Abstract
In the realm of linguistics, the concept of “semanticity” was recently introduced as a novel measure designed to study linguistic networks. In a given text, semanticity is defined as the ratio of the potential number of meanings associated with a word to the number of different words with which it is linguistically linked. This concept provides a quantitative indicator that reflects a word’s semantic complexity and its role in a language. In this pilot study, we applied the semanticity measure to the Catalan language, aiming to investigate its effectiveness in automatically distinguishing content words from function words. For this purpose, the measure of semanticity has been applied to a large corpus of texts written in Catalan. We show that the semanticity of words allows us to classify the word classes existing in Catalan in a simple way so that both the semantic and syntactic capacity of each word within a language can be integrated under this parameter. By means of this semanticity measure, it has been observed that adverbs behave like function words in Catalan. This approach offers a quantitative and objective tool for researchers and linguists to gain insights into the structure and dynamics of languages, contributing to a deeper understanding of their underlying principles. The application of semanticity to Catalan is a promising pilot study, with potential applications in other languages, which will allow progress to be made in the field of theoretical linguistics and contribute to the development of automated linguistic tools.
1. Introduction
Human language is a complex system where words interact with each other in a way that is far from random, allowing us to create a huge variety of meaningful linguistic utterances from a limited set of words. This intricate system is a subtle mirror of the underlying organization of language, with two key features (Ferrer-i-Cancho and Solé 2001): (i) the small-world effect, which implies that for a large corpus, on average, the length of the chain of connections between any two words is significantly lower than expected (Motter et al. 2002), and (ii) the scale-free distribution of word connections, meaning that some words are far more connected than others, becoming true hubs for languages (Barabási and Bonabeau 2003).
The small-world structure of linguistic networks is characterized by the combination of highly clustered neighborhoods and a short average path length, as in many other complex networks (Watts and Strogatz 1998). Thus, frequent and early acquired words are more densely linked and, at short Euclidean distances1, all words are connected. In most semantic networks, practically all words have an average path length of three, whereas the maximum path length is five (Steyvers and Tenenbaum 2005).
All of this suggests that the organization of language reflects a long evolutionary and cultural history. Thus, the order of words in the linguistic chain, and their context and combinatorics, plays a key role in determining meaning. Under the distributional hypothesis (Harris 1954), meaning is learned by inferring how words co-occur in natural language (Kumar 2021; Sahlgren 2008). Going beyond word co-occurrences, in a syntagmatic context in a Saussurean sense, the so-called principle of compositionality is generally assumed, as proposed by Donatelli and Koller (2023, p. 465)
The meaning of a natural-language expression is determined by the meanings of its immediate sub-expressions and the way in which they were combined.
How can we quantitatively address this dichotomy between syntax and semantics? The intricacies of meaning make it a difficult concept to quantify: Is it the polysemy of a word or the semantic ambiguity (Hoffman et al. 2013), understood as the number of entries in a dictionary, or the meanings in each individual’s brain, that makes it a totally subjective measure? Should the study of the senses of each word be considered as paradigmatic units of syntactic structures (Feist 2022)? There is no clear solution yet, and maybe there will not be one.
In this paper, we review a new magnitude that takes into account both the semantic ambiguity and co-occurrence of words within a sentence: semanticity (Català et al. 2023). In short, semanticity is a quantitative measure that relates the number of meanings of a word to its connections in the linguistic network. Here we analyze a large corpora of Catalan to study this measure experimentally. As we will see, this allows us to automatically differentiate content words from function words without any intervention other than supplying the meaning data and the distance between words in the linguistic network. The definitions of semanticity and the protocols developed in this paper can be extrapolated to any language for which we have the appropriate data to study. We have used Catalan because of the availability of access to the official normative dictionary and corpora and also because it is a language for which the relationship between the frequency of words and their meaning has already been statistically analyzed in a robust way (Catala et al. 2021), along with other patterns or linguistic laws (Hernández-Fernández et al. 2019, 2022).
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 reviews and discusses the main areas that are related to our proposal, which is presented in its full length in Section 3. Section 4 describes the corpus studied and its processing. Section 5 comprehensively presents the results that we have obtained. Finally, Section 6 offers some conclusions.
2. Related Work
In this section, we review the state-of-the-art in different areas related to the proposal presented in this paper. The new measure we discuss, semanticity, relates to the number of meanings of a word to its connectivity with other words. Both components of the relationship depend, directly or indirectly, on the frequency of the word. For this reason, and similar to other statistical laws of linguistics, the behavior of semanticity has been analyzed as a function of frequency rank. This is what we discuss in Section 2.1 and Section 2.2. One of the outcomes of our analysis is the capacity to distinguish different lexical categories, which is the subject discussed in Section 2.3.
2.1. Word Connectivity, Co-Occurrence, and Compositionality
There are different approaches to semantics research, with some terminological details that are worth commenting on. The distinctions between connection (or link) in a linguistic network, co-occurrence, and compositionality in linguistic theory are critical for understanding how language structures and meanings emerge. Connection, observed in network structures like web graphs or semantic networks, emphasizes the interrelationships and dependencies between nodes within a network. It is a graph-based concept that focuses on the structural organization and strength of links between linguistic units (Barabási and Bonabeau 2003; Baronchelli et al. 2013; Watts and Strogatz 1998). On the other hand, co-occurrence pertains to the statistical observation of two or more linguistic units appearing together within a specific context, so word frequency can be related to phonotactic probability and neighborhood density (Mahowald et al. 2018). It is a statistical phenomenon that highlights the frequency and proximity of word pairs or other linguistic units. In contrast, compositionality is a principle that underlies the formation of meaning in complex linguistic expressions. It asserts that the meaning of a whole expression is derived from the meanings of its constituent parts and the rules governing their combination (Donatelli and Koller 2023). Unlike connection and co-occurrence, which are more structural and statistical, compositionality is both semantic and syntactic, concerned with the hierarchical organization and semantic relations within language constructs. By disentangling these notions, researchers can better grasp the intricate dynamics underlying language structure and meaning.
Although the ideal is to work with compositionality, considering long-distance connections between words (Ferrer-i-Cancho 2019), due to the information available from the corpora, our methodology only focuses on semantic relationships rather than syntactic compositionality within phrases. Therefore, our work does not directly address how syntactic phrases are related.
We can establish that two words are connected in the first order if they are one before or after the other (both co-occur), in the second order if they appear one word before or after the other, and so on, with other linear arrangements possible. In this sense, words are related to their neighbors, forming a linguistic network with a cognitive correlation (Baronchelli et al. 2013). This linguistic system can then be represented as a semantic network, where each node corresponds to a word, and the edges are associations between words, in an underlying representation of the so-called semantic memory (Borge-Holthoefer and Arenas 2010; Kumar 2021).
