Conflict Detection, Resolution, and Collision Avoidance for Decentralized UAV Autonomy: Classical Methods and AI Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. New Machine Learning Approaches and Their Challenges
- Transparency in ML-based systems can be achieved by providing open and accessible information about the model—its architecture, training data, and assumptions. Alternatively, ML can be used as an optimization layer atop transparent rule-based algorithms. An example of this hybrid strategy is presented in [7], where a reinforcement learning agent is combined with a rule-based controller.
- Interpretability refers to the degree to which an artificial intelligence (AI) system’s outputs can be directly comprehended and logically assessed by a human observer; while not clearly defined, it generally emphasizes simplicity and clarity. For instance, Q-learning [11] can be considered interpretable due to its straightforward policy representation.
1.2. Related Work
2. Free Flight and Autonomy
3. Conflict Detection, Resolution, and Collision Avoidance: Classical and AI-Based Approaches
3.1. Sensing
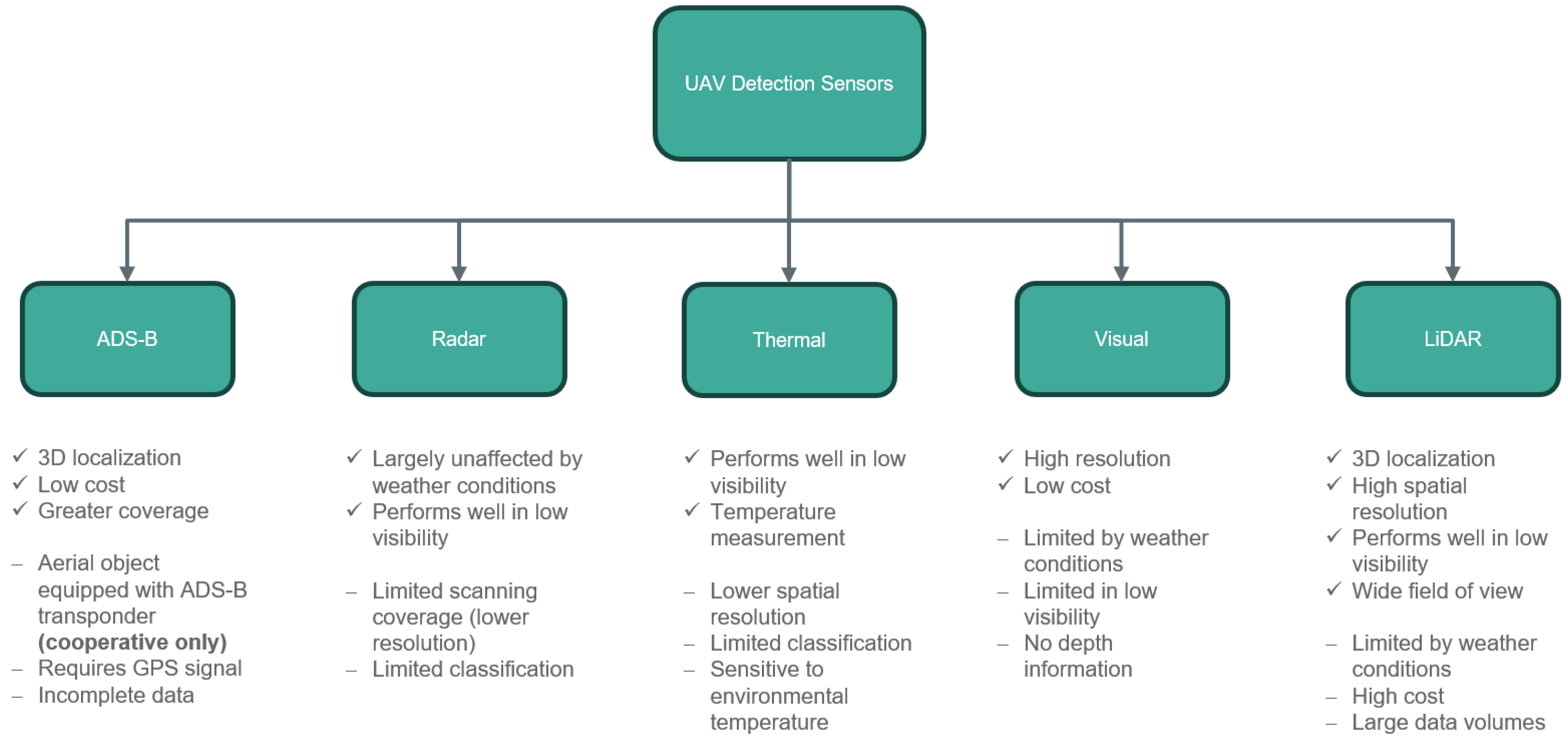
3.1.1. Sensor Types
3.1.2. Classical Approaches for Detection
3.1.3. Machine Learning Approaches for Detection
3.2. Reasoning and Alerting
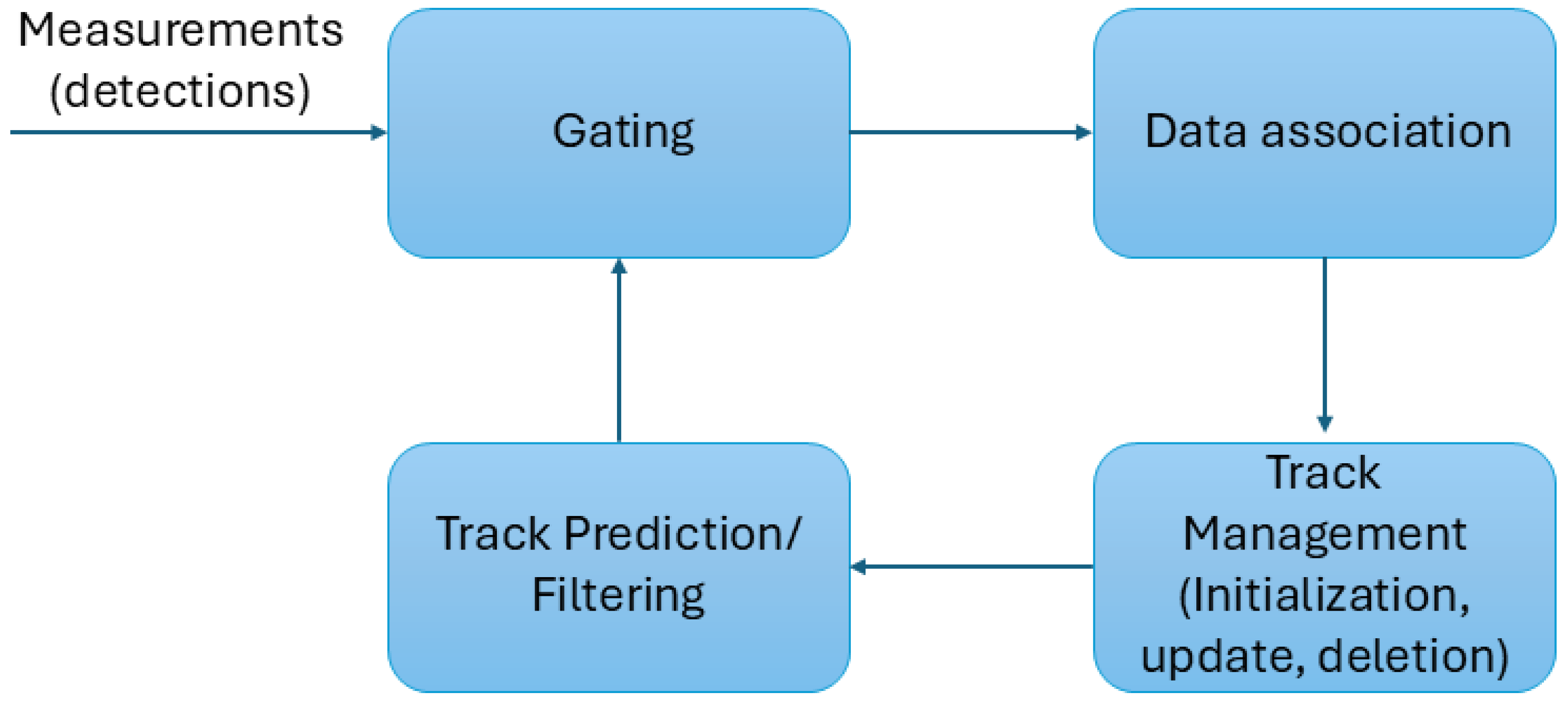
3.2.1. Classical Approaches for Intruder Tracking
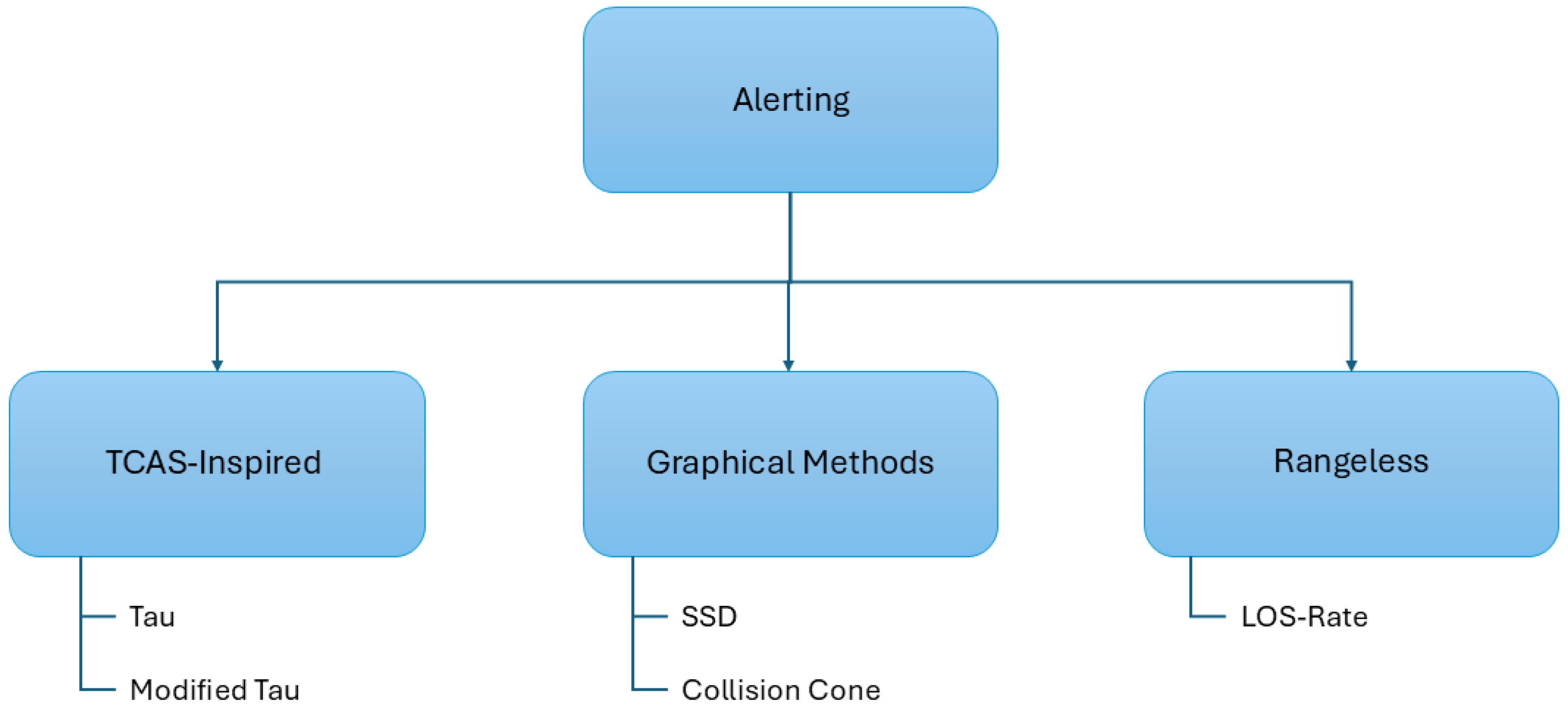
3.2.2. Classical Approaches for Alerting
