Abstract
Pharmaceutical poisoning is a significant global public health concern, causing approximately 190,000 deaths annually. This scoping review aims to comprehensively map the available literature on pharmaceutical poisoning and compare patterns between high-income countries (HICs) and low-middle-income countries (LMICs). A systematic search was performed across the following databases: Embase, PubMed, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and CINAHL. Studies included were from 1 January 2011 to 31 December 2020, in English, with full text available. Seventy-nine articles were included in the study; 21 were from LMICs and 58 were from HICs. Toxic exposure was largely intentional (77%) in LMICs and accidental (68%) in HICs. Drugs acting on the nervous system were responsible for 95% of toxicities worldwide with analgesics accounting for the largest subtherapeutic group in both LMICs (40%) and HICs (58%). Notable statistics were that HICs accounted for 99% of opioid overdoses, and LMICs accounted for 19% of anti-epileptic-induced toxicities. Overall, the medical outcomes due to poisonings were generally worse in LMICs. The review provides possible interventions to target specific geographic locations, based on the trends identified, to reduce the burden worldwide. Many gaps within the literature were recognised, calling for more robust analytical research.
1. Introduction
Toxic exposure to medicines remains a significant, under-recognised global public health concern. The World Drug Report estimates that pharmaceutical poisoning causes 190,000 fatalities annually [1]; with non-fatal poisoning 20–30 times more prevalent and often causing long-term morbidities [2]. The most prevalent long-term conditions are respiratory, renal or hepatic failure, cognitive impairment, and hypoxic brain injury, depending on the drug(s) involved [3]. This severely reduces patients’ quality of life and puts a strain on healthcare services and society worldwide.
Drug-induced toxicities require immediate action by emergency medicine and national toxicology centres. This creates immense pressure on healthcare systems, apparent from observing hospital admissions alone. In the United Kingdom (UK), approximately 100,000 patients present to emergency departments annually due to drug poisoning, which in turn is responsible for 10% of general ward admissions [4]. Likewise, almost 75% of drug overdose cases in Japan require ambulance services, which account for 15% of intensive care unit (ICU) admissions [5]. Similar trends have been observed worldwide highlighting the burden on emergency services, consuming valuable resources and delaying care for other life-threatening emergencies [5].
Pharmaceutical poisoning can be categorised as intentional (deliberate) or unintentional (accidental). The latter ranks fifth in European injury-related mortality, with the highest rates in Lithuania, Ireland, Estonia, Romania and Latvia [6]. Most unintentional drug poisoning cases occur in children under five, from having a natural curiosity to explore unfamiliar objects and failing to recognise the associated dangers due to their developing cognitive function [7]. Such incidents are most common within a household setting where 10–20% of child exposures are due to their grandparent’s medicines being easily accessible [8]. Many co-morbidities in the elderly require multiple medications, which accumulate in homes [9]. Patients often self-manage their medicines using blister packs, removing the drugs from their original, child-resistant, packaging—consequently increasing the risk of accidental consumption and overdose [10]. Therapeutic errors can also cause unintentional toxicity as well accidental consumption. Such errors are often caused by dosing errors, especially for high-risk medications with a narrow therapeutic index [6].
Alarmingly, most drug toxicity cases are due to intentional self-harm. These intentional exposures occur in countries worldwide regardless of income status, often due to distressing life events, poverty, and psychiatric illnesses, with the highest rates among adults aged 33–44 [11,12]. In 2016, over one billion people worldwide were diagnosed with a mental health condition, 20% of whom were children or adolescents [13,14]. Many of these patients are prescribed drugs to help manage their conditions, highlighting the magnitude of the population’s vulnerability and exposure to medicines with potential toxicities. Over 60% of drug poisoning suicides in Asia are from people with psychiatric conditions, highlighting the correlation between mental illness and pharmaceutical poisoning [1,15,16]. Furthermore, overdosing with prescribed and over-the-counter medicines accounts for 79% of UK emergency department presentations due to self-harm [3,16,17].
Opioids are the major cause of drug-induced toxicity globally [18]. In the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017, 109,500 people died from opioid usage, including prescription, synthetic, and illegal opioids [17,19]. Due to relaxed drug classification and illicit marketplaces availability, the USA has an opioid pandemic. Indeed, over the past 20 years, the USA opioid pandemic has quadrupled in mortality [20]. Similarly, opioids are the main driver of fatal overdoses in Europe, responsible for approximately eight out of 10 drug-induced deaths [21]. The UK and Germany, in particular, account for almost half (47%) of all opioid overdose mortalities in Europe [22].
Socioeconomic marginalisation and cultural differences affect pharmaceutical poisoning regionally. In high-income countries (HICs), medicines are responsible for over 50% of all poisonings [23]. In contrast, in low-middle-income countries (LMICs) such as Ethiopia, India, and Sri Lanka, household products, organophosphates, and pesticides are the major contributors to poisonings, with pharmaceuticals accounting for as little as 10% of toxicities [24]. Because a substantial portion of the population in these places rely on agriculture for money or work, such products are readily available and commonly misused [25,26]. However, drug-overdose mortality is still estimated to be four times higher in LMICs compared to HICs [27]. These inconsistencies are caused by differences in global medicine regulation authority. The lack of regulatory bodies in many LMICs leads to poor access to quality medicines, a higher risk of exposure to falsified drugs, poor prescribing policies, and lenient laws surrounding over-the-counter medicines, where 60% of drugs in developing countries are prescribed or sold inappropriately [28,29,30], contributing to global drug-poisoning disparities.
While extensive literature has been published on pharmaceutical poisoning in specific countries, no efforts have been made to collate this data and analyse trends globally. This would provide an overall evaluation of the key themes of pharmaceutical poisoning and highlight the impact of a country’s income level on such patterns.
This scoping review aims to identify the available literature and compare the patterns of pharmaceutical poisoning between LMICs and HICs, specifically focusing on the reason(s) for exposure, the drug(s) responsible, and the medical outcome(s). All drug poisoning cases are avoidable, so understanding patterns can assist in developing preventative strategies and prioritising geographical areas most in need to target such campaigns.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) (Supplementary Table S1) [31].
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
A comprehensive, systematic search was completed using five electronic databases: Embase, PubMed, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials and CINAHL. In order to form the search strategy, the study objectives were translated into search terms to ensure all relevant articles were captured. This was achieved by completing an initial search on PubMed to identify relevant papers on the topic. Papers were analysed for keywords used in the title and abstract to describe the subject area. The keywords identified formed the search strategy that was used to search the five databases, available in Appendix A. The terms were a combination of words to describe ‘poisoning’ and ‘pharmaceuticals’ as displayed in Table 1. The search results were restricted to articles published from 1 January 2011 to 31 December 2020. In 1997, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued recommendations for poison control. The guidelines highlighted the importance of standardizing poisoning diagnostic and treatment data collection, toxicovigilance, and poison prevention initiatives [32]. The revised version of ‘Guidelines for Establishing a Poison Centre’ followed in early 2021 [33]. We analyzed a decade-long trend using a 2011–2020 criterion prior to the publication of the updated version. A further manual search on Google Scholar was completed to identify any grey literature.

Table 1.
Search terms.
Search results were imported into Endnote 20 (Thomson Reuters, New York, NY, USA) where they were grouped according to the database they were sourced from. Each group was then uploaded to Covidence for screening where duplicates of articles were removed. Two reviewers (CC and AL) independently screened all titles and abstracts of the remaining articles. Bibliographies of relevant studies were also checked for additional publications. Full-texts of potentially relevant studies were then reviewed independently by both reviewers to confirm eligibility according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Any discrepancies were discussed between both reviewers, and if a consensus could not be reached, the lead researcher (SAJ) was consulted.
2.2. Study Selection
Studies were included if they fulfilled the following criteria: (1) the study reported on poisoning due to pharmaceuticals; (2) the published date was between 1 January 2011–31 December 2020; (3) full texts and abstracts were available in English; (4) the country where the study was conducted was stated; and (5) the article stated both the reason(s) (e.g., accidental or intentional) and outcome(s) (e.g., length of hospital stay, morbidity or mortality) of the poisoning. Studies were excluded from this review if: (1) they reported on poisoning due to toxins other than medicines (e.g., household products, pesticides etc.) or there was no separation of results between different toxins; and (2) they reported on illicit drug poisoning or did not separate results between medicinal drugs and illicit substances. Reviews, systemic reviews, scoping reviews, meta-analyses, in vitro and in vivo studies, animal studies, conference abstracts or proceedings, reports, letters to the editor, and comments were also excluded.
2.3. Data Extraction and Synthesis
A data-charting form was developed to capsulate the variables required to be extracted from the included studies. This was trialed on five articles to ensure the relevant data was easily charted and the form was altered accordingly. The following data were extracted and tabulated from included studies: (1) author and year of publication; (2) study design and objectives; (3) location of the study; (4) sample size; (5) demographic characteristics including age and gender; (6) reason for exposure; (7) drug(s) responsible for toxicity; and (8) patient-related outcome(s) of poisoning. Extracted information from studies were grouped according to the income status of the country where the study was conducted. Income status was categorised into ‘LMIC’ and ‘HIC’ with reference to the World Bank Country Classifications by Income Level 2021–2022, defined by gross national income per capita [34].
In order to aid identification of the common drug classifications responsible for the poisoning, the Anatomic Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) and Defined Daily Dose (DDD) (ATC/DDD) Toolkit was used to classify drugs into the organ or biological system they target [35]. Some publications present the outcome of the drug poisoning according to the Poisoning Severity Score (PSS), which ranks the severity of the toxicity. The system scores poison outcomes as (0) no effect (patient is asymptomatic); (1) minor effect (mild symptoms); (2) moderate effect (prolonged symptoms); (3) severe (life-threatening symptoms with significant residual disability or disfigurement), or (4) fatal [36]. Finally, age categories were defined and categorised using the WHO definition, which states that a child is under the age of 18 and an adult is 18 years or over. These categories were used when analysing patient demographic trends and the effect of age on pharmaceutical poisoning [37]. Key patterns identified from the extracted data were summarised narratively with the aid of tables and charts into key categories.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
The initial search identified 135,936 publications, with four additional studies identified during a manual search on Google Scholar. After screening titles and abstracts, 1359 studies met the inclusion criteria. Full texts of the 1359 studies were assessed for eligibility, where a further 1280 were excluded for the following reasons: wrong study design (n = 796), no separation of results between pharmaceutical drugs and illicit substances (n = 239), no separation of results between pharmaceutical poison and other types of poisoning (n = 111), no full-text available (n = 62), and the study failed to state the reason(s) for poisoning (n = 50) or outcome(s) (n = 22). This resulted in 79 studies being included in the data synthesis of this scoping review, as summarised in the PRISMA-ScR diagram (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
PRISMA-ScR flowchart of study selection.
