Community Pharmacists’ Experiences and Perception about Transitions of Care from Hospital to Home in a Midwestern Metropolis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Transition of Care Summary. May 2014. Available online: https://www.cms.gov/regulations-and-guidance/legislation/ehrincentiveprograms/downloads/8_transition_of_care_summary.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Hansen, L.O.; Young, R.S.; Hinami, K.; Leung, A.; Williams, M.V. Interventions to reduce 30-day rehospitalization: A systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, A.J.; Murff, H.J.; Peterson, J.F.; Gandhi, T.K.; Bates, D.W. The incidence and severity of adverse events affecting patients following discharge from the hospital. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, A.J.; Murff, H.J. Adverse drug events occurring following hospital discharge. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2005, 20, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGaw, J.; Conner, D.A.; Delate, T.M.; Chester, E.A.; Barnes, C.A. A multidisciplinary approach to transition care: A patient safety innovation study. Perm J. 2007, 11, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnipper, J.L.; Kirwin, J.L.; Cotugno, M.C.; Wahlstrom, S.A.; Brown, B.A.; Tarvin, E.; Kachalia, A.; Horng, M.; Roy, C.L.; McKean, S.C.; et al. Role of pharmacist counseling in preventing adverse drug events after hospitalization. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, P.C.; Bernstein, S.J.; Tucker Jones, J.N.; Piersma, J.; Kim, H.-W.; Regal, R.E.; Kuhn, L.; Flanders, S.A. Impact of a pharmacist-facilitated hospital discharge program. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 169, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, K.B.; Savitz, L.A.; Maddalone, T.; Stoner, S.E.; Hunt, J.S.; Wells, R. Evaluation of patient care interventions and recommendations by a transitional care pharmacist. Ther Clin. Risk Manag. 2007, 3, 695–703. [Google Scholar]
- Vira, T.; Colquhoun, M.; Etchells, E. Reconcilable differences: Correcting medication errors at hospital admission and discharge. Qual Saf Health Care. 2006, 15, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations. Hospital: 2021 National Patient Safety Goals. Available online: https://www.jointcommission.org/standards/national-patient-safety-goals/hospital-national-patient-safety-goals/ (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- Lu, Y.; Clifford, P.; Bjorneby, A.; Thompson, B.; VanNorman, S.; Won, K.; Larsen, K. Quality improvement through implementation of discharge order reconciliation. Am. J. Health-Syst Pharm. 2013, 70, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, T.M.; Shelsky, C.; Powell, S.; Farris, K.B.; Carter, B.L. Effect of clinical pharmacist intervention on medication discrepancies following hospital discharge. Int J. Clin. Pharm. 2014, 36, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roughead, E.E.; Kalisch, L.M.; Ramsay, E.N.; Ryan, P.; Gilbert, A.L. Continuity of care: When do patients visit community healthcare providers after leaving hospital? Int. Med. J. 2011, 41, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, R.; Paloumpi, E.; Rana, N.; Morgan, J. Communicating medication changes to community pharmacy post-discharge: The good, the bad, and the improvements. Int J. Clin. Pharm. 2013, 35, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, L.M.; Li, S.; Fernandes, O.; Cameron, K.; Liu, P.; Wong, G.; Pariser, P.; Farrell, J.; Luke, M.J.; Guilcher, S.J.T. Enhanced communication between inpatient and community pharmacists to optimize medication management during transitions of care. J. Am. Pharm Assoc. 