A Bi-Gram Approach for an Exhaustive Arabic Triliteral Roots Lexicon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
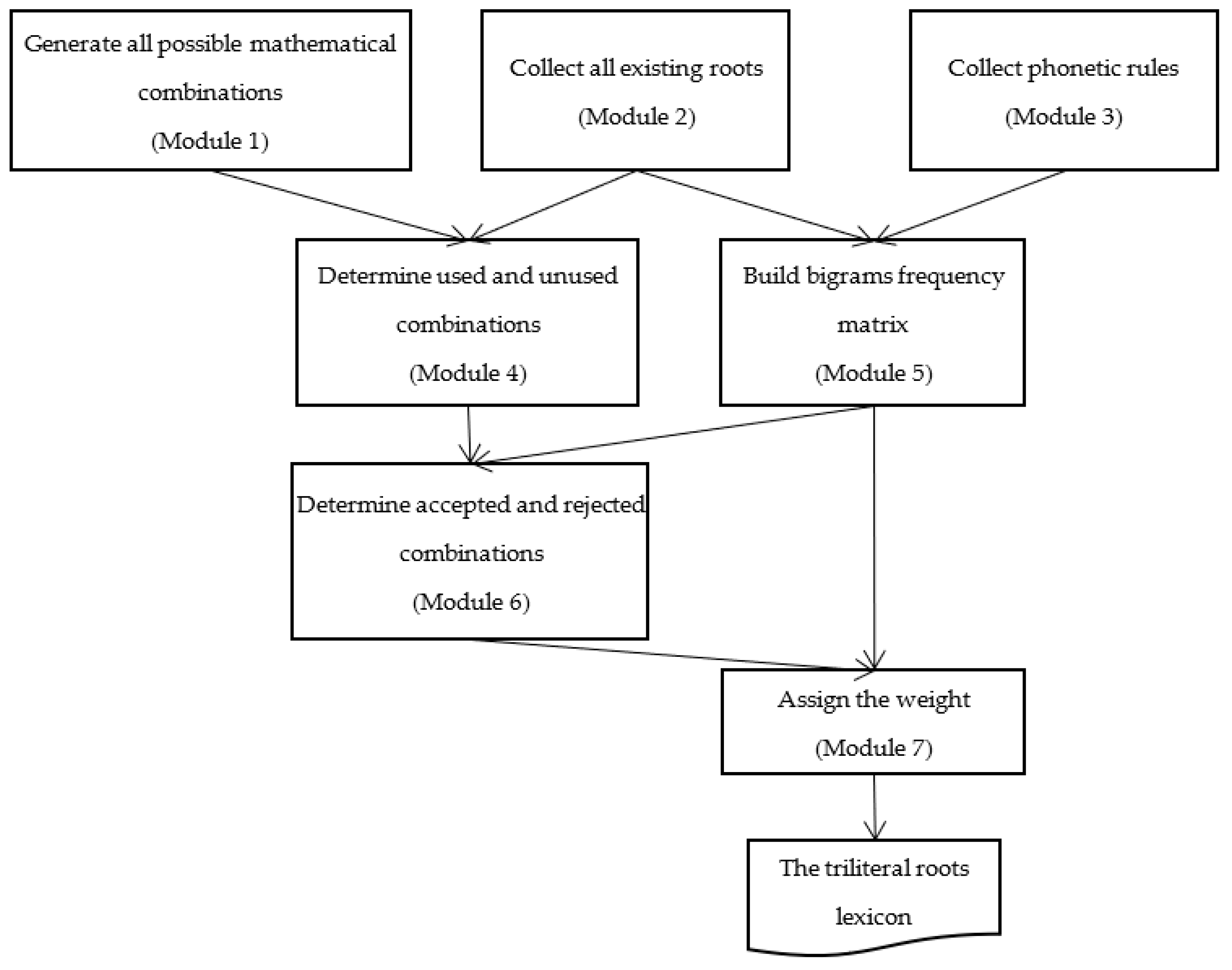
3. Methodology
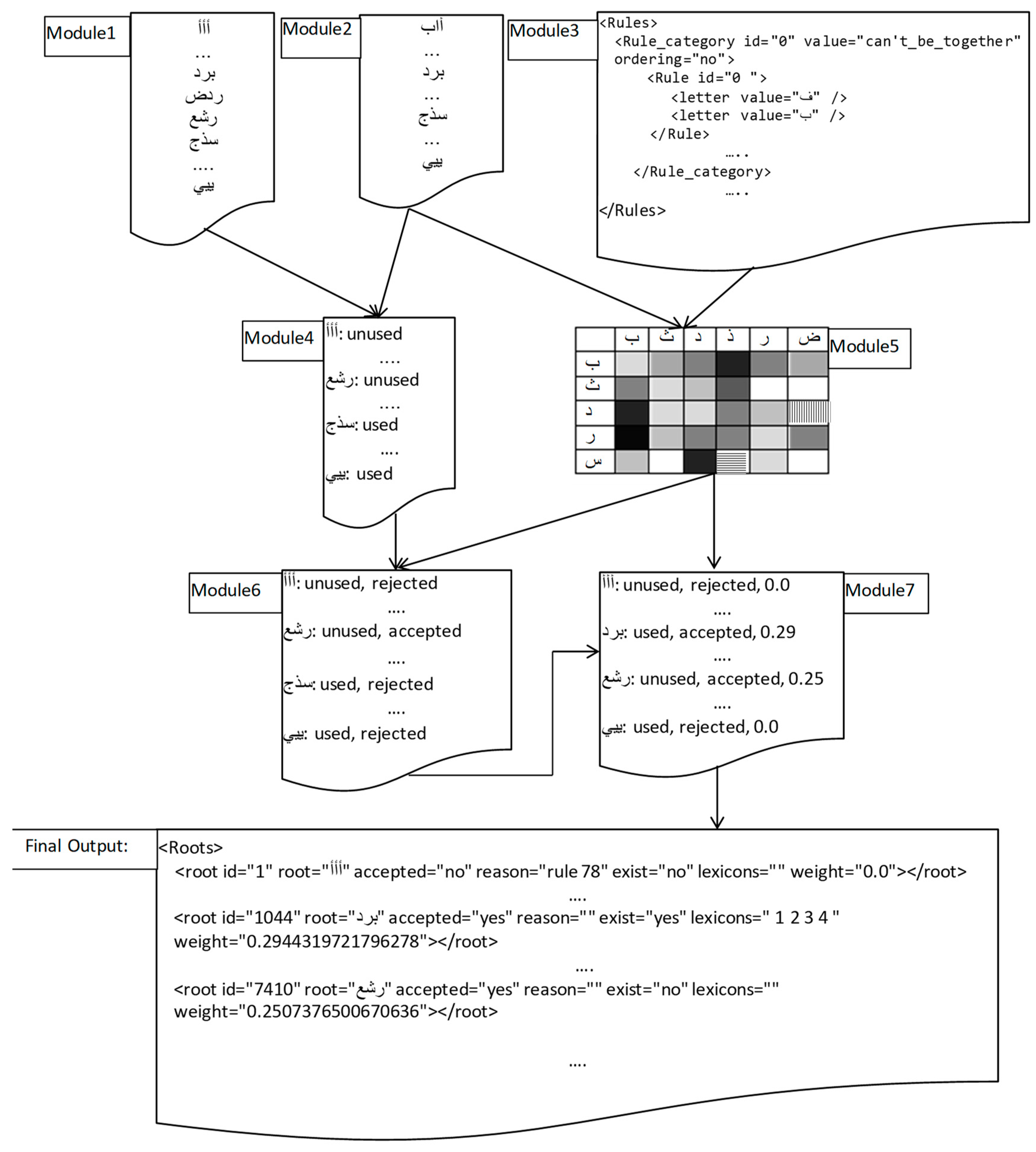
3.1. Generating All Roots
3.2. Collecting the Existing Roots
3.3. Collecting Phonetic Rules
3.4. Building Bigrams Frequency Matrix
3.5. Assigning the Weight
- : .
- weight of the first and second letters bigram
- weight of the second and third letters of bigram
- weight of the first and third letters bigram.
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | All words transliterated according to Buckwalter transliteration (Buckwalter 2002). |
| 2 | The file is available at http://arabic.emi.ac.ma/alelm/#Resources/ (accessed on 4 March 2023). |
References
- Abbas, Hassan. 1998. Khasais Al-Horoof Al-Arbea Wa Maaneeha, 1st ed. Damascus: Etihad Al-Kottab Al-Arb. [Google Scholar]
- Abdoalrasool, Amro Jumaa. 2010. Tatweer Alta’rof Alali Ala Alhoroof Alarabiea Min Khilal Aliea Loghawiea. In International Computing Conference in Arabic. Edited by Yasmine Hammamet, Moncef Charfi and Hani Ammar. Tunisia: Phillips Publishing. Available online: http://www.phillips-publishing.com/ (accessed on 7 October 2020).
