Abstract
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) has brought revolutionary changes to the world, enabling businesses to create new experiences by combining virtual and physical worlds. As the use of GAI grows along with the Metaverse, it is explored by academics, researchers, and industry communities for its endless possibilities. From ChatGPT by OpenAI to Bard AI by Google, GAI is a leading technology in physical and virtual business platforms. This paper focuses on GAI’s economic and societal impact and the challenges it poses. Businesses must rethink their operations and strategies to create hybrid physical and virtual experiences using GAI. This study proposes a framework that can help business managers develop effective strategies to enhance their operations. It analyzes the initial applications of GAI in multiple sectors to promote the development of future customer solutions and explores how GAI can help businesses create new value propositions and experiences for their customers, and the possibilities of digital communication and information technology. A research agenda is proposed for developing GAI for business management to enhance organizational efficiency. The results highlight a healthy conversation on the potential of GAI in various business sectors to improve customer experience.
1. Introduction
Over the past few decades, there has been a growing emphasis on technological innovation within organizations leading to increased attention in research [1,2]. Organizations have recognized the potential of technological innovations to enhance their competitive advantage. Numerous studies have demonstrated that firms can leverage technology to improve their performance and drive innovation [3,4]. Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of AI in today’s market has been shown to have a significant impact on firms’ innovation strategies, as evidenced by several studies [5]. Economists and industry experts have been attempting to comprehend the effect of GAI on innovation and have urged for further investigation on the subject [6,7]. Scholars, who are focused on utilizing technology in creation, have also started to investigate this issue [8,9,10]. Studies on the use of GAI by customers in various sectors have primarily focused on identifying the barriers that prevent them from achieving the maximum outcome and how AI can assist them in making decisions and enhancing their operations [11,12].
Conceived as a sub-discipline within AI, GAI allows users to create new content, such as text, images, audio, and videos. It has attracted the interest of various tech companies, such as Google, Microsoft, Baidu, and Apple. OpenAI’s Codex, DALL-E, and ChatGPT are some of the tools used for this process [13]. Every year, a single overarching idea tends to define the major tech trend. For instance, in 2022, XAI and Web3 emerged as buzzwords that caught the tech world’s attention. Although these trends show no signs of slowing down, 2023 is expected to be dominated by GAI. The concept of GAI involves using algorithms to generate new content. ChatGPT, a chatbot capable of producing articles, poems, and computer programs, is a prominent example of this technology. Its ability to generate high-quality content is both impressive and a little scary [14]. ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI—a research organization backed by Microsoft—has garnered significant attention since its unveiling in November 2022. Its debut has led some to believe that AI is becoming more mainstream. With the commercial success of ChatGPT, Google recently launched an experimental service called Bard, which demonstrates how AI could potentially revolutionize search by providing more nuanced responses to users. [15]. The same week, Microsoft also unveiled a new Bing-powered version by ChatGPT, designed to provide users with more accurate and timely search results. Instead of relying on the traditional ladder approach to search results, ChatGPT takes a request, scans for answers, and provides a response that includes citations to the sources.
Despite the increasing importance of the role of GAI in innovation studies, there has been little effort to establish a comprehensive theoretical framework for analyzing its applications in various sectors. Moreover, the lack of a clear framework for assessing the impact of GAI on the innovation management process has hindered the development of effective strategies [16,17]. To tackle these issues, a comprehensive theoretical review of the literature on GAI was conducted. The aim of the review is to provide a basis for developing new theoretical models to study GAI in different sectors [18]. Understanding the diverse needs of customers is essential for creating value that resonates with them. This is because their subjective evaluation of wants and needs can significantly influence the design and implementation of strategies to meet those needs. In addition to identifying customers’ requirements, research emphasizes the importance of customer involvement in co-creating value [19]. Value co-creation refers to the process of involving various stakeholder groups in the creation of a product or service [20]. To enable this process, organizations must leverage appropriate technologies. This can lead to a better customer experience. Information and communications technology (ICT) has become integral to all aspects of life, allowing businesses to enhance their customer experience. By using GAI, companies can further improve their customer experience and provide personalized services [21]. Due to the increasing number of people using social media platforms, the demand for interactive technology has become more prevalent in every industry. It has led to the emergence of GAI as a leading technology flag bearer.
This paper takes a multi-disciplinary approach to explore the potential impact of GAI on customers’ experience across various sectors. It reviews the volume and trends of operative outputs related to GAI applications and identifies factors that influence the adoption of GAI by firms. The paper also proposes a conceptual business model for implementing GAI to achieve goals. However, the study is limited by a lack of comprehensiveness and a narrow scope, making it challenging for scholars to identify relevant gaps in understanding the topic.
To broaden the field’s scope, the research agenda aims to develop new research tools and methods that can enhance the understanding of the various factors influencing the decision-making process and the adoption of GAI. The paper’s main findings suggest that the framework for GAI applications should be interpretive, interactive, and immersive (3I), providing a deeper understanding of the technology’s drivers and outcomes. As GAI applications continue to impact our daily lives, developing a particular framework for sustainable behavior in the future is feasible.
The paper is organized into several sections. It begins with an exploration of GAI, followed by a discussion of its impact on consumers and content creation, as well as the advantages it offers manufacturers. Best Practices for using GAI in the Customer Experience Journey are presented. The paper also includes a discussion of GAI’s potential for businesses, and its future applications. Next, the practical and industrial implications of GAI are examined, as well as a policy framework to address its limitations. Finally, the paper concludes with a summary of the findings.
2. Exploration of GAI
GAI is used to create new content such as videos, audio, and text. Recent breakthroughs in this field have the potential to significantly change how we create content. One example of a chatbot that uses GAI is ChatGPT, which can answer questions on the spot. The OpenAI chatbot (ChatGPT), released to the public in November 2022, is regarded as the best. It already had over a million users in just five days [22]. Its creators also posted impressive examples of its output, such as poems and computer code. While the impact of GAI on content creation is still uncertain, some experts in fields such as advertising and education are keeping a close eye on developments in this area.
While there are concerns about the impact of GAI and machine learning on various industries, there is also significant potential for these technologies to have a positive impact. In recent years, machine learning has demonstrated potential in a variety of fields, including medical imaging. Aside from the technology, multiple questions must be answered to develop GAI models [23]. For instance, how does it fit into the broader machine learning framework?
Although ChatGPT has received a lot of attention recently, it is not the first text-based AI model to generate interest. Google’s BERT and OpenAI’s GPT-3 have been released to some fanfare in the past couple of years. Despite their impressive capabilities, AI chatbots were not always well reviewed [24]. Google’s chatbots have been criticized in some cases for their limited abilities and inability to provide satisfactory responses to user queries. However, recent advancements in GAI have shown promise, and chatbots such as ChatGPT demonstrate the potential for these technologies to continue to evolve and improve. It will be important to continue to explore new ways to apply AI chatbots in a way that maximizes their benefits and minimizes their limitations.
In the past, human-trained models could classify text according to labels suggested by researchers. This type of training is referred to as supervised learning and involves a human overseeing and instructing the model. Text-based models, on the other hand, are currently being trained using a self-supervised learning approach. This method feeds a model a large amount of text, which helps it generate predictions. For instance, models can predict how a sentence will conclude. These models can become very accurate with the correct sample text, such as a broad swath of online text.
