Toward a Representation of Semantic Change in Linked Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
Given a lexico-ontological resource with a lexicon(s) to provide a linguistic description of words (and other linguistic phenomena) and an ontological (ideally language independent) description of concepts, how can we show (i) how the meanings of words change over time with reference to concepts in an ontology and, in the other direction, (ii) how can we trace the different lexemes used to refer to the same (ontological) concept over time?
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Two Important Scenarios
- In the first scenario, we would like to model (or, from the point of view of a user of the resource, to query) how a concept, c in , is referred to in . To make the scenario even simpler, we assume that there exist a series of words, or more broadly lexemes, in that are ,,..., all of which refer to this concept.6For instance, the ontological concept Mammal might be associated with the words mammal and, possibly, mammalia in an English language lexicon. We call this scenario the onomasiological case.
- In the second scenario, we would like to be able to associate a lexeme w in with (and again from the user’s point of view, to be able to retrieve it) all of the different concepts in that it can be used to refer to. We call this the semasiological scenario. For instance, the word ’mouse’ is associated with both a kind of rodent and a kind of computer input device.
2.2. Senses as Intensions
A South-African quadruped (Orycterdpus capensts Cuv.), about the size of the badger, belonging to the insectivorous division of the Edentata, where it occupies an intermediate position between the Armadillos and Ant-eaters.10
2.3. Senses and Language Use
2.4. What Is an Ontology?
3. Introducing the Intensional–Ontological Meaning Model
- Word Meaning in IOM
- The lexical sense s is used to describe commonalities and tendencies in the use of w (those that are part of the description of the semantics of that word when it refers to the language-independent concept o) in situations of actual language production; this part of the description of l is dependent on a particular language;
