Crosslinguistic Influence in the Discrimination of Korean Stop Contrast by Heritage Speakers and Second Language Learners
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
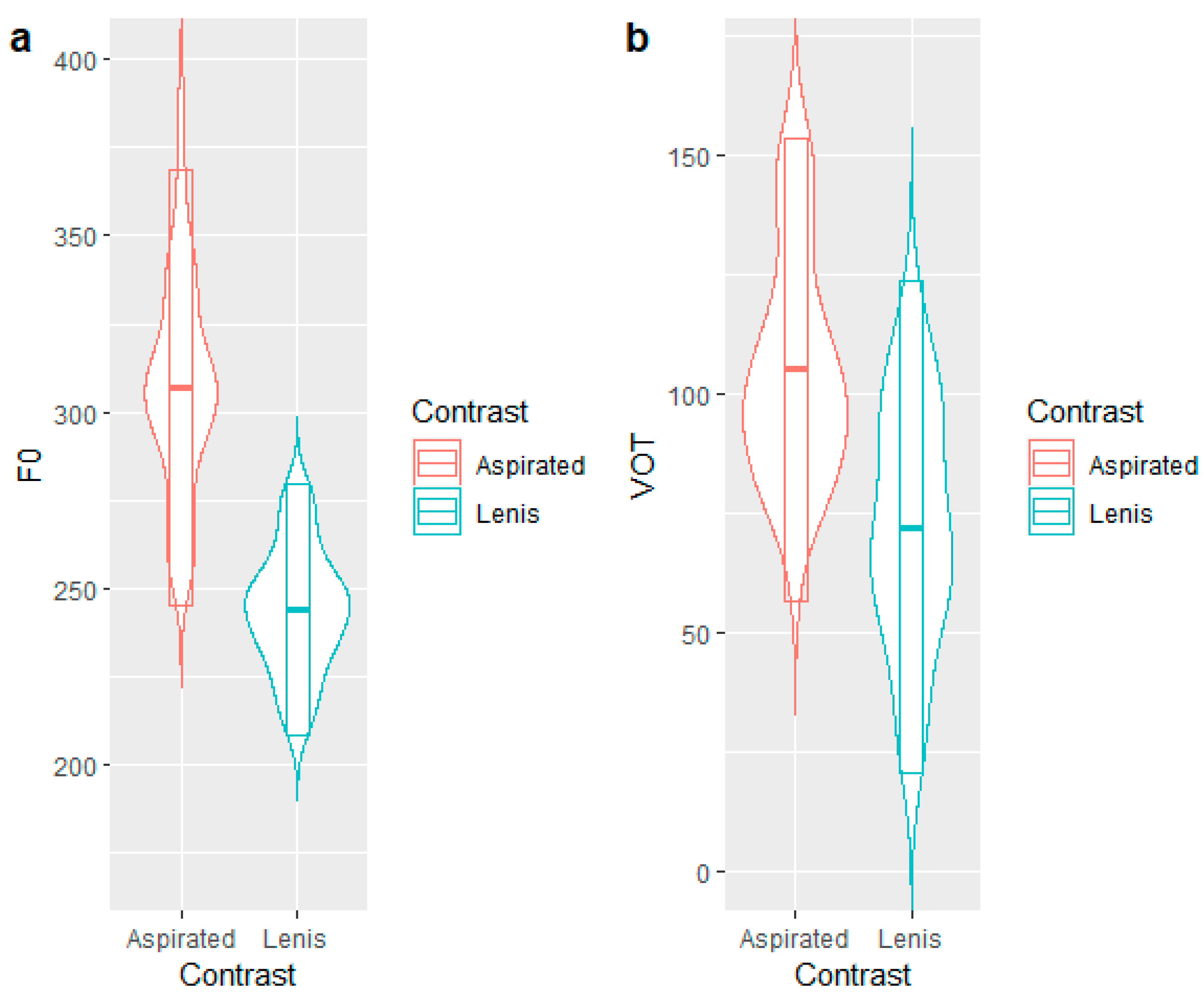
2.2.1. Stimuli for the AX Discrimination Task
2.2.2. Verbal Narrative for Proficiency Estimation
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. AX Discrimination Task
2.3.2. Picture Description Narrative Task
2.4. Analyses
3. Results
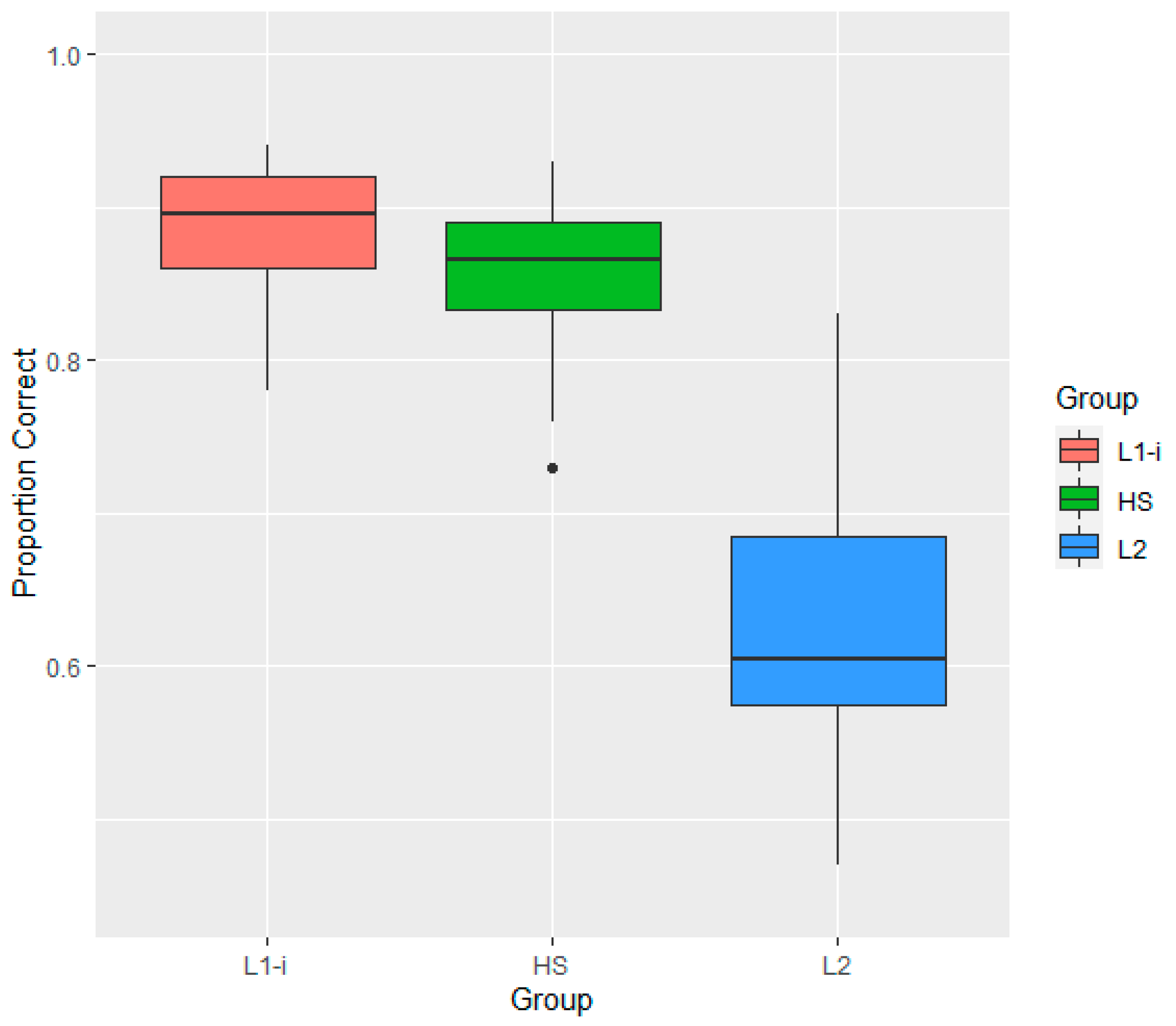
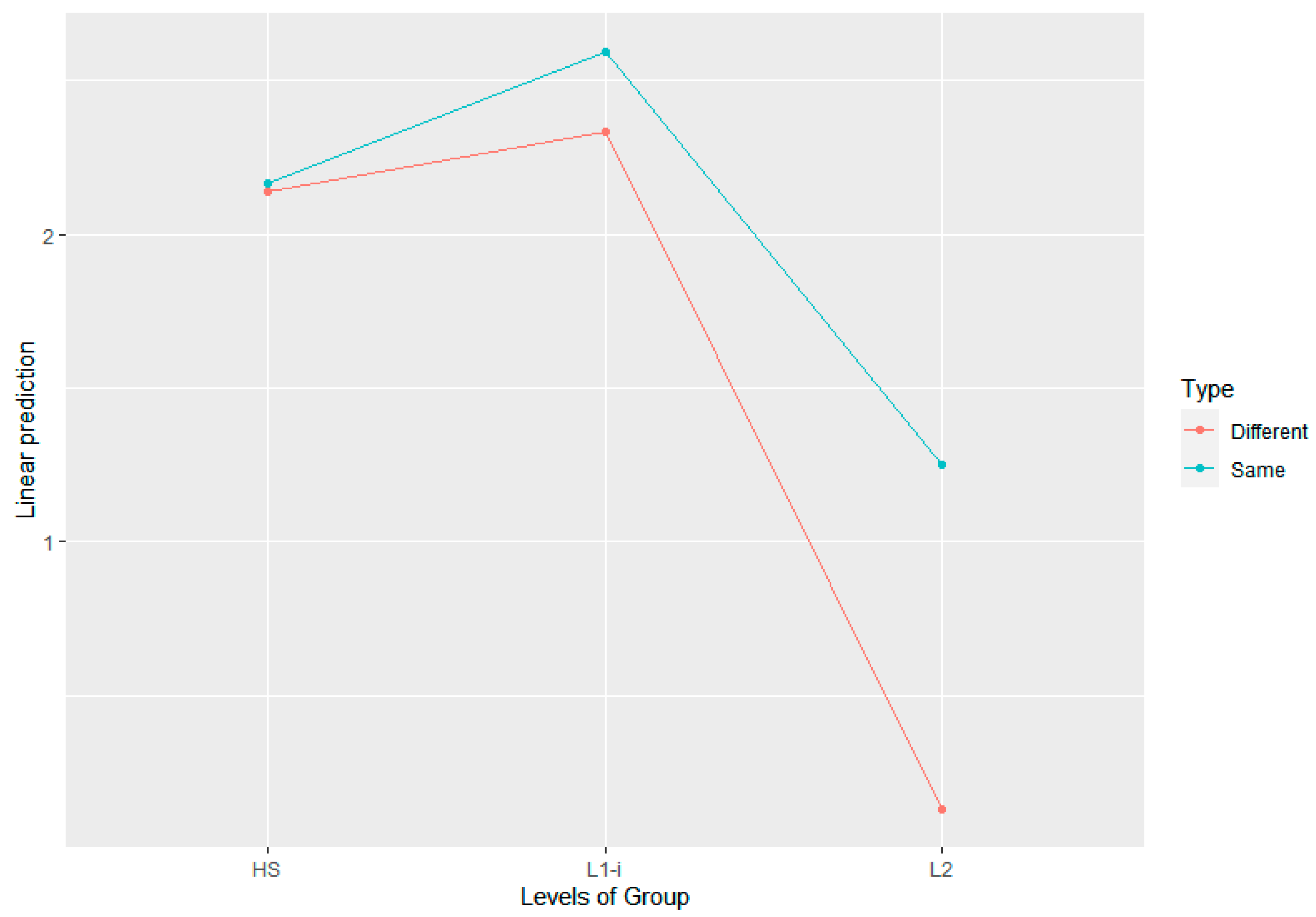
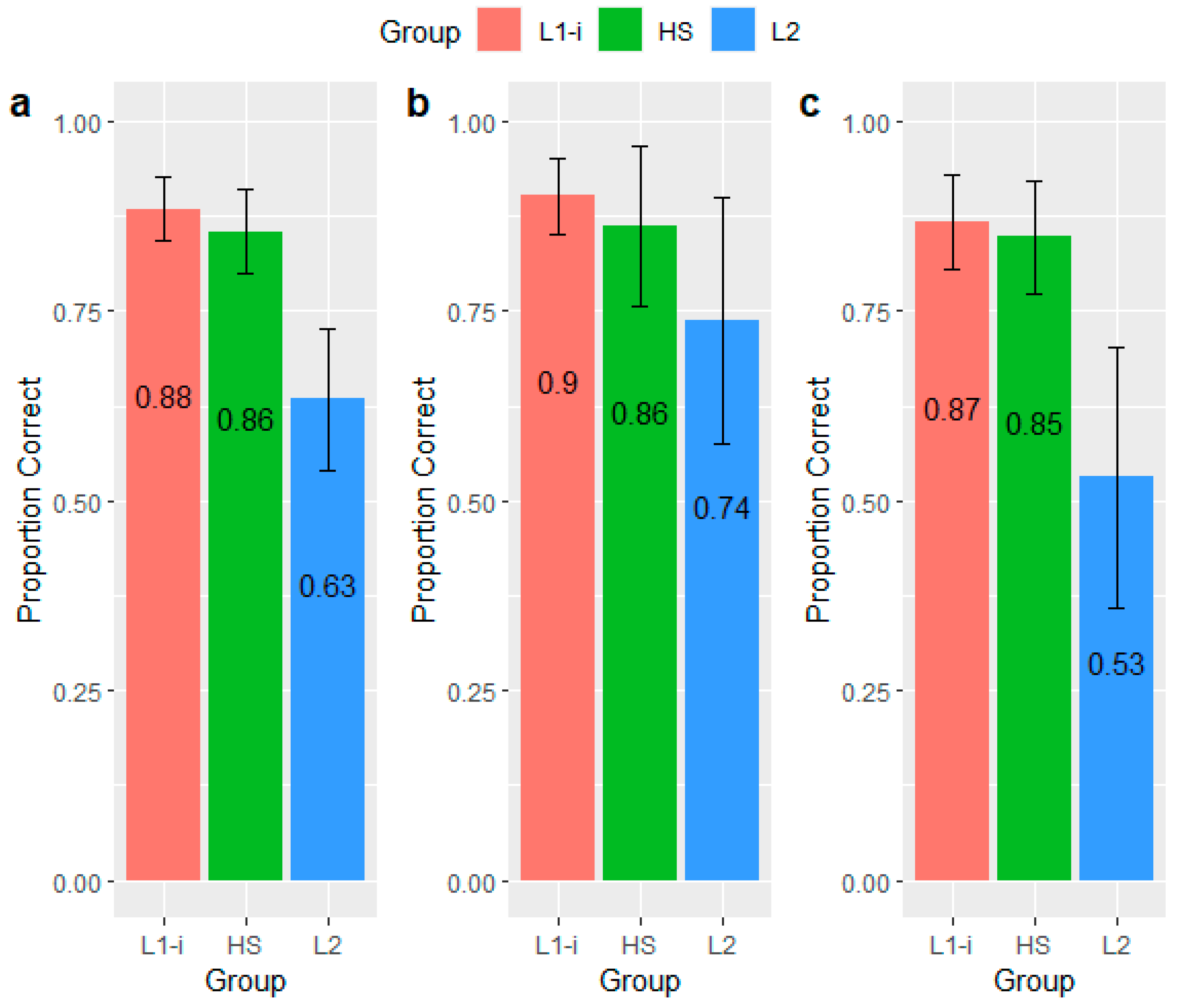
3.1. Effects of Group on Perceptual Accuracy
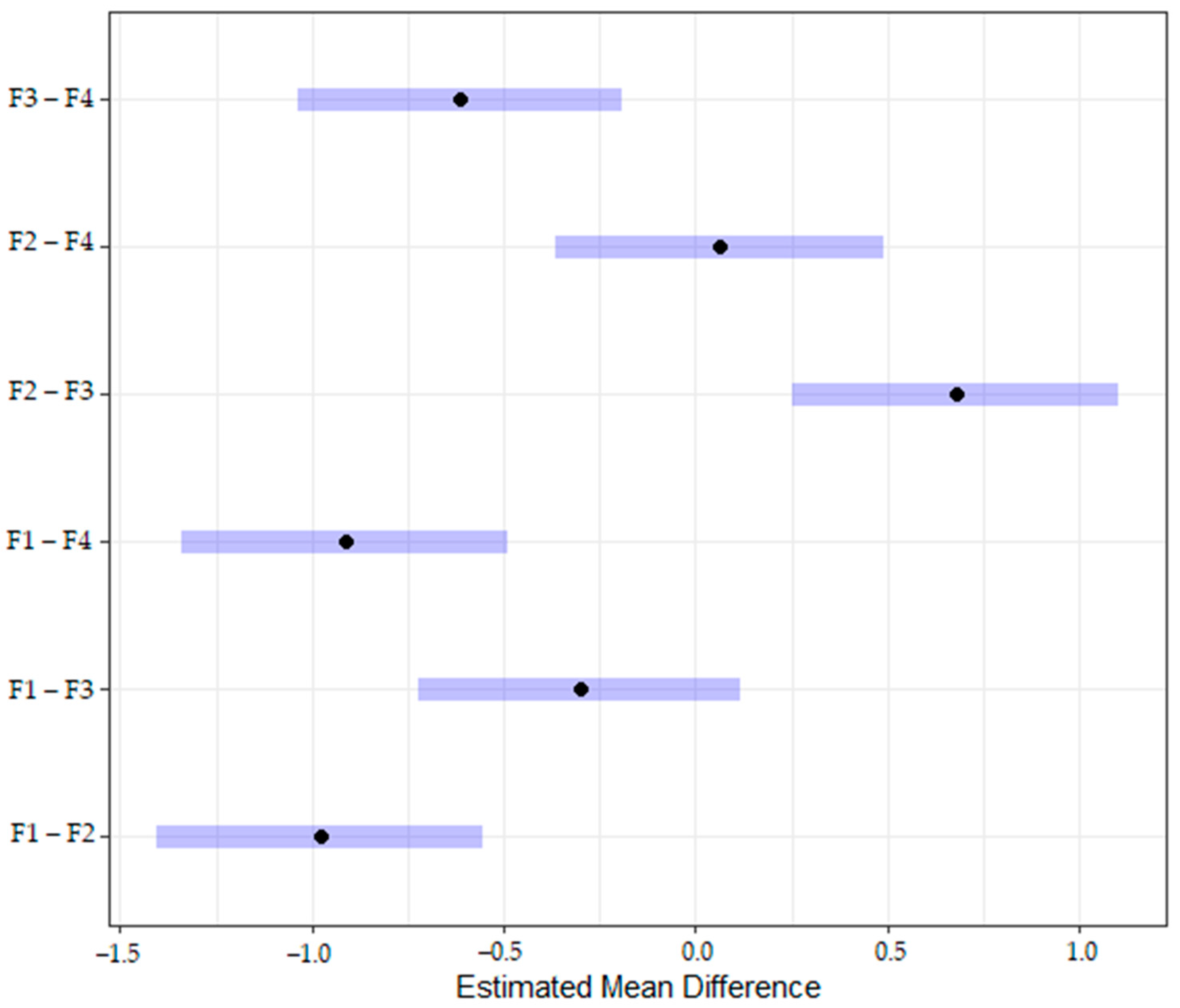
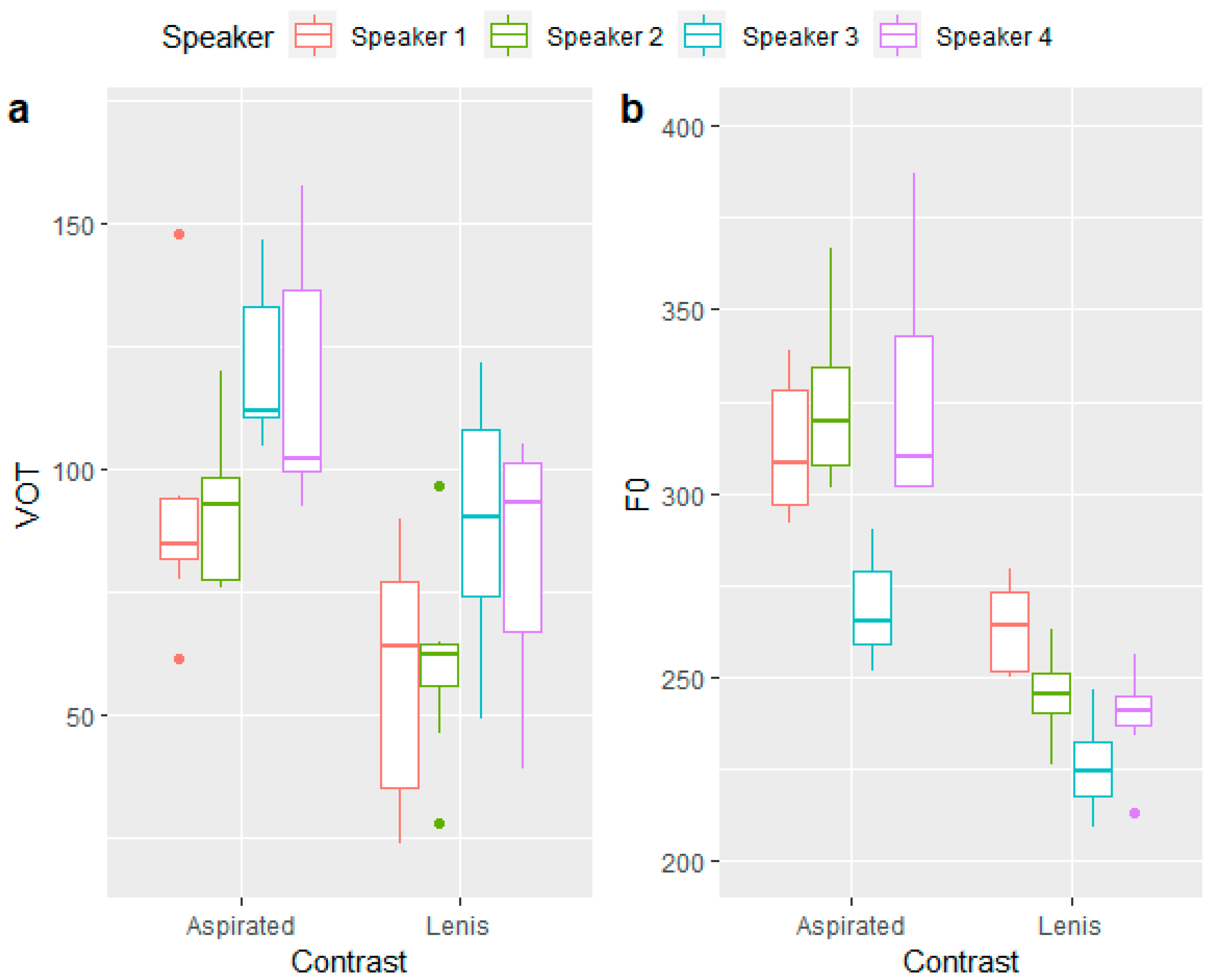
3.2. Effects of Speaker on Perceptual Accuracy
3.3. Effects of Trial Type on Perceptual Accuracy
3.4. Effects of Articulation Rate on Perceptual Accuracy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abramson, Arthur S., and Leigh Lisker. 1985. Relative power of cues: f0 shift versus voice timing. Phonetic Linguistics: Essays in Honor of Peter Ladefoged, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, Sunyoung, Charles B. Chang, Robert DeKeyser, and Sunyoung Lee-Ellis. 2017. Age effects in first language attrition: Speech perception by Korean-English bilinguals. Language Learning 67: 694–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, Mark, Michael D. Tyler, and Catherine T. Best. 2012. Two ways to listen: Do L2-dominant bilinguals perceive stop voicing according to language mode? Journal of Phonetics 40: 582–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwyl-Irvine, Alexander L., Jessica Massonnié, Adam Flitton, Natasha Kirkham, and Jo K. Evershed. 2020. Gorilla in our midst: An online behavioral experiment builder. Behavior Research Methods 52: 388–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, Wendy, and Pavel Trofimovich. 2005. Interaction of native-and second-language vowel system (s) in early and late bilinguals. Language and Speech 48: 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker-Smemoe, Wendy, Dan P. Dewey, Jennifer Bown, and Rob A. Martinsen. 2014. Does measuring L2 utterance fluency equal measuring overall L2 proficiency? Evidence from five languages. Foreign Language Annals 47: 707–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, Hye-Young, Morgan Sonderegger, Yoonjung Kang, Meghan Clayards, and Tae-Jin Yoon. 2018. The emergence, progress, and impact of sound change in progress in Seoul Korean: Implications for mechanisms of tonogenesis. Journal of Phonetics 66: 120–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, Jessica A., Paige E. Branson, and Ignatius S. B. Nip. 2013. Phonetic equivalence in the acquisition of /l/by Spanish–English bilingual children. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 16: 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, Douglas, Martin Mächler, Ben Bolker, and Steve Walker. 2015. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software 67: 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, Christopher, Amber Nota, Simone A. Sprenger, and Monika S. Schmid. 2016. L2 Immersion Causes Non-Native-like L1 Pronunciation in German Attriters. Journal of Phonetics 58: 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernthal, John E., Nicholas W. Bankson, and Peter Flipsen, Jr. 2013. Articulation and Phonological Disorders: Speech Sound Disorders in Children. Boston: Pearson. [Google Scholar]
