The Phonetics of Tone and Voice Quality Interactions in Sylheti
Abstract
1. Introduction
The Language: Sylheti
2. Phonation Types
Acoustic Correlates of Phonation
3. Methods
3.1. Speakers and Data
3.2. Data Annotation and Acoustic Measures
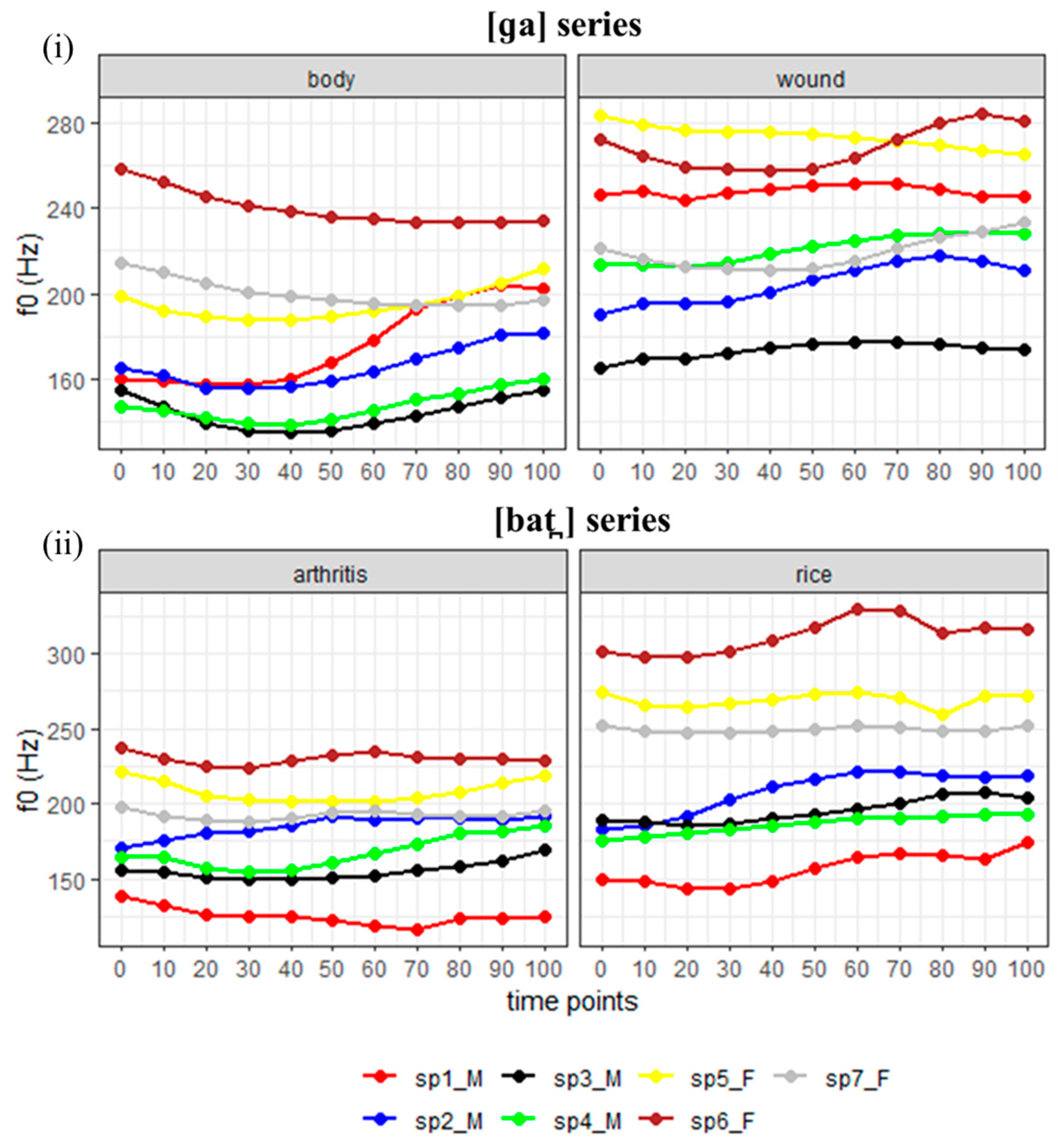
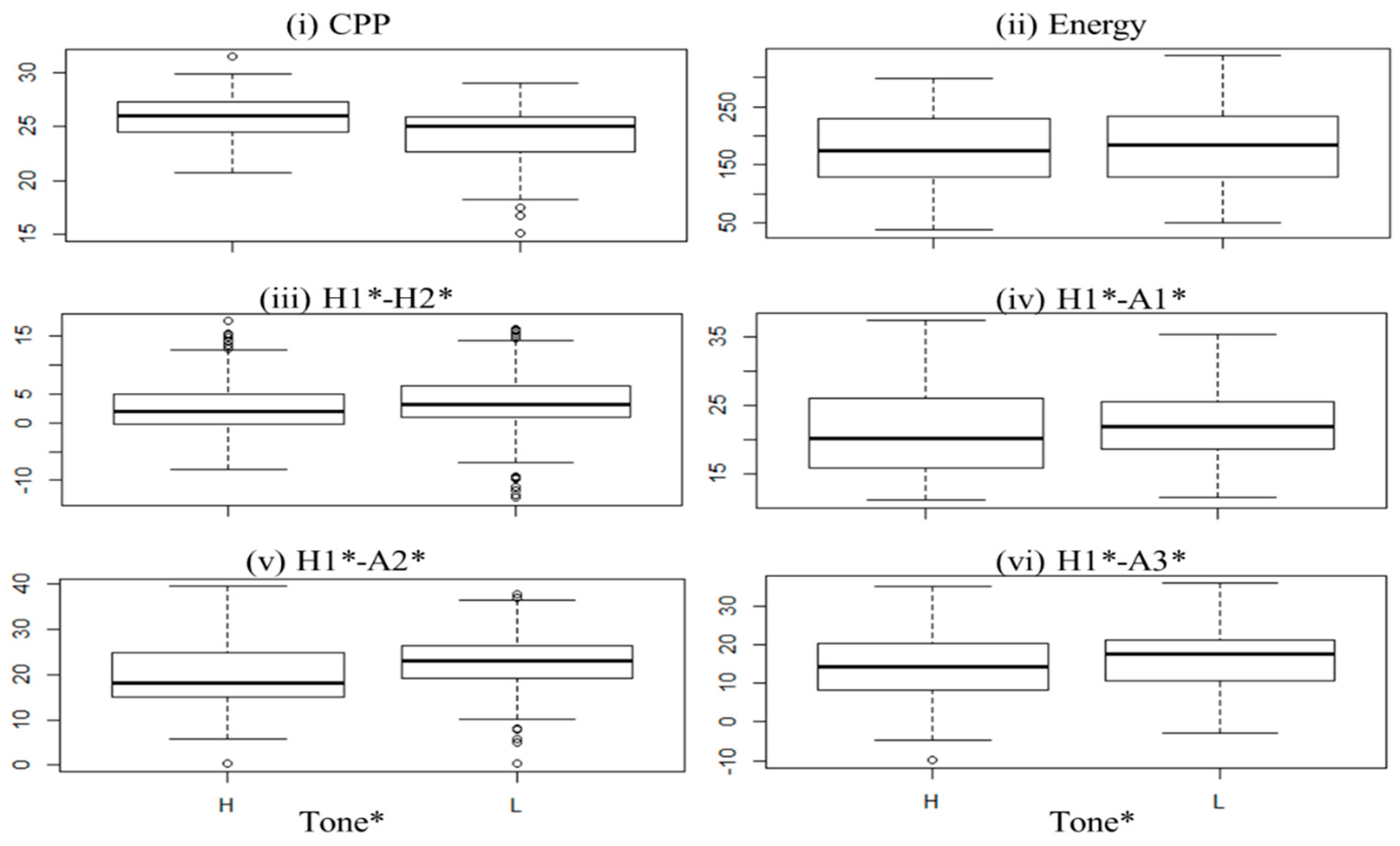
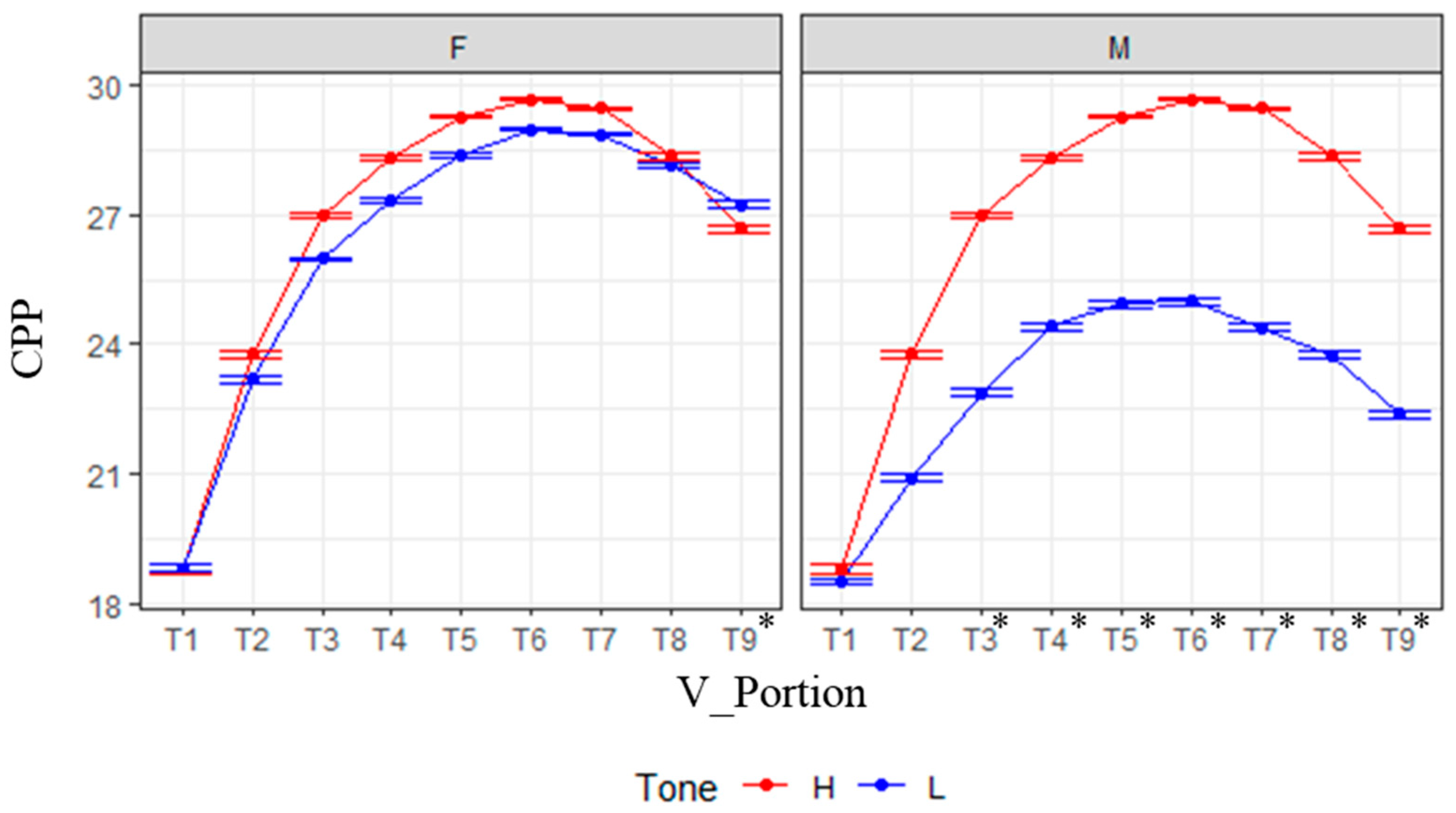
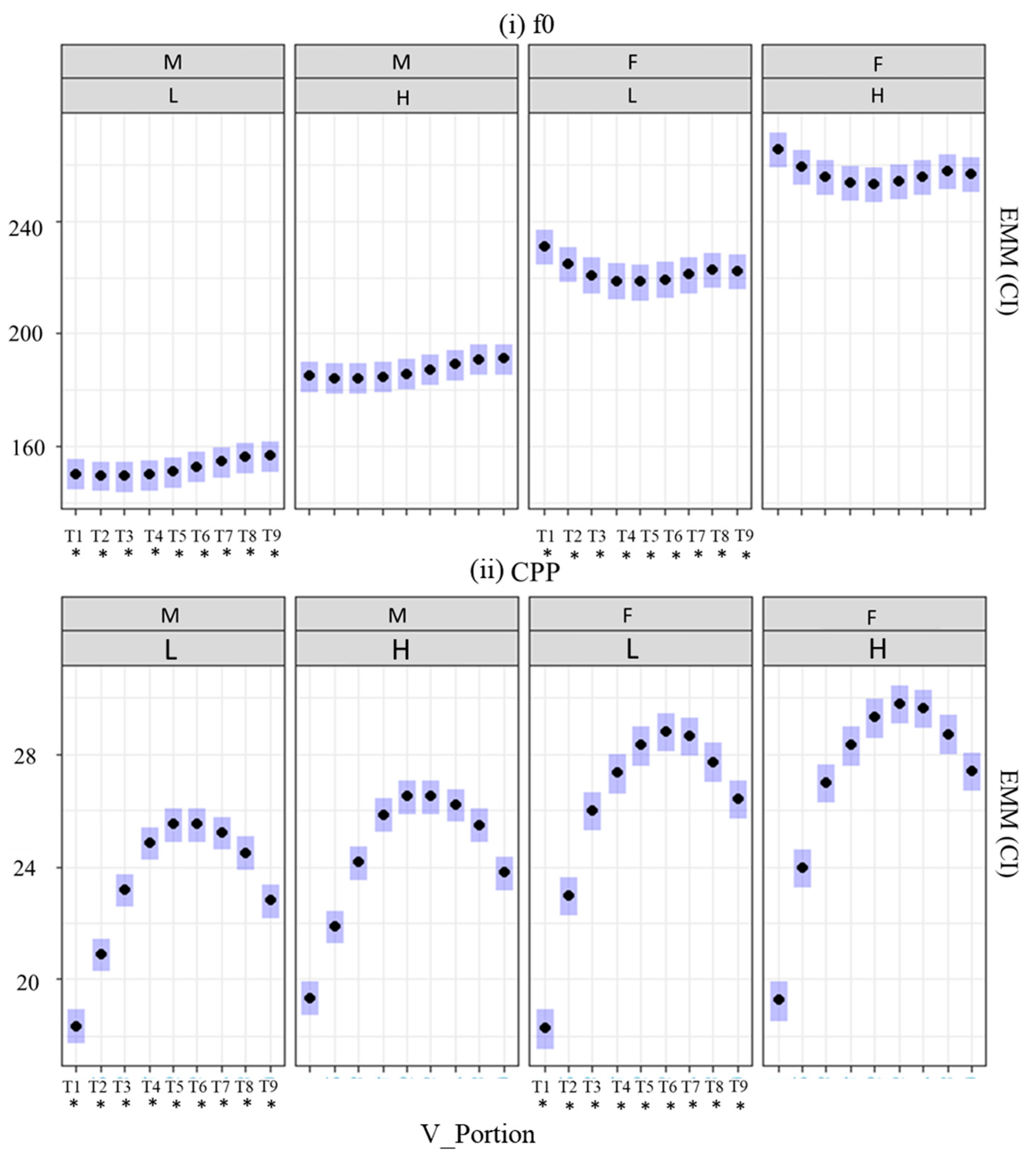
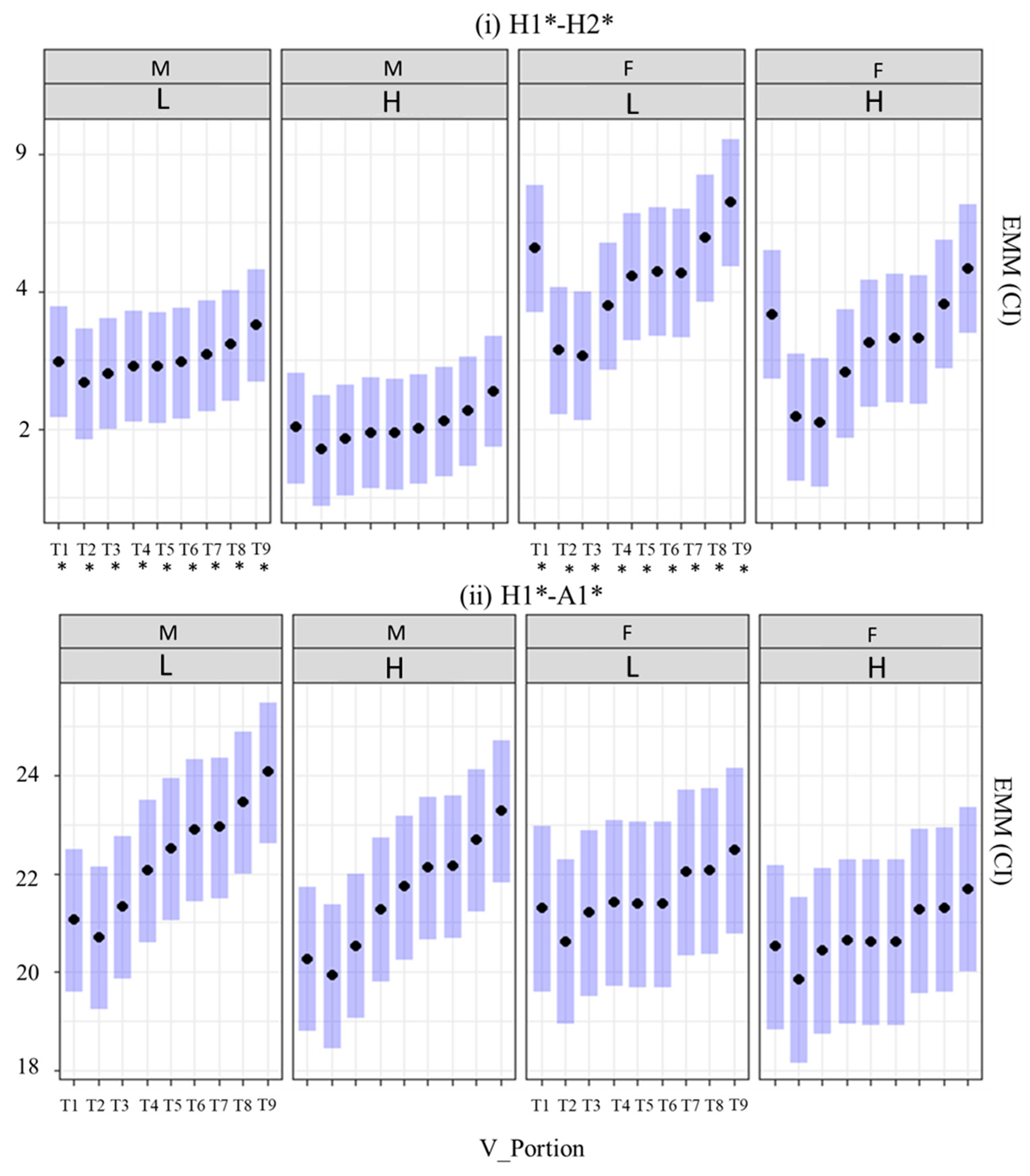
4. Results
4.1. Fundamental Frequency (f0), CPP, Energy, and Spectral Tilt Measures
4.2. Statistical Model
4.2.1. Model Generation
4.2.2. Outcomes of the Generated Model
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | The current paper is a revised and updated version of the paper ‘Correlation between Sylheti tone and Phonation’ presented in Speech Prosody 2016 (Gope and Mahanta 2016a). The content of this paper is a rework that is extracted from my Ph.D. thesis The Phonetics and Phonology of Sylheti Tonogenesis. In this paper, I have primarily concentrated on the (mono-syllabic) data discussed in Gope and Mahanta (2016a). Most of these word-pair that are specified for high tone at present, contained the feature (−voice, +spread glottis). It is quite evident that, the loss of the feature (+spread glottis) in both the voiced and voiceless series led to the development of a high tone in Sylheti. In this paper, however, I did not include voiceless series (only one pair is included) primarily due to lack of sufficient number of tokens. See Gope (2016) for more discussion on how the loss of aspiration in both voiced and voiceless obstruents led to a high tone in Sylheti. |
| 2 | The loss of aspiration reported in this paper is a case of historical development and not an instance of the synchronic allophonic process. |
| 3 | Gope (2016) first claimed that the tonogenesis in Sylheti is indeed triggered by the loss of underlying aspiration in the obstruents; the process of fricativization and deaffrication of the obstruents was just a simultenous process and did not have much role in the formation of tonal contrasts in this language. The study by Raychoudhury and Mahanta (2020) further confirmed this claim. Note that, most of the high tone words considered in this study contained the feature (−voice, +aspiration). |
