Abstract
Over the last decades, there has been great interest in understanding the aerodynamics of flapping flight and development of flapping wing Micro Air Vehicles (FWMAVs). The camber deformation and twisting has been demonstrated quantitatively in a number of insects, but making artificial wings that mimic those features is a challenge. This paper reports the development and characterization of artificial wings that can reproduce camber and twisting deformations. By replacing the elastic material at the wing root vein, the root vein would bend upward and inward generating an angle of attack, camber, and twisting deformations while the wing was flapping due to the aerodynamic forces acting on the wing. The flapping wing apparatus was employed to study the flexible wing kinematics and aerodynamics of real scale insect wings. Multidisciplinary experiments were conducted to provide the natural frequency, the force production, three-dimensional wing kinematics, and the effects of wing flexibility experienced by the flexible wings. The results have shown that the present artificial wing was able to mimic the two important features of insect wings: twisting and camber generation. From the force measurement, it is found that the wing with the uniform deformation showed the higher lift/power generation in the flapping wing system. The present developed artificial wing suggests a new guideline for the bio-inspired wing of the FWMAV.
1. Introduction
Insects are particularly well adapted for flight [1]. The excellent flight performance of insects is primarily attributable to their large power-to-weight ratio [2]. Insects are capable of long-distance flight, hovering and swift maneuvering [3,4]. Wing flexibility is believed to be a key factor for the aerodynamic performance of insect flight [5]. Wing interaction characteristics and flexibility during the flapping motion are primary issues because they are believed to be the main reasons for the best aerodynamic performance of a flying insect [6]. A recent investigation of the effect of wing camber deformations on aerodynamic performance shows that wing deformations are important for enhancing efficiency [7]. Using a dynamically scaled-up robotic model, the influence of wing flexibility on the aerodynamics of flapping wings has been characterized for the artificial wing in the research of Zhao et al. [8]. The significance of wing camber deformation was evident in a wide range of insect groups, such as dragonflies, moths, honeybees, locusts, and hover flies [5]. In the flight of a dragonfly, a positive camber deformation of the hind wing during a downstroke generates a vertical force, whereas a negative camber deformation of the wing during an upstroke generates a thrust force [9]. Spanwise flexibility was found to be beneficial for thrust generation in a numerical study on flapping wing propulsion. The spanwise flexibility yields a small increase in the thrust coefficient and a small decrease in the input power requirement, which results in higher efficiency [10].
Insect flight possesses the perfected design of wings through millions of years of evolution [11]. To remain aloft, insect wings must be moved or deformed during the flapping cycle so that they generate overall more upward than downward force [11]. Walker et al. used photogrammetry to reconstruct and analyze the time histories of wing deformations on the desert locust and hoverflies [12,13]. Both wings were found to be twisted from the root to the tip, the camber was positive on both wings during downstrokes, and the airfoils became corrugated during the upstrokes. In free-flying hoverflies, the angle of incidence and camber both show a recoil effect as they change abruptly at stroke reversal [13]. The flexible wing kinematics of beetle wings in forward flight have been reported in Truong et al. [5]. Hind wings exhibited a twisted shape showing a large variation of the angle of attack from the root to the tip during the upstroke. Despite many efforts to characterize the deformation modes of insect wings, the considerable variations between individual species and between experiments are the major challenges in conducting a study of aerodynamics in flying species [14]. In contrast, man-made flapping-wing models can be studied explicitly under full experimental control [14].
More recently, improving the aerodynamic performance of a flexible flapping wing by mimicking flying insect wings has attracted the interest of researchers. Micro aerial vehicles possess many advantageous characteristics such as small size, low weight, difficult to detect, high maneuverability, and an ability to hover. In order to design an insect-like MAV, the aerodynamic characteristics of flapping flight have been investigated [4,15,16,17,18,19]. Researchers have attempted to develop flapping wing systems that mimic animal flight, including a butterfly-type ornithopter [20], Nano Hummingbird [21], a beetle mimicking flapper [22]. Similar to the wings of flying insects, the artificial wing is the key to the force generation and flight control in the flapping wing MAV. Many researchers, therefore, working on the FWMAV, pay much attention mimicking insect wings. Most insect-scale artificial wings were made of carbon fiber, balsa wood, or thin metal as the wing veins, with different polymer films as the wing membrane. The artificial wings have been fabricated using microelectromechanical systems photolithography and an etching method [23], combination of smart composite microstructures and soft lithography technique [24], fabrication method based on the composite manufacturing technique [22,25]. Few studies have been conducted to study the aerodynamics of flexible artificial wings. Bhayu et al. [26] fabricated an artificial, cambered wing that mimicked the hind wing of a beetle. The thrust produced by the flapper with the cambered-wings was about 10% higher than that of the flapper with uncambered-wings [26]. However, the camber deformation of the wing was the pre-camber by using a balsa mold with an inclined height. It was noted that the camber deformation in an insect wing is a result of the wing motion [11]. Pin Hu et al. [25] experimentally analyzed the aerodynamics of flexibility of six hummingbird shaped membrane wings. Driven by a single DOF (degree of freedom) flapping wing mechanism, the wings could produce twisting and bending deformations. It was found that for a specific spatial distribution of flexibility, there existed an effective frequency range in thrust production [25]. Most recently, by using wrinkled film, a passive camber deformation was generated during flapping [27]. Although there has been considerable progress in developing flapping wing micro air vehicles and artificial wings, there is a lack of literature in mimicking the important features of the insect wing.
In this work, we designed and fabricated the artificial wing MAV that can mimic and reproduce camber and twisting. We developed and employed the flapping wing apparatus to study the flexible wing kinematics and the aerodynamics of a real scale insect wing. The flapping wing mechanism could achieve a maximum stroke amplitude of 92°, which is within the flapping angle range of insect flight (60° for honey bee [28] and 77° to 103° for hawkmoth [29]). Lightweight artificial wings with the venation patterns of insect wings have been fabricated based on a composite material manufacturing process. Multidisciplinary experiments were conducted to provide the natural frequency, force production, and three-dimensional wing kinematics as well as the effects of wing flexibility experienced by the flexible wings. The aerodynamic performance of the present flapping wing MAV was carried out in the hovering condition. Stereoscopic digital particle image velocimetry (SDPIV) was used to obtain the flow structures around the wing at the Reynold number of approximately 3500. The results of unsteady aerodynamics of the flexible wings presented in this work can be used in the efficient wing design for the flapping wing MAV.
2. Flapping Mechanism and Wing Design
2.1. Flapping Mechanism
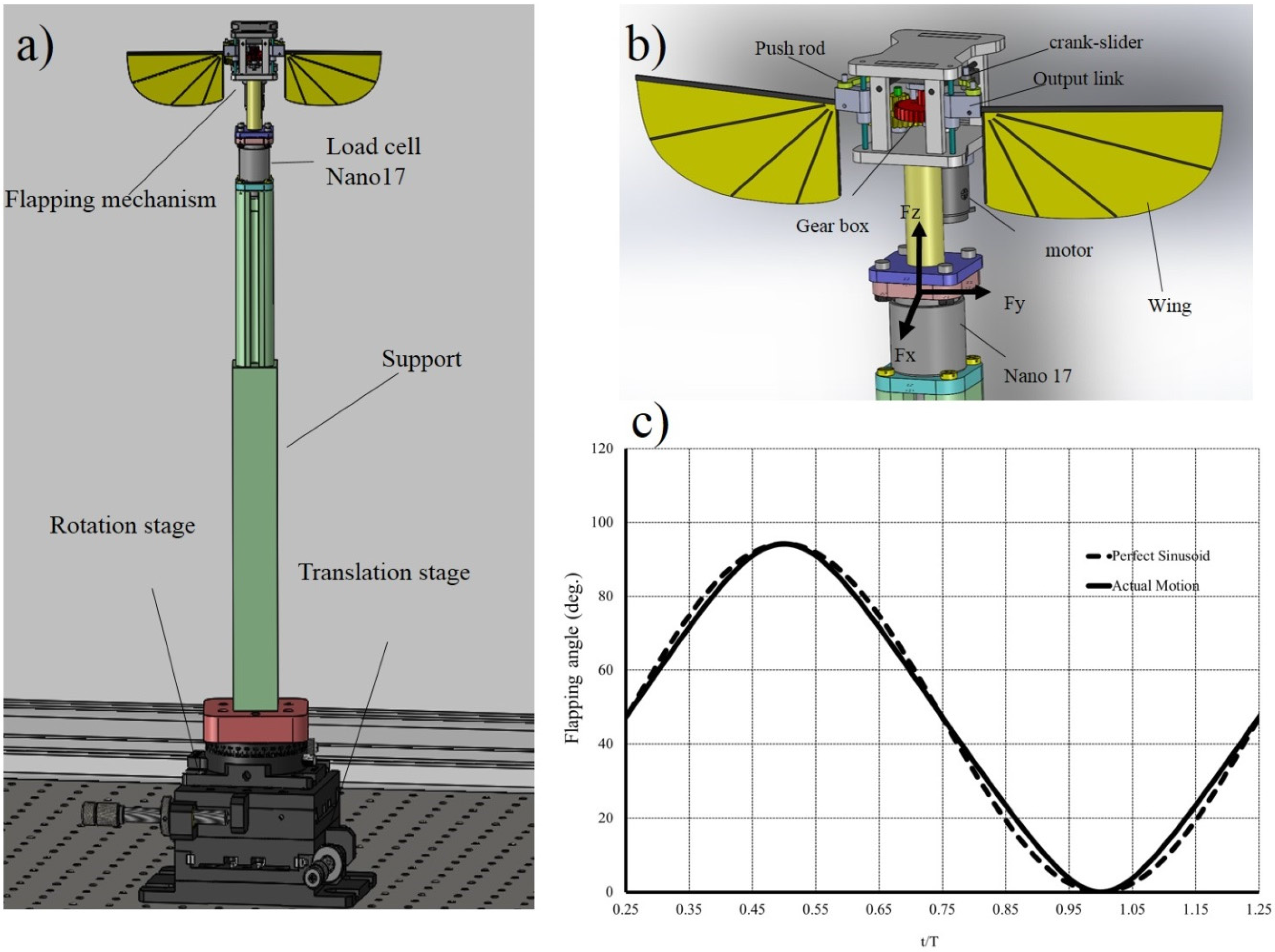
The flapping mechanism consists of a Scotch-yoke and crank-slider mechanism (Figure 1). The rotating output from the motor is first converted into linear motion with a crank slider mechanism. The flapping wing mechanism can achieve a maximum stroke amplitude of 92°, which is within the flapping angle range of insect flight. The kinematics of the flapping mechanism are close to the sinusoidal kinematic profile as shown in Figure 1c. The flapper is powered by a DC power supply and can flap at flapping frequency of 10 to 25 Hz.
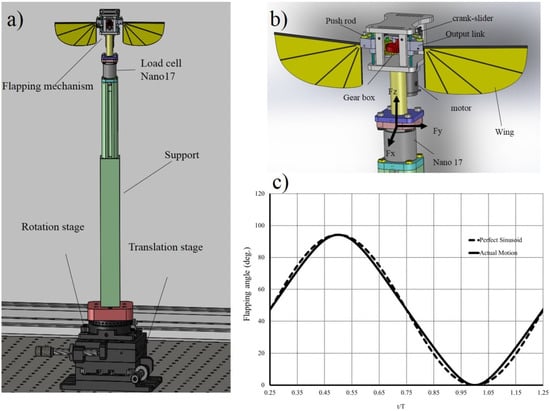
Figure 1.
(a) CAD drawing of a fully assembled flapping wing; (b) flapping mechanism; and (c) output flapping angle of the flapper at flapping frequency of 15 Hz.
The flapping mechanism was mounted on a Nano 17 (Nano 17 IP68, ATI Industrial Automation, Apex, NC, USA) six-component force balance and a supporting frame. The wings were aligned vertically and flapped in the horizontal plane. The support frame was mounted on a rotating mount and a translation stage (Figure 1). The total height of the flapping wing system was 484 mm. This was designed to isolate the apparatus from outside disturbance, whilst minimizing the wall interference effects in the experiment. The linkages and the supporting frame of the flapper were fabricated by a precision computer numerical control (CNC) machining of acrylic sheet.
2.2. Flexible Wing Design
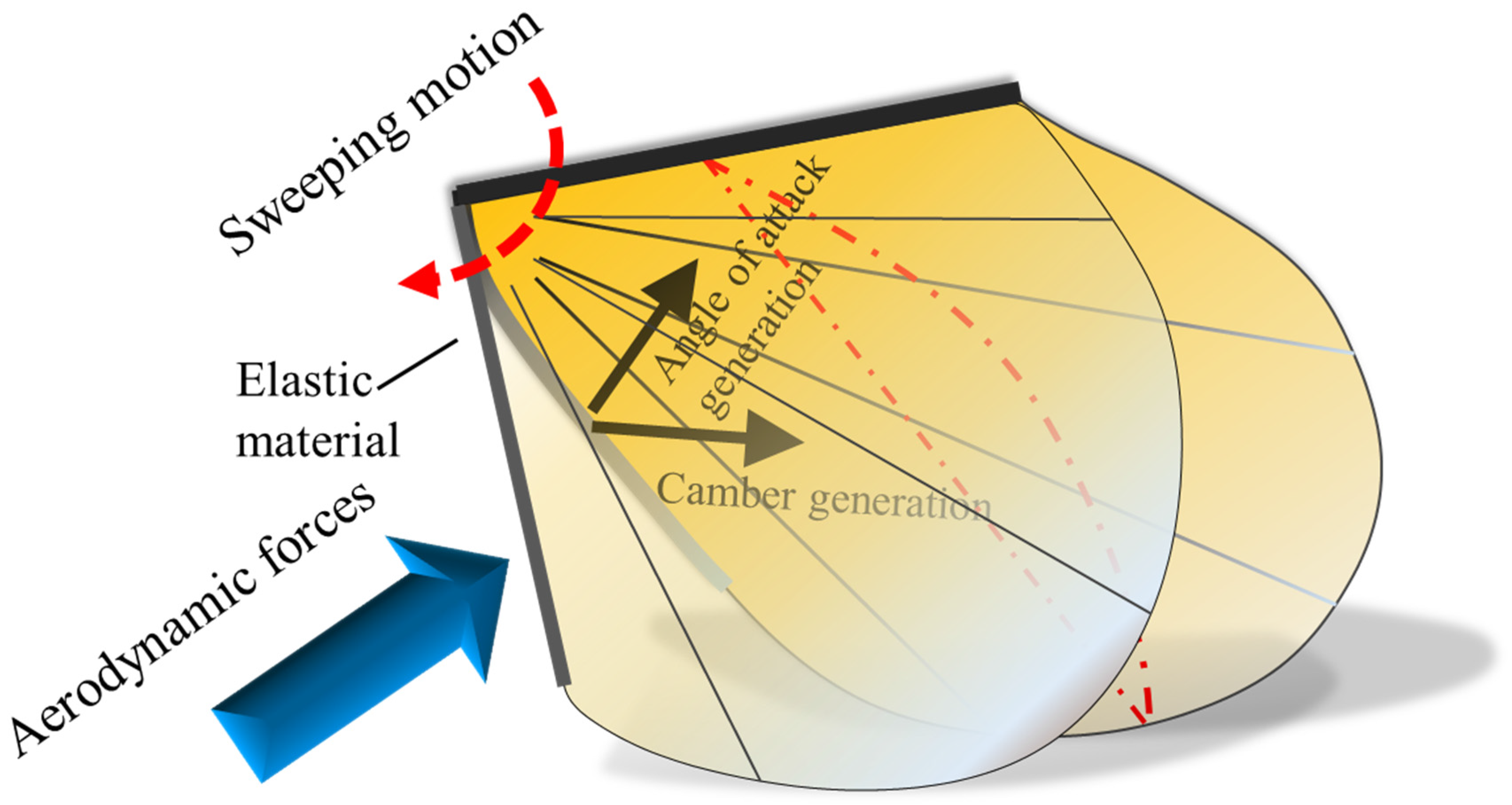
Insect wings are remarkable structures, apparently unique among animal propulsive appendages in the degree of automation in their function [30]. The major challenge in designing the FWMAV is mimicking the flexibility of the insect wing. Due to the requirement of low weight, the complexity of mechanisms in the FWMAV should be minimized as far as possible. Most of the active wing motion in the FWMAV is typically 1-DOF flapping which means that the wing must passively deform due to the approximate angle of attack [27]. In addition, during flapping flight, the insect wing is passively deformed [31]. In this study, we propose a passive deformed wing based on elastic bending. Figure 2 shows the conceptual schematic of the flexible wing design. To be able to generate the angle of attack during flapping, the root vein stiffness is created using an elastic material. Due to the aerodynamic forces acting on the wing, the elastic root vein will bend upward while the wing is flapping. Moreover, the elastic root vein is able to bend in the spanwise direction, producing the camber.
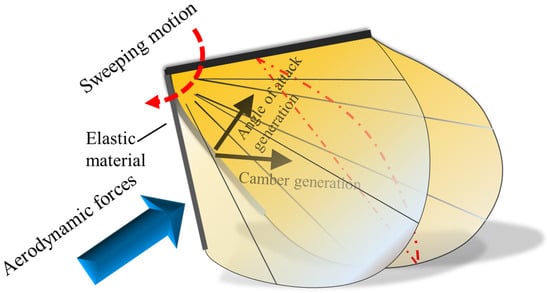
Figure 2.
Conceptual schematic design of an elastic deformation wing. While the wing is moving in sweeping motion, the root vein is bending due to the aerodynamic forces acting on the wing. It bends upward, producing the angle of attack, and bends inward, producing the camber.
