Abstract
The study assessed a new interactive technology system for helping six people with intellectual and visual disabilities exercise relevant physical responses embedded within a fairly straightforward activity (i.e., placing objects in containers). Activity responses consisted of the participants taking objects from the floor or a low shelf and placing those objects in a container high up in front of them (thus bending their body and legs and stretching their arms and hands). The technology involved a portable computer, a webcam, and three mini speakers whose basic functions included monitoring the participants’ responses, delivering preferred stimulation contingent on the responses and verbal encouragements/prompts for lack of responses, and assisting in data recording. The study was conducted following a non-concurrent multiple baseline design across participants. During baseline (i.e., when the system was used only for data recording), the participants’ mean frequency of responses per session varied between zero and nearly 12. During intervention (i.e., when the system was fully working), the participants’ mean frequency of responses per session increased to between about 34 and 59. Mean session duration varied between nearly 10 and over 14 min. The new system may be a valuable tool for supporting relevant physical activity engagement in people with intellectual and multiple disabilities.
1. Introduction
A large number of studies have shown that people with intellectual or multiple disabilities (e.g., combinations of intellectual disability and motor or sensory impairments), tend to have low levels of physical activity compared to their typical peers [1,2,3,4,5]. A low level of physical activity is generally considered responsible for a variety of adverse effects. Among those effects, one may include (a) a limitation of people’s interaction with their environment and a consequent reduction of their opportunities to learn new associations, (b) an increased level of passivity and sedentariness interfering with initiative and limiting stimulation input, (c) a decline in the health condition in areas such as breathing, muscle tone, and blood circulation, and (d) a proneness to be overweight and develop cardiovascular diseases [6,7,8,9,10,11].
In light of the above, there is a consensus on the need to help people with intellectual and multiple disabilities get involved in physical activity [6,12,13]. Various intervention programs have been suggested for reaching this goal. Many of those programs were based on the use of staff supervision and prompts to support the participants’ activity engagement with or without the involvement of exercise devices (e.g., treadmills and stationary bicycles) [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Other programs were based on the use of interactive technologies, that is, technologies monitoring the participants’ activity engagement and responding to it with the delivery of positive (potentially motivating) stimulation [7,20,21,22,23].
Programs utilizing interactive technologies may be considered a useful resource for three reasons. First, through the use of positive stimulation, they motivate independent activity engagement of participants who may benefit from enhanced personal appreciation of the importance of engaging in physical activity [7,24,25]. Second, by promoting the participants’ spontaneous (self-regulated) activity engagement, they (a) ensure respect for the participants’ self-determination and choice, and (b) counter any experience of stress and anxiety, which could occur in the case of strict staff supervision [7,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Third, by automatically monitoring the participants’ engagement and regulating stimulation, they limit the demands on staff supervision time and thus make the intervention relatively feasible within daily contexts [8,31,32].
Two main groups of studies have been reported with the use of interactive technologies. The first group includes studies that were aimed at fostering participants’ performance of specific physical activity responses (e.g., arm stretching and leg movements) through technology-regulated delivery of brief periods of preferred stimulation contingent on those responses [23,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. The second group includes studies that were aimed at fostering participants’ engagement in physical activity responses (e.g., performing sport-related movements) with the help of video games (exergames) and the auditory and visual stimulation connected to those games [41,42,43,44,45].
While both groups of studies have reported satisfactory results, there is a difference in the characteristics of the participants involved in the studies. The studies based on contingent stimulation for specific responses have typically involved people with severe or profound intellectual and multiple disabilities [8,25,40,46]. The studies based on video games have typically involved people with mild-to-moderate intellectual disability and/or autism [8,42,43,47,48]. Video games, in fact, may not suit participants with severe-to-profound intellectual disabilities and visual or motor impairment (i.e., for participants who generally lack the prerequisites for playing those games).
The present study extended the research work carried out with the use of contingent stimulation for specific responses and included six participants who presented with severe or severe-to-profound intellectual disability and visual impairment. The responses selected for the participants to perform/exercise (a) were part of a fairly straightforward activity, which was meaningful and adaptive for them (i.e., taking objects from the floor or a low shelf and placing those objects in a container high up in front of them), and (b) involved motor schemes (i.e., bending and stretching sequences) whose exercise was considered highly beneficial for them. The use of a meaningful activity was seen as a practical and advantageous condition for helping the participants understand and organize the responses and related motor schemes targeted within the study (i.e., responses and motor schemes that would be difficult to explain and perform in abstract).
The technology used for the study did not involve sensors/microswitches physically connected to the participants’ body or their engagement material (as typically occurred in previous studies in the area [8,28,33,36,38,39,40]). Rather, it entailed a webcam linked to a portable computer, which monitored from a distance the participants’ response engagement in three successive activity stations, regulated the delivery of brief periods of positive stimulation contingent on each response, guided the transition from one station to the next, and provided encouragements/prompts when there was no responding. The new technology system was seen as advantageous over previous systems using sensors in two respects, that is, it was non-intrusive (while still totally adequate for monitoring responses and delivering stimulation) and included the encouragements/prompts option. The authors’ hypothesis was that the combination of a meaningful activity and the new technology system would prove effective in helping the participants increase and consolidate functional physical responses.
