Analysis of the Cosmic Ray Effects on Sentinel-1 SAR Satellite Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Image Data
2.2. Cosmic Ray Density Data
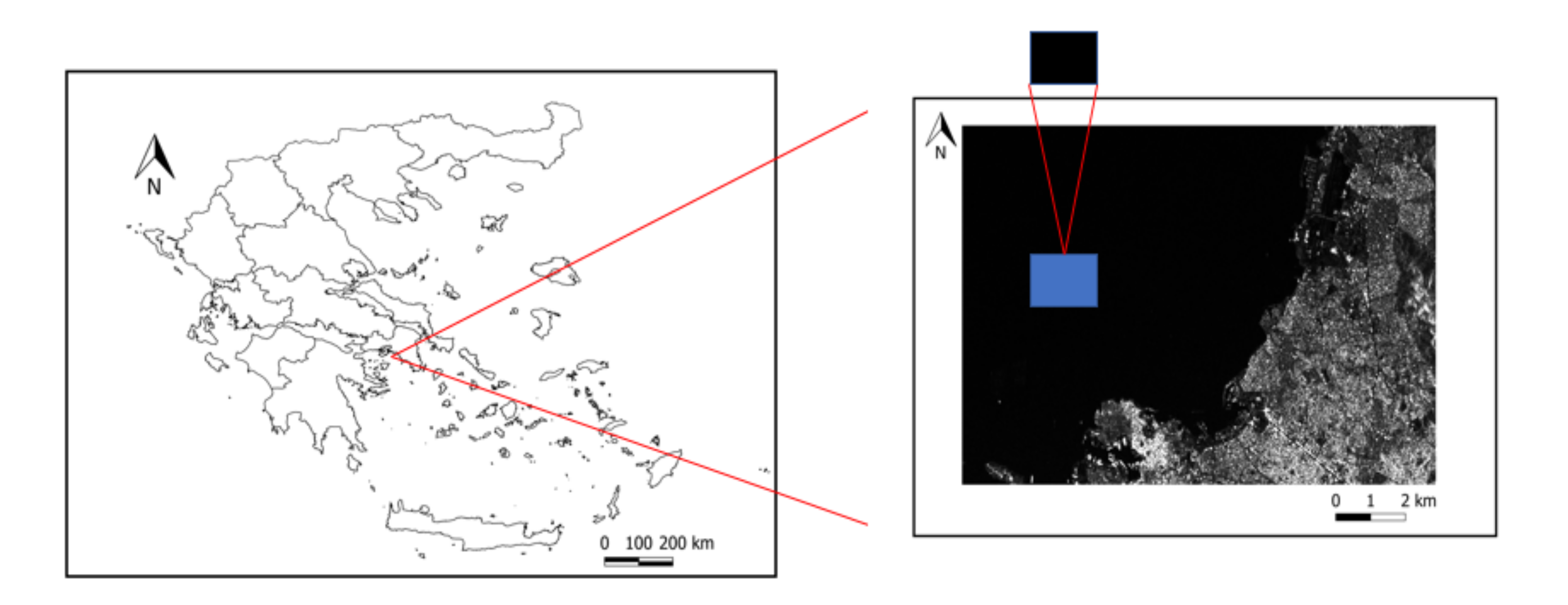
2.3. Test Areas
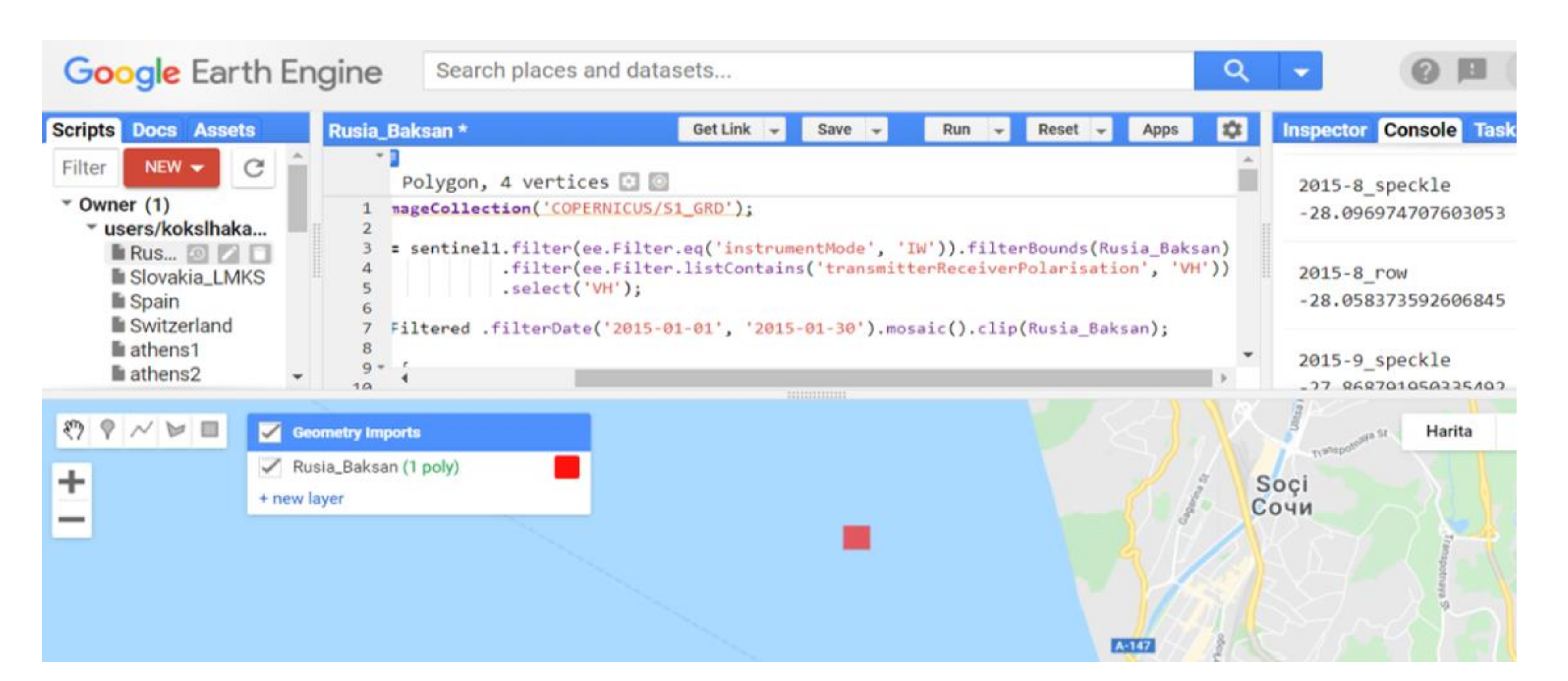
2.4. Method
2.4.1. Calculation of the Amount of the Speckles
2.4.2. Analysis of the Differences
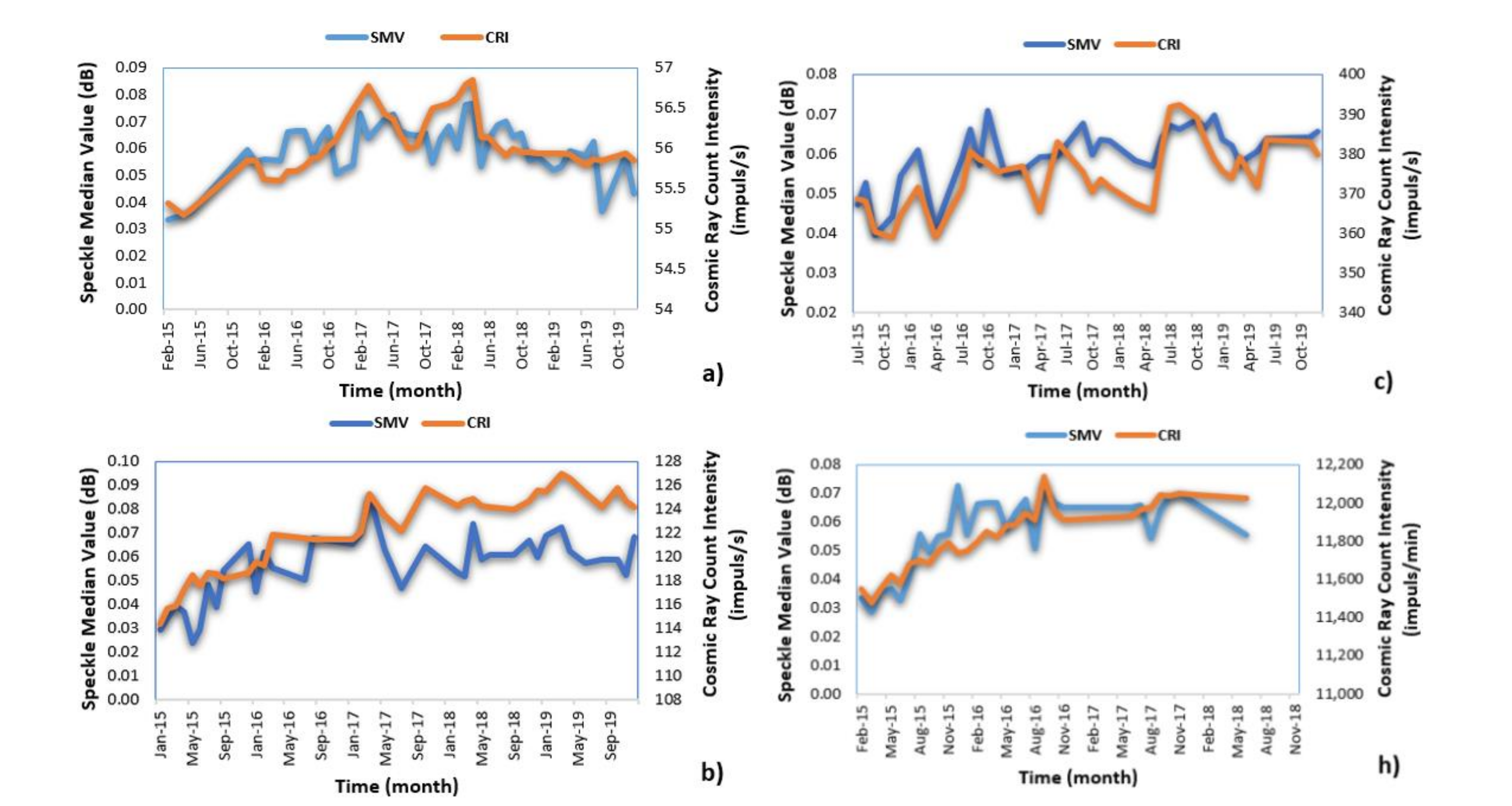
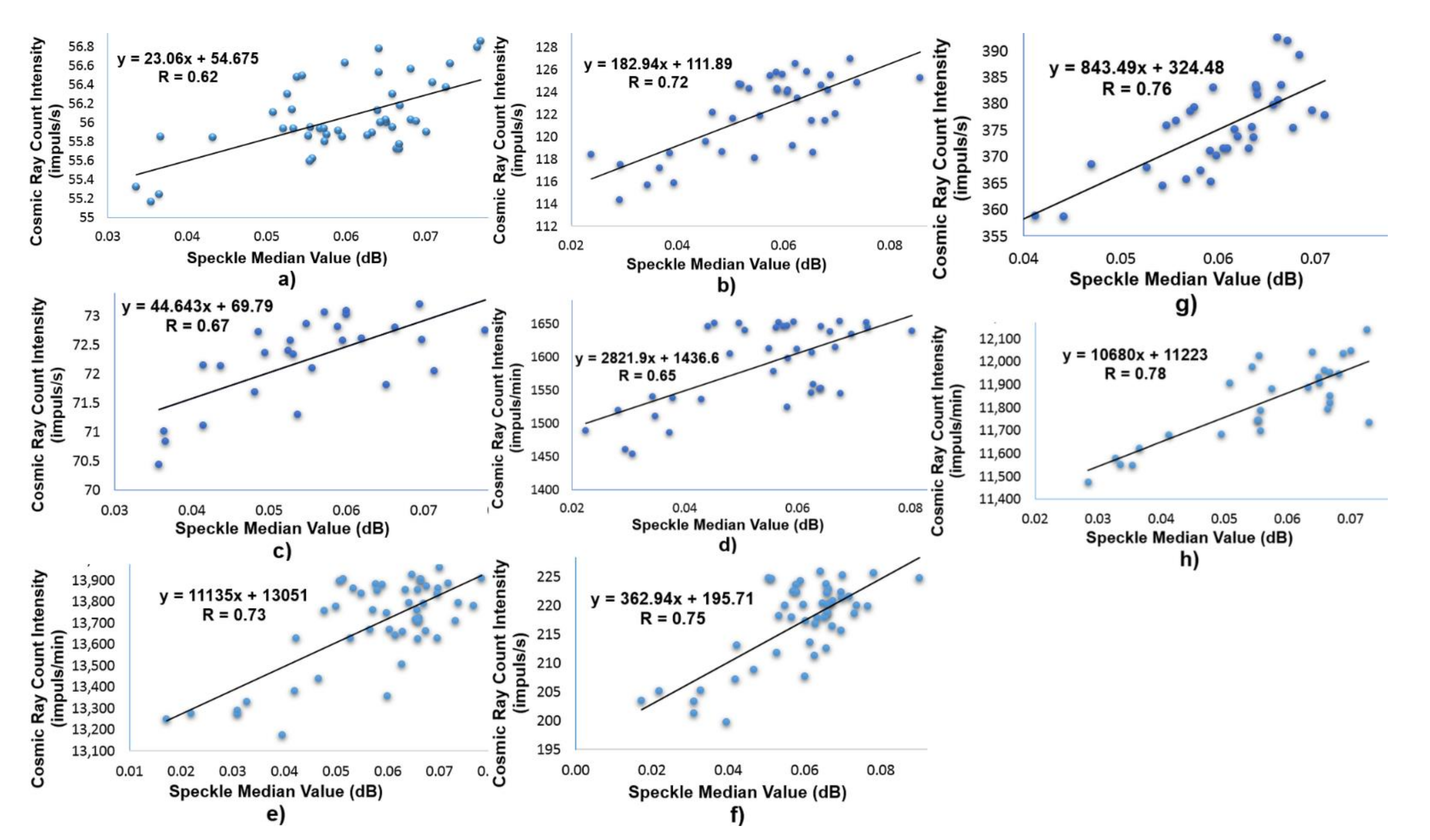
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howell, E. What Are Cosmic Rays? Available online: https://www.space.com/32644-cosmic-rays.html (accessed on 19 December 2020).
- Smart, D.F.; Shea, M.A. Galactic cosmic radiation and solar energetic particles. In Handbook of Geophysics and the Space Environment; Air Force Geophysics Laboratory: Bedford, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 6–29. [Google Scholar]
- Horne, R.B.; Glauert, S.A.; Meredith, N.P.; Boscher, D.; Maget, V.; Heynderickx, D.; Pitchford, D. Space weather impacts on satellites and forecasting the Earth’s electron radiation belts with SPACECAST. Space Weather 2013, 11, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaman, B. Uydularımız Tehdit Altında-Uzay Radyasyonu (In Turkish). TUBITAK Bilim Tek. 2018, 630, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Nwankwo, V.U.J.; Jibiri, N.N.; Kio, M.T. The Impact of Space Radiation Environment on Satellites Operation in Near-Earth Space. In Satellites Missions and Technologies for Geosciences; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo, I.; Lidtke, A.A.; Bendoukha, S.A.; Gonzalez-Llorente, J.; Rodríguez, R.; Morales, R.; Faizullin, D.; Matsuoka, M.; Urakami, N.; Kawauchi, R.; et al. Design, Implementation, and Operation of a Small Satellite Mission