| 4 | |
| 5 | Words of other shapes, including fillers, were also recorded, but not analyzed for the current study for the sake of increased quantitative comparability |
| 6 | Originally I recorded 9 native speakers (6 male, 3 female). However, data recorded from three older speakers were not analyzed here due to possible generational differences in tonogenesis. |
| 7 | For example, to initiate the meaning [bát̪] ‘rice’, an example sentence ‘I eat rice’ [àmì bát̪ xái. ár] is recorded first. |
| 8 | Mean f0 is averaged across all the tokens produced by each subject. |
| 9 | In this study, a p-value of ≤ 0.05 is considered to be significant. |
| 10 | Note that, most of the high tone words considered in this study contained the feature (−voice, +aspiration). |
| 11 |
References
- Andruski, Jean A., and Martha Ratliff. 2000. Phonation types in production of phonological tone: The case of Green Mong. Journal of the International Phonetic Association 30: 37–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotel-Grenié, Agnès, and Michel Grenié. 1994. Phonation types analysis in Standard Chinese. Paper presented at 3rd International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, Yokohama, Japan, September 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Berkson, Kelly Harper. 2019. Acoustic correlates of breathy sonorants in Marathi. Journal of Phonetics 73: 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskararao, Peri. 1998. Voiced Aspiration and Tonogenesis in Some South-Asian Languages. In Symposium on Cross-Linguistic Studies of Tonal Phenomena: Tonogenesis, Typology, and Relate Topics. Edited by Kaji Shigeki. Tokyo: ILCAA, pp. 337–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, Tej K. 1975. The Evolution of Tones in Punjabi. Studies in the Linguistic Sciences 5: 12–24. [Google Scholar]
- Blankenship, Barbara. 1997. The time course of breathiness and laryngealization in Vowels. Ph.D. dissertation, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Blankenship, Barbara. 2002. The Timing of Non-modal Phonation in Vowels. Journal of Phonetics 30: 163–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafe, Wallace. 1977. Accent and related phenomena in the Five Nations Iroqouis languages. In Studies in Stress and Accent. Edited by Larry Hyman. Los Angeles: University of Southern California Press, pp. 169–81. [Google Scholar]