Of the included studies, eight were prospective studies: one survey, five cross-sectional studies, one cohort study, and one observational follow-up. The remaining 71 were retrospective studies: 63 cohort and eight cross-sectional studies. Tables presenting a summary of the study characteristics included in this review can be found in Table A1 and Table A2 in Appendix B.
3.2. Overview
The collective sample size of participants was 1,660,165 (HICs: 1,653,519; LMICs: 6646), with ages ranging from one month old to 100 years old. Of the total study group where gender was stated, 51.1% were female (n = 694,234). Twenty-one of the studies (27%) were conducted in LMICs: one each in Algeria, Argentina, Jordan, Morocco, Romania, South Africa, and Sri Lanka; two in India, three in Turkey, and nine in Iran. Fifty-eight studies (73%) were conducted in HICs: 27 in the USA, four in Switzerland, three each in Canada, France, and Denmark; two each in Australia, Israel, Japan, Poland, Finland, and Saudi Arabia, and one study each in the Czech Republic, Republic of Ireland, New Zealand, Singapore, Taiwan, and the UK (Table 2).

Table 2.
List of all countries and their economic status where studies were conducted.
3.3. Trends
The results of the scoping review are presented in three broad categories: (i) the reason behind the exposure to drug poisoning, (ii) the pharmaceutical agent responsible for toxicity, and (iii) the medical outcomes of poisonings.
3.3.1. Reason behind Toxic Exposure
The reason for poisoning was classified into two broad categories: intentional or unintentional (accidental). Of the overall sample size, 95% (n = 1,577,159) stated the known reason for being exposed to the drugs at toxic levels with the remaining 5% unknown. For studies that were set in LMICs, 76.2% of exposures were intentional (n = 4809). Further reasons for intentional poisoning were stated for 67% (n = 3216), with attempted suicide accounting for 91.8% (n = 2952), self-harm for 5.3% (n = 172), relationship conflicts noted for 2.2% (n = 72) and homicide for 0.6% (n = 20). For the 23.8% (n = 1503) of patients that were exposed to drug poisoning accidently, detailed reasons were given for 15% (n = 232) and included 31.5% due to careless storage (n = 72), 18.1% due to parental mistakes (n = 42), 18.5% due to therapeutic errors (n = 43), and 31.9% due to ingestion by children while playing (n = 74).
In HICs, 31.7% (n = 499,332) of exposures were intentional. Additional explanations for intentional exposure were given for 5% (n = 25,828); with 92.3% stating attempted suicide (n = 23,829), 6.8% as misuse (n = 1763) and the remaining 0.9% stating abuse of the drug (n = 236). Unintentional poisoning was reported in 68.3% (n = 1,075,873) of cases. Further explanations for accidental exposures included 94.7% as therapeutic errors (n = 508,402), 1.3% as adverse drug reactions (n = 6847), and 4% due to one or more products containing the same active ingredient being consumed (n = 21,361). (Figure 2).
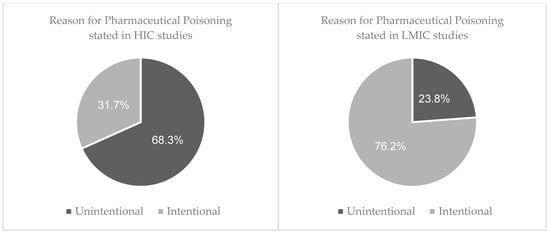
Figure 2.
Comparing the reason behind pharmaceutical poisoning between LMIC and HIC’s.
A common trend seen over the included studies was that the intent behind the pharmaceutical poisoning varied depending on age. Fifteen of the studies reported on pharmaceutical poisoning in children, of which 70.2% were exposed accidently (n = 76,398) [42,49,61,67,75,76,78,82,86,91,92,94,95,96,97]. Five studies had separated results for adult exposure where 80.9% of exposures were intentional (n = 725) [73,78,94,96,98].
3.3.2. Types of Pharmaceuticals Responsible for Poisoning
Using the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification toolkit via the WHO, causative drugs responsible for poisoning were divided into the 1st level classification, which has 14 main anatomical or pharmacological groups (Table 3). Of the studies that specifically mentioned the drug(s) responsible for the poisoning, 94.7% (n = 1,368,876) were pharmaceuticals categorised under ‘Nervous System’: 54% (n = 3069) and 95% (n = 1,365,780) in LMICs and HICs respectively.

Table 3.
Drugs responsible for poisoning in LMICs and HICs grouped into the ATC 1st level categories *.
Looking more closely at the ‘Nervous System’ identified the therapeutic subgroups most commonly responsible (Table 4). In LMICs, 40% (n = 1236) of the central nervous system (CNS)-acting medicines exposed were analgesics, of which 39% were paracetamol, and 31% were from exposure to prescription opioids. In HICs, analgesics accounted for close to 60% of drugs acting on the nervous system, of which 73% (n = 567,925) were prescription opioids and 25% (n = 198,282) paracetamol. Psychoanaleptics (antidepressants, psychostimulants, and anti-dementia drugs) accounted for more than 30% (n = 461,019) of CNS agents. When looking at the global exposures to nervous system agents, LMICs were responsible for less than 1% of toxicities from analgesics, psycholeptics, and psychoanaleptics; 4% of drugs used in opioid dependence, and 19% of toxicities due to antiepileptics.

Table 4.
Drugs responsible for poisoning in LMIC and HIC studies categorised into the ATC 2nd level classification for drugs acting on the nervous system.
3.3.3. Outcome of Pharmaceutical Poisoning
Of those hospitalised, 85% were in LMICs (n = 5668) and 20% in HICs (n = 327,439). Across all studies, the average time hospitalised varied from 17.1 h to 13.9 days ranging from 5 h to 91 days [38,54,73]. Less than 1% (n = 11,237) were admitted to the ICU due to poison exposure, where admissions accounted for 10% of the LMIC population outcomes (n = 666) and less than 1% of HIC outcomes (n = 10,571). The most common medical outcomes were all observed in less than 1% of the total study size and included acute kidney injury (n = 9126), organ failure (n = 2765), coma (n = 6776), respiratory depression (n = 6839) and seizures (n = 418).
Nine out of the 79 studies utilised the PSS as a measure of medical outcome [46,50,87,95,96,97,99,100,101]. One was set in Jordan (LMIC) and the remaining eight reported on outcomes from HICs. In the Jordan study, 40% were asymptomatic (n = 363), 39% had mild symptoms (n = 355), 17% were moderate (n = 150) and 4% severe (n = 32). For those reporting using the PSS in HICs (n = 285,481), 56% were asymptomatic (n = 161,269), 32% experienced minor symptoms (n = 90,819), 11% had moderate effects (n = 30,035), 1% were severe (n = 3075) and less than 1% of the poisonings were classified as fatal (n = 283).
Overall, 20,314 deaths were recorded across all included studies. In LMICs, 2% of the pharmaceutical poisoning outcome was death (n = 137), while in HIC 1.2% deaths (n = 20,177) were reported. A key trend observed was the exposure to toxic levels of CNS-acting drugs causing mortality. Eight articles reported deaths as the sole outcome of drug poisoning. Over the eight articles, the collative sample size was 16,175. The five major drug groups responsible for mortality were opioids (47%), anxiolytics (14%), antidepressants (12%), anti-epileptics (5%) and methadone for opioid substitution therapy (4%) [58,60,65,70,89,90,102,103].
4. Discussion
After synthesising the data from the 79 papers that met the inclusion criteria, specific trends between economically developed and developing countries were identified, and research gaps were recognised.
4.1. Reason behind Toxic Exposure
The disparity in reasons for pharmaceutical poisoning between LMICs and HICs was remarkable. Over 75% of LMICs’ exposures were deliberate self-poisonings, with 92% further stating overdose with the intent of suicide. Previous literature has recognised the gravity of the issue in the developing world, with eight of the top ten countries with the highest suicide rates being LMICs [104]. In contrast, accidental exposure to pharmaceuticals accounted for 68% of toxicities in HICs, with over 94% of these due to therapeutic errors, including administration errors, consuming multiple medicines with the same active ingredient, adverse drug reactions, and poor storage leading to child exposure. This finding may be due to more efficient error reporting and surveillance systems in developed countries [105].
With regard to the effect of age on poisoning, the results reaffirmed that child toxicities are predominantly unintentional, with adults mostly intentional in both LMICs and HICs [7]. The disparity in the causes of pharmaceutical poisoning between LMIC and HIC is likely attributable to a number of socioeconomic factors, including the availability of healthcare resources, poverty, access to treatment and support services, cultural attitudes towards mental health, and other socioeconomic factors. Higher rates of intentional self-poisoning with suicidal intent in LMICs reflect a lack of access to mental health resources and support, poverty and bad living conditions, or a cultural stigma associated with seeking assistance for mental health difficulties. In contrast, accidental poisonings may be more widespread in HICs due to higher access and availability of pharmaceutical medications, and a lack of knowledge or education regarding their proper use and potential risks [106,107,108].
4.2. Types of Pharmaceuticals Responsible for Poisoning
The overwhelming majority (94.7%) of pharmaceutical toxicities worldwide were from drugs acting on the nervous system, with analgesics accounting for the largest sub-group responsible. Opioids were responsible for most analgesic exposures, with the problem largely residing in HICs, likely due to their accessibility in these areas being far greater than for LMICs, where a considerable lack of pain relief medications is available [109]. Indeed, in a Lancet Commission Report, it was reported that only 0.1 metric tonne of morphine-equivalent opioids are delivered to LMICs, from almost 300 metric tonnes [110]. Furthermore, overprescribing and long-term use of opioids are considered the root cause of toxicities in HICs due to risks of dependence, often leading to misuse and overconsumption [111]. Medicines used in opioid substitution treatment were also commonly responsible for the poisoning, perhaps due to the vulnerability of patients receiving such treatment and the risk of co-ingesting opiates along with substitution therapy.