- The ontology vocabulary item o is used to describe the ‘intensional’ part of w’s meaning (that part of the meaning of w corresponding to s that it shares with words in other languages that it can be translated into), where this ‘intensional’ meaning is ‘extra-linguistic’, in the limited sense that the same item can be used to describe the meaning of different linguistic entities and in different languages (i.e., o represents the sense as intension of an entry as mentioned above).
3.1. The Ontolex-Lemon Model and IOM
the lexical meaning of a lexical entry when interpreted as referring to the corresponding ontology element. A lexical sense thus represents a reification of a pair of a uniquely determined lexical entry and a uniquely determined ontology entity it refers to. A link between a lexical entry and an ontology entity via a Lexical Sense object implies that the lexical entry can be used to refer to the ontology entity in question.
| Listing 1. An OntoLex-Lemon example. |
| Individual: lex1 Types: ontolex:LexicalEntry Facts: ontolex:sense sense1, ontolex:sense sense2 Individual: sense1 Types: ontolex:LexicalSense Facts: ontolex:isSenseOf lex1, ontolex:reference o:c1 Individual: sense2 Types: ontolex:LexicalSense Facts: ontolex:isSenseOf lex1, ontolex:reference o:c2 |
3.2. Previous Work in Semantic/Conceptual Change in RDF
3.2.1. The Limitations of RDF
3.2.2. Semantic Change, Etymologies, and Beyond
- SemanticShift represents instances of semantic shift f relating together two instances of LexicalSense, and , where the former is the source of the shift, and the latter is the target;
- shiftSource is an object property that has as its domain the class SemanticShift and its range LexicalSense and relates together an instance of the semantic shift with its source, i.e., ;
- The object property shiftTarget has as its domain the class SemanticShift and its range LexicalSense and relates together an instance of the semantic shift with its target, i.e., ;
- The object property senseShiftsTo has LexicalSense as its domain and range and holds between two senses to represent that the latter derives from the former due to some kind of etymological process. The property senseShiftsTo is equivalent to the following property chain:
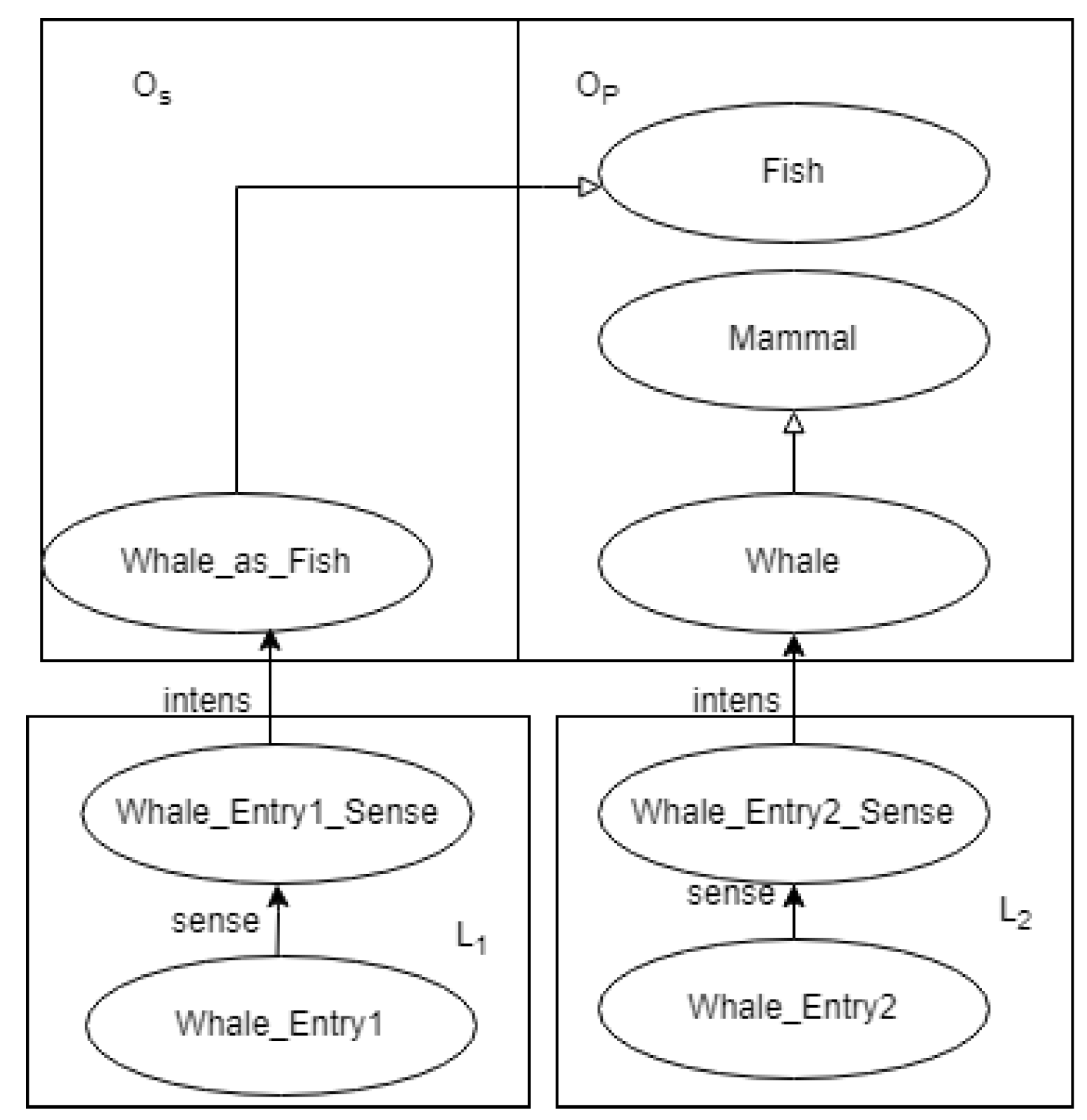
4. Using IOM to Model Semantic Change in Case of Conceptual Evolution
- By making the lexicon dynamic while keeping the ontology static27 (ontology as static pivot);
- By making both the lexicon and the ontology dynamic (dynamic ontology).
