Experimental Study of the Aerodynamic Interaction between the Forewing and Hindwing of a Beetle-Type Ornithopter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design and Fabrication
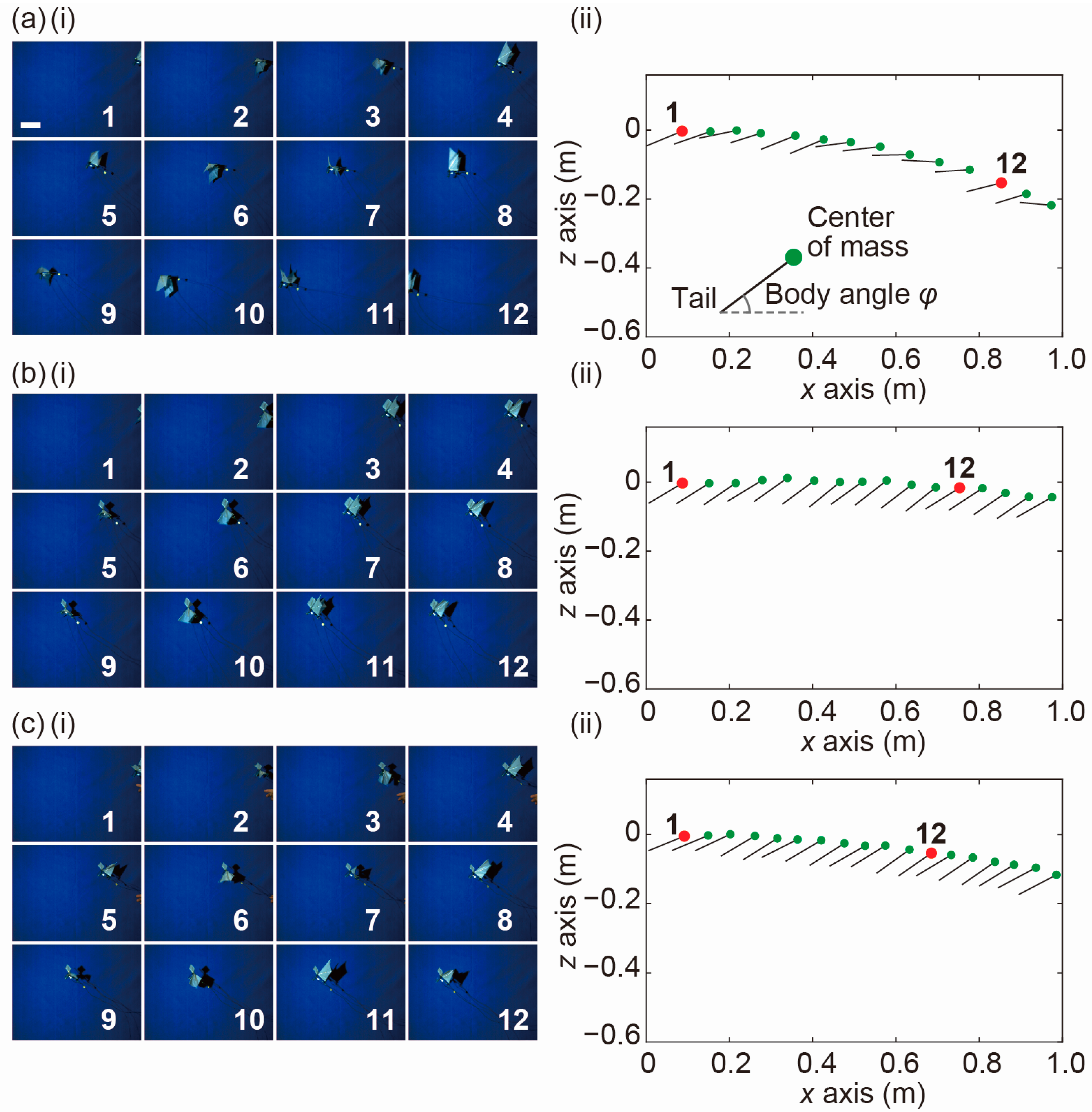
3. Experiments
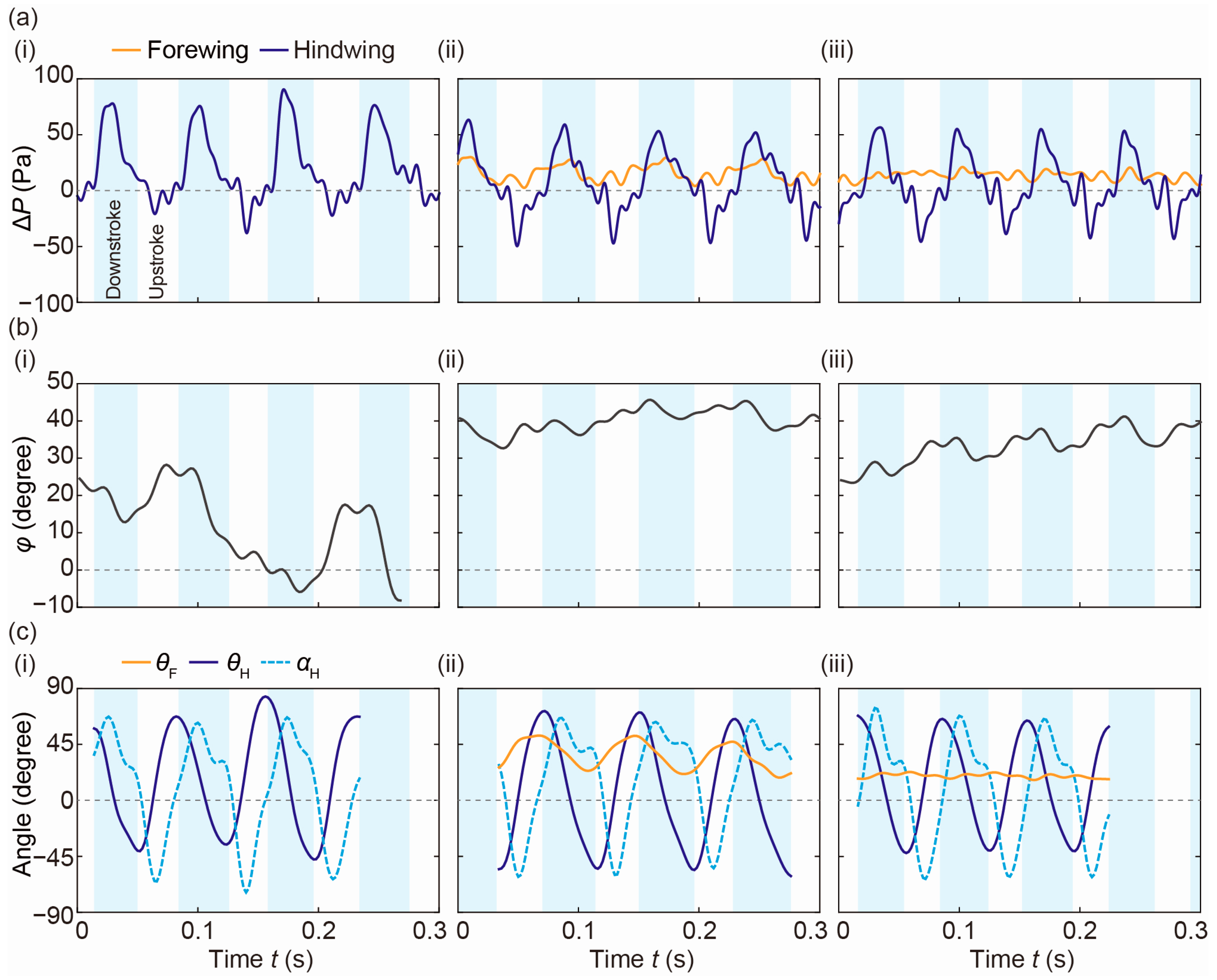
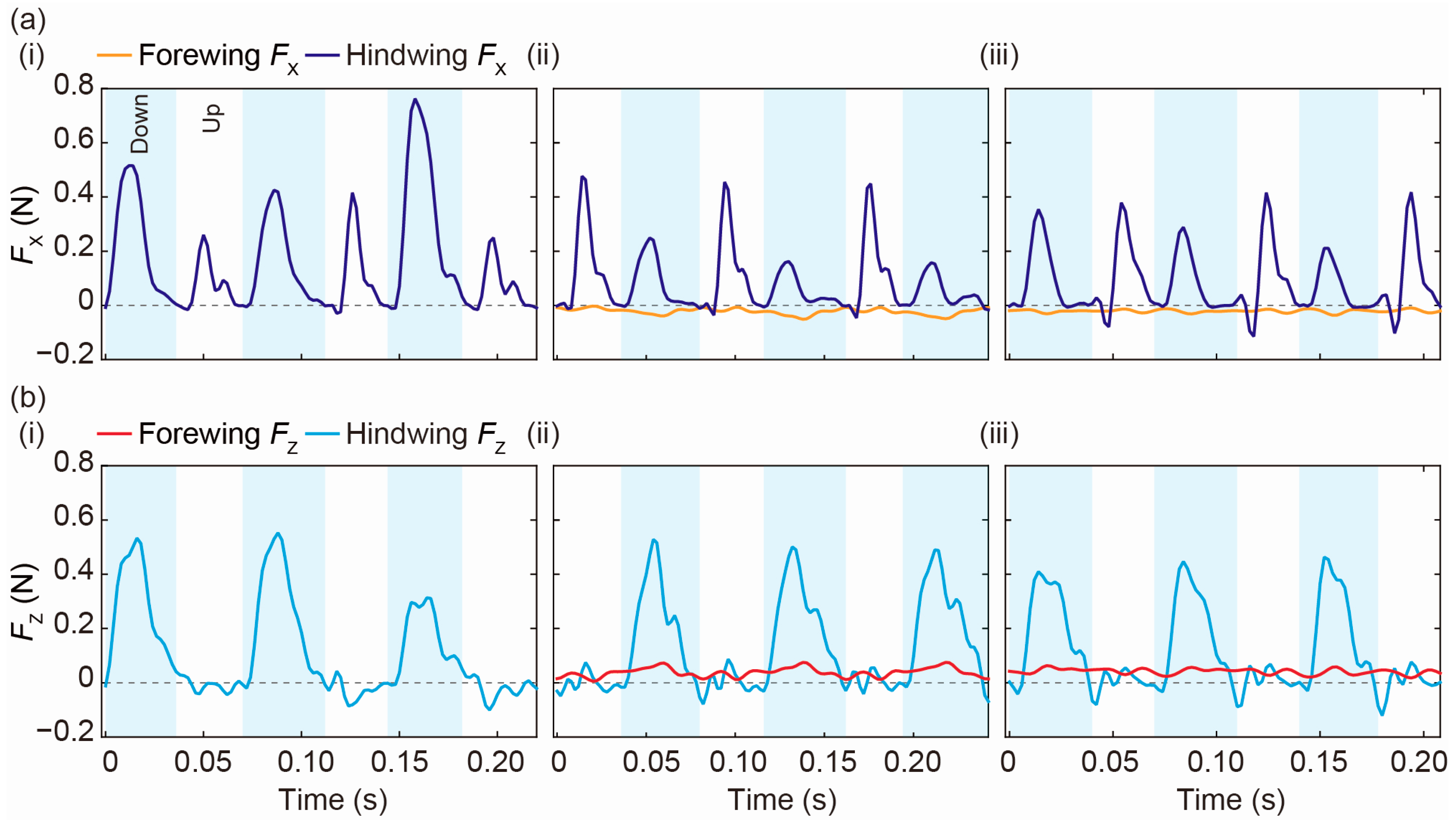
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Result of Differential Pressure Measurement
4.2. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dudley, R. The Biomechanics of Insect Flight: Form, Function, Evolution; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Maruyama, M.; Okabe, Y. Asymmetric hindwing foldings in rove beetles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16349–16352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuribayashi, S. Insects in Flight (Japanaese); Heibonsha Limited: Tokyo, Japan, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- San, H.N.; Tri, T.Q.; Seo, G.N.; Cheol, P.H. Relationship between wingbeat frequency and resonant frequency of the wing in insects. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 046008. [Google Scholar]