to Explore the Space Weather Effects in LEO. Aerospace 2019, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya’acob, N.; Zainudin, A.; Magdugal, R.; Naim, N.F. Mitigation of space radiation effects on satellites at Low Earth Orbit (LEO). In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering ICCSCE2016, Penang, Malaysia, 25–27 June 2016; pp. 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.H. Satellite Anomalies, Recent Events, and Possible Causes. In Space Weather Study Using Multipoint Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Harboe-Sørensen, R.; Daly, E.; Teston, F.; Schweitzer, H.; Nartallo, R.; Perol, P.; Vandenbussche, F.; Dzitko, H.; Cretolle, J. Observation and analysis of single event effects on-board the SOHO satellite. In Proceedings of the RADECS 2001 6th European Conference on Radiation and Its Effects on Components and Systems (Cat. No.01TH8605), Grenoble, France, 10–14 September 2001; pp. 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Koons, H.C.; Chen, M.W. An Update on the Statistical Analysis of MILSTAR Processor Upsets. In Proceedings of the Government Microcircuit Applications, Monterey, CA, USA, 3 August–3 November 1999; pp. 816–819. [Google Scholar]
- Koons, H.C.; Fennel, J.F. Space Weather Effects on Communications Satellites. URSI Radio Sci. Bull. 2006, 316, 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, I.; Mandell, M.; Jongeward, G.; Gussenhoven, M.S. The importance of accurate secondary electron yields in modeling spacecraft charging. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 13739–13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vampola, A.L. Thick dielectric charging on high-altitude spacecraft. J. Electrostat. 