- DiCanio, Christian. 2009. The Phonetics of Register in Takhian Thong Chong. Journal of International Phonetic Association 39: 162–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, R. Prakash. 1989. Glottal Gestures in Hindi Plosives. Journal of Phonetics 17: 213–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, Brian. 1993. The acoustic-phonetic correlates of Cayuga word-stress. Ph.D. dissertation, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, Indranil. 2007. Four-way stop contrasts in hindi: An acoustic study of voicing, fundamental frequency and spectral tilt. Ph.D. thesis, University of Illinois, Urbana, IL, USA. [Google Scholar]
- England, Nora C. 1983. A Grammar of Mam, a Mayan Language. Austin: University of Texas Press. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, Christina M. 2010a. The effects of linguistic experience on the perception of phonation. Journal of Phonetics 38: 306–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, Christina M. 2010b. Variation in Contrastive Phonation in Santa Ana del Valle Zapotec. Journal of the International Phonetic Association 40: 181–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, Christina M. 2012. An Acoustic and Electroglottographic Study of White Hmong Phonation. Journal of Phonetics 40: 466–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, Christina M., and Sameer ud Dowla Khan. 2012. Contrastive Breathiness Across Consonants and Vowels: A comparative study of Gujarati and White Hmong. Journal of the International Phonetic Association 42: 123–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Esposito, Christina M., and Sameer ud Dowla Khan. 2020. The cross-linguistic patterns of phonation types. Lang Linguist Compass 14: e12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, Christina M., Kelly Harper Berkson, and Nelson Max. 2019. Distinguishing breathy consonants and vowels in Gujarati. Journal of South Asian Languages and Linguistics 6: 214–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Jorgensen, Eli. 1967. Phonetic Analysis of Breathy (murmured) Vowels. Indian Linguistics 28: 71–139. [Google Scholar]