- Boersma, Paul, and David Weenink. 2021. Praat: Doing Phonetics by Computer [Computer Program]. Version 6.1.40. Available online: http://www.praat.org/ (accessed on 27 February 2021).
- Caramazza, Alfonso, Grace H. Yeni-Komshian, Edgar B. Zurif, and Ettore Carbone. 1973. The acquisition of a new phonological contrast: The case of stop consonants in French-English bilinguals. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 54: 421–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, Juli. 2006. Experience and the use of non-native duration in L2 vowel categorization. Journal of Phonetics 34: 372–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Charles. B. 2012. Rapid and multifaceted effects of second-language learning on first-language speech production. Journal of Phonetics 40: 249–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Charles B. 2016. Bilingual perceptual benefits of experience with a heritage language. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 19: 791–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Charles B. 2021. Phonetics and phonology of heritage languages. In The Cambridge Handbook of Heritage Languages and Linguistics. Edited by Sivina Montrul and Maria Polinsky. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 581–612. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Seung-Eun, and Karina Mandock. 2019. A phonetic study of Korean heritage learners’ production of Korean word-initial stops. Heritage Language Journal 16: 273–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Andrew. 2017. VOT merger and f0 contrast in Heritage Korean in California. UC Berkeley PhonLab Annual Report 13: 281–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, Sang Yee, and Teresa Lee. 2013. The perception of Korean stops by heritage and non-heritage learners: Pedagogical implications for beginning learners. Korean Language in America 18: 23–39. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/42922375 (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Cho, Taehong, Sun-Ah Jun, and Peter Ladefoged. 2002. Acoustic and aerodynamic correlates of Korean stops and fricatives. Journal of Phonetics 30: 193–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Youngon, Minji Nam, Reiko Mazuka, Hyun-Kyung Hwang, Minha Shin, Jisoo Kim, Sunho Jung, Jimin Beom, and Naoto Yamane. 2019. Development of speech perception in Korean infants: Discriminating unusual sound contrasts with diachronic change. Paper presented at the 2nd Hanyang International Symposium on Phonetics and Cognitive Sciences of Language, Seoul, Korea, May 24–25; pp. 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cuza, Alejandro. 2010. The L2 acquisition of aspectual properties in Spanish. Canadian Journal of Linguistics 55: 1001–28. [Google Scholar]
- De Jong, Nivja H. 2018. Fluency in second language testing: Insights from different disciplines. Language Assessment Quarterly 15: 237–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, Nivja H., and Ton Wempe. 2009. Praat script to detect syllable nuclei and measure speech rate automatically. Behavior Research Methods 41: 385–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrieva, Olga. 2019. Transferring perceptual cue-weighting from second language into first language: Cues to voicing in Russian speakers of English. Journal of Phonetics 73: 128–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrieva, Olga, Allard Jongman, and Joan Sereno. 