1987, 20, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koons, H.C.; Mazur, J.E.; Selesnick, R.S.; Blake, J.B.; Fennell, J.F.; Roeder, J.L.; Anderson, P.C. The impact of the space environment on space systems. In Proceedings of the 6th Spacecraft Charging Technology Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 1 September 2000; Volume 670, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, S.; Godinez, H.; Angling, M.J.; Koller, J. Improved Modelling of Upper Atmospheric Densities using Multi-Model Ensembles. In Proceedings of the 3rd IMA Mathematics in Defence Conference, Malvern, UK, 23–24 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Radicella, S.M. Ionosphere/Positioning and Telecommunications. In Space Weather Research Towards Applications in Europe; Lilensten, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 125–127. [Google Scholar]
- Akioka, M.; Nagatsuma, T.; Miyake, W.; Ohtaka, K.; Marubashi, K. The L5 mission for space weather forecasting. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 35, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Some fundamental properties of speckle. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1976, 66, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Jurkevich, I.; Dewaele, P.; Wambacq, P.; Oosterlinck, A. Speckle filtering of synthetic aperture radar images: A review. Remote Sens. Rev. 1994, 8, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruniquel, J.; Lopes, A. Multi-variate optimal speckle reduction in SAR imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 603–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, L.; Jouan, A. Speckle Filtering of SAR Images: A Comparative Study Between Complex-Wavelet-Based and Standard Filters. In Proceedings of the Wavelet Applications in Signal and Image Processing V, San Diego, CA, USA, 30 July–1 August 1997; pp. 199–200. [Google Scholar]