| Listing 2. Ontolex-Lemon example in Turtle. |
| ## Op ontology Op:Whale rdfs:subClassOf Op:Mammal . Op:Whale rdf:type owl:NamedIndividual . ## Os ontology Op:Whale_as_Fish rdfs:subClassOf Op:Fish . Os:Whale_as_Fish rdf:type owl:NamedIndividual . ## L1 lexicon L1:Whale_Entry1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; ontolex:sense L1:Whale_Entry1_Sense . L1:Whale_Entry1_Sense rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; ontolex:reference Os:Whale_as_Fish . ## L2 lexicon L2:Whale_Entry2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; ontolex:sense L2:Whale_Entry1_Sense . L2:Whale_Entry2_Sense rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; ontolex:reference Op:Whale . |
4.1. Latin Examples
| Listing 3. Ontolex-Lemon example in turtle. |
| ex:entry_ciuitas rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_ciuitas ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_ciuitas_1, ex:sense_ciuitas_2 . ex:lemma_ciuitas rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "ciuitas"@la . ex:sense_ciuitas_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "citizenship"@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/resource/Citizenship> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_ciuitas_2 . ex:sense_ciuitas_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "city"@en . ex:shift_ciuitas rdf:type ex:senseShift ; rdfs:comment "Second meaning became more common in Middle Ages" ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_ciuitas_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_ciuitas_2 . |
5. Explicitly Representing Time in Conceptual Change
- In the dynamic version of Scenario 1, we wish to formally describe how a concept c in our ontology is lexicalised over time using words in a lexicon for the language (again, this can be easily extended to more than one language). So, for instance, this could be a concept like Element or Democracy (in our pivot ontology) that has different sub-concepts, ,..., (with these representing Kuukkanen’s core and margin, respectively). In this dynamic version, we add time as a parameter in order to allow us to enumerate, for a specific time period, t, all of the lexical entries, or rather the lexical senses, that referred to c during t.
- In the dynamic version of the second scenario, given a specific word (or lexical sense) we wish to retrieve all pof the different concepts that it referred to over a given time period t (focusing on the concepts in a pivot ontology). Again, in this scenario, we could assume a fixed core concept c and look at how the marginal concepts changed.
5.1. Endurantism vs. Perdurantism
| Listing 4. Definition of 4dsense. |
| ObjectProperty: 4dsense Domain: 4dFluents:temporalPartOf only ontolex:LexicalEntry Range: 4dFluents:temporalPartOf only ontolex:LexicalSense |
| Listing 5. Modelling of example. |
| Individual: lex1@t1 Types: 4dFluents:TemporalPart Facts: 4dFluents:temporalPartOf lex1, 4dsense sense1@t1 Individual: lex1@t2 Types: 4dFluents:TemporalPart Facts: 4dFluents:temporalPartOf lex1, 4dsense sense1@t2 Individual: sense1@t1 Types: 4dFluents:TemporalPart Facts: 4dFluents:temporalPartOf sense1 Individual: sense2@t2 Types: 4dFluents:TemporalPart Facts: 4dFluents:temporalPartOf sense2 |
| Listing 6. Definitions. |
| Class: Perdurant Class: TimeSlice ObjectProperty: hasTimeSlice Domain: Perdurant Range: TimeSlice ObjectProperty: timeSliceOf Domain: TimeSlice Range: Perdurant ObjectProperty: hasTime Domain: TimeSlice Range: owl:Time |
| Listing 7. Running example. |
| Class: ontolex:LexicalEntry SubClassOf: Perdurant Class: ontolex:LexicalSense SubClassOf: Perdurant Individual: lex1@t1 Types: ontolex:LexicalEntry Facts: timeSliceOf lex1, ontolex:sense sense1@t1, hasTime t1 Individual: lex1@t2 Types: ontolex:LexicalEntry Facts: timeSliceOf lex1, ontolex:sense sense1@t2, hasTime t2 Individual: sense1@t1 Types: ontolex:LexicalSense Facts: timeSliceOf sense1, hasTime t1 Individual: sense2@t2 Types: ontolex:LexicalSense Facts: timeSliceOf sense2, hasTime t2 |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IOM | Intensional–Ontological Meaning |
| ODP | Ontology Design Pattern |
| RDF | Resource Description Framework |
| SPARQL | SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language |
| OTTR | Reasonable Ontology Templates |
| OWL | Web Ontology Language |
Appendix A
| Listing A1. Full Ontolex example in turtle. |