Findings from this review also revealed that poisoning due to psychoanaleptics accounted for the second largest subtherapeutic group in HICs, while psycholeptics were the second largest in LMICs. Similar results have previously been reported where analgesics, psycholeptics (mostly benzodiazepines), and pschoanaleptics (particularly antidepressants) were the groups largely responsible for intoxication [112]. The results also matched previous findings where toxicity due to a combination of drugs was common in LMICs and HICs due to the risks of drug-drug interactions. Despite these three subgroups accounting for most pharmaceutical toxicities worldwide, LMICs were responsible for less than 1% of these poisonings meaning the problem significantly exists within HICs. However, a subgroup where LMICs were particularly accountable for the global burden was exposure to antiepileptics, where almost 20% of toxicities occurred in these developing countries. Part of the explanation may be that 85% of epileptic patients reside in LMICs [113]. Furthermore, antiepileptics are approved for a number of indications besides the treatment of epilepsy, including neuropathic pain and mood stabilisation, common conditions prevalent in these areas and two major groups vulnerable to intentional overdose and suicide ideation [113,114]. Additionally, access to anticonvulsants is far more attainable than analgesics in these deprived countries, particularly first-generation anticonvulsants, which are notorious for their poor safety profile with a high risk of toxicity in comparison to second-generation agents [113].
4.3. The Outcome of Pharmaceutical Poisoning
Analysing the outcome of drug-related poisoning, findings revealed that 85% and 20% of those exposed were in LMICs and HICs respectively, with the duration of hospital stay ranging from five hours to 91 days. Admissions to the ICU were over 10 times more common in the developing world, and fatality rates from overdose were almost twice as high compared to HICs. This can be explained by the intent affecting the outcome where there is a direct correlation between the dose consumed and a worse prognosis. Thus, mortalities are higher in LMICs as far larger quantities are likely to be consumed when the exposure was intentional. Furthermore, the disparities in healthcare resources are also responsible for poorer outcomes. Access to healthcare resources and poison information centres that advise on the management of poisoning is far scarcer in LMICs, leading to delayed treatment and interventions, increasing the exposure length and ultimately worsening the outcome [115]. For studies in this scoping review that reported according to the PSS, most outcomes were asymptomatic and mild in severity, and very little of the study population suffered from severe (life-threatening) or fatal effects. Therefore, findings reveal that pharmaceutical poisoning is associated with more short-term illnesses and morbidities than mortality.
4.4. Future Research and Recommendations
When considering the geographical location of included studies, an uneven distribution between those conducted in LMICs and HICs was apparent. Despite over 85% of the world’s population residing in LMICs, there was a poor representation of the developing world, with 73% of the studies reporting on HICs [114]. Thus, obtaining an in-depth comparison of poisoning patterns between the economically developed and developing world was difficult. The low number of papers could be due to the exclusion of a large number of papers which did not separate between poisoning due to pharmaceuticals and other types of poisons. However, the lack of poison information centres partly justifies this, a major resource for collecting such data. According to the WHO, only 47% of countries have an established poison centre, with African, Eastern Mediterranean, and Western Pacific regions particularly lacking [116]. Therefore, it should be a public health priority for governments to invest funding into establishing and strengthening these centres. This would not only improve surveillance for future research but also guide managing drug-induced poisons, thus improving outcomes.
Globally, the expenditure on mental health services is inadequate and is disproportionately worse in LMICs compared to HICs, with regard to the magnitude of the problem and the poisonings that arise from it [114]. It is estimated that globally, there is an average of 3.96 psychiatrists per 100,000 people. However, in developing countries such as Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, and Pakistan, those rates are 0.04, 0.301, 0.06, and 0.185, respectively [114]. Furthermore, within countries, there are large variations in access to mental health workers, with the majority often concentrated in urban areas meaning those living rurally have poor access and minimal support available [114]. There is an urgent need to train and employ more individuals in the mental health workforce to increase accessibility to non-pharmacological treatment. This would also limit the prescribing of psycholeptics and psychoanaleptics; two major drug classes highlighted in this scoping review to be responsible for toxicities. Furthermore, setting up referral schemes after patients are discharged from an intentional overdose to provide appropriate support would reduce the likelihood of reoccurrence.
Due to the overwhelming impact of opioids on the burden of pharmaceutical poisoning, it is essential that improvements in national policies are made in the areas where opioid overdose is particularly problematic. There is an urgent need for improved legislation and policies with regard to the prescribing and duration of treatment with opioids as well as improved education on chronic pain management. Furthermore, better recognition of those requiring support from addiction services and increased access to the opioid-reversal agent naloxone would reduce the burden of opioid toxicities [117].
Those most vulnerable to opioid toxicity are often regular patients to pharmacies [118]; thus, having a supply of naloxone in every pharmacy and training staff on recognising the signs of an overdose and the protocol to follow would be immense in the prevention of life-threatening toxicities. That being said, it is important to consider the difficulties of implementing such strategies in both HICs and LMICs. In HICs such as the USA, there are relaxed policies and opioids are easily accessible [119]. While in LMICs, pharmacy services are reported to be lacking, with the drive being profit over patient care [120]. Furthermore, access to medicines is also limited [121], so having naloxone available in every community pharmacy may be logistically difficult. Perhaps having a national initiative scheme available to pharmacies to widen access to services within the community would help improve patient-centred care and reduce toxicities from occurring or refer those who present at risk in a reasonable time.
Many countries have yet to prioritise poisoning prevention strategies despite the severity of the issue. Public health campaigns focusing on increasing parental awareness of storing medicines in their original packaging and keeping them out of sight and reach of children are required to prevent the risk of confusing them for ‘sweets’ [6]. Many intentional poisonings are often impulsive; thus, limiting the accumulation of medicines stored in households by promoting safe disposal via pharmacies would be an effective strategy. Such campaigns could be promoted within healthcare settings and social media should be utilised to target large audiences [122].
Several research gaps were identified whilst conducting this scoping review. As discussed above, data available from LMICs were minimal, underlining the need for more robust analytical studies to reduce the disparity and underrepresentation of the developing world. In addition, research understanding the barriers to establishing poison information centres in LMICs and how these could be addressed would be valuable for enhancing the response to drug-induced toxicity in these regions despite the availability of multiple guidelines for establishing poison centres and other aspects of dealing with poisonings [33,123].
To address the disparity in patterns of pharmaceutical poisoning between LMICs and HICs, a less costly strategy of increasing awareness would be beneficial. This could be achieved by collecting and analysing the attitudes and competencies of healthcare professionals practising outside of hospitals towards managing drug-induced poisonings. This research could identify areas where further education and awareness of resources available, such as tox-based apps, would improve the triaging of patients and reduce unnecessary referrals from community settings to emergency departments.
As well as this, the findings revealed that hospitalisation and utilisation of emergency departments is a common outcome of drug-related poisoning despite many toxicities being asymptomatic or mild in severity. Thus, attempts to collect and analyse the attitudes and competencies of healthcare professionals practising in sectors beyond hospitals in advising and managing drug-induced poisons would be valuable. Additional personnel or qualified emergency physicians and the development of multidisciplinary teams in major hospitals in LMICs are also required to address the issue of pharmaceutical poisoning better. This will ensure that patients in emergency settings receive prompt and effective care and lessen the burden on the healthcare system.
Generative AI technology has the ability to revolutionise how individuals obtain information about poisonings and seek medical care. By providing free and immediate access to information about various types of poisonings, their symptoms, and risk reduction strategies, this technology can assist individuals in determining if they or someone they know has been exposed to a harmful substance, thereby facilitating more targeted and effective treatment. There are limitations to chatbot AI technology despite its potential benefits. Challenges such as the quality and diversity of training data, the limitations of pre-programmed responses, and platform constraints can impact the accuracy and relevancy of the delivered information. It is crucial to use chatbot AI technology to complement professional medical advice, not as a replacement.
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
This scoping review is the first attempt to collate the broad field of literature and identify patterns of pharmaceutical poisoning at a global level. A few limitations were noted. Firstly, only articles that were available in English were included, which likely limited the data available in non-native English-speaking countries. Secondly, a large number of initial studies were found during the search. Despite this ensuring all relevant papers were captured, it perhaps reflects that the search strategy was not specific enough to the study’s aims. We also excluded from the scoping review all categories of reports, ranging from individual institution annual reports to health organization reports, that would have provided a deeper understanding of the trend. However, this will necessitate translation in addition to other difficulties, as not all nations have such reports.
Thirdly, the USA was overrepresented in this review accounting for 47% of HIC studies. Although this highlights the ongoing issues in the USA with the opioid epidemic, it reduces the attempt to analyse trends of pharmaceutical poisoning in HICs in general. In addition, the reported trend may be understated due to the availability of panels of substance analysis in various nations. Despite this, the majority of poisoning cases are treated based on clinical judgment of the information acquired, and drug concentration monitoring is not always used to determine causality. Finally, where articles collected the data from poison databases, this often required voluntary reporting. Self-reported data has the potential risk of bias, thus, the accuracy of poison reports is unknown. Furthermore, data is also compiled from the volume of calls poison centres receive from physicians. However, many physicians are familiar with the diagnosis and management plan for often-occurring toxicities and so do not need to refer to the centres for advice. Thus, the available data is unlikely to comprehensively reflect the magnitude of the problem.