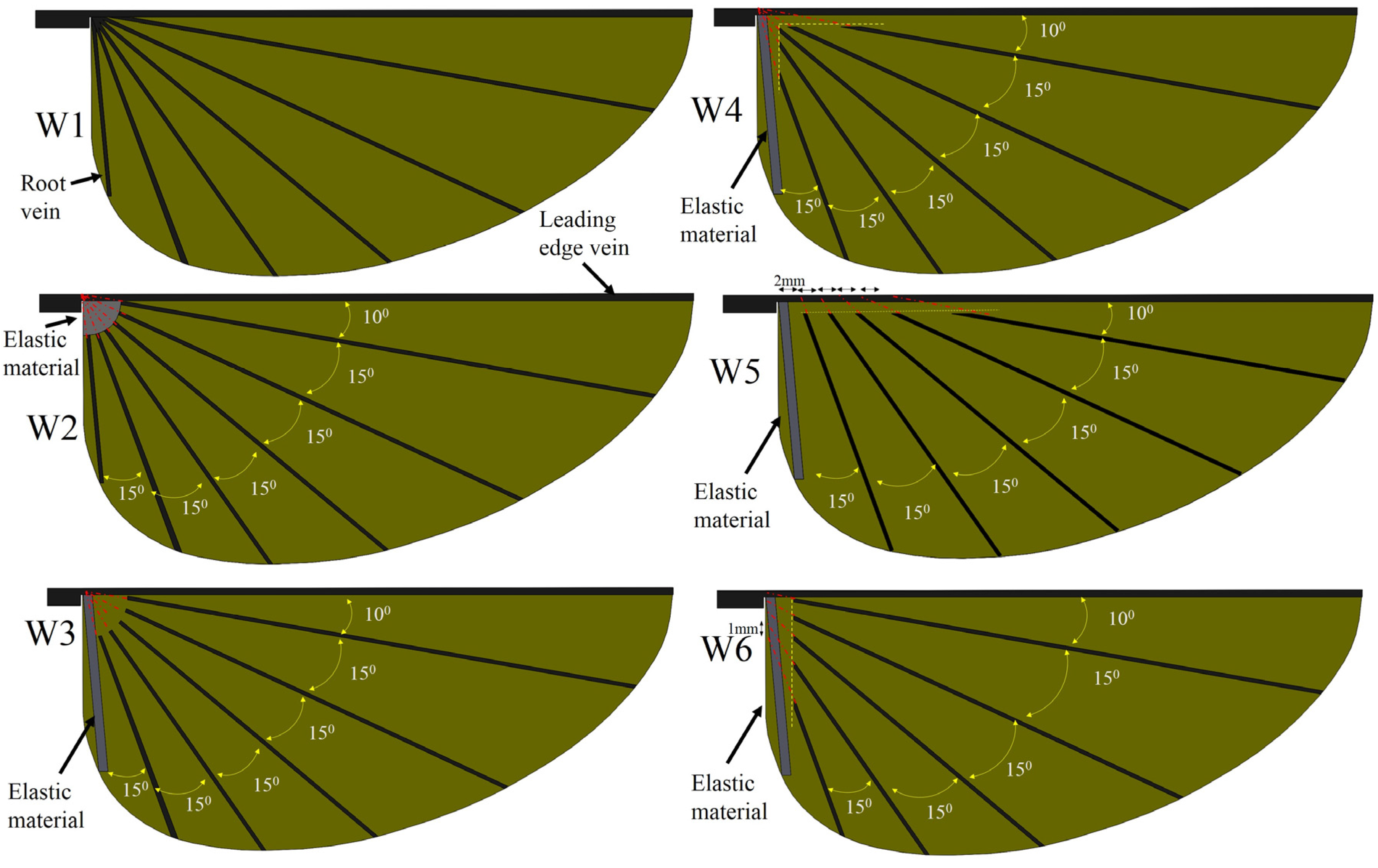
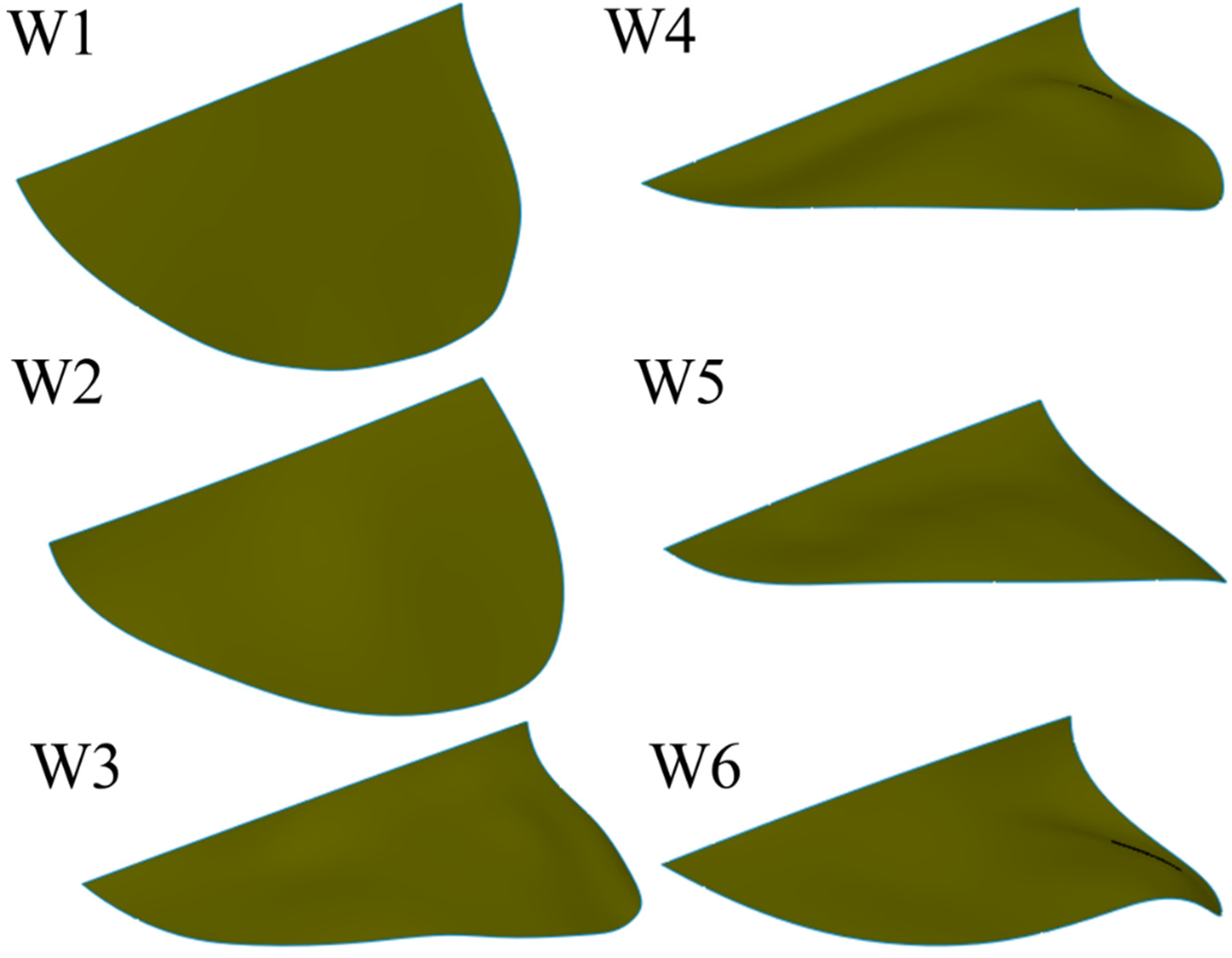
The wings are made of three materials: carbon fiber sheet (density of 1600 kg/m3, Young’s modulus of 70 GPa), Kapton film (density of 1390 kg/m3, Young’s modulus of 0.75 GPa) and Mylar film (density of 1400 kg/m3, Young’s modulus of 2.6 GPa). A flat Kapton film with a uniform thickness serves as the wing membrane. To mimic the insect wing, the thickness of designed veins is different, as the vein of the leading edge is generally thicker than the other veins. In the present wing design, carbon fiber strips of 0.8 mm width are used for the leading edges, while other veins are made with carbon fiber strips of 0.2 mm width. The thickness of the leading edge and other veins are 0.5 mm and 0.2 mm, respectively. The membrane thickness of the wings is designed to be 0.012 mm. The thickness of Mylar film (elastic material) is 0.1 mm. Beta probability density function (BPDF) was proposed by Ellington [32] to describe wing shapes based on data of different insects’ morphological parameters. The present designed wing shape coincided very well with the real hawkmoth wing, and the slight difference was due to the straight leading edge of the BPDF described wing shape [33]. The leading edge is straight and the trailing edge is an elliptical shape. The wing has a length of 65 mm. The mean chord is around 23 mm and the wing area is 1503 mm2. Six wings were designed, fabricated, and tested. Details of the wing vein positions and angles are presented in Figure 3. The angle between the veins is maintained at 15° for all six wing models.
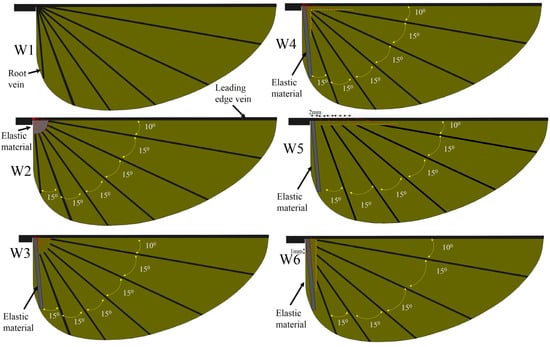
Figure 3.
Schematic of wing designs.
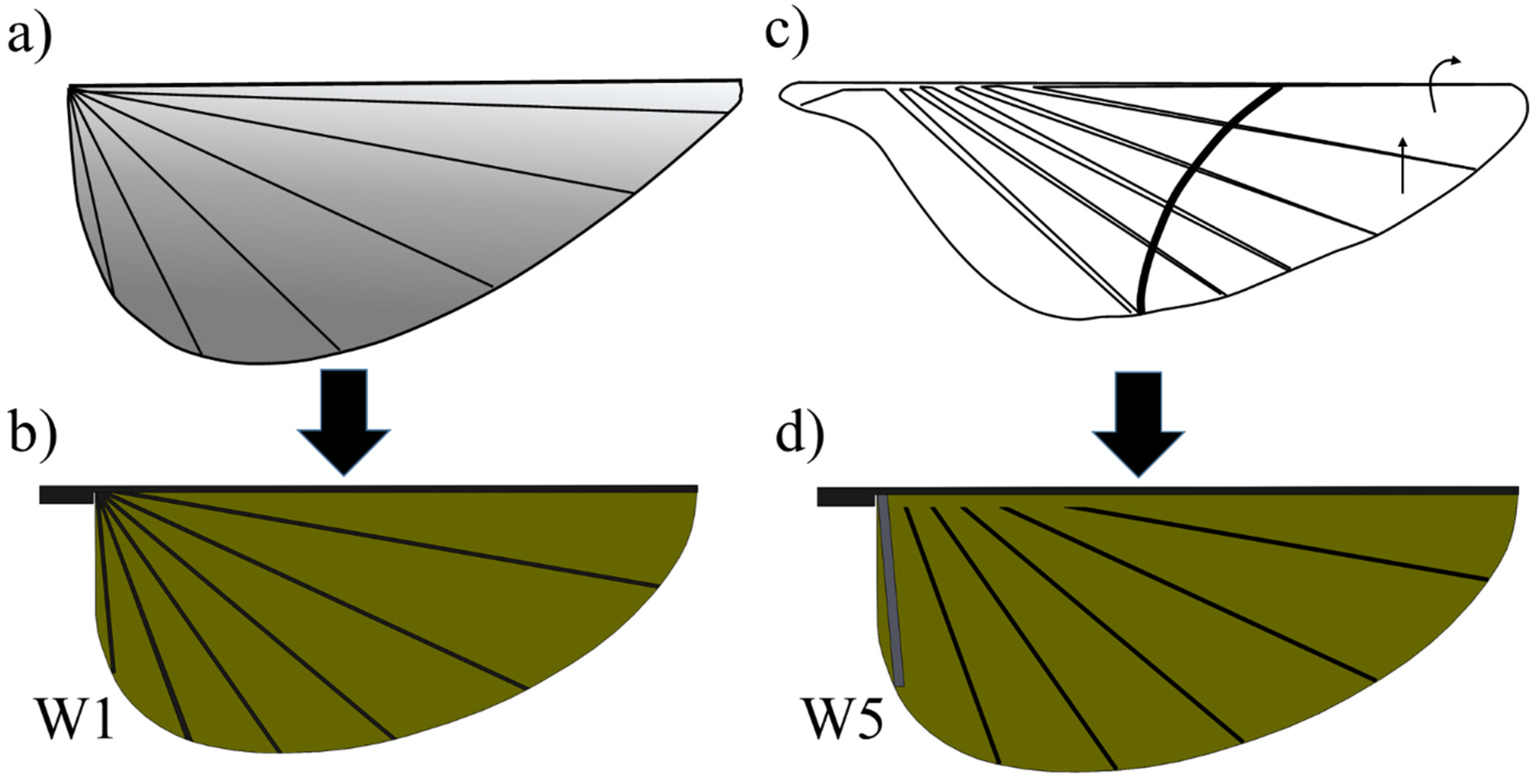
The vein pattern of the artificial wing in this study was derived from the insect wing model of Wootton [30] and Ennos [34]. In Wootton’s model, the wing veins were compressed and bent like the spokes of an umbrella, curving the wing surface as shown in Figure 4a. Ennos [34] proposed two insect wing vein pattern that created the camber; the wing with curved veins and veins spread out along the leading edge and straight veins offset from near the wing base at equal intervals and deliver to the tip (Figure 4c). In the first model, the camber of the wing is divided into two zones; for the first, the camber is positive at near the leading edge and negative near the trailing edge. In the second model, the veins will transverse a chordwise wing section closer together near the front of the chord, causing a higher curvature camber near the leading edge and the center of the camber will be brought in front of the mid-chord [34]. This model produces the best camber profile shape. Figure 3 shows the conceptual schematic of vein designs. The wings are named W. For W1, the root vein is made of carbon fiber and the veins in the wing are fixed to the wing base. The vein patterns of W1, W2, W3 and W4 are inspired by the spokes of an umbrella. The wings are reinforced by veins that travel from the base to the trailing edge. The base of W2 is made of an elastic material, and the root vein is made of carbon fiber and fixed to the wing base. W2 is designed to test the concept of a wing with an elastic base that can produce camber or not.
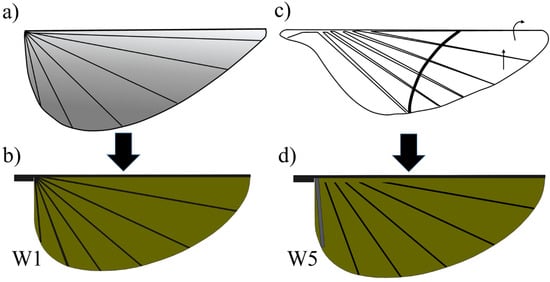
Figure 4.
Conceptual schematic of vein designs: (a) wing veins like the spokes of an umbrella (redrawn from [30]); (b) vein pattern of W1 is derived from (a); (c) the straight veins offset from near the wing base at equal intervals and diverge to the tip ( redrawn from [34]); and (d) vein pattern of W5 is derived from (c).
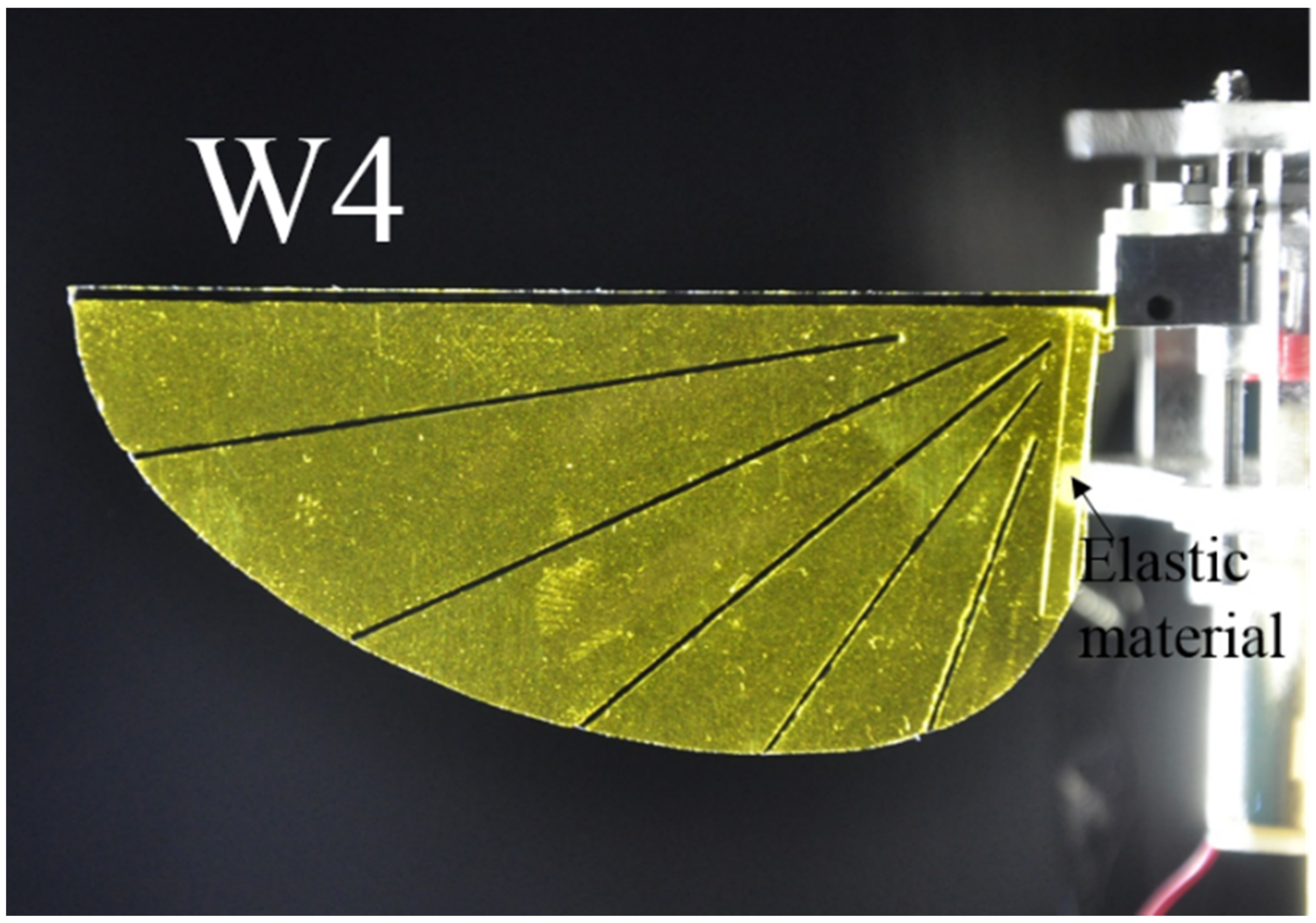
The root veins of W3, W4, W5, and W6 are made of an elastic material and have shown be generated camber and twisting deformations. The Mylar film serves as the elastic material. The veins inside these wings are not connected to the leading edge. The leading edge vein and root vein are constrained. The wing pattern of W5 is derived from the second model of Ennos (see Figure 4)). In Ennos’s model (Figure 4c), the camber is created by the torsion of the leading vein, the U-shape structure, to which other slant veins are connected. However, the technique to fabricate the U-shape leading edge vein is beyond the scope of this study. The slant veins are not connected to the leading vein in the wing models in the present work. Only the layout of the slant vein in Ennos’s model is desired in this work. The wing with curved veins in the first Ennos’s model is hard to fabricate and this model does not produce the positive camber as described above. The first model is thus not applied is this study. Patterns of supporting veins in insect wings vary widely among the insect orders and affect to the flexural stiffness and deformability of insect wing during flight [35]. W3, W4, W5, and W6 are also designed to evaluate the influence of the vein patterns on the camber deformation. The layout of veins in W3, W4, W5, and W6 are different as shown in detail in Figure 3. In W3, the straight veins stretch from the trailing edge and form the curve near the base (Figure 3). The veins stretch to both the trailing edge and root veins in W4, to the leading edge only in W5 and to the root vein only in W6. The vein pattern of W5 is close to that of Ennos’s wing model [34] except that the veins are not fixed to the trailing edge. Our experiments show that those wings with veins connected to the leading edge or root vein were not able to generate camber or twisting deformations. The wing mass is less than 0.14 g. Figure 5 shows a photograph of the flexible W4.
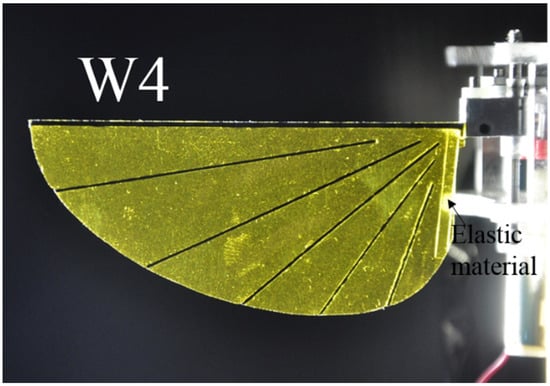
Figure 5.