- Garellek, Marc, and Patricia A. Keating. 2011. The acoustic consequences of phonation and tone interactions in Jalapa Mazatec. Journal of the International Phonetic Association 41: 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobl, Christer, and Ailbhe Ní Chasaide. 2012. Voice source variation and its communicative functions. In The Handbook of Phonetic Sciences. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, pp. 378–423. [Google Scholar]
- Gope, Amalesh. 2016. The Phonetics and Phonology of Sylheti Tonogenesis. Ph.D. dissertation, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India. [Google Scholar]
- Gope, Amalesh. 2018. The Phoneme Inventory of Sylheti: Acoustic Evidences. Journal of Advanced Linguistic Studies 7: 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gope, Amalesh, and Shakuntala Mahanta. 2014. Lexical Tone in Sylheti. Paper presented at 4th International Symposium on Tonal Aspects of Languages, Nijmegen, The Netherlands, May 13–16; pp. 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gope, Amalesh, and Shakuntala Mahanta. 2015. An Acoustic Analysis of Sylheti Phonemes. Paper presented at 18th International Congress of Phonetic Sciences, Glasgow, UK, August 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gope, Amalesh, and Shakuntala Mahanta. 2016a. Correlation between Sylheti tone and phonation. Paper presented at Speech Prosody 2016, Boston, MA, USA, May 31–June 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gope, Amalesh, and Shakuntala Mahanta. 2016b. Perception of Lexical Tones in Sylheti. Paper presented at TAL-2016, Buffalo, NY, USA, May 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, Mathew. 2001. Linguistic aspects of voice quality with special reference to Athabaskan. Paper presented at 2001 Athabaskan Languages Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, May 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, Mathew, and Peter Ladefoged. 2001. Phonation Types: A Cross-Linguistic Overview. Journal of Phonetics 29: 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenbrand, James, Ronald A. Cleveland, and Robert L. Erickson. 1994. Acoustic correlates of breathy voice quality. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 37: 769–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hombert, Jean-Marie. 