2019, 59, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooyman, C.D.A.; Witry, M.J. The developing role of community pharmacists in facilitating care transitions: A systematic review. J. Am. Pharm Assoc. 2019, 59, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luder, H.R.; Frede, S.M.; Kirby, J.A.; Epplen, K.; Cavanaugh, T.; Martin-Boone, J.E.; Conrad, W.F.; Kuhlmann, D.; Heaton, P.C. TranstionRx: Impact of community pharmacy postdischarge medication therapy management on hospital readmission rate. J. Am. Pharm Assoc. 2015, 55, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaver, A.; Morano, M.; Pogodzinski, J.; Fredrick, S.; Essi, D.; Slazak, E. Impact of a community pharmacy transitions-of-care program on 30-day readmission. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2019, 59, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, J.E.; Martin, B.A.; Kieser, M.A.; Williams, S.M.; Sutter, S.L. Transitions in care: Medication reconciliation in the community pharmacy setting after discharge. Innov Pharm. 2013, 4, article 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennelty, K.A.; Chewning, B.; Wise, M.; Kind, A.; Roberts, T.; Kreling, D. Barriers and facilitators of medication reconciliation processes for recently discharged patients from community pharmacists’ perspectives. Res. Soc. Admin. Pharm. 2015, 11, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enderlin, C.A.; McLeskey, N.; Rooker, J.L.; Steinhauser, C.; D’Avolio, D.; Gussewelle, R.; Ennen, K.A. Review of current conceptual models and frameworks to guide transitions of care in older adults. Geriatr Nurs. 2013, 34, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, M.; Brooten, D.; Jones, R.; Lavizzo-Mourey, R.; Mezey, M.; Pauly, M. Comprehensive discharge planning for the hospitalized elderly. A randomized clinical trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, M.D.; Brooten, D.; Campbell, R.; Jacobsen, B.S.; Mezey, M.D.; Pauly, M.V.; Schwartz, J.S. Comprehensive discharge planning and home follow-up of hospitalized elders: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 1999, 281, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, M.D.; Brooten, D.A.; Campbell, R.L.; Maislin, G.; McCauley, K.M.; Schwartz, J.S. Transitional care of older adults hospitalized with heart failure: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Am. Geriatr Soc. 2004, 52, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschman, K.B.; Shaid, E.; McCauley, K.; Pauly, M.V.; Naylor, M.D. Continuity of Care: The Transitional Care Model. Online J. Issues Nurs. 2015, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, M.D.; Hirschman, K.B.; Toles, M.P.; Jarrin, O.F.; Shaid, E.; Pauly, M.V. Adaptations of the evidence-based Transitional Care Model in the U.S. Soc. Sci Med. 2018, 213, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, D.P.; Reidenbach, R.E.; Forrest, P.J. The perceived importance of an ethical issue as an influence on the ethical decision-making of ad managers. J. Bus. Res. 1996, 35, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolle, R.J.; Strand, L.M.; Morley, P.C. Chapter 5. Drug Therapy Problems. In Pharmaceutical Care Practice: The Patient-Centered Approach to Medication Management, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
| Component a | Survey Item (Supplementary Materials) |
|---|---|
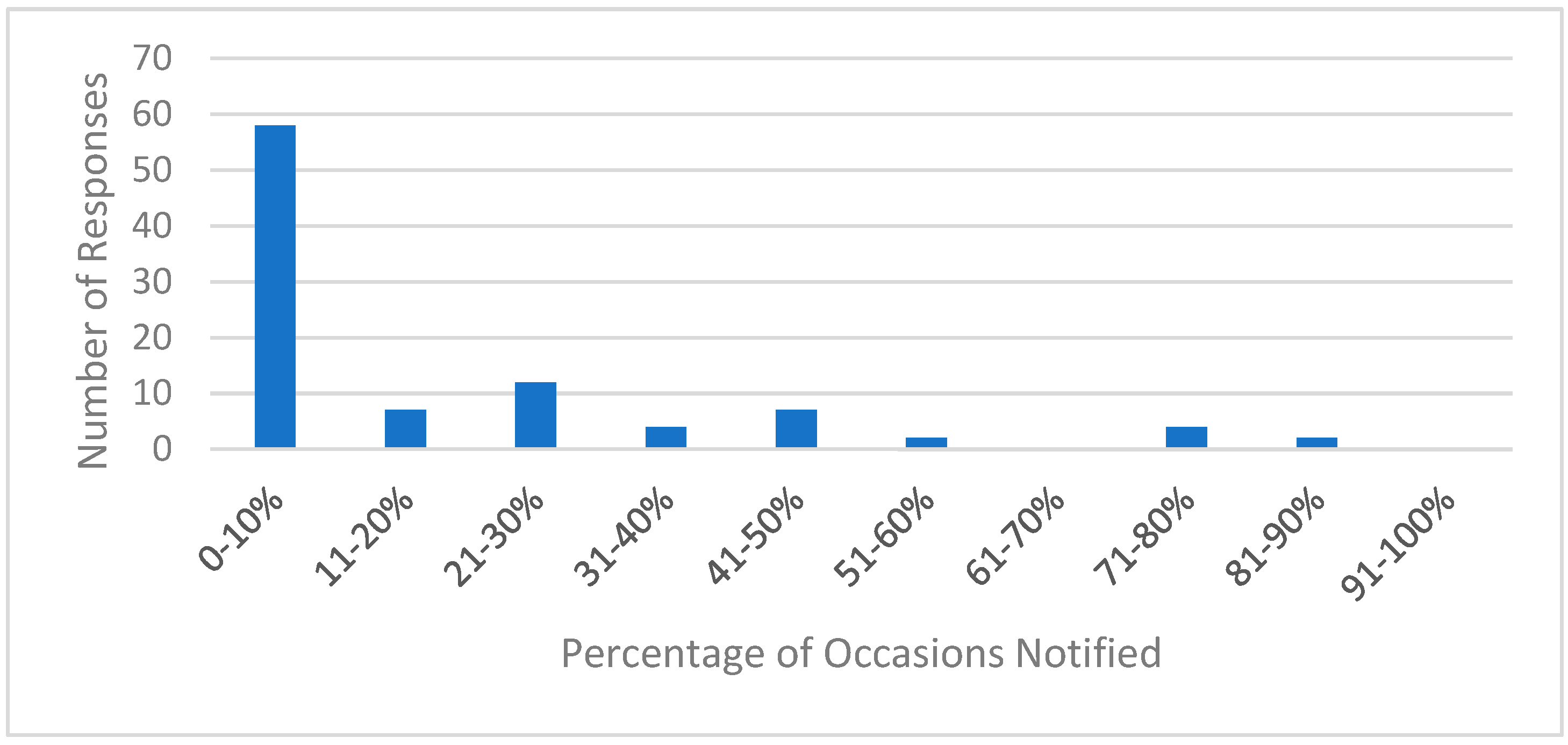
| Collaborating [25]; Collaborating with Patients, Caregivers, and Team [26] | The mechanism to learn of a patient’s discharge (Q5), and medication changes (Q6–Q7); The frequency to be notified of a patients’ discharge (Q18) Perceived importance of TOC activities (Q19) |