2010. Phonological Neutralization by Native and Non-Native Speakers: The Case of Russian Final Devoicing. Journal of Phonetics 38: 483–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrieva, Olga, Fernando Llanos, Amanda A. Shultz, and Alexander L. Francis. 2015. Phonological status, not voice onset time, determines the acoustic realization of onset f0 as a secondary voicing cue in Spanish and English. Journal of Phonetics 49: 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, Paola. 2000. Developmental Patterns in the Adult L2 Acquisition of New Contrasts: The Acoustic Cue Weighting in the Perception of Scottish Tense/Lax Vowels by Spanish Ppeakers. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Escudero, Paola. 2001. The role of the input in the development of L1 and L2 sound contrasts: Language-specific cue weighting for vowels. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual Boston University Conference on Language Development. Somerville: Cascadilla Press, vol. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Flege, James Emil. 1987. The production of “new” and “similar” phones in a foreign language: Evidence for the effect of equivalence classification. Journal of Phonetics 15: 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flege, James E. 1995. Second Language Speech Learning Theory, Findings, and Problems. In Speech Perception and Linguistic Experience: Issues in Cross-Language Research. Edited by Winifred Strange. Timonium: York Press, pp. 233–77. [Google Scholar]
- Flege, James E. 2003. Assessing Constraints on Second-Language Segmental Production and Perception James Emil Flege. In Phonetics and Phonology in Language Comprehension and Production: Differences and Similarities. Edited by Antje S. Meyer and Niels O. Schiller. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter, pp. 319–58. [Google Scholar]
- Flege, James E., and Ocke-Schwen Bohn. 2020. The revised speech learning model (SLM-r). In Second Language Speech Learning: Theoretical and Empirical Progress. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 3–83. [Google Scholar]
- Flege, James E., and Wieke Eefting. 1987a. Production and perception of English stops by native Spanish speakers. Journal of Phonetics 15: 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flege, James E., and Wieke Eefting. 1987b. Cross-language switching in stop consonant perception and production by Dutch speakers of English. Speech Communication 6: 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, Carol A., Valery Sramko, David J. Ostry, Sarah A. Rowland, and Pierre Hallé. 2008. Cross Language Phonetic Influences on the Speech of French-English Bilinguals. Journal of Phonetics 36: 649–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sierra, Adrian, Randy L. Diehl, and Craig Champlin. 2009. Testing the double phonemic boundary in bilinguals. Speech Communication 51: 369–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginther, April, Slobodanka Dimova, and Rui Yang. 2010. Conceptual and empirical relationships between temporal measures of fluency and oral English proficiency with implications for automated scoring. Language Testing 27: 379–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guion, Susan G. 2003. The vowel systems of Quichua-Spanish bilinguals. Phonetica 60: 98–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Mieko S., and Raymond S. Weitzman. 