1978. Consonant types, vowel height, and tone in Yoruba. In Tone: A Linguistic Survey. Edited by Victoria A. Fromkin. New York: Academic Press, pp. 77–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hombert, Jean-Marie, John J. Ohala, and William G. Ewan. 1979. Phonetic Explanations for the Development of Tones. Language 55: 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, Marie. K. 1987. Measures of phonation type in Hmong. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 81: 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, Larry M. 2010. Does tone have features. In Tones and Features: Phonetic and Phonological Perspectives. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter, pp. 50–80. [Google Scholar]
- Iseli, Markus, Yen-Lian Shue, and Abeer Alwan. 2007. Age, sex, and vowel dependencies of Acoustic measures related to the voice source. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 121: 2283–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, Ted E., and Lyle M. Knudson. 1977. Guelavia Zapotec phonemes. In Studies in OtoManguean Phonology. Edited by William Merrifield. Dallas: SIL/University of Texas, Arlington, pp. 163–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara, Hideki, Alain de Cheveigné, and Roy D. Patterson. 1998. An instantaneous-frequency-based pitch extraction method for high-quality speech transformation: Revised TEMPO in the STRAIGHT-suite. Paper presented at 5th International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, Sydney Convention Centre, Sydney, Australia, November 30–December 4. [Google Scholar]
- Keating, Patricia, Christina M. Esposito, Marc Garellek, Sameer ud Dowla Khan, and Jianjing Kuang. 2010. Phonation contrasts across languages. UCLA Working Papers in Phonetics 108: 188–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kelterer, Anneliese, and Barbara Schuppler. 2020. Phonation type contrasts and tone in Chichimec. Journal of Acoustic Society of America 147: 3043–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Sameer ud Dowla. 2010. Bengali (Bangladeshi Standard). Journal of the International Phonetic Association 40: 221–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Sameer ud Dowla. 