2. Method
2.1. Participants
Table 1 provides the chronological age and the Vineland age equivalents for Daily Living Skills (personal sub-domain) for the six participants, who are referred to via their pseudonyms. Their chronological ages varied between 24 and 56 years. Their Vineland age equivalents measured via the second edition of the Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales [49,50] ranged between 2 years and 7 months and 3 years and 2 months. Five participants (i.e., all except Vance) were totally blind. Vance had a minimal residual vision that allowed him to see large objects in his proximity. The visual impairments (i.e., blindness and minimal residual vision) were linked to the participants’ congenital cerebropathy. All participants attended rehabilitation and care centers in which they were involved in simple occupational activities (e.g., sorting objects, putting objects away, and washing fruit items), typically under staff supervision. Given their condition, no formal testing had been conducted with them. Estimates of their level of intellectual disability made by the psychological services of the centers they attended ranged between severe and severe-to-profound.

Table 1.
Participants’ chronological age and Vineland age equivalents for Daily Living Skills (personal sub-domain) (DLSP).
The participants were included in the study based on various conditions. First, they were known to engage in occupational tasks involving mild physical activity (e.g., putting away objects) under staff supervision. Second, they responded to verbal prompts (e.g., started or resumed their occupational responses in relation to the prompts) and appeared interested in environmental stimulation. Staff and our preliminary observations had indicated that the participants showed seemingly positive reactions (e.g., smiles, orienting, head, and hands movements) in relation to forms of stimulation such as specific music pieces and combinations of music and staff praise. Third, physiotherapists had pointed out the importance that the participants’ physical activity would include responses, which were rarely exercised within typical occupational tasks (e.g., going down to reach the ground or a low shelf with their hands, raising to a standing position, and stretching arms and hands upward). Fourth, staff were highly supportive of a program that would include the aforementioned responses within an occupational (meaningful/functional) activity. Staff also considered the use of an interactive technology system to support the participants’ activity engagement (i.e., to make it independent of their strict/direct supervision) essential to make such engagement feasible within the daily context.
2.2. Ethical Approval and Informed Consent
Being involved in a program that would provide preferred stimulation for the performance of occupational activities containing relevant body movements was considered to be a positive experience for the participants (i.e., an experience that they could find beneficial and also enjoyable given the stimulation available during the program). While staff readily agreed on this point, the research team did not feel confident that they could provide the participants with accessible information about the study or that they could assess the participants’ capacity to consent to the study. Given the low-risk nature of the study, it was therefore deemed acceptable that legal representatives would be involved in providing consent on the participants’ behalf. The study complied with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments and was approved by an institutional Ethics Committee.
2.3. Setting, Sessions, Activity Stations and Responses, Stimuli, and Research Assistants
The setting for the baseline and intervention sessions consisted of rooms in the rehabilitation and care contexts that the participants attended. Every room contained three activity stations. The stations were arranged along two contiguous walls of the room (distributed across the angle the two walls made) and separated from one another by a distance typically exceeding 2 m. Each station involved a series of objects that were on the floor or a low shelf in front of a cupboard or cabinet and a container, which was on top of the cupboard or cabinet. The position/height of the container could vary across participants based on the participants’ height. The participants’ responses consisted of taking the objects on the floor or low shelf and putting them into the container on top of the cupboard/cabinet. Taking objects from the floor or shelf required them to bend their knees or body and putting the objects in the containers required them to straighten their shoulders and stretch their arms and hands upward (i.e., to execute the motor schemes recommended for them by physiotherapists; see Section 2.1). The objects available varied across stations and sessions (e.g., water bottles, salt and pasta packages, and soap). The weight of the single objects was typically 1 Kg. The number of objects available at each station ranged between 9 and 21 depending upon the participants’ response speed. The length of the sessions was planned to range between about 10 and 15 min.
The stimuli available for the participants contingent on their responses involved music and songs, which could be combined with short verbal praise from staff. Those stimuli were selected following a stimulus preference screening in which different segments of each specific stimulus (e.g., three 10 s segments of a particular song) were presented to determine the participants’ reactions to them. Every segment was presented about 10 non-consecutive times. A stimulus was used during the study if the research assistants who carried out the screening agreed that the participant had positive reactions (e.g., smiles and vocal emissions) during 50% or more of the segment presentations.
The research assistants were four psychology graduates. All of them had work experience with people with intellectual and multiple disabilities and had previously been in charge of technology-aided intervention programs.