Photographs of the flexible W4.
2.3. Wing Manufacturing
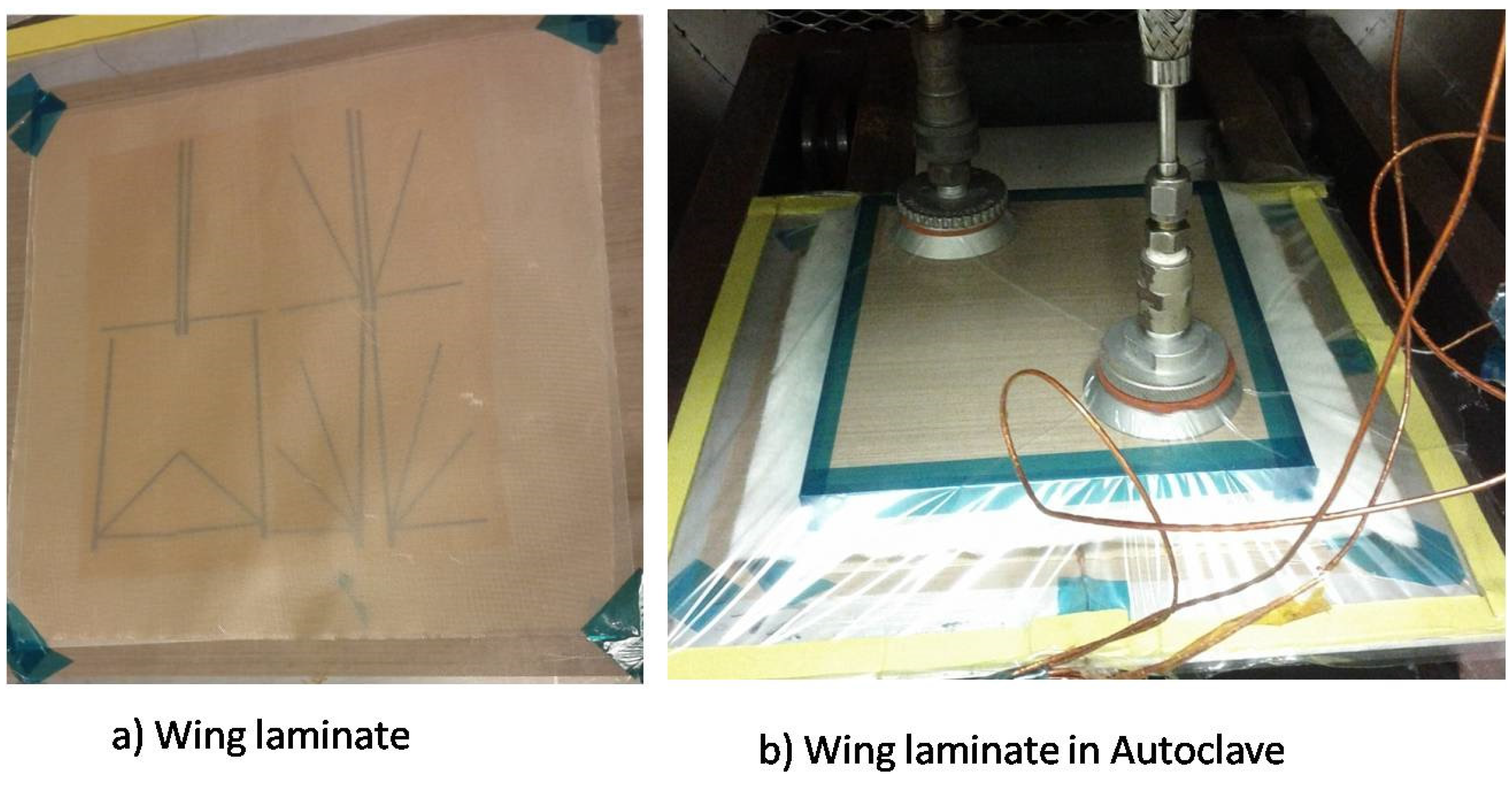
The wings are fabricated using a composite material manufacturing technique, similar to a previous study [22]. First, the wing mold is made out of paper with the vein pattern of an insect wing printed on. A carbon fiber sheet is cut in the desired venation structure of the wing using a precision CNC machine. The veins are bonded to the Mylar film with an adhesive. After patterning, another Teflon film was placed to cover the aluminum plate, and a sealed bag is made to apply vacuum pressure. The wings are cured in the autoclave oven for 5 h with an approximate profile temperature to bond the carbon fiber and Mylar film together as shown in Figure 6. First, the temperature was increased from 30 to 130 °C in 1 h. Then, this temperature was kept constant for 2.5 h. Finally, the temperature was gradually reduced from 130 to 30 °C over a 1.5 h period. The cured wings were released from the base and taped on the mold. The artificial wing shapes were then cut following the designed shape.
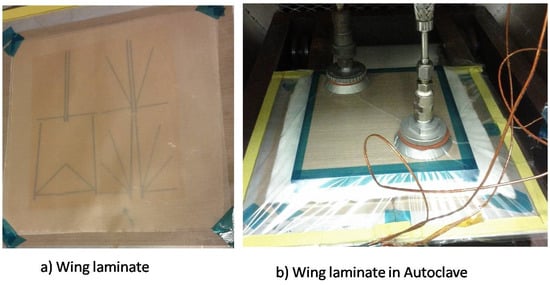
Figure 6.
Wing manufacturing: (a) the composite laminate; and (b) cured in autoclave.
3. Experimental Apparatus and Procedure
3.1. Force Measurement
A six-axis force/torque sensor (Nano17, ATI industrial Automation Inc., Apex, NC, USA) is used to measure the instantaneous aerodynamic forces on the flapping wing mechanism. The force sensor (17 mm diameter, 20.1 mm length) is attached to the base of the flapping mechanism (Figure 1a). Using a data-acquisition board and programs written in LabView (National Instruments, Austin, TX, USA) (A/D conversion), the force data are recorded at the sampling rate of 3000 Hz. The LabView program collects raw voltages from the sensor during testing. These voltages are later post-processed with the ATI-supplied calibration matrices to generate the forces and moments. The LabView program is synchronized with the flapping motion. The force signal is filtered offline with a zero phase delay low-pass digital Butterworth filter. A Hall sensor (Melexis, Rozendaalstraat, Belgium) was mounted on the mechanism, in conjunction with magnets mounted on the crank. The Hall sensor is mounted on the setup so that through the course of the beginning of the downstroke, it transverses magnet, thereby giving the triggering signal to synchronize the motion with the force measurement. It should be noted that the flapping mechanism is a complicated mechanical system that consists of many parts (gears, bars, etc.), generating vibration that contaminates the force sensor signal. Because both the wings and the actuation mechanism are in reciprocal motion, the inertial loading of parts during acceleration and deceleration is significant. To evaluate the forces produced by the mechanism, force measurement is conducted by flapping without wings. The flapping frequencies of the mechanism both with and without the wing attachments are adjusted to be matched. The data is filtered by using a low-pass filter with a cut-off frequency that is three times greater than the flapping frequency.
3.2. Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) and Deformation Measurement
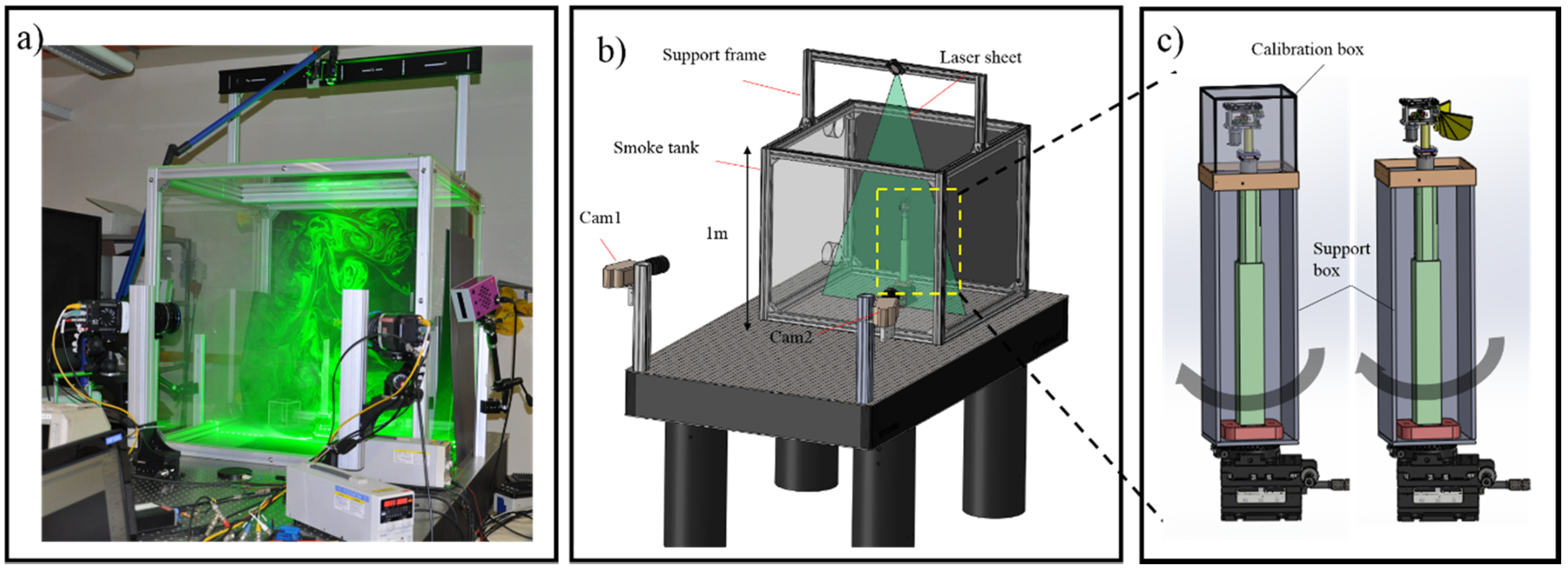
To quantify the instantaneous flow structures and measure flow fields of flapping wings, we used a Stereoscopic PIV (S-PIV) system. The components and arrangement of the S-PIV experiment setup are shown in Figure 7. The S-PIV system comprises two high speed camera Phantom Micro 320s (Ameteck, Wayne, NJ, USA) and a laser Nd:LDY double pulsed with a wave length of 527 nm generated laser sheet. The laser beam converts to a light sheet by light sheet optics. Two cameras are aligned to the laser sheet with approximate angles and lenses of the cameras are relative to the bodies of the cameras according to the Scheimplug condition. The smoke tank, which is a cube with 1000 mm on each side, is designed and fabricated to assure the correct concentration of smoke particles in the flow (Figure 7a). The air in the smoke tank is seeded with smoke particles generated from a smoke generator. The fully assembled flapping mechanism is housed at the center of the smoke tank and operated in the desired quiescent environment (Figure 7b). In comparison to previous studies [36,37,38] the size of the tank is sufficiently large to ensure the absence of wall effects. The images are captured by the Phantom Micro high speed cameras and then processed by the commercial PIV software TSI (TSI Inc, Shoreview, MN, USA) using a standard cyclic Fast Fourier Transform (FFT)-base cross-correlation algorithm. In the cross-correlation procedure, the first pass initial interrogation window size is fixed at 64 × 64 pixels, followed by a second pass with 32 × 32 pixels and 50% overlap.
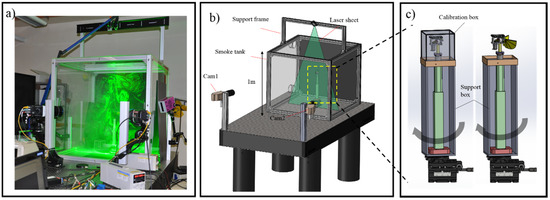
Figure 7.
(a) Photograph; (b) schematics of S-PIV experimental set up; and (c) experimental setup of 3D reconstruction.
In 3D wing reconstruction experiments, 44 black ink dots of approximately 1 mm diameter are marked on the wings as anatomical landmarks for digitization purposes. Two high-speed video cameras are used to obtain the three-dimensional kinematics of the flapping wing. Since the two cameras cannot provide a full view of whole dots on the wing when the wing is flapping, the calibration box and support box are designed to overcome this limitation. The Hall sensor is mounted on the setup so that through the course of the beginning of the downstroke, it transverses magnet, thereby giving the triggering signal to synchronize the motion. By rotating the assembly of the flapping mechanism, more than two pairs of images can be recorded at the same instant of the flapping cycle as shown Figure 7c. Before recording images, the calibration box is placed on the top of the support box and the wings are removed (Figure 7c). The calibration box has the dimension of 200 mm × 200 mm × 200 mm and 50 circular dots distributed with a spacing 20 mm in lateral and vertical directions. After the calibration box is captured to calibrate the camera, it is removed from the flapping wing system. The wings are then assembled to the flapping mechanism for the motion capture. The images are recorded at 1200 fps with a pixel resolution of 1900 × 800. The three-dimensional coordinates of each point are built up using the direct linear transformation method (DLT) [39]. The kinematic data (angle of attack, camber deformation) were filtered with a Butterworth filter at a cut-off frequency of nearly four times the flapping frequency as follows a previous study [5].
3.3. Natural Frequency Measurement
The natural frequency is an important parameter in the design of an artificial wing and can be used to provide guidelines for the design of biomimetic insect scale artificial wings. Moreover, the flexibility characteristics of the wings could be investigated in the natural frequencies. Therefore, in this work, we experimentally measured the resonant frequency of six wing models to study the relationship between dynamic characteristics and flexibility.
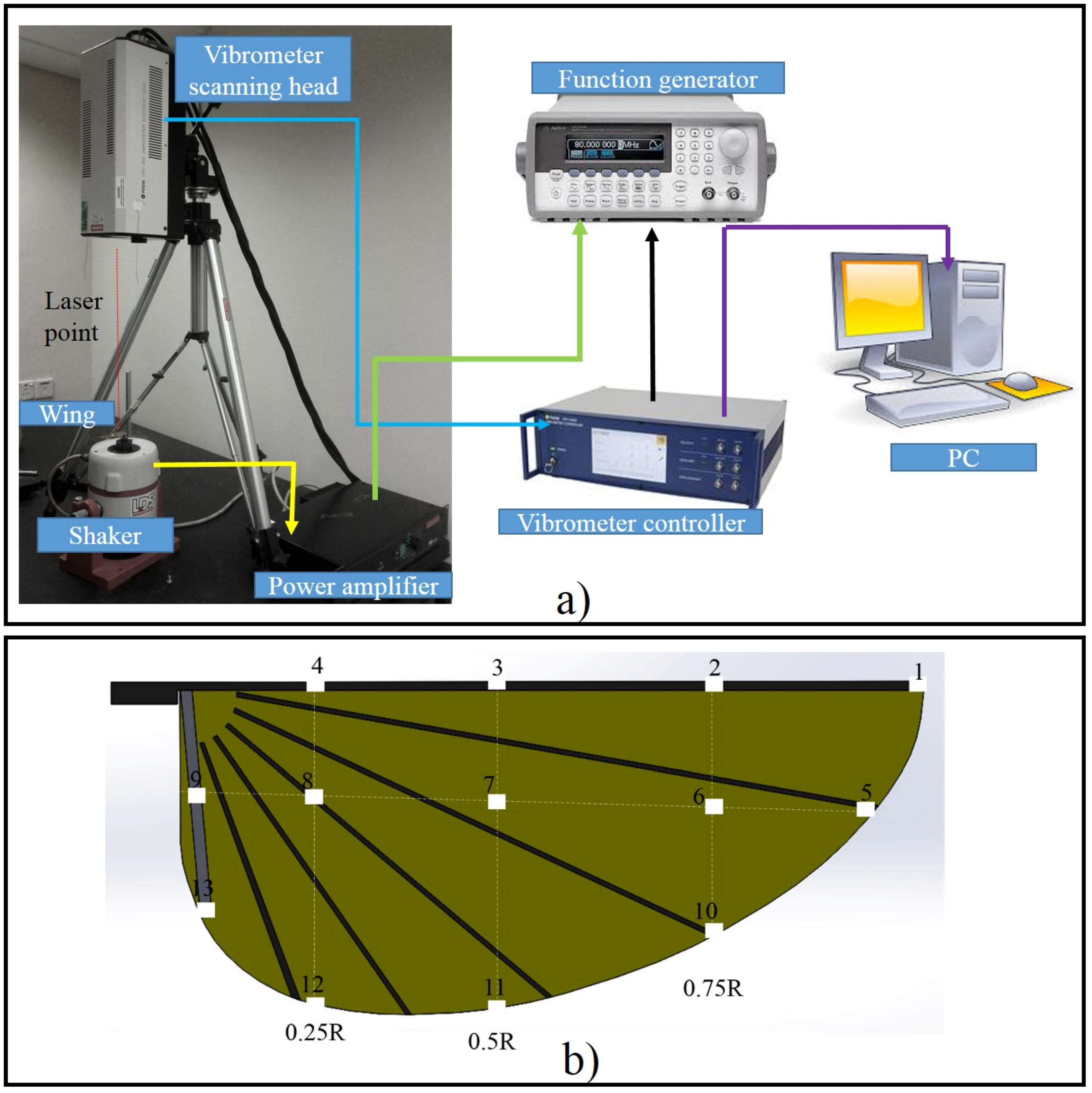
The base-excitation modal testing technique was employed in this work to measure the natural frequency of the artificial wing. It has been used in recent studies to investigate the dynamic characteristics of the insect wing [40]. The schematic diagram of the experimental apparatus is presented in Figure 8a. The artificial wing was glued onto the vibrating base of an electro-mechanical shaker (TIRA TV 50009, TIRA Inc, Schalkau, Germany) with cyanoacrylate-based adhesive. The Polytec PSV-400 Scanning Laser Vibrometer (Plytec Inc, Irvine, CA, USA) was used to capture the displacement of the wing at every spot over the wings. The scanning laser followed a pre-set pattern of spots over the surface of the wings. The photon probe of the Vibrometer scanning head was adjusted and calibrated so that one light beam was perpendicular to each of the spots. The shaker was connected to an amplifier that received signals from a function waveform generator (33120A, Agilent, Aligent Technologies Inc, Loveland, CO, USA). The power amplifier provided sufficient power to the shaker to excite harmonic motion at certain frequencies. In order to isolate contaminating noise from the floor, the shaker and Vibrometer Scanning head were placed on a vibration isolation table, as shown in Figure 8a. An FFT analyzer was used to conduct sweep-sine measurements and an average of five scans per point was recorded and processed. The measurements were conducted for all 13 painted spots on each wing. All signal processing, including coherence plots and frequency response function plots, were transferred to and stored in a personal computer and automatically archived with the Polytec software (Plytec Inc, Irvine, CA, USA) suite. After the preliminary testing, there were no resonance peaks higher than 400 Hz. The range of the swept-sine signal was therefore applied across the best range from 0 to 400 Hz in this experiment.
