Thermal Numerical Analysis of the Primary Composite Structure of a CubeSat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
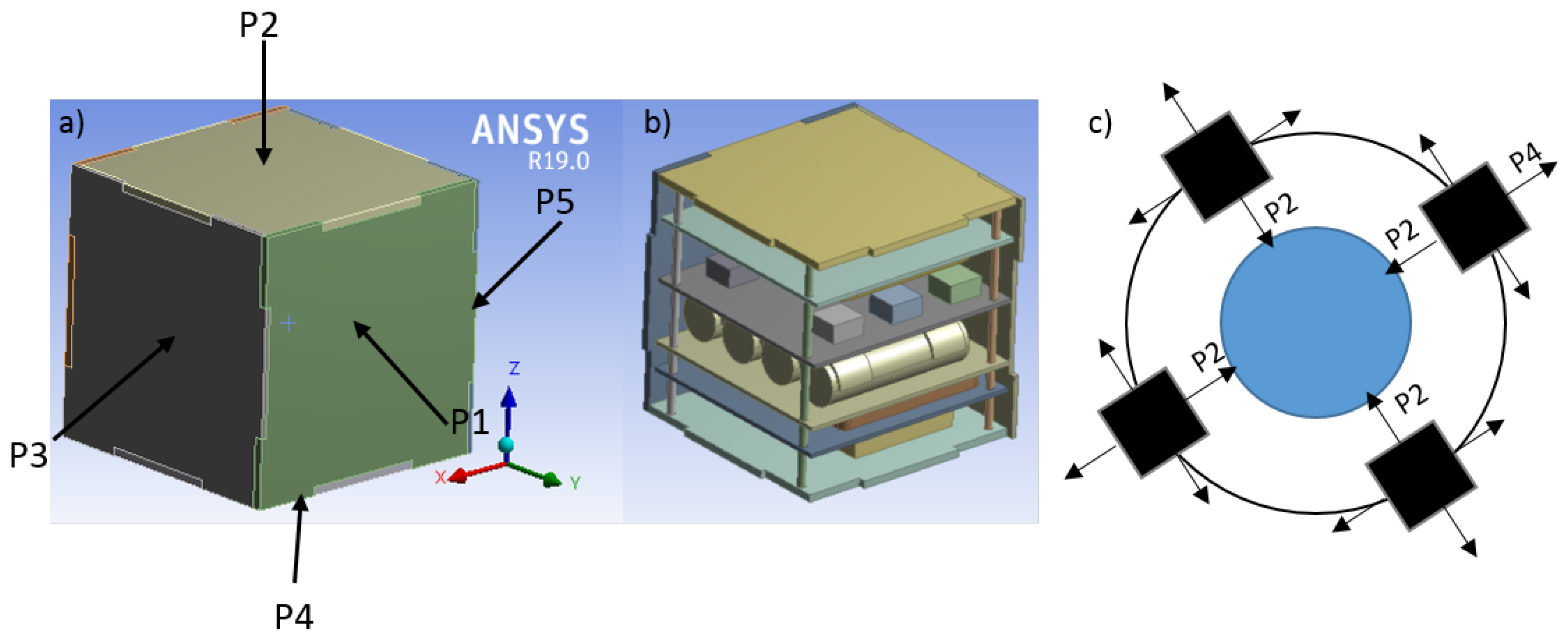
2.1. Conceptual Design
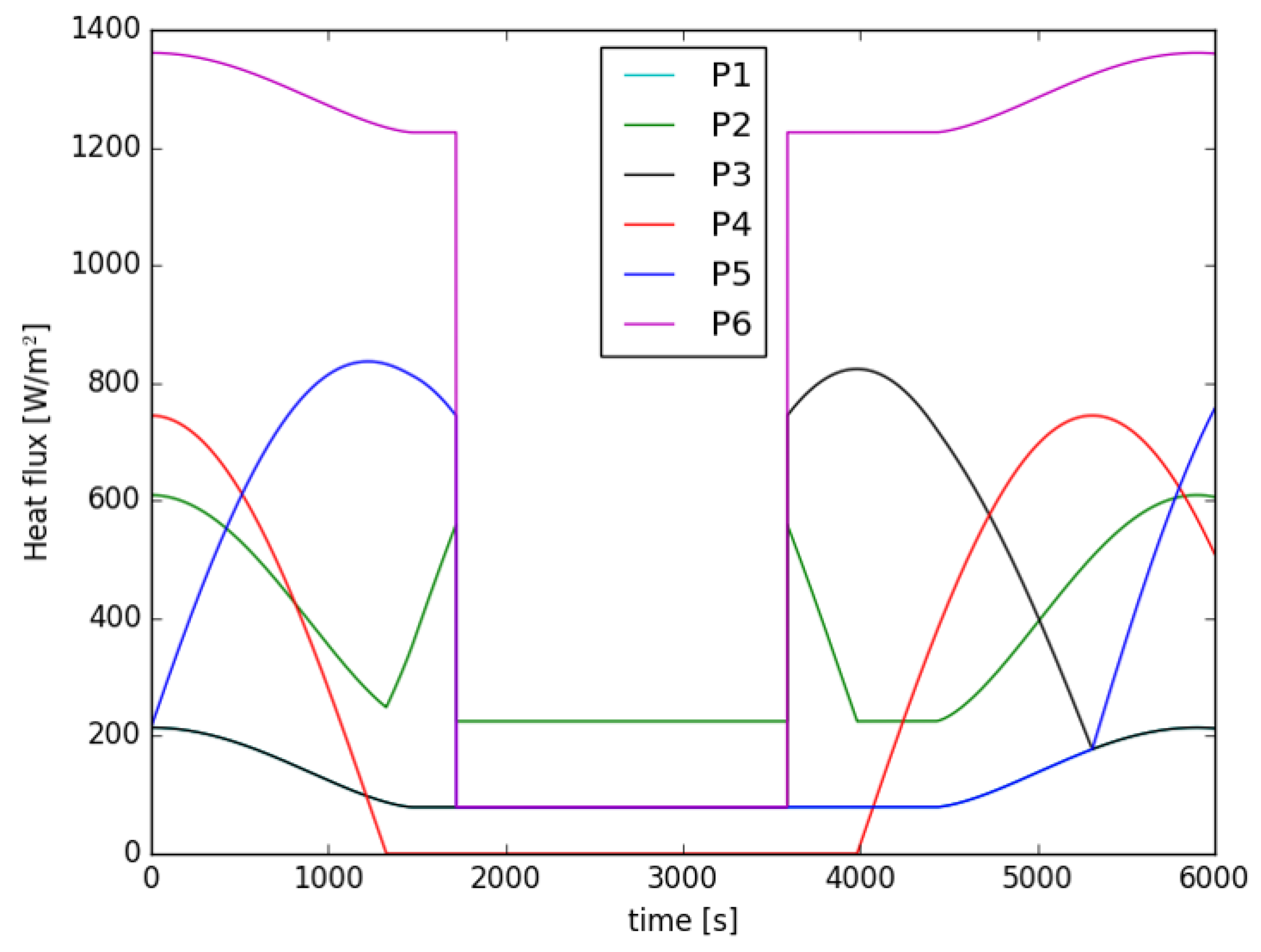
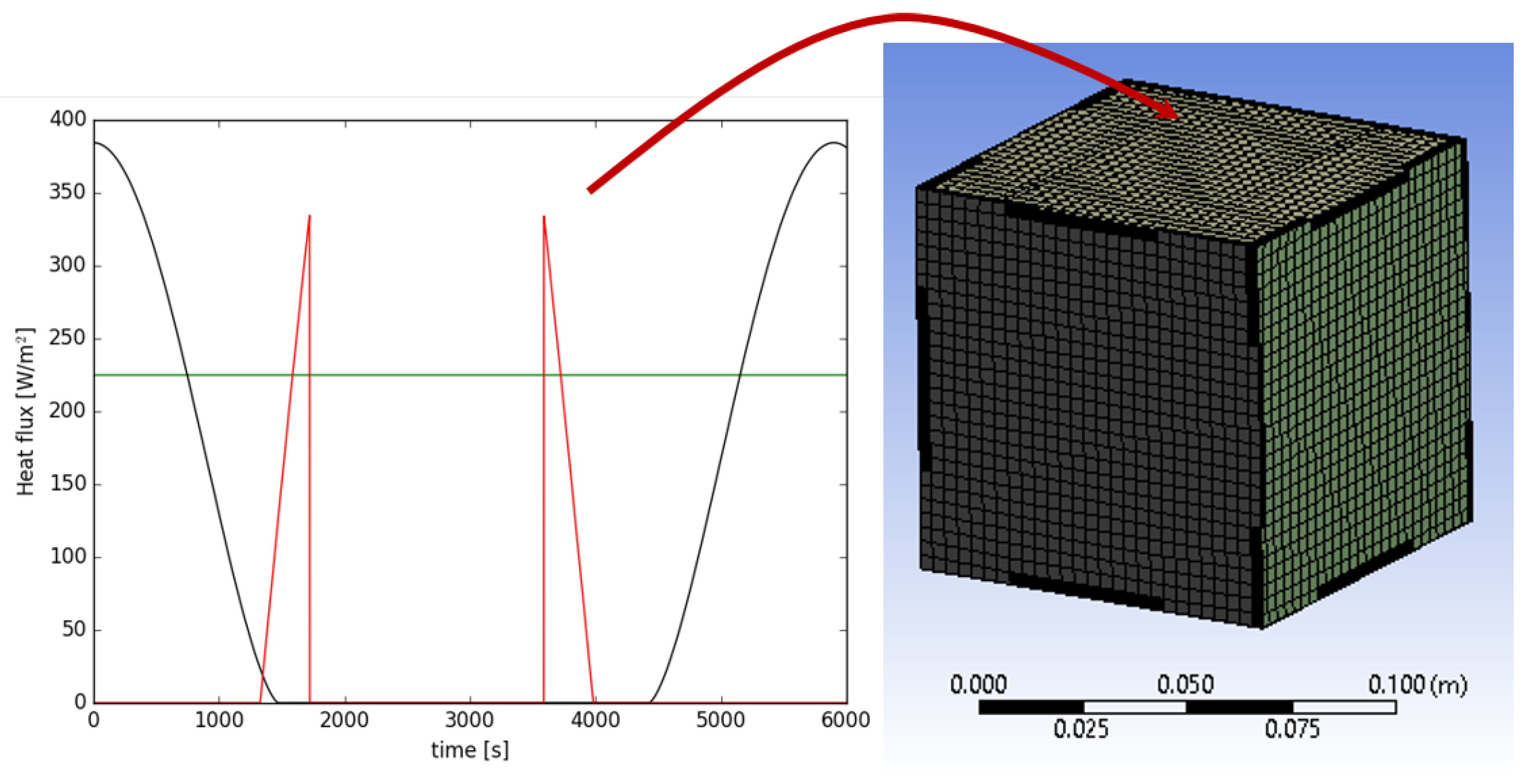
2.2. Heat Radiation Sources
2.3. Model Implementation
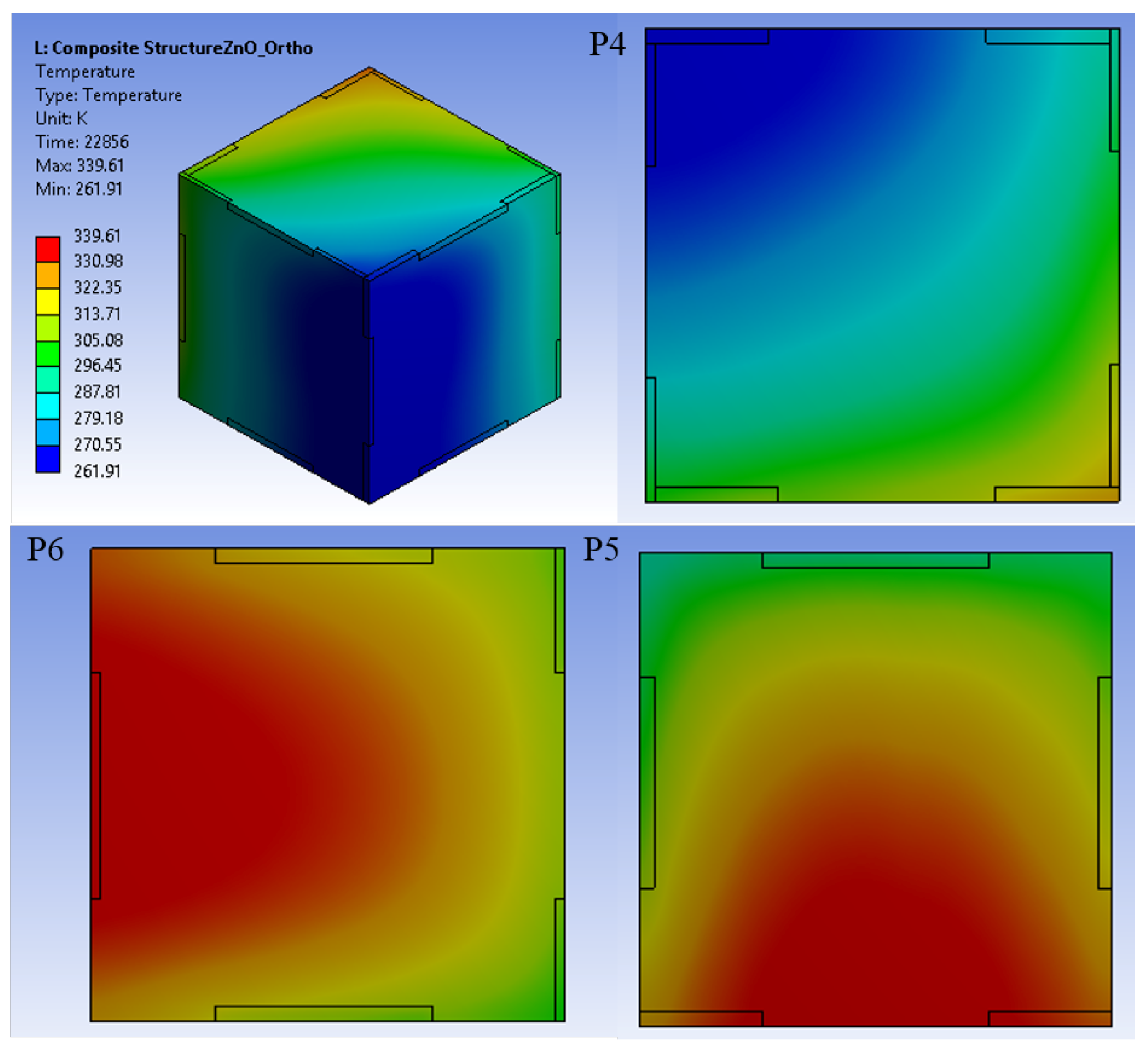
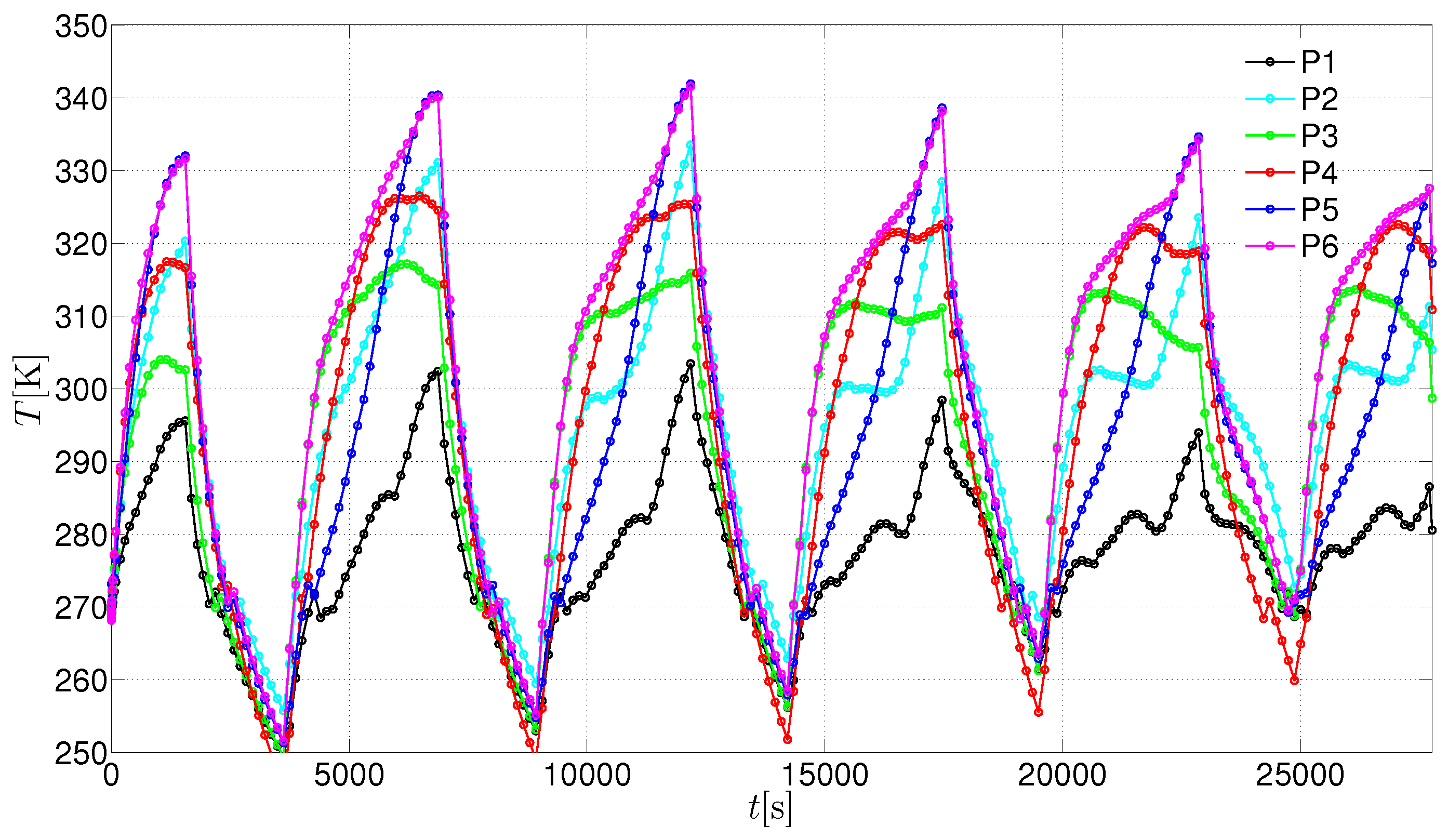
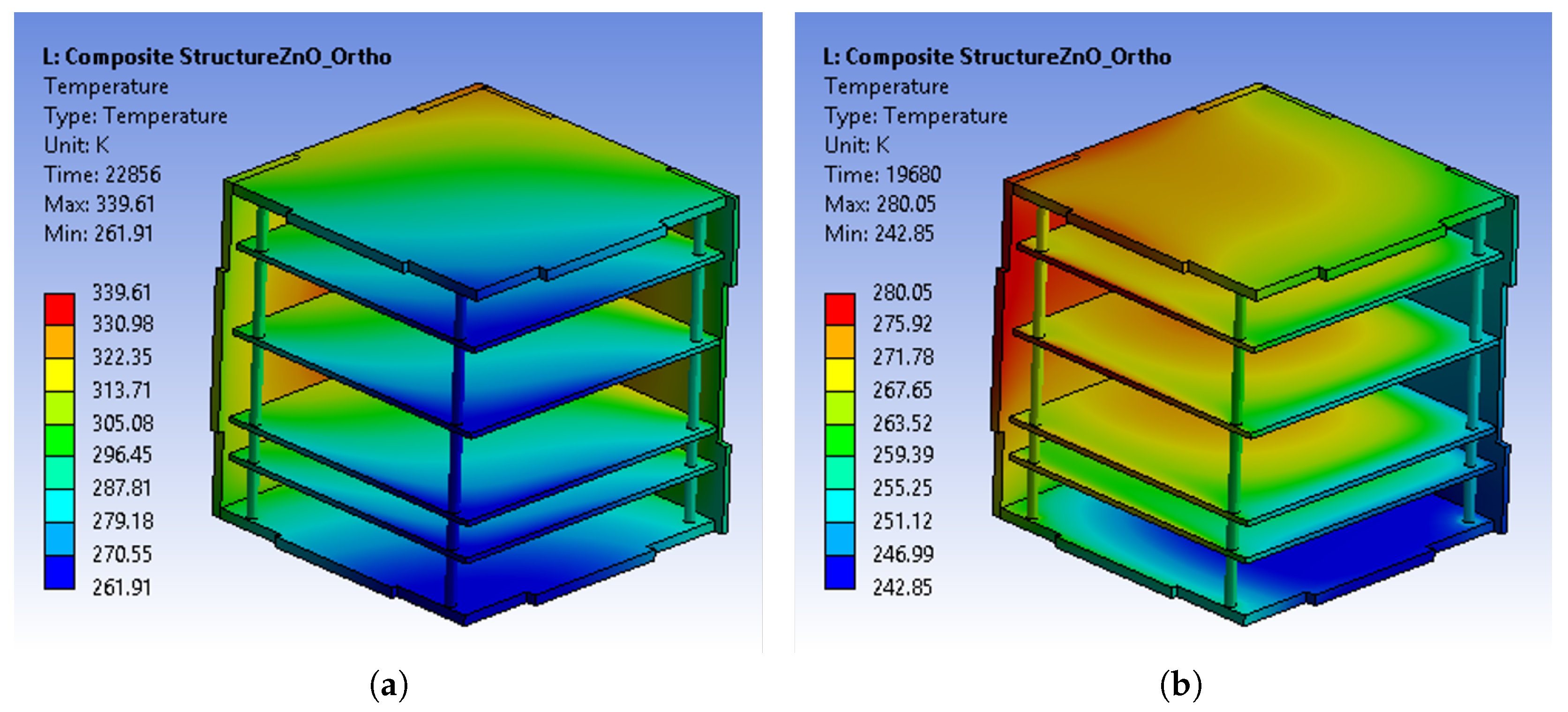
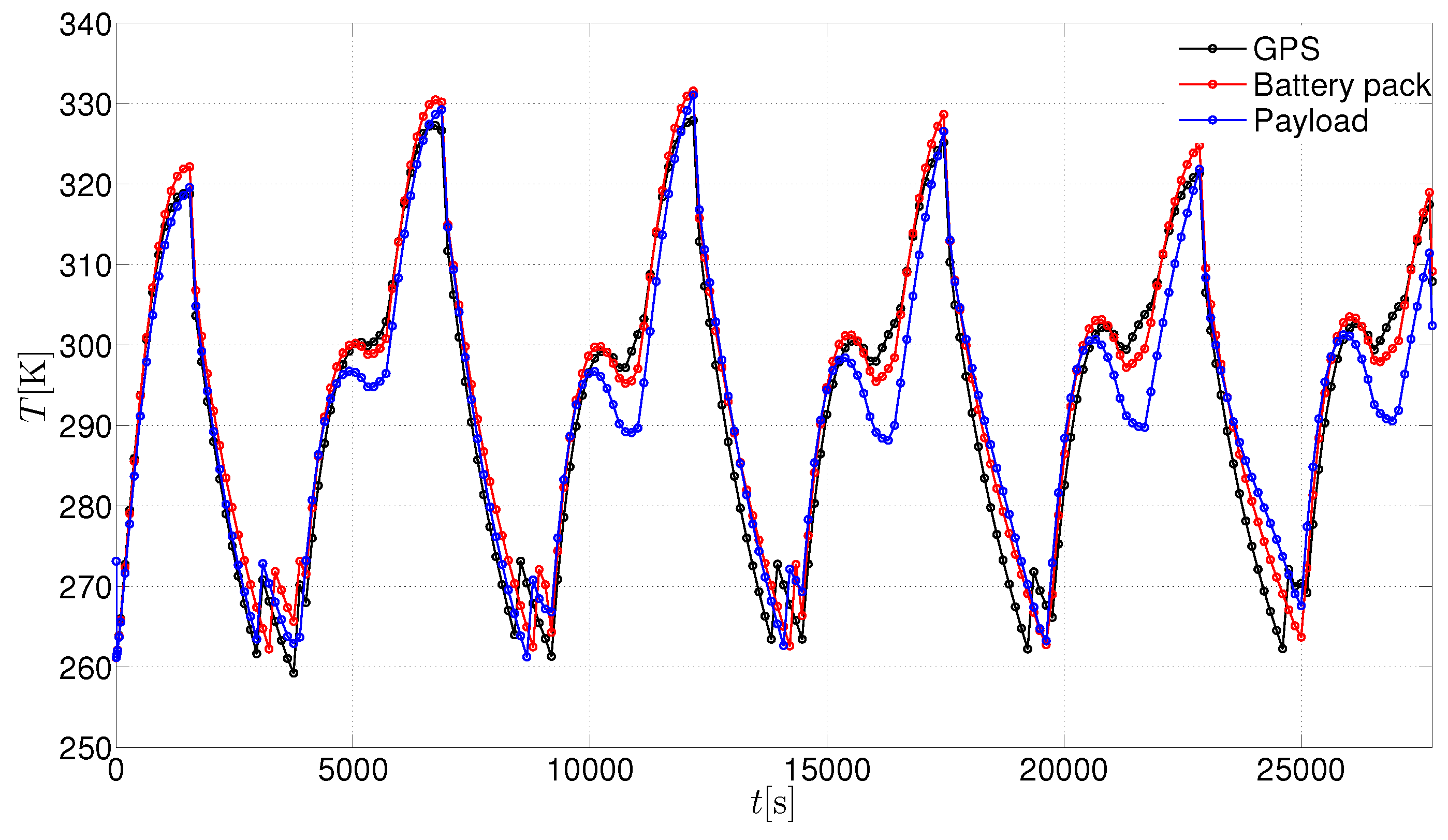
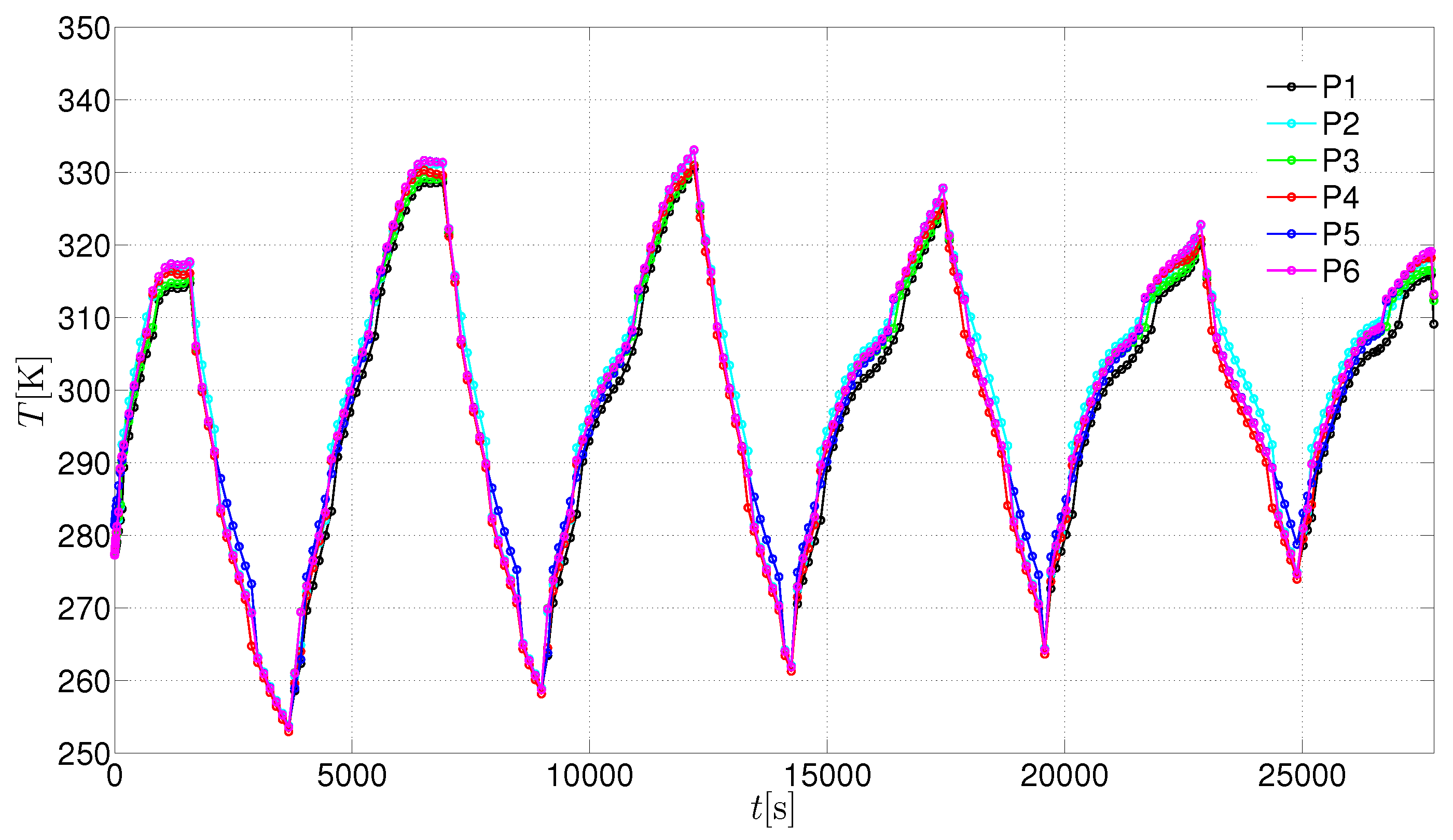
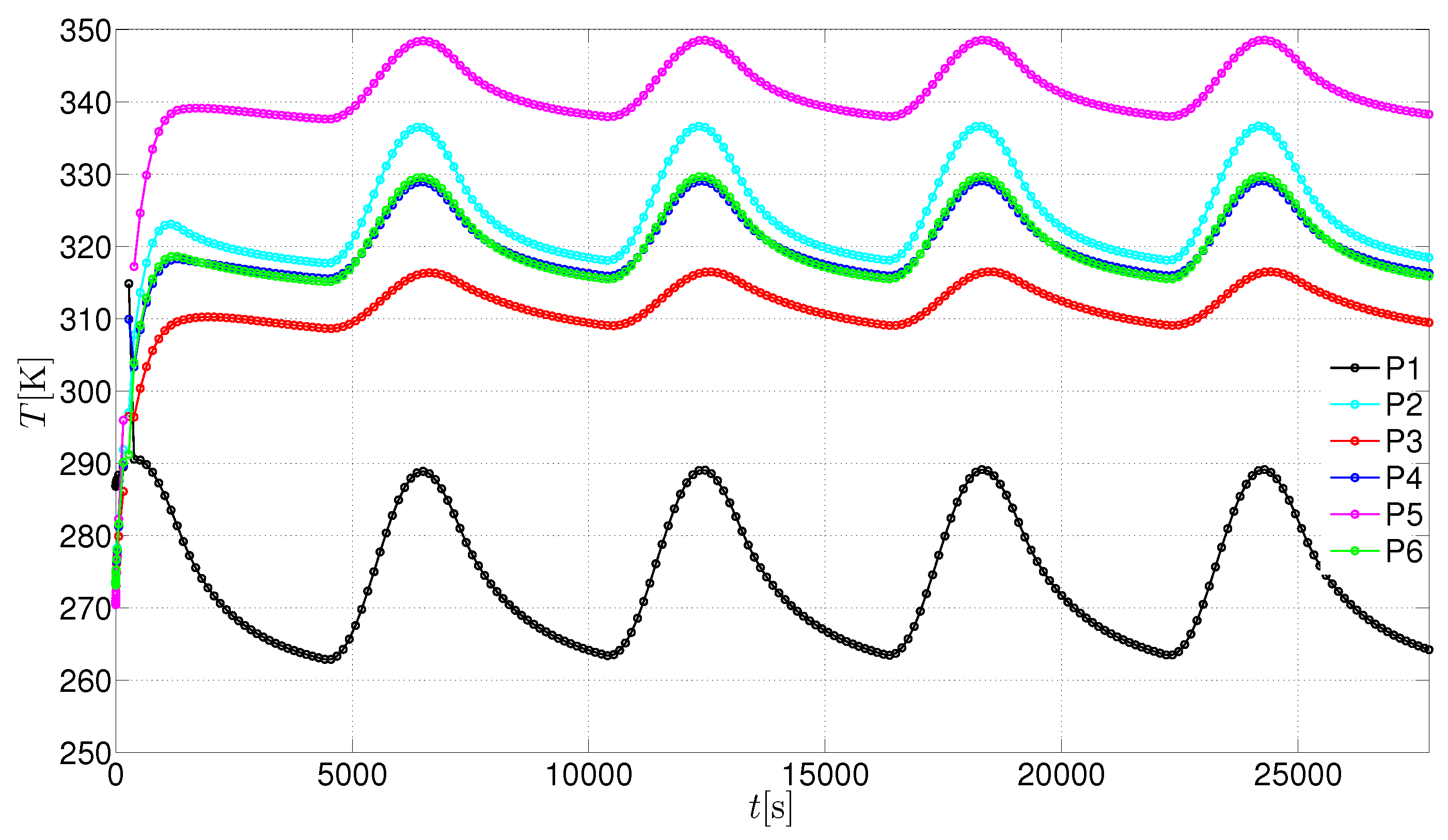
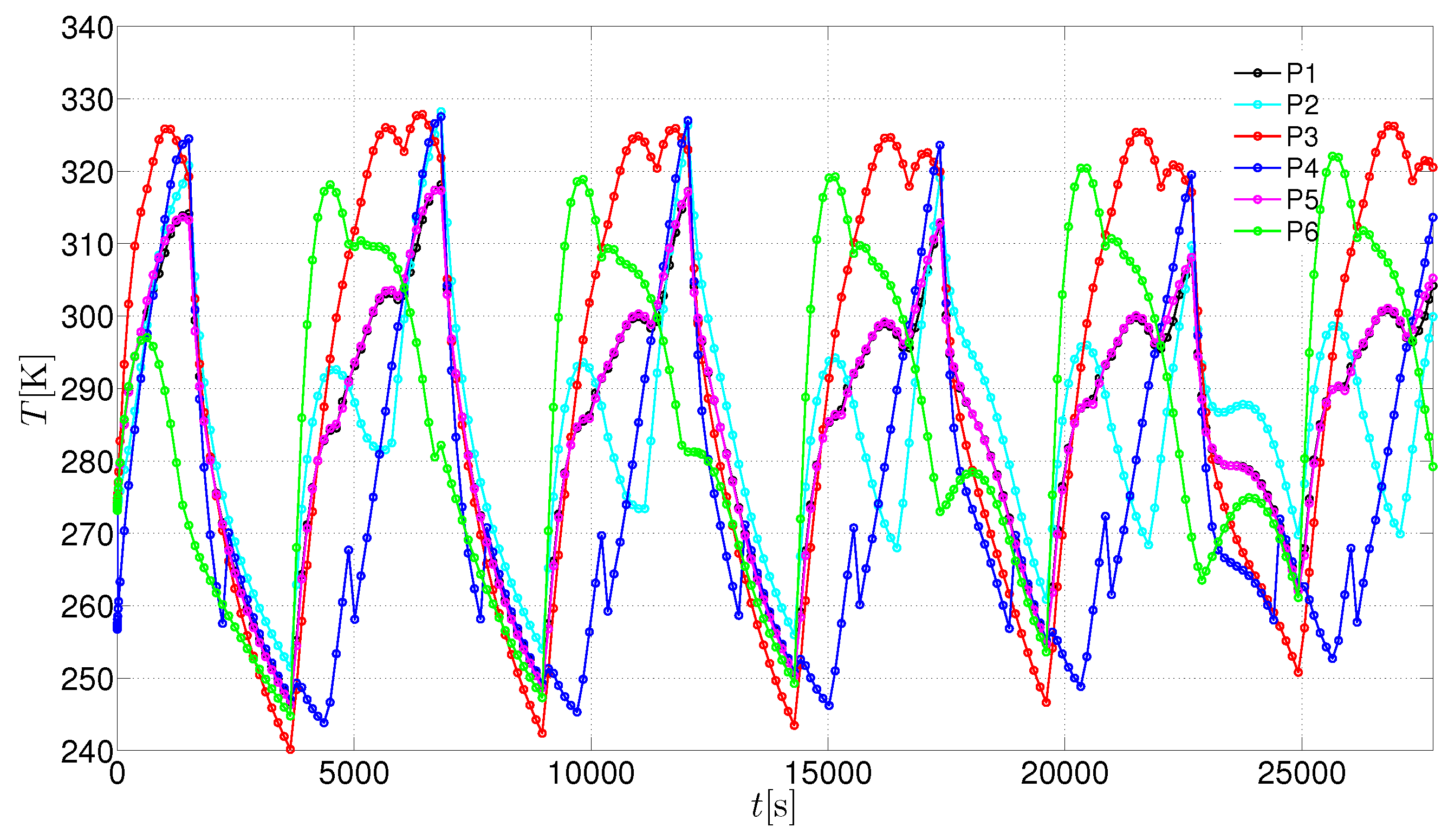
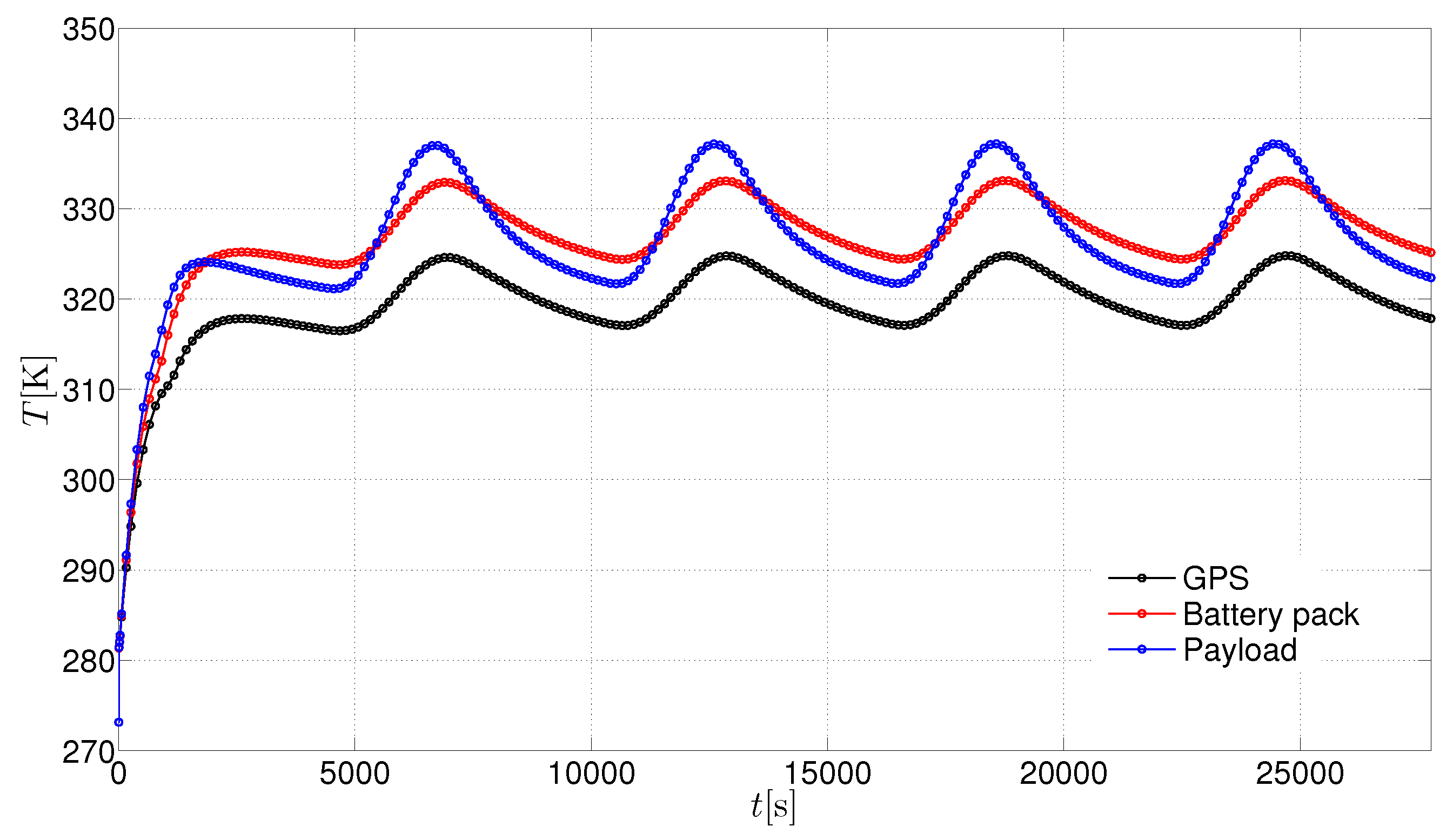
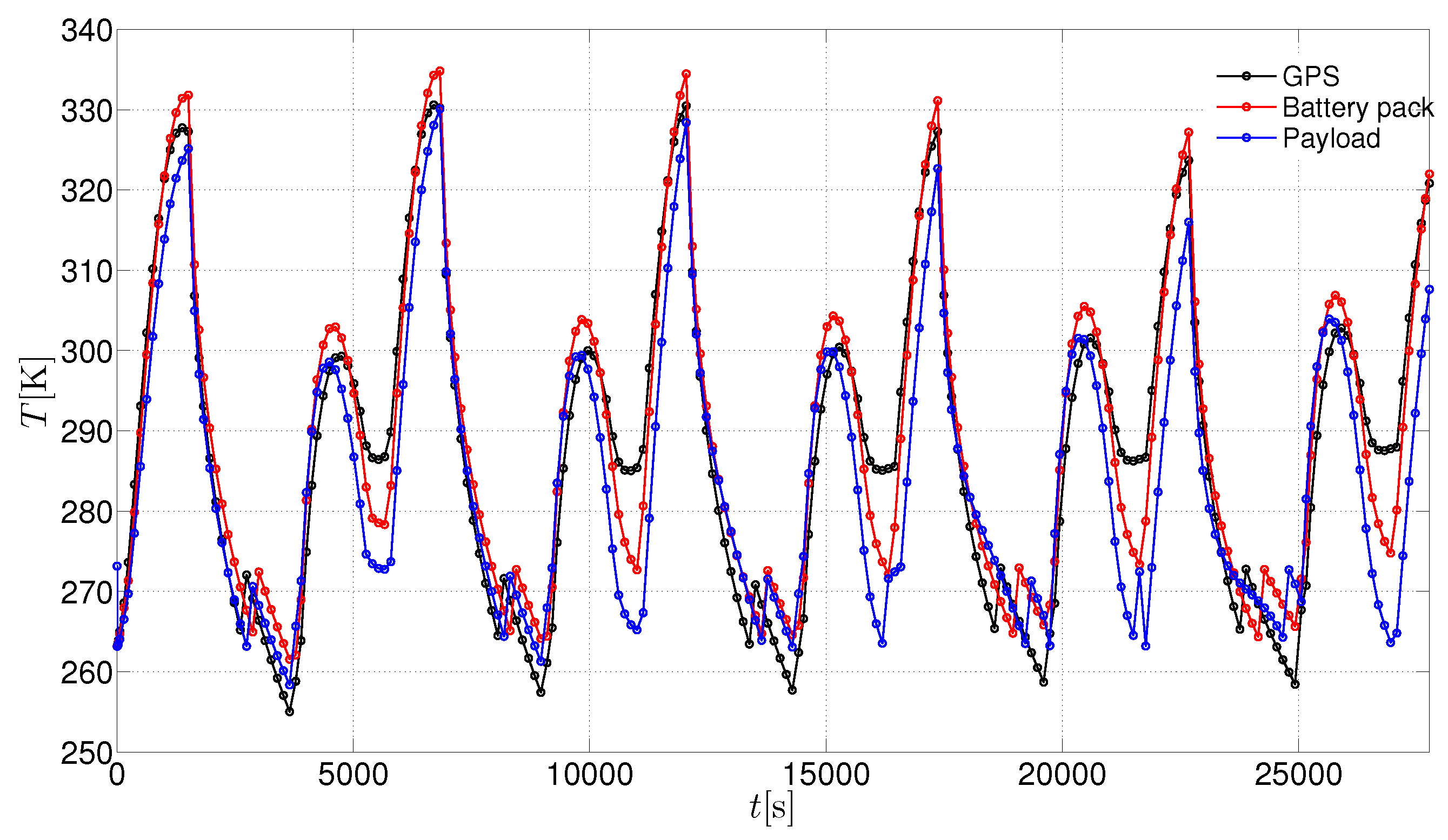
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corpino, S.; Caldera, M.; Nichele, F.; Masoero, M.; Viola, N. Thermal design and analysis of a nanosatellite in low earth orbit. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 115, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrparvar, A. Cubesat Design Specifications Rev. 13; California Polytechnic State University: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Niaki, K.S.; Anvari, A.; Farhani, F. Aluminum and composite materials for satellite