If we construct a linguistic graph, such that two words i and j are connected to each other if they appear together in the linguistic chain, but taking into account the classical sentence boundaries (represented in the written corpus by ‘.’), we can define the type adjacency matrix, , as follows:
where if words i and j co-occur and if not. Therefore, usually, this adjacency matrix will be binary, square, and undirected if we consider that the semantic connection between words is bidirectional; the diagonal elements will be mainly (Ipsen 2004), except in cases where a word is repeated, so that the word would be connected to itself and then . Both word co-occurrence networks and their spectra have already been studied from the perspective of physics of complex systems (i.e., see for English (Liang 2017)). The sum of each row of this binary matrix provides the degree of a word, a measure of potential semantic connectivity, so that we define word i as follows:
Thus, the degree is a scalar that provides the total number of different words with which the word i is connected in first order (at distance d = 1) or, in other terms, the total number of words with which word i co-occurs in a corpus. In this case, using symmetry, the same result would be obtained for the sum of columns (). In linguistic scale-free networks, the fraction of words with degree k (i.e., ) follows a power-law distribution , where , although such scale-free networks may not be as common as they appear to be (Broido and Clauset 2019). In the same way as Equation (1), one could define the matrix of word connections that are at a distance d from a given word with , providing the total number of different words connected at distance d, again considering the boundaries of the sentences in the written corpus. provides the number of paths of a length of two between words i and j and, in general, provides the number of paths of length p.
Analogous to this adjacency matrix of word types, , we define the matrix of connections between tokens, , i.e., where we would count how many times one word is connected to another, so that if two words, i and j, appear together n times in a corpus, then and . Dividing each by the total number of connections for each word (, see below) provides an associative matrix showing connections among words defined in associative linguistic experiments (Nelson et al. 1999). In this case, the following equation is applicable:
Therefore, provides the total number of connections of the word i, or the total co-occurrences in the first order, and similarly, provides the number of connections at distance d. Trivially, in many cases, , where is the frequency of word i; however, we must consider the exceptions of words at the beginning or end of a sentence or when a word is repeated or appears more than once in a sentence, e.g., cases which are statistically rare in large corpora.
Simply by counting words, we see that there are some words that are very frequent and, therefore, generally linked with many others, while other words are rarer and have fewer connections. In this linguistic network, the words most linked to other words form the hubs of the network (Barabási and Bonabeau 2003). The most linked words in human languages are called “function words” in linguistic tradition, “grammatical words”, or even “junk words” or “empty words” as they do not contribute much to the meaning but serve as “the cement that holds the content words together” (Chung and Pennebaker 2007). Nevertheless, there is still controversy about the lexico–syntactic relationship between the frequency and meaning of some of these function words, as is the case with highly polysemous English prepositions (Schneider et al. 2015) or adverbs (Hallonsten Halling 2018). So-called “content words”, such as nouns, verbs, and adjectives, often carry the primary lexical meaning of a sentence, while function words, like prepositions, conjunctions, and articles, serve grammatical and structural roles. Classical classification methods have relied on linguistic intuition and manual categorization, making the process time-consuming and subject to individual interpretation.
2.2. Statistical Laws on Meaning
G. K. Zipf formulated two statistical laws on the relationship between the frequency of a word and its number of meanings (Zipf 1932, 1945, 1949): the law of meaning distribution, relating the number of meanings of a word and its frequency rank, and the meaning–frequency law, relating the frequency of a word with its number of meanings. The Zipfian law of meaning distribution shows that the number of word meanings follows an approximate power law with respect to its frequency rank r:
where (Catala et al. 2021). To unify the terminology, we refer to the number of meanings of a word () as the sum of the total number of senses that appear in the dictionary, i.e., what has also been called semantic ambiguity (Hoffman et al. 2013).
However, linguistic systems are dynamic and experience-based. The set of linguistic elements of a language (e.g., the emergent lexicon) reflects linguistic experience inseparably from grammar (Bybee 1998). The unavoidable contextual variability of linguistic acts has led to the study of semantic diversity, considering other measures of semantic ambiguity based on the variability of the context of changing word usage, beyond the sum of dictionary senses (Hoffman et al. 2013), or considering statistical distributions of word frequency and meaning, as well as principles governing efficiency in communication and lexicon organization (Mahowald et al. 2022, 2018).
Some principles of communication, such as compression (Ferrer-i-Cancho et al. 2013; Hernández-Fernández and Torre 2022), unification and diversification (Zipf 1949), and simplicity and informativeness (Regier et al. 2015), compete with each other. Ultimately, semantic diversity in linguistic networks is related to word frequency and context (Hoffman et al. 2013).
Furthermore, the relationship between and word frequency, f, the so-called Zipf’s meaning-frequency law, follows (Zipf 1932):
where typically, (Baayen and del Prado Martín 2005; Ferrer-i-Cancho and Vitevitch 2018; Ilgen and Karaoglan 2007). Albeit with precedents (Condon 1928), the most known Zipf’s law, the rank–frequency law, approximately interrelates word frequency f with its rank r, as shown in (Torre et al. 2019; Zipf 1932):
Thus, word frequency f, frequency rank r, and its number of meanings , a quantity that dictionaries approximately capture, are related in such a way that the exponents of these equations satisfy that (Catala et al. 2021; Ferrer-i-Cancho and Vitevitch 2018).
However, after Zipf’s groundbreaking research, one of the most noteworthy findings regarding the rank–frequency law in sizable textual corpora with multiple authors is that the power law proposed by Zipf (Equation (6)) must, for the most part, be expanded into a double-power law (Ferrer-i-Cancho and Solé 2001; Montemurro 2001; Williams et al. 2015), something related to the small-world structure of the linguistic network (Ferrer-i-Cancho and Solé 2001). In fact, in the case of Catalan, the target language of the present study, the existence of these two Zipfian regimes for Equations (4) and (6) has already been documented in previous studies for multi-author corpora (Catala et al. 2021). The structure of the linguistic network means that, in the first regime of low ranks, there is an abundance of function words. Content words make up a large part of the low-frequency linguistic elements, forming part of the less frequent vocabulary, such as hapax legomena (words that only appear once in a corpus) or dis legomena (words that appear twice).
2.3. Lexical Categories
The lexicon is traditionally divided into word classes or lexical categories, a division that is considered to have a neural substrate under study (Bell et al. 2009; Pulvermüller 1999), and has even been linked to biological activity (Chung and Pennebaker 2007), especially because of the existence of cases of language pathologies, such as different types of aphasia (De Zubicaray and Schiller 2019). It is generally argued that the differentiation between content and function words is relevant for the description of impairment in aphasia patients, where their separate degradation or loss has been documented, as is the case of agrammatism (involving impairment of function words) or anomia (involving impairment of content words) (Gaskell et al. 2007).