| ex:entry_ciuitas rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_ciuitas ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_ciuitas_1, ex:sense_ciuitas_2 . ex:lemma_ciuitas rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "ciuitas"@la . ex:sense_ciuitas_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "citizenship"@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/resource/Citizenship> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_ciuitas_2 . ex:sense_ciuitas_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "city"@en . ex:shift_ciuitas rdf:type ex:senseShift ; rdfs:comment "Second meaning became more common in Middle Ages" ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_ciuitas_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_ciuitas_2 . ex:entry_cohors rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_cohors ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_cohors_1, ex:sense_cohors_2 . ex:lemma_cohors rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "cohors"@la . ex:sense_cohors_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "cohort"@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/ontology/cohort> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_cohors_2 . ex:sense_cohors_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "imperial court"@en . ex:shift_cohors rdf:type ex:senseShift ; rdfs:comment "Generalisation, then Narrowing" ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_cohors_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_cohors_2 . ex:entry_consul rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_consul ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_consul_1, ex:sense_consul_2 . ex:lemma_consul rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "consul"@la . ex:sense_consul_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "consul"@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/ontology/consul> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_consul_2 . ex:sense_consul_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "municipal official"@en . ex:shift_consul rdf:type ex:senseShift ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_consul_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_consul_2 . ex:entry_dolus rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_dolus ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_dolus_1, ex:sense_dolus_2 . ex:lemma_dolus rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "dolus"@la . ex:sense_dolus_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "deceit"@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/resource/Deception> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_dolus_2 . ex:sense_dolus_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "pain"@en . ex:shift_dolus rdf:type ex:senseShift ; rdfs:comment "Not Christian. Similar change to iter..." ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_dolus_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_dolus_2 . ex:entry_dux rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_dux ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_dux_1, ex:sense_dux_2 . ex:lemma_dux rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "dux"@la . ex:sense_dux_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "leader"@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/resource/Leadership> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_dux_2 . ex:sense_dux_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "duke"@en . ex:shift_dux rdf:type ex:senseShift ; rdfs:comment "Early Medieval Period" ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_dux_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_dux_2 . ex:entry_humanitas rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_humanitas ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_humanitas_1, ex:sense_humanitas_2 . ex:lemma_humanitas rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "humanitas"@la . ex:sense_humanitas_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "humanity"@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/resource/Human> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_humanitas_2 . ex:shift_humanitas rdf:type ex:senseShift ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_humanitas_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_humanitas_2 . ex:sense_humanitas_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "benevolence"@en . ex:entry_imperator rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_imperator ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_imperator_1, ex:sense_imperator_2 . ex:lemma_imperator rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "imperator"@la . ex:sense_imperator_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "general"@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/resource/General> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_imperator_2 . ex:sense_imperator_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "emperor"@en . ex:shift_imperator rdf:type ex:senseShift ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_imperator_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_imperator_2 . ex:entry_potestas rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_potestas ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_potestas_1, ex:sense_potestas_2 . ex:lemma_potestas rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "potestas"@la . ex:sense_potestas_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "power "@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/ontology/power> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_potestas_2 . ex:sense_potestas_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "angel"@en . ex:shift_potestas rdf:type ex:senseShift ; rdfs:comment "Christian. Direct translation of the Greek." ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_potestas_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_potestas_2 . ex:entry_scriptura rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_scriptura ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_scriptura_1, ex:sense_scriptura_2 . ex:lemma_scriptura rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "scriptura"@la . ex:sense_scriptura_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "writing "@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/resource/Writing> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_scriptura_2 . ex:sense_scriptura_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "Holy Scripture"@en . ex:shift_scriptura rdf:type ex:senseShift ; rdfs:comment "Christian. Not used in reference to holy texts..." ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_scriptura_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_scriptura_2 . ex:entry_uirtus rdf:type ontolex:LexicalEntry ; lexinfo:partOfSpeech <http://www.lexinfo.net/ontology/2.0/lexinfo#noun> ; ontolex:canonicalForm ex:lemma_uirtus ; ontolex:sense ex:sense_uirtus_1, ex:sense_uirtus_2 . ex:lemma_uirtus rdf:type ontolex:Form ; ontolex:writtenRep "uirtus"@la . ex:sense_uirtus_1 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "manliness "@en ; ontolex:reference <https://dbpedia.org/resource/Masculinity> ; ex:senseShiftsTo ex:sense_uirtus_2 . ex:sense_uirtus_2 rdf:type ontolex:LexicalSense ; skos:definition "Christian virtues"@en . ex:shift_uirtus rdf:type ex:senseShift ; ex:shiftSource ex:sense_uirtus_1 ; ex:shiftTarget ex:sense_uirtus_2 . |
| 1 | We would argue that conceptual changes always affect the lexicon in some way. In any case, in the present work, we take a lexico-centric view, and do not look at conceptual change in isolation from the lexicon. |
| 2 | See, in particular, the five-star linked data deployment scheme: https://5stardata.info/en/ (accessed on 16 May 2024). |
| 3 | Note that in the rest of the article, we will not be interested in purely theoretical descriptions of lexical semantics but will instead be concerned with digital resources (especially lexical resources and ontologies). This is despite the fact that in many cases, we are dealing with idealised descriptions of such resources—abstractions. We are especially interested in how such resources can help meet the information needs of scholars in different fields, but also of the general public. The decision to work with linked data and the Semantic Web limited the level of sophistication of the formal models we are concerned with. |
| 4 | In this article, we assume that these are linked data resources. However, although our focus here is on RDF, much of what we write here should apply to any formal knowledge representation approach to modelling language change on the basis of the assumptions set out in the previous section, for which we have a basic architecture consisting of the lexicon of a language and an ontology to work with (we do not abstract more than this). Even our recourse to perdurants can be justified independently of the need to overcome the limitations of RDF. |
| 5 | The latter can indeed be regarded as a de facto standard for the creation of lexicons in linked data. |
| 6 | The paradigmatic case here would be common nouns such as mammal, whale, water, and bank. |
| 7 | ‘A Turkish governor of a province or district: also a title of rank’ from Murray et al. (1888). |
| 8 | |
| 9 | These states of affairs are formal descriptions of possible worlds. |
| 10 | Definition from Murray et al. (1888). |
| 11 | This is evidenced rather infamously, of course, by the title of the article itself. Our view is that it is possible to appreciate, and indeed to incorporate, this usage-based approach in our work without having to go as far as Kilgarriff in challenging the validity of the notion of word sense itself. |
| 12 | |
| 13 | There are of course many more but these two are arguably the most salient in terms of current work in Natural Language Processing, computational linguistics, computational lexicography, and the digital humanities. |