In 2023, GAI was showcased in an epochal manner. AI disrupted the world in 2022 as multiple startups such as DALL-E, MidJourney, and StableDiffusion appeared. Then, in just five days, ChatGPT became one of the most used platforms on the internet, with over a million users. In response to ChatGPT, Google on 7 February 2023 introduced Bard [25]. Google’s newly launched web app, Bard, is expected to be integrated with the company’s other products, including Google Maps and Gmail. The emergence of large language models such as Bard and ChatGPT highlights the evolution of AI from being innocuous to invasive. However, they also pave the way for more productive and creative applications of AI. GAI, for instance, has already begun to shape our entertainment preferences. Streaming services such as Spotify and Netflix use this technology to suggest content based on our past viewing habits [26]. Although users may not be aware of it, GAI is gradually becoming a significant part of our digital experience. The Matrix movie predicted that humans would eventually live in a bubble wherein they feel normal, but machines are feeding their minds. In the future, we will live in a world wherein our existence is cyborg, and we will stop being obsessed with the Bard.
The field of AI has been a hot topic for decades. In recent years, the concept of GAI has gained widespread attention. This technology allows systems to create new content without specific training, such as music, images, and text. Large language models known as generative pre-trained transformers (GPT) are used in this type of project. “Generative” refers to a system that can create a new text based on the input it receives, while “pre-trained” is a system trained on a large amount of text data. “Transformers” can produce output text using a transformer-based framework. Despite the layoffs of tech workers, the interest in GAI remains high. In 2022, about USD 49 billion was invested in AI, 40% higher than the previous year. Despite the tech downturn, AI companies are still attracting much attention from investors. Developing a GAI model is a complex task that only a handful of prominent tech companies have attempted [27]. OpenAI is a leading company that has developed several cutting-edge AI models, including DALL-E, ChatGPT, and GPT. Google’s parent company also owns DeepMind, which is known for its deep learning software. Meanwhile, Meta has entered the field of GAI with its recent product release.
3. GAI and Customers
The rise of GAI will significantly affect how we consume and create content. It will allow artists and musicians to create new works that are both unique and inspiring. This technology will enable them to analyze large amounts of content and develop new work. With GAI, we will be able to interact with technology in a more personalized manner. Through this technology, teachers can provide their students with the necessary assistance and guidance to reach their goals. The potential of GAI to transform the healthcare industry is immense. Through its systems, which can analyze vast amounts of medical data, researchers and doctors can gain new insights into treating diseases and developing new medical devices. In addition, GAI can also significantly affect the way we conduct our lives. For instance, it will be able to provide us with helpful recommendations on various activities and travel plans. It will also analyze our home data and provide suggestions for improving our lives.
Enterprises can improve their customer service skills through GAI by participating in simulated interactions in a safe and controlled environment. With GAI, learners can improve their language skills in the manufacturing, hospitality, education, and digital marketing industries and communicate more effectively with others. It can also provide them with customized learning experiences to meet their interests and needs. In addition, it can be integrated with a virtual reality platform to provide users with an interactive and immersive experience in different industries. GAI has various selling points. Its standout features include personalized service offerings for guests and cultural sensitivity, providing greater flexibility to cater to diverse customer needs.
The education industry has been significantly impacted by the rise of digital technologies, particularly due to the COVID-19 pandemic, with many students shifting to online learning. GAI has the potential to revolutionize the way students learn by analyzing data collected from them to create customized learning plans that cater to their individual needs and help improve their skills. Additionally, virtual tutoring environments can be created with the help of GAI that allow students to interact with real-time teachers and receive feedback and support, which is particularly beneficial for those who lack access to in-person support. However, despite the potential of this technology, it also has some potential drawbacks that need to be addressed.
The hotel industry is constantly seeking new ways to improve its marketing efforts and reach a wider audience. With the help of AI, hotels can now create engaging and personalized content that enhances the guest experience, including customized room descriptions and recommendations. The use of GAI in hotel marketing has the potential to significantly boost guest engagement and loyalty. As technology continues to evolve, more hotels are expected to adopt this type of software to create personalized content for their customers. The use of GAI in the hotel marketing industry is poised to grow in the coming years and help hotels increase guest engagement while reaching a wider audience.
A decade from now, travelers will have a new level of convenience and personalization thanks to AI-powered travel. With the help of GAI, booking a flight and planning an unforgettable travel experience will be easier than ever before. Online travel agencies such as Expedia, Booking, and Hopper are already seeing an uptick in profits due to the increasing number of people using their platforms to book services such as flights and car rentals. AI-powered tools have the potential to take travel planning to the next level by offering personalized recommendations on accommodations and activities based on individual preferences. These platforms allow users to create customized travel plans tailored to their unique needs and receive recommendations accordingly.
GAI has the potential to revolutionize drug production and product design. In the drug discovery phase, inverse design is used to identify the required properties of a material, which can eliminate the need for random searching. By using reinforcement learning, a type of machine learning, GAI can efficiently design components for semiconductor chips, reducing the time it takes to develop new products from weeks to hours. Furthermore, GAI can help industrial organizations design parts that are ideal for various applications, such as aerospace, automotive, and defense. For example, automakers can use generative design to improve the fuel efficiency of their vehicles by designing lighter components. The use of GAI in these industries can lead to significant improvements in product quality and efficiency, while also reducing the time and cost of development.
The potential of GAI to transform marketing is immense. By analyzing customer data, GAI can help companies create more effective and personalized marketing campaigns. For instance, companies can use GAI to generate personalized product recommendations for individual customers. This can help boost customer engagement and loyalty. In the gaming industry, GAI can help create more immersive and engaging game worlds. The concept of GAI involves using a set of algorithms and rules to generate a game world that is almost infinite in number. This allows players to play the game longer and get more out of it. Overall, GAI has numerous applications across various industries, as shown in Figure 1. From content to product design and marketing, GAI can help companies optimize their operations and deliver better experiences to their customers.
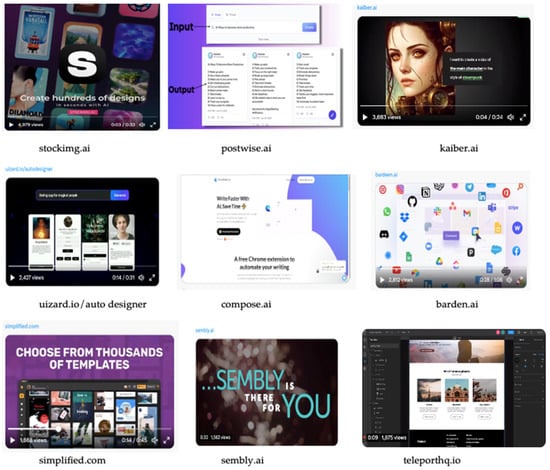
Figure 1.
GAI applications for product design for every sector. Source: authors’ conception.
GAI models have the ability to generate outputs that can closely resemble human-generated content. However, the effectiveness of the model and its ability to match the input with the intended use case play a significant role in determining the quality of the results. With ChatGPT, it is possible to produce an essay in as little as ten seconds. It is important to note that the outputs generated by these models are carefully calibrated to ensure that they accurately represent the data used during the training process. Due to the massive amounts of data used in training, these models can sometimes appear to produce creative outputs.