2012. The phonetics of contrastive phonation in Gujarati. Journal of Phonetics 40: 780–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, John. 2011. Tonogenesis. In The Blackwell Companion to Phonology. Edited by Marc van Oostendorp, Colin J. Ewen, Elizabeth V. Hume and Keren Rice. Malden: Blackwell, vol. IV. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, James P. 2014. Incipient tonogenesis in Phnom Penh Khmer: Acoustic and perceptual studies. Journal of Phonetics 43: 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, Paul L., Jenny Ladefoged, and Peter Ladefoged. 1993. Quantifying acoustic properties of modal, breathy and creaky vowels in Jalapa Mazatec. In American Indian Linguistics and Ethnography in Honor of Lawrence C. Thompson. Edited by Anthony Mattina and Timothy Montler. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan, pp. 435–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Jianjing, and Patricia Keating. 2013. Glottal articulations in tense vs. lax phonation contrasts. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 134: 4069–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Jianjing, and Patricia Keating. 2014. Vocal fold vibratory patterns in tense versus lax phonation contrasts. Journal of Acoustical Society of America 136: 2784–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladefoged, Peter. 1971. Preliminaries to Linguistic Phonetics. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, pp. 1–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ladefoged, Peter. 1983. The linguistic use of different phonation types. In Vocal Fold Physiology: Contemporary Research and Clinical Issues. Edited by Diane Bless and James Abba. San Diego: College-Hill Press, pp. 351–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ladefoged, Peter, Ian Maddieson, and Michael Jackson. 1988. Investigating phonation types in different languages. In Vocal Fold Physiology: Voice Production, Mechanisms and Functions. Edited by O. Fujimura. New York: Raven Press, pp. 297–317. [Google Scholar]
- Leer, Jeef. 1979. Proto-Athabaskan Verb Stem Variation, Part One: Phonology. Research Papers 1. Fairbanks: Alaska Native Language Center, p. 100. [Google Scholar]
- Maddieson, Ian, and Susan Hess. 1986. ‘Tense’ and ‘Lax’ revisited: More on phonation type and pitch in minority languages in China. UCLA Working Papers in Phonetics 63: 103–9. [Google Scholar]