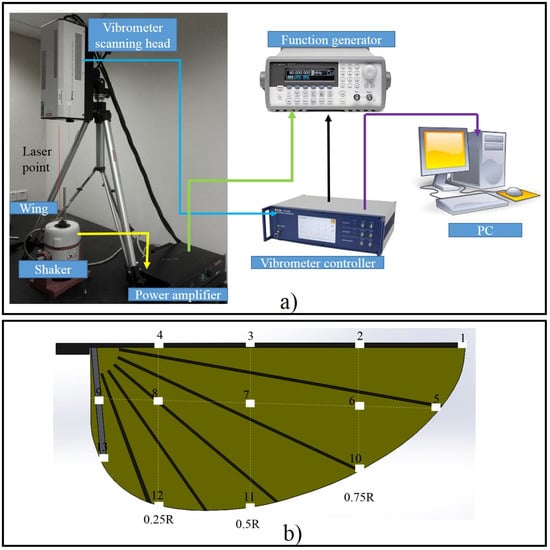
Figure 8.
(a) Schematic diagram of the experimental setup for natural frequency measurement; and (b) artificial wing with 13 spots of tape.
The Kapton film (DuPont Inc, Wilmington, DE, USA) membrane of the artificial wing is transparent and does not reflect a laser light. Retroreflective tape (3M™ Scotchlite™, 3M Inc, St.Paul, MN, USA) was placed on the surface as a special treatment. The grids of 13 spots of tape with a side of 2 mm × 2 mm were placed on the wing as shown in Figure 8b. Each of these 13 locations was assigned a unique number. Points 1–4 were on the leading edge. Points 5–9 were near the middle of the wing. These spots increased the wing mass, which in turn caused a change in the natural frequency. It should be noted here that the true natural frequency of the wing is from the wing without taped spots. The wings were subsequently weighed with the tape spots again to find out how much the mass increased so that the correct natural frequency could be calculated. The weight of the artificial wing with the taped spots increased 6.81%. If the taped spots only added mass onto the wing structure and did not change its stiffness, the relationship between the true fundamental frequency with and without ink spot was assumed to be [40]:
where and were the measured natural frequency and wing mass with the spot, respectively; and and were the measured natural frequency and wing mass without the spot, respectively.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Natural Frequency of Flexible Wings
Higher frequency modes have small effects on the deformed shape of the wing. Since the first three resonant frequencies are critical in characterizing the response of the artificial wing in this study, we are concerned with only the first three modes in the Frequency Response Function (FRF) diagram. Table 1 gives the first three natural frequencies of 13 spots on the W3 observed in this experiment. It can be seen that the first three natural frequencies of all 13 dots are almost similar. The averaged natural frequencies are identified as 26.09, 50.04 and 81.31 Hz. Table 2 shows the first three natural frequencies of all six studied wings. Since the flapping frequency of the flapper in this study is 10 to 20 Hz, the higher mode may have small effects on the deformation of the wing. Therefore, the first mode is dominant in the characteristics of the wing flexibility. The root vein made of elastic material seems to affect the natural frequency; the first natural frequencies of W3, W4, W5 and W6 are much smaller than that of W1. Note that this paper has not focused on investigating the dynamic structure of artificial wings, so the mode shape of those wings is not studied. It is observed that the W1, which is more rigid than that of the other wings, shows the higher natural frequencies.

Table 1.
Measured natural frequency of W3 at 13 spots.

Table 2.
Measured natural frequency of six model wings.
4.2. Wing Deformation
4.2.1. Camber Deformation
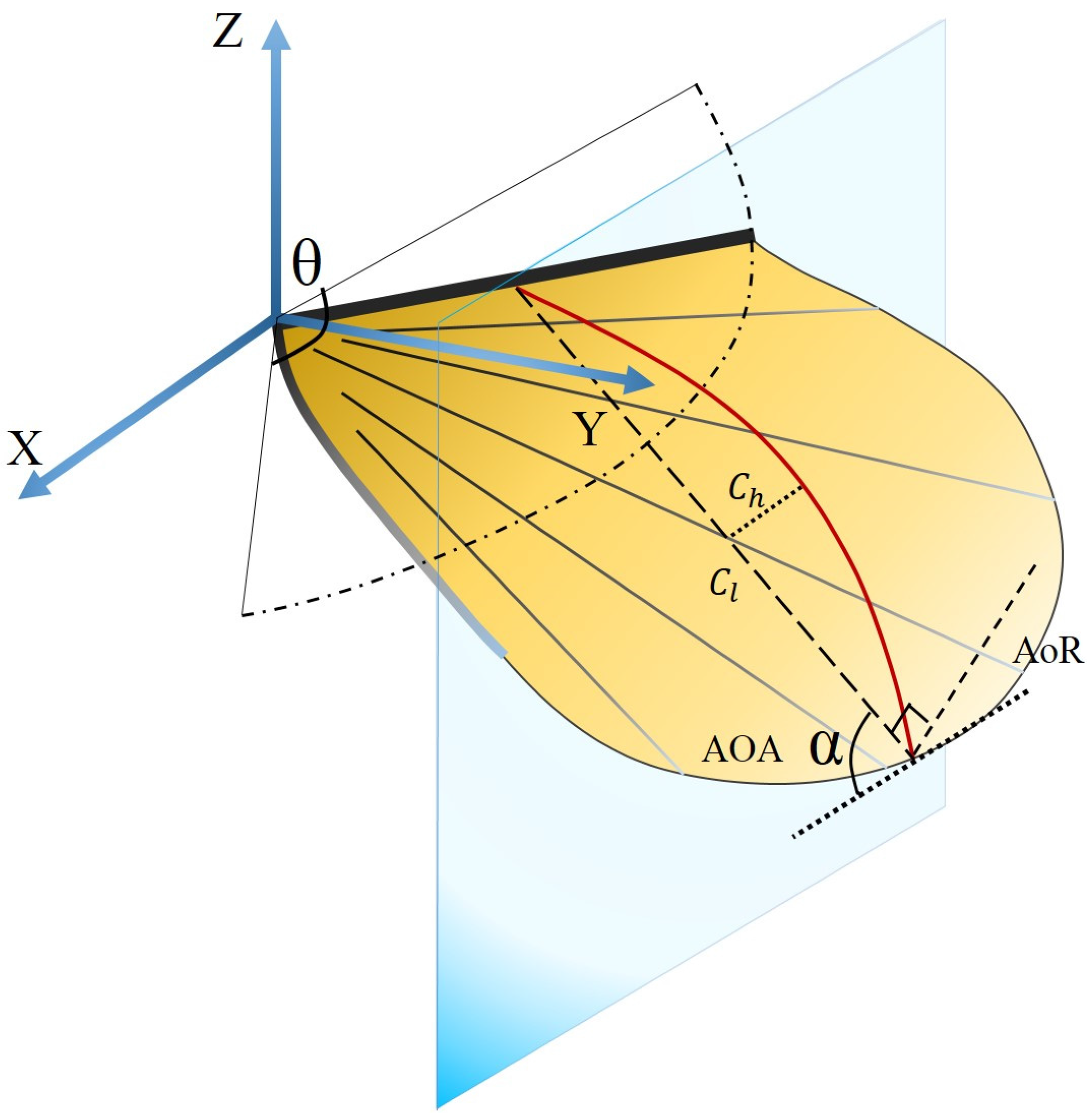
The definition of the camber and angle of attack is illustrated in Figure 9. The origin of the coordinate system was located at the wing base, and the x, y, and z axes were aligned along the longitudinal, lateral, and gravity directions respectively. The chord line is defined as the line joining the leading edge and trailing edge markers at a specified spanwise position. The angle of attack (AOA) α was defined as the angle between the stroke plane and the chord line. The angle of attack during upstroke is equal to AOA plus 90°. The angle of rotation (AoR) is defined as the angle between the stroke plane (horizontal plane) and the line perpendicular to the chordwise direction [41]. The camber deformation was the ratio of the mid-chord height () to the chord length (). The mid-chord height was used instead of the maximum chord height in measuring the camber because the maximum height changed irregularly. The direction of the camber is from the lower surface to the upper surface of the model wing. A positive camber is defined as the convex shape of the model wing.
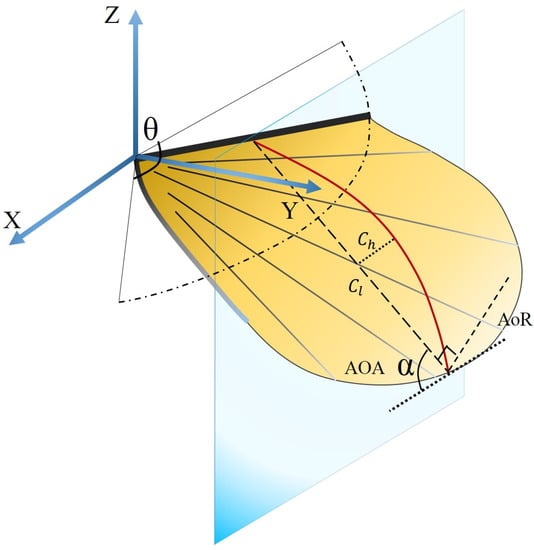
Figure 9.
Definition of wing kinematic variables.
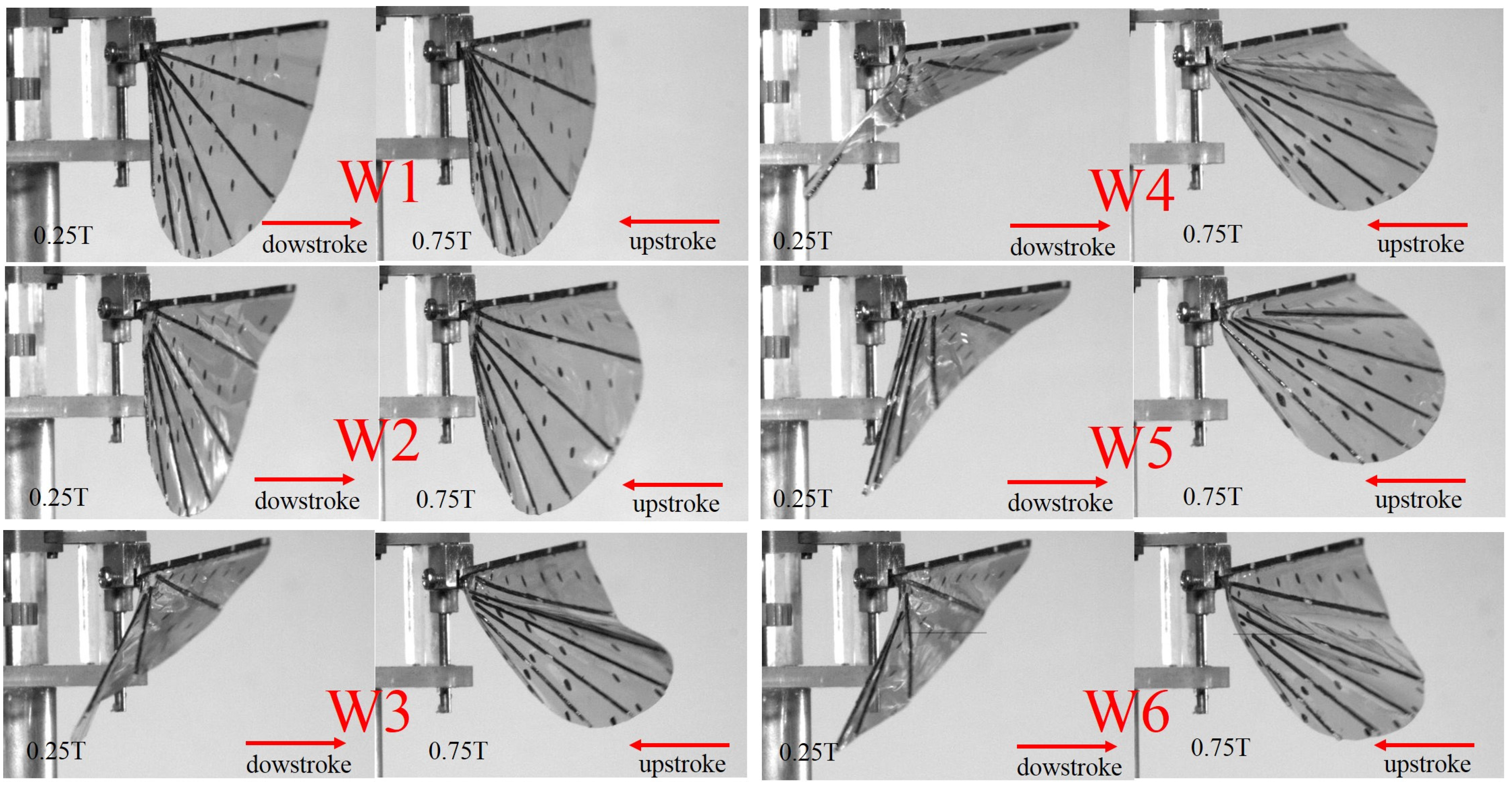
The deformation of the six wings at the middle of both the downstroke and upstroke can be seen clearly in frames taken with high speed cameras in Figure 10 (see Supplementary Material Movie 1). The wing deformations were captured at 15 Hz because this frequency is either the most compliant or has the best performance. W1 generated no camber and angle of attack during flapping. The carbon fiber root vein in W1 produced the very small bending during flapping, it can be regarded as a rigid bar. W2 produced a small camber and a low angle of attack. The W4 and W5 proved to be the best wing in generating the correct wing deformation. W3 and W6 could generate the camber deformation, however, it was bent downwards generating a negative camber.

Figure 10.
Photographs of wing deformation of six model wings at the middle of the downstroke and upstroke. The movie of images is available as Supplementary Material Movie 1.
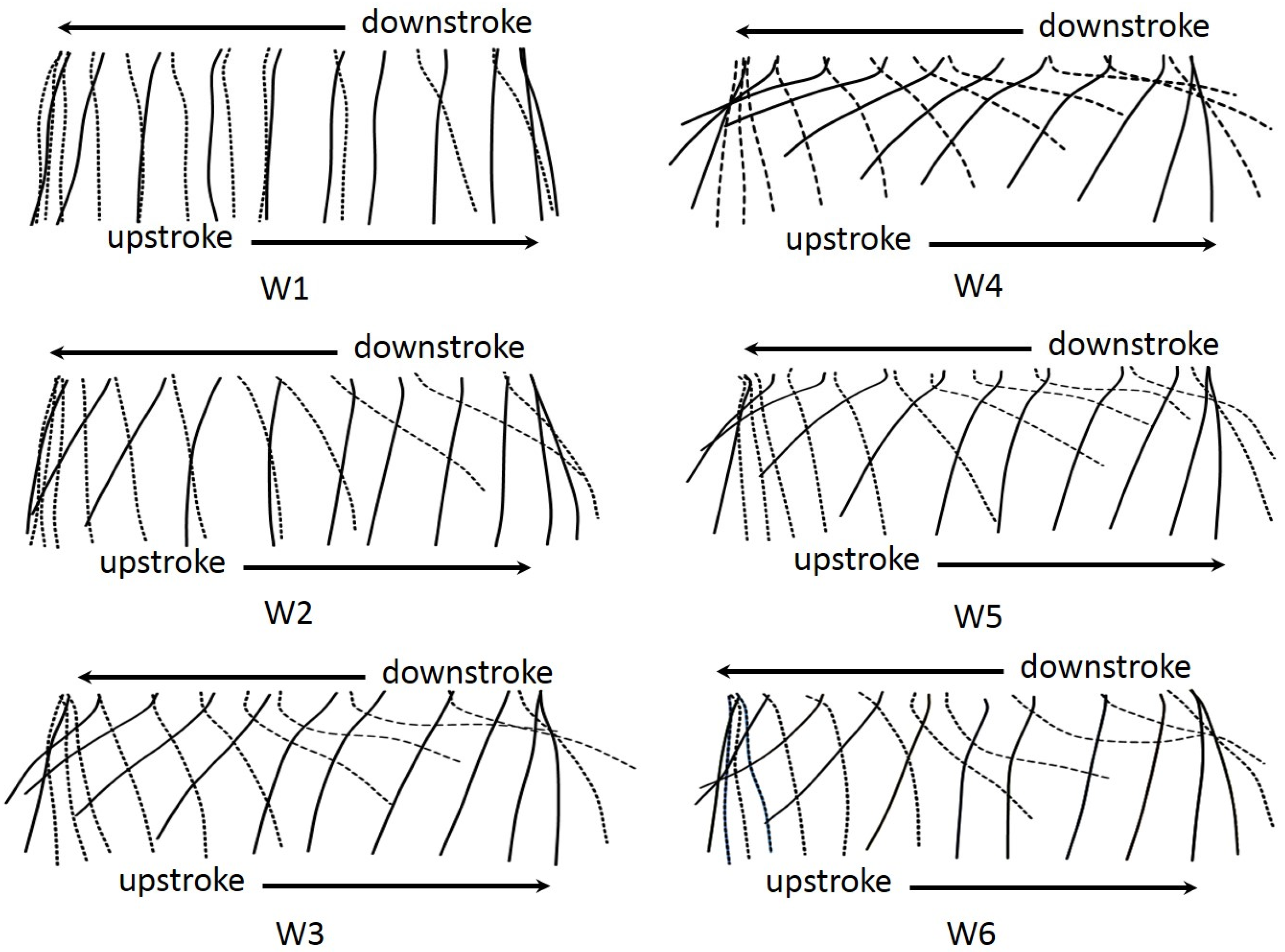
Figure 11 shows the diagram of the instantaneous wing profiles at the middle of the wing span of all six wings through one wing beat cycle with a flapping frequency of 15 Hz. The 3D deformation of six wings can be seen clearly in the movies in Supplementary Materials. The variation of the angle of attack of the wing during sweeping motion plays an important role in force production [17]. It can be seen from the section profile that the W1 performed a non-uniform movement. Note that the dot lines represented wing profiles in the downstroke. It is clear that for the W1, there is mostly no angle of attack, and is displayed waviness during strokes. W2, with the flexible material at the base, could produce the camber and angle of attack due to the bending of the flexible base. During the first stage of the down stroke and the upstroke, the wing deflected upward attributing to relatively chord wise deformation, generating a favorable angle of attack, whereas, in the second half of the stroke, the angle of attack was high (the wing is almost perpendicular to the horizontal plane) due to the low acceleration at the end of the strokes. A small camber wing profile was formed near the middle of the stroke.
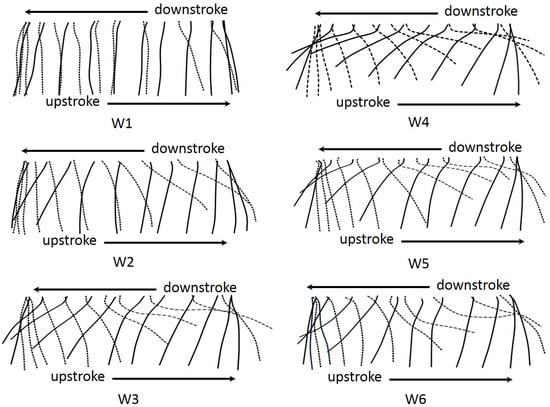
Figure 11.
Diagram of wing motion as two-dimensional projections showing the instantaneous wing profiles at 50% wing length in one cycle for six wings. The wing profiles are drawn as they were projected to the wing section plane for the flat wing. Note that broken lines represent for the wing profiles proceed in a motion of the downstroke.