- Somps, C.; Luttges, M. Dragonfly Flight—Novel Uses of Unsteady Separated Flows. Science 1985, 228, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, C.P.; van den Berg, C.; Willmott, A.P.; Thomas, A.L.R. Leading-edge vortices in insect flight. Nature 1996, 384, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srygley, R.B.; Thomas, A.L.R. Unconventional lift-generating mechanisms in free-flying butterflies. Nature 2002, 420, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.L.R.; Taylor, G.K.; Srygley, R.B.; Nudds, R.L.; Bomphrey, R.J. Dragonfly flight: Free-flight and tethered flow visualizations reveal a diverse array of unsteady lift-generating mechanisms, controlled primarily via angle of attack. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 4299–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ellington, C.P.; Kawachi, K.; van den Berg, C.; Willmott, A.P. A computational fluid dynamic study of hawkmoth hovering. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aono, H.; Liang, F.; Liu, H. Near- and far-field aerodynamics in insect hovering flight: An integrated computational study. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.; Walker, S.M.; Bomphrey, R.J.; Taylor, G.K.; Thomas, A.L.R. Details of Insect Wing Design and Deformation Enhance Aerodynamic Function and Flight Efficiency. Science 2009, 325, 1549–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, M.H.; Lehmann, F.O.; Sane, S.P. Wing rotation and the aerodynamic basis of insect flight. Science 1999, 284, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, J.M.; Dickinson, M.H. Spanwise flow and the attachment of the leading-edge vortex on insect wings. Nature 2001, 412, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, F.O.; Sane, S.P.; Dickinson, M. The aerodynamic effects of wing-wing interaction in flapping insect wings. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 3075–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Fry, S.N.; Huang, Q.; Deng, X. Aerodynamic damping during rapid flight maneuvers in the fruit fly Drosophila. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.V.; Park, H.C.; Goo, N.S.; Byun, D. Characteristics of a Beetle’s Free Flight and a Flapping-Wing System that Mimics Beetle Flight. J. Bionic Eng. 2010, 7, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.Q.; Truong, T.V.; Park, S.H.; Truong, T.Q.; Ko, J.H.; Park, H.C.; Byun, D. Improvement of the aerodynamic performance by wing flexibility and elytra–hind wing interaction of a beetle during forward flight. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.Q.; van Truong, T.; Tran, H.T.; Park, S.H.; Ko, J.H.; Park, H.C.; Byun, D. How Could Beetle’s Elytra Support Their Own Weight during Forward Flight? J. Bionic Eng. 2014, 11, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.C.; Engel, S.; Baird, E.; Dacke, M.; Muijres, F.T.; Hedenström, A. Elytra boost lift, but reduce aerodynamic efficiency in flying beetles. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 2745–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Truong, T.; Le, T.Q.; Byun, D.; Park, H.C.; Kim, M. Flexible Wing Kinematics of a Free-Flying Beetle (Rhinoceros Beetle Trypoxylus Dichotomus). J. Bionic Eng. 2012, 9, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Truong, T.; Le, T.Q.; Tran, H.T.; Park, H.C.; Yoon, K.J.; Byun, D. Flow Visualization of Rhinoceros Beetle (Trypoxylus dichotomus) in Free Flight. J. Bionic Eng. 2012, 9, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.Q.; Truong, T.V.; Tran, H.T.; Park, S.H.; Ko, J.H.; Park, H.C.; Byun, D. Two- and Three-Dimensional Simulations of Beetle Hind Wing Flapping during Free Forward Flight. J. Bionic Eng. 2013, 10, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maybury, W.L.; Lehmann, F.O. The Fluid Dynamics of Flight Control by Kinematic Phase Lag Variation between Two Robotic Insect Wings. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 4707–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Deng, X.Y. Aerodynamic interaction between forewing and hindwing of a hovering dragonfly. Acta Mech. Sin. 2014, 30, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Sun, M. Dragonfly forewing-hindwing interaction at various flight speeds and wing phasing. AIAA J. 2007, 45, 508–511. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H.; Dung, N.M.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimoyama, I. Differential pressure sensor using a piezoresistive cantilever. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 055015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Tanaka, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimoyama, I. Differential pressure distribution measurement with an MEMS sensor on a free-flying butterfly wing. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2012, 7, 036020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Aoyama, Y.; Ohsawa, K.; Tanaka, H.; Iwase, E.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimoyama, I. Differential pressure measurement using a free-flying insect-like ornithopter with an MEMS sensor. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2010, 5, 036005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Sato, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimoyama, I. Measuring differential pressures with multiple MEMS sensors during takeoff of an insect-like ornithopter. J. Biomech. Sci. Eng. 2014, 9, JBSE0004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Concordel, A.; Paik, J.; Shimoyama, I. The Effect of the Phase Angle between the Forewing and Hindwing on the Aerodynamic Performance of a Dragonfly-Type Ornithopter. Aerospace 2016, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, L.T.; Doyoung, B.; Hoon, Y.Y.; Hwan, K.J.; Park, H.C. Experimental and numerical investigation of beetle flight. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Bangkok, Thailand, 22–25 February 2009; pp. 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Yudhono, R.; Park, H.C.; Han, C.H. Investigation of wing interaction by using a beetle-inspired flapping system. In Proceedings of the 2012 ICME International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering (CME), Kobe, Japan, 1–4 July 2012; pp. 353–356. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Shimoyama, I. Forward flight of swallowtail butterfly with simple flapping motion. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2010, 5, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, M. Wing and body motion and aerodynamic and leg forces during take-off in droneflies. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muijres, F.T.; Chang, S.W.; van Veen, W.G.; Spitzen, J.; Biemans, B.T.; Koehl, M.A.R.; Dudley, R. Escaping blood-fed malaria mosquitoes minimize tactile detection without compromising on take-off speed. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 3751–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