5. Conclusions
This review is the first attempt to analyse the data available on pharmaceutical poisoning worldwide. Findings reveal that most drug toxicities are intentional in LMICs and accidental in HICs. Globally, the problem mostly lies with drugs acting on the nervous system, particularly analgesics, and medical outcomes from poisoning are generally worse in LMICs. Implementation of the suggested recommendations including the establishment of poison information centres worldwide, strengthening mental health resources, tightening medicine regulations, improving healthcare professional awareness surrounding drug toxicity and public health prevention campaigns would make a positive contribution towards alleviating the burden of these preventable injuries. Despite recognising the epidemiological patterns of poisoning, gaps in the literature were recognised calling for more robust analytical research.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pharmacy11060184/s1, Table S1. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) Checklist.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: S.A.J.; Data curation: C.C. and A.L.; Formal analysis: C.C. and A.L.; Investigation: C.C. and A.L.; Methodology: S.A.J.; Project administration: S.A.J. and B.T.; Supervision: S.A.J. and B.T.; Validation: All authors; Writing—original draft: C.C.; Writing—review and editing: All authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the following experts for reviewing the manuscript and providing valuable feedback, which were used to make significant improvements to the manuscript: Vikneswaran Murugaiyah; Daniel Malone. His areas of expertise include neurophysiology and pharmacology of drugs used for central nervous system disorders; and Tye Sok Cin, Research Fellow with the Section of Genetics and Epidemiology, Joslin Diabetes Center, Harvard Medical School. She specializes in personalized medicine, specifically the prediction of individualized treatment responses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| ADR | Adverse drug reaction |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| ATC | Anatomic Therapeutic Chemical |
| BB | Beta blocker |
| CCB | Calcium channel blocker |
| CVS | Cardiovascular |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DDD | Defined Daily Dose |
| ED | Emergency departments |
| ENT | Ear, nose, and throat |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| HICs | High-income countries |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| LMICs | Low-middle-income countries |
| MI | Myocardial infarction |
| MALA | Metformin associated lactic acidosis |
| NSAID | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory |
| OTC | Over the counter |
| POU | Pyrexia of unknown origin |
| PSS | Poisoning Severity Score |
| SSRI | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor |
| TCA | Tricyclic antidepressant |
| TB | Tuberculosis |
| UK | United Kingdom |
| USA | United States of America |
Appendix A. Search Strategy
| 1. | Poison*.mp. |
| 2. | toxic.mp. |
| 3. | overdose.mp or intoxication/ |
| 4. | excessive.mp. |
| 5. | substance abuse/ |
| 6. | drug misuse/ |
| 7. | 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 |
| 8. | pharmaceutical.mp. |
| 9. | medicine/ |
| 10. | drug/ |
| 11. | opioid.mp. |
| 12. | 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 |
| 13. | 7 and 12 |
| 14. | limit 13 to (English and yr = 2011–2020) |
Appendix B

Table A1.
Characteristics and data extracted from included studies set in low-middle income countries.
Table A1.
Characteristics and data extracted from included studies set in low-middle income countries.
| Author (Year) | Study Design | Setting | Sample Size | Patient Demographics (Age (Years) * and Gender a) | Reason for Exposure | Drug Responsible for Poisoning b | Outcome from Exposure c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ghaemia et al. [42] | A prospective cross-sectional study at a tertiary toxicology centre in Northeast Iran | Northeast Iran | 126 | Ages 1–14: 126 Mean age: 2.8
| Accidental: 126
|
| Symptoms:
Hospitalised 126Deaths: 3 |
| Hamedi et al. [49] | Cross-sectional study on children admitted to EDb of Imam Reza Hospital. Data was collected from laboratory results and subjective data from parents’ responses. | Northeast Iran | 79 | (3 months–15 years)
| Accidental: 74
Intentional (suicide attempt): 1Unknown: 4 |
| Hospitalised: 79
Deaths: 2 (due to prolonged hypoxia and delay in hospitalisation) |
| Jabbehdari et al. [43] | Descriptive-sectional study on hospital admissions with methadone poisoning at Loghman-Hakim Hospital in the second half of 2012. | Iran | 31 | Mean age: 4.6
| Accidental: 31 |
| Hospitalised: 31
|
| Bilel et al. [38] | A retrospective descriptive study on poisonings received at the Oran University Hospital over 8 years using a pre-established information sheet on patient and circumstances of poisoning along with biological samples. | Algeria | 400 |
| Accidental: 72 Intentional (suicide attempts): 328 |
| Hospitalised: 400
Death: 5 |
| Kara et al. [124] | Retrospective study comprised records of patients admitted to ED of Konya Numune Hospital between 2009–2011. | Turkey | 932 |
| Intentional (suicide attempts): 932 |
| Hospitalised: 932
Death: 1 |
| Buffone et al. [39] | Descriptive, retrospective study based on the data collected from reviewing the medical records of patients 10–19 years at ED of Municipal Hospital of Bahia Blanca. | Argentina | 72 | Mean age: 16 (10–19)
| Intentional: 72
|
| Hospitalised: 72
|
| Hocaoglu et al. [54] | Cross-sectional descriptive study reviewing theophylline exposure cases reported to Dokuz Eylul University Drug and Poison Information Centre (DPIC). | Turkey | 354 |
| Intentional: 291 Accidental: 46 Unknown: 17 |
| Hospitalised: 354
Death: 2 |
| Mehrpour et al. [44] | Retrospective cross-sectional review based on hospital records of acute poisonings managed in ICU during a 7-year period in a single center in Birjand, Iran | Iran | 267 |
| Accidental: 22 Intentional: 151
|
| ICU: 267 Death: 52 |
| Azekour et al. [51] | Epidemiological retrospective study reviewing medicinal poisoning registered with the Provincial Delegation of Health in Errachidia between 2004–2016 | Morocco | 180 | Mean age: 21 (2–75)
| Accidental: 101 Intentional: 72 Unknown: 7 |
| Hospitalised: 132 Death: 3 |
| Taheri et al. [125] | Descriptive analytical study performed from 2010–2012 in the poisoning emergency and clinical toxicology departments of Noor Hospital affiliated with Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. | Iran | 385 | Mean age: 32.1 (1–90)
| Intentional: 222 Accidental: 153 |
| Hospitalised: 385
Death: 7 |
| Weerasinghe et al. [53] | Retrospective analysis of self-harm cases. Data collected from primary and referral hospitals. | Sri Lanka | 54 |
| Intentional: 52 Accidental: 2 |
| Hospitalised: 54
|
| Bagherian Rad et al. [45] | Cross sectional retrospective study carried out on all patients referred to Loghman Hakim Hospital from 2011–2016. | Iran | 229 | Mean age: 24 (13–90)
| Intentional: 224 Unintentional: 5 |
| Hospitalised: 229 ICU: 8 Duration of hospital stay:
Death: 1 |
| Nagaralu et al. [40] | Retrospective review using data from ED at four tertiary care hospitals | India | 708 |
| Intentional: 484 Accidentall: 149 Homicidal: 20 Unknown: 55 |
| Hospitalised: 708 Death: 42 |
| Anthony et al. [41] | Observational retrospective review using records from a tertiary care hospital over 15 months | India | 91 | Mean age: 28.1
| Intentional: 72 Accidental: 19 |
| ICU: 61
Deaths: 3 |
| Shadnia et al. [46] | Retrospective cohort study using data from patients admitted to Loghman Hakim Hospital Poison Centre over 4-month period. | Iran | 100 |
| Intentional (suicide attempt): 93 Unknown: 7 |
| Hospitalised: 100
|
| Yehya et al. [50] | Retrospective descriptive study using data from PharmacyOne Poison call centre, 2014–2018 | Jordan | 900 |
| Intentional: 236
|
| PSS
|
| Van hoving et al. [11] | Retrospective review extracting data from Khayelitsha Hospital Emergency Care database | South Africa | 192 |
| Intentional: 192 |
| Hospitalised: 192
Death: 4 |
| Hashemneiad et al. [47] | Cross sectional study using data from patients admitted with drug poisoning at Karaj Shariati Hospital over 1 year | Iran | 172 | Mean age 29.8 (12–80)
| Intentional: 172 |
| Hospitalised: 172
Death: 10 |
| Yaylaci et al. [55] | Retrospective study of patients at follow-up admitted with intoxication to the ICU between 2009–2011 | Turkey | 153 |
| Intentional (suicide attempt): 144 Accidental: 9 |
| ICU: 153 Average length of stay: 2.4 days |
| Khodabandeh et al. [48] | Prospective cross-sectional study among acute drug poisoning patients at a single hospital over 1 year | Iran | 410 |
| Accidental: 35 Intentional: 375
|
| Hospitalised: 410
|
| Sorodoc et al. [52] | Retrospective review using data from a single tertiary center from Iasi County, Romania | Romania | 811 |
| Accidental: 63 Intentional (Suicide attempt): 748 |
| Hospitalised: 811
Death: 2 |
* Where available, age ranges are displayed in brackets below the noted age categories and mean age of the sample size. a M:male; F: female. b NSAIDs: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; GI: Gastrointestinal; CVS: cardiovascular; CNS: central nervous system; TB: Tuberculosis. c ED: emergency departments; ICU: Intensive care unit.

Table A2.
General characteristics of included studies set in high-income countries.
Table A2.
General characteristics of included studies set in high-income countries.