| 14 | This kernel can be shared by different linguistic layers, however, so a better, but slightly more involved analogy would be to see the lexical sense as the planetary atmosphere through which we see the light of a particular star (the intension). |
| 15 | https://www.w3.org/2016/05/ontolex/#semantics (accessed on 18 May 2024). |
| 16 | https://www.w3.org/2016/05/ontolex/#lexical-sense-reference (accessed on 18 May 2024). |
| 17 | For instance, our interpretation differs considerably from that set out by Cimiano et al. (2013), which describes the theoretical significance of senses in lemon, the predecessor to the OntoLex-Lemon model, and as laid out by some of the contributors to that model. In this case, we would not have aligned our classes with those of the original model so freely, since there is less scope for interpretation; our understanding of the word–sense–concept relationship so clearly differs from that of Cimiano et al. (2013). |
| 18 | https://www.w3.org/2016/05/ontolex/#variation-translation-vartrans (accessed on 18 May 2024). |
| 19 | By reification here, we mean the representation of a relationship R that holds between two individuals s and t, i.e., , as a separate individual r, of which we can predicate properties in the same way we do for other individuals, rather than, or in addition to, being a relation. This is useful in the case of formalisms such as RDF because it allows us to more easily describe the particulars of the relationship itself. |
| 20 | https://www.w3.org/2019/09/lexicog/ (accessed on 18 May 2024). |
| 21 | This draft can be found at https://github.com/ontolex/frequency-attestation-corpus-information (accessed on 18 May 2024). |
| 22 | The Ontolex-Lemon W3C Community Report in its description of OntoLex-Lemon’s treatment of word meaning introduces a further class: Lexical Concept, (a subclass of skos:Concept) that ’represents a mental abstraction, concept or unit of thought that can be lexicalised by a given collection of senses’. Lexical concepts are related to lexical entries through the evokes property. This is equivalent to the property chain sense o isLexicalizedSenseOf and to Lexical Senses through the lexicalizedSense property; further, they are related to references (potentially any subclass, not proper of owl:Thing) through the concept. It is not entirely clear what lexical concept really adds to the description of word meaning over and above lexical senses and their relationship to ontologies (it is not found in related standards/models such as the Lexical Markup Framework, or in the Dictionary chapter of the Text Encoding Initiative guidelines). Accordingly we decided to make no reference to it in the following. |
| 23 | Note that although the IOM is compatible with OntoLex-Lemon, it does not derive from it. |
| 24 | Enhanced interoperability being the most obvious one, however, we would like to be able to reason over our datasets and to derive new facts too since the Semantic Web stack includes several technologies and standards allowing for this. |
| 25 | https://github.com/anasfkhan81/lemonEty (accessed on 18 May 2024). |
| 26 | https://lila-erc.eu/#page-top (accessed on 17 May 2024). |
| 27 | By keeping the ontology static here, we mean that we do not explicitly represent the process of change among concepts as part of the ontology. |
| 28 | http://www.lateralmag.com/articles/issue-29/when-whales-were-fish (accessed on 18 May 2024). |
| 29 | This snapshot could potentially summarise the state of the lexicon over a number of years, but as the term ’snapshot, suggests, it is treated as a single point in time. |
| 30 | And here, we need to emphasise, just in case it was not already clear, that we are talking about ontologies from the point of view of Computer Science and not of philosophy, that is, as computational artefacts. |
| 31 | https://www.dbpedia.org/ (accessed on 17 May 2024). |
| 32 | https://lexinfo.net/ (accessed on 18 May 2024). |
References
- Chalmers, David J. 2002. On Sense and Intension. Philosophical Perspectives 16: 135–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarcos, Christian, Frank Abromeit, Christian Fäth, and Maxim Ionov. 2016. Etymology Meets Linked Data. A Case Study In Turkic. Paper presented at the Digital Humanities 2016, Krakow, Poland, July 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chiarcos, Christian, Maxim Ionov, Jesse de Does, Katrien Depuydt, Fahad Khan, Sander Stolk, Thierry Declerck, and John Philip McCrae. 2020. Modelling frequency and attestations for ontolex-lemon. Paper presented at the 2020 Globalex Workshop on Linked Lexicography, Marseille, France, May 12; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cimiano, Philipp, John McCrae, Paul Buitelaar, and Elena Montiel-Ponsoda. 2013. On the Role of Senses in the Ontology-Lexicon. In New Trends of Research in Ontologies and Lexical Resources. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 43–62. [Google Scholar]