Under this perspective, meaningful content categories (mainly verbs, nouns, and adjectives (Diaz and McCarthy 2009) but also adverbs and other categories) are contrasted with grammatical function categories (Corver and van Riemsdijk 2001). Articles, conjunctions, pronouns, prepositions, and auxiliary verbs, among other linguistic units, are usually considered function words (Baayen et al. 1995; Chung and Pennebaker 2007). Although healthy adult speakers of a language have between 20,000 and 100,000 words, only approximately 400 in English are function words (Baayen et al. 1995; Baddeley 1997). Being very frequent words, function words tend to be short, following Zipf’s law of abbreviation (Torre et al. 2019), and are often pronounced quickly, both in spontaneous speech and in reading (Chung and Pennebaker 2007) but not always (Bell et al. 2009).
However, as some controversial studies on the distinction of these word classes and their neural substrate also attest (Diaz and McCarthy 2009), the problem of classifying word classes remains open. According to neurolinguistic theory and physiological evidence, the retrieval of function words is faster than that of content words; however, this discrepancy can only be explained by the predictability (cloze value) and familiarity (frequency) of the words because the difference in frequency effect between function and content words only exists for lower frequency words and not for higher frequency ones (Segalowitz and Lane 2000).
3. Semanticity
Charles F. Hockett introduced the concept of “semanticity” as one of several design features in language (Hockett 1960). It signifies how linguistic components (e.g., words or symbols) have the ability to represent or trigger particular meanings or ideas associated with elements or features of the world around us (Hockett 1960). This classical notion of semanticity suggests that, in language, expressions or messages can convey specific meanings because consistent and firm connections or associations exist between these linguistic elements and phenomena, objects, actions, or situations in the real world. In summary, Hockett (1960) presented semanticity as an essential qualitative aspect of language, highlighting the connection between linguistic elements and their real-world referents. He also emphasized the intricate interplay between syntax and semantics when analyzing language. The complexity arises in linguistics when considering how the structure of language and semantics interact. Semantic units, which encapsulate meaning, pose a significant challenge due to their intricate nature and variability.
A new quantitative feature for a word has recently been proposed (Català et al. 2023), semanticity, which relates the meanings of a word to the number of different words with which it appears in different lexical contexts. As will be seen, semanticity is an objective quantitative measure that brings together the inherent relationship between semantics and syntax at close range, understood as the lexical context, as two sides of the same coin. Thus, semanticity at distance d for word w is easily defined as follows:
where is the number of meanings of the word w, and is the number of different words at distance d from word w (independent of direction).
So, for the most linked words in the linguistic network, high-frequency words with high values, semanticity will tend to be zero. On the other hand, words that occur infrequently, such as hapax legomena or dis legomena, will show higher semanticity values. Thus, semanticity brings together elements of lexical context and semantics and makes it possible to order words quantitatively, avoiding the traditional dichotomy between function words and content words.
Although the definition of semanticity already allows us to deal with the fitting of experimental data, as we will see in this paper, taking into account the known phenomenon of small-world in language (Ferrer-i-Cancho and Solé 2001), the maximum distance d considered for is four. This means that the maximum distance at which different words of a given word are computed is . From this distance, the whole linguistic network is connected.
Semanticity vs. Frequency Rank
Following Equations (4) and (6), and considering that the maximum number of different words at distance from the word w is (upper bound), the semanticity is related to the exponents of Zipf’s laws:
In order to mitigate the impact of highly frequent words in the values, normalization is first proposed by calculating the ratio of to , the latter corresponding to the total number of words at distance d from the word w (independent of direction). We refer to this ratio as normalized lambda (noted as ). When normalized lambda is used to compute semanticity, we obtain lambda normalized semanticity (noted as ). Then, lambda normalized semanticity at distance d for the word w is calculated as follows:
where
The idea behind lambda normalization is that the corpus has a limited size. With a much larger corpus, a word’s frequency would probably be higher, as would its number of connections with neighboring words. Therefore, in order to assign the appropriate lambda weight to a word and make it independent of the corpus size, the number of different connections must be made relative to the total number of connections.
Another possible type of normalization is to consider that, in a given context, the number of meanings of word w, , cannot exceed the number of links of the word. That is, the number of meanings of a word (which in the dictionary can be many) cannot exceed the number of different lexical contexts in which this word appears. This restriction acknowledges that language speakers typically select the meaning that best suits the context rather than knowing and considering in a linguistic interaction all possible meanings listed in a dictionary. It is obvious that situations of semantic ambiguity do occur (Hoffman et al. 2013), both in speech and in writing, but statistically, if we consider large corpora, these are the exception rather than the norm. Otherwise, both conversations and reading would become unmanageable. Under this constraint, we obtain the meaning normalized semanticity for word w, , formulated as follows:
where
So, refers to the minimum number of meanings or senses that word w can have in a given linguistic network. This takes into account the variability in word interpretation depending on the context and ensures that is a suitable measure in situations where a word may have multiple meanings; however, only some of them are relevant in a particular lexical context. For example, the word raó (reason, in Catalan) has 17 different senses in the DIEC2 dictionary, but if this word appears only twice in a written text, we consider it cannot express more than two different senses in the corpus. Rather, it could have more meanings than the number of different words with which it has appeared (semantic ambiguity), although, in general, the communicative receiver will generally conform to a number of meanings that will be around the number of occurrences of the word.
By applying both types of normalization, normalized number of connections (), and normalized number of meanings (), normalized semanticity at distance d for word w becomes
It is important to note that none of the normalization functions modify or reduce the number of possible meanings of a word, but they do weight it in the calculation of semanticity, considering the lexical context in which it is found.
4. Data
To explore the semanticity measure, we processed the CTILC corpus, which contains texts written in Catalan from different sources. From this corpus, we computed the number of connections at a given distance within the same corpus. Finally, we obtained the number of meanings for each word from the DIEC2 dictionary, which contains (among other information) the lexical category of a lemma and its number of uses, which, in the present case, was taken as the number of different meanings of a lemma. It is worth remembering here that what we defined as the meaning of a word coincides with the concept of semantic ambiguity in some approaches (Hoffman et al. 2013).
We now explain in detail the contents of the CTILC corpus and the DIEC2 dictionary, as well as the processing steps and the final number of tokens that have been obtained.
4.1. CTILC Corpus
The Corpus Textual Informatitzat de la Llengua Catalana (CTILC) contains texts written in Catalan from 1833 to 1988 (available at https://ctilc.iec.cat/, accessed on 29 March 2024). The CTILC corpus is a linguistically rich dataset comprising 1,193,266 sentences, with 1,081,646 sentences having a length greater than 1. The largest sentence within the corpus extends to 153 words, while the most prevalent sentence length is 3 words. In total, the corpus contains 8,531,530 tokens, offering a diverse range of linguistic elements. The vocabulary of the corpus is extensive, encompassing 90,720 types. This comprehensive collection of textual data provides a valuable resource for linguistic analysis and computational research, capturing a broad spectrum of sentence structures and linguistic diversity.