| Author (Year) | Study Design | Setting a | Sample Size | Patient Demographics (Age (Years) * and Gender b) | Reason for Exposure | Drug Responsible for Poisoning c | Outcome from Exposure d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jensen et al. [62] | A retrospective nationwide descriptive study using 2 databases; the Danish Poison and Information Centre (DPIC) and the State Serum Institute of Denmark. (SSI) | Denmark | 1505 |
| Intentional: 1142
Unknown: 71 |
| Hospitalised: 456
Deaths: 14 |
| Martin et al. [86] | Retrospective review of all paediatric admission at Eastern Maine Medical Centre (EMMC) from 1999–2009. | USA | 22 |
| Accidental: 16 (All aged between 1–12) Intentional: 6 (All aged between 13–17) Drug source was family or friend for 82% of cases |
| Hospitalisation: 22
|
| Gregoriano et al. [94] | Retrospective analysis of reports to a National Poison Centre 1995–2013 | Switzerland | 40 |
| Children:
| Children:
| Hospitalised: 40
|
| Martos et al. [78] | An observational study reported to national poison centre between 1995–2013 | Switzerland | 75 |
| Accidental: 22
Intentional: 50
|
| No effect:
|
| Cairns et al. [56] | Retrospective observational study. Data collected from NSW poisons information centre 2004–2014 | Australia | 1735 | Mean age: 17
| Intentional: 1735 |
| Hospitalised: 1594 Referred to toxicologist: 60 |
| Alruwaili et al. [81] | Prospective, descriptive cross-sectional study looking at 2 paediatric ED in Riyadh over 2 years | Saudi Arabia | 1035 |
| Unintentional: 906 Intentional: 22 Unknown: 104 |
| Hospitalised: 1035
|
| Eluri et al. [87] | Retrospective analysis of errors reported to USA poison control centre from 2000–2012 | USA | 533,763 |
| Accidental:
|
|
|
| Ichikura et al. [72] | Cohort study from an ICU in Japan from 2006–2013 | Japan | 676 |
| Intentional: 676
|
| ICU: 676 |
| Post et al. [88] | Retrospective analysis of calls to USA poison control centres (NPDS) from 2007–2016 | USA | 11,275 |
| Accidental: 10,053 Intentional: 1001 |
| Hospitalised: 8401 Deaths: 11 |
| Kamour et al. [85] | Retrospective study using NPIS telephone enquires related to 4 NSAIDs between 2007–2013 | UK | 22,937 | (14–98)
| Intentional: 11,104 Drug misuse: 65 Accidental: 9826 Unknown: 602 |
|
|
| Tan et al. [83] | Retrospective review of paracetamol overdose presenting to a tertiary hospital in Singapore | Singapore | 177 | Mean age: 25 (21–36)
| Intentional: 136 Unintentional: 40 Intent unclear: 1 |
| Hospitalised: 177
|
| Madadi et al. [58] | Retrospective study using the Office of the Chief Coroner of Ontario. All deaths coded drug-related were reviewed. | Canada | 1359 | Mean age: 44 Age range: 16–89
| Accident: 924 Unknown: 221 Suicide: 214 |
| Death: 1359 |
| Austin et al. [89] | Population based study using North Carolina death certificate data to identify drug overdose decedents | USA | 1221 |
| Intentional: 207 Accidental: 1014 |
| Death: 1221 |
| Friedrich et al. [90] | Retrospective database analysis of NPDS from 2000–2015 | USA | 296,838 |
Gender not stated | Intentional: 142,482 Accidental: 154,356 |
| Death: 253
|
| Torrents et al. [67] | A 6-year prospective national study. Patients identified using records reported to poison centre and contacted to complete survey | France | 87 | Mean age 2 (0.5–17 years)
| Accidental: 87 |
| Emergency unit: 42 Paediatric unit: 21 ICU: 13 Death: 5 |
| Toce et al. [91] | Retrospective cohort study at a single paediatric tertiary care centre of children between 6 months and 7 years between 2006–2014 | USA | 88 | Mean age: 2 (10 months–6.4 years)
| Accidental: 88 |
| Hospitalised: 88
|
| Gomes et al. [59] | Population-based cross-sectional study of patients admitted for acute care in hospitals across Canada due to prescribed opioids | Canada | 2599 |
| Accidental: 648 Intentional: 291 Unknown: 248 |
| Hospitalised: 2599 |
| Shipton et al. [74] | Population based cohort study using records from the Coronial Services Office in Wellington from 2008–2012 | New Zealand | 325 |
| Unintentional: 179 Intentional: 110 Unknown: 37 |
| Death: 325 |
| Tadros et al. [92] | Retrospective study using data from the Nationwide ED Sample (NEDS) from 2006–2012 | USA | 21,928 | Mean age: 9 (0–17)
| Intentional: 5316 Accidental: 13,524 Unknown: 2126 |
| All ED visits
Deaths: 11 |
| Tadros et al. [93] | Retrospective cohort study utilising 2006–2011 data from the Nationwide ED Sample | USA | 259,093 |
| Unintentional: 138,603 Intentional: 68,641 Unknown: 51,849 |
| All ED visits
|
| Vakkalanka et al. [99] | Retrospective review of loperamide exposures reported to NPDS between 2010 and 2015. | USA | 1736 |
| Abuse: 228 Misuse: 569 Attempted suicide: 848 Other: 91 |
| PSS
|
| Creswell et al. [126] | Cross sectional study. Data of children aged 0–19 exposed to opioids was collected using hospital admissions and Wisconsin Poison Control Centre (WPC) | USA | 3320 |
| Accidental: 2522
|
| ICU: 3320 Death: 3 |
| Feingold et al. [70] | Retrospective study. Data was obtained from the National database on causes of death. Drug poisoning deaths were coded as opioid-related | Israel | 875 |
| Accidental: 9 Intentional: 4 Unknown: 409 |
|
|
| Koskela et al. [65] | Retrospective study. Data was collected from Cause of Death Registry death certificates provided by Statistics Finland from 2007–2011. | Northern Finland | 684 | Urban:
Rural:
| Urban: Intentional (suicide attempt): 82 Rural: Intentional (suicide attempt): 40 | Urban:
| Death: 684 |
| Tobaiqy et al. [82] | Retrospective study. Chart review of all acute paediatric poisoning incidence in ED at East Jeddah Hospital over 4-year period | Saudi Arabia | 69 |
| Accidental: 46
|
| Hospitalised: 69
Death: 1 |
| Kriikku et al. [66] | Retrospective review of post-mortem toxicology cases positive for urinary buprenorphine between 2010–2014 | Finland | 775 | Mean age: 31
| Accidental: 463 Intentional parenteral instead of sublingual: 167 suicide: 90 other: 55 |
| Death: 369 |
| Thongprayoon et al. [127] | Retrospective review. Data extracted from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) coded as ICD-9 diagnosis. | USA | 13,805 |
| Intentional (suicide attempt): 9029 Unknown: 4776 |
| Hospitalised: 13,805
Death: 132 |
| Miller et al. [102] | Prospective cross-sectional study. Analysis of censuses of live emergency department and inpatient discharges for 11 USA states as well as Multiple Cause of Death census data between 2011–2012 | USA | 10,525 |
| Intentional (suicide attempt): 6716 Unknown: 3809 |
| Death: 10,525 |
| Manini et al. [128] | Prospective cohort study looking at two tertiary care hospitals over 12 months. | USA | 274 | Mean age: 40.3
| Intentional: 217 Accidental: 57 |
| Hospitalised: 274
Death: 2 |
| Lee et al. [57] | Retrospective review using data from calls to Victorian Poisons Information Centre (VPIC) over a 10-year period. | Australia | 4412 |
| Accidental: 781
|
co-ingested with:
| Hospitalised: 4412 Death: 1066 |
| Vilay et al. [129] | Retrospective case-control study of exposures reported to the NPDS between 2001–2007 | USA | 9074 |
| Intentional: 5009 Accidental: 3152 |
|
|
| Wheatley et al. [130] | Retrospective review of poison centre records between 2001–2010 | USA | 162 | Mean age: 27
| Intentional: 49 Accidental: 113 |
| ICU: 9 Coma: 1 |
| Kominek et al. [75] | Retrospective analysis of patients hospitalised with paracetamol poisoning in a Paediatric Clinic between 2004–2012 | Poland | 44 |
| Intentional: 30 Accidental: 10 Dosing error: 4 |
| Hospitalised: 44 |
| Haoka et al. [73] | Retrospective observational study analysisng medical records in a single tertiary hospital in Japan | Japan | 145 |
| Accidental: 102 Intentional: 43 |
| Hospital visits: 145
|
| Mroczkowska-Juchkiewicz et al. [76] | Retrospective evaluation of intentional poisoning cases in department of paediatrics, Childrens University Hospital in Lubin from 2007–2012 | Poland | 145 | Mean age: 15.1 (12–15)
| Intentional: 145 reasons including psychiatric disorders, family conflicts, school conflicts, sexual assault, lack of self-acceptance from chronic disease |
| Hospitalisation: 145
|
| Lasoff et al. [98] | Retrospective review using state-wide poison control system electronic database from 2002–2015 | USA | 224 | Mean age: 41 (18–90)
| Intentional.
|
| Hospitalised: 64
Deaths: 3 |
| Feng et al. [131] | Cross-sectional study. Cases were identified from a database by ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes | USA | 9647 |
| Accidental: 2305 ADR: 1663 Suicidal: 930 |
| Death: 53 |
| Lavon et al. [71] | Prospective observational follow-up study of all medication errors outside healthcare facilities reported to IPIC | Israel | 1381 |
| Accidental (therapeutic error): 1381 |
|
|
| Stevens et al. [68] | Retrospective study analysing metformin poisoning reported to Western France PCC from 1999–2016 | France | 382 |
| Accidental: 197 Intentional: 127 Therapeutic error: 58 |
|
Death: 21 |
| Torrents et al. [69] | Retrospective descriptive study of cases of methadone exposure reported to French poison centres over a 7-year-period | France | 1415 | Mean age: 34 (10–74)
| Misuse: 670 Suicide attempt: 584 Unintentional: 12 Medication errors: 140 |
|
Death: 219 |
| Zakharov et al. [61] | Retrospective review using the database of the Czech Toxicological Information Centre from 2007–2011 | Czech Republic | 2339 |
| Intentional (suicide attempt): 2339 |
| Medical care: 2339 |
| Caupp et al. [100] | Retrospective review using Poison Control Centre Data in Ohio from 2002–2014 | USA | 619 |
| Accidental: 97 Intentional: 504 Other/unknown: 37 |
| PSS:
|
| Okic et al. [103] | Retrospective review of descents from forensic pathology in Kansas City autopsied between 2001–2011 | USA | 789 | Mean age: 43 (2–92)
| Accident 332 Intentional (suicide attempt): 43 Unknown: 101 |
| Death: 789 |
| Christenses et al. [63] | Retrospective review looking at enquires concerning CBBs reported to the Danish Poisons Information Centre (DPIC) from 2009–2015 | Denmark | 339 |
| Intentional (suicide attempt): 156 Accidental: 183 | CCB;
| Hospitalised: 275
Death: 7 |
| Truitt et al. [132] | Retrospective chart review of PCC charts by running a search on all calls received between 2007–2009 | USA | 436 |
| Accidental: 436 |
| Hospitalised: 32 Death: 1 |
| Christensen et al. [64] | Retrospective study of drug poisoning cases reported to Danish Poison Information Centre (DPIC) | Denmark | 239 |
| Intentional (suicide attempt): 175 Accidental: 64 | aripiprazole: 239 combined with:
| Hospital visits: 239
|
| King et al. [101] | Retrospective review of NPDS data from 2000–2014 to identify paediatric ADHD medication exposures | USA | 156,365 |
| Accidental: 128,119 Intentional: 23,034 ADR: 4040 Unknown: 1172 |
| PSS:
|
| Vohra et al. [95] | Retrospective study of exposures using electronic health records and reports to NPDS (2004–2014) | USA | 99 |
| Accidental: 88
|
|
|
| Lin et al. [84] | Retrospective evaluation of medical records of children under 18 who presented to the ED with pharmaceutical poisoning (2001–2008) | Taiwan | 87 | Mean age: 11.26
| Accidental: 34 Intentional: 53 |
| Hospitalised: 87
|
| Conner et al. [96] | Retrospective review of intentional self-poisoning (ISP) cases aged 13–65 treated at a USA University Medical Centre | USA | 673 |
| Intentional (suicide attempt): 673 |
| PSS:
|
| Piotrowska et al. [79] | Retrospective, observational study of patients presenting to ED of Bern University Hospital. Cases were identified using electronic database. | Switzerland | 181 | Mean age: 25 (16–85)
| Accidental: 38 Intentional: 143 |
| Hospitalised: 181
Deaths: 2 |
| Patel et al. [97] | Retrospective, cross-sectional analysis using NPDS from 2010–2014 identifying patients <18 years with exposure to opioid. | USA | 83,418 |
| Accidental: 61,206 Intentional: 20,064 ADR: 1088 Other: 227 |
| PSS:
|
| Reichert et al. [80] | Retrospective review of acute single-agent exposures to pharmaceutical reported to Swiss Toxicological Information Centre (STIC) between 1997–2012 | Switzerland | 313 |
| Accidental: 42 Intentional: 266 Other: 5 |
| Seizures: 313 |
| Sinyor et al. [60] | Retrospective review of drug induced suicides in Toronto using Coroner’s data | Canada | 397 |
| Intentional (suicide attempt): 397 |
| Death: 397 |
| Glaizal et al. [133] | Retrospective review using results of a 2-year national survey by the toxicovigilance network (2008–2010) | USA | 135 | Mean age: 31 (13–58)
| Intentional (suicide attempt): 135 |
| ED: 85 ICU: 38 Death: 10 |
| Cassidy et al. [77] | Prospective study over 3-years on medication errors reported to NPIC | Republic of Ireland | 2348 |
| Accidental (medication error): 2348 |
| PSS:
|
| Calcaterra et al. [134] | Retrospective chart review of data from NPDS between 2001–2014 | USA | 188,452 | Mean age: 31.5
| Intentional: 188,452 |
| Coma: 6264 Respiratory depression: 6766 Death: 124 |
| Eigner et al. [135] | Retrospective review of overdose deaths using Indiana State Department of Health death certificates available through Allen County Coroner’s Office. | USA | 418 |
| Accidental: 336 Intentional: 66 Unknown: 16 |
| Death: 418 |
* Where available, age ranges are displayed in brackets below the noted age categories and mean age of the sample size. a USA: United States of America; UK: United Kingdom. b M:male; F: female. c NSAIDS: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; CVS: cardiovascular; GI: gastrointestinal; CCB: calcium channel blocker; BB: beta blocker; CNS: central nervous system; OTC: over the counter; TCA: tricyclic antidepressant; SSRI: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; ACEI: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. d PICU: Paediatric intensive care unit; ICU: Intensive care unit; ED: emergency department; ADR: adverse drug reaction; MI: myocardial infarction; ENT: ear nose and throat; AKI: acute kidney injury; MALA: metformin associated lactic acidosis; POU: Pyrexia of unknown origin; PSS: Poisoning severity score.