During translation periods, W3 exhibited camber formation. However, the wing generated a negative camber during the first half of both strokes and the trailing edge of the wing deformed upward extremely, causing the low angle of attack. A similar pattern of deformation had appeared on W6. For W5, the positive camber was displayed during the strokes. However, at the beginning of the downstroke, the wing presented an S-shape deformation due to inertial and elastic forces occurring during this phase. It can be seen that there was no wave formed in W4. The layout of the veins inside the wing plays important role in camber formation. In the W4, the veins were placed in the direction of the leading edge and root vein, promoting camber deformation. It should be highlighted that the convex camber was generated thought out the strokes in W4. The concave camber appearing at stroke reversal enabled the indispensable transition for camber reversal. The original artificial W4 mimicked the two important features of the insect wing, i.e., both twisting and camber generation.
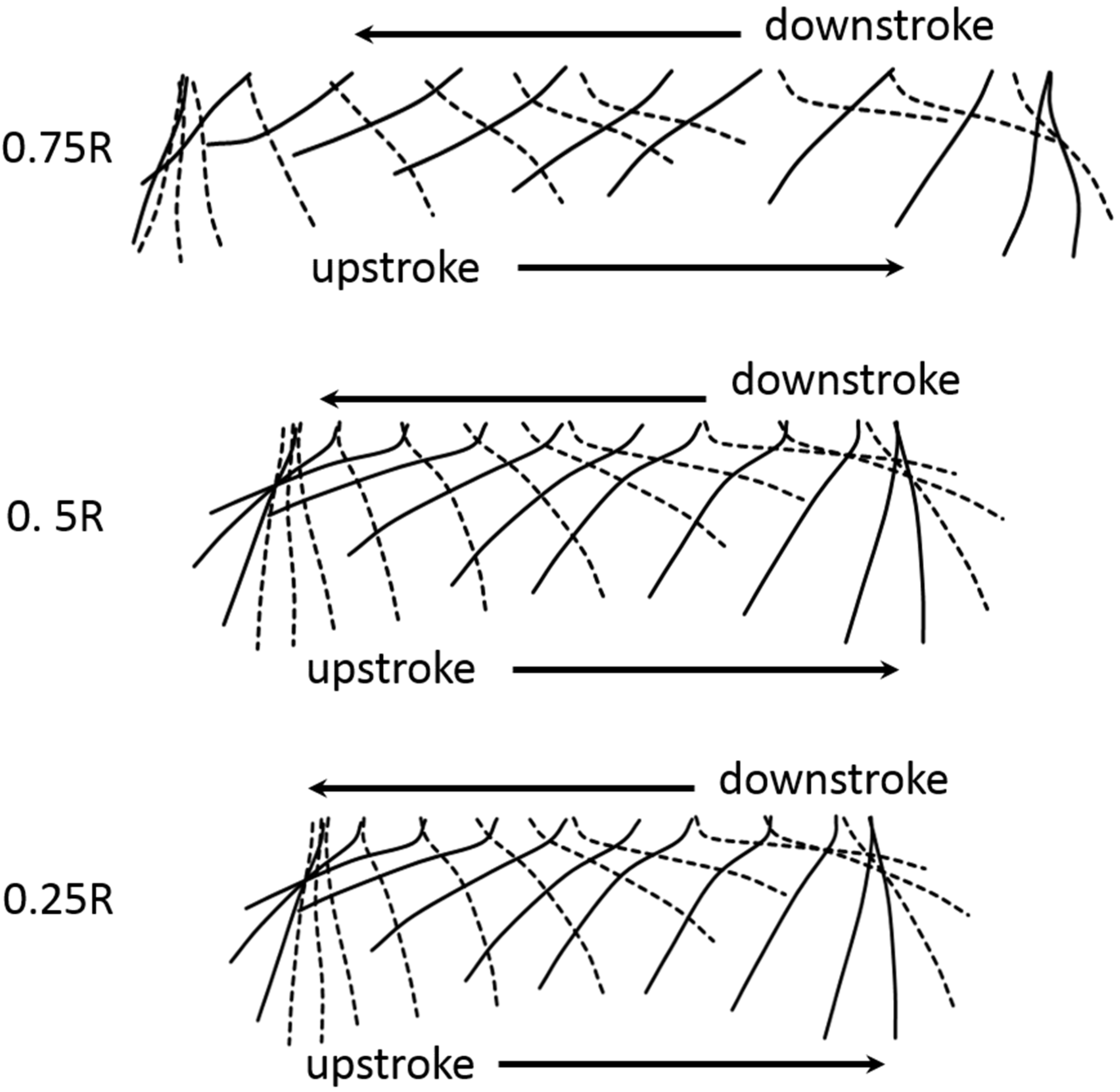
Figure 12 shows the detail of the wing motion diagrammatically for the W4 along the spanwise direction. The diagram shows the instantaneous wing profiles at three distances along the wing; 25%, 50% and 75% wing length with one wing beat cycle for the flapping frequency of 15 Hz. It is clear that, toward the wing tip, the deformation of the wing was smaller than that of the inner wing.
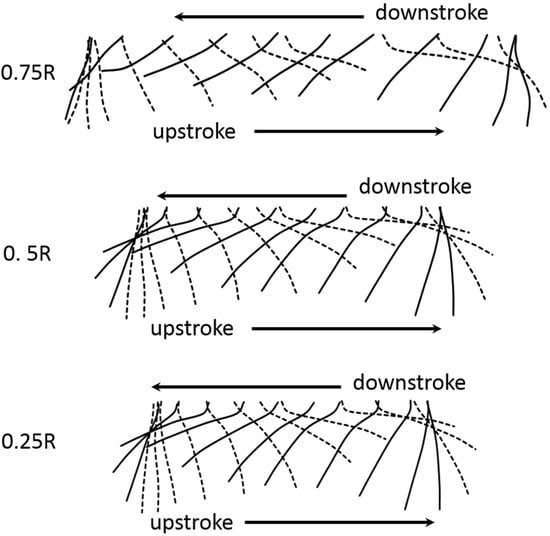
Figure 12.
Diagram of wing motion as two-dimensional projections showing the instantaneous wing profiles at 25%, 75%, and 50% wing length (0.25R, 0.5R, 0.75R) in one cycle of W4. The wing profiles are drawn as they were projected to the wing section plane of the flat wing. Note that broken line represents for the wing profile proceeding in motion a downstroke motion.
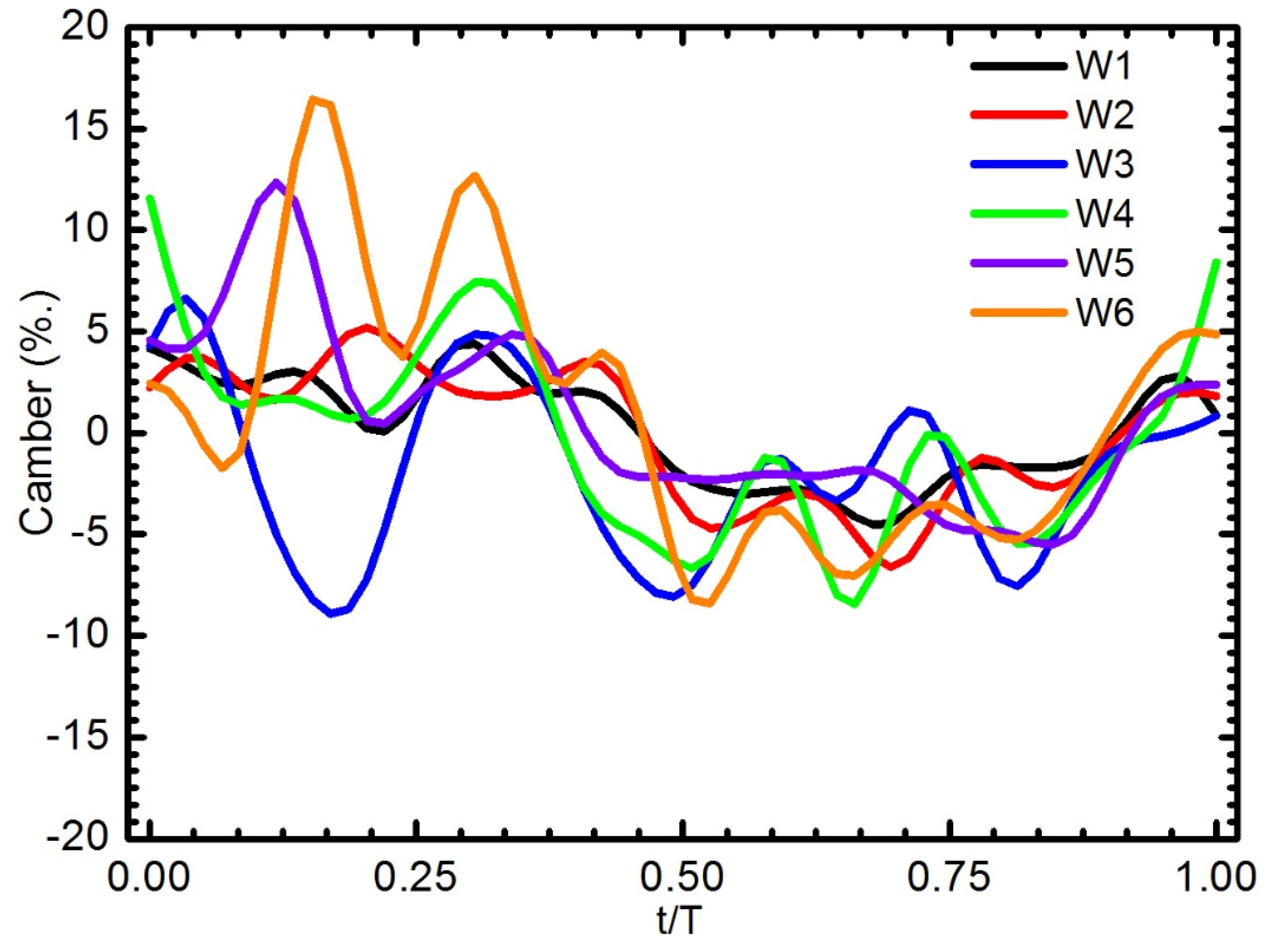
The role of the chordwise flexibility of the artificial wing was demonstrated through the camber deformation. The instantaneous wing camber of all six wings is plotted in Figure 13. Note that the wing is inverted on the upstroke, and the negative sign is the convex of the wing in a reversed direction. W1 and W2 showed a relatively small camber, less than 4%. It can be seen that the strong influence of vein configurations on the camber deformation as indicated in the pattern profiles. W3, W5, and W6 produced a fluctuating camber though out the stroke and most prominently during the downstroke. Particularly, W3 shows a negative camber in the first half of the downstroke, which was the opposite of the other wings. At the middle of the downstroke, the positive camber of both W3 and W6 increased sharply. The second peak of the camber also appeared in the second stage of the downstroke. The evidence suggests the effect of wing vein configuration on the camber formation could be observed clearly. The veins directed toward the leading edge and trailing edge on W4 caused the camber to be positive throughout the translation periods.
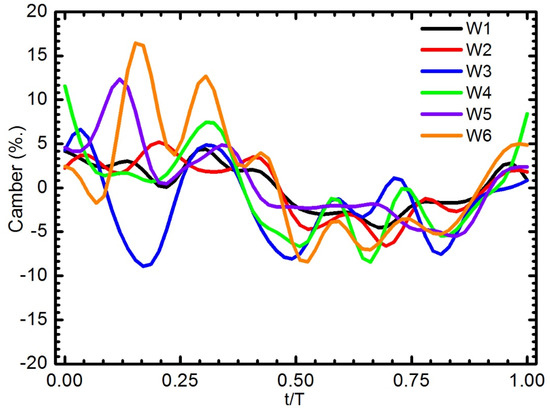
Figure 13.
Camber deformation of six wings at 50% wing length during one wingbeat cycle for a flapping frequency of 15 Hz.
Figure 14 depicts the detail of camber deformation of the W4, which showed the best camber formation. In general, the W4 was bent downward, generating a negative camber due to the opposite movement at the initial stage of the upstroke. Subsequently, the wing’s camber remained at a positive value until the end of the downstroke. The change in the camber was prominent during the supination and at the beginning of the pronation. The wing was flatter at the tip and the inner part (0.25R) had more camber than that of the outer part (0.75R). The camber variation at the outer part (r/R = 0.75) seemed to be small, whereas the camber variation at the inner parts (r/R = 0.5 and 0.25) fluctuated largely. Near the end of the downstroke (t/T = 0.4), the wing was convex with respect to the movement direction of the wing. The difference of camber along the wing span was most prominent during the rotational periods. At the start of the downstroke, the positive camber was high, and, afterward, the camber reduces notably to t/T = 0.1. Typically, the camber deformation decreased from 11.72% at t/T = 0.0 to 3% t/T = 0.1 at r/R = 0.5. During translation periods, the camber peaked twice at 0.15T and 0.35T. The camber pattern of the wing W4 was similar to that of the locust wing as presented in a previous study [12].
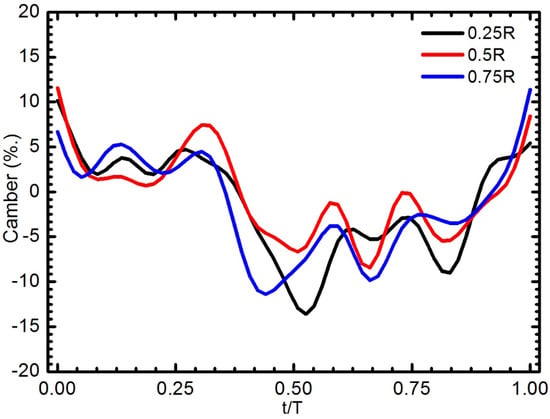
Figure 14.
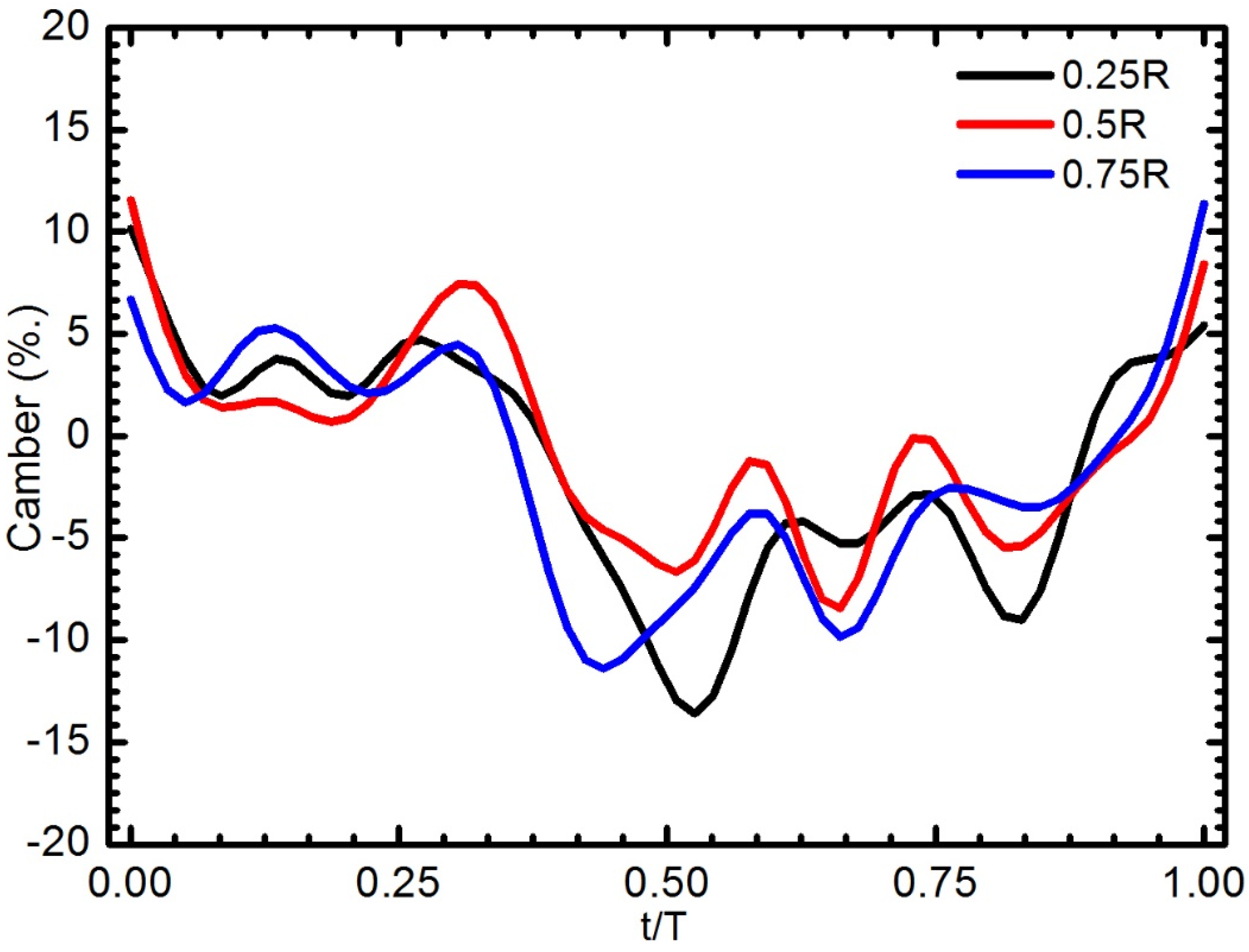
Camber deformation of the W4 along the spanwise direction during a flapping cycle for the flapping frequencies of 15 Hz: 0.25R (black line), 0.5R (red line), and 0.75R (blue line).