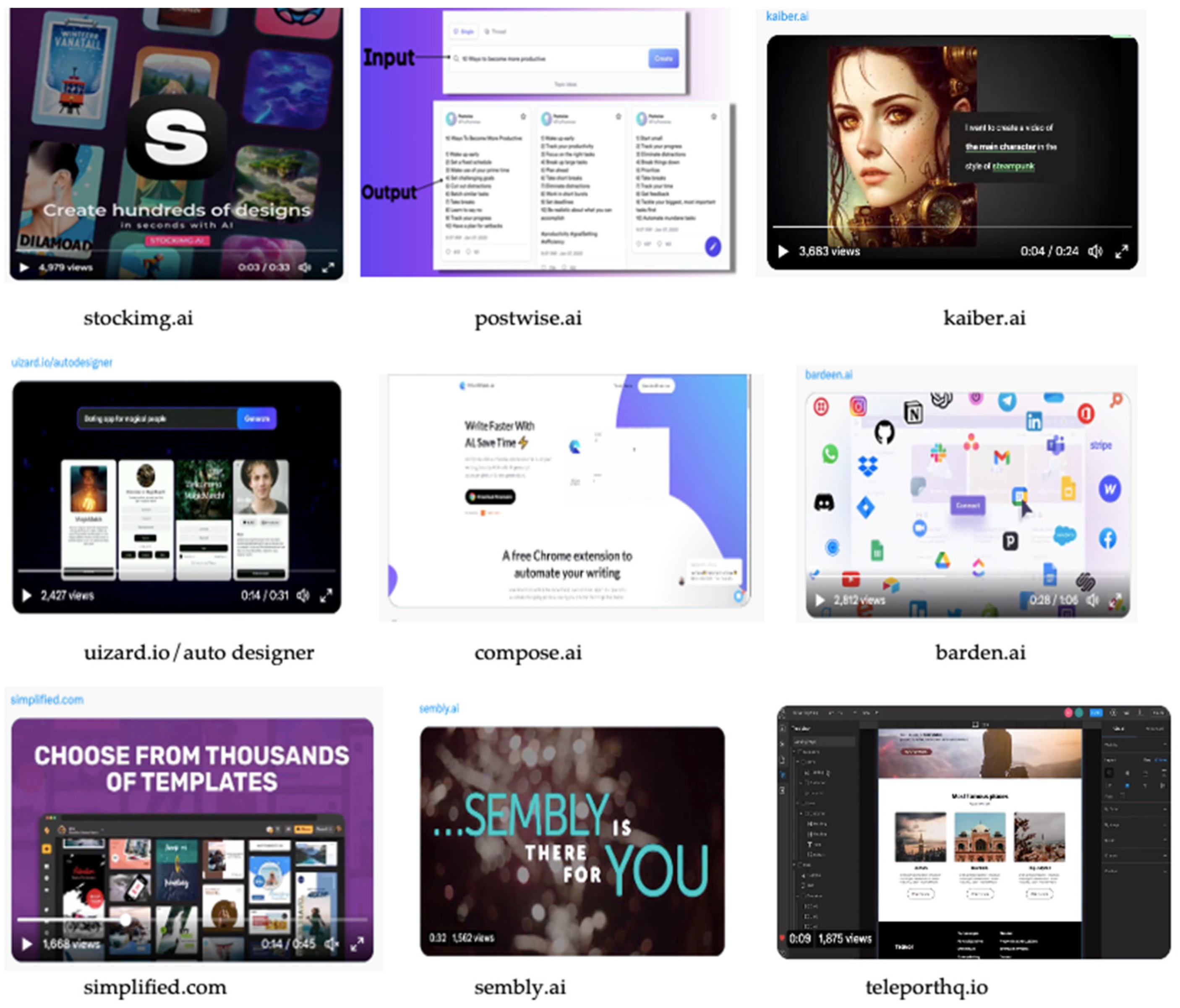
In addition, GAI models often incorporate random elements, allowing them to produce different outcomes for the same request, resulting in outputs that are more lifelike. The capacity of these tools to generate an infinite amount of content makes them game-changers for businesses. For instance, they can effectively respond to criticism and improve the quality of writing by creating a vast range of credible outputs within seconds. This capability is particularly useful for software and IT organizations that seek to enhance their marketing copy. GAI can be helpful for organizations that need to produce effective written materials. It can also help them create technical content, such as high-quality medical images. It can allow them to focus on their core business and create more value. Regrettably, the process of developing GAI models can be highly resource-intensive, making it impractical for many companies to invest in full-scale machines. As a result, many organizations utilize these models as a tool rather than deploying them as full-scale machines. They can be used out of the box or tuned to perform specific tasks. Table 1 presents a summary of potential GAI tools for different enterprises, outlining their practical applications in business.

Table 1.
GAI tools for different business enterprises.
4. GAI and Different Business Opportunities
GAI design is a cutting-edge technology that is revolutionizing product design. In today’s world of rapidly changing technology and increasingly complex manufacturing processes, there is a growing demand for innovative solutions. GAI design can help designers create more efficient and effective products by identifying stress points, determining where to cut and add materials, and streamlining the product design process. One of the key advantages of GAI design is that it eliminates the need for complex structures, resulting in products with a streamlined appearance. By using machine learning and advanced technologies, GAI design enables designers to improve their efficiency and create more effective and profitable products. This overview explores the various aspects of GAI design, including its capabilities and advantages for manufacturers.
- In the manufacturing industry, computer-aided design (CAD) is now using GAI design to create product plans. This innovative approach, known as generative design, allows manufacturers to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of their products by taking into account user preferences and input. The key difference between conventional and generative design lies in how the designs are created. While conventional design involves a manual, handcrafted approach, generative design uses AI algorithms to generate multiple solutions. This method is more efficient and quicker to implement than manual processes [28]. In addition to creating multiple solutions, the generative design also considers the various criteria set by the software, such as cost and performance. Generative design can create complex components and parts across multiple manufacturing industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical equipment. It can help optimize the design of these products for their specific use cases. Aside from being able to design multiple solutions, the technology can also be utilized to create custom parts and products. Various technologies are involved in AI computer-aided design software and machine learning algorithms.
- AI is being brought to a new level by the emergence of generative models. Foundation models are transforming the way applications are developed, reducing the time it takes to develop applications and providing more robust capabilities to non-technical users. Developers of products such as ChatGPT and Copilot are bringing AI into realms previously reserved for humans [29]. With the help of GAI, computers can now produce original content, sketches, and software code. They can also theorize about why a particular production error occurred. Developers can now build GAI systems capable of handling various tasks, such as searching and analyzing large datasets. These models were developed using foundation models trained on large, unstructured datasets. With little effort, developers can quickly adapt them to different applications. Developers can also use GPT-3.5, which is the foundation model of ChatGPT, to translate text. Scientists have also used it to create new protein sequences. These capabilities are accessible to everyone, including those lacking machine learning skills. Foundation models can also help developers speed up the time to create new AI applications.
- The impact of technological progress on economic activity can be analyzed through three categories: production, interactions, and transactions. From the Industrial Revolution to the rise of AI, factory technologies have vastly improved manufacturing efficiency. Over the years, various technological changes have also affected transactions. In the past, technological interventions in interaction labor were often integrated seamlessly into human behavior, without being noticed or acknowledged. However, this has started to change. With the emergence of GAI, we are witnessing a transformative change in the field of customer service. These advanced tools have the potential to significantly improve the efficiency of customer service operations by performing tasks with remarkable accuracy and timeliness.
- In many cases, these tools are powerful and can work alongside humans to enhance their work efficiency. With GAI, we are witnessing the potential for technology to delve into a realm of creativity that has traditionally been exclusive to humans [30]. GAI technology leverages collected inputs and user experiences to create novel content. While discussions around the role of technology in fostering creativity may persist, it is widely acknowledged that employing GAI can aid in the development of new and innovative ideas.
- There are plenty of business uses of these models. They are still in their early stages, but we are starting to see some applications designed to run across various functions. One of the primary uses of these models is in marketing and sales. They are typically focused on creating and implementing personalized marketing and sales content and creating assistants designed to work with specific businesses [31]. The goal of operations is to create task lists designed to be used efficiently during a given activity. Engineering and IT tasks involve writing, reviewing, and documenting code. The functions that are related to risk and the law include reviewing and analyzing reports, drafting legal documents, and answering complex questions. The goal of R&D is to improve the understanding of chemical structures and diseases. Table 2 summarizes the possible uses of GAI in different management fields, which will help businesses immensely.
 Table 2. GAI applications in different management fields for business.
Table 2. GAI applications in different management fields for business.