2.4. Technology System
The technology system included a portable computer, a webcam, and three mini speakers. The computer was fitted with a Windows 11 operating system and specific software and contained a large selection of music stimuli considered to be preferred by the participants as well as verbal encouragements/prompts and calls to move to a new station (see below). The webcam, which was linked to the computer, was fixed on a camera tripod so as to monitor from a distance the three activity stations available during the sessions. The mini speakers were located at the activity stations (one per station) and served to deliver stimulation for the responses and encouragements/prompts after preset intervals of no responding, and to call (guide) the participants from one station to the other. The specific software, which is available to the reader (https://osf.io/kd9gx/?view_only=6be9eafdc61d4613adad0368bf02f0bb accessed on 6 September 2023), was developed with Python programming language and was based on two widely used open-source libraries: OpenCV for image processing and MediaPipe Pose for detecting human body landmarks in 3D space. Based on the software, the system was able to fulfil a number of functions critical for the intervention. First, it monitored, via the webcam, the participants’ movements and in particular the position of their arms/hands in relation to the top edge of the containers where they were to place the objects collected from the floor or low shelf. Once the participants’ hands were spotted in that area, the system assumed that the participants were performing a response. Second, it provided the participants with a 12 s period of preferred stimulation (typically music and songs, which could occasionally be combined with recorded verbal praise from staff) contingent on each response. If the participants performed a new response while the stimulation for the previous response was still on, the system automatically started a new stimulation period. Third, it provided the participants with verbal encouragements/prompts to put an object in the container after a specific time period had elapsed without response (see below). Fourth, it called, via the mini speaker, the participants to the next activity station (i.e., from the first to the second and from the second to the third) after the participants (a) had used all the objects available in the previous station or (b) had used most of the objects available (i.e., a number of objects that was preset for the different participants) and were not immediately responding to the computer’s encouragements/prompts. In the latter case, the system assumed that the participants had problems finding the last objects of the series to put in the container and acted to limit participants’ failure and frustration. Fifth, it assisted in data recording (see below). The first and the last of the aforementioned functions were also enacted during the baseline.
2.5. Data Recording
Data recording concerned (a) the number of responses performed in total (i.e., the number of times the participants raised their arms and hands to the cupboard/cabinet containers to put objects in those containers), (b) the number of those responses that occurred following system encouragements/prompts, and (c) the duration of the sessions. All three measures were recorded automatically via the technology system.
2.6. Experimental Conditions and Data Analysis
The study was implemented in line with the rules of a non-concurrent multiple baseline across participants design [51,52]. The participants received different numbers of baseline sessions before the start of the intervention phase. During this phase, the technology system was available to provide the participants with preferred stimulation after each response, verbal encouragements/prompts after preset periods of no responding, and calls to move from a station to the next so as to continue the engagement. To ensure a high level of procedural fidelity during the study (i.e., to ensure that the research assistants would be accurate in implementing the baseline and intervention conditions [53]), regular feedback was provided to them about their performance. Feedback was delivered by a study supervisor who had access to video recordings of the sessions.
The percentage of non-overlapping data method (PND [54]) was used to assess the effects of the intervention with the technology system on the participants’ response performance. This method served specifically to determine the percentage of intervention data points that showed a response frequency higher than the highest baseline frequency score for each participant.
2.7. Baseline
During the baseline phase, the system was available, but it only served to monitor the participants’ responses and record the data. The setting was equipped with three activity stations and related objects as in the intervention phase (see Section 2.3). At the start of each baseline session, the research assistants guided the participants through the three stations making them touch the objects to be placed in the containers and then accompanied them to the first of the three stations and verbally instructed them to put the objects displayed on the floor or low shelf in the container on the cupboard/cabinet. The research assistants would repeat the instruction after intervals of about 2 min of no responding. The sessions ended after 10 min if the participants had performed no responses for at least 30 s. At the end of the session, the participants were provided with about 30 s of their preferred music stimulation.
2.8. Intervention
The intervention phase, which was preceded by four to six practice sessions, involved the use of the technology system that worked as described in Section 2.4. During the practice sessions, the participants (a) familiarized with the technology system (i.e., with its stimulation deliveries for the responses, calls to a new station, and encouragements/prompts), and (b) could receive research assistants’ verbal or verbal and physical prompts in combination with the system encouragements/prompts. During the regular intervention sessions, which followed the practice sessions, research assistants’ prompts were no longer available. At the start of each session, the research assistants accompanied the participants to the first activity station and told the participants that they could put the objects in the container. The system provided 12 s of preferred stimulation after each response detected (see Figure 1). In case of no responding (i.e., after an interval of 22 s had elapsed from the previous response), the system delivered a verbal encouragement/prompt to put an object in the container (see Figure 1). The encouragement/prompt was automatically repeated at 10 s intervals until a response was detected.
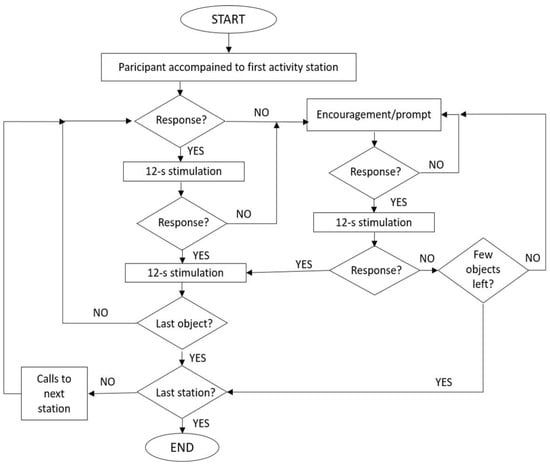
Figure 1.
Flowchart summarizing the functioning of the technology system.
