Abstract
This study examines the influence of Tamil (L1) on the processing of English (L2) collocations during reading for Tamil-English bilingual children. Building on existing research in formulaic language, we used an online processing tool to investigate whether cross-linguistic transfer can be extended beyond single lexical items to collocations in bilingual children, a population that is underrepresented in this research area. Fifty-eight children aged 9–10 years from a school in Chennai, India, took part. Using self-paced reading, children’s reading times were measured for both congruent (with equivalent in L2) and incongruent (without equivalent in L2) English collocations embedded in short passages. There were two reading modes (single and chunk), which allowed reading times for the whole collocations and the individual words of the collocations to be examined. Results showed that children read congruent collocations more quickly than incongruent collocations in both modes. For congruent collocations, children read the second word more quickly than the first word, but the reverse was true for incongruent collocations. These results suggest that the L1 (Tamil) is activated during the processing stage of reading English collocations for Tamil-English bilingual children in this context.
1. Introduction
With an increasing number of children learning English as a second or additional language in India, the UK, and around the world, it is important to develop our understanding of how second language (L2) vocabulary learning in children takes place, especially in relation to the influence of the first language (L1) on this process. Understanding this can help educators support second language learners by effectively using L1 to teach L2 vocabulary (Zulfikar 2019). As mentioned by Hiebert et al. (2019), research in the area of L1 influence on L2 vocabulary learning has until recently focused on single words. We often think of vocabulary in terms of individual words, but words actually co-occur frequently in systematic ways to form collocations and other multiword units, that is, formulaic language. Since we know that vocabulary is also acquired and stored in multiword units (Schmitt 2010), not just as single words, it is essential that we expand our knowledge of the role of the L1 in how bilingual children process formulaic language in the L2. Studying the processing of formulaic language can further our understanding of how monolingual and bilingual lexicons are formed and how they differ. This knowledge can help in the design of vocabulary instruction material for children as well as inform vocabulary teaching practices in the classroom (Lindsay and Gaskell 2010).
Collocations are a subset of formulaic language that can be broadly defined as words that occur together more frequently than would be expected by chance (Carrol and Conklin 2020), e.g., strong wind. A simple but rather broad definition of a collocation is a frequently recurring two-to-three word syntagmatic unit (Henriksen 2013). Hunston (2002) describes it as the tendency of two words to co-occur or the tendency of one word to attract another. Wray (2002) observes a critical difference between collocations and other kinds of formulaic language such as idioms: collocations are more “fluid” in nature, whereas idioms are fixed, e.g., to make a mountain out of a molehill is a fixed expression, while though rain often collocates with heavy, it is still associated with other words. Studies have shown that collocations, like other kinds of formulaic language, are processed more quickly than nonformulaic language (Bonk and Healy 2005; Siyanova-Chanturia and Sidtis 2018; Wolter and Gyllstad 2011). A number of studies have investigated how the correspondence between L1 and L2 contributes to online processing of formulaic language (Carrol et al. 2016): if formulaic language shares form and meaning across both a speaker’s languages, then speakers perform better on comprehension and production tasks, which could be indicative of faster processing (Paquot and Naets 2015; Pritchett et al. 2016).
1.1. Cross-Linguistic Processing of Collocations
Although older models of bilingual lexical storage and access, such as the Revised Hierarchical Model (RHM) (Kroll and Stewart 1994), viewed the L1 and L2 lexica as two separate entities, the more recent Bilingual Activation Model (BIA) (Dijkstra and Van Heuven 1998) and Multilink Model (Dijkstra and Rekké 2010), suggest there is one integrated lexicon in which both L1 and L2 lexical items are stored. Jiang’s model of L2 lexical representation and development (Jiang 2000) posits that the acquisition of L1 words with an L2 equivalent is quicker because the learner already has access to the required semantic and syntactic information at the lemma level and thus only needs to acquire the phonological and orthographic information at the lexeme level. However, when a word does not have an L2 equivalent, the learner has to acquire the L2 information at both the lexeme and lemma level, and this process requires more effort and time.
Collocations can vary considerably from language to language (Wolter and Gyllstad 2011), and it has been observed that this variation is arbitrary (Henriksen 2013), i.e., there is often no logical or grammatical explanation for why certain words collocate with each other and others do not. The influence of the L1 on the acquisition of collocations (intralexical links) is an area that has attracted a great deal of scholarly attention over the last decade, as detailed below. Although there are different explanations for the influence of L1 on L2 collocation acquisition, the understanding of how this influence works is still in its early stages. This influence of L1 has mostly been examined by studying the differences in the production, reception, and processing of congruent collocations (collocations that have a direct equivalent in the learners’ native language) and incongruent collocations (collocations that do not have a direct equivalent in the learners’ native language).
Yamashita and Jiang (2010) presented verb-noun and adjective-noun collocations in an acceptability judgment task to Japanese EFL (English as a Foreign Language) and ESL learners. The researchers found that while there was no difference in processing times or error rates between congruent and incongruent collocations for the monolingual speakers (as expected), for both ESL (English as a Second Language) and EFL Japanese learners, the error rates were higher for the incongruent phrases. Additionally, the EFL learners had slower reaction times for the incongruent phrases, but this was not the case for the ESL learners. They also used a cloze test with the Japanese speakers to determine the difference in levels of L2 proficiency between the EFL and ESL learners—there was a significant difference in mean scores between both groups, with the ESL learners outperforming the EFL learners. This led the researchers to conclude that L2 collocations are processed independently of the L1 lexicon only at the later stages of language acquisition, i.e., when the learners become more proficient. This means that the influence of the L1 is greater during the initial stages of language acquisition and gradually subsides in the later stages.