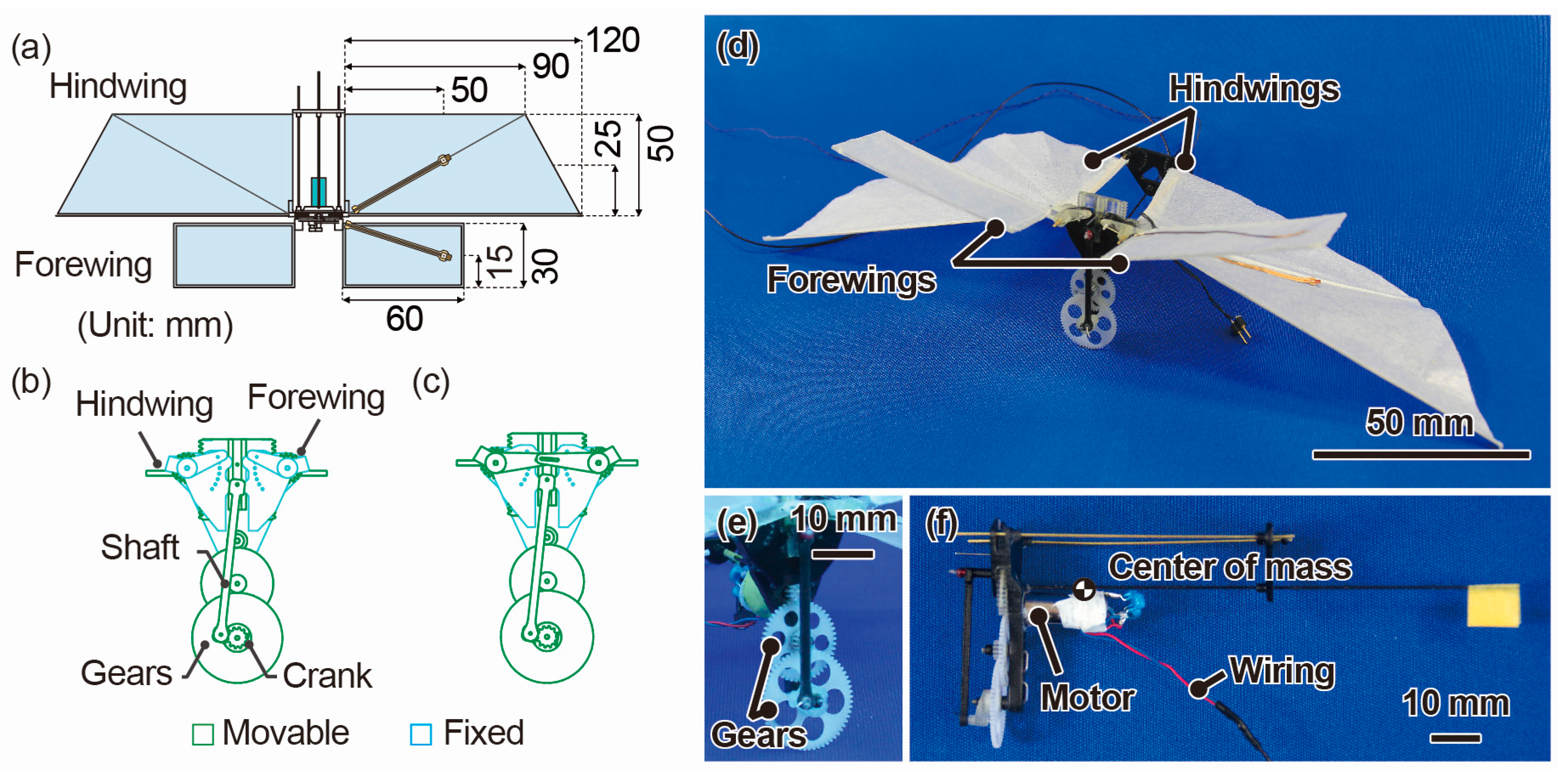
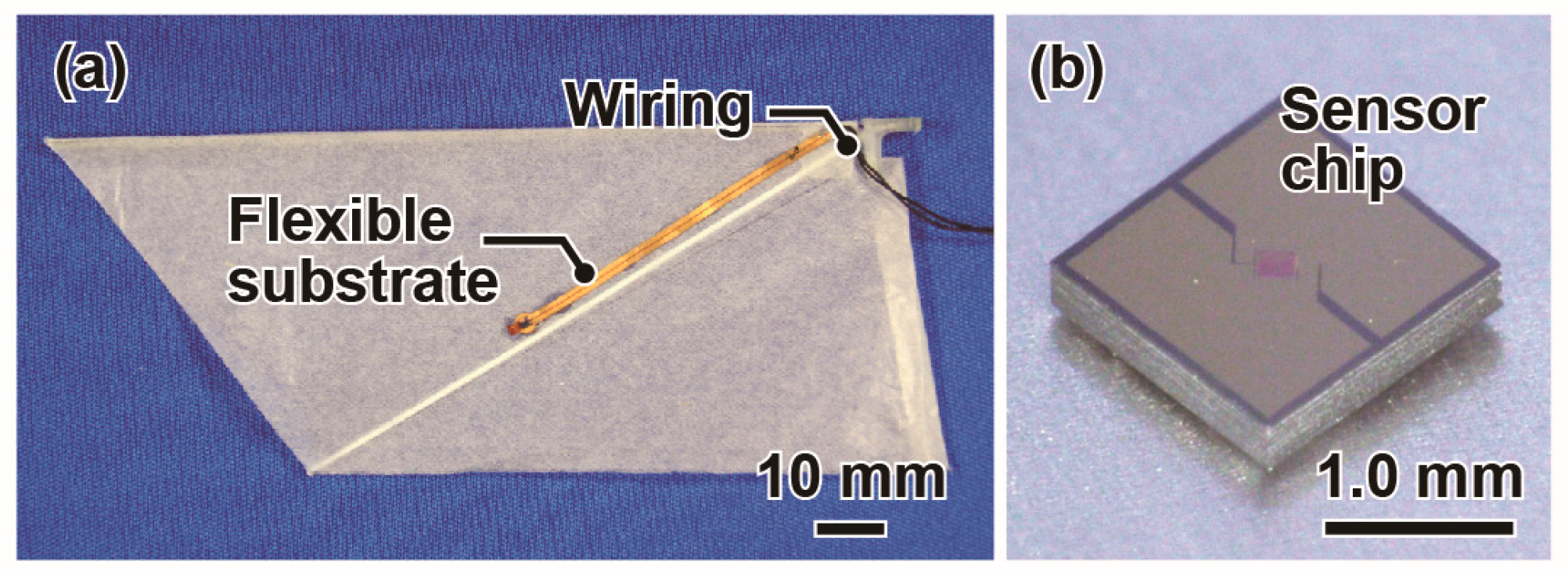
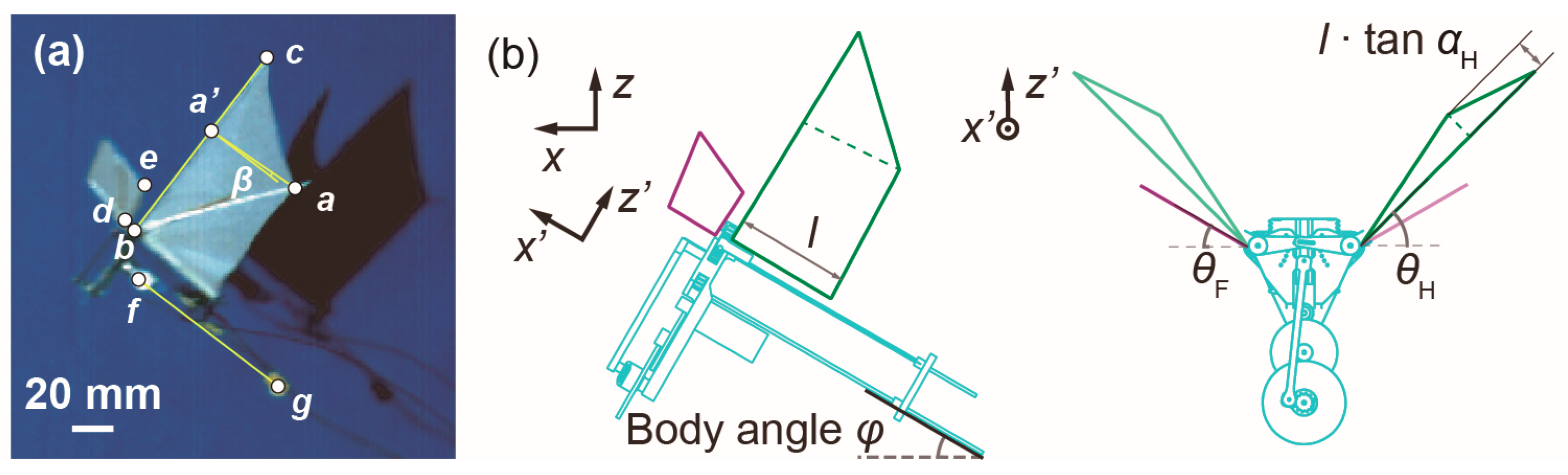
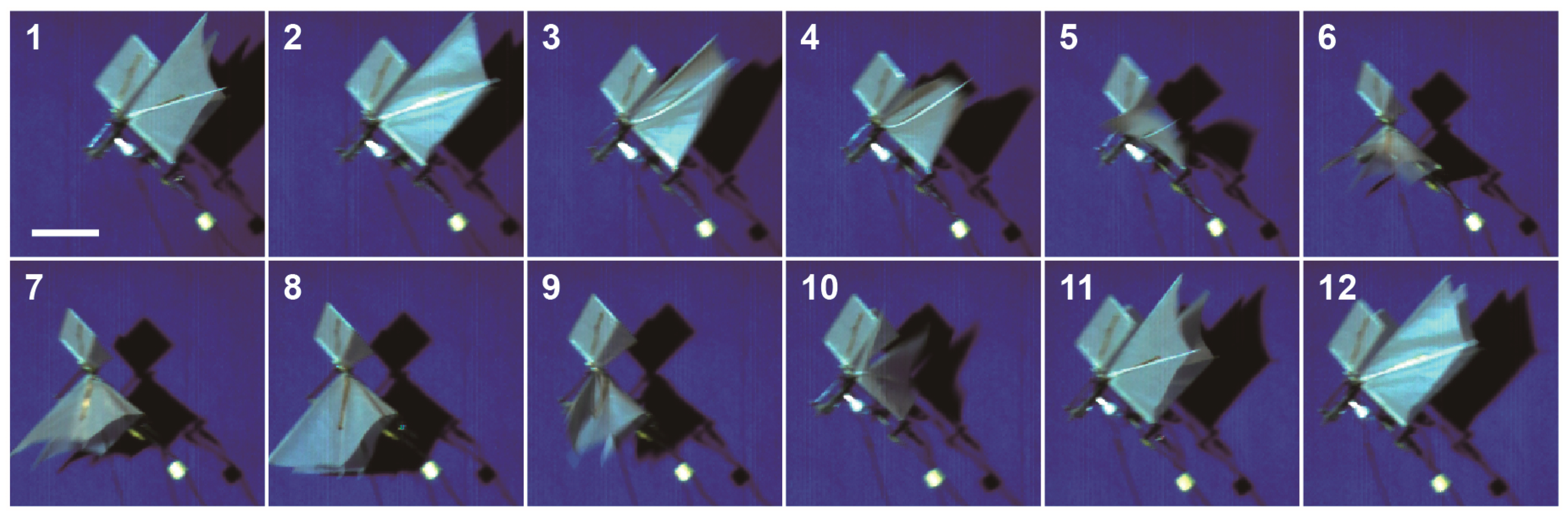
| Characteristics | Unit | Beetle [16,31,32] | Ornithopter with/without Forewing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beetle species | Allomyrina dichotoma | ||
| Hindwing length, s | mm | 56 | 120 |
| Aspect ratio of forewing | ‒ | 2.1 | 2 |
| Aspect ratio of hindwing | ‒ | 2.8 | 2.4 |
| Mass | g | 6~10 | 13.9/12.5 |
| Flapping frequency, f | Hz | 35 | 14/13 |
| Amplitude θP-P of forewing | degree | +10~+50 | +10~+50 |
| Amplitude θP-P of hindwing | degree | −70~+86 | −70~+90 |
| Wing load | N/m2 | 50 (without forewing) | 10.0/12.3 |
| Reynolds number, Re | ‒ | 3.0 × 103 | 6.5 × 103 |
| Reduced frequency, k | ‒ | 0.13 | 0.15 |
| Ornithopter | Body frame | 6.28 |
| Forewings | 0.94 | |
| Hindwings | 0.57 | |
| Total | 7.79 | |
| Cables | Cables for motor supply | 3.60 |
| Cables for sensor signal | 2.51 | |
| Total | 6.11 |
| Characteristics | (i) | (ii) | (iii) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forewing | none | flapping | fixed |
| θF (degree) | ‒ | +10~+50 | +14 |
| f (Hz) | 13 | 14 | 14 |
| Trial number | 7 | 8 | 7 |