- Köksal, H.; Demir, N.; Kilcik, A. Investigation of the cosmic ray effects on sentinel-1 SAR images. In Proceedings of the 41st Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Online, 9–11 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Milne, K.A.; Forster, B.C. A sar speckle filtering algorithm towards edge sharpening. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. Sen Refined filtering of image noise using local statistics. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1981, 15, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using Multivariate Statistics, 6th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 0205849571. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, X. Ionospheric Effects on Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar and a New Capability of Imaging the Ionosphere From Space. Space Weather 2015, 13, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannix, C.R.; Belcher, D.P.; Cannon, P.S. Measurement of Ionospheric Scintillation Parameters from SAR Images Using Corner Reflectors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6695–6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Test Area | Number of Processed Images | Time Period |
|---|---|---|
| Athens | 376 | February 2015–December 2019 |
| Baksan | 304 | February 2015–December 2019 |
| Castilla–La Mancha | 224 | May 2015–April 2018 |
| Lomnicky | 312 | January 2015–November 2019 |
| Mexico City | 408 | January 2015–December 2019 |
| Nain | 400 | January 2015–Dcember2019 |
| Jungfraujoch | 288 | July 2015–December 2019 |
| Tsumeb | 240 | February 2015–June 2018 |
| Station | Detector | Cutoff Rigidity | Operation Start Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Athens | 6-NM64 | 8.53 GV | 2000 |
| Baksan | 6NM64 | 5.6 GV | 2003 |
| Castilla–La Mancha | 15-NM64 | 6.95 GV | 2012 |
| Lomnicky_stit | 8-SNM15 | 3.84 GV | 1981 |
| Mexico City | 6-NM-64 | 8.2 GV | 1990 |
| Nain | 63-NM-64 | 0.3 GV | 2000 |
| Jungfraujoch | 3-NM64 | 4.5 GV | 1986 |
| Tsumeb | 18-NM64 | 9.15 GV | 1976 |
| Test Area | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
| Athens | 37°55′34.44′′ E | 23°40′05.74′′ N |
| Baksan | 39°38′32.91′′ E | 43°35′7.50′′ N |
| Castilla–La Mancha | 0°32′15.44′′ E | 40°26′22.40′′ N |
| Lomnicky | 20°16′43.93′′ E | 49°26′23.20′′ N |
| Mexico City | 94°54′54.78′′ W | 29°7′58.35′′ N |
| Nain | 138°41′1.10′′ W | 58°54′22.13′′ N |
| Tsumeb | 22°34′36.33′′ E | 34°1′1.94′′ S |
| Jungfraujoch | 8°24′7.88′′ E | 47°0′58.86′′ N |
| Test Site and Data | Skewness | Kurtosis | Skewness Standard Deviation | Kurtosis Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Athens–SD | 0.186 | −0.858 | 0.350 | 0.688 |
| Athens–CRI | −0.240 | 0.054 | 0.333 | 0.656 |
| Baksan–SD | −0.504 | 0.026 | 0.388 | 0.759 |
| Baksan–CRI | −0.393 | −0.802 | 0.347 | 0.681 |
| Castilla–La Mancha–SD | −0.533 | −0.445 | 0.421 | 0.821 |
| Castilla–La Mancha–CRI | −0.447 | −1.016 | 0.374 | 0.733 |
| Lomnicky–SD | −0.552 | −0.494 | 0.383 | 0.750 |
| Lomnicky–CRI | −0.442 | 0.247 | 0.393 | 0.768 |
| Mexico City–SD | −0.673 | 0.072 | 0.374 | 0.733 |
| Mexico City–CRI | −0.603 | −0.825 | 0.357 | 0.702 |
| Nain–SD | −0.550 | 0.134 | 0.383 | 0.750 |
| Nain–CRI | −0.053 | −1.021 | 0.361 | 0.709 |
| Jungfraujoch–SD | 0.077 | −0.187 | 0.357 | 0.702 |
| Jungfraujoch–CRI | 0.111 | −0.497 | 0.327 | 0,644 |