3.2.3. Machine Learning Approaches for Reasoning and Alerting
3.3. Collision Avoidance
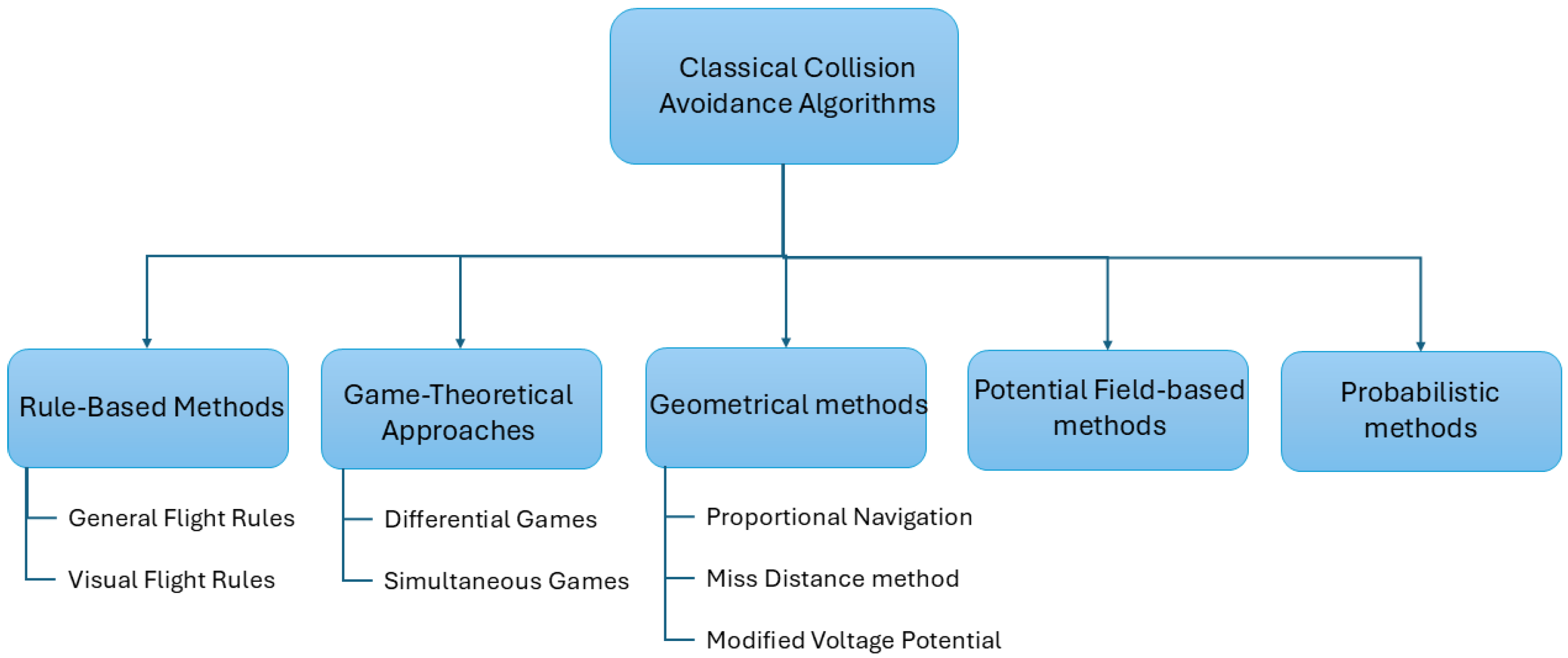
3.3.1. Classical Approaches
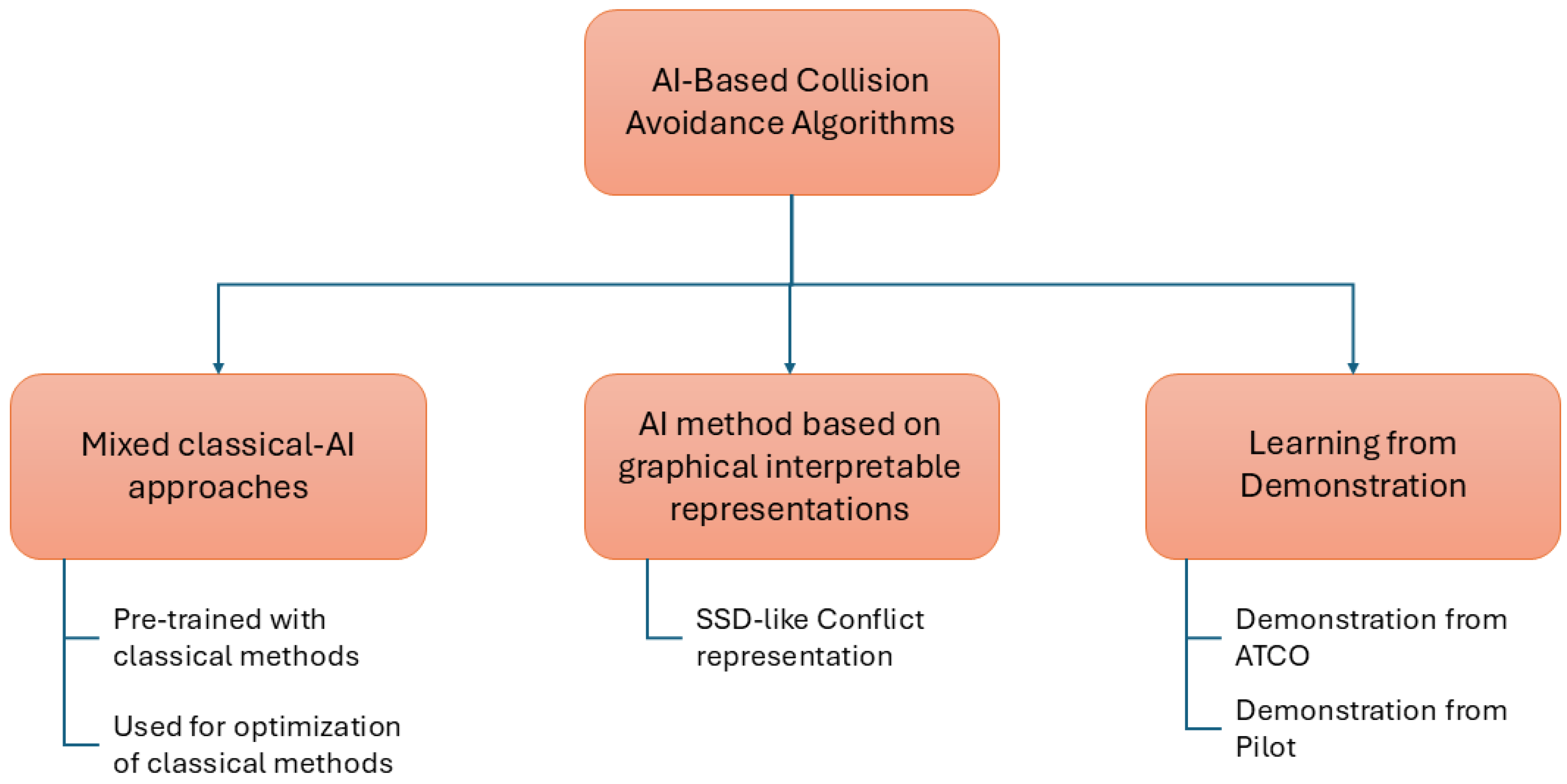
3.3.2. Machine Learning Approaches
3.4. Summary of Sensing, Reasoning, and Avoidance Methods
4. Discussion and Outlook
4.1. Certification-Driven Patterns in AI-Based CA
4.2. Explainability, Transparency, and Levels of Autonomy
4.3. Towards Standardized Benchmarks and Test Beds
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shakhatreh, H.; Sawalmeh, A.H.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Dou, Z.; Almaita, E.; Khalil, I.; Othman, N.S.; Khreishah, A.; Guizani, M. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): A Survey on Civil Applications and Key Research Challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 48572–48634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Yue, C.; Chen, A. Are we working on the safety of UAVs? An LDA-based study of UAV safety technology trends. Saf. Sci. 2022, 152, 105767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.R.; Grubesic, T.H.; Wallace, D.; Chamberlain, A.W. The View from Above: A Survey of the Public’s Perception of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles and Privacy. J. Urban Technol. 