structures—A comparison of thermal performance. Mater. Sci. Res. India 2007, 4, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condruz, M.R.; Voicu, L.R.; Puscasu, C.; Vintila, I.S.; Sima, M.; Deaconu, M.; Dragasanu, L. Composite material designs for lightweight space packaging structures. INCAS Bull. 2018, 10, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampatzoglou, A.; Baltopoulos, A.; Kotzakolios, A.; Kostopoulos, V. Qualification of Composite Structure for Cubesat Picosatellites as a Demonstration for Small Satellite Elements. IJASAR 2014, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemelya, C.; De la Rosa, A.; Torrado, A.R.; Yu, K.; Domanowski, J.; Bonacuse, P.J.; Martin, R.E.; Juhasz, M.; Hurwitz, F.; Wicker, R.B.; et al. Anisotropy of thermal conductivity in 3D printed polymer matrix composites for space based cube satellites. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 16, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, W.M.; Zemba, M.; Shemelya, C.; Wicker, R.; Espalin, D.; MacDonald, E.; Keif, C.; Kwas, A. Using Additive Manufacturing to Print a CubeSat Propulsion System. In Proceedings of the 51st AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 27–29 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Borgeaud, M.; Scheidegger, N.; Noca, M.; Roerhlisberger, G.; Jordan, F.; Choueiri, T.; Steiner, N. SwissCube: The First Entirely-Built Swiss Student Satellite with an Earth Observation Payload. In Small Satellite Missions for Earth Observation; Sandau, R., Roeser, H.P., Valenzuela, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 207–213. ISBN 978-3-642-03501-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, F.; Hojjati, M.; Okamoto, M.; Gorga, R.E. Review article: Polymer-matrix Nanocomposites, Processing, Manufacturing, and Application: An Overview. J. Compos. Mater. 2006, 40, 1511–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.R.; Robeson, L.M. Polymer nanotechnology: Nanocomposites. Polymer 2008, 49, 3187–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Garcia, P.; Ramirez-Aguilar, R.; Torres, M.; Franco-Urquiza, E.A.; May-Crespo, J.; Camacho, N. Mechanical and thermal behavior dependence on graphite and oxidized graphite content in polyester composites. Polymer 2018, 153, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Oh, H.U. On-Orbit Thermal Design and Validation of 1U Standardized CubeSat of STEP Cube Lab. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2016, 2016, 4213189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panczak, T.D.; Ring, S.G. RadCAD®: Next Generation Thermal Radiation Analyzer. SAE Int. 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, V.; Subramanian, E.R. Transient thermal analysis of a nanosatellite in low earth orbit. In Proceedings of The Eighth International Conference on Engineering Computational Technology; Topping, B.H.V., Ed.; Civil-Comp Press: Stirlingshire, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.; Jin, H.; Seon, J.; Jeong, Y.H.; Glaser, D.; Lee, D.H.; Lin, R.P. Thermal Analysis of TRIO-CINEMA Mission. J. Astron. Space Sci. 2012, 29, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelbauer, A. Cyanate Esters. In Handbook of Thermoset Plastics, 3rd ed.; Dodiuk, H., Goodman, S.H., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 425–457. [Google Scholar]
- Toray Advanced Composites. Toray EX-1510 Cyanate Resin, Two Part System Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.toraytac.com/product-explorer/products/ntro/EX-1510 (accessed on 8 August 2019).
- FAR 25.853—Appendix F Part II. Fire Test to Aircraft Material—Flammability of Seat Cushions; Federal Aviation Administration, Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Sika-AXSON Corporation. EPOLAM 2500, Epoxy System FAR 25 Approved. Available online: https://advanced-resins.sika.com (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Nakamura, S.; Fuji, T.; Matsukawa, S.; Katagiri, M.; Fukuyama, H. Specific heat, thermal conductivity, and magnetic susceptibility of cyanate-ester resins—An alternative to commonly used epoxy resins. Cryogenics 2018, 95, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldy, A.; Szlancsik, A.; Szolnoki, B. Reactive flame retardancy of cyanate ester/epoxy resin blends and their carbon fibre reinforced composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 128, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Yan, L. Transport of thermal energy in epoxy matrix composites reinforced with a hybrid carbon nanofiller. Results Phys. 2019, 14, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Directorate-General for Energy. Horizon 2020, EU Energy Trends to 2030. Climate Action DG and Mobility and Transport DG, 2020 Climate and Energy Package; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, M.; Piedra, S.; Ledesma, S.; Perez, R.; Franco, J.A. Thermal and mechanical analysis of a Carbon-Epoxy laminates for CubeSat primary structures. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Mechanics of Composites (MechComp 2019), Lisbon, Portugal, 1–4 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, B.A.; Sodano, H.A. Enhanced Interfacial Strength and UV Shielding of Aramid Fiber Composites through ZnO Nanoparticle Sizing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 33963–33971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salla, J.; Pandey, K.K.; Srinivas, K. Improvement of UV resistance of wood surfaces by using ZnO nanoparticles. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, N.; May-Crespo, J.F.; Rojas-Trigos, J.B.; Mondragon-Rodriguez, G.C.; Martinez, K.; Marin, E. Thermal properties and degradation kinetics of epoxy-γ-alumina and epoxy-zinc oxide composites. Polym. Test. 2019. Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-San Juan, S.; Gonzalez-Llorente, J.; Hurtado-Velasco, R. Comparison of the Incident Solar Energy and Battery Storage in a 3U CubeSat Satellite for Different Orientation Scenarios. J. Aerosp. Technol. Manag. 2016, 8, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HEXCEL Corporation. HexTow AS4 Carbon fibre Datasheet; Hexcel Corporation: Stamford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, B.J.; Justus, C.J.; Batts, G.W. Guidelines for the Selection of Near-Earth Thermal Environment Parameters for Spacecraft Design; NASA/TM-2001-211221; NASA: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2001.
- Jaques, L. Thermal Design of the OUFTI-1 Nanosatellite. Master’s Thesis, University of Liege, Liege, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore, D. Spacecraft Thermal Control Handbook, Volume 1: Fundamental Technologies; Aerospace Press: Reston, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- ANSYS Mechanical User’s Guide. Available online: https://www.sharcnet.ca/Software/Ansys/18.2.2/en-us/help/ai_sinfo/mech_intro.html (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- Dasgupta, A.; Agarwal, R.K. Orthotropic thermal conductivity of plain-weave fabric composites using a homogenization technique. J. Compos. Mater. 1992, 26, 2736–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, J.A.; Brown, A.L.; Dodd, A.B.; Gomez-Vasquez, S.; Ramirez, C.J. Carbon Fiber Composite Characterization in Adverse Thermal Environments; SAND2011-2833; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2011.

| Unit | Power Dissipation (W) | Operating Temperature Range (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPS board | 0.1 | −40 | 85 |
| Battery pack | 0.6 | −2060 | 60 |
| GPS board | 0.27 | −40 | 85 |
| Communication board | 0.27 | −30 | 60 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piedra, S.; Torres, M.; Ledesma, S. Thermal Numerical Analysis of the Primary Composite Structure of a CubeSat. Aerospace 2019, 6, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6090097
Piedra S, Torres M, Ledesma S. Thermal Numerical Analysis of the Primary Composite Structure of a CubeSat. Aerospace. 2019; 6(9):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6090097
Chicago/Turabian StylePiedra, Saul, Mauricio Torres, and Saul Ledesma. 2019. "Thermal Numerical Analysis of the Primary Composite Structure of a CubeSat" Aerospace 6, no. 9: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6090097
APA StylePiedra, S., Torres, M., & Ledesma, S. (2019). Thermal Numerical Analysis of the Primary Composite Structure of a CubeSat. Aerospace, 6(9), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6090097