The number of objects available at each station varied across participants and over sessions based on the participants’ performance. In essence, the number of objects, which varied between 9 and 21 per station, was adjusted to ensure that the sessions would be adequate (in terms of duration and occupational engagement) for the different participants. Once the participants had performed the last response of each of the first two stations (used the last object available at that station), the system activated the mini speaker of the following station. The speaker called the participants to move to the next station/activity. The calls were repeated until the system detected the first response at the new station. If the participants required encouragements/prompts for responding, the mini speaker of the following station could be activated early, that is, once the participants had used most of the objects available (see Section 2.4 and Figure 1). In case the participants moved to a new station independent of any calls and started responding there, the system provided regular stimulation for their responses at the new station.
3. Results
The six panels of Figure 2 report the baseline and intervention response data for the six participants. Black diamonds represent the mean frequency of responses performed per session over blocks of baseline and intervention sessions. Asterisks represent the mean frequency of the responses recorded during the intervention blocks that were performed following system encouragements/prompts. The blocks, which are used to simplify the graphic presentation of the data, include two sessions during the baseline and three sessions during the intervention. Blocks with different numbers of sessions are marked with a numeral specifying the sessions included. The figure does not report the practice sessions used at the start of the intervention phase.
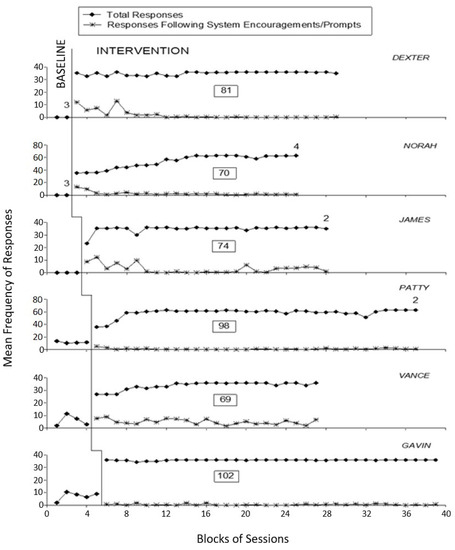
Figure 2.
The six panels report the participants’ baseline and intervention response data. Black diamonds represent the mean frequency of responses performed per session over blocks of baseline and intervention sessions. Asterisks represent the mean frequency of the responses recorded during the intervention blocks that were performed following system encouragements/prompts. The blocks include two sessions during the baseline and three sessions during the intervention. Blocks with different numbers of sessions are marked with a numeral specifying the sessions included. The values on the ordinate axes vary across participants. The boxes with numerals indicate the number of intervention sessions available.
During the baseline, which included 5 to 10 sessions, the participants’ mean frequency of responses varied between zero (Dexter, Norah, and James) and nearly 12 (Patty) per session. The participants who failed to perform any responses tended to be passive or wander in the room. The participants who performed a number of responses were typically using the objects available at the first activity station and seemed mostly unable to move to the other stations and continue their response engagement using the objects available at those stations. The mean session duration was slightly above 10 min.
During the intervention, which included 69 to 102 sessions, the mean frequency of responses performed by the participants increased to between about 34 (Vance) and 59 (Patty) per session. The differences were due to the fact that the participants were provided with varying numbers of objects at the three stations based on their response speed. It should also be noted that the number of objects available at the stations was increased over time for Norah, Patty, and Vance based on their increasing response speed. The mean frequency of responses that followed system encouragements/prompts varied from less than one per session (Gavin) to about five per session (Vance). Occasionally, it occurred that participants could move to a new station before receiving a call to that station from the system (i.e., before they had used all the objects of the previous station). The mean session duration varied between nearly 10 min (Patty) and over 14 min (James). The overall mean duration across participants was about 12 min.
The percentage of non-overlapping data method (PND) showed indices of one for all participants. In fact, all intervention data points were above the highest baseline data point for each of the participants. While these indices confirm the strong impact of the intervention with the technology system, one has to take into consideration that the intervention sessions lasted somewhat longer than the baseline sessions for four participants (i.e., Dexter, James, Vance, and Gavin).
4. Discussion
The results suggest that a technology-regulated intervention using preferred stimulation contingent on specific activity responses was effective in helping participants with severe or severe-to-profound intellectual disability and visual impairment increase the level of their responses. These results confirm previous findings on the effectiveness and applicability of such an approach with people with severe and multiple disabilities [7,8,33,34,40,46]. The same results also show the possibility of (a) having the participants engage in a functional/meaningful activity rather than in abstract responses without specific links within the context, and (b) using a technology system that does not involve sensors/microswitches physically connected to the participants’ body or their engagement material (as typically occurred in previous studies in the area) and also includes an option to provide encouragements/prompts. In light of the above, a number of considerations may be put forward.