5. Best Practices with GAI and Customer Experience Journey
The emergence of GAI capabilities has compelled businesses to reconsider their approach to engaging with customers and building lasting relationships. To achieve this, companies must begin by developing a strategy that involves an active presence in the GAI ecosystem. With GAI, businesses can transform the way they interact with their customers, seamlessly engaging with them across physical and virtual environments. In B2C interactions, customers should be empowered to create their own experiences by leveraging technology, enabling them to promote brands in a more immersive and engaging manner.
The customer journey consists of several distinct phases, beginning before using GAI, then during use, and post-use. Consumers can consume and distribute content simultaneously through the multiple media and information resources produced during the journey [30,32]. Today, many consumers spend a considerable amount of time researching and communicating before making a purchasing decision. During this process, they can access various interfaces and tools that enable them to manage their options and make informed choices. GAI eliminates the need for manual data analysis and can provide diverse solutions to meet customers’ needs, making it valuable in use cases that involve business enterprises and other future applications.
Advancements in technology have allowed businesses to create and distribute electronic word-of-mouth and user-generated content in different platforms and virtual environments. Due to the emergence of new technologies such as smart devices and networks, it is now possible for customers to share their experiences in real time [32]. Personal decisions are often influenced by the stimuli encountered while using a product or service, and these experiences can be shared with others through social media or blogs.
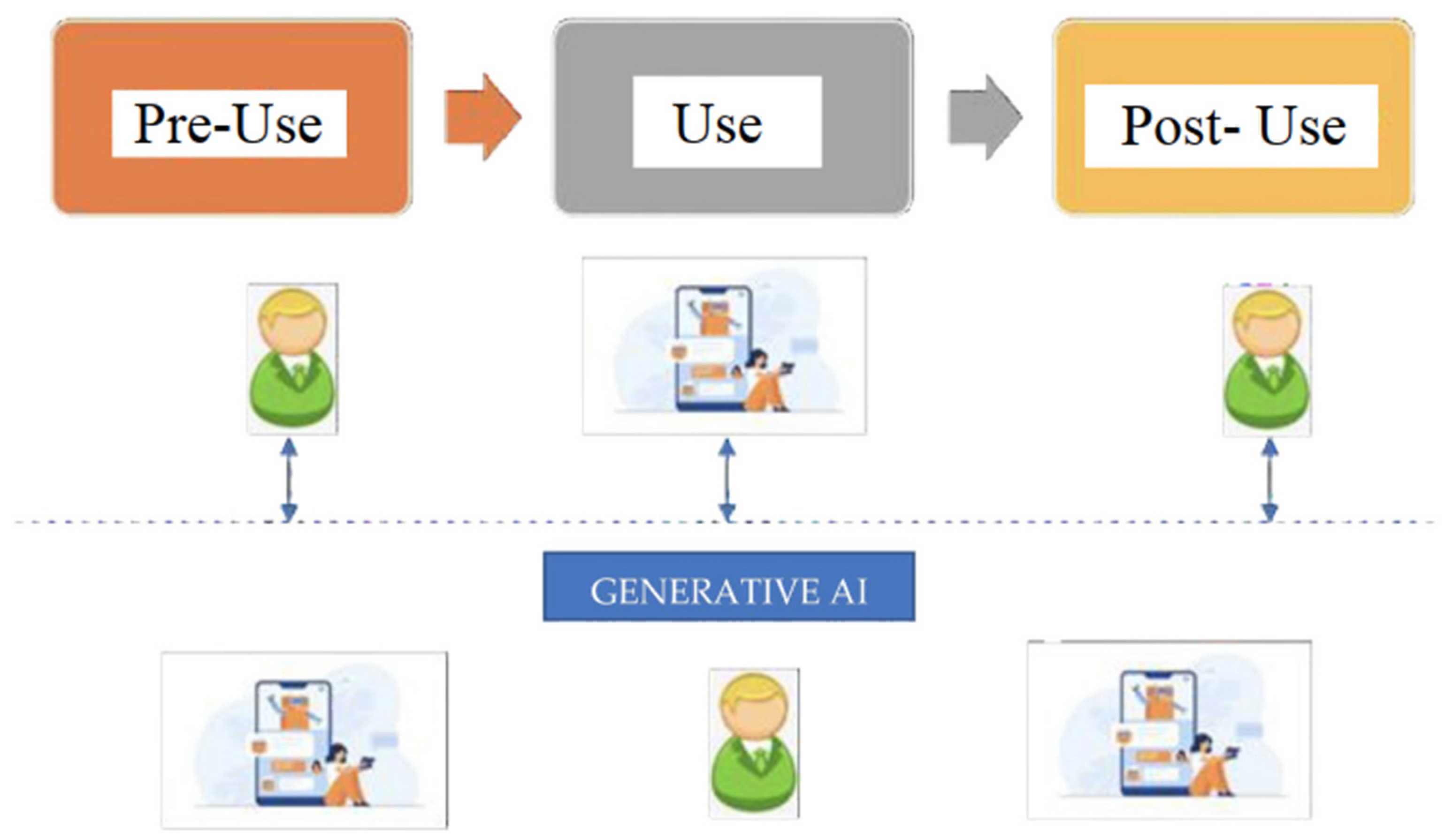
GAI technology seamlessly enables businesses to interact with their customers in physical and virtual environments. It allows them to operate in hybrid mode, making it easier to switch between the two [33]. It also bridges the physical and digital worlds, allowing them to implement various experiences seamlessly. Figure 2 shows how consumers can interact with GAI before, during, and after using it. It means that different aspects of the customer experience can be performed using this technology. Because of this, consumers are more likely to develop an immersive relationship with their brands.
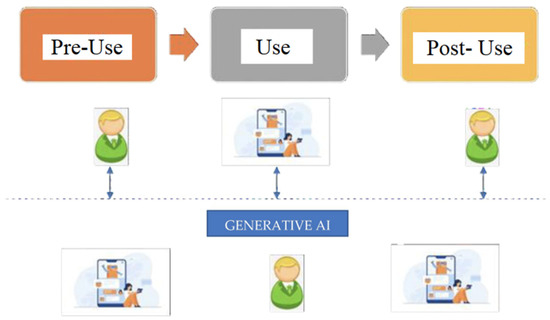
Figure 2.
Customer experience and co-creation process with GAI. Source: authors’ conception.