- Michelson, Karin. 1988. A Comparative Study of Lake-Iroquoian Accent. Dordrecht: Kluwer. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, Amanda L. 2007. Guttural vowels and guttural co-articulation in Juj’hoansi. Journal of Phonetics 35: 56–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mooshammer, Christine. 2010. Acoustic and laryngographic measures of the laryngeal reflexes of linguistic prominence and vocal effort in German. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 127: 1047–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohala, John J. 1990a. Respiratory activity in speech. In Speech Production and Speech Modelling. Edited by W. J. Hardcastle and A. Marchal. Dordrecht: Kluwer, pp. 23–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ohala, John J. 1990b. The phonetics and phonology of aspects of assimilation. [And: A response to Pierrehumbert’s commentary]. In Papers in Laboratory Phonology I: Between the Grammar and the Physics of Speech. Edited by J. Kingston and M. Beckman. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 258–75, 280–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ohala, John J. 1993a. The phonetics of sound change. In Historical Linguistics: Problems and Perspectives. Edited by C. Jones. London: Longman Academics, pp. 237–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ohala, John J. 1993b. Sound change as nature’s speech perception experiment. Speech Communication 13: 155–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, Boersma, and David Weenink. 2008. Praat: Doing Phonetics by Computer (Version 5.3.04_win32) [Computer Program]. Available online: http://www.praat.org/Bradley (accessed on 22 December 2011).
- Raychoudhury, Priti, and Shakuntala Mahanta. 2020. The Three Way Tonal System of Sylheti. Paper presented at 10th International Conference on Speech Prosody, Tokyo, Japan, May 25–28; pp. 503–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shue, Yen-Liang, Patricia A. Keating, and Chad Vicenik. 2009. VoiceSauce: A program for voice analysis. The Journal of the Acoustical Society America 124: 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, Daniel, Barbara Blankenship, Paul L. Kirk, and Peter Ladefoged. 