1970. Acoustic features of Korean /P, T, K/,/p, t, k/and/ph, th, kh. Phonetica 22: 112–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazan, Valerie L., and Georges Boulakia. 1993. Perception and production of a voicing contrast by French-English bilinguals. Language and Speech 36: 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, Tetsuo. 2003. L2 influence on L1 speech in the production of VOT. Paper presented at the 15th International Congress of Phonetic Sciences, Barcelona, Spain, August 3–9; Edited by Maria-Josep Solé, Daniel Recasens and Joaquín Romero. Barcelona: Causal Productions, pp. 1085–88. [Google Scholar]
- House, Arthur S., and Grant Fairbanks. 1953. The influence of consonant environment upon the secondary acoustical characteristics of vowels. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 25: 105–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idemaru, Kaori, Lori L. Holt, and Howard Seltman. 2012. Individual differences in cue weights are stable across time: The case of Japanese stop lengths. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 132: 3950–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Sun-Ah. 2007. Phonological development of Korean: A case study. UCLA Working Papers in Phonetics 105: 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Kagaya, Ryohei. 1974. A fiberscopic and acoustic study of the Korean stops, affricates and fricatives. Journal of Phonetics 2: 161–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Kyoung-Ho, and Susan G. Guion. 2006. Phonological systems in bilinguals: Age of learning effects on the stop consonant systems of Korean-English bilinguals. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 119: 1672–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Kyoung-Ho, and Susan G. Guion. 2008. Clear speech production of Korean stops: Changing phonetic targets and enhancement strategies. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 124: 3909–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Okim, Don Rubin, and Lucy Pickering. 2010. Suprasegmental measures of accentedness and judgments of language learner proficiency in oral English. The Modern Language Journal 94: 554–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Yoonjung. 2014. Voice onset time merger and development of tonal contrast in Seoul Korean stops: A corpus study. Journal of Phonetics 45: 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Yoonjung, and Naomi Nagy. 2016. VOT merger in Heritage Korean in Toronto. Language Variation and Change 28: 249–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Mi-Ran Cho. 1994. Acoustic Characteristics of Korean Stops and Perception of English Stop Consonants. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Mi-Ryoung. 2012. L1-L2 transfer in VOT and f0 production by Korean English learners: L1 sound change and L2 stop production. Phonetics and Speech Sciences 4: 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, Mi-Ryoung, Patrice Speeter Beddor, and Julie Horrocks. 2002. The contribution of consonantal and vocalic information to the perception of Korean initial stops. Journal of Phonetics 30: 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Minjung, and Carol Stoel-Gammon. 