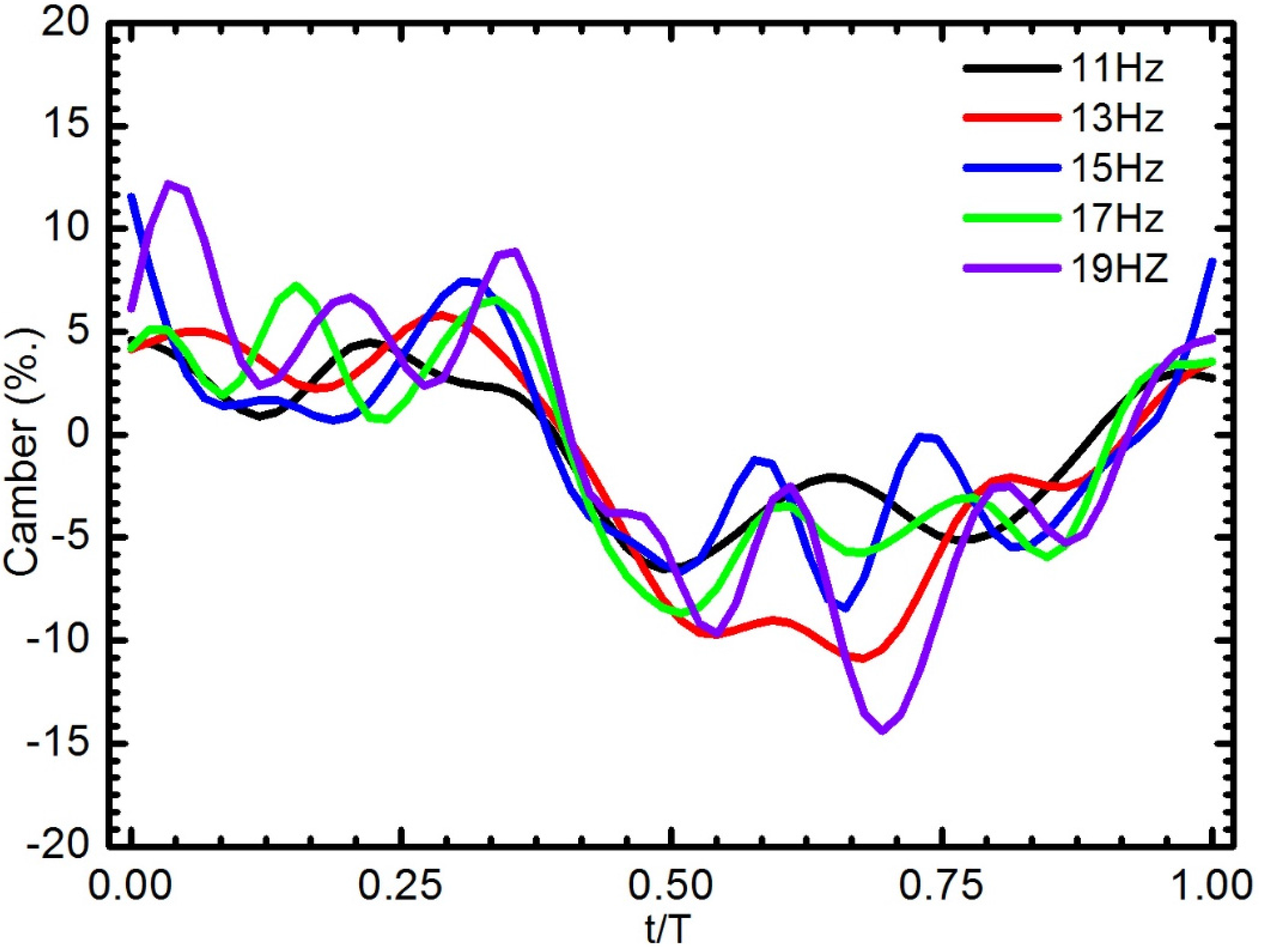
The change of the wing camber through a complete stroke was highly correlated to the flapping frequency. The relationship between the camber deformation of W4 and the flapping frequency was illustrated in Figure 15. At low flapping frequency, the wing was flatter and variation during the course of the stroke was small. As the flapping wing frequency increased, the behavior of the wing was more complicated. At a frequency of 19 Hz, the camber reached three peaks in both the down and up strokes. At the start of the downstroke, the camber increased that reverse to other frequencies. The wing profile and camber are not perfectly symmetric between the downstroke and upstroke due to the slant veins being located on one side of the Mylar film.
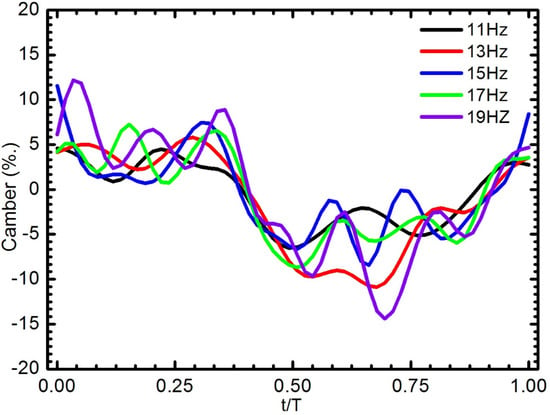
Figure 15.
Camber deformation of the W4 as a function of flapping frequency during one wing beat cycle.
4.2.2. Twisting Deformation
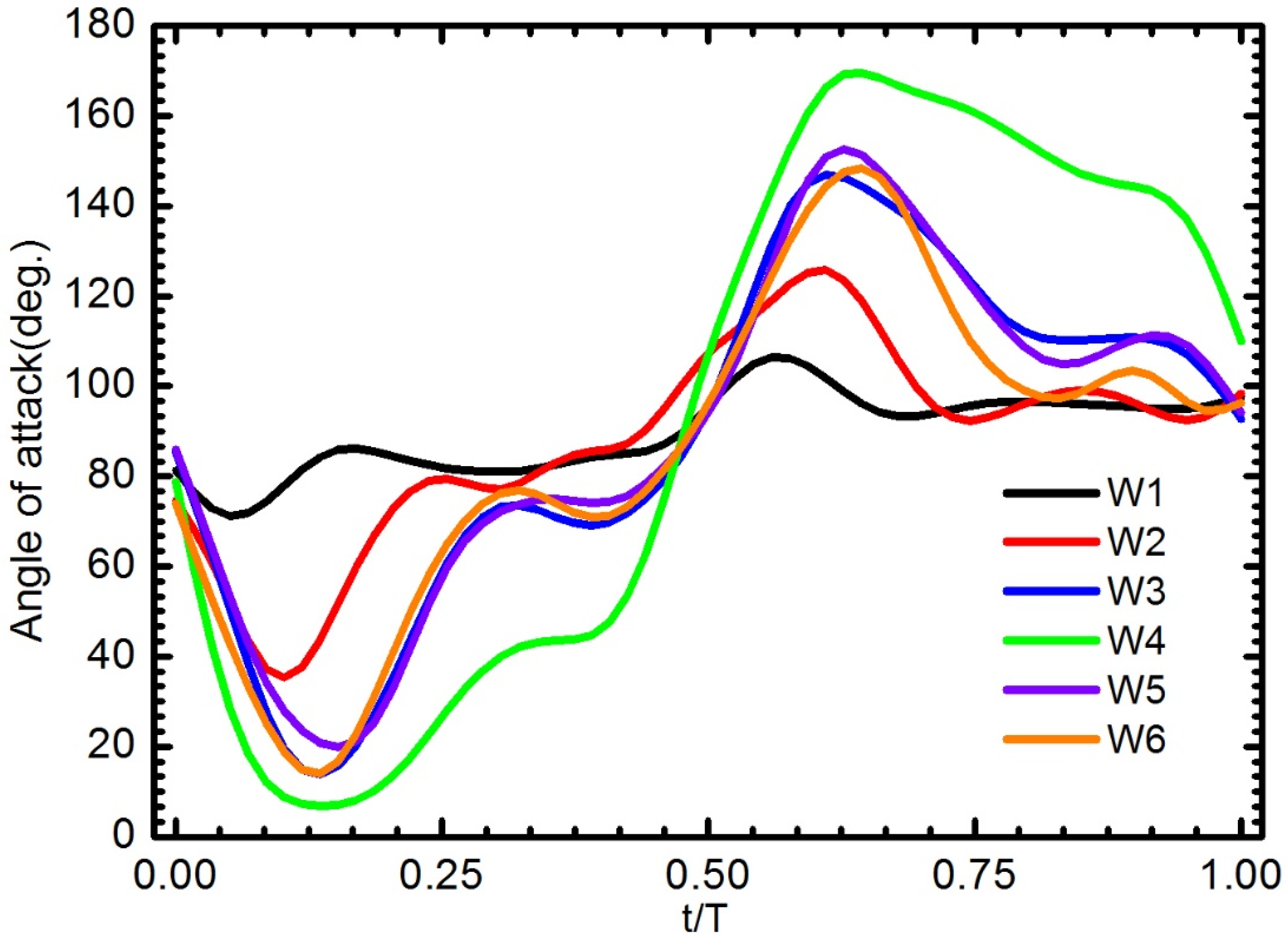
Figure 16 shows the angle of attack AOA (geometric angle of the chord relative to the X–Y plane) of six model wings at the middle of the wing length (50% R) at the flapping frequency of 15 Hz. The AOA of W1 was large, almost 90°. W2, W3, W5, and W6 showed the most prominent change in angle of attack during the first half of both the downstroke and upstroke. The AOA reduced rapidly from approximate 80° at the start of the downstroke to 15° at t/T = 0.125 for W3 and W6, then increased quickly to around 78°. The wings were bent upward shortly and dropped sharply just after the first quarter of the downstroke, which resulted in the wing becoming almost vertical during the latter half of the downstroke. The behavior the AOA in those wings was similar for the upstroke. The AOA of these wings displayed much greater variability in that stage than that of W4. In contrast to W3 and W6, W4 displayed a proximate constant angle of attack during the translation periods. The rapid wing rotation of W4 occurred at the end of the upstroke (t/T = 0.5), which was classified as delayed rotation following a previous study [4]. It is worth noting that the present wing rotation relies purely on the passive mechanism, the wing rotates back after stroke reversal. The delayed rotation can be seen more clearly in the movies in Supplementary Materials (Movies 1–7). The changing of the angle of attack of the wing during sweeping motion plays important role in force production [13].
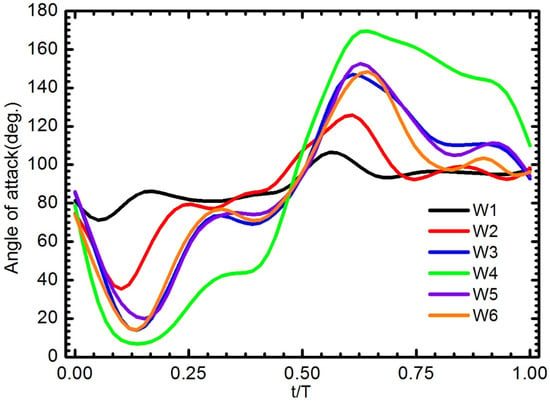
Figure 16.
The angle of attack of six wings at the middle of wing length (r/R = 0.5) through one wing beat cycle for a flapping frequency of 15 Hz.
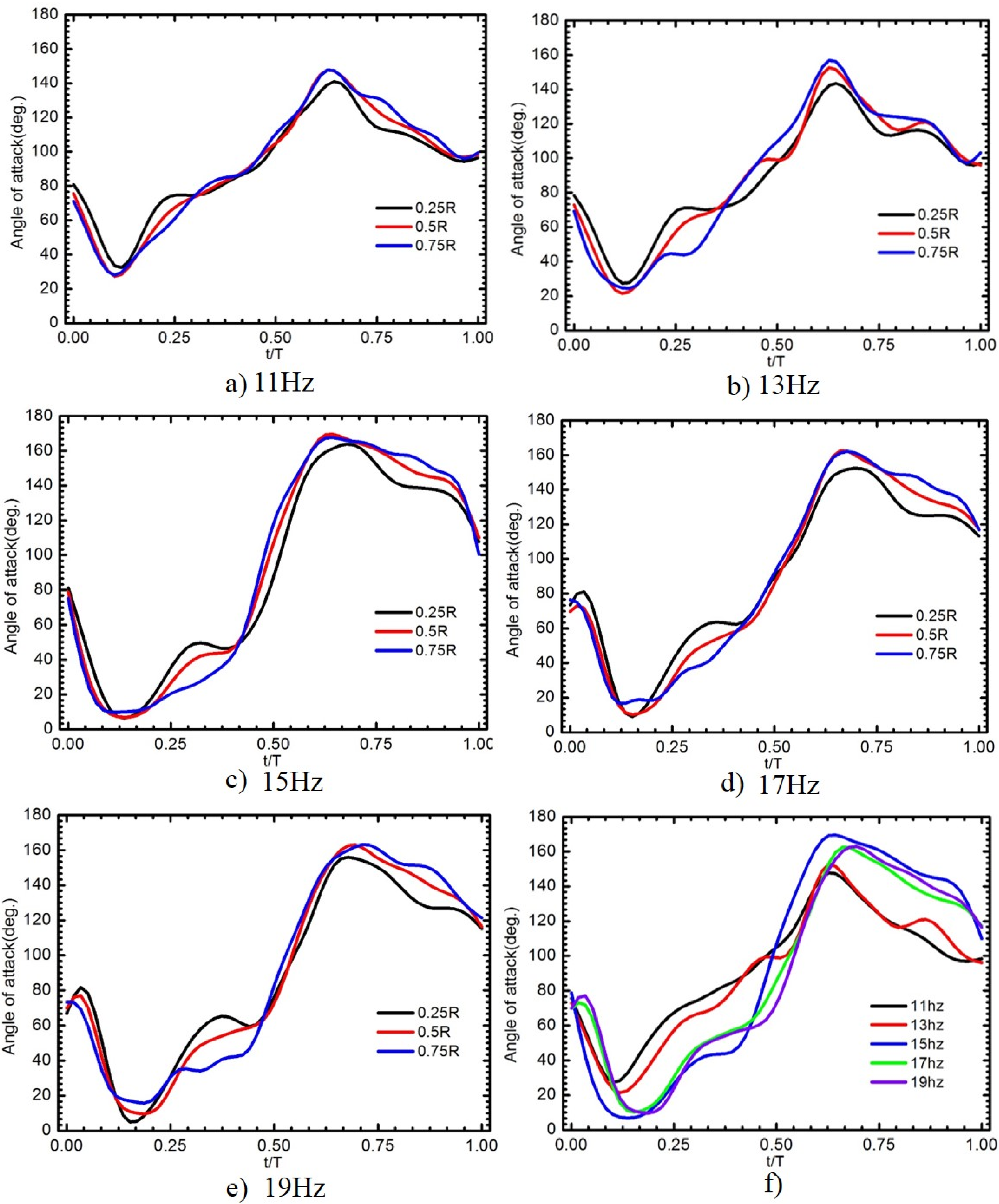
Figure 17 shows the angle of attack in three sections, along the spanwise direction of W4 for five flapping frequencies. The variances of AOA through the stroke were highly correlated to the flapping frequency as shown in Figure 17f. With the flapping frequencies lower than 15 Hz, the AOA behavior of the wing W4 was similar to that of W2, W3, W5, and W6 indicated that the wing bent upward and then recovered quickly in the first half of the downstroke. Different levels of the angles of attack among these sections exhibited the wing deformation or twist angle along the spanwise direction. Closer to the wing tip, the variation of the angle of attack became smaller. As the frequency of flapping increased, the distribution of spanwise twist from the root to the tip was emerging. The variation of the angle of attack from the inner part to the outer part was more pronounced during the latter half of the downstroke for the flapping frequencies ranging from 13 to 19 Hz and also during the latter half of the upstroke for the flapping frequencies of 15 to 19 Hz. For example, the difference in the angle of attack between the r/R = 0.25 section and the r/R = 0.75 section was 27.56° at t/T = 0.27 for the flapping frequency of 13 Hz. Although this variation seemed to be smaller in the upstroke, a similar angular difference along the spanwise direction was also evident at near the end of the downstroke. The AOA and twisting deformation of W4 were symmetrical for the upstroke and downstroke through the course of the cycle frequency. At a low flapping frequency (11 Hz), W4 performed a small twisting deformation.
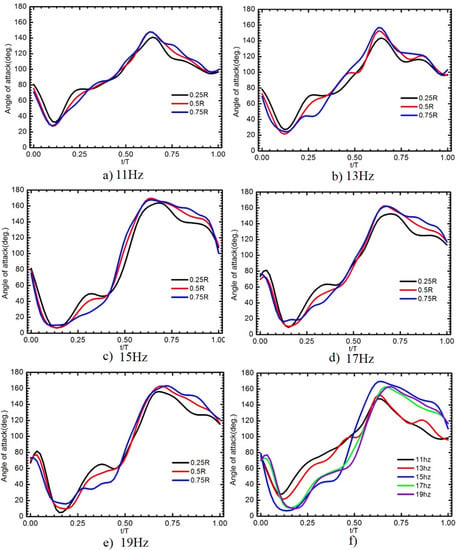
Figure 17.
(a–e) Variation in the angle of attack of the flexible W4 along the span wise direction for different flapping frequencies; and (f) the angle of attack as a function of flapping frequency.
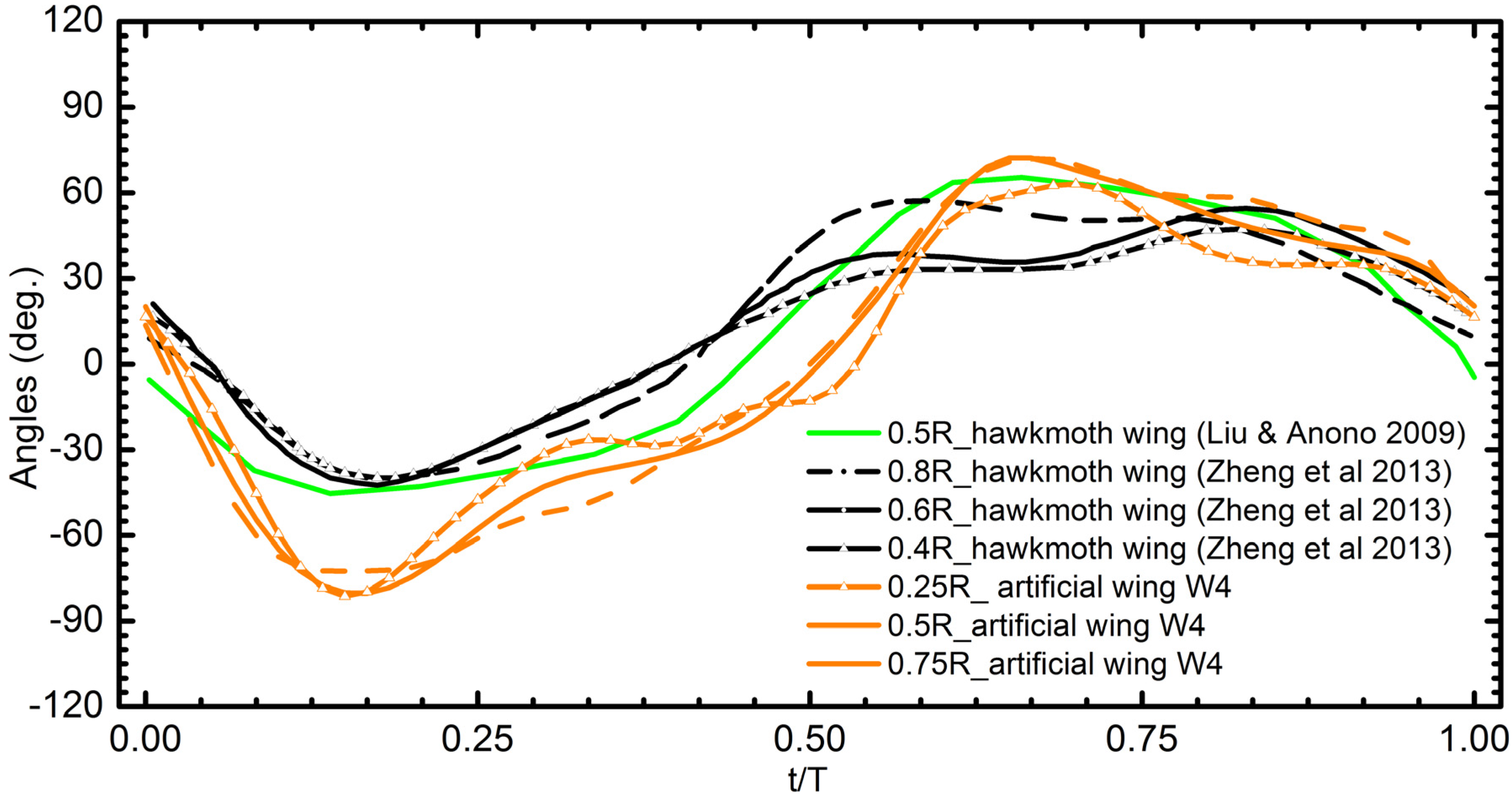
The comparison of AoR between the artificial W4 and the real hawk moth wing in previous studies [10,42] is presented in Figure 18. The difference in AoR between 0.2R and 0.8R section of hawkmoth wing was around 20° at t/T = 0.6 and W4 at t/T = 0.7 the value was around 25°. The twisting deformation of the artificial wing was close to that of the real insect wing, except that the hawk moth wing presented the asymmetric twisting deformation between the downstroke and upstroke. The deformation was not perfectly matched due to the limitation of robotics. Figure 19 showed the match of the twisting deformation between the hawkmoth wing and artificial wing at one instant in time. The first image presents snapshots of the hawkmoth wing extracted from Zheng et al. [10]. In previous studies, the artificial wing could generate the camber and twisting deformation during flapping [21]. However, the twisting modulation of the wing was controlled mechanically by adding the mechanism at the trailing edge instead of at the wing base. It is worth noting here that an insect modulates its wings only by the wing base, and not by controlling the trailing edge of the wing.