2019, 26, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, A. Public Perception of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. In Aviation Technology Graduate Student Publications; Purdue University: West Lafayette, Indiana, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, J.M.; van Gent, R.N.H.W.; Ruigrok, R.C.J. Designing for safety: The ‘free flight’ air traffic management concept. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2002, 75, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Yin, S.; Wu, Y. Explainable and safe reinforcement learning for autonomous air mobility. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.13474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likmeta, A.; Metelli, A.M.; Tirinzoni, A.; Giol, R.; Restelli, M.; Romano, D. Combining reinforcement learning with rule-based controllers for transparent and general decision-making in autonomous driving. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 131, 103568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipovetsky, S.; Conklin, M. Analysis of Regression in Game Theory Approach; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?”: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’16, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, C.J.; Dayan, P. Q-learning. Mach. Learn. 1992, 8, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- European Union Aviation Safety Agency. Artificial Intelligence Roadmap: A Human-Centric Approach to AI in Aviation. 2024. Available online: https://www.easa.europa.eu/en/domains/research-innovation/ai (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- European Union Aviation Safety Agency. EASA Artificial Intelligence (AI) Concept Paper Issue 2: Guidance for Level 1 & 2 Machine-Learning Applications; Technical Report; European Union Aviation Safety Agency: Cologne, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hamissi, A.; Dhraief, A.; Sliman, L. A Comprehensive Survey on Conflict Detection and Resolution in Unmanned Aircraft System Traffic Management. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 1395–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennedy, K.; Hilburn, B.; Nadirsha, T.N.; Alam, S.; Le, K.D.; Li, H. Do ATCOs Need Explanations, and Why? Towards ATCO-Centered Explainable AI for Conflict Resolution Advisories. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.03117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degas, A.; Islam, M.R.; Hurter, C.; Barua, S.; Rahman, H.; Poudel, M.; Ruscio, D.; Ahmed, M.U.; Begum, S.; Rahman, M.A.; et al. A survey on artificial intelligence (ai) and explainable ai in air traffic management: Current trends and development with future research trajectory. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Sejan, M.A.S.; Aziz, M.A.; Tabassum, R.; Baik, J.I.; Song, H.K. A Comprehensive Survey of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Detection and Classification Using Machine Learning Approach: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Directions. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Fasano, G.; Carrio, A.; Lei, M.; Bavle, H.; Campoy, P. A comprehensive survey on non-cooperative collision avoidance for micro aerial vehicles: Sensing and obstacle detection. J. Field Robot. 2023, 40, 1697–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, H.; Geißler, D.; Ray, L.; Müller-Divéky, S.; Müller, P.; Kittrell, S.; Liu, M.; Zhou, B.; Lukowicz, P. Towards certifiable AI in aviation: Landscape, challenges, and opportunities. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.08666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletsos, J.; Ntakolia, C. Air traffic management and energy efficiency: The free flight concept. Energy Syst. 2017, 8, 709–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.; Qin, V.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Balakrishnan, H. Traffic management protocols for advanced air mobility. Front. Aerosp. Eng. 2023, 2, 1176969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, Í.R.; Neto, E.C.P.; Matsumoto, T.T.; Yu, H. Decentralized air traffic management for advanced air mobility. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu noz, C.; Narkawicz, A.; Hagen, G.; Upchurch, J.; Dutle, A.; Consiglio, M.; Chamberlain, J. DAIDALUS: Detect and avoid alerting logic for unmanned systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/AIAA 34th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), Prague, Czech Republic, 13–17 September 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 5A1-1–5A1-12. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, M.P.; Panken, A.; Moss, R.; Alvarez, L.; Leeper, C. ACAS Xu: Integrated collision avoidance and detect and avoid capability for UAS. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/AIAA 38th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), San Diego, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- RTCA, Inc. Minimum Operational Performance Standards (MOPS) for Detect and Avoid (DAA) Systems; Do-365c; RTCA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin, A.D. Progress on Requirements and Standards for Sense & Avoid. 2010. Available online: https://www.mitre.org/sites/default/files/pdf/10_2799.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2026).
- Aldao, E.; González-de Santos, L.M.; González-Jorge, H. LiDAR Based Detect and Avoid System for UAV Navigation in UAM Corridors. Drones 2022, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corucci, L.; Meta, A.; Coccia, A. An X-band radar-based airborne collision avoidance system proof of concept. In Proceedings of the 2014 15th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Gdansk, Poland, 16–18 June 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Small UAS DAA Requirements for BVLOS Operations; Technical Report; ASSURE (Alliance for System Safety of UAS through Research Excellence): Dayton, OH, USA, 2017; Available online: https://assureuas.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/A2-Final-Report.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2026).