2009. The acquisition of Korean word-initial stops. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 125: 3950–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Eon-suk. 2018. Mothers would rather speak clearly than spread innovations: The case of Korean VOT. Paper presented at the 1st Hanyang International Symposium on Phonetics and Cognitive Sciences of Languages, Seoul, Korea, May 18–19; pp. 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Eun Jong. 2012. Perception of Korean stops with a three-way laryngeal contrast. Phonetics and Speech Sciences 4: 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kong, Eun Jong, and Hyunjung Lee. 2018. Attentional modulation and individual differences in explaining the changing role of fundamental frequency in Korean laryngeal stop perception. Language and Speech 61: 384–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Eun Jong, and In Hee Yoon. 2013. L2 proficiency effect on the acoustic cue-weighting pattern by Korean L2 learners of English: Production and perception of English stops. Phonetics and Speech Sciences 5: 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Eun Jong, Mary E. Beckman, and Jan Edwards. 2011. Why are Korean tense stops acquired so early?: The role of acoustic properties. Journal of Phonetics 39: 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormos, Judit, and Mariann Dénes. 2004. Exploring measures and perceptions of fluency in the speech of second language learners. System 32: 145–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Benjamin, and Lisa Davidson. 2019. Effects of exposure and vowel space distribution on phonetic drift: Evidence from American English learners of French. Language and Speech 62: 30–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Ellis, Sungyoung. 2012. Looking into Bilingualism through the Heritage Speaker’s Mind. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Hyunjung, and Allard Jongman. 2019. Effects of sound change on the weighting of acoustic cues to the three-way laryngeal stop contrast in Korean: Diachronic and dialectal comparisons. Language and Speech 62: 509–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Hyunjung, Jeffrey J. Holliday, and Eun Jong Kong. 2020. Diachronic change and synchronic variation in the Korean stop laryngeal contrast. Language and Linguistics Compass 14: e12374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Hyunjung, Stephen Politzer-Ahles, and Allard Jongman. 2013. Speakers of tonal and non-tonal Korean dialects use different cue weightings in the perception of the three-way laryngeal stop contrast. Journal of Phonetics 41: 117–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Sue Ann S., and Gregory K. Iverson. 2012. Stop consonant productions of Korean–English bilingual children. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 15: 275–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehiste, Ilse, and Gordon E. Peterson. 1961. Some basic considerations in the analysis of intonation. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 33: 419–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanos, Fernando, Olga Dmitrieva, Amanda Shultz, and Alexander L. Francis. 2013. Auditory enhancement and second language experience in Spanish and English weighting of secondary voicing cues. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 134: 2213–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, Joanna H., and Susan Nittrouer. 2008. Patterns of acquisition of native voice onset time in English-learning children. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 124: 1180–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanchenko, Anna, and Kyra Gor. 2011. Perceptual correlates of phonological representations in heritage speakers and L2 learners. Paper presented at the 35th Annual Boston University Conference on Language Development, Boston, MA, USA, November 5–7; Somerville, MA: Cascadilla Press, vol. 2, pp. 414–26. [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod, Andrea A. N., Carol Stoel-Gammon, and Alicia B. Wassink. 2009. Production of high vowels in Canadian English and Canadian French: A comparison of early bilingual and monolingual speakers. Journal of Phonetics 37: 374–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, Roy C. 1992. Losing English as a first language. The Modern Language Journal 76: 190–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, Viorica, Henrike K. Blumenfeld, and Margarita Kaushanskaya. 2007. The language experience and proficiency questionnaire (LEAP-Q): Assessing language profiles in bilinguals and multilinguals. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing 50: 940–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrul, Silvina. 2002. Incomplete acquisition and attrition of Spanish tense/aspect distinction in adult bilinguals. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 5: 39–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Naomi, and Marisa Brook. 2020. Constraints on speech rate: A heritage-language perspective. Special Issue: Effects of Limited Input. International Journal of Bilingualism, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Eunhae. 2019. Korean-English bilingual children’s production of stop contrasts. Phonetics and Speech Sciences 11: 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Janet S., Sun-Ah Jun, Leah M Knightly, and Terry Kit-fong Au. 2003. Holding on to childhood language memory. Cognition 86: B53–B64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Janet S., Terry Kit-Fong Au, and Sun-Ah Jun. 2010. Early childhood language memory in the speech perception of international adoptees. Journal of Child Language 37: 1123–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Mira, and Robert Daland. 2011. Stops and phrasing in Korean and English monolinguals and bilinguals. Paper presented at the 17th International Congress of Phonetic Sciences, Hongkong, China, August 17–21; pp. 1530–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ohde, Ralph N. 1984. Fundamental frequency as an acoustic correlate of stop consonant voicing. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 75: 224–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Shu-hui. 1993. Cross-language influence on the production of Mandarin /f/ and /x/ and Taiwanese /h/ by native speakers of Taiwanese Amoy. Phonetica 50: 245–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinsky, Maria. 2008. Gender under incomplete acquisition: Heritage speakers’ knowledge of noun categorization. Heritage Language Journal 6: 40–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinsky, Maria. 2011. Reanalysis in adult heritage language: New evidence in support of attrition. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 33: 305–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinsky, Maria, and Olga Kagan. 2007. Heritage languages: In the ‘wild’ and in the classroom. Language and Linguistics Compass 1: 368–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, Raúl, and Aquiles Iglesias. 2013. The language growth of Spanish-speaking English language learners. Child Development 84: 630–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. 2020. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Boston: Rstudio Team. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Sancier, Michele L., and Carol A. Fowler. 1997. Gestural drift in a bilingual speaker of Brazilian Portuguese and English. Journal of Phonetics 25: 421–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, Anna M. 1996. Cross-language identification of consonants. Part 1. Korean perception of English. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 99: 3201–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, Anna M. 2007. Cross-language consonant identification. In Language Experience in Second Language Speech Learning: In Honor of James Emil Flege. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company, vol. 17, pp. 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastián, Eugenia, and Dan I. Slobin. 1994. Development of linguistic forms: Spanish. In Relating Events in Narrative: A Crosslinguistic Developmental Study. Edited by Ruth A. Berman and Dan I. Slobin. Hillsdale: Erlbaum, pp. 239–84. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, David J. 2006. Acoustic evidence for the emergence of tonal contrast in contemporary Korean. Phonology 23: 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Gayeon. 2020. Korean-speaking children’s perceptual development in multidimensional acoustic space. Journal of Child Language 47: 579–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoehr, Antje, Titia Benders, Janet G. Van Hell, and Paula Fikkert. 2017. Second language attainment and first language attrition: The case of VOT in immersed Dutch–German late bilinguals. Second Language Research 33: 483–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundara, Megha, and Shari Baum. 2006. Production of coronal stops by simultaneous bilingual adults. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 9: 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tees, Richard C., and Janet F. Werker. 1984. Perceptual flexibility: Maintenance or recovery of the ability to discriminate nonnative speech sounds. Canadian Journal of Psychology 38: 579–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Census Bureau. 2018. Detailed Languages Spoken at Home and Ability to Speak English for the Population 5 Years and over for United States: 2014–2018. Available online: https://data.census.gov/cedsci/table?q=Languages&hidePreview=true&tid=ACSST1Y2018.S1601&vintage=2018 (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Valdés, Guadalupe. 2000. Introduction. Spanish for Native Speakers. AATSP Professional Development Series Handbook for Teachers K-16. New York: Harcourt College, vol. I. [Google Scholar]