1995. Phonetic structures in Jalapa Mazatec. Anthropological Linguistics 37: 70–88. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, Kenneth N., and Helen M. Hanson. 1995. Classification of glottal vibration from acoustic measurements. In Vocal Fold Physiology: Voice Quality Control. Edited by O. Fujimura and H. Minoru. San Diego: Singular Publishing Group. [Google Scholar]
- Thurgood, Graham. 2002. Vietnamese and tonogenesis: Revising the model and the analysis. Diachronica 19: 333–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traill, Anthony. 1985. Phonetic and Phonological Studies of !Xóõ Bushman. Hamburg: Buske. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, Justin. 2002. The Phonetics of Wa: Experimental Phonetics, Phonology, Orthography and Sociolinguistics. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics. [Google Scholar]
- Wayland, Ratree, and Allard Jongman. 2002. Acoustic correlates of breathy and clear vowels: The case of Khmer. Journal of Phonetics 31: 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, Moira. 2002. Tone. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]




| Sylheti Words | Gloss | Sylheti Words | Gloss |
|---|---|---|---|
| [bán] | ‘to pretend’ | [bàn] | ‘to tie’ |
| [bát̪] | ‘rice’ | [bàt̪] | ‘arthritis’ |
| [ɖáx] | ‘drum’ | [ɖàx] | ‘roaring of cloud’ |
| [d̪án] | ‘paddy’ | [d̪àn] | ‘donate’ |
| [zál] | ‘hot/spicy’ | [zàl] | ‘net’ |
| [ɡá] | ‘wound’ | [ɡà] | ‘body’ |
| [xál] | ‘drain’ | [xàl] | ‘skin’ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gope, A. The Phonetics of Tone and Voice Quality Interactions in Sylheti. Languages 2021, 6, 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages6040154
Gope A. The Phonetics of Tone and Voice Quality Interactions in Sylheti. Languages. 2021; 6(4):154. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages6040154
Chicago/Turabian StyleGope, Amalesh. 2021. "The Phonetics of Tone and Voice Quality Interactions in Sylheti" Languages 6, no. 4: 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages6040154
APA StyleGope, A. (2021). The Phonetics of Tone and Voice Quality Interactions in Sylheti. Languages, 6(4), 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages6040154