| Average ΔP of forewing (Pa) | ‒ | 14.7 ± 1.9 | 12.0 ± 2.2 |
| Maximum ΔP of hindwing (Pa) | 72.8 ± 8.2 | 57.0 ± 4.6 | 51.1 ± 4.3 |
| Minimum ΔP of hindwing (Pa) | −46.4 ± 10.6 | −39.8 ± 5.0 | −41.0 ± 4.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, H.; Abe, K.; Takahata, T.; Shimoyama, I. Experimental Study of the Aerodynamic Interaction between the Forewing and Hindwing of a Beetle-Type Ornithopter. Aerospace 2018, 5, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace5030083
Takahashi H, Abe K, Takahata T, Shimoyama I. Experimental Study of the Aerodynamic Interaction between the Forewing and Hindwing of a Beetle-Type Ornithopter. Aerospace. 2018; 5(3):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace5030083
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Hidetoshi, Kosuke Abe, Tomoyuki Takahata, and Isao Shimoyama. 2018. "Experimental Study of the Aerodynamic Interaction between the Forewing and Hindwing of a Beetle-Type Ornithopter" Aerospace 5, no. 3: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace5030083
APA StyleTakahashi, H., Abe, K., Takahata, T., & Shimoyama, I. (2018). Experimental Study of the Aerodynamic Interaction between the Forewing and Hindwing of a Beetle-Type Ornithopter. Aerospace, 5(3), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace5030083