First, increasing the physical activity of people with severe-to-profound intellectual and multiple disabilities is a valued objective of rehabilitation and care contexts that may have important health implications [5,6,12]. Pursuing this objective through the use of interactive technology may be considered profitable and convenient for at least two basic reasons. The first reason is that the participants are not forced to engage in activity responses through staff guidance, but rather motivated to do so through the availability of preferred stimulation and simple encouragements/prompts [8,46]. An intervention program that relies on participants’ motivation and promotes self-determination and independence is more likely to be perceived as respectful of the participants (i.e., the participants are essentially in charge of their responses) and less likely to create stress and anxiety to the participants [8,29,30]. The second reason is that the use of technology to support the participants’ activity engagement saves staff time. An intervention program whose application requires little staff time is more likely to be suitable for daily contexts [8,32].
Second, the possibility of involving the participants in meaningful activities rather than in isolated responses (i.e., with no links to the immediate reality) may be advantageous for the participants and relevant for the context. For example, the request to exercise responses such as bending legs and body and stretching shoulders and arms might be more difficult for the participants to understand and follow than the request to carry out the same responses as part of a meaningful/practical task [25]. Within the task, those responses are essentially instrumental to pick up the objects and to put the objects away, respectively. Having the participants engage in meaningful occupational tasks may be considered by staff more important and acceptable than asking the participants to exercise apparently insignificant responses/body schemes [26,47,55].
Third, a technology system that does not require to be linked to the participants’ body or the task material is much more practical and applicable than a technology system that involves sensors connected to the participants or the material they use, as it was generally done in previous studies [8,28,39,40,56,57]. The most immediate advantages of the new system are that (a) the participants do not have to carry any foreign element interfering with their freedom or appearance and (b) the technology can be set up more easily and rapidly independent of the participants or material involved in the intervention sessions.
Fourth, while the use of the system brought about a positive change with all participants, two of the differences characterizing the participants’ performance may be noteworthy. One such difference concerned the response frequency/speed. Some participants (i.e., Norah and Patty) performed a larger number of responses than all other participants in sessions whose length was generally shorter than that of the other participants. The other difference was the participants’ use of system encouragements/prompts. Four of them (i.e., Dexter, Norah, Patty, and Gavin) used the encouragements/prompts at (very) low rates with possible exceptions for the beginning of the intervention phase. The other two participants (i.e., James and Vance) seemed to have a somewhat larger use of the encouragements/prompts.
Limitations and Future Research
Limitations of the study may concern the small number of participants, the lack of assessment of the participants’ satisfaction with the intervention, the lack of maintenance and generalization data, and the absence of a social validation check. The use of a small number of participants, albeit highly common in this research area [8,52], prevents one from making definite statements about the robustness and generality of the data reported. New direct and systematic replication studies will help gather the evidence necessary to draw those statements [58,59,60]. An assessment of the participants’ satisfaction with the intervention could be important from a theoretical and practical standpoint. The assumption made in this study was that the participants would be fairly satisfied with the intervention sessions because they allowed them consistent access to preferred stimulation via their activity engagement [8]. Future studies could assess this aspect in two different ways. That is, they could (a) observe the participants’ indices of satisfaction/happiness during the sessions and during other daily situations or (b) have the participants choose between the sessions and other daily occupational situations [61,62].
With regard to the maintenance and generalization issue, future studies would need to include larger numbers of sessions as well as different contexts and activity situations in the assessment process [63,64]. Notwithstanding the need for new research, the relatively large and stable intervention data of this study and the fact that the technology system may ensure stable across-settings conditions might be taken as relevant elements to foresee positive maintenance and generalization outcomes. Finally, a social validation of the technology system used for the intervention and the effects of the intervention would be a relevant research step. Such a step could be accomplished with the involvement of staff personnel working with people with intellectual and multiple disabilities in daily contexts [65,66]. These personnel could be presented with video clips of the participants’ intervention sessions with the system and then asked to rate the system and its applicability across contexts as well as the overall benefits of the intervention.
5. Conclusions
The study has shown that the technology system used during the intervention sessions was helpful for supporting the participants’ engagement in relevant physical activity and increasing their responses. Indeed, the data reported appear quite promising and their implications may be significant for daily contexts responsible for the rehabilitation and care of people with intellectual and multiple disabilities. In spite of this encouraging evidence, caution is required in drawing conclusions about the technology system used and its general impact and applicability for two reasons. The first reason concerns the limitations of the present study listed above. The second reason concerns the absence of strategies (protocols) for verifying and weighing the specific benefits of moderate levels of physical activity distributed over relatively brief intervention sessions [7,8,22,28]. Future research would need to (a) address the limitations of this study, (b) investigate ways of measuring the possible (physiological and psychological) benefits of different forms and doses of physical activity for participants with severe-to-profound intellectual and multiple disabilities, and (c) plan for possible upgrades of the present technology system to facilitate its future use across participants and settings.
Author Contributions
G.E.L. was responsible for setting up the study, acquiring and analyzing the data, and writing the manuscript. G.A., C.F. and V.C. collaborated in setting up the study and the technology system, in acquiring and analyzing the data, and in editing the manuscript. N.N.S., M.F.O. and J.S. collaborated in setting up the study, analyzing the data, and writing/editing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by an institutional Ethics Committee. All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent Statement
The participants’ legal representatives provided written informed consent for the participants’ involvement in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The software they set up for the study is freely available online https://osf.io/kd9gx/?view_only=6be9eafdc61d4613adad0368bf02f0bb (accessed on 6 September 2023).