| Tsumeb–SD | −0.653 | 0.518 | 0.347 | 0.681 |
| Tsumeb–CRI | −0.079 | −0.080 | 0.409 | 0.798 |
| Station | Date | Max Speckle Median Value (dB) | Max Cosmic Ray Intensity Value (impuls/s or min *) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Athens | April 2018 | 0.0769 | 56.86 |
| Mexico City | October 2018 | 0.0781 | 13,960 * |
| Nain | September 2019 | 0.090 | 225.88 |
| Tsumeb | September 2016 | 0.073 | 12,141 * |
| Station | Average Cosmic Ray Number Density (Impuls/s) | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| Athens | 55.96 | 62% |
| Baksan | 122.45 | 72% |
| Castilla–La Mancha | 71.92 | 67% |
| Nain | 217.4 | 75% |
| Jungfraujoch | 371.38 | 76% |
| Station | Correlation | Station | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Athens | 62% | Mexico City | 73% |
| Baksan | 72% | Nain | 75% |
| Castilla–La Mancha | 67% | Jungfraujoch | 76% |
| Lomnicky | 65% | Tsumeb | 78% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Köksal, H.; Demir, N.; Kilcik, A. Analysis of the Cosmic Ray Effects on Sentinel-1 SAR Satellite Data. Aerospace 2021, 8, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8030062
Köksal H, Demir N, Kilcik A. Analysis of the Cosmic Ray Effects on Sentinel-1 SAR Satellite Data. Aerospace. 2021; 8(3):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8030062
Chicago/Turabian StyleKöksal, Hakan, Nusret Demir, and Ali Kilcik. 2021. "Analysis of the Cosmic Ray Effects on Sentinel-1 SAR Satellite Data" Aerospace 8, no. 3: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8030062
APA StyleKöksal, H., Demir, N., & Kilcik, A. (2021). Analysis of the Cosmic Ray Effects on Sentinel-1 SAR Satellite Data. Aerospace, 8(3), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8030062