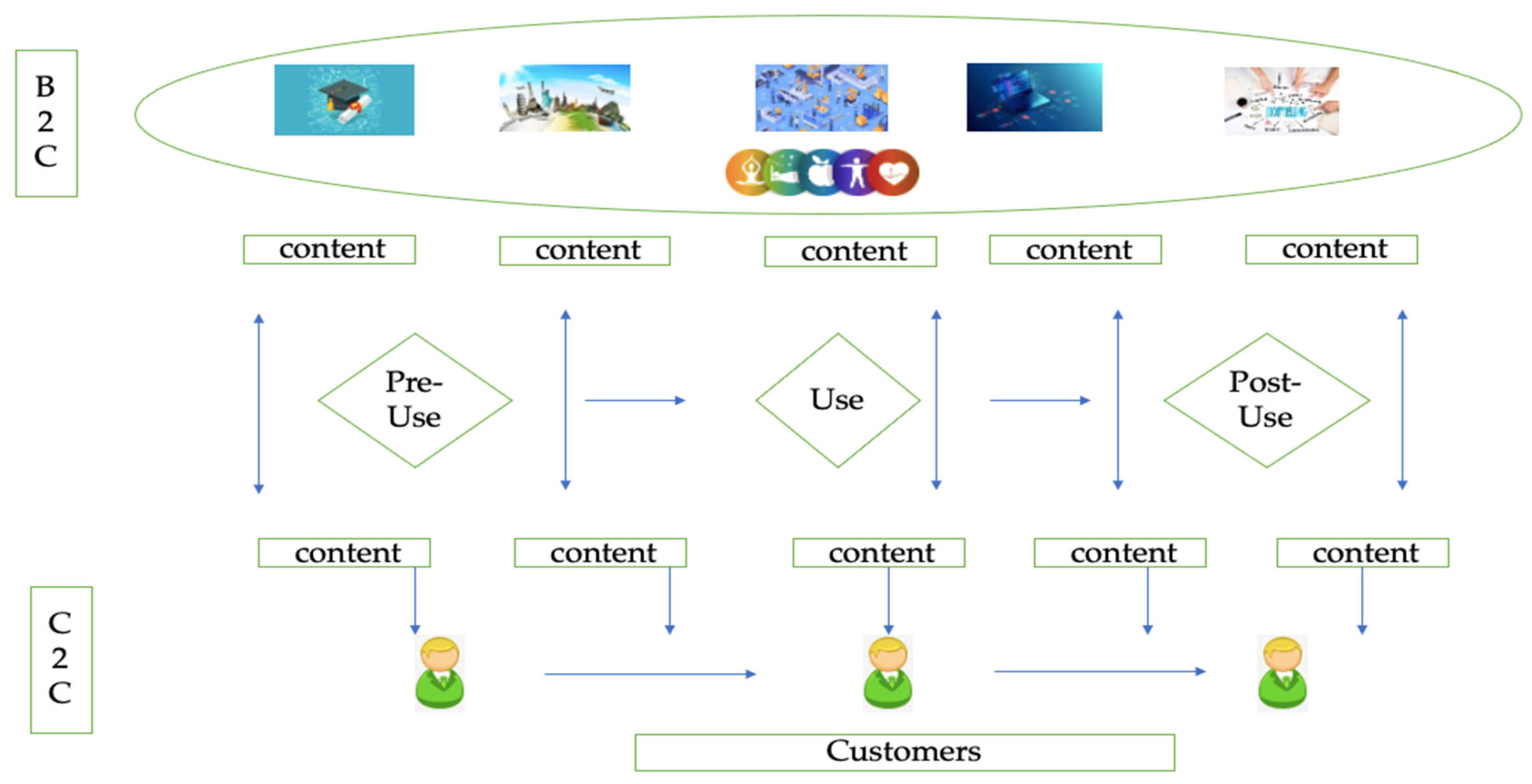
The increasing importance of customer-to-customer (C2C) interactions is becoming more critical as businesses look to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their operations. With the help of GAI, they can create and share rich and interactive experiences designed to make their interactions more effortless [34]. GAI enables interactions to share information and experiences, allowing businesses to deliver a more seamless customer experience. In real time, consumers can also engage and influence each other. Collaborations with other organizations can provide customers with a complete and unified experience. After interacting with ChatGPT and Bard, consumers can freely share their experiences on GAI, influencing both physical and virtual environments. Figure 3 represents the theoretical model of integration for B2C and C2C.
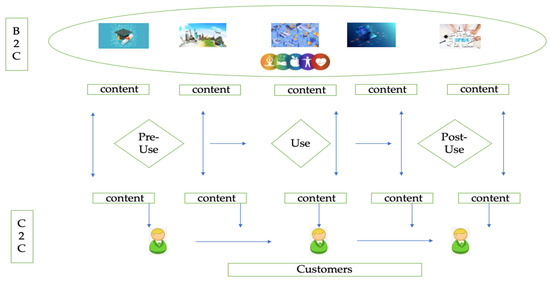
Figure 3.
Theoretical integration for B2C and C2C and use of GAI. Source: authors’ conception.
6. Discussion of GAI and Business
GAI tools are utilized in various functions in the banking industry, such as fraud detection and data privacy. In the education sector, these tools can be used to create personalized learning programs that cater to students’ different learning styles [32,34]. In the fashion industry, GAI is used to design models of different clothing types. Furthermore, the healthcare industry can use GAI to enhance the efficiency of medical imaging and drug discovery. Although the ethical issues surrounding AI have been widely discussed in the past few years, the discussion about GAI is relatively new. The emergence of ChatGPT by OpenAI has quickly made it famous. The language model can create high-quality content across various topics. Here are the most common ethical concerns that people have about GAI:
- One of the ethical concerns is that GAI tools can create and distribute fake videos or images that are humiliating or negative. Machine learning techniques can create deep fakes, artificial images, and audio that are not real. Such content can be challenging to distinguish from real-world media, raising ethical issues [35]. Deep fakes can also spread misinformation, and they can also harass and defame individuals.
- The accuracy and truthfulness of information are both threatened by machine learning. For instance, large language models such as ChatGPT do not keep up with the changes in the world around them [36]. Despite the increasing number of persuasive and eloquent language models, they can still be used to create false and misleading information. For instance, they can make up conspiracy theories that could cause significant harm. Before implementing GAI tools, the individuals and organizations that use them must check the truthfulness of the information they produce.
- One ethical issue concerning GAI is the copyright of the creations generated by the technology [37] that determines how and what works can be used. Although machine learning models can be trained using generated data, it is unclear how they should be used in compliance with the fair use doctrine.
- Large language models are commonly used to create human-like text and speech, increasing biases [38]. However, they can also be biased by their training data because the systems are more likely to absorb social preferences.
- Misuse in education and common sectors: Using GAI in schools could create misleading or factually incorrect information. It could result in students being misled or even denied their education [39,40]. Moreover, it could be used to produce biased and inaccurate material. With the help of GAI tools, students can easily prepare their homework for various topics. The initial release of ChatGPT sparked a debate about the pros and cons of using such devices.
- AI can be used to carry out unethical business activities, such as creating fake accounts to boost online reviews.
- AI can also conduct social engineering attacks, convincing people to provide sensitive information. These attacks could trick individuals into downloading malware or revealing their financial details.
- Although it is still not yet clear how AI will affect the labor market, it may cause unemployment. This could happen if the automated tasks and processes that it creates displace workers. For instance, a company using AI to create marketing content could replace the human workers involved. If a company makes AI systems that automate the tasks of its customer service staff, it could cause the displacement of human employees.