- Effingham, Nikk. 2012. Endurantism and perdurantism. The Bloomsbury Companion to Metaphysics, 170–97. [Google Scholar]
- Fokkens, Antske, Serge Ter Braake, Isa Maks, and Davide Ceolin. 2016. On the Semantics of Concept Drift: Towards Formal Definitions of Semantic Change. Paper presented at Drift-a-LOD@EKAW, Bologna, Italy, November 20. [Google Scholar]
- Garbacz, Paweł, and Robert Trypuz. 2017. Representation of Tensed Relations in OWL. In Metadata and Semantic Research. Edited by Getaneh Alemu, Emmanouel Garoufallou, Rania Siatri, Damiana Koutsomiha and Sirje Virkus. Communications in Computer and Information Science. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer International Publishing, vol. 755, pp. 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Guarino, Nicola, Daniel Oberle, and Steffen Staab. 2009. What Is an Ontology? In Handbook on Ontologies. Edited by Steffen Staab and Rudi Studer. International Handbooks on Information Systems. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, Theo, and Thomas Ede Zimmermann. 2021. Montague Semantics. In The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Summer 2021 ed. Edited by Edward N. Zalta. Stanford: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. [Google Scholar]
- Kauppinen, Tomi, and Eero Hyvönen. 2007. Modeling and reasoning about changes in ontology time series. In Ontologies. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 319–338. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Anas Fahad. 2018. Towards the Representation of Etymological Data on the Semantic Web. Information 9: 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Anas Fahad, Christian Chiarcos, Thierry Declerck, Daniela Gifu, Elena González-Blanco García, Jorge Gracia, Maxim Ionov, Penny Labropoulou, Francesco Mambrini, and John P. McCrae. 2022. When linguistics meets web technologies. Recent advances in modelling linguistic linked data. Semantic Web 13: 987–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Fahad. 2020. Representing Temporal Information in Lexical Linked Data Resources. Paper presented at the 7th Workshop on Linked Data in Linguistics (LDL-2020), Marseille, France, May 11; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Fahad, and Jack Bowers. 2020. Towards a Lexical Standard for the Representation of Etymological Data. Paper presented at the Convegno Annuale dell’Associazione per l’Informatica Umanistica e la Cultura Digitale, Milan, Italy, January 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kilgarriff, Adam. 1997. I Don’t Believe in Word Senses. Computers and the Humanities 31: 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, Hans-Ulrich. 2010. A General Methodology for Equipping Ontologies with Time. Paper presented at the LREC, Valletta, Malta, May 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kuukkanen, Jouni M. 2008. Making Sense of Conceptual Change. History and Theory 47: 351–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mambrini, Francesco, and Marco Passarotti. 2020. Representing Etymology in the LiLa Knowledge Base of Linguistic Resources for Latin. Paper presented at the 2020 Globalex Workshop on Linked Lexicography, Marseille, France, May 11–16; Edited by Ilan Kernerman, Simon Krek, John P. McCrae, Jorge Gracia, Sina Ahmadi and Besim Kabashi. Paris: European Language Resources Association, pp. 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- McCrae, John P., Dennis Spohr, and Philipp Cimiano. 2011. Linking lexical resources and ontologies on the semantic web with lemon. Paper presented at The Semantic Web: Research and Applications: 8th Extended Semantic Web Conference, ESWC 2011, Heraklion, Greece, May 29–June 2; Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 245–59. [Google Scholar]
- McCrae, John P., Julia Bosque-Gil, Jorge Gracia, Paul Buitelaar, and Philipp Cimiano. 2017. The OntoLex-Lemon Model: Development and Applications. Brno-Královo Pole: Lexical Computing CZ s.r.o., pp. 587–97. [Google Scholar]