Wolter and Gyllstad (2011, 2013) investigated collocational priming on congruent and incongruent collocations in monolingual speakers of English and Swedish learners of English and found similar results to Yamashita and Jiang’s study. For the Swedish learners of English, the processing times for the target word for the incongruent collocations were significantly longer than the same measure for the congruent collocations. Wolter and Gyllstad concluded that the advantage for congruent collocations may be due to a lexical priming effect: the knowledge of the collocation in the L1 primes their knowledge of the equivalent L2 collocation, i.e., the congruent collocation, thus reducing the processing time for such collocations. Thus, the L1 appears to be providing easier access to L2 collocations that have an equivalent in the L1, which is not possible for L2-only collocations. In terms of frequency, for both monolingual speakers and the Swedish learners of English, the biggest predictor of reaction times was the frequency of the collocations in relation to the English corpus. Wolter and Gyllstad cite other studies (e.g., Durrant and Schmitt 2010), which also found that high-proficiency language learners are sensitive to frequency effects just like monolingual speakers. The findings from this second study by Wolter and Gyllstad (2013) suggest that advanced L2 learners are sensitive to frequency effects not only at the word level, but also at the collocational level. Additionally, it must be noted that collocational frequency was the biggest predictor of reaction times, not word frequency. This indicates that both monolingual speakers and the Swedish learners of English processed the collocations holistically as single units and not as separate words.
Wolter and Yamashita (2018) followed up on these previous studies by conducting a study that examined the effects of word frequency, collocational frequency, L1–L2 congruency, and language proficiency on L2 collocational processing in Japanese speakers of English (intermediate and advanced) and monolingual English speakers. With respect to frequency, the results showed that the monolingual English speakers and the advanced Japanese speakers of English showed a greater sensitivity to collocational frequency than the intermediate Japanese speakers of English. Interestingly, further analysis of the word frequency and collocational frequency with both groups of Japanese learners showed that, with increased proficiency there was a shift away from reliance on word frequency to reliance on collocational frequency. This indicates that with increasing proficiency, L2 learners move towards monolingual-like collocational processing. However, it must be noted that even the most advanced L2 Japanese learners in this study relied more heavily on word frequency than the monolingual English speakers, which supports the conclusions of previous studies that even advanced L2 learners have difficulties with acquiring and processing L2 collocations.
Taking the results of these studies together, it is clear that across different contexts and with different groups of learners, the L1 influences L2 collocational processing, i.e., there is a congruency effect in which the L1 is activated during L2 collocational processing. Congruent collocations are recognized and processed more accurately than incongruent collocations, i.e., L1-only or L2-only collocations. Also, once a collocation is registered in the L2 lexicon, its L2 frequency influences its processing.
1.2. Sequential Bilingualism in Children
In early second language acquisition (ESLA), children encounter a second language after beginning to acquire their first, typically when they start childcare, nursery, or school. This process, known as sequential (successive) bilingualism, contrasts with simultaneous bilingualism, where children hear both languages at birth. Unlike the typical view of L2 acquisition in adults, where a second language is introduced after the first is fully developed, children who are sequential bilinguals usually hear their first language (L1) at home and are exposed to the second language (L2) in educational settings while there L1 is still developing.
McLaughlin (1995, 2013) highlights several factors that influence these components and processes, such as cultural, linguistic, and social differences, along with variations in educational systems, individual attitudes, and cognitive abilities. Paradis et al. (2011), studying 169 sequential bilinguals aged four to seven, found that internal factors like age, nonverbal intelligence, and phonological short-term memory predicted L2 proficiency better than external factors like length of exposure or the richness of English use at home. A study on Russian-Hebrew and English-Hebrew bilingual children (Armon-Lotem et al. 2014) revealed that L2 proficiency was closely tied to attitudes towards the heritage language and L2, with greater proficiency in communities with mixed language use, such as the Russian-Hebrew community.
This brief overview of sequential bilingualism in children shows that there are many different variables that influence the development of both languages in a sequentially bilingual child, which differ from a bilingual adult. The children in this study are sequential bilinguals, and it is important to consider these factors when analyzing how Tamil influences their processing of English collocations.
1.3. Cross-Linguistic Influence on Language Processing in Bilingual Children
It is worth noting that most of the previous research examining the extent of L1 influence on L2 collocational processing has been conducted with adults (e.g., Yamashita and Jiang 2010; Wolter and Gyllstad 2011, 2013; Wolter and Yamashita 2018). Since differences have been observed between cross-linguistic activation in bilingual children and adults (Paradis et al. 2011; Yip and Matthews 2000), it is important to establish whether the pattern of effects observed in adults is also observed in children. From studies that have investigated the cross-linguistic influence in children and adults (Murphy 2014; Paradis et al. 2011), it seems that bilingual children are more prone than adults to quantitative cross-linguistic influence, i.e., they are more likely to use their knowledge of one language while producing constructions in their other language. A recent case study by Babatsouli and Nicoladis (2019) investigated cross-linguistic influence in a 4-year-old bilingual child in the context of fixed expressions and found that the child showed evidence of cross-linguistic transfer in her use of collocations. However, whether older bilingual children exhibit this pattern too is as yet under-researched.