The sources of this corpus are very varied. As an example, approximately of the sources are of non-literary origin. From a chronological point of view, the time period most represented extends from 1989 to the present time. For a complete explanation of the styles, genres, subjects, chronology, and linguistic varieties present in this corpus, please see https://ctilc.iec.cat/scripts/CTILCQDadesNum.asp (accessed on 29 March 2024).
As the corpus is continually evolving, it is important to note that certain inconsistencies may be inherent. Specifically, newly emerged and trendy words, such as coronavirus, may not be fully represented, while occasional archaisms, like coquessa, referring to a holiday meal preparer, may appear. This dynamic nature reflects the ongoing nature of the corpus.
The processing of the CTILC corpus consists of three classic steps in the Natural Language Processing pipeline: sentence segmentation, text tokenization, and morphological analysis (part-of-speech tagging) by means of the FreeLing library. The processing that has been performed here follows the same steps as in (Catala et al. 2021).
4.2. DIEC2 Dictionary
The official dictionary of the Catalan language, DIEC2 (Diccionari de la llengua catalana de l’Institut d’Estudis Catalans), available at DIEC2, serves as a valuable linguistic resource. It provides information on the part-of-speech (PoS) of a lemma, along with the corresponding number of uses, serving as a proxy of the lemma’s diverse meanings. It is noteworthy that the recorded number of uses is often higher than anticipated. The dictionary encompasses a total of 69,173 tuples, each comprising a lemma and its associated part-of-speech.
4.3. CTILC Corpus and DIEC2 Dictionary Intersection
For the analysis, we conducted an intersection between the CTILC corpus and DIEC2 dictionary to extract tuples of lemmas and their corresponding part-of-speech that are common to both resources. The count of tuples (lemma, PoS) in CTILC stands at 129,269, and the DIEC2 dataset comprised 69,173 tuples (lemma, PoS). Notably, the two resources exhibited an overlap of 31,670 common tuples (lemma, PoS), as can be seen in Table 1. Not included in this overlap are 32,516 (lemma, PoS) that have been labeled as proper nouns (NP) by the part-of-speech tagger and are also processed but, obviously, they did not appear in the DIEC2 dictionary. In this case, we assigned one meaning to each of these tuples, assuming that each of them represents one single entity.

Table 1.
Summary of the parts of speech. Number of nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, and function words (which includes pronouns, adpositions, conjunctions, determiners, and interjections) that are common in both CTILC and DIEC2.
However, it is important to acknowledge that 65,083 tuples (lemma, PoS) from CTILC were not found in DIEC2. This absence of certain lemmas in DIEC2 (excluding those tagged as NP), despite their presence in CTILC, can be attributed to various factors. Firstly, discrepancies in part-of-speech tagging between CTILC and DIEC2 may contribute to instances where lemmas are not accurately matched. Additionally, some lemmas in CTILC may represent foreign words from languages such as Latin, Spanish, French, and others, which are not included in the DIEC2 dictionary. Furthermore, potential errors in lemma analysis by the FreeLing morphological analyzer, such as misclassifying gender or number (e.g., erroneously treating a feminine or plural noun as masculine), could further explain the observed disparities.
The final number of tuples (lemma, PoS) in common that were obtained after processing the CTILC corpus and crossing it with the information provided by the DIEC2 dictionary (31,670) are presented by part-of-speech in Table 1.
5. Results
Before exploring the semanticity of content words and function words, the relationship between semanticity and frequency rank was studied by considering each part of speech separately. In this work, as described in Section 4, the subsets2 of the FreeLing part-of-speech tagset found in the CTILC corpus are nouns (N), verbs (V), adjectives (A), adverbs (R), proper nouns (NP), pronouns (P), adpositions (S), conjunctions (C), and interjections (I).
Figure 1 shows the relationship between semanticity and frequency rank for co-occurrences at distance 1 of each word type, as expressed in Equations (7), (9), (11), and (13) for no normalization, lambda normalization (), mu normalization (), and both normalizations at the same time, respectively.
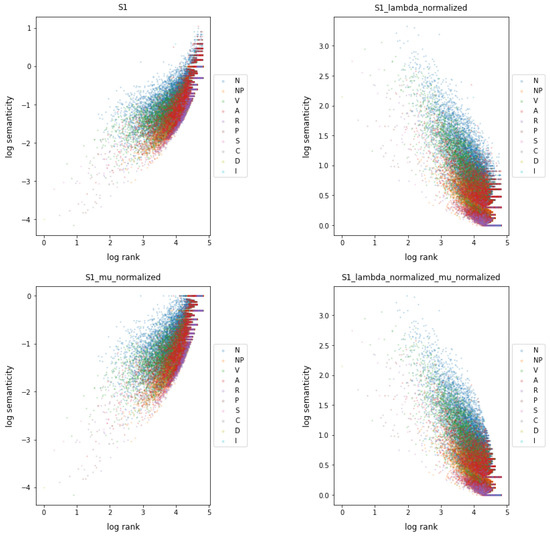
Figure 1.
Semanticity vs. frequency rank for co-occurrences at distance 1 by performing no normalization, lambda normalization (), mu normalization (), and both normalizations. All plots are in log–log scale.
Figure 2 shows the semanticity versus frequency rank for word connections at distances from 1 to 4. The parts of speech are represented in different groups: nouns (N), which here includes proper nouns (NP), verbs (V), adjectives (A), and adverbs (R), and another group that includes all other categories referred to as function words. In linguistics, nouns and proper nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs are usually considered content words. However, how to treat adverbs as a linguistic category is still debated (Hallonsten Halling 2018; Rauh 2015) and probably implies a differentiated approach depending on the language (Hallonsten Halling 2018; Hengeveld 2023). As can be seen in Figure 2, at a distance of 1, the semanticity of the group of content words is highly distinct compared to that of the group of function words, with the exception of the adverbs (labeled as R and shown in red). As the distance between words increases, the semanticity of the function words remains differentiated (always smaller) than that of the content words, and the behavior of adverbs stays closer to that of function words than to that of content words.
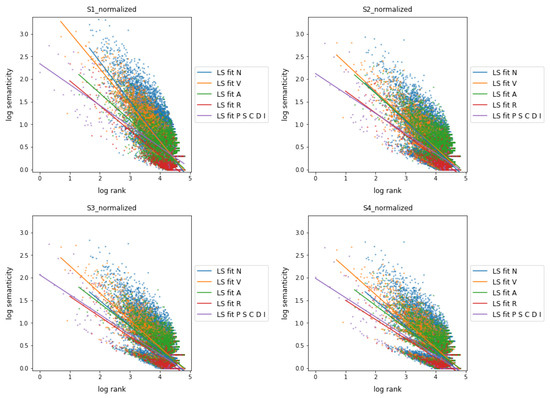
Figure 2.