- Abusair, Mai I. 2012. Improving Arabic Text Entry Methods Using Word Bigrams Prediction And Keys Reassignment. Paper presented at International Conference on Intelligent Computational Systems, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, January 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Alfozan, Abdulrahman Ibrahim. 1989. Assimilation in Classical Arabic: A Phonological Study. Scotland: University of Glasgow. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Huri, Ibrahim. 2015. Arabic Language: Historic and Sociolinguistic Characteristics. English Literature and Language Review 1: 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ali Al-foadi, Raheem. 2018. Derivation as the Main Way of Adapting New Terms to Arabic. Modern Journal of Language Teaching Methods (MJLTM) 8: 194–99. [Google Scholar]
- Al-kabeerm, Abdollah, Mohammed Ahmed Hasboallah, and Hashim Al-shazli. 1981. Lisan Al-Arab Li Ibn Manzour. Cairo: Dar Al-Maarif. Available online: www.lesanarab.com (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Alm, Yahya Meer, and Shakir Mohammed Al-Faham. 1983. Derasa Ehsaiea Lidwaran Alhoroof Fi Aljozoor Al-Arabiea. Damascus: Damascus University. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Radaideh, Qasem A., and Kamal H. Masri. 2011. Improving Mobile Multi-Tap Text Entry for Arabic Language. Computer Standards & Interfaces 33: 108–13. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Salih, Subhi. 1968. Dirasast Fi Fiqh Al-Lugha, 3rd ed. Lebanon: Dar al-ilm. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shbiel, Abeer Obeid. 2017. Arabization and Its Effect on the Arabic Language. Journal of Language Teaching and Research 8: 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees, Ibrahim, Abdoalhaleem Muntasir, Ateea Al-Swalhi, and Mohammed Khalf-Allah Ahmed. 2004. Al-Mujam Al-Waseet, 4th ed. Cairo: MujamE Allogha Alarbeia-maktabat Alshorooq Aldowaliea. [Google Scholar]
- Aqchaboyevna, Xasanova Mahfuza. 2020. Word-formation in modern english. Science and Education 1: 174–76. [Google Scholar]
- Attar, Ahmed AbdoAlghafoor. 1987. Kitab Al-Sahah Li Aljawhary, 4th ed. Bayrut: Dar al-ilm. [Google Scholar]
- Balabaki, Ramzi Monir. 1987. Jamhrat Al-Logha Li Ibn Duraid, 1st ed. Bayrut: Dar al-ilm. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzoubaa, Karim, Younes Jaafar, Driss Namly, Ridouane Tachicart, Rachida Tajmout, Hakima Khamar, Hamid Jaafar, Si Lhoussain Aouragh, and Abdellah Yousfi. 2021. A Description and Demonstration of SAFAR Framework. Paper presented at the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, Kiev, Ukraine, April 19–23; pp. 127–34. [Google Scholar]
- Brakhw, Abobaker Ali, and Rabea Mansur Milad. 2019. Appropriate strategies to transfer neologisms from english into arabic. International Journal of Research in Humanities, Arts and Literature 7: 351–60. [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter, Tim. 2002. Buckwalter Arabic Morphological Analyzer Version 1.0. Linguistic Data Consortium. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania. [Google Scholar]
- Chomsky, Noam, and Morris Halle. 1968. The Sound Pattern of English. New York: Harper & Row. [Google Scholar]
- Crystal, David. 2011. A Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics. New York: John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, Kareem, Nizar Habash, Mourad Abbas, Hend Al-Khalifa, Huseein T. Al-Natsheh, Samhaa R. El-Beltagy, Houda Bouamor, Karim Bouzoubaa, Violetta Cavalli-Sforza, Wassim El-Hajj, and et al. 2021. A Panoramic Survey of Natural Language Processing in the Arab World. Communications of the ACM, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwaidri, Rajaa Waheed. 2010. Al-Mostalah Al-Elmi Fi Al-Logha Al-Arabiea, Omqaho Al-Turathi Wa Boadho Al-Moassir, 1st ed. Damascus: Dar al-fikr. [Google Scholar]
- Elmgrab, Ramadan Ahmed. 2011. Methods of Creating and Introducing New Terms in Arabic. IPEDR-International Proceedings of Economics Development and Research 26: 491–500. [Google Scholar]