- McGillivray, Barbara, Daria Kondakova, Annie Burman, Francesca Dell’Oro, Helena Bermúdez Sabel, Paola Marongiu, and Manuel Márquez Cruz. 2022. A new corpus annotation framework for Latin diachronic lexical semantics. Journal of Latin Linguistics 21: 47–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillivray, Barbara, Pierluigi Cassotti, Davide Di Pierro, Paola Marongiu, Fahad Khan, Stefano Ferilli, and Pierpaolo Basile. 2023. Graph Databases for Diachronic Language Data Modelling. Paper presented at the 4th Conference on Language, Data and Knowledge, Vienna, Austria, September 13–15; pp. 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, Steven, Martin Brümmer, Christian Chiarcos, Philipp Cimiano, Thierry Declerck, and John McCrae. 2013. Lemon-aid: Using Lemon to aid quantitative historical linguistic analysis. Paper presented at the 2nd Workshop on Linked Data in Linguistics (LDL-2013): Representing and Linking Lexicons, Terminologies and Other Language Data, Pisa, Italy, September 23; pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, James A. H., Charles T. Onions, and William A. Craigie. 1888. Philological Society (Great Britain). In A New English Dictionary on Historical Principles: Founded Mainly on the Materials Collected by the Philological Society. Oxford: Clarendon Press. [Google Scholar]
- Presutti, Valentina, Eva Blomqvist, Enrico Daga, and Aldo Gangemi. 2012. Pattern-based ontology design. In Ontology Engineering in a Networked World. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 35–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ribary, Marton, and Barbara McGillivray. 2020. A Corpus Approach to Roman Law Based on Justinian’s Digest. Informatics 7: 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sider, Theodore. 1997. Four-Dimensionalism. Oxford: Oxford University Press, vol. 106, pp. 197–231. [Google Scholar]
- Skjæveland, Martin G., Daniel P. Lupp, Leif Harald Karlsen, and Henrik Forssell. 2018. Practical ontology pattern instantiation, discovery, and maintenance with reasonable ontology templates. Paper presented at the Semantic Web–ISWC 2018: 17th International Semantic Web Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, October 8–12; Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 477–94. [Google Scholar]
- Speaks, Jeff. 2019. Theories of Meaning. In The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Winter 2019 ed. Edited by Edward N. Zalta. Stanford: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. [Google Scholar]
- Tahmasebi, Nina, Lars Borin, and Adam Jatowt. 2021. Survey of Computational Approaches to Lexical Semantic Change. In Computational Approaches to Semantic Change. Edited by Nina Tahmasebi, Lars Borin, Adam Jatowt, Yang Xu and Simon Hengchen. Berlin: Language Science Press, vol. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Shenghui, Stefan Schlobach, and Michel Klein. 2011. Concept drift and how to identify it. Journal of Web Semantics First Look 9: 247–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welty, Chris, Richard Fikes, and Selene Makarios. 2006. A reusable ontology for fluents in OWL. Paper presented at the FOIS, Annecy, France, July 6–9, vol. 150, pp. 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson, Henry. 2020. 1. Contextual meaning and the legacy of J. R. Firth. In On the Subject of English: The Linguistics of Language Use and Learning. Berlin and Boston: De Gruyter Mouton, pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zalta, Edward N. 2023. Gottlob Frege. In The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Summer 2023 ed. Edited by Edward N. Zalta and Uri Nodelman. Stanford: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. [Google Scholar]




| Lemma | First Sense | Second Sense | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| ciuitas | citizenship | city | Metonymy. Second meaning became more common in Middle Ages. |
| cohors | cohort | imperial court | Generalisation, then narrowing. |
| consul | consul | municipal official | Not Christian. |
| dolus | deceit | pain | |
| dux | leader | duke | Narrowing. Early medieval period. |
| humanitas | humanity | benevolence | |
| imperator | general | emperor | |
| potestas | power | angel | Christian. Direct translation of the Greek. |
| scriptura | writing | Holy Scripture | Christian. Not used in reference to holy texts prior to Christianity. Influenced by Greek. |
| uirtus | manliness | Christian virtues |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.F.; Frontini, F. Toward a Representation of Semantic Change in Linked Data. Languages 2024, 9, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9060215
Khan AF, Frontini F. Toward a Representation of Semantic Change in Linked Data. Languages. 2024; 9(6):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9060215
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Anas Fahad, and Francesca Frontini. 2024. "Toward a Representation of Semantic Change in Linked Data" Languages 9, no. 6: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9060215
APA StyleKhan, A. F., & Frontini, F. (2024). Toward a Representation of Semantic Change in Linked Data. Languages, 9(6), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9060215