Semanticity vs. frequency rank at distances from 1 to 4 with and normalizations applied showing fitting functions. Parts of speech are represented in different groups: nouns (N), which includes proper nouns (NP), verbs (V), adjectives (A), adverbs (R), and another group that includes all other categories. All plots are in log–log scale.
In Figure 1 and Figure 2, different behavior is observed for parts of speech belonging to classical content words (nouns, proper nouns, verbs, and adjectives, excluding adverbs) with respect to function words (pronouns, adpositions, conjunctions, determiners, and interjections). Content words, excluding adverbs, whatever their frequency rank (i.e., their frequency of occurrence), show higher semanticity values than function words. Interestingly, the semanticity measure further shows that adverbs, when used in written texts in Catalan, tend to act more as function words than as content words.
This fact leads us to treat adverbs as a category belonging to the class of function words. So, Figure 3 shows the relationship between semanticity and frequency rank for co-occurrences at a distance of 1 when parts of speech are grouped into the following two classes of words: content words (nouns, proper nouns, verbs, and adjectives) and function words (all other categories, now including adverbs). As a proxy for the general behavior and trend of distributions, a linear regression (LS) fit was applied to both word classes on the logarithmic scale data. Content words, regardless of their rank or frequency of occurrence, exhibit notably higher semanticity values compared to function words. For large ranges, i.e., for low occurrence frequencies, both classes of words show low semanticity values, as expected according to Equation (13). However, when a minimum frequency is required for a word of the corpus to be represented in one of both word classes, semanticity turns out to be a useful measure to characterize and distinguish both classes.
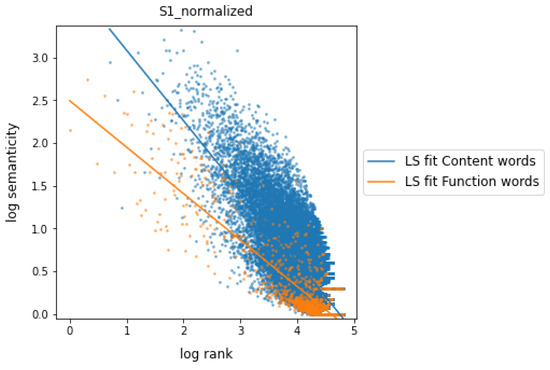
Figure 3.
Semanticity vs. frequency rank for co-occurrences at distance 1 with and normalizations applied showing fitting functions. Parts of speech are grouped into two word classes: content words (nouns, proper nouns, verbs, and adjectives) and function words (all other categories). The data are shown in logarithmic scale.
Figure 4 shows the semanticity versus frequency rank for connections at distances from 1 to 4, again using fitting functions in a log–log scale. At distance 1, the semanticity of the group of content words is markedly different from that of the group of function words, being more noticeable in the case of very frequent words. As the distance between related words increases, the semanticity of the function words remains differentiated (always smaller) compared to that of content words.
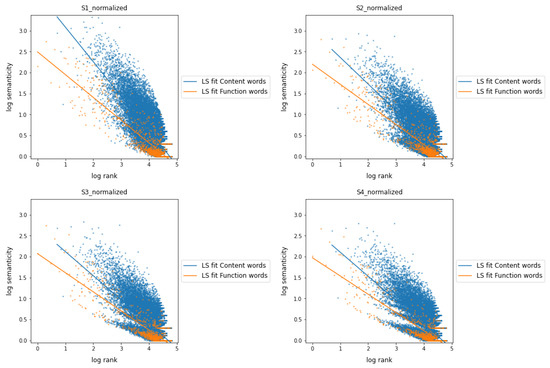
Figure 4.
Semanticity vs. frequency rank at distances from 1 to 4 with and normalizations applied showing fitting functions. Parts of speech are grouped into two word classes: content words and function words. Adverbs are considered function words here. All plots are in log–log scale.
Figure 5 shows the relationship between semanticity and frequency rank for co-occurrences at a distance of 1 when the parts of speech are divided into four classes: nouns, verbs and adjectives, individually, and all function words grouped together, including adverbs. A linear regression (LS) fit was applied to each word class on the logarithmic scale data.
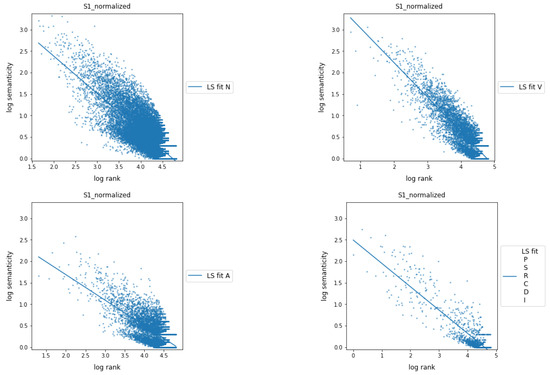
Figure 5.
Semanticity vs. frequency rank at distance 1 with and normalizations applied showing fitting functions. Each part of speech belonging to content words (nouns, verbs, and adjectives) is shown separately, and those belonging to function words, including adverbs, are shown together. All plots are in log–log scale.
Although the general trend of semanticity is perceptible in Figure 5, Table 2 provides a more nuanced perspective by presenting the slopes of the linear fit for each word class across varying distances of word connections, ranging from 1 to 4. The analysis shows that the trend in the semanticity values of nouns and verbs is very similar, evolving in parallel as the distance between words increases. Interestingly, adjectives display a tendency closer to function words than to nouns and verbs, yet they maintain a discernible difference that persists across different word connection distances.

Table 2.
Summary of the fittings for nouns, verbs, adjectives, and function words. Slope values of the linear fit for the parts of speech by varying the distance of the word connections from 1 to 4. In parenthesis, one standard deviation of the estimation of slopes.
In the context of considering two main word classes, content words and function words, Table 3 provides the slopes derived from linear fits for each class across different distances of word connections, ranging from 1 to 4. The table underscores a distinctive contrast in the trends of the semanticity values between the two classes. Moreover, it can be seen that the divergence in trends persists even with word connections at greater distances.

Table 3.
Summary of the fittings for content words and function words. Slope values of the linear fitting for the two word classes by varying the distance of the word connections from 1 to 4. In parenthesis, one standard deviation of the estimation of slopes.
Considering two word classes, we observed different slopes in log–log plots of semanticity and frequency rank (see Table 3 and Figure 3). Even so, we must ponder whether these differences are statistically significant.
In our testing framework, we set up a null hypothesis positing that both classes of words have the same slope, implying they statistically belong to the same population. The chosen statistic to quantify this comparison is the absolute value of the difference in slopes between content and function words. In our specific case, this difference, as indicated in Table 3, is . To assess whether this value is statistically distinguishable from zero, we conducted a permutation test. This involved randomly shuffling the labels of content and function words and computing the absolute difference in slopes for each group. This process aligns with the null hypothesis, assuming similar behavior in log–log plots of semanticity and frequency rank for both word classes. We repeated this procedure 1000 times, generating the histogram shown in Figure 6. All differences obtained under the null hypothesis fell below the dotted orange line, corresponding to a p-value of after 1000 tests, while the difference observed with true labels () is marked with a black arrow. Since the observed differences with true labels exceed this threshold, we statistically reject the null hypothesis, concluding that the differences in slopes are highly significant.