1.4. Socioenvironmental Background of the Study
In the highly multilingual setting of India, English has the constitutional status as one of the two official languages and serves as a lingua franca (Ayyar 1993), particularly in large cities such as Chennai. In Chennai, English-medium schools include: (1) schools that follow an international curriculum that cater to high-income families; (2) elite private schools that follow the state curriculum (Tamil Nadu State Board) or a national curriculum (Central Board of Secondary Education); and (3) low-income state and private schools that cater to children from less privileged families. Schools in this last category are only English-medium in a formal sense—although the whole curriculum is meant to be taught in English, classroom interactions are mostly in the regional language since teachers themselves struggle with communicating effectively in English. In most of these schools, class sizes range from 40 to 60, and virtually all teachers of English have learned English in the same education system (Ponnuchamy 2012). Typically, children who attend these low-income schools have very minimal or no contact with English outside the school setting. As noted by Ponnuchamy (2012), the state government’s efforts to promote English at these schools have been met with criticism due to poor school facilities, a lack of adequate and effective training for teachers, and teachers’ inefficiency at communicating in English. Gargesh (2006) observes that after approximately 12 years of education in state or low-income private schools (English-medium), most of these students in Tamil Nadu are unable to cope with the academic demands of tertiary education in colleges and universities, which all have English as the medium of instruction. The school that participated in this study belongs to this category and caters to children from low-income families in Chennai. Since these children are not very proficient in English and their main source of English exposure is from an L2 speaker who is not very proficient (their teacher), it is likely that these children’s processing of English collocations will be influenced by their Tamil. This lack of English competence of English teachers world-wide is an issue that has been well documented (Dearden 2014).
1.5. Rationale for the Current Study
The current study examined L1 influence on L2 collocational processing in bilingual English-Tamil speaking children. While previous research has focused mostly on collocation processing in adults (e.g., Yamashita and Jiang 2010; Wolter and Gyllstad 2011, 2013; Wolter and Yamashita 2018), the current study focuses on collocation processing in children, who we know differ from adults in important ways (Murphy 2014; Paradis et al. 2011), which is likely to affect the extent to which their L1 impacts their L2 processing. By examining transfer between languages that are orthographically different, we were able to broaden our understanding of L1 activation during L2 processing beyond the usual suspects (European alphabetic languages). Finally, we explored the role of proficiency and vocabulary in both languages, as previous research suggests that with advanced proficiency in L2, L1 influence of formulaic language diminishes (Carrol et al. 2016).
This study used self-paced reading to examine whether Tamil-English bilingual children showed a congruency effect when reading passages containing congruent and incongruent collocations. We had two main research questions:
- Is the L1 activated when Tamil-English bilingual children process collocations in L2?
- What is the relationship between the proficiency levels/vocabulary size of children and the time they take process congruent versus incongruent collocations?
In relation to the first research question, it was predicted that congruent collocations would be processed more quickly than the incongruent ones, which would be an indication that Tamil (L1) was activated during the processing of English (L2) collocations. This prediction followed previous studies showing that the influence of the L1 is greater at initial stages of language acquisition (e.g., Yamashita and Jiang 2010). Furthermore, it was predicted that congruency would have a priming effect (when the first word of the collocation prepares the reader for the second word) on the second word of collocations during the processing stage of collocations for Tamil-English bilingual children (Wolter and Gyllstad 2011).
In relation to the second research question, it was predicted that children with a larger vocabulary in Tamil than in English would show a larger congruency effect than those with a larger vocabulary size in English. Additionally, it was predicted that children with higher levels of English proficiency would show a smaller congruency effect than those with lower proficiency. This would be consistent with previous empirical studies (Bonk and Healy 2005; Wolter and Gyllstad 2011).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Fifty-eight 5th grade students (34 girls) participated in this study. All participants were 9–10 years old and attended an English-medium primary school in Chennai, India. The selection of this age group was based on the requirement of a certain level of reading ability and English proficiency for the self-paced reading task. All participants had Tamil as their L1 and English as their L2, and they did not speak any other languages. The medium of instruction in their school was English, but they also learned Tamil as a separate subject. The students had 6–7 years of English-medium education since the beginning of their schooling. The selected school was a low-tier private school with affordable fees and catered to children from low-income families who desired English-medium education for their children but could not afford more expensive, well-resourced private schools. Although English was the medium of instruction in their school, the students had limited exposure to English outside school, and Tamil was their preferred language of communication. However, they had more exposure to written English than written Tamil due to the English language textbooks used in their school.
2.2. Preparation of Stimuli
Since the definition of collocations is inclusive of various kinds of word combinations, a critical part of every collocation study is determining and defining the kind of collocations to include in the study. In this study, collocations were extracted from the textbooks of the participating children instead of corpora. This decision was made because the children had limited exposure to English outside the classroom, and using a corpus might not reflect their actual exposure to English. Additionally, using the children’s textbooks ensured that the selected collocations were already familiar to the learners. This approach aligns with the findings of Northbrook and Conklin (2019), who observed that beginner Japanese learners of English were more sensitive to formulaic language extracted from their learning materials rather than from a corpus based on frequency. The frequency of the collocations was determined using the BNC. The Oxford Collocation Dictionary and Collins CoBuild English Dictionary were consulted to ensure that the selected collocations were used in standard English. The collocations were chosen based on their frequency (from the 5000 most frequent English words according to the BNC) and an MI (Mutual Information) score above 3, which indicates a recognizable association between collocates (Hunston 2002). This shortlist of collocations was crosschecked with the children’s textbooks as mentioned above, and then the final list of collocations was chosen. The selected collocations were then translated into Tamil by the researcher and cross-checked for accuracy and congruency by two other adult first language speakers of Tamil who are also proficient in English. An equal number of incongruent and congruent collocations were chosen based on their fit into the mini stories.
The stimuli for the experiment consisted of eleven mini stories, each comprising three to four sentences. Each story contained a mixture of four to five congruent and incongruent collocations, with a maximum of two collocations per sentence. The collocations consisted of adjective+noun, verb+noun, and verb+adverb combinations. The length and number of collocations in the stories were controlled to ensure comparability between single and chunk modes of presentation. An example of a mini story with collocations in bold was provided.