- Elmgrab, Ramadan Ahmed. 2016. The Creation of Terminology in Arabic. American International Journal of Contemporary Research 6: 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, Stefan A., Janet B. Pierrehumbert, and Michael B. Broe. 2004. Similarity Avoidance and the OCP. Natural Language & Linguistic Theory 22: 179–228. [Google Scholar]
- Habash, Nizar. 2010. Introduction to Arabic Natural Language Processing. New York: Columbia University. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, Sameh Saad. 2017. Translating Technical Terms into Arabic: Microsoft Terminology Collection (English-Arabic) as an Example. Translation & Interpreting 9: 67–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hegazi, Mohamed Osman. 2016. An Approach for Arabic Root Generating and Lexicon Development. International Journal of Computer Science and Network (IJCSNS) 16: 9. [Google Scholar]
- Hindawi, Hassan. 1993. Sir Sinaat Al-Erab Li Ibn Jinni. Damascus: Dar Al-Qalam. [Google Scholar]
- Imane, Guellil, Houda Saâdane, Faical Azouaou, Billel Gueni, and Nouvel Damien. 2021. Arabic Natural Language Processing: An Overview. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences 33: 497–507. [Google Scholar]
- Kishli, Ḥikmat. 1996. Kitab Alain Lil-Khalil Ibn Ahmed Al-Farahidi. Bayrut: Dar Al-Kutub Al-Ilmiyah. [Google Scholar]
- Kossmann, Maarten. 2013. Borrowing. In The Oxford Handbook of Arabic Linguistics. Edited by Jonathan Owens. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 349–68. [Google Scholar]
- Musa, Ali Hilmi. 1978. Dirasa Ihsaeia Lijzoor Muajm Al-Sahah Bistikhdam Al-Computer, 1st ed. Ciro: Al-haiaa Al-masriea Al-ama lilkitab. [Google Scholar]
- Nowas, Kefah Ibrahim Mahmoud, Yahia Jabr, and Mohammed Alnory. 2009. Zahirat Al-Osool Almuhmala Fi Alarabiea Abadoha Wa Elaloha. Nanlus: Alnajah Alwataneia. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, Ahmed Mukhtar. 1995. Muhadrat Fi Ilm Alloghah Al-Hadeeth. Ciro: Ealm Alkutub Lilnashr wa altawzeee wa altebaea. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, Ahmed Mukhtar. 2008. Mujam Al-Logha Al-Arabea Al-Moassira, 1st ed. Cairo: Aalm Al-Kutub. [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock, Alan, and C. P. Ormell. 1970. An Introduction to Probability and Statistics. The Mathematical Gazette. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, vol. 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, Ali. 1994. Taj Al-Arous Min Jawahir Al-Qamoos Li Al-Zobaidy. Bayrut: Dar Al-Fikr. [Google Scholar]
- Yenikeyeva, Saniya, and Olga Klymenko. 2021. Synergy of Modern English Word-Formation System. Linguistics and Culture Review, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Triliteral | Quadriliteral | Quinqueliteral | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Sahah | 4814—86% of total | 766 | 38 | 5618 |
| Lisan Al-Erab | 6538—71% | 2548 | 187 | 9273 |
| Taj Al-Arous | 7597—63% | 4081 | 300 | 11,978 |
| Al-Wassit | 5155—78% | 1332 | 153 | 6640 |
| Al-Moassir | 3292—67% | 1092 | 535 | 4919 |
| Possible Roots | Used Roots in Taj Al-Arous | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Triliteral | 21,952 | 7597 | 34.6% |
| Quadriliteral | 548,800 | 4081 | 0.74% |
| Quinqueliteral | 9,765,625 | 300 | 0.003% |
| All possible combinations 21,952 | |||
| Phonetically accepted combinations 13,410 | Phonetically rejected combinations 8542 | ||
| Unused 5383 | Used 8027 | Used 399 | Unused 8143 |
| 8426 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mustafa, E.; Bouzoubaa, K. A Bi-Gram Approach for an Exhaustive Arabic Triliteral Roots Lexicon. Languages 2023, 8, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages8010083
Mustafa E, Bouzoubaa K. A Bi-Gram Approach for an Exhaustive Arabic Triliteral Roots Lexicon. Languages. 2023; 8(1):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages8010083
Chicago/Turabian StyleMustafa, Ebtihal, and Karim Bouzoubaa. 2023. "A Bi-Gram Approach for an Exhaustive Arabic Triliteral Roots Lexicon" Languages 8, no. 1: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages8010083
APA StyleMustafa, E., & Bouzoubaa, K. (2023). A Bi-Gram Approach for an Exhaustive Arabic Triliteral Roots Lexicon. Languages, 8(1), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages8010083