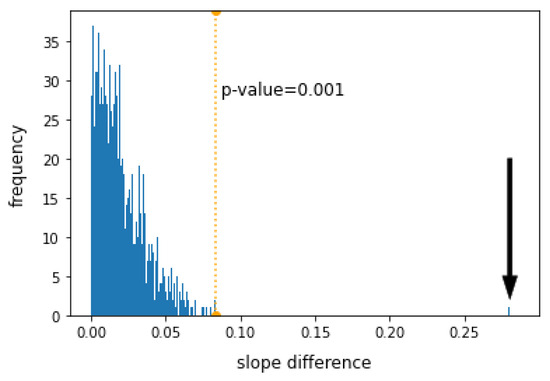
Figure 6.
Results of the permutation test. All differences obtained under the null hypothesis fell below the dotted orange line, corresponding to a p-value of after 1000 tests, while the difference between the slopes of function and content words () is marked with a black arrow.
In our investigation, we also conducted an analysis to assess the predictive efficacy of semanticity in anticipating two distinct word classes: content words and function words. To ensure robust representation, we imposed a minimum frequency criterion of 50 occurrences for a word within the corpus to be considered in either of these classes. Figure 7 illustrates the relationship between semanticity and frequency rank for co-occurrences at a distance of 1, with parts of speech grouped into the two specified word classes. The figure includes a comprehensive overview featuring the confusion matrix derived from predictions on both classes within a test set and the evaluation measures associated with the results.
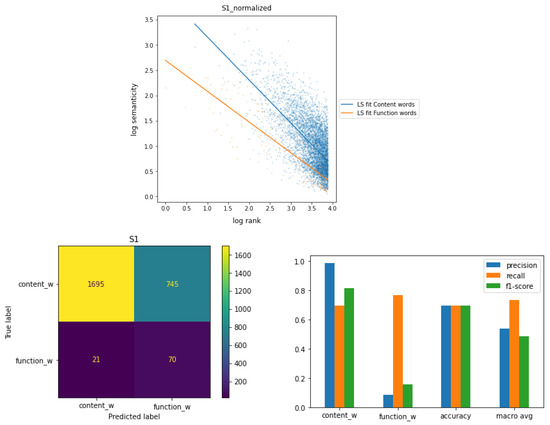
Figure 7.
Semanticity vs frequency rank at distance 1 with and normalizations applied with fitting functions. Minimum frequency of a word set at 50 occurrences. The parts of speech are divided into two classes: content words and function words. Confusion matrix derived from predictions on both classes within a test set and evaluation measures associated with the results.
We can conclude that our experiments show that content words significantly exhibit higher semanticity than function words, and that this tendency is (a) irrespective of the rank and (b) continues for longer distance connections. We have also shown that, according to this semanticity measure, adverbs in Catalan can be treated as belonging to the class of function words.
6. Discussion
A key question in linguistic research is whether parts-of-speech primarily represent word classes or functional classes (Duplatre and Modicom 2022). The concept of parts-of-speech is a fundamental aspect in syntactic and semantic descriptions and theories, posing challenges for those advocating a cross-linguistic, comparative approach (Duplatre and Modicom 2022; Haspelmath 2001). Furthermore, in the ongoing debate on the classification of words, the necessity of lexico–semantic tests becomes apparent, shedding light on the intricate nature of parts-of-speech and enhancing our understanding of the interplay between semantic and lexical criteria.
In this context, the new quantitative definition of semanticity (Català et al. 2023) emerges as a necessary tool for automatically exploring lexico–semantic interstices. So far, semanticity captures, at a general level, the semantic and lexical behavior of words well, showing, for example, how a certain class of words, such as adverbs, in Catalan, behave more like function words than content words. Of course, the potential of semanticity as a feature of linguistic elements still needs to be explored further at other levels (in morphology, phrases, sentences, etc.). It is clear that between the statistical approach developed here and the specific descriptive semantics of a linguistic element (see, for example, (Bosque 2024)), there is a whole quantitative path still to be explored.
Some approaches have argued for intermediate positions between the function/content word dichotomy: function words have semantic content beyond their syntactic functions, and content words also have grammatical value. There has also been talk of semi-lexical categories (Corver and van Riemsdijk 2001). In fact, this definition of semi-lexical categories brings to the surface the existing difficulties of qualitative dichotomous classification of word classes. This can be seen in the literature by noting the categories included in content words, which are sometimes limited to nouns, verbs, and adjectives but sometimes other word classes are included, which makes us think more of a lexical continuum, all the more so given the significant differences between the world’s languages (Haspelmath 2001). This lexical continuum dilutes the traditional qualitative classification between function and content words and pushes us to propose a quantitative measure to help improve existing linguistic theories. On the one hand, quantitative parameters in linguistics should be promoted in order to put an end to false qualitative dichotomies in the linguistic continuum, while, on the other hand, we should try to propose good qualitative descriptions of natural and artificial phenomena (Hernández-Fernández 2021). As Corver and van Riemsdijk (2001, p. 3) rightly point out (Corver and van Riemsdijk 2001):
The distinction between content words and function words is a central one in studies on the syntactic categories of natural language. (...) a number of characteristic properties have been identified, which make it possible to classify some lexical item as belonging to the class of content words or that of function words. But as with all types of categorization, there are elements, which cannot be put straightforwardly under one of the two classes. Certain lexical items display ambiguous behavior: they share properties with lexical categories and at the same time they display functional characteristics.
The paradigmatic case we have seen here is that of adverbs. In this sense, adverbs are defined as a “lexical word that may be used as a modifier of a non-nominal head” (Hengeveld 2023; Schachter and Shopen 2007) but frequently show some degree of overlap with other word classes (Hallonsten Halling 2018; Hengeveld 2023). Here, we have shown that, as far as semanticity is concerned, the behavior of adverbs in Catalan overlaps with function words.
This pilot study of Catalan paves the way for studies in other languages. As we have seen, it is enough to have a dictionary from which to extract the number of senses and an extensive corpus to compute the links between words at different Euclidean distances in order to calculate semanticity. Thus, the ability to differentiate between word classes could be tested by calculating this objective parameter in languages of different language families where there are often different behaviors for each word class. One of the limitations of semanticity is that the measure remains a snapshot of the language in the corpus. Semanticity does not capture how word associations and meanings evolve over time, but it provides a stable and comparable baseline for the analysis of different texts (and different languages) within the same time frame. Future work should analyze how semanticity, as a quantitative but static measure of the words in a corpus, can be related to other dynamic measures such as semantic diversity (Hoffman et al. 2013) or be integrated into theories of semantic memory (Kumar 2021).