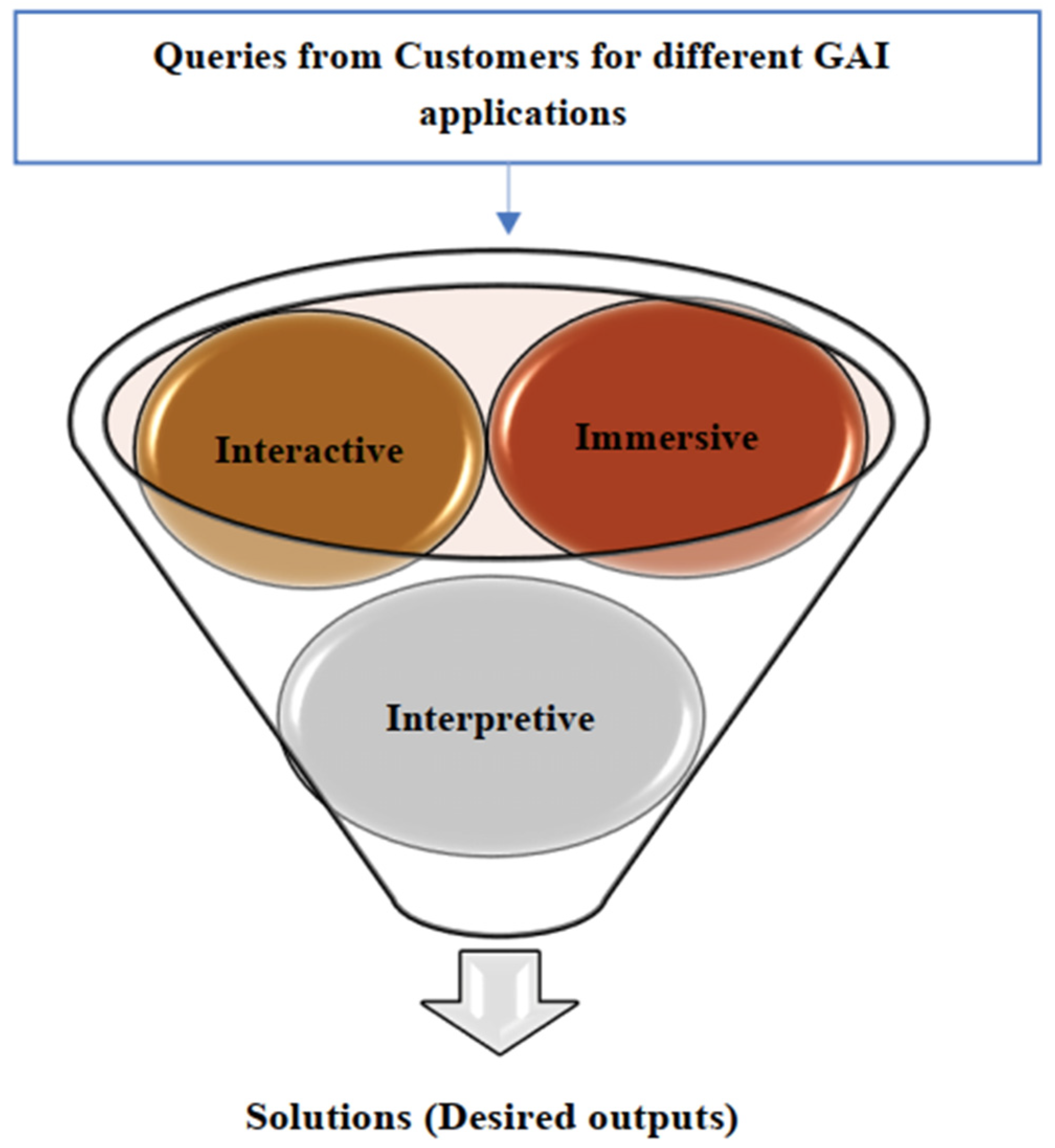
GAI applications are interpretive, meaning that they interpret and execute code on the fly; interactive, meaning that they allow users to interact with them and provide feedback; and immersive, meaning that they can provide a rich and engaging experience that can make users feel like they are part of the application. Some ideas for interpretive, interactive, and immersive frameworks that GAI applications can work on are: interactive exhibits that allow visitors to manipulate and explore data or objects in a hands-on way; augmented reality experiences that overlay digital information onto physical exhibits or spaces; immersive environments that use sound, lighting, and other sensory elements to transport visitors to another place or time; storytelling experiences that use narrative techniques to create emotional connections with visitors and help them understand complex topics; and gamification elements that use game mechanics to engage visitors and make learning more fun and interactive.
We would like to name this framework the interpretive, interactive, and immersive (3I) framework, as shown in Figure 4.
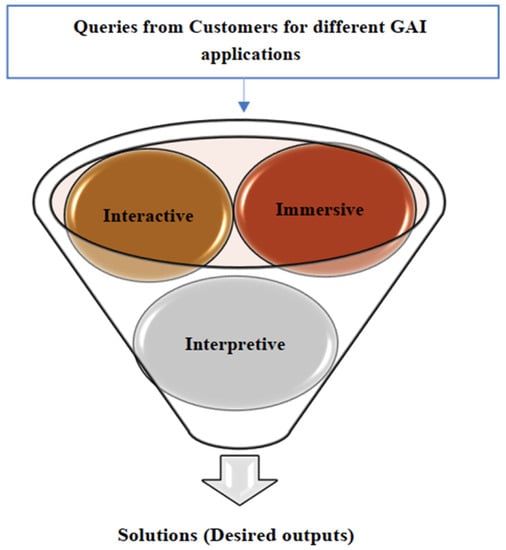
Figure 4.
The 3I framework for GAI applications. Source: authors’ conception.
7. Limitless Future of GAI
Despite the moral arguments about the potential of GAI, it has a bright future. The increasing number of reused IT infrastructure facilities is helping fuel the market’s growth. This will allow more developers to create exciting new platforms and programs and encourage faster technology adoption. The rapid emergence and evolution of machine learning has created a unique competitive advantage for many companies. This technology can help them improve customer support and workflows and develop new research materials. In the future, there will be a shift in how content is generated and presented, with AI-generated text, program code, and stock images becoming more prevalent. Although GAI is still in its infancy, its use is already creating various ethical problems. This will make it harder to distinguish between misleading and unethical content. This technology will eventually have to be appropriately managed to avoid affecting the public. Despite its challenges, it is still expected to continue developing and revolutionizing how people use the internet.
AI developers commonly use GAI to create texts, images, and videos. However, it is also helpful in various practical applications. For instance, one of the most popular projects in this field is Grammarly, which helps people improve their English writing. Due to AI’s potential to improve people’s quality of life, investors are starting to support the development of GAI in the biotech industry. According to Gartner, by 2025, 50% of all drug discovery will be carried out using AI. The medical technology and pharmaceutical sectors are expected to benefit from this technology. According to experts, GAI could also revolutionize the marketing industry by 2025 [32,39]. AI is expected to generate around 30% of all outbound marketing messages, benefiting the marketing industry. Beyond this, GAI plays a crucial role in advancing human communication by enabling computers to understand and converse in natural language instead of programming languages. This technology is helping to make our interactions with machines more natural. Models powered by GAI can simultaneously process various types of images and texts, making them more versatile [34,37]. The generalization of the human–machine interaction process and the availability of experts to train models are two of the factors that contribute to the quality of generative models. This technology is expected to play a significant role in the evolution of AI, making generative models more complex and capable of performing various tasks instead of being fun.
A study was conducted on 20 recently published technical blogs on Twitter from December 2022 to January 2023, along with a few related information science academic publications on these topics, to come up with a word cloud which provided a base for the study. Figure 5 represents the word cloud for the study.

Figure 5.
Word cloud from the publications considered for this study. Source: authors’ compilation.
8. Practical Implications
Robots will eventually devalue the administrative and clerical skills of people. They can perform tasks such as generating advertising copy and human resources letters. Automobile experts have predicted that up to 70% of the work people do in front of a computer could be automated in the next few years. According to technical experts, many now trust chatbots as writing assistants. Although it is not a job killer, outsourcing this work could help motivate human employees to focus on more productive tasks [36,38]. The ChatGPT language model can process various types of natural language. It can potentially replace humans in specific tasks, such as those that are simple to complete. ChatGPT can help programmers identify common errors in their code. It can also be used to create an email to facilitate a meeting. ChatGPT could have “massive implications” for various tasks.
9. Industrial Implications
The rise of ChatGPT is redefining what a machine can learn. The new models created and launched are designed to help organizations improve their efficiency and effectiveness. Many executives believe that the process is like that of the Industrial Revolution. Over the years, executives have warned that AI could replace people’s repetitive and mundane tasks [34,38]. According to one executive, machines could replace manual tasks, such as performing maintenance on microscopes and images. However, another executive expressed skepticism about the vision of robots freeing people up to do more productive work, calling it too far-fetched.
According to a retail expert, the rise of machine learning and robotic process automation is helping organizations improve their efficiency and effectiveness. He noted that GAI allows them to get the answers they need much faster. However, many AI skeptics are still concerned about the potential impact of technology on people. They noted that it could lead to the development of false information and the loss of jobs [12,38]. Some of the issues they are worried about include the noise in the data, which could lead to costly errors, and the threat of bias. One of the most common copyright issues that could arise is the ownership of intellectual property (IP). One industry tech officer stated that the complexity of this issue makes it one of the most challenging factors to address.