Example mini story (with collocations in bold):
It was the rainy season (incongruent), and Timmy could not go out to play. It was the first time (congruent) this year that he had seen such a strong wind (congruent) blowing outside. In broad daylight (incongruent), he saw all the birds fly away (incongruent) to take shelter in the trees.
2.3. Design
The study followed a 2 × 2 within-participants design with congruency and presentation mode as independent variables. Congruent collocations could be translated word-for-word from English to Tamil while retaining the same meaning, while incongruent collocations lacked equivalents in Tamil. The presentation mode consisted of single and chunk modes. In the single mode, sentences were presented word-by-word, requiring participants to press a button to proceed to the next word, including the collocations. In the chunk mode, each sentence was presented in two/three-word units (chunks), allowing participants to read each collocation as a single unit. Care was taken to ensure the collocations remained within the chunk, and so certain units contained three words (usually a conjunction or article) to accommodate this. This was done so that the reading times for collocations as a whole could be recorded, as well as each individual word to investigate whether there was a priming effect (when the first word of the collocation prepares the reader for the second word). This was how the collocations were presented, but on later reflection, we decided that this manipulation is not relevant for most of the analyses. We will report minimally on these conditions for transparency but not discuss them in detail. The first five stories were presented in single mode, and the remaining six were presented in chunk mode for all participants. Thus, each participant was exposed to four experimental reading conditions: single congruent, single incongruent, chunk congruent, and chunk incongruent. The dependent variable was reading time, measured in milliseconds, with vocabulary and proficiency measures in both languages serving as covariates.
2.4. Research Instruments
2.4.1. X-lex Tests
The X-lex 5000 test, developed by Meara and Milton (2003), was used to measure receptive vocabulary size. It includes both real words and pseudowords and focuses on vocabulary breadth. The test employs a Yes/No format, where participants mark the words they know. The test has been found reliable and valid for screening, placement, and measuring average vocabulary size. Although it was originally designed for EFL students at the college level, it has successfully been used with children (Milton 2006; Daller and Ongun 2018). It uses the 5000 most frequent English words in the BNC. Each test consists of 100 words, with 20 words from each of the first five frequency bands, and includes 20 pseudowords that are phonologically and orthographically valid but are not actual words, e.g., flimsale. For every correct word, the participants received 50 points, and they lost 250 points for every pseudoword they marked as known. Thus, the pseudowords act as a correction formula to control for response bias and cheating.
The X-lex has been reported as reliable and valid for screening and placement purposes and also as a measure of average vocabulary size (Milton 2007). Due to the fact that it is easy to administer and score and also allows for a sampling of a large number of items, it has been used widely in vocabulary testing in second language research (Harsch and Hartig 2015). In a study that measured the relationship between X-lex scores and reading and listening skills, Harsch and Hartig (2015) found a significant positive correlation between the X-lex scores and the reading proficiency levels of the learners.
For the X-lex English test in this study, the existing test was used (Meara and Milton 2003). For the X-lex Tamil test, the researcher developed the test using the Tamil corpora available on the Sketch Engine website (https://www.sketchengine.eu/) (accessed on 23 September 2024) and in accordance with the pattern of the English X-lex test. The test was piloted with seven Tamil-English bilingual children and three Tamil-English bilingual adults, and no changes were needed.
2.4.2. C-Test
The C-test, an integrative written test of general language proficiency, was administered to measure overall English language skills. It consists of authentic short texts covering different topics, where half of every second word is deleted, excluding one-letter words, proper nouns, and numbers. Test-takers fill in the blanks. In most cases, there is only one right answer for each blank. Each right answer gets one point, and there is no negative marking.
Since its introduction, various studies have been carried out to validate the reliability of the C-test as a test of general language proficiency and have reported positive results (e.g., Babaii and Ansary 2001; Dörnyei and Katona 1992). In a study designed to test the predictive power of C-test scores on reading ability, Harsch and Hartig (2015) found that the C-test had high correlations with both reading and listening skills. Eckes and Grotjahn (2006) and Grotjahn (2002) report the C-test to be easy to administer, objective, and a reliable measure of language proficiency.
The C-test for this study was developed from scratch based on topics from the children’s English textbooks, and there were 50 blanks in total. The test was piloted with Tamil-English children from the relevant age group, and following this, necessary changes were made.
2.4.3. Self-Paced Reading Experiment
Since it gives a measure of processing in real time, self-paced reading has been used in a range of linguistic processing studies—from studying the effects of language switching on reading comprehension (Bultena et al. 2015) to examining the processing of past tense morphology (Pliatsikas and Marinis 2013). There are also numerous studies that have used the self-paced reading task to study the processing of formulaic sequences: Kim and Kim (2012) used it to study the effects of frequency on multiword processing in L2 learners and first language speakers, Schmitt and Underwood (2004) used it to analyze the processing of component words in formulaic sequences, and Siyanova and Schmitt (2008) used it to study the processing of L2 collocations.
The self-paced reading task was conducted using PsychoPy (Peirce 2007) v1.8, an open-source application designed to control stimulus display and measure timing. It presents stimuli on a computer monitor, and participants press the spacebar to proceed to the next unit. The application records the time between button presses as the reading time. The stimuli, consisting of mini stories, were entered word-by-word for the single mode and in two-word chunks for the chunk mode. The order of presentation was randomized for each participant within the single and chunk blocks. PsychoPy automatically recorded the reading times for each word and chunk in separate files for each participant.
2.5. Procedure
The X-lex tests and C-test were group-administered to the participants in their classrooms (X-lex in the morning and C-test in the afternoon). The participants marked the words they understood and knew how to use in the X-lex tests, without being informed of the presence of pseudowords. The format of the C-test was explained, and participants were given an example to understand the task.