References
- Dixon-Ibarra, A.; Driver, S.; Vanderbom, K.; Humphries, K. Understanding Physical Activity in the Group Home Setting: A Qualitative Inquiry. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, E.; Nordén, H.; Ohlsson, M.L. Adolescents with Intellectual Disability (ID) and Their Perceptions of, and Motivation for, Physical Activity and Organised Sports. Sport Educ. Soc. 2023, 28, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto, M.; Vitorino, A.S.; Palmeira, D.; Antunes, R.; Matos, R.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bento, T. Perceived Barriers of Physical Activity Participation in Individuals with Intellectual Disability—A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koritsas, S.; Iacono, T. Weight, Nutrition, Food Choice, and Physical Activity in Adults with Intellectual Disability. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2016, 60, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreinbucher-Bekerle, C.; Ruf, W.; Bartholomeyczik, A.; Wieber, F.; Kiselev, N. Recommending Physical Activity for People with Intellectual Disabilities: The Relevance of Public Health Guidelines, Physical Activity Behaviour and Type of Contact. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzas, S.; Martínez-Lemos, R.I.; Ayan, C. Effects of Exercise on the Physical Fitness Level of Adults with Intellectual Disability: A Systematic Review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 41, 3118–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancioni, G.E.; Singh, N.N.; O’Reilly, M.F.; Sigafoos, J.; Alberti, G.; Perilli, V.; Zimbaro, C.; Boccasini, A.; Mazzola, C.; Russo, R. Promoting Physical Activity in People with Intellectual and Multiple Disabilities through a Basic Technology-Aided Program. J. Intellect. Disabil. 2018, 22, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancioni, G.E.; Singh, N.N.; O’Reilly, M.; Sigafoos, J.; Alberti, G.; Desideri, L. Programs Using Stimulation-Regulating Technologies to Promote Physical Activity in People with Intellectual and Multiple Disabilities: Scoping Review. JMIR Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2022, 9, e35217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Cho, M.-H. Effectiveness of Leg Movement in Reducing Leg Swelling and Discomfort in Lower Extremities. Appl. Ergon. 2012, 43, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segizbaeva, M.O.; Pogodin, M.A.; Lavrova, I.N.; Balykin, M.V.; Aleksandrova, N.P. Effect of Head-down Tilt on Respiratory Responses and Human Inspiratory Muscle Activity. Hum. Physiol. 2011, 37, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, A.; Chan, H.C.-K.; Ou, A.X.; Zhang, D.; Xie, Y.; Fong, S.S.; Gao, Y. Effectiveness of an Adapted Physical Activity Intervention on Health-Related Physical Fitness in Adolescents with Intellectual Disability: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitchford, E.A.; Dixon-Ibarra, A.; Hauck, J.L. Physical Activity Research in Intellectual Disability: A Scoping Review Using the Behavioral Epidemiological Framework. Am. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 123, 140–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queralt, A.; Vicente-Ortiz, A.; Molina-García, J. The Physical Activity Patterns of Adolescents with Intellectual Disabilities: A Descriptive Study. Disabil. Health J. 2016, 9, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassette, L.; Titus-Dieringer, S.; Zoder-Martell, K.; Cremeans, M. The Use of Video-based Instruction to Promote Independent Performance of Physical Activity Skills in Students with Developmental Disabilities in a School and Community Setting. Psychol. Sch. 2020, 57, 1439–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkoni, E.; Mavroudi, E.; Zehfroosh, A.; Galloway, J.C.; Vidal, R.; Heinz, J.; Tanner, H.G. GEARing Smart Environments for Pediatric Motor Rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrusnikova, I.; Cavalier, A.R.; Novak, H.M.; Blair, A.E. The Effect of Systematic Prompting on the Acquisition of Two Muscle-Strengthening Exercises by Adults with Moderate Intellectual Disabilities. J. Behav. Educ. 2020, 29, 584–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, E.; Johnson, J.W.; Boden, T. Using Video Modeling to Facilitate Students’ Independent Use of a Community Fitness Center. Educ. Treat. Child. 2021, 44, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptomey, L.T.; Willis, E.A.; Greene, J.L.; Danon, J.C.; Chumley, T.K.; Washburn, R.A.; Donnelly, J.E. The Feasibility of Group Video Conferencing for Promotion of Physical Activity in Adolescents with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities. Am. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2017, 122, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptomey, L.T.; Washburn, R.A.; Lee, J.; Greene, J.L.; Szabo-Reed, A.N.; Sherman, J.R.; Danon, J.C.; Osborne, L.N.; Little, T.D.; Donnelly, J.E. Individual and Family-Based Approaches to Increase Physical Activity in Adolescents with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities: Rationale and Design for an 18 Month Randomized Trial. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2019, 84, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.X.; Kornspan, A.S. The Use of Exergaming with Developmentally Disabled Students. Strategies 2012, 25, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.M.; Harvey, L.A.; Hassett, L.M. Do People with Intellectual Disability Use Nintendo Wii When Placed in Their Home as Part of a Physiotherapy Program? An Observational Study. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2016, 11, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, D.R.; Farhat, H.; Gavrila, R.; Caeyenberghs, K.; Shields, N. Do Active Video Games Improve Motor Function in People with Developmental Disabilities? A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancioni, G.E.; Singh, N.N.; O’Reilly, M.F.; Sigafoos, J.; Campodonico, F.; Oliva, D.; Alberti, G.; D’Amico, F. Using Microswitch-Aided Programs for People with Multiple Disabilities to Promote Stimulation Control and Mild Physical Exercise. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 43, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossink, L.W.; van der Putten, A.A.; Vlaskamp, C. Understanding Low Levels of Physical Activity in People with Intellectual Disabilities: A Systematic Review to Identify Barriers and Facilitators. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2017, 68, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalsen, H.; Wangberg, S.C.; Anke, A.; Hartvigsen, G.; Jaccheri, L.; Arntzen, C. Family Members and Health Care Workers’ Perspectives on Motivational Factors of Participation in Physical Activity for People with Intellectual Disability: A Qualitative Study. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2020, 64, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embregts, P.J.; van Oorsouw, W.M.; Wintels, S.C.; Van Delden, R.W.; Evers, V.; Reidsma, D. Comparing a Playful Interactive Product to Watching Television: An Exploratory Study for People with Profound Intellectual and Multiple Disabilities. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2020, 45, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.E.; Zack, E.; Battaglini, C.; Viru, M.; Viru, A.; Hackney, A.C. Exercise and Circulating Cortisol Levels: The Intensity Threshold Effect. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2008, 31, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.; Gardiner, P.A.; Cavalheri, V.; Jenkins, S.C.; Healy, G.N. Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour: Applying Lessons to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Intern. Med. J. 2015, 45, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillier, A.; Murphy, D.; Ferrara, C. A Pilot Study: Short-term Reduction in Salivary Cortisol Following Low Level Physical Exercise and Relaxation among Adolescents and Young Adults on the Autism Spectrum. Stress Health 2011, 27, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, V.A.; Zigmond, M.J.; Dimatelis, J.J.; Daniels, W.M.; Mabandla, M.V. The Interaction between Stress and Exercise, and Its Impact on Brain Function. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 29, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, A.K.; McMahon, D.D. Exercise Technology Interventions and Individuals with IDD. Div. Autism Dev. Disabil. Online J. 2016, 3, 42–53. [Google Scholar]
- McMahon, D.D.; Barrio, B.; McMahon, A.K.; Tutt, K.; Firestone, J. Virtual Reality Exercise Games for High School Students with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities. J. Spec. Educ. Technol. 2020, 35, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-L.; Shih, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-C. Encouraging Obese Students with Intellectual Disabilities to Engage in Pedaling an Exercise Bike by Using an Air Mouse Combined with Preferred Environmental Stimulation. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 3292–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-J.; Chang, M.-L.; Shih, C.-H. Encouraging Overweight Students with Intellectual Disability to Actively Perform Walking Activity Using an Air Mouse Combined with Preferred Stimulation. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2016, 55, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancioni, G.E.; O’Reilly, M.F.; Sigafoos, J.; Alberti, G.; Campodonico, F.; Chiariello, V. Promoting Occupational Engagement and Personal Satisfaction in People with Neurodevelopmental Disorders via a Smartphone-Based Intervention. Adv. Neurodev. Disord. 2019, 3, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancioni, G.E.; Singh, N.N.; O’Reilly, M.F.; Sigafoos, J.; Alberti, G.; Campodonico, F.; Tedone, R.; Quaranta, S.; Caffò, A.O. Non-Ambulatory People with Intellectual Disabilities Practice Functional Arm, Leg or Head Responses via a Smartphone-Based Program. J. Dev. Phys. Disabil. 2019, 31, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-H.; Shih, C.-T.; Chiang, M.-S. A New Standing Posture Detector to Enable People with Multiple Disabilities to Control Environmental Stimulation by Changing Their Standing Posture through a Commercial Wii Balance Board. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2010, 31, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-T.; Shih, C.-H.; Luo, C.-H. Assisting People with Disabilities in Actively Performing Physical Activities by Controlling the Preferred Environmental Stimulation with a Gyration Air Mouse. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 4328–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-H.; Chiu, Y.-C. Assisting Obese Students with Intellectual Disabilities to Actively Perform the Activity of Walking in Place Using a Dance Pad to Control Their Preferred Environmental Stimulation. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 2394–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasolla, F.; Caffò, A.O.; Perilli, V.; Boccasini, A.; Damiani, R.; D’Amico, F. Fostering Locomotion Fluency of Five Adolescents with Rett Syndrome through a Microswitch-Based Program: Contingency Awareness and Social Rating. J. Dev. Phys. Disabil. 2018, 30, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Becker, T.; Martian, A.; Danielle, P.K.; Wingen, J. Motor Control Outcomes Following Nintendo Wii Use by a Child with Down Syndrome. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2012, 24, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, P.W.-C.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.-J. Effectiveness of Active Video Game Usage on Body Composition, Physical Activity Level and Motor Proficiency in Children with Intellectual Disability. J. Appl. Res. Intellect. Disabil. 