- Fasano, G.; Accardo, D.; Moccia, A.; Carbone, C.; Ciniglio, U.; Corraro, F.; Luongo, S. Multi-sensor-based fully autonomous non-cooperative collision avoidance system for unmanned air vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, CA, USA, 6–8 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fasano, G.; Accardo, D.; Tirri, A.E.; Moccia, A.; De Lellis, E. Radar/electro-optical data fusion for non-cooperative UAS sense and avoid. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, L.R.; Sabatini, R.; Ramasamy, S.; Gardi, A. A novel system for non-cooperative UAV sense-and-avoid. In Proceedings of the European Navigation Conference, Vienna, Austria, 23–25 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- de Haag, M.U.; Bartone, C.G.; Braasch, M.S. Flight-test evaluation of small form-factor LiDAR and radar sensors for sUAS detect-and-avoid applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/AIAA 35th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), Sacramento, CA, USA, 25–29 September 2016; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.; Cha, J.; Lyu, H. Detect and avoid system based on multi sensor fusion for UAV. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 17–19 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1107–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Coraluppi, S.; Carthel, C.; Wu, C.; Stevens, M.; Douglas, J.; Titi, G.; Luettgen, M. Distributed MHT with active and passive sensors. In Proceedings of the 2015 18th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 July 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 2065–2072. [Google Scholar]
- Coraluppi, S.; Carthel, C.; Zimmerman, B.; Allen, T.; Douglas, J.; Muka, J. Multi-stage MHT with airborne and ground sensors. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 3–10 March 2018; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamm, R.J.; Glaneuski, J.; Kennett, P.R.; Belanger, J.M. Advances in the Use of NAS Infrastructure and GBDAA for UAS Operations. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/AIAA 37th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), London, UK, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, T.; Wijesekera, D.; Costa, P.; Barreto, A. An ADS-B intrusion detection system. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ISPA, Tianjin, China, 23–26 August 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 544–551. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi, M.; Di Fausto, D. ADS-B signal signature extraction for intrusion detection in the air traffic surveillance system. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Rome, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2564–2568. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, G.; Ray, J. Detecting ADS-B replay cyberattacks in the national airspace system. Issues Inf. Syst. 2023, 24, 170–185. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A.; Studer, F.A. A Review of CFAR Detection Techniques in Radar Systems. In Optimised Radar Processors; The Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 1986; pp. 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, Y.; Heo, J.; Jung, Y.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y. FPGA implementation of efficient CFAR algorithm for radar systems. Sensors 2023, 23, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safa, A.; Verbelen, T.; Keuninckx, L.; Ocket, I.; Hartmann, M.; Bourdoux, A.; Catthoor, F.; Gielen, G.G. A low-complexity radar detector outperforming OS-CFAR for indoor drone obstacle avoidance. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9162–9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F.; Ritchie, M.; Fioranelli, F.; Charlish, A.; Griffiths, H. Micro-Doppler based detection and tracking of UAVs with multistatic radar. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2–6 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, S.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y. Radar detection of low-slow-small UAVs in complex environments. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 10th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 17–19 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; Volume 10, pp. 1153–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowicz, J.; Lefebvre, S.; Maire, F.; Moulines, E. Detecting aircraft with a low-resolution infrared sensor. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 3034–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Ma, J.; Tao, C.; Yang, C.; Tian, J. A robust directional saliency-based method for infrared small-target detection under various complex backgrounds. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 10, 495–499. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, H.; Gu, Y.; Napolitano, M. A survey of optical flow techniques for UAV navigation applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Atlanta, GA, USA, 28–31 May 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 710–716. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, T.; Scherer, S. First results in detecting and avoiding frontal obstacles from a monocular camera for micro unmanned aerial vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1750–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Mejias Alvarez, L.; Ford, J.; Lai, J. Towards the implementation of vision-based UAS sense-and-avoidance system. In Proceedings of the 27th Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences, Nice, France, 19–24 September 2010; International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences: Bonn, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Molloy, T.L.; Ford, J.J.; Mejias, L. Detection of aircraft below the horizon for vision-based detect and avoid in unmanned aircraft systems. J. Field Robot. 2017