The self-paced reading experiment took place in individual sessions using a laptop in a designated room at the school. The researcher demonstrated the task using an example mini story, followed by a practice trial. Subsequently, participants read the 11 mini stories in a different random order within the single and chunk modes. Each session lasted 30–40 min.
3. Results
Although PsychoPy recorded the reading times for each word and unit during the self-paced reading, only the reading times for the collocations were required for data analysis. The researcher extracted the reading times for the whole collocation in the chunk mode and the reading times for each word of the collocations in the single mode. Since the design was not fully crossed (all stories appeared either in single or chunk mode, not in both), two-way ANOVAs rather than linear mixed effects models were used to analyze the data.
Mean reading times for each condition are shown in Table 1. Note that the reading times on Word 1 and Word 2 were summed in the single condition, to produce overall means for the collocation. As is usually the case with reading time data, the data were not normally distributed, i.e., p < 0.05 in the Shapiro–Wilk’s test. Based on accepted practice in the field, any reading times that were 2.5 deviations away from the mean for each of the four conditions were excluded (Conklin and Pellicer-Sánchez 2016). This set of data was normally distributed for all conditions (p > 0.05 in the Shapiro–Wilk’s test), and the analyses were performed on these data. The slower reading time of the single mode can be accounted for by the required key press between words in this mode (not required for chunk mode). Means and standard deviations for vocabulary test scores (out of 5000) and English proficiency test scores (out of 50) as well as Cronbach’s alpha for all three tests are listed in Table 2.

Table 1.
Mean reading times for congruent and incongruent, and single and chunked collocations (ms). Standard deviations are in parentheses.

Table 2.
Means and standard deviations for vocabulary test scores (out of 5000) and English proficiency test scores (out of 50). Cronbach’s alpha for all three tests.
3.1. Effects of Congruency, Presentation Mode, and Test Scores
A two-way repeated measures ANCOVA was run to determine the effects of congruency on mean reading times while also accounting for participants’ vocabulary knowledge in English and Tamil and for their proficiency in English. The distribution of these scores is seen in Figure 1. There was a main effect of congruency with longer reading times on the incongruent than congruent collocations F1(1,48) = 50.93, p < 0.001; F2(1,42) = 16.36, p = 0.016. There was a main effect of presentation mode with longer reading times for single mode than for chunk mode F1(1,48) = 48.21, p = 0.034; F2(1,42) = 20.31, p = 0.008. The interactions between congruency and presentation mode were not significant F1(1,48) = 16.48, p = 0.101; F2(1,42) = 12.78, p = 0.119.
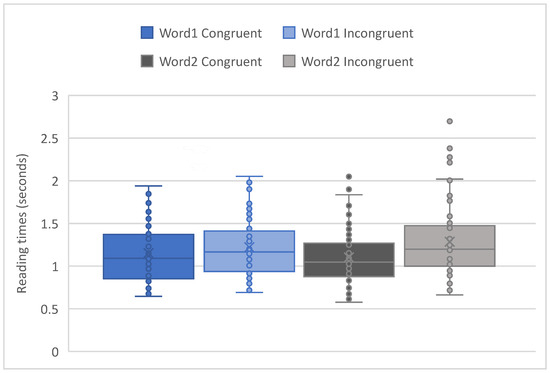
Figure 1.
Reading times (in ms) for Word 1 and Word 2 in the congruent and incongruent conditions in single mode.
In terms of the vocabulary and proficiency scores, there were no significant covariate effects (all Fs < 1; all ps > 0.1) on reading times, that is, vocabulary knowledge in English and Tamil as well as English proficiency did not affect how long the children took to read the collocations. Furthermore, there were no significant interactions between congruency and X-lex English Test score, F1(1) = 0.029, p = 0.866; X-lex Tamil Test score F1(1) = 0.666, p = 0.419; or C Test score, F1(1) = 0.122, p = 0.729.
3.2. Congruency Effect on Word 2 in the Single Mode
To further examine the congruency effect on Word 2, Word 2 reading times were isolated and analyzed. Since the congruent and incongruent collocations were not matched for word length and frequency, reading times were transformed into z-scores in order to ensure that reading times for both kinds of collocations could be compared. The difference between the standardized reading times for Word 2 of the incongruent collocations and the standardized reading times for Word 2 of the congruent collocations was calculated as a new variable: Word 2 Difference. Preliminary analyses showed the values to be normally distributed as assessed by Shapiro–Wilk’s test (p > 0.05). A Pearson’s correlation test was run to examine the correlation between the Tamil and English vocabulary scores and Word 2 Difference. This was performed to see if the vocabulary scores in either language were correlated with the size of the congruency effect on Word 2. The correlation between Tamil vocabulary and Word 2 Difference as well as the correlation between English vocabulary and Tamil vocabulary, were not significant. There was, however, a significant negative correlation between English vocabulary scores and Word 2 Difference r(58) = −0.84, p < 0.001, showing that children with higher English scores showed a smaller congruency effect on Word 2.
4. Discussion
This study examines L1 influence on L2 processing of collocations in bilingual Tamil-English children. While we know quite a lot about cross-linguistic influence in adults, we know much less about multiword phrases and in younger readers who differ from adult learners in significant ways (see Section 1.2). Results of the self-paced reading experiment supported the congruency effect was on Word 2, as expected (see Wolter and Gyllstad 2011). The lack of positive correlations between the collocation reading times and vocabulary and proficiency test scores was unexpected and will be explored in more detail.
4.1. Congruency
Children read congruent collocations faster than they read incongruent ones even when vocabulary knowledge in English and Tamil, and proficiency in English were controlled for. This robust congruency effect indicates that children activated their L1 (Tamil) while reading L2 (English) collocations, in both presentation modes, i.e., when they were presented with the collocations as single words as well as when they were presented as complete multiword phrases.