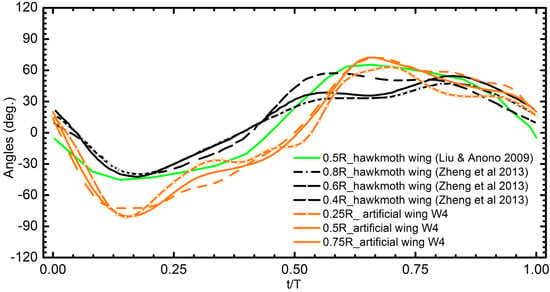
Figure 18.
Comparison of AoR angle of the wing W4 and hawkmoth wing (0.4R [10], 0.5R [43], 0.6R [10], 0.8R [10]).

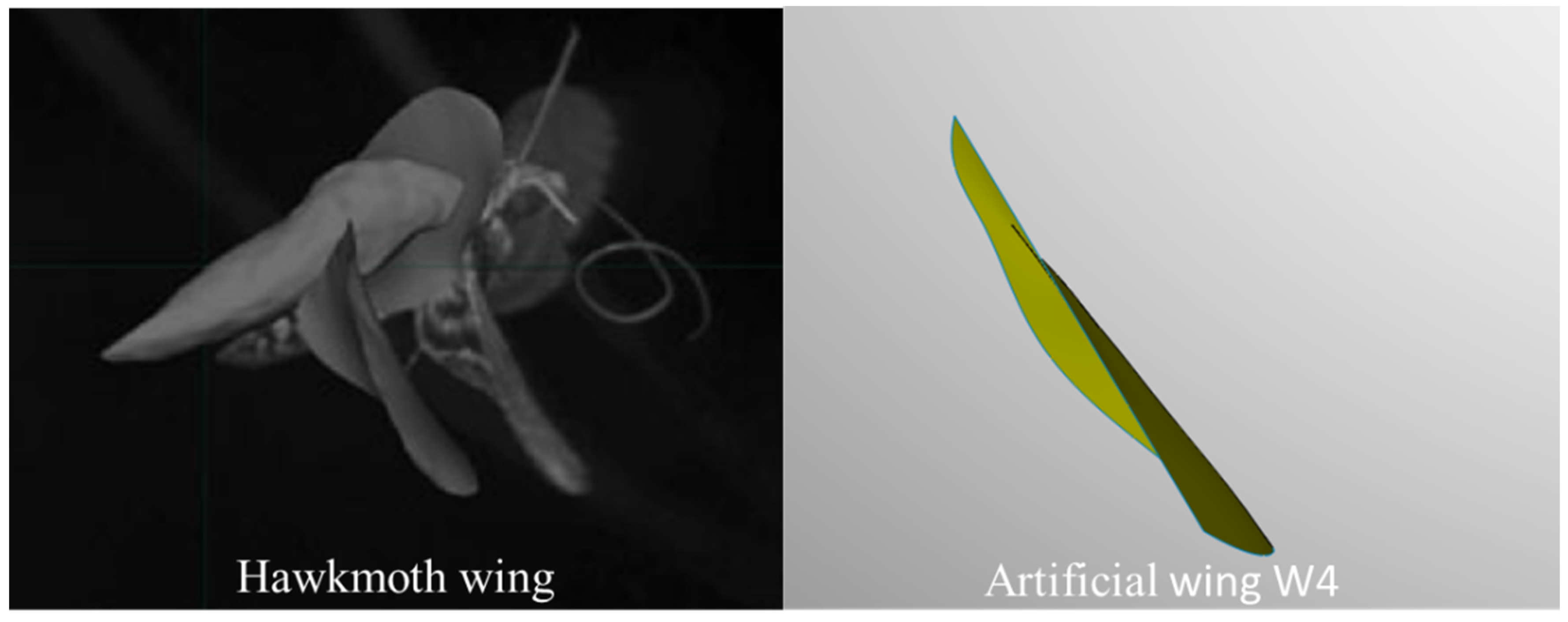
Figure 19.
Twisting deformation of the hawkmoth [10] wing and artificial wing.
Figure 20 plots the three-dimensional reconstruction of W4 during the downstroke and the upstroke at a flapping frequency of 15 Hz (see Supplementary Material Movie 5). Three-dimensional coordinates of each point were built up using direct linear transformation method (DLT). The wing was twisted during all stages of the wingbeat, and most noticeable at the end of the stroke. It also can be seen that the camber was positive throughout the stroke. Figure 21 shows the deformation of the six artificial wings at the middle of the upstroke at a flapping frequency of 15 Hz. The 3D deformation of six wings is fully presented in Supplementary Materials (see Movies 2–7). It is clear that W3 and W6 displayed the waveform on the surface, and there was a very small camber deformation in W1 and W2.
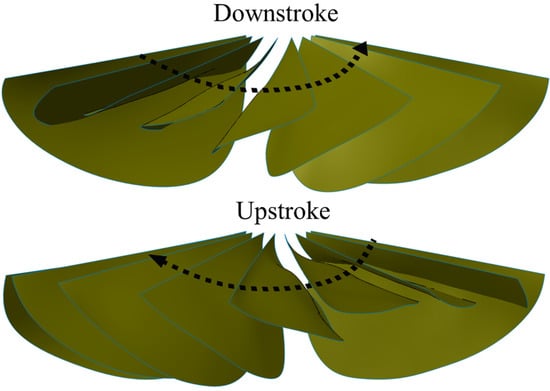
Figure 20.
Deformation of W4 is shown for a flapping frequency of 15 Hz.
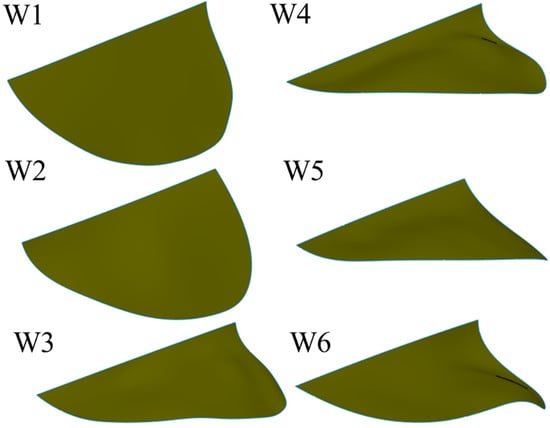
Figure 21.
Deformation of six model wings is shown at the middle of the upstroke for a flapping frequency of 15 Hz.
4.3. Force Generation
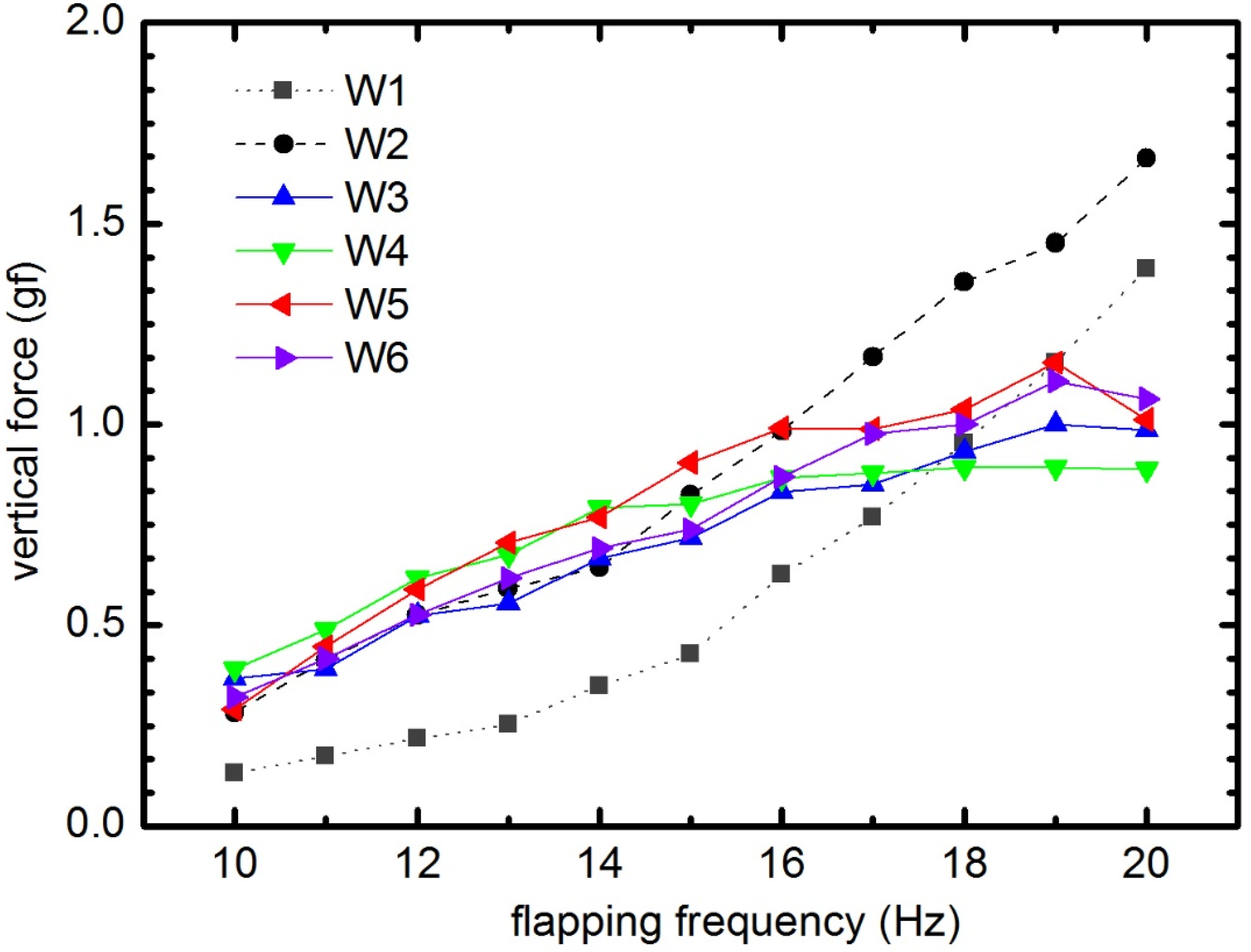
Figure 22 shows the averaged lift produced by all six wings at various frequencies. In general, the average lift increases as the flapping frequency increases, although the rates of increase of different wings vary. The difference in the effect of flexibility on lift production was clearly observed when the frequency was lower than 17 Hz. The lowest lift was produced by the stiffest wing, W1. It is worth noting here that W1 generated a very large angle of attack (the AOA is higher 45°, approximately 90°). In deformable wing groups, from 10 to 15 Hz, W4 and W5 generated more camber, and generated more lift than the other three wings (W2, W3, and W6), with the maximum lift appearing at a flapping frequency of 15 Hz. Higher than this frequency, the lift of W3 (the wing with a flexible base) and stiffest W1 grew rapidly while the other wings became less sensitive to frequency. It could be due to small AOAs with higher frequency in the deformable wing group. In addition, from flapping frequencies greater than 15 Hz, W3, W4, and W5 reached its resonant frequency. In particular, after 19 Hz, the lift force of those wings reduced.
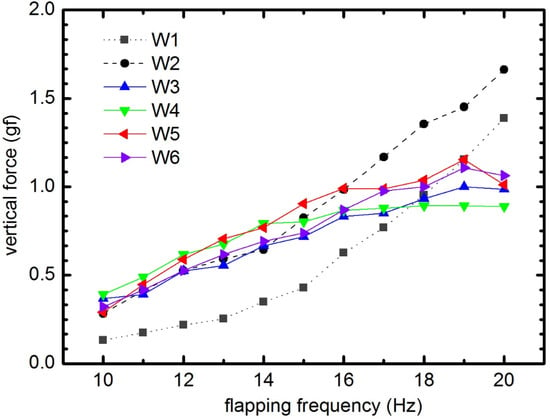
Figure 22.
Average vertical force as a function of flapping frequency for all six wings.
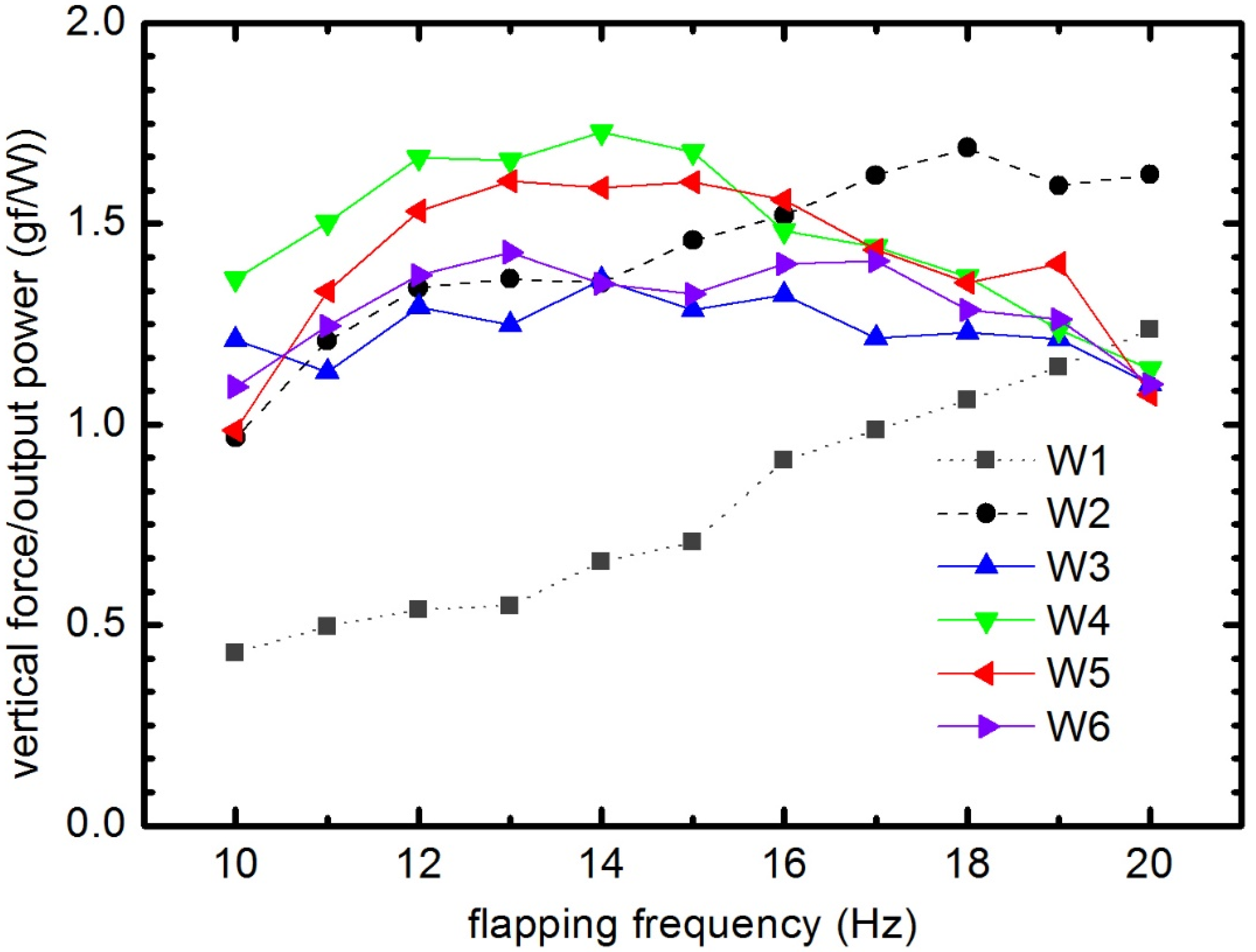
In order to estimate the efficiency of lift generation of the flexible wings for the flapping wing MAV, the ratio of the lift to the electric power consumption of six wings was measured. This evaluation was proposed by Tanaka et al. [27] to examine the lift efficiency of the wings in the flapping-wing system. The aerodynamic power was notoriously difficult to estimate and the power consumption was therefore calculated from voltage and current generated by the power supply. The power expenditure comprised the aerodynamic power, the power corresponding to the inertia of the wing, mechanical loss due to transmission and the electrical loss due to the electric motor [27]. In Figure 23 we can see that the stiffest wing (W1) produced much lower lift/power than that of flexible wings. Especially, the lift/power of the uncambered wings (W1 and W2) increased linearly with the flapping frequency, while in the camber wing group this was a parabolic relationship. The optimal lift/power based on vertical force to the power consumption of W4 and W5 was achieved at the flapping frequencies of 14 and 15 Hz. From 10 to 15 Hz, this ratio of W4 and W5 were higher than that of the other wing. At frequencies higher than 15 Hz, the lift/power of the camber wing group decreased lower than that of W2. It should be noted here that at high flapping frequencies the deformable wing group generated a low vertical force (as presented above). At the flapping frequency of 15 Hz, the lift/power of W4 has been estimated around 1.7 gfW−1, 2.4 times greater than that of W1. Overall, W4 exhibited the highest lift/power when the flapping frequency is 15 Hz or less. Taken together, the wings with the better camber performance presented the higher lift/power, which means less energy consumption, with neglecting the effects of AOA. It should be noted here that previous studies have reported an impressive improvement of efficiency for the flexible insect wings [6,10,31,44]. These results are consistent with the role of wing flexibility.
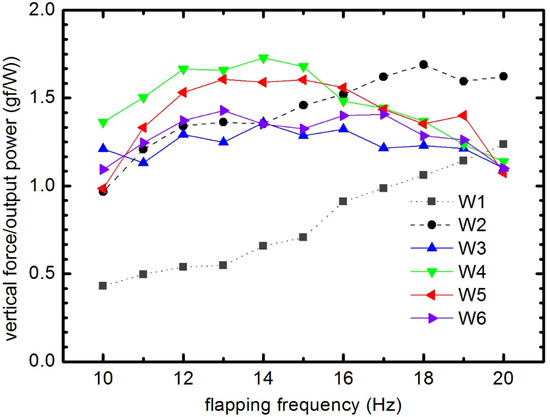
Figure 23.
The ratio of average vertical force/output power as a function of flapping frequency for all six wings.