| Assessing/Managing Risks and Symptoms [25]; Managing Symptoms and Other Risks [26] | Prescription- and medication-related problems, and relevant interventions (Q8–Q15) Patient receiving prescribed medications upon discharge (Q16–Q17) |
| Item | Instrument a |
|---|---|
| How important to optimal patient care is each of the following items? | |
| Item 1 | Community pharmacist is notified when one of their patients is discharged. |
| Item 2 | Community pharmacist receives discharge documentation/ updated medication list upon patient discharge. |
| Item 3 | Community pharmacists have access to information needed to identify medication and discharge errors. |
| Item 4 | Community pharmacists have access to information needed to answer patient questions about discharge plan or medications. |
| Item 5 | Community pharmacists can directly contact the original prescriber to resolve prescription or medication problems |
| Item 6 | Community pharmacists notify primary care providers when patients do not receive discharge medications |
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Years in Practice, mean ± SD (range) | 15.8 ± 12.3 (1–41) |
| Gender, no. (%) | |
| Female | 71 (60.2) |
| Male | 47 (39.8) |
| Practice Setting, no (%) | |
| Independent Pharmacy (<4 stores under same ownership) | 32 (27.1) |
| Small Chain Pharmacy (4–10 stores under same ownership) | 8 (6.8) |
| Large Chain Pharmacy (>10 stores under same ownership) | 32 (27.1) |
| Mass Merchandiser Pharmacy (e.g., Wal-Mart, Kmart) | 9 (7.6) |
| Supermarket Pharmacy (e.g., Price Chopper, Hy-Vee) | 26 (22.0) |
| Other | 11 (9.3) |
| Problems | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Prescription-related problems a | |
| Incomplete or unclear directions | 53 (51.5) |
| Issues with prescriber identity or verification | 47 (45.6) |
| No prescription problems identified | 34 (33.0) |
| Mismatch between quantity prescribed and days therapy | 23 (22.3) |
| Discrepancy among medication list, prescription written, and patient’s old medications | 9 (8.7) |
| C-II prescription not valid | 8 (7.8) |
| Medication-related problems a | |
| Drug interactions/adverse reactions | 32 (31.1) |
| Duplicate therapy | 30 (29.1) |
| Wrong dose/route | 19 (18.4) |
| Adherence (patient unable or unwilling to adhere to treatment) | 17 (16.5) |
| Wrong drug | 8 (7.8) |
| Untreated indication for therapy | 6 (5.8) |
| Suboptimal drug therapy | 1 (1.0) |
| Drug not needed | 1 (1.0) |
| Other | 2 (1.9) |
| Item | Component 1 |
|---|---|
| Item 1 | 0.830 |
| Item 2 | 0.858 |
| Item 3 | 0.920 |
| Item 4 | 0.955 |
| Item 5 | 0.889 |
| Item 6 | 0.818 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vossen, R.K.; Liu, Y.; Kuehl, P.G. Community Pharmacists’ Experiences and Perception about Transitions of Care from Hospital to Home in a Midwestern Metropolis. Pharmacy 2021, 9, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy9040193
Vossen RK, Liu Y, Kuehl PG. Community Pharmacists’ Experiences and Perception about Transitions of Care from Hospital to Home in a Midwestern Metropolis. Pharmacy. 2021; 9(4):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy9040193
Chicago/Turabian StyleVossen, Rachel K., Yifei Liu, and Peggy G. Kuehl. 2021. "Community Pharmacists’ Experiences and Perception about Transitions of Care from Hospital to Home in a Midwestern Metropolis" Pharmacy 9, no. 4: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy9040193
APA StyleVossen, R. K., Liu, Y., & Kuehl, P. G. (2021). Community Pharmacists’ Experiences and Perception about Transitions of Care from Hospital to Home in a Midwestern Metropolis. Pharmacy, 9(4), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy9040193