In other approaches not considered here, there have been notable recent developments, from symbolic paradigms of semantics to compositional distributional semantics based on information theory (Amigó et al. 2022), which account for the complexity of the problem of the relation between syntax and semantics in a field that is still also controversial in psycholinguistics (Krauska and Lau 2022) and neural language models (NLM) (Devlin et al. 2019; Radford et al. 2019; Thoppilan et al. 2022).
However, some classical qualitative conceptions of word meaning still remain, on which, with one approach or another, subsequent developments are based. For example, the technical achievements of NLM, based on computational brute force (Devlin et al. 2019; Radford et al. 2019; Thoppilan et al. 2022), are undeniable. Nevertheless, we cannot forget to try to theoretically ground linguistics using the computational tools at our disposal and following the fundamental empirical methods for the study of language (Riezler and Hagmann 2021), starting from definitions and models which, as in any science, must be in constant revision (Bunge 2013).
Although it has been suggested that, thanks to computational advances, a greater focus on prediction rather than explanation may ultimately lead to a better understanding of language and human behavior (Yarkoni and Westfall 2017), in science, we should not give up on theoretical modeling and explanation. Quantitative linguistics must persevere and continue to propose theoretical models that go beyond computational prediction and, indeed, lie behind it. Improved linguistic theories will subsequently lead to technological improvements.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.H.-F.; methodology, N.C., J.B. and A.H.-F.; software, N.C. and J.B.; formal analysis, N.C., J.B. and A.H.-F.; writing—review and editing, N.C., J.B. and A.H.-F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by project PRO2023-S03 HERNANDEZ from Secció de Ciències i Tecnologia de l’Institut d’Estudis Catalans (https://www.iec.cat/). Jaume Baixeries and Antoni Hernández-Fernández are supported by a recognition 2021SGR-Cat (01266 LQMC) from AGAUR (Generalitat de Catalunya) and the grants AGRUPS-2022 and AGRUPS-2023 from Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya. Neus Català is supported by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation through TADIA-MED project (https://futur.upc.edu/28881334/) [PID2019-106942RB-C33].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The CTILC corpus is available at https://ctilc.iec.cat/. The DIEC2 dictionary is available at https://dlc.iec.cat. A Zenodo repository has been set up containing: (a) preprocessed dataset material from both CTILC and DIEC2 corpora (https://zenodo.org/record/4120887/files/DIEC2_CTILC_senseCG.zip), and (b) FreeLing configuration and execution commands used to process the above dataset (https://zenodo.org/record/5547977/files/freeling.zip).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Notes
| 1 | See (Ferrer-i-Cancho 2004) for a definition of Euclidean distance between linked words. |
| 2 | For a part-of-speech to be considered, it must have more than 20 different tokens. |
References
- Amigó, Enrique, Alejandro Ariza-Casabona, Victor Fresno, and M. Antònia Martí. 2022. Information theory–based compositional distributional semantics. Computational Linguistics 48: 907–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baayen, R. Harald, and Fermín Moscoso del Prado Martín. 2005. Semantic density and past-tense formation in three germanic languages. Language 81: 666–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baayen, R. Harald, Richard Piepenbrock, and Leon Gulikers. 1995. The celex lexical database (release 2). In Distributed by the Linguistic Data Consortium. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania. [Google Scholar]
- Baddeley, Alan D. 1997. Human Memory: Theory and Practice. London: Psychology Press. [Google Scholar]
- Barabási, Albert-László, and Eric Bonabeau. 2003. Scale-free networks. Scientific American 288: 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baronchelli, Andrea, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Romualdo Pastor-Satorras, Nick Chater, and Morten H. Christiansen. 2013. Networks in cognitive science. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 17: 348–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, Alan, Jason M. Brenier, Michelle Gregory, Cynthia Girand, and Dan Jurafsky. 2009. Predictability effects on durations of content and function words in conversational English. Journal of Memory and Language 60: 92–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borge-Holthoefer, Javier, and Alex Arenas. 2010. Categorizing words through semantic memory navigation. The European Physical Journal B 74: 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosque, Ignacio. 2024. Four dialectal uses of the adverb Siempre and their grammatical properties. Languages 9: 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broido, Anna D., and Aaron Clauset. 2019. Scale-free networks are rare. Nature Communications 10: 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunge, Mario. 2013. La ciencia: Su método y su filosofía. Pamplona: Laetoli. [Google Scholar]
- Bybee, Joan. 1998. The emergent lexicon. Chicago Linguistic Society 34: 421–35. [Google Scholar]
- Català, Neus, Jaume Baixeries, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Lluís Padró, and Antoni Hernández-Fernández. 2021. Zipf’s laws of meaning in Catalan. PLoS ONE 16: e0260849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Català, Neus, Jaume Baixeries, Lucas Lacasa, and Antoni Hernández-Fernández. 2023. Semanticity, a new concept in quantitative linguistics: An analysis of Catalan. Paper presented at the Qualico 2023, 12th International Quantitative Linguistics Conference, Lausanne, Switzerland, June 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Cindy, and James W. Pennebaker. 2007. The psychological functions of function words. Social Communication 1: 343–59. [Google Scholar]
- Condon, Edward U. 1928. Statistics of vocabulary. Science 67: 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corver, Norbert, and Henk van Riemsdijk. 2001. Semi-Lexical Categories: The Function of Content Words and the Content of Function Words. Berlin and New York: Walter de Gruyter. [Google Scholar]
- De Zubicaray, Greig I., and Niels O. Schiller. 2019. The Oxford Handbook of Neurolinguistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, Jacob, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee, and Kristina Toutanova. 2019. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers). Minneapolis: Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 4171–86. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, Michele T., and Gregory McCarthy. 2009. A comparison of brain activity evoked by single content and function words: An FMRI investigation of implicit word processing. Brain Research 1282: 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donatelli, Lucia, and Alexander Koller. 2023. Compositionality in computational linguistics. Annual Review of Linguistics 9: 463–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duplâtre, Olivier, and Pierre-Yves Modicom. 2022. Introduction–adverbs and adverbials: Categorial issues. Adverbs and adverbials: Categorial issues 371: 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Feist, Jim. 2022. Significance in Language: A Theory of Semantics. Abingdon: Taylor & Francis. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ramon. 2004. Euclidean distance between syntactically linked words. Physical Review E 70: 056135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ramon. 2019. The sum of edge lengths in random linear arrangements. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment 2019: 053401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ramon, Antoni Hernández-Fernández, David Lusseau, Govindasamy Agoramoorthy, Minna J. Hsu, and Stuart Semple. 