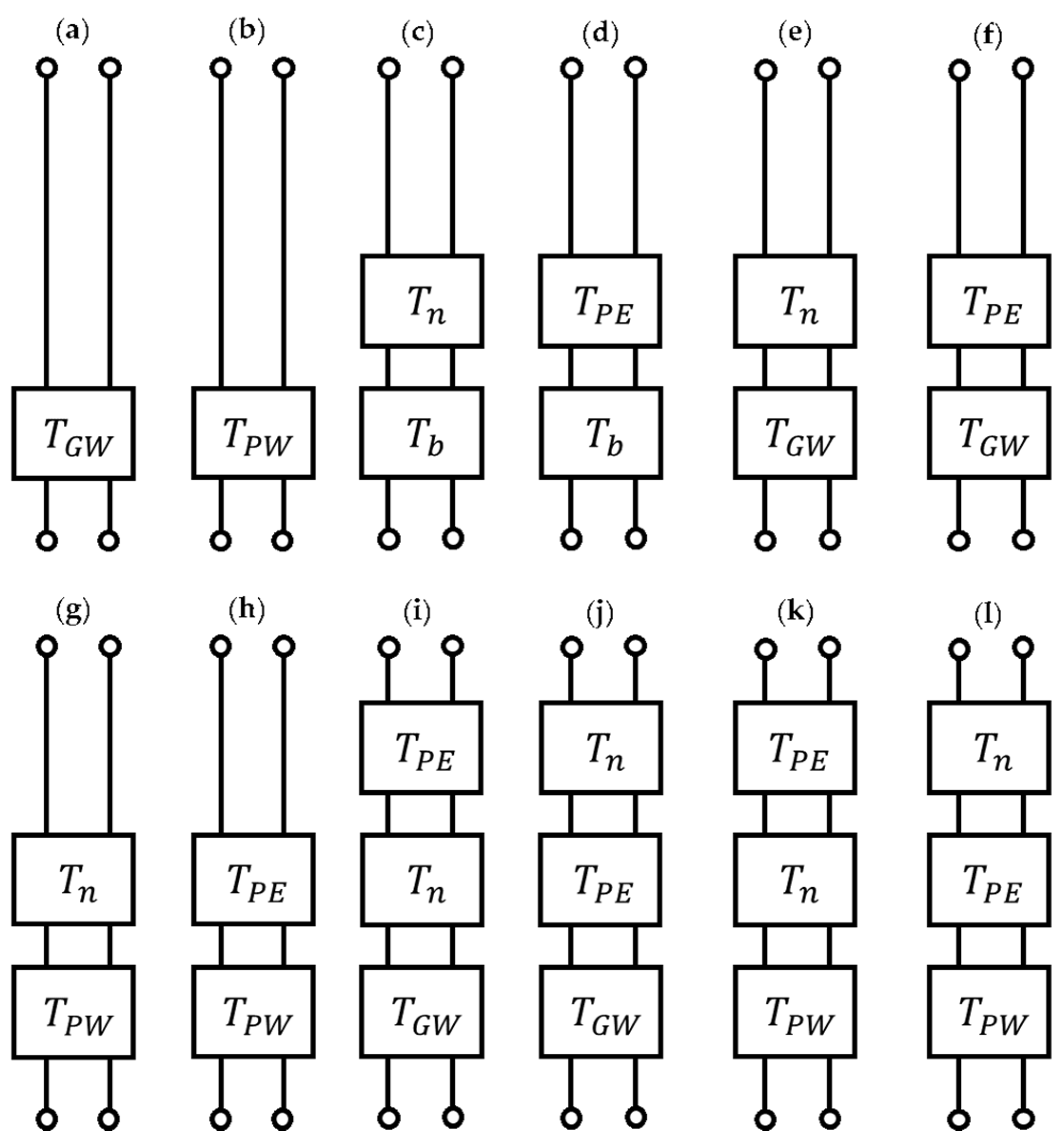
3.1. Analytical Model for Each Stacked Structure
3.2. Transfer Matrix Based on One-Dimensional Wave Equation
3.3. Transfer Matrix of Back Air Space
3.4. Transfer Matrix of Porous Materials
3.5. Transfer Matrix of PE Membrane
3.6. Overall Transfer Matrix and Sound-Absorption Coefficient
4. Experimental and Theoretical Values of Sound-Absorption Coefficient
4.1. Sound-Absorption Coefficient of Individual Materials
4.2. Sound-Absorption Coefficient of Samples with Two Materials Stacked Together
4.3. Experimental and Theoretical Values for Samples with Three Material Stacks
4.4. Sensitivity Analysis of the Theoretical Results for Different Nonwoven Fabric Thicknesses
4.5. Improvement of Sound-Absorption Coefficient by Addition of Thin Film
4.6. Comparison with Samples with an Occupied Thickness of 20 mm
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.W.; Park, S.W. Effect of Fiber Cross Section Shape on the Sound Absorption and the Sound Insulation. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 2937–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, D.V.; Chen, Y.; Sun, L. Reducing Automotive Interior Noise with Natural Fiber Nonwoven Floor Covering Systems. Text. Res. J. 2006, 76, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Mohanty, A.R. Acoustical and fire-retardant properties of jute composite materials. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, T.F.; Sarradj, E. Self Noise Reduction and Aerodynamics of Airfoils with Porous Trailing Edges. Acoustics 2019, 1, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Iizuka, R.; Nozawa, T. Effect of sheet vibration on the theoretical analysis and experimentation of Nonwoven fabric sheet with back air space. Materials 2022, 15, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Nozawa, T.; Sato, K. Nonwoven fabric sheet with back air space serving as Helmholtz resonator. Noise Control Eng. J. 2024, 72, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, J.W.S. The Theory of Sound, 2nd ed.; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1945; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Delany, M.E.; Bazley, E.N. Acoustic Properties of Fibrous Absorbent Materials. Appl. Acoust. 1970, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, J.F.; Champoux, Y. New empirical equations for sound propagation in rigid frame fibrous materials. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 3346–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, Y. Acoustical properties of porous materials-Modifications of Delany-Bazley models. J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. 1990, 11, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, T. Improvement of the Delany-Bazley and Miki models for fibrous sound-absorbing materials. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2008, 29, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horai, H. Characteristics and the latest trend of glass-wool insulation. Sen’i Gakkaishi 2008, 64, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugie, S.; Yoshimura, J.; Ogawa, H. Absorption characteristics of fibrous material covered with perforated facing and film. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2006, 27, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosten, C.W. Absorption of Sound by Coated Porous Rubber Wallcovering Layers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1946, 18, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.; Buehner, W.L. Effects of Light Coatings on Impedance and Absorption of Open-Celled Foams. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1963, 35, 1507–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, K.; Nishio, J.; Morimoto, M. Effect of impervious films on the absorption characteristics of porous absorbent materials. Report. Res. Cent. Urban Saf. Secur. Kobe Univ. 2009, 13, 211–217. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, J.P.; Pearse, J.R.; Latimer, M.D. Sound absorption of elastic framed porous materials in combination with impervious films: Effect of bonding. Appl. Acoust. 2002, 63, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Fujisawa, K.; Watanabe, S. Small plate vibration sound-absorbing device with a clearance and without surrounding restriction: Theoretical analysis and experiment. Noise Control Eng. J. 2021, 69, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yan, X. Sound Absorption Properties of Nonwoven Fabric Based Multi-Layer Composites. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, K.; Kiyama, M.; Morimoto, M.; Takahashi, D. Sound absorption of a cavity-backed membrane: A step towards design method for membrane-type absorbers. Appl. Acoust. 1996, 49, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeia, K.A.; Gooneie, A.; Simonetti, P.; Nazir, R.; Kaiser, J.P.; Rippl, A.; Hirsch, C.; Lehner, S.; Rupper, P.; Hufenus, R.; et al. Comprehensive study on flame retardant polyesters from phosphorus additives. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 155, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10534 2; Acoustics—Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes—Part 2: Transfer-Function Method. International Standard: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- Yu, G.C.; Park, J.J.; Kang, E.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Huh, Y.; Lee, S.G. Study on the Sound Absorption Properties of Recycled Polyester Nonwovens through Alkaline Treatment and Dimple Processing. Surfaces 2024, 7, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyama, E.; Hirata, M. The four terminal matrices of tube system based on assuming of plane wave propagation with frictional dissipation: Acoustic characteristic analysis of silencing systems based on assuming of plane wave propagation with frictional dissipation part 2. J. Acoust. Soc. J. 1979, 35, 165–170. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Name | Ventilation Resistance R [kPa·s/m] | Thickness t [mm] | Resistivity σ [kPa·s/m2] | Areal Density ρa [g/m2] | Density ρ [kg/m3] | Fiber Diameter [μm] | Porosity * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass wool 74k | 0.425 | 10 | 57.3 | 738.5 | 73.85 | 12.4 | 0.029 |
| Polyester wool | 0.218 | 10 | 21.8 | 900 | 90.00 | 20 | 0.065 |
| Nonwoven fabric (3A01A) | 0.336 | 0.4 | 880 | 103 | 257.5 | 12.1 | 0.19 |
| PE membrane | 0.017 | 16.15 | 950 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakamoto, S.; Sato, K.; Muroi, G. Improvement of Sound-Absorbing Wool Material by Laminating Permeable Nonwoven Fabric Sheet and Nonpermeable Membrane. Technologies 2024, 12, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12100195
Sakamoto S, Sato K, Muroi G. Improvement of Sound-Absorbing Wool Material by Laminating Permeable Nonwoven Fabric Sheet and Nonpermeable Membrane. Technologies. 2024; 12(10):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12100195
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakamoto, Shuichi, Kodai Sato, and Gaku Muroi. 2024. "Improvement of Sound-Absorbing Wool Material by Laminating Permeable Nonwoven Fabric Sheet and Nonpermeable Membrane" Technologies 12, no. 10: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12100195
APA StyleSakamoto, S., Sato, K., & Muroi, G. (2024). Improvement of Sound-Absorbing Wool Material by Laminating Permeable Nonwoven Fabric Sheet and Nonpermeable Membrane. Technologies, 12(10), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12100195