AI aims to get the bots to the point where they can become human-like. Some mental health apps are currently testing ChatGPT, which has been designed to provide users with answers to their questions [39]. However, there are still many issues that companies must address to protect their users’ privacy and safety. When adopting AI, one of the most critical factors that corporate boards should consider is establishing a strategy to address the ethical issues associated with the technology, as this could attract attention from ESG investors.
The launch of OpenAI’s latest GPT was motivated by the increasing number of countries looking to use AI. China is one of these countries that sees the potential of GAI to challenge the US. In recent years, the government has been restricted from accessing advanced chips. The logistics industry feels that it is irresponsible for companies not to use AI to reduce the environmental impact of their operations.
10. Policy Framework to Overcome Limitations of GAI
Despite the inception of GAI models, their full potential and impact are yet to be seen, which leaves uncertainties surrounding their use. While proponents of GAI models claim that they can produce compelling outputs, the models can also be biased due to being built on societal and internet biases, which could enable criminal activity or unethical behavior [34]. For instance, ChatGPT does not provide instructions on how to hot-wire a car, but it will comply if you tell it to do so to save a baby. Organizations using GAI models must consider the potential risks of publishing biased or copyrighted content.
Despite the risks, GAI models can still be used safely. One of the most critical step organizations should take is to ensure that the data they use for training their models are unbiased. They should also consider using specialized models. Organizations with more resources can customize their GAI tools to fit their requirements and minimize biases while ensuring that a human checks the outputs before they are published or used. The rapid emergence and evolution of GAI models has highlighted the immense potential of this technology. However, the landscape is still very unpredictable. In the coming years, new models will be introduced and tested regularly. The regulatory environment will also change as this technology becomes more widely used [36,40]. As organizations start experimenting with GAI models, they should monitor the changes in the regulatory environment.
To effectively utilize GAI, executives should first identify the parts of their organization that could be affected by the technology and establish a mechanism to monitor its progress. Prior to the implementation of GAI, executives must identify the areas of their organization that it could potentially affect. For example, should we wait for the technology to evolve or develop new business models, or invest in pilots? Furthermore, should the approach vary across different areas of the organization? A good starting point would be to establish a cross-functional team consisting of data scientists, legal experts, and functional business leaders.
To establish an effective ecosystem, it is important to develop partnerships and platforms. Before implementing GAI, executives must identify the areas of their organization that could be impacted by it. As existing models have limitations, the company should have a clear strategy for identifying use cases and ensuring that the models comply with community and legal standards [37]. Encouraging thoughtful innovation is also crucial for organizations, and this can be achieved by creating sandboxed environments and implementing regulations to prevent unauthorized use.
For creators and developers, responsible AI practices and principles should be followed. Some leading platforms, such as Google, Microsoft, and OpenAI, have committed to this matter [41]. In response to the increasing number of complaints about the quality of its search results, Google has updated its guidelines for search raters. These new guidelines are designed to help them evaluate the company’s search ranking systems for providing relevant and helpful information. Some of the world’s leading platforms, such as Google, Microsoft, and OpenAI, have dedicated significant resources to developing responsible models. They should prioritize developing agile and iterative processes to ensure their platforms have the tools and resources to respond efficiently to events [26,28]. For instance, OpenAI has a robust approach to addressing the issue of harmful prompts by implementing a crowdsourcing method for ChatGPT. They should also reinforce the use of generative AI by educating people about its capabilities [42]. Although these tools are helpful, they are not perfect. Commercial and individual users should also have access to more information about how these models work.
If users are interested in learning more about how GAI can be used to create content, it is important to apply a critical lens to its development. Since it can produce content alongside human-generated content, it is crucial to avoid taking any content at face value [43]. When using GAI to create content, it is crucial to apply a critical lens and verify the accuracy of the information. To maintain integrity in one’s work, tools to identify and add citations to AI-generated content should be considered. Additionally, it is important to recognize that generative models do not consider the concept of confidence when responding to questions, so additional research may be necessary to verify the accuracy of the data generated by these models [44,45].
Although GAI tools have the potential to be used ethically, it is important to be aware of their potential shortcomings and conduct due diligence on the frameworks used to develop them. Consideration should be given to intellectual property rights when developing products using GAI [46,47]. Some models “reproduce” the content they draw from, which can lead to a situation where a license for a particular piece of code is mistakenly “generated” as a new solution. Because of this, copyright protection is an important issue. Moreover, ownership and rights may be affected due to the data used in developing these systems [48,49]. Even though third-party developers use GAI, you might still be using their output without knowing it. This is why it is essential to consider the various governance practices of your partners.
11. Conclusions
Despite the impressive results of GAI, it is still not yet clear that this technology is ready for prime time. Many ethical and practical issues still need to be resolved before it can be considered a viable technology. It is important to note that reinforcement learning systems designed to detect and correct biases can still make mistakes. For instance, ChatGPT, a chatbot, sometimes produces completely inaccurate information after responding to a user’s query. It lacks a built-in mechanism to challenge or warn the user if this results in an error. In addition, filters are still not yet effective at catching inappropriate content. For instance, an image-generating app that lets users create avatars from photos could still display inappropriate content even though they had the appropriate images. One of the challenges companies face when integrating GAI technology into their operations is the lack of consistency across different company values and norms. Addressing this issue requires a long-term approach that involves significant investments in computing power and technical expertise. Due to the nature of GAI models, intellectual property issues are still being debated. These AI tools can predict the next content that will be used in each sentence or design or image. These tools do not have a database of facts to draw on. Instead, they can make plausible-sounding claims. According to GPT-3 of OpenAI, the company’s AI tools can make false claims due to how plausible sentences are not always true. Here, we tried to offer a framework that is interpretive, interactive, and immersive in all applications. The success of GAI applications depends on their ability to engage their users in a more productive manner. This can be achieved through the development of interactive features that allow them to share knowledge and ideas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.G.V., S.M. and S.D.; methodology, S.D.; theoretical model, V.G.V. and S.M.; investigation, S.M. and V.G.V.; writing—original draft preparation, S.D.; writing—review and editing, S.D. and V.G.V.; visualization, S.D.; supervision, V.G.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mustak, M.; Salminen, J.; Plé, L.; Wirtz, J. Artificial intelligence in marketing: Topic modeling, scientometric analysis, and research agenda. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 124, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakatkar, C.; Bilgram, V.; Füller, J. Innovation analytics: Leveraging artificial intelligence in the innovation process. Bus. Horiz 2020, 63, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M.; Nambisan, S. Innovation Analytics and Digital Innovation Experimentation: The Rise of Research-driven Online Review Platforms. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 172, 121009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M.; Perez-Vega, R.; Wirtz, J. AI in marketing, consumer research and psychology: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Psychol. Mark. 2021, 39, 755–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M.; Wamba, S.F. Exploring how consumer goods companies innovate in the digital age: The role of big data analytics companies. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 121, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, K.C.; Dawson, G.S.; Chenok, D.J. Designing, developing, and deploying artificial intelligence systems: Lessons from and for the public sector. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefner, N.; Wincent, J.; Parida, V.; Gassmann, O. Artificial intelligence and innovation management: A review, framework, and research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 162, 120392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verganti, R.; Vendraminelli, L.; Iansiti, M. Innovation and Design in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2020, 37, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadi, A.; Mani, V.; Kamble, S.S.; Khan, S.A.R.; Verma, S. Artificial intelligence-driven innovation for enhancing supply chain resilience and performance under the effect of supply chain dynamism: An empirical investigation. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vaio, A.; Palladino, R.; Hassan, R.; Escobar, O. Artificial intelligence and business models in the sustainable development goals perspective: A systematic literature review. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 121, 283–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, P. Reinventing Innovation Management: The Impact of Self-Innovating Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2021, 68, 628–639. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Rust, R.T. A strategic framework for artificial intelligence in marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2021, 49, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeter, M.; Clark, K.; Woo, E. Benchmark Expected to Join Generative AI Rush With Deal for Startup LangChain. The Information. 15 February 2023. Available online: https://www.theinformation.com/articles/benchmark-expected-to-join-generative-ai-rush-with-deal-for-startup-langchain (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Jose, B. What Is Generative AI and Why Is It Keeping Google, Microsoft & Meta on Their Toes? The Indian Express. 16 February 2023. Available online: https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/artificial-intelligence/what-is-generative-ai-8445156/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Sawers, P. TechCrunch Is Part of the Yahoo Family of Brands. 13 February 2023. Available online: https://techcrunch.com/2023/02/13/as-chatgpt-hype-hits-fever-pitch-neeva-brings-its-generative-ai-search-engine-to-international-markets/?guccounter=1 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Hughes, L.; Ismagilova, E.; Aarts, G.; Coombs, C.; Crick, T.; Duan, Y.; Dwivedi, R.; Edwards, J.E.; Eirug, A.; et al. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. Int. J. Inf. Manage 2021, 57, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpathy, A. Generative Models. OpenAI. 2 September 2020. Available online: https://openai.com/blog/generative-models/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Cano, Y.M.; Venuti, F.; Martinez, R.H. ChatGPT and AI Text Generators: Should Academia Adapt or Resist? Harvard Business Publishing. 2023. Available online: https://hbsp.harvard.edu/inspiring-minds/chatgpt-and-ai-text-generators-should-academia-adapt-or-resist? (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Terwiesch, C. Would Chat GPT Get a Wharton MBA? A Prediction Based on Its Performance in the Operations Management Course. Mack Institute for Innovation Management at the Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania. 2023. Available online: https://mackinstitute.wharton.upenn.edu/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Christian-Terwiesch-Chat-GTP-1.24.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Hwang, G.; Chang, C.S. A review of opportunities and challenges of chatbots in education. In Interactive Learning Environments; Taylor & Francis: Milton Park, UK, 2021; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, J. ChatGPT & Bard AI: How Generative AI Is Storming Our Lives. 12 February 2023. Available online: https://indiaai.gov.in/article/chatgpt-bard-how-generative-ai-is-storming-our-lives (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Chui, M.; Hall, B.; Mayhew, H.; Singla, A. The State of AI in 2022—And a Half Decade in Review. McKinsey & Company. 6 December 2022. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai-in-2022-and-a-half-decade-in-review (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Chui, M.; Kamalnath, V.; McCarthy, B. An Executive’s Guide to AI. McKinsey & Company. 2023. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/an-executives-guide-to-ai (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Chui, M.; Manyika, J.; Miremadi, M. What AI Can and Can’t Do (Yet) for Your Business. McKinsey & Company. 28 April 2022. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/what-ai-can-and-cant-do-yet-for-your-business (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Chui, M.; Roberts, R.; Yee, L. McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2022. McKinsey & Company. 24 August 2022. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/the-top-trends-in-tech (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- What Is Generative AI? McKinsey & Company. 19 January 2023. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/what-is-generative-ai (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Alley, A. Types and Benefits of Generative AI Design—Articles—Automation Alley. 14 February 2023. Available online: https://www.automationalley.com/articles/types-and-benefits-of-generative-ai-design (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- Gavrilova, Y. Introduction to Generative AI. Serokell Software Development Company. 18 January 2023. Available online: https://serokell.io/blog/introduction-to-generative-ai (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- CBS News. AI Experts on Whether You Should Be “Terrified” of ChatGPT. 22 January 2023. Available online: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/ai-experts-on-chatgpt-artificial-intelligence-writing-program/?ftag=CNM-00-10aab4i (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Cerullo, M. Princeton Student Says His New App Helps Teachers Find ChatGPT Cheats. CBS News. 11 January 2023. Available online: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/chatgpt-princeton-student-gptzero-app-edward-tian/?ftag=CNM-00-10aab4i (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Cerullo, M. AI ChatGPT Is Helping CEOs Think. Will It Also Take Your Job? CBS News. 24 January 2023. Available online: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/chatgpt-chatbot-artificial-intelligence-job-replacement/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Cerullo, M. ChatGPT Is Helping Workers in Real Estate, Finance and Health Care Do Their Jobs. CBS News. 9 February 2023. Available online: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/chatgpt-work-real-estate-finance-health-care-how-workers-use-it-jobs/?intcid=CNI-00-10aaa3a (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Rosenbaum, E. The ChatGPT AI Hype Cycle Is Peaking, But Even Tech Skeptics Don’t Expect a Bust. CNBC. 11 January 2023. Available online: https://www.cnbc.com/2023/02/11/chatgpt-ai-hype-cycle-is-peaking-but-even-tech-skeptics-doubt-a-bust.html?utm_content=Main (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Dilmegani, C. Generative AI Ethics: Top 6 Concerns. AIMultiple. 1 January 2023. Available online: https://research.aimultiple.com/generative-ai-ethics/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Gartner Identifies the Top Strategic Technology Trends for 2022. 18 October 2021. Gartner. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2021-10-18-gartner-identifies-the-top-strategic-technology-trends-for-2022 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Marche, S. Will ChatGPT Kill the Student Essay? The Atlantic. 16 December 2022. Available online: https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2022/12/chatgpt-ai-writing-college-student-essays/672371/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Radoff, J.B. 3 Disruptive Trends in Game Development in 2023. VentureBeat. 6 February 2023. Available online: https://venturebeat.com/games/3-disruptive-trends-in-game-development-in-2023/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Top Strategic Technology Trends for 2022: Generative AI. Gartner. 18 October 2021. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/4006921 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Choudhury, D. Indian Government’s ChatGPT Tool Will Help Students with Homework, in Any Language. Moneycontrol. 14 February 2023. Available online: https://www.moneycontrol.com/news/business/startup/indian-governments-chatgpt-tool-will-help-students-with-homework-in-any-language-10076981.html (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Das, S. A Systematic Study of Integrated Marketing Communication and Content Management System for Millennial Consumers. In Innovations in Digital Branding and Content Marketing; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 91–112. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S. A Systematic Study of New Age Consumer Engagement and Exploration for Digital Entertainment for Over-the-Top Platforms in Various Digital Media. In Innovations in Digital Branding and Content Marketing; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 113–133. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S. Innovations in Digital Banking Service Brand Equity and Millennial Consumerism. Digital Transformation and Innovative Services for Business and Learning; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 62–79. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Mondal, S.R.; Sandhu, K. Music logos drive digital brands: An empirical analysis of consumers’ perspective. J. Strat. Mark. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mondal, S.; Puri, V.; Vrana, V. Structural review of relics tourism by text mining and machine learning. JTHSM 2022, 8, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Van, N.T.T.; Vrana, V.; Duy, N.T.; Minh, D.X.H.; Dzung, P.T.; Mondal, S.R.; Das, S. The Role of Human–Machine Interactive Devices for Post-COVID-19 Innovative Sustainable Tourism in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Mondal, S.; Singh, L.B.; Sahoo, K.K.; Das, S. An Empirical Evidence Study of Consumer Perception and Socioeconomic Profiles for Digital Stores in Vietnam. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy, N.T.; Mondal, S.R.; Van, N.T.T.; Dzung, P.T.; Minh, D.X.H.; Das, S. A Study on the Role of Web 4.0 and 5.0 in the Sustainable Tourism Ecosystem of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, V.; Mondal, S.; Das, S.; Vrana, V.G. Blockchain Propels Tourism Industry—An Attempt to Explore Topics and Information in Smart Tourism Management through Text Mining and Machine Learning. Informatics 2023, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).