4.4. Flow Structures
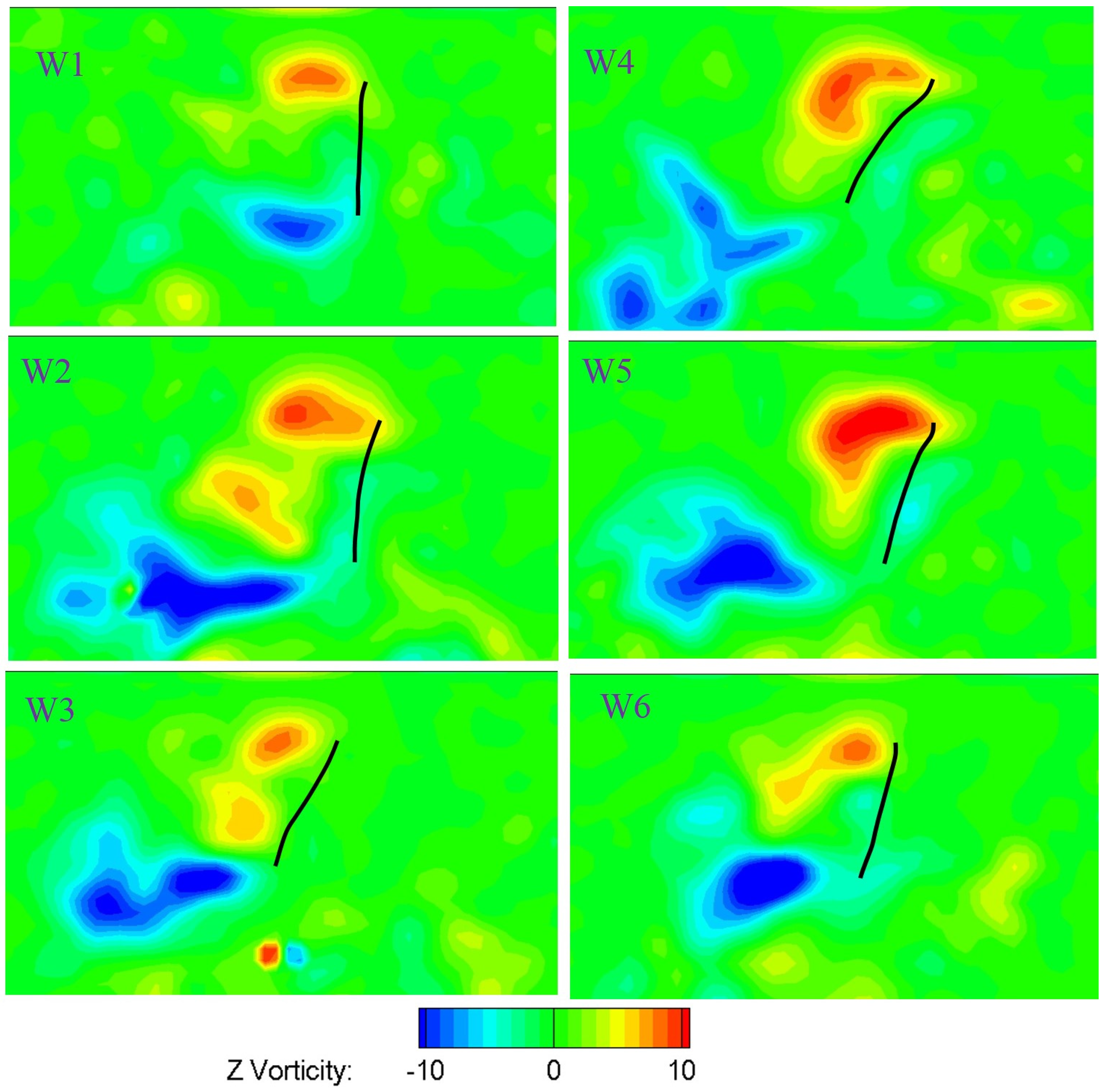
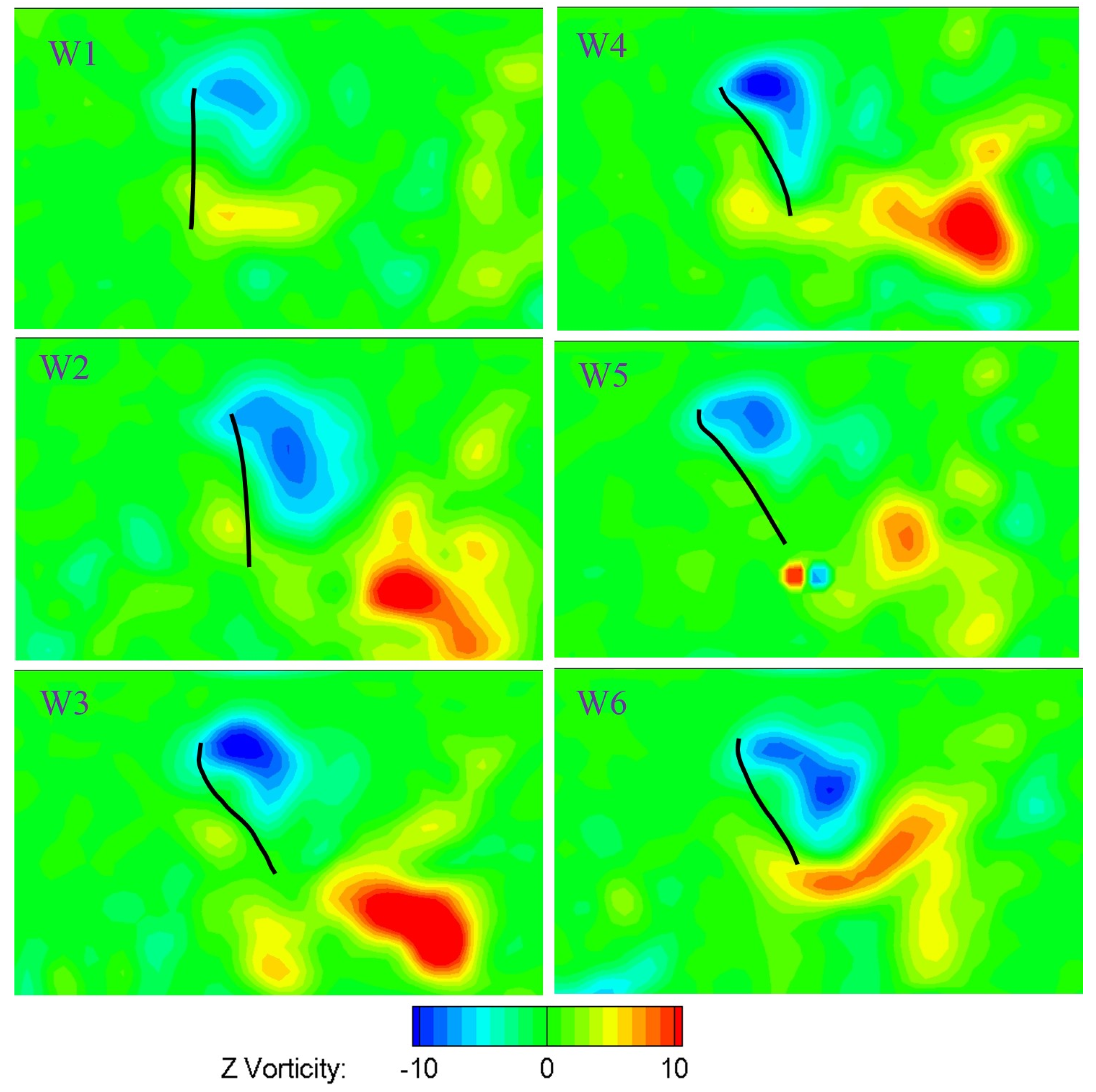
Figure 24 and Figure 25 show the vortices structure at the middle span of the six wings at the middle of both the downstroke and the upstroke at the flapping frequency of 15 Hz. The Reynolds number is approximately 3500 based on the mean chord and the mean velocity (where and are average angular velocity, non-dimensional second moment of wing area and distance from the center of rotation to wing tip, respectively). The upper region of the leading edge corresponds to a counter-clockwise leading edge vortex (LEV). A strong LEV was formed on the upper wing surface. The camber deformation of the wing shape at the middle span for all six wings was also presented. The effect of camber deformation on leading edge vorticity was also illustrated in Figure 24 and Figure 25. The LEV formed on the stiffest W1 was much smaller than that of the deformable wing group, resulting in low lift force production as depicted in Figure 22. Positive camber produced larger leading edge vortex on the wing than that of negative camber. The negative vorticity shed from the trailing edge of the stiffest W1 was much weaker compared to that of the deformable wing. In addition, the strength of LEV on the deformable wing group is stronger than that of the rigid wing (W1). The complicated wing deformation caused the leading edge vortex attached to the upper surface to display different forms as shown in Figure 24 and Figure 25.
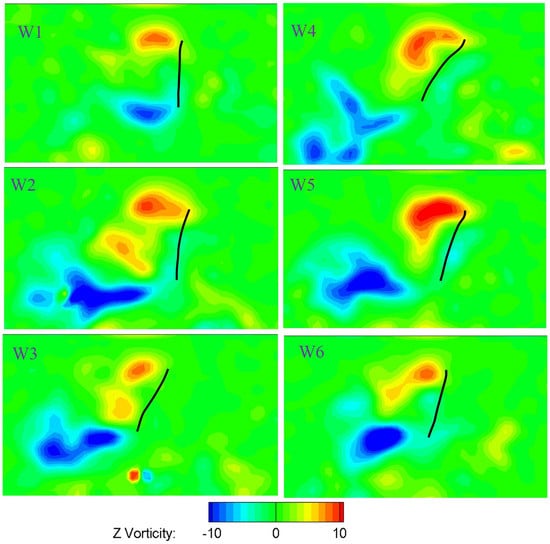
Figure 24.
Contours of the instantaneous vorticity around the middle span of six wings at the middle of the downstroke.
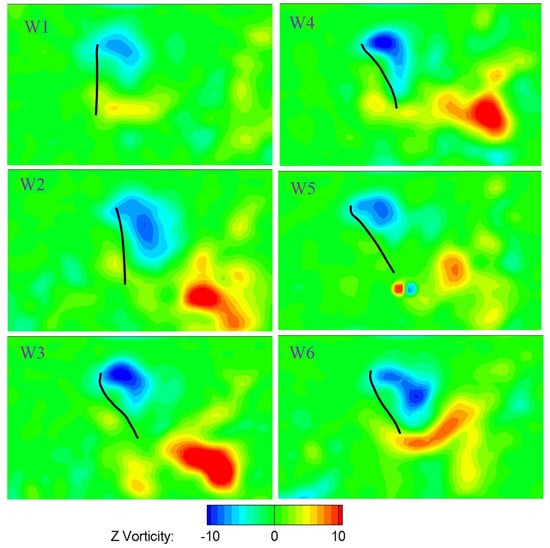
Figure 25.
Contours of the instantaneous vorticity around the middle span of six wings at the middle of the upstroke.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we developed a feasible biologically inspired insect wing using a simple but effective concept. By replacing the elastic material at the wing root vein, the root vein would bend upward and inward generating an angle of attack, camber and twisting deformation while the wing was flapping due to the aerodynamic and inertial forces acting on the wing. The original artificial wing has been designed and fabricated to mimic the two important features of the insect wing; twisting and camber generation. The aerodynamic experiments, including wing motion captures, force measurements, and PIV measurements were conducted to obtain the three-dimensional wing kinematics, force production and flow structures generated by the flexible wings. In addition, the dynamic characteristics of the six designed wings (natural frequency) were determined using a Base-Excitation model testing method. The present work can lead to further study fluid structure interaction of bio-flexible wing that was notoriously difficult to conduct in the real insect wing.
A flapping wing mechanism which replicated the general kinematics pattern of insect flight in the hovering condition has been performed to study the detail of the deformation and aerodynamics of biological wings. The twisting and camber deformations matched reasonably well between the real insect wing and the artificial wing. Additionally, different wing vein layouts were also designed to evaluate the influence of the vein patterns on the camber deformations. Although without the measurement of drag forces, the lift/power has been measured to estimate the beneficial effects of the flexible wing for the flapping wing MAV. The force measurement results indicated that the uniform deformed wings have the comparable lift/power at the flapping frequency less than 16 Hz. In a future study, more qualitative investigations, especially flow structures (PIV), will be carried out to provide a more in-depth picture of the complicated, unsteady aerodynamic problem of the flexible wing.
Supplementary Materials
Movies 1–7 are available online at www.mdpi.com/2226-4310/4/3/37/s1.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Kumar A. Senthil, Lua Kim Boon, Yeo Khoon Seng, and Lim Tee Tai of the National University of Singapore for their support.
Author Contributions
Tien Van Truong proposed the ideas, performed the work, and wrote the manuscript. Quoc-Viet Nguyen and Heow Pueh Lee contributed in reviewing the paper and provided the feedback and advice.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Truong, T.V.; Doyoung, B.; Laura, C.L.; Douglas, J.E.; Park, H.C.; Kim, M.J. Flight behavior of the rhinoceros beetle trypoxylus dichotomus during electrical nerve stimulation. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, M. Insect flight. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, R309–R314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, R. The Biomechanics of Insect Flight: Form, Function, Evolution; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, M.H.; Lehmann, F.-O.; Sane, S.P. Wing rotation and the aerodynamic basis of insect flight. Science 1999, 284, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, T.V.; Le, T.Q.; Byun, D.; Park, H.C.; Kim, M. Flexible wing kinematics of a free-flying beetle (rhinoceros beetle Trypoxylus dichotomus). J. Bionic Eng. 2012, 9, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.Q.; Truong, T.V.; Park, S.H.; Quang Truong, T.; Ko, J.H.; Park, H.C.; Byun, D. Improvement of the aerodynamic performance by wing flexibility and elytra–hind wing interaction of a beetle during forward flight. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.; Walker, S.M.; Bomphrey, R.J.; Taylor, G.K.; Thomas, A.L.R. Details of insect wing design and deformation enhance aerodynamic function and flight efficiency. Science 2009, 325, 1549–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Deng, X.; Sane, S.P. Aerodynamic effects of flexibility in flapping wings. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.; Zeng, L.; Yin, C. Measuring the body position, attitude and wing deformation of a free-flight dragonfly by combining a comb fringe pattern with sign points on the wing. Measurement Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 903. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Hedrick, T.L.; Mittal, R. A multi-fidelity modelling approach for evaluation and optimization of wing stroke aerodynamics in flapping flight. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 721, 118–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootton, R.J. The mechanical design of insect wings. Sci. Am. 1990, 263, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.M.; Thomas, A.L.; Taylor, G.K. Deformable wing kinematics in the desert locust: How and why do camber, twist and topography vary through the stroke? J. R. Soc. Interface 2009, 6, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.M.; Thomas, A.L.R.; Taylor, G.K. Deformable wing kinematics in free-flying hoverflies. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkarayev, S.; Silin, D.; Abate, G.; Albertani, R. Aerodynamics of cambered membrane flapping wings. In Proceedings of the 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 4–7 January 2010; pp. 2010–2058. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, T.V.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Park, H.; Yoon, K.; Byun, D. Flow structures around a flapping wing considering ground effect. Exp. Fluids 2013, 54, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.V.; Le, T.Q.; Tran, H.T.; Park, H.C.; Yoon, K.J.; Byun, D. Flow visualization of rhinoceros beetle (Trypoxylus dichotomus) in free flight. J. Bionic Eng. 2012, 9, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.V.; Doyoung, B.; Kim, M.J.; Yoon, K.J.; Park, H.C. Aerodynamic forces and flow structures of the leading edge vortex on a flapping wing considering ground effect. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, T.V.; Le, T.Q.; Park, H.C.; Yoon, K.J.; Kim, M.J.; Byun, D. Non-jumping take off performance in beetle flight (rhinoceros beetle Trypoxylus dichotomus). J. Bionic Eng. 2014, 11, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.Q.; Truong, T.V.; Tran, H.T.; Park, S.H.; Ko, J.H.; Park, H.C.; Byun, D. How could beetle’s elytra support their own weight during forward flight? J. Bionic Eng. 2014, 11, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Shimoyama, I. Forward flight of swallowtail butterfly with simple flapping motion. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthew, K.; Karl, K.; Henry, W. Development of the nano hummingbird: A tailless flapping wing micro air vehicle. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Nashville, TN, USA, 9–12 January 2012; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.V.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Truong, Q.T.; Truong, T.V.; Park, H.C.; Goo, N.S.; Byun, D.; Kim, M.J. Stable vertical takeoff of an insect-mimicking flapping-wing system without guide implementing inherent pitching stability. J. Bionic Eng. 2012, 9, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimoyama, I. Fabrication of a three-dimensional insect-wing model by micromolding of thermosetting resin with a thin elastmeric mold. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Combes, S.; Finio, B.; Wood, R. Artificial insect wings of diverse morphology for flapping-wing micro air vehicles. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Stanford, B.; Sällström, E.; Ukeiley, L.; Ifju, P. Structural dynamics and aerodynamics measurements of biologically inspired flexible flapping wings. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhayu, P.R.; Nguyen, Q.-V.; Park, H.C.; Goo, N.S.; Byun, D. Artificial cambered-wing for a beetle-mimicking flapper. J. Bionic Eng. 2010, 7, S130–S136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Okada, H.; Shimasue, Y.; Liu, H. Flexible flapping wings with self-organized microwrinkles. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyy, W.; Kang, C.-K.; Chirarattananon, P.; Ravi, S.; Liu, H. Aerodynamics, sensing and control of insect-scale flapping-wing flight. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Deng, X.; Hedrick, T.L. The mechanics and control of pitching manoeuvres in a freely flying hawkmoth (Manduca sexta). J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 4092–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootton, R.; Herbert, R.; Young, P.; Evans, K. Approaches to the structural modelling of insect wings. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 358, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, T.; Liu, H. A fluid–structure interaction model of insect flight with flexible wings. J. Comput. Phys. 2012, 231, 1822–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, C.P. The aerodynamics of hovering insect flight. II. Morphological parameters. Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. B 1984, 305, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Goosen, J.; Van Keulen, A. Optimal hovering kinematics with respect to various flapping-wing shapes. In Proceedings of the International Micro Air Vehicle Conference and Flight Competition (IMAV), Toulouse, France, 17–20 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ennos, A.R. The importance of torsion in the design of insect wings. J. Exp. Biol. 1988, 140, 137–160. [Google Scholar]
- Combes, S.; Daniel, T. Flexural stiffness in insect wings: Effects of wing venation and stiffness distribution on passive bending. Am. Entomol. 2005, 51, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubel, T.Y.; Tropea, C. Experimental Investigation of a Flapping Wing Model. In Animal Locomotion; Taylor, G.K., Triantafyllou, M.S., Tropea, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 383–399. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-K.; Han, J.-H.; Kwon, K.-J. Wind tunnel tests for a flapping wing model with a changeable camber using macro-fiber composite actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 024008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, D.; Ukeiley, L.; Bernal, L. Flow around flapping flexible flat plate wings. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Nashville, TN, USA, 2012; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tyson, L.H. Software techniques for two- and three-dimensional kinematic measurements of biological and biomimetic systems. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-S.; Chen, J.-Y.; Chou, Y.-F. On the natural frequencies and mode shapes of dragonfly wings. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 313, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.M.; Thomas, A.L.R.; Taylor, G.K. Photogrammetric reconstruction of high-resolution surface topographies and deformable wing kinematics of tethered locusts and free-flying hoverflies. J. R. Soc. Interface 2009, 6, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aono, H.; Shyy, W.; Liu, H. Vortex dynamics in near wake of a hovering hawkmoth. In Proceedings of the 46th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 7–10 January 2008; p. 583. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Aono, H. Size effects on insect hovering aerodynamics: An integrated computational study. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2009, 4, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Hedrick, T.L.; Mittal, R. Time-varying wing-twist improves aerodynamic efficiency of forward flight in butterflies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).