From a theoretical standpoint, it is clear that nonselective lexical activation in the Multilink model (Dijkstra and Rekké 2010) and BIA model (Dijkstra and Van Heuven 1998), wherein both the L1 and L2 are activated even though the learner is presented with input only in the L2, is not limited to single words but can also be extended to collocations (Bonk and Healy 2005; Wolter and Gyllstad 2011). It can be assumed that the L1 provides quicker access to L2 collocations that have an L1 equivalent than those L2 collocations that have no L1 equivalent. It is clear that L1 is not suppressed when L2 collocations are activated; instead, there is a process of nonselective activation. It is plausible that when the child encounters the first word of the collocation, the L1 translation is activated along with the L1 collocates, and these L1 collocates activate the L2 collocates, thus allowing for quicker processing times. Based on the congruency effect found in this study, it can be assumed that collocational knowledge is part of the L1 semantic and syntactic information that the learner retains and uses while acquiring L2 vocabulary.
Earlier studies by Yamashita and Jiang (2010); Wolter and Gyllstad (2011), and Siyanova and Schmitt (2008) found that with an increase in L2 proficiency, the L1 influence on collocation acquisition decreases. Although the participants in this study have all been learning English for 5–7 years and also study in a school where the medium of instruction is English, Tamil is dominant in their lives, and this may be why the congruency effect is evident. As seen in the results, there was a lack of positive correlations between English proficiency and the congruency effect. These findings suggest that the relationship between proficiency and congruency effects seen in adults is not necessarily the same for children and support previous research showing this relationship is not always linear (Ding and Reynolds 2019; Fang and Zhang 2021).
4.2. L2 Vocabulary and Congruency Effects
Analyses of Word 2 of the collocation showed that children with larger English vocabularies showed a smaller congruency effect, i.e., the Word 2 Difference was smaller for those with larger English vocabularies. This is supported by Kroll and Stewart’s (1994) theory that the frequency with which bilinguals need to access the L1 translation while processing words in the L2 presumably decreases as they advance in L2 proficiency. This is also supported by a study by Yamashita and Jiang (2010), who found that only the lower proficiency learners showed significantly lower processing times for incongruent collocations. This led the researchers to conclude that L2 collocations are gradually processed independently of the L1 lexicon only at the later stages of language acquisition, i.e., when the learners become more proficient.
Thus, children with larger English vocabularies would not access their knowledge of L1 (Tamil) collocations while reading L2 (English) collocations as frequently as those children with smaller English vocabularies, and this accounts for the smaller congruency effect in the former group.
4.3. Vocabulary and Proficiency Tests and Collocation Reading Times
There was a positive correlation between the English vocabulary scores and Tamil vocabulary scores, as well as between the English vocabulary scores and the English proficiency scores. The test scores from both the vocabulary tests, English and Tamil, did not, however, correlate with the reading times. For the Tamil X-lex test, the words were taken from a corpora of the 5000 most frequently occurring words in written Tamil from the website Sketch Engine, since there is no comparable corpora for spoken Tamil. While the frequency discrepancy between the most frequent words in Tamil and the most frequent words in a child’s lexicon could also explain the lack of correlation between the test scores and the reading times, for the Tamil test there is an additional factor that should be taken into consideration. Tamil is diglossic in nature—there is a wide gap between the spoken and written forms of the language. The children in this study are more familiar with the spoken form of Tamil because they encounter it far more in daily life than they encounter the written form, as explained earlier. Therefore, their written Tamil vocabulary could be smaller than their written English vocabulary. This could also explain to some extent why the mean score of the Tamil X-lex was much lower than the mean score of the English X-lex; while Tamil is their dominant spoken language, English is the medium of instruction, most written text is in English, and English does not present the additional challenge of diglossia.
Additionally, the method of administration of the test could have affected the test score. In other studies, with children, the test was orally administered (Daller and Ongun 2018) in order to prevent confusion with unfamiliar spellings. In the present study, the children were given copies of the test and asked to circle the words, which may have led to lower scores. For the Tamil test in particular, this could have resulted in the children marking fewer words than they actually knew due to the effect of diglossia.
The scores of the C-test did not correlate with the collocation reading times either. It is not clear why we did not observe this correlation, but it should be noted that a recent meta-analysis highlighted that more work is needed to understand the construct of the C-test and the extent to which it reflects different aspects of language processing (McKay et al. 2021). However, there was still a correlation between the X-lex English score and the C-test scores, showing a correspondence between vocabulary size and language proficiency.
5. Implications of the Findings
From a pedagogical perspective, the overarching finding that the L1 plays a significant role in the processing of L2 collocations for young learners suggests that the L1 should not be ignored when it comes to teaching of collocations. It is well established that knowledge of collocations is essential for progression in proficiency levels, and integrating them into vocabulary teaching and learning is an important step in this direction. Teachers, as well as developers of learning materials, should give special attention to L2-only collocations. Teachers, wherever possible, should be aware of the L1 and whether L2 collocations exist in the L1. This is not feasible in contexts where children may have multiple L1s, but in contexts where all children have the same L1, this can be used to the benefit of both the children and the teacher.
Theoretically, the findings lend support to the developing understanding of dual activation in the bilingual mental lexicon. Despite structural differences, the latest versions of models such as the BIA model (Dijkstra and Van Heuven 1998) and the Multilink model (Dijkstra and Rekké 2010) support the notion that dual activation occurs when a bilingual is presented with a lexical item, although this varies with individual proficiency and the translatability of the item in question. With the contribution of results from the increasing number of experimental studies on the processing of formulaic language, more detailed frameworks and theories can be developed.