2020, 33, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrot, A.; Maillot, P.; Le Foulon, A.; Rebillat, A.-S. Effect of Exergaming on Physical Fitness, Functional Mobility, and Cognitive Functioning in Adults with Down Syndrome. Am. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2021, 126, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryuh, Y.J.; Chen, C.-C.; Pan, Z.; Gadke, D.L.; Elmore-Staton, L.; Pan, C.-Y.; Cosgriff, A. Promoting Physical Activity through Exergaming in Young Adults with Intellectual Disabilities: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Dev. Disabil. 2022, 68, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Campos, C.; Sá, A.; Cavadas, M.; Pinto, J.; Simões, P.; Machado, S.; Murillo-Rodríguez, E.; Barbosa-Rocha, N. Wii-based Exercise Program to Improve Physical Fitness, Motor Proficiency and Functional Mobility in Adults with Down Syndrome. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2017, 61, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasolla, F.; Caffò, A.O.; Perilli, V.; Albano, V. Supporting Locomotion Fluency of Six Children with Cornelia de Lange Syndrome: Awareness of Microswitch Responding and Social Validation. Technol. Disabil. 2019, 30, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkelaar, L.; Oosterom-Calo, R.; Zhou, D.; Nijhof, N.; Barakova, E.; Sterkenburg, P. The LEDs Move Pilot Study: The Light Curtain and Physical Activity and Well-being among People with Visual and Intellectual Disabilities. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2021, 65, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Álvarez, N.; Mortecinosb, A.V.; Rodríguezb, V.Z.; Fontanillab, M.L.; Vásquezb, M.M.; Pavez-Adasmea, G.; Hernández-Mosqueiraa, C. Effect of an Intervention Based on Virtual Reality on Motor Development and Postural Control in Children with Down Syndrome. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2018, 89, 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Balboni, G.; Belacchi, C.; Bonichini, S.; Coscarelli, A. Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales, 2nd ed.; Vineland-II; Giunti Psychometrics: Firenze, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow, S.S.; Cicchetti, D.V.; Balla, D.A. Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales, 2nd ed.; Vineland II; Pearson: Madrid, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, D.H.; Nock, M.; Hersen, M. Single-Case Experimental Designs: Strategies for Studying Behavior Change, 3rd ed.; Allyn & Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ledford, J.R.; Gast, D.L. Single Case Research Methodology: Applications in Special Education and Behavioral Sciences, 3rd ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 1-134-07371-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sanetti, L.M.H.; Collier-Meek, M.A. Increasing the Rigor of Procedural Fidelity Assessment: An Empirical Comparison of Direct Observation and Permanent Product Review Methods. J. Behav. Educ. 2014, 23, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.I.; Vannest, K.J.; Davis, J.L. Effect Size in Single-Case Research: A Review of Nine Nonoverlap Techniques. Behav. Modif. 2011, 35, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancioni, G.E.; Singh, N.N.; O’Reilly, M.F.; Sigafoos, J.; Desideri, L. Examples of Technology-Aided Programs to Support Physical Activity in Individuals with Intellectual and Multiple Disabilities. Life Span Disabil. 2020, 23, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, G.; Rossow-Kimball, B.; Lee, Y. Effects of 12-Week Combined Exercise Program on Self-Efficacy, Physical Activity Level, and Health Related Physical Fitness of Adults with Intellectual Disability. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2018, 14, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J.; Taylor, D.; Gamboa, P.; Vlaev, I.; Darzi, A. Using Motion-Sensor Games to Encourage Physical Activity for Adults with Intellectual Disability. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2016, 220, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kazdin, A.E. Single-Case Research Designs: Methods for Clinical and Applied Settings, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Locey, M.L. The Evolution of Behavior Analysis: Toward a Replication Crisis? Perspect. Behav. Sci. 2020, 43, 655–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travers, J.C.; Cook, B.G.; Therrien, W.J.; Coyne, M.D. Replication Research and Special Education. Remedial. Spec. Educ. 2016, 37, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, D.; Healy, O.; McEnaney, E. Defining and Measuring Indices of Happiness and Unhappiness in Children Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Behav. Anal. Pract. 2023, 16, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullis, C.A.; Cannella-Malone, H.I.; Basbigill, A.R.; Yeager, A.; Fleming, C.V.; Payne, D.; Wu, P.-F. Review of the Choice and Preference Assessment Literature for Individuals with Severe to Profound Disabilities. Educ. Train. Autism Dev. Disabil. 2011, 46, 576–595. [Google Scholar]
- Kazdin, A.E. Behavior Modification in Applied Settings, 7th ed.; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, W.D.; Cheney, C.D. Behavior Analysis and Learning: A Biobehavioral Approach, 6th ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Plackett, R.; Thomas, S.; Thomas, S. Professionals’ Views on the Use of Smartphone Technology to Support Children and Adolescents with Memory Impairment Due to Acquired Brain Injury. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2017, 12, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthen, D.; Luiselli, J.K. Comparative Effects and Social Validation of Support Strategies to Promote Mindfulness Practices among High School Students. Child Fam. Behav. Ther. 2019, 41, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).