2013. Compression as a universal principle of animal behavior. Cognitive Science 37: 1565–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ramon, and Ricard V. Solé. 2001. Two regimes in the frequency of words and the origins of complex lexicons: Zipf’s law revisited. Journal of Quantitative Linguistics 8: 165–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ramon, and Ricard V. Solé. 2001. The small world of human language. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 268: 2261–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ramon, and Michael S. Vitevitch. 2018. The origins of Zipf’s meaning-frequency law. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology 69: 1369–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskell, M. Gareth, Gerry Altmann, and Gerry T.M. Altmann. 2007. The Oxford Handbook of Psycholinguistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hallonsten Halling, Pernilla. 2018. Adverbs: A Typological Study of a Disputed Category. Ph. D. thesis, Department of Linguistics, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, Zellig S. 1954. Distributional structure. Word 10: 146–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haspelmath, Martin. 2001. Language Typology and Language Universals: An International Handbook. Berlin and New York: Walter de Gruyter, vol. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Hengeveld, Kees. 2023. Adverbs. In The Oxford Handbook of Word Classes. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Fernández, Antoni. 2021. Qualitative and quantitative examples of natural and artificial phenomena. Biosemiotics 14: 377–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Fernández, Antoni, Iván G. Torre, Juan-María Garrido, and Lucas Lacasa. 2019. Linguistic laws in speech: The case of Catalan and Spanish. Entropy 21: 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Fernández, Antoni, Juan María Garrido, Bartolo Luque, and Iván González Torre. 2022. Linguistic laws in Catalan. Quantitative Approaches to Universality and Individuality in Language 75: 49. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Fernández, Antoni, and Iván G. Torre. 2022. Compression principle and Zipf’s law of brevity in infochemical communication. Biology Letters 18: 20220162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockett, Charles F. 1960. The origin of speech. Scientific American 203: 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, Paul, Matthew A. Lambon Ralph, and Timothy T. Rogers. 2013. Semantic diversity: A measure of semantic ambiguity based on variability in the contextual usage of words. Behavior Research Methods 45: 718–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgen, Bahar, and Bahar Karaoglan. 2007. Investigation of Zipf’s ‘law-of-meaning’ on turkish corpora. Paper presented at the 2007 22nd International Symposium on Computer and Information Sciences, Ankara, Turkey, November 7–9; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipsen, Mads. 2004. Evolutionary reconstruction of networks. In Function and Regulation of Cellular Systems. Basel: Birkhäuser, pp. 241–49. [Google Scholar]
- Krauska, Alexandra, and Ellen Lau. 2022. Moving away from lexicalism in psycho-and neuro-linguistics. Frontiers in Language Sciences 2: 1125127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Abhilasha A. 2021. Semantic memory: A review of methods, models, and current challenges. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 28: 40–80. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Wei. 2017. Spectra of English evolving word co-occurrence networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 468: 802–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, Kyle, Isabelle Dautriche, Mika Braginsky, and Ted Gibson. 2022. Efficient communication and the organization of the lexicon. In The Oxford Handbook of the Mental Lexicon. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 200–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mahowald, Kyle, Isabelle Dautriche, Edward Gibson, and Steven T. Piantadosi. 2018. Word forms are structured for efficient use. Cognitive Science 42: 3116–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemurro, Marcelo A. 2001. Beyond the Zipf–Mandelbrot law in quantitative linguistics. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications 300: 567–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motter, Adilson E., Alessandro P. S. De Moura, Ying-Cheng Lai, and Partha Dasgupta. 2002. Topology of the conceptual network of language. Physical Review E 65: 065102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L. Douglas, Cathy L. McEvoy, and Thomas A. Schreiber. 1999. The University of South Florida Word Association Norms. Available online: http://w3.usf.edu/FreeAssociation (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Pulvermüller, Friedemann. 1999. Words in the brain’s language. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 22: 253–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, Alec, Jeffrey Wu, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei, and Ilya Sutskever. 2019. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 1: 9. [Google Scholar]
- Rauh, Gisa. 2015. Adverbs as a linguistic category (?). In Adverbs: Functional and Diachronic Aspects. Edited by Karin Pittner, Daniela Elsner and Fabian Barteld. Amsterdam and Philadelphia: John Benjamins Publishing Company, pp. 19–46. [Google Scholar]
- Regier, Terry, Charles Kemp, and Paul Kay. 2015. Word meanings across languages support efficient communication. In The Handbook of Language Emergence. Hoboken: Wiley-Blackwell, pp. 237–63. [Google Scholar]
- Riezler, Stefan, and Michael Hagmann. 2021. Validity, reliability, and significance: Empirical methods for nlp and data science. Synthesis Lectures on Human Language Technologies 14: 1–165. [Google Scholar]
- Sahlgren, Magnus. 2008. The distributional hypothesis. Italian Journal of Disability Studies 20: 33–53. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, Nathan, Vivek Srikumar, Jena D. Hwang, and Martha Palmer. 2015. A hierarchy with, of, and for preposition supersenses. Paper presented at 9th Linguistic Annotation Workshop, Denver, CO, USA, June 5; pp. 112–23. [Google Scholar]
- Segalowitz, Sidney J., and Korri C. Lane. 2000. Lexical access of function versus content words. Brain and Language 75: 376–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachter, Paul, and Timothy Shopen. 2007. Parts-of-speech systems. In Language Typology and Syntactic Description. Vol. 1: Clause Structure. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Steyvers, Mark, and Joshua B. Tenenbaum. 2005. The large-scale structure of semantic networks: Statistical analyses and a model of semantic growth. Cognitive Science 29: 41–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoppilan, Romal, Daniel De Freitas, Jamie Hall, Noam Shazeer, Apoorv Kulshreshtha, Heng-Tze Cheng, Alicia Jin, Taylor Bos, Leslie Baker, Yu Du, and et al. 2022. Lamda: Language models for dialog applications. arXiv arXiv:2201.08239. [Google Scholar]
- Torre, Iván G, Bartolo Luque, Lucas Lacasa, Christopher T Kello, and Antoni Hernández-Fernández. 2019. On the physical origin of linguistic laws and lognormality in speech. Royal Society Open Science 6: 191023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, Duncan J., and Steven H. Strogatz. 1998. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 393: 440–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, Jake Ryland, James P. Bagrow, Christopher M. Danforth, and Peter Sheridan Dodds. 2015. Text mixing shapes the anatomy of rank-frequency distributions. Physical Review E 91: 052811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarkoni, Tal, and Jacob Westfall. 2017. Choosing prediction over explanation in psychology: Lessons from machine learning. Perspectives on Psychological Science 12: 1100–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipf, George Kingsley. 1932. Selected Studies of the Principle of Relative Frequency in Language. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Zipf, George Kingsley. 1945. The meaning-frequency relationship of words. The Journal of General Psychology 33: 251–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipf, George Kingsley. 1949. Human Behavior and the Principle of Least Effort: An Introduction to Human Ecology. Cambridge: Addison-Wesley. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).