6. Limitations of the Study and Recommendations for Future Research
The study had a number of limitations, which must be acknowledged. First, word length and frequency, which are known to influence reading times, were not controlled in the design of the stimuli. To address this, we checked the effects of word length and frequency as follows:
Regarding word frequency, it is established in vocabulary acquisition research that higher-frequency words are processed faster than lower-frequency words due to their increased exposure. It was found that the words with shorter reading times in the study had higher frequencies, supporting previous findings. However, it is worth noting that a study by Schmitt and Underwood (2004) found that the frequency of formulaic language had a significant effect on the processing speed of first-language speakers, but this effect was not observed in bilingual speakers. This discrepancy could be due to the frequency index used, which might not be suitable for bilingual speakers.
Regarding word length, it has been found that shorter words tend to have shorter reading times compared to longer words, which was also true in this study. In future studies, it is important to control for length and frequency to ensure that this does not interfere with analyzing the congruency effect.
Second, the use of self-paced reading as the methodology may have masked subtle differences in reading behavior and, in addition, may compromise natural reading behavior (Paape and Vasishth 2021). Eye-tracking could provide more insights into more natural reading (including regressions to reread parts of text) and should be considered in future research. Third, more objective measures of vocabulary knowledge (rather than relying on children’s own judgments) might have been preferable, especially given the issue with diglossia in Tamil highlighted above. Similarly, while the C-test is widely used in the L2 literature, separate measures of vocabulary, grammar, and other components of language proficiency may have given a more detailed picture of children’s proficiency (in both languages).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.L. and H.J.; Methodology, R.L.; Software, R.L.; Validation, R.L.; Formal analysis, R.L.; Investigation, R.L.; Resources, R.L.; Writing—original draft, R.L.; Writing—review and editing, H.J.; Supervision, H.J. and M.D.; Project administration, R.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Felix Scholarship awarded by the University of Reading.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the University of Reading Ethics Committee (Date of approval: 2 March 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all parents of all subjects involved in the study since the subjects themselves are below the age of consent.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Armon-Lotem, Sharon, Susan Joffe, Hadar Abutbul-Oz, Carmit Altman, and Joel Walters. 2014. Language exposure, ethnolinguistic identity and attitudes in the acquisition of Hebrew as a second language among bilingual preschool children from Russian-and English-speaking backgrounds. Input and Experience in Bilingual Development 13: 77–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyar, Rajamalai Vaidyanatha. 1993. Educational Planning and Administration in India: Retrospect and Prospect. Journal of Educational Planning and Administration 7: 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Babaii, Esmat, and Hasan Ansary. 2001. The C-test: A valid operationalization of reduced redundancy principle? System 29: 209–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatsouli, Elena, and Elena Nicoladis. 2019. The acquisition of English possessives by a bilingual child: Do input and usage frequency matter? Journal of Child Language 46: 170–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonk, William, and Alice F. Healy. 2005. Priming effects without semantic or associative links through collocation. Paper presented at the 46th Annual Meeting of the Psychonomic Society, Toronto, ON, Canada, November 10–13; pp. 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bultena, Sybrine, Ton Dijkstra, and Janet G. Van Hell. 2015. Language switch costs in sentence comprehension depend on language dominance: Evidence from self-paced reading. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 18: 453–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrol, Gareth, and Kathy Conklin. 2020. Is all formulaic language created equal? Unpacking the processing advantage for different types of formulaic sequences. Language and Speech 63: 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrol, Gareth, Kathy Conklin, and Henrik Gyllstad. 2016. Found in translation: The influence of the L1 on the reading of idioms in a L2. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 38: 403–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conklin, Kathy, and Ana Pellicer-Sánchez. 2016. Using eye-tracking in applied linguistics and second language research. Second Language Research 32: 453–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daller, Michael, and Zehra Ongun. 2018. The threshold hypothesis revisited: Bilingual lexical knowledge and non-verbal IQ development. International Journal of Bilingualism 22: 675–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, John. 2014. English as a Medium of Instruction—A Growing Global Phenomenon. London: British Council. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra, Ton, and Steven Rekké. 2010. Towards a localist-connectionist model of word translation. The Mental Lexicon 5: 401–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, Ton, and Walter J. Van Heuven. 1998. The BIA model and bilingual word recognition. In Localist Connectionist Approaches to Human Cognition. London: Psychology Press, pp. 189–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Chen, and Barry L. Reynolds. 2019. The effects of L1 congruency, L2 proficiency, and the collocate-node relationship on the processing of L2 English collocations by L1-Chinese EFL learners. Review of Cognitive Linguistics 17: 331–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnyei, Zoltán, and Lucy Katona. 1992. Validation of the C-test amongst Hungarian EFL learners. Language Testing 9: 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, Philip, and Norbert Schmitt. 2010. Adult learners’ retention of collocations from exposure. Second Language Research 26: 163–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckes, Thomas, and Rüdiger Grotjahn. 2006. A closer look at the construct validity of C-tests. Language Testing 23: 290–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Nan, and Ping Zhang. 2021. L1 congruency, word frequency, collocational frequency, L2 proficiency, and their combined effects on Chinese–English bilinguals’ L2 collocational processing. International Journal of Bilingualism 25: 1429–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargesh, Ravinder. 2006. Language issues in the context of higher education in India. In Symposium on Language Issues in English-Medium Universities across Asia. Pok Fu Lam: University of Hong Kong, pp. 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Grotjahn, Rüdiger. 2022. Konstruktion und Einsatz von C-Tests: Ein Leitfaden für die Praxis. Der C-Test. Theoretische Grundlagen und praktische Anwendungen 4: 211–25. [Google Scholar]
- Harsch, Claudia, and Johannes Hartig. 2015. What are we aligning tests to when we report test alignment to the CEFR? Language Assessment Quarterly 12: 333–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, Birgit. 2013. Research on L2 learners’ collocational competence and development–a progress report. In L2 Vocabulary Acquisition, Knowledge and Use. Edited by Camilla Bardel, Christina Lindqvist and Batia Laufer. Morrisville: Lulu.com, pp. 29–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert, Elfrieda H., Judith A. Scott, Ruben Castaneda, and Alexandra Spichtig. 2019. An analysis of the features of words that influence vocabulary difficulty. Education Sciences 9: 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunston, Susan. 2002. Corpora in Applied Linguistics. Ernst Klett Sprachen. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Nan. 2000. Lexical representation and development in a second language. Applied Linguistics 21: 47–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Soo Hyon, and Ji Hyon Kim. 2012. Frequency effects in L2 multiword unit processing: Evidence from self-paced reading. Tesol Quarterly 46: 831–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, Judith F., and Erika Stewart. 1994. Category interference in translation and picture naming: Evidence for asymmetric connections between bilingual memory representations. Journal of Memory and Language 33: 149–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, Shane, and Gareth M. Gaskell. 2010. A complementary systems account of word learning in L1 and L2. Language Learning 60: 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, Todd H., Yasser Teimouri, Aysenur Sağdıç, Bradford Salen, Derek Reagan, and Margaret E. Malone. 2021. The cagey C-test construct: Some evidence from a meta-analysis of correlation coefficients. System 99: 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, Barry. 1995. Fostering Second Language Development in Young Children: Principles and Practices. Berkeley: UC Berkeley: Center for Research on Education, Diversity and Excellence. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/23s607sr (accessed on 23 September 2024).