- Valdés, Guadalupe. 2005. Bilingualism, heritage learners, and SLA research: Opportunities lost or seized? Modern Language Journal 89: 410–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werker, Janet F. 1989. Becoming a native listener. American Scientist 77: 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Whalen, Douglas H., Arthur S. Abramson, Leigh Lisker, and Maria Mody. 1993. F0 gives voicing information even with unambiguous voice onset times. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 93: 2152–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Reiko A., and Yoh’ichi Tohkura. 1990. Perception and production of syllable-initial English /r/ and /l/ by native speakers of Japanese. Paper presented at First International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, Tokyo, Japan, November 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, Reiko A., and Yoh’Ichi Tohkura. 1992. The effects of experimental variables on the perception of American English /r/ and /l/ by Japanese listeners. Perception & Psychophysics 52: 376–92. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Sook-Youn. 2015. Acoustic properties of Korean stops as L1 produced by L2 learners of the English language. Communication Science & Disorders 20: 178–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Question | HS | L2 | L1-i |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 25.5 (5.9) | 26.3 (7.2) | 24.2 (3.3) |
| AOA (HS, L1-i: English, L2: Korean) | 2.1 (1.6) | 22.3 (9.5) | 7.5 (2.9) |
| Current exposure to Korean a | 39% (20.4%) | 17% (13%) | 76.1% (27.7%) |
| Percentage of choosing to speak Korean over English b | 30.4% (27.9%) | 17.1% (19.2%) | 69.1% (35.2%) |
| Korean speaking proficiency c | 4.7 (1.6) | 2.7 (1.8) | 6.9 (0.3) |
| Korean comprehension | 5.1 (1.3) | 3 (1.8) | 6.9 (0.3) |
| English speaking proficiency | 6.8 (0.7) | 7 (0) | 3.3 (1.4) |
| English comprehension | 6.7 (1.3) | 7 (0) | 4.2 (1.4) |
| Estimate | SE | z-Value | p-Value | Odds Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 1.59 | 0.17 | 9.23 | <0.001 | 4.90 |
| Group L1-i | 0.20 | 0.17 | 1.18 | 0.24 | 1.22 |
| Group L2 | −2.01 | 0.16 | −12.33 | <0.001 | 0.13 |
| TypeSame | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.84 | 1.03 |
| Speaker 2 | 0.98 | 0.17 | 5.92 | <0.001 | 2.66 |
| Speaker 3 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 1.85 | 0.06 | 1.35 |
| Speaker 4 | 0.91 | 0.16 | 5.55 | <0.001 | 2.50 |
| Group L1-i:TypeSame | 0.23 | 0.12 | 1.95 | 0.05 | 1.26 |
| Group L2:TypeSame | 1.10 | 0.10 | 10.56 | <0.001 | 2.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, Y.; Dmitrieva, O.; Cuza, A. Crosslinguistic Influence in the Discrimination of Korean Stop Contrast by Heritage Speakers and Second Language Learners. Languages 2022, 7, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages7010006
Seo Y, Dmitrieva O, Cuza A. Crosslinguistic Influence in the Discrimination of Korean Stop Contrast by Heritage Speakers and Second Language Learners. Languages. 2022; 7(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages7010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Yuhyeon, Olga Dmitrieva, and Alejandro Cuza. 2022. "Crosslinguistic Influence in the Discrimination of Korean Stop Contrast by Heritage Speakers and Second Language Learners" Languages 7, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages7010006
APA StyleSeo, Y., Dmitrieva, O., & Cuza, A. (2022). Crosslinguistic Influence in the Discrimination of Korean Stop Contrast by Heritage Speakers and Second Language Learners. Languages, 7(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages7010006