References
- Alwan, I.A.; Awadh, A.I.; Tangiisuran, B.; Khan, H.R.M.; Yahaya, N.; Majid, M.I. Pharmaceuticals Poisoning: Reported by the National Poison Centre in Malaysia between 2010 and 2015. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2020, 12, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darke, S.; Mattick, R.P.; Degenhardt, L. The ratio of non-fatal to fatal heroin overdose. Addiction 2003, 98, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.S.; Sampson, L.; Cerdá, M.; Galea, S. Worldwide Prevalence and Trends in Unintentional Drug Overdose: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, e29–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanacoody, R.; Anderson, M. Epidemiology of poisoning. Medicine 2020, 48, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Ishikawa, K.B.; Matsuda, S.; Fushimi, K.; Ito, H. Comparison of emergency hospital admissions for drug poisoning and major diseases: A retrospective observational study using a nationwide administrative discharge database. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e001857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintegi, S.; Esparza, M.J.; González, J.C.; Rubio, B.; Sánchez, F.; Vila, J.J.; Yagüe, F.; Benítez, M.T. Recommendations for the prevention of poisoning. An. Pediatría Engl. Ed. 2015, 83, 440.e441–440.e445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assar, S.; Hatami, S.; Lak, E.; Pipelzadeh, M.; Joorabian, M. Acute poisoning in children. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 25, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, D.A. Out of Sight and Locked Up Tight: Pediatric Pharmaceutical Poisoning. BC Med. J. 2013, 55, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Kurt, M.; Akdeniz, M.; Kavukcu, E. Assessment of Comorbidity and Use of Prescription and Nonprescription Drugs in Patients Above 65 Years Attending Family Medicine Outpatient Clinics. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 5, 2333721419874274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerden, M. What is the place for monitored dosage systems? Drug Ther. Bull. 2018, 56, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hoving, D.J.; Hunter, L.D.; Gerber, R.E.J.; Lategan, H.J.; Marks, C.J. The burden of intentional self-poisoning on a district-level public Hospital in Cape Town, South Africa. Afr. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 8, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedegaard, H.; Miniño, A.M.; Spencer, M.R.; Warner, M. Drug Overdose Deaths in the United States, 1999–2020; Statistics, N.C.F.H., Ed.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2021; Volume NCHS Data Brief, no 428. [CrossRef]
- Rehm, J.; Shield, K.D. Global Burden of Disease and the Impact of Mental and Addictive Disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Mental Health ATLAS 2017; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 68. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, K.K.; Ho, C.S.H.; Zhang, M.W.B.; Day, J.R.; Ho, R.C.M. Characteristics of overdose and non-overdose suicide attempts in a multi-ethnic Asian society. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2013, 6, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, J.; Smyth, R.S. 23—Suicide and self-harm. In Companion to Psychiatric Studies, 8th ed.; Johnstone, E.C., Owens, D.C., Lawrie, S.M., McIntosh, A.M., Sharpe, M., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2010; pp. 693–713. [Google Scholar]
- Sharareh, N.; Sabounchi, S.S.; McFarland, M.; Hess, R. Evidence of Modeling Impact in Development of Policies for Controlling the Opioid Epidemic and Improving Public Health: A Scoping Review. Subst. Abus. Res. Treat. 2019, 13, 1178221819866211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Opioid Overdose; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Keen, C.; Kinner, S.A.; Young, J.T.; Snow, K.; Zhao, B.; Gan, W.; Slaunwhite, A.K. Periods of altered risk for non-fatal drug overdose: A self-controlled case series. Lancet Public Health 2021, 6, e249–e259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.; Cunliffe, J.; Décary-Hétu, D.; Aldridge, J. Effect of restricting the legal supply of prescription opioids on buying through online illicit marketplaces: Interrupted time series analysis. BMJ 2018, 361, k2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. Drug-Induced Deaths—The Current Situation in Europe (European Drug Report 2023); European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction: Lisbon, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. Drug-Related Deaths and Mortality in Europe: Update from the EMCDDA Expert Network; European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction: Lisbon, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dayasiri, K.; Jayamanne, S.F.; Jayasinghe, C.Y. Accidental and Deliberate Self-Poisoning with Medications and Medication Errors among Children in Rural Sri Lanka. Emerg. Med. Int. 2020, 2020, 9872821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waktola, L.G.; Melese, E.B.; Mesfin, N.; Altaye, K.D.; Legese, G.L. Prevalence of unfavorable outcome in acute poisoning and associated factors at the University of Gondar comprehensive specialized hospital, Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia: A hospital-based cross-sectional study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1160182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariam, E.T. Global Epidemiology of Acute Poisoning with an Emphasis to Ethipia: Systematic Review. Int. J. Pharma Sci. Sci. Res. 2016, 2, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, C.; Singh, S.; Kumar, -M.P.; Varthya, S.B. Toxicoepidemiology of poisoning exhibited in Indian population from 2010 to 2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, M.; Oyegbite, K.; Ozanne-Smith, J.; Hyder, A.A.; Branche, C.; Rahman, F.; Rivara, F.; Bartolomeos, K. World Report on Child Injury Prevention; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Ndomondo-Sigonda, M.; Miot, J.; Naidoo, S.; Dodoo, A.; Kaale, E. Medicines Regulation in Africa: Current State and Opportunities. Pharmaceut. Med. 2017, 31, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sithole, T.; Salek, S.; Mahlangu, G.; Walker, S. Comparison of the registration process of the medicines control authority of Zimbabwe with Australia, Canada, Singapore, and Switzerland: Benchmarking best practices. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 15, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Vu, H.; Xie, Z.; Chen, W.; Tang, S. Systematic review on irrational use of medicines in China and Vietnam. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Guidelines for Poison Control; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organisation. Guidelines for Establishing a Posion Centre; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hamadeh, N.; van Rompaey, C.; Metreau, E. New World Bank Country Classifications by Income Level: 2021–2022. Available online: https://blogs.worldbank.org/opendata/new-world-bank-country-classifications-income-level-2021-2022 (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- World Health Organisation. Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classidication; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, R.; Buckley, N.A. The Poisoning Severity Score: If It Did Not Exist, We Would Have To Invent It. J. Med. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organsiation. Recognizing Adolescence; World Health Organsiation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bilel, C.; Zergui, A.; Rahmani, C.; Belmessabih, M.; Rezk-Kallah, H. Acute paracetamol poisonings received at the Oran University Hospital. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffone, I.; Dejter, M.; Fortunatti, E.; García Elliot, F.; Irazabal, C.; Marlia, R.; Mujica, D.; Parrou, M.; Romano, M.; Speciale, G.; et al. Characterization of drug poisoning among adolescents seen at the municipal hospital of Bahía Blanca, Province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2018, 116, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, K.; Ganapathy, R.S. Pattern of pharmaceutical drug poisoning in south indian tertiary care hospitals. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2016, 7, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, L.; Kulkarni, C. Patterns of poisoning and drug overdosage and their outcome among in-patients admitted to the emergency medicine department of a tertiary care hospital. Indian. J. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 16, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, N.; Alikhani, S.; Bagheri, S.; Sezavar, M. A Cross Sectional Study of Opioid Poisoning in Children at a Tertiary Center. Asia Pac. J. Med. Toxicol. 2016, 5, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbehdari, S.; Farnaghi, F.; Shariatmadari, S.F.; Jafari, N.; Mehregan, F.-F.; Karimzadeh, P. Accidental children poisoning with methadone: An Iranian pediatric sectional study. Iran. J. Child. Neurol. 2013, 7, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrpour, O.; Akbari, A.; Jahani, F.; Amirabadizadeh, A.; Allahyari, E.; Mansouri, B.; Ng, P.C. Epidemiological and clinical profiles of acute poisoning in patients admitted to the intensive care unit in eastern Iran (2010 to 2017). BMC Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherian Rad, N.; Rahimi, M. Pattern of NSAID Poisoning in a Referral Poisoning Center of Iran: Solutions to Reduce the Suicide. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadnia, S.; Brent, J.; Mousavi-Fatemi, K.; Hafezi, P.; Soltaninejad, K. Recurrent Seizures in Tramadol Intoxication: Implications for Therapy Based on 100 Patients. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 111, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmnejad, M.; Fatehi, R. Epidemiological Study of Poisoning in Patients of Karaj Shariati Hospital in 2011 to 2012. Int. J. Med. Toxicol. Forensic Med. 2014, 4, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabandeh, F.; Agin, K. Assessment of Aspiration-Induced Lung Injuries among Acute Drug Poisoning Patients.; Loghman Hakim Hospital, Poisoning Center. Int. J. Med. Toxicol. Forensic Med. 2016, 6, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Hamedi, A.; Ghahremani, S.; Nakhaei, A.A.; Balali, M.R.; Ghahremani, S. A Cross Sectional Study on Pediatric Methadone Poisoning in Northeast of Iran. Asia Pac. J. Med. Toxicol. 2016, 5, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yehya, A.; Albals, D.; Issa, R.; Fawadleh, A. Retrospective assessment of acute poisoning incidents by pharmaceutical agents in Jordan: Data from Pharmacy OneTM Poison Call Center, 2014 to 2018-Part II. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2020, 8, e00583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azekour, K.; Belamalem, S.; Soulaymani, A.; El Houate, B.; El Bouhali, B. Epidemiological Profile of Drug Overdose Reported in South-East Morocco from 2004 to 2016. Drugs Real World Outcomes 2019, 6, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorodoc, V.; Jaba, I.M.; Lionte, C.; Mungiu, O.C.; Sorodoc, L. Epidemiology of acute drug poisoning in a tertiary center from Iasi County, Romania. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasinghe, M.; Konradsen, F.; Eddleston, M.; Pearson, M.; Agampodi, T.; Storm, F.; Agampodi, S. Overdose of oral contraceptive pills as a means of intentional self-poisoning amongst young women in Sri Lanka: Considerations for family planning. J. Fam. Plan. Reprod. Health Care 2017, 43, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocaoğlu, N.; Yıldıztepe, E.; Bayram, B.; Aydın, B.; Tunçok, Y.; Kalkan, Ş. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Theophylline Exposures between 1993 and 2011. Balk. Med. J. 2014, 31, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaylaci, S.; Genc, A.B.; Demir, M.V.; Cinemre, H.; Tamer, A. Retrospective evaluation of patients at follow-up with acute poisoning in Intensive Care Unit. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2016, 19, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, R.; Daniels, B.; Wood, D.A.; Brett, J. ADHD medication overdose and misuse: The NSW poisons information centre experience, 2004–2014. Med. J. Aust. 2016, 204, 154.e151–154.e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Pilgrim, J.; Gerostamoulos, D.; Robinson, J.; Wong, A. Increasing rates of quetiapine overdose, misuse, and mortality in Victoria, Australia. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2018, 187, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadi, P.; Hildebrandt, D.; Lauwers, A.E.; Koren, G. Characteristics of Opioid-Users Whose Death Was Related to Opioid-Toxicity: A Population-Based Study in Ontario, Canada. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, T.; Khuu, W.; Craiovan, D.; Martins, D.; Hunt, J.; Lee, K.; Tadrous, M.; Mamdani, M.; Paterson, J.; Juurlink, D. Comparing the contribution of prescribed opioids to opioid-related hospitalizations across Canada: A multi-jurisdictional cross-sectional study. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2018, 191, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinyor, M.; Howlett, A.; Cheung, A.H.; Schaffer, A. Substances used in completed suicide by overdose in Toronto: An observational study of coroner’s data. Can. J. Psychiatry 2012, 57, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, S.; Navratil, T.; Pelclova, D. Non-fatal suicidal self-poisonings in children and adolescents over a 5-year period (2007–2011). Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 112, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.L.; Rømsing, J.; Dalhoff, K. A Danish Survey of Antihistamine Use and Poisoning Patterns. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 120, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, M.B.; Petersen, K.M.; Bøgevig, S.; Al-Gibouri, S.; Jimenez-Solem, E.; Dalhoff, K.P.; Petersen, T.S.; Andersen, J.T. Outcomes following calcium channel blocker exposures reported to a poison information center. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 19, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, A.P.; Boegevig, S.; Christensen, M.B.; Petersen, K.M.; Dalhoff, K.P.; Petersen, T.S. Overdoses with Aripiprazole: Signs, Symptoms and Outcome in 239 Exposures Reported to the Danish Poison Information Centre. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskela, L.; Raatiniemi, L.; Bakke, H.K.; Ala-Kokko, T.; Liisanantti, J. Fatal poisonings in Northern Finland: Causes, incidence, and rural-urban differences. Scand. J. Trauma. Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2017, 25, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriikku, P.; Hakkinen, M.; Ojanpera, I. High buprenorphine-related mortality is persistent in Finland. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 291, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrents, R.; Picot, C.; Glaizal, M.; Courne, M.A.; Schmitt, C.; Richard, N.; Simon, N.; Cardona, F.; De Haro, L. Child poisonings with methadone in France: A 6-year prospective national survey since the availability of capsules in 2008. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.; Hamel, J.F.; Toure, A.; Hadjadj, S.; Boels, D. Metformin overdose: A serious iatrogenic complication-Western France Poison Control Centre Data Analysis. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrents, R.; Glaizal, M.; Sinno-Tellier, S.; Richard, N.; Nisse, P.; Vodovar, D.; Bloch, J.; Simon, N.; de Haro, L. Methadone poisonings: A seven-year retrospective study of the French poison center network focusing on suicide attempts vs. misuses. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, D.; Goldberger, N.; Haklai, Z.; Lev-Ran, S. Fatal Overdoses of Opioids in Israel 2005–2014. Eur. Addict. Res. 2017, 23, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavon, O.; Ben-Zeev, A.; Bentur, Y. Medication errors outside healthcare facilities: A national poison centre perspective. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 114, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikura, K.; Okumura, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Associations of Adverse Clinical Course and Ingested Substances among Patients with Deliberate Drug Poisoning: A Cohort Study from an Intensive Care Unit in Japan. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoka, T.; Sakata, N.; Okamoto, H.; Oshiro, A.; Shimizu, T.; Naito, Y.; Onishi, S.; Morishita, Y.; Nara, S. Intentional or unintentional drug poisoning in elderly people: Retrospective observational study in a tertiary care hospital in Japan. Acute Med. Surg. 2019, 6, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipton, E.E.; Shipton, A.J.; Williman, J.A.; Shipton, E.A. Deaths from Opioid Overdosing: Implications of Coroners’ Inquest Reports 2008–2012 and Annual Rise in Opioid Prescription Rates: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Pain Ther. 2017, 6, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kominek, K.; Pawłowska-Kamieniak, A.; Mroczkowska-Juchkiewicz, A.; Krawiec, P.; Pac-Kożuchowska, E. Intentional and accidental paracetamol poisoning in childhood—A retrospective analysis. Postep. Hig Med Dosw Online 2015, 69, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mroczkowska-Juchkiewicz, A.; Krawiec, P.; Pawłowska-Kamieniak, A.; Gołyska, D.; Kominek, K.; Pac-Kożuchowska, E. Intentional poisonings in urban and rural children—A 6-year retrospective single centre study. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2016, 23, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, N.; Duggan, E.; Williams, D.J.P.; Tracey, J.A. The epidemiology and type of medication errors reported to the National Poisons Information Centre of Ireland. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martos, V.; Hofer, K.E.; Rauber-Lüthy, C.; Schenk-Jaeger, K.M.; Kupferschmidt, H.; Ceschi, A. Acute toxicity profile of tolperisone in overdose: Observational poison centre-based study. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, N.; Klukowska-Rötzler, J.; Lehmann, B.; Krummrey, G.; Haschke, M.; Exadaktylos, A.K.; Liakoni, E. Presentations Related to Acute Paracetamol Intoxication in an Urban Emergency Department in Switzerland. Emerg. Med. Int. 2019, 2019, 3130843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, C.; Reichert, P.; Monnet-Tschudi, F.; Kupferschmidt, H.; Ceschi, A.; Rauber-Luthy, C. Seizures after single-agent overdose with pharmaceutical drugs: Analysis of cases reported to a poison center. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruwaili, N.D.; Halimeh, B.; Al-Omar, M.; Alhatali, B.; Sabie, I.I.; Alsaqoub, M. An epidemiological snapshot of toxicological exposure in children 12 years of age and younger in Riyadh. Ann. Saudi Med. 2019, 39, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobaiqy, M.; Asiri, B.A.; Sholan, A.H.; Alzahrani, Y.A.; Alkatheeri, A.A.; Mahha, A.M.; Alzahrani, S.S.; MacLure, K. Frequency and Management of Acute Poisoning among Children Attending an Emergency Department in Saudi Arabia. Pharm 2020, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.J.; Sklar, G.E. Characterisation and outcomes of adult patients with paracetamol overdose presenting to a tertiary hospital in Singapore. Singap. Med. J. 2017, 58, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.R.; Liu, T.H.; Liu, T.A.; Chang, Y.J.; Chou, C.C.; Wu, H.P. Pharmaceutical poisoning exposure and outcome analysis in children admitted to the pediatric emergency department. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2011, 52, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamour, A.; Crichton, S.; Cooper, G.; Lupton, D.J.; Eddleston, M.; Vale, J.A.; Thompson, J.P.; Thomas, S.H.L. Central nervous system toxicity of mefenamic acid overdose compared with other NSAIDs: An analysis of cases reported to the United Kingdom National Poisons Information Service. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.C.; Rocque, M. Accidental and non-accidental ingestion of methadone and buprenorphine in childhood: A single center experience, 1999-2009. Curr. Drug Saf. 2011, 6, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eluri, M.; Spiller, H.A.; Casavant, M.J.; Chounthirath, T.; Conner, K.A.; Smith, G.A. Analgesic-Related Medication Errors Reported to US Poison Control Centers. Pain. Med. 2018, 19, 2357–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, S.; Spiller, H.A.; Casavant, M.J.; Chounthirath, T.; Smith, G.A. Buprenorphine exposures among children and adolescents reported to us poison control centers. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20173652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, A.E.; Proescholdbell, S.K.; Creppage, K.E.; Asbun, A. Characteristics of self-inflicted drug overdose deaths in North Carolina. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2017, 181, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.M.; Sun, C.; Geng, X.; Calello, D.P.; Gillam, M.; Medeiros, K.L.; Smith, M.; Ruck, B.; Mazer-Amirshahi, M. Child and adolescent benzodiazepine exposure and overdose in the United States: 16 years of poison center data. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toce, M.S.; Burns, M.M.; O’Donnell, K.A. Clinical effects of unintentional pediatric buprenorphine exposures: Experience at a single tertiary care center. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 55, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, A.; Layman, S.M.; Davis, S.M.; Bozeman, R.; Davidov, D.M. Emergency department visits by pediatric patients for poisoning by prescription opioids. Am. J. Drug Alcohol. Abus. 2016, 42, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, A.; Layman, S.M.; Davis, S.M.; Davidov, D.M.; Cimino, S. Emergency Visits for Prescription Opioid Poisonings. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 49, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoriano, C.; Ceschi, A.; Rauber-Lüthy, C.; Kupferschmidt, H.; Banner, N.R.; Krähenbühl, S.; Taegtmeyer, A.B. Acute thiopurine overdose: Analysis of reports to a National Poison Centre 1995–2013. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, R.; Huntington, S.; Koike, J.; Le, K.; Geller, R.J. Pediatric Exposures to Topical Benzocaine Preparations Reported to a Statewide Poison Control System. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 18, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, K.R.; Wiegand, T.J.; Gorodetsky, R.; Schult, R.F.; Kaukeinen, K. Poisoning Severity Associated with a Range of Medications in Suicide Attempts by Ingestion. Suicide Life Threat. Behav. 2019, 49, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.M.; Wheeler, D.C.; Rose, S.R.; Nadpara, P.A.; Pakyz, A.L.; Carroll, N.V. Prevalence and Characteristics of Pediatric Opioid Exposures and Poisonings in the United States. J. Pediatr. 2019, 206, 148–155.e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasoff, D.R.; Koh, C.H.; Corbett, B.; Minns, A.B.; Cantrell, F.L. Loperamide Trends in Abuse and Misuse Over 13 Years: 2002–2015. Pharmacotherapy 2017, 37, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakkalanka, J.P.; Charlton, N.P.; Holstege, C.P. Epidemiologic Trends in Loperamide Abuse and Misuse. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2017, 69, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caupp, S.; Steffan, J.; Shi, J.; Wheeler, K.K.; Spiller, H.A.; Casavant, M.J.; Xiang, H. Opioid drug poisonings in Ohio adolescents and young adults, 2002–2014. Clin. Toxicol. 2018, 56, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.A.; Casavant, M.J.; Spiller, H.A.; Hodges, N.L.; Chounthirath, T.; Smith, G.A. Pediatric ADHD Medication Exposures Reported to US Poison Control Centers. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20173872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.R.; Swedler, D.I.; Lawrence, B.A.; Ali, B.; Rockett, I.R.H.; Carlson, N.N.; Leonardo, J. Incidence and Lethality of Suicidal Overdoses by Drug Class. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e200607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okic, M.; Cnossen, L.; Crifasi, J.A.; Long, C.; Mitchell, E.K. Opioid Overdose Mortality in Kansas, 2001–2011: Toxicologic Evaluation of Intent. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iemmi, V.; Bantjes, J.; Coast, E.; Channer, K.; Leone, T.; McDaid, D.; Palfreyman, A.; Stephens, B.; Lund, C. Suicide and poverty in low-income and middle-income countries: A systematic review. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, I.; Balkrishnan, R. Medication Error Management around the Globe: An Overview. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 72, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawer, S.; Rajabali, F.; Zheng, A.; Pike, I.; Purssell, R.; Zargaran, A.; Babul, S. Socioeconomic factors and substances involved in poisoning-related emergency department visits in British Columbia, Canada. Health Promot. Chronic Dis. Prev. Can. 2021, 41, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getie, A.; Belayneh, Y.M. A Retrospective Study of Acute Poisoning Cases and Their Management at Emergency Department of Dessie Referral Hospital, Northeast Ethiopia. Drug Healthc. Patient Saf. 2020, 12, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Social Determinants of Mental Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadelia, A.; De Lima, L.; Arreola-Ornelas, H.; Kwete, X.J.; Rodriguez, N.M.; Knaul, F.M. Solving the Global Crisis in Access to Pain Relief: Lessons from Country Actions. Am. J. Public. Health 2019, 109, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaul, F.M.; Farmer, P.E.; Krakauer, E.L.; De Lima, L.; Bhadelia, A.; Jiang Kwete, X.; Arreola-Ornelas, H.; Gómez-Dantés, O.; Rodriguez, N.M.; Alleyne, G.A.O.; et al. Alleviating the access abyss in palliative care and pain relief-an imperative of universal health coverage: The Lancet Commission report. Lancet 2018, 391, 1391–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Addressing Problematic Opioid Use in OECD Countries; OECD: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnell, D.; Ho, D.; Murray, V. Medical management of deliberate drug overdose: A neglected area for suicide prevention? Emerg. Med. J. 2004, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Jovel, C.; Toledano, R.; Aledo-Serrano, Á.; García-Morales, I.; Gil-Nagel, A. Epidemiological profile of epilepsy in low income populations. Seizure 2018, 56, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, S.; Pinninti, N.; Irfan, M.; Gorczynski, P.; Rathod, P.; Gega, L.; Naeem, F. Mental Health Service Provision in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Health Serv. Insights 2017, 10, 1178632917694350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, S.; Liu, D. Unequable spatial accessibility to hospitals in developing megacities: New evidence from Beijing. Health Place 2020, 65, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Poison Control and Unintentional Poisoning; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- National Academiesof-Sciences, Engineering and Medicine; Healthand-Medicine-Division; Board-on-Health-Sciences-Policy; Committee on Pain Management and-Regulatory Strategies-to-Address Prescription Opioid Abuse. 5. Evidence on Strategies for Addressing the Opioid Epidemic. In Pain Management and the Opioid Epidemic: Balancing Societal and Individual Benefits and Risks of Prescription Opioid Use; Jonathan, K., Phillips, M.A.F., Richard, J.B., Eds.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tabeefar, H.; Chang, F.; Cooke, M.; Patel, T. Community pharmacists and chronic pain: A qualitative study of experience, perception, and challenges. Can. J. Pain. 2020, 4, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, N.; Beletsky, L.; Ciccarone, D. Opioid Crisis: No Easy Fix to Its Social and Economic Determinants. Am. J. Public Health 2018, 108, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.; Goodman, C. Performance of retail pharmacies in low- and middle-income Asian settings: A systematic review. Health Policy Plan. 2016, 31, 940–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisinger, K.M.; Garabedian, L.F.; Wagner, A.K. Improving access to medicines in low and middle income countries: Corporate responsibilities in context. South. Med. Rev. 2012, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hamid, H.; Masood, R.A.; Tariq, H.; Khalid, W.; Rashid, M.A.; Munir, M.U. Current pharmacy practices in low- and middle-income countries; recommendations in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Drugs Ther. Perspect. 2020, 36, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Guidelines on the Prevention of Toxic Exposures: Education and Public Awareness Activities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, H.; Bayir, A.; Degirmenci, S.; Akinci, M.; Ak, A.; Kayis, S.; Agacayak, A.; Azap, M. Causes of poisoning in patients evaluated in a hospital emergency department in Konya, Turkey. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2014, 64, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri, F.; Yaraghi, A.; Sabzghabaee, A.M.; Moudi, M.; Eizadi-Mood, N.; Gheshlaghi, F.; Farajzadegan, Z. Methadone toxicity in a poisoning referral center. J. Res. Pharm. Pract. 2013, 2, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, P.D.; Gibson, C.; Theobald, J.; Meiman, J.G. Exposures to Opioids among Wisconsin Children and Adolescents, 2002-2016. Wmj 2019, 118, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Petnak, T.; Kaewput, W.; Mao, M.A.; Kovvuru, K.; Kanduri, S.R.; Boonpheng, B.; Bathini, T.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Pivovarova, A.I.; et al. Hospitalizations for Acute Salicylate Intoxication in the United States. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, A.F.; Nelson, L.S.; Stimmel, B.; Vlahov, D.; Hoffman, R.S. Incidence of adverse cardiovascular events in adults following drug overdose. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2012, 19, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilay, A.; Wong, C.; Schrader, R.; Mercier, R.-C.; Seifert, S. Indicators for serious kidney complications associated with toxic exposures: An analysis of the National Poison Data System. Clin. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheatley, M.A.; Shah, B.B.; Morgan, B.W.; Houry, D.; Kazzi, Z.N. Injury secondary to antiretroviral agents: Retrospective analysis of a regional poison center database. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 12, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Iser, J.; Yang, W. Medical encounters for opioid-related intoxications in Southern Nevada: Sociodemographic and clinical correlates. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2016, 16, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truitt, C.A.; Brooks, D.E.; Dommer, P.; LoVecchio, F. Outcomes of unintentional beta-blocker or calcium channel blocker overdoses: A retrospective review of poison center data. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Glaizal, M.; Gazin, V.; Aymard, I.; Messina-Gourlot, C.; Richard, N.; Mallaret, M.; Saviuc, P.; De Haro, L. Suicidal poisonings with methadone in France: Results of a two year national survey by the Toxicovigilance Network. Clin. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, S.L.; Severtson, S.G.; Bau, G.E.; Margolin, Z.R.; Bucher-Bartelson, B.; Green, J.L.; Dart, R.C. Trends in intentional abuse or misuse of benzodiazepines and opioid analgesics and the associated mortality reported to poison centers across the United States from 2000 to 2014. Clin. Toxicol. 2018, 56, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigner, G.; Henriksen, B.; Huynh, P.; Murphy, D.; Brubaker, C.; Sanders, J.; McMahan, D. Who is Overdosing? An Updated Picture of Overdose Deaths from 2008 to 2015. Health Serv. Res. Manag. Epidemiol. 2017, 4, 233339281772742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).