- McLaughlin, Barry, ed. 2013. Second Language Acquisition in Childhood: Volume 2: School-Age Children. London: Psychology Press. [Google Scholar]
- Meara, Paul M., and James Milton. 2003. X-lex: The Swansea Levels Test. Berkshire: Express Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Milton, James. 2006. X-Lex: The Swansea vocabulary levels test. In Proceedings of the 7th and 8th Current Trends in English Language testing (CTELT) Conference. Dubai: TESOL Arabia, vol. 4, pp. 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Milton, James. 2007. Lexical profiles, learning styles and the construct validity of lexical size tests. In Modelling and Assessing Vocabulary Knowledge. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, Victoria A. 2014. Second Language Learning in the Early School Years: Trends and Contexts-Oxford Applied Linguistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Northbrook, Julian, and Kathy Conklin. 2019. Is what you put in what you get out?—Textbook-derived lexical bundle processing in beginner English learners. Applied Linguistics 40: 816–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paape, Dario, and Shravan Vasishth. 2021. When Nothing Goes Right, Go Left: A Large-Scale Evaluation of Bidirectional Self-Paced Reading. Available online: https://osf.io/d7pvz (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Paquot, Magali, and Hubert Naets. 2015. Adopting a relational model of co-occurrences to trace phraseological development. Paper presented at the Learner Corpus Research, Nijmegen, The Netherlands, September 11. [Google Scholar]
- Paradis, Johanne, Elena Nicoladis, Martha Crago, and Fred Genesee. 2011. Bilingual children’s acquisition of the past tense: A usage-based approach. Journal of Child Language 38: 554–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirce, Jonathan W. 2007. PsychoPy—psychophysics software in Python. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 162: 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliatsikas, Christos, and Theodoros Marinis. 2013. Processing of regular and irregular past tense morphology in highly proficient second language learners of English: A self-paced reading study. Applied Psycholinguistics 34: 943–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnuchamy, Gitarani. 2012. School English-as-a-Second-Language Experiences of Students at Tertiary Institutions in Tamil Nadu, India: A Phenomenological Study. Ph.D. thesis, University of Phoenix, Phoenix, AZ, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett, Lena K., Jyotsna Vaid, and Sumeyra Tosun. 2016. Of black sheep and white crows: Extending the bilingual dual coding theory to memory for idioms. Cogent Psychology 3: 1135512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, Norbert. 2010. Researching Vocabulary: A Vocabulary Research Manual. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, Norbert, and Geoffrey Underwood. 2004. Exploring the processing of formulaic sequences through a self-paced reading task. In Formulaic Sequences: Acquisition, Processing and Use. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company, pp. 173–89. [Google Scholar]
- Siyanova, Anna, and Norbert Schmitt. 2008. L2 learner production and processing of collocation: A multi-study perspective. Canadian Modern Language Review 64: 429–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyanova-Chanturia, Anna, and Diana V. L. Sidtis. 2018. What online processing tells us about formulaic language. In Understanding Formulaic Language. London: Routledge, pp. 38–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wolter, Brent, and Henrik Gyllstad. 2011. Collocational links in the L2 mental lexicon and the influence of L1 intralexical knowledge. Applied Linguistics 32: 430–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, Brent, and Henrik Gyllstad. 2013. Frequency of input and L2 collocational processing. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 35: 451–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, Brent, and Junko Yamashita. 2018. Word frequency, collocational frequency, L1 congruency, and proficiency in L2 collocational processing: What accounts for L2 performance? Studies in Second Language Acquisition 40: 395–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, Alison. 2002. Formulaic Language and the Lexicon. Port Chester: Cambridge University Press, p. 10573. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, Junko, and Nan Jiang. 2010. L1 influence on the acquisition of L2 collocations: Japanese ESL users and EFL learners acquiring English collocations. Tesol Quarterly 44: 647–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, Virginia, and Stephen Matthews. 2000. Syntactic transfer in a Cantonese–English bilingual child. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 3: 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfikar, Zulfikar. 2019. Rethinking the use of L1 in L2 classroom. Englisia: Journal of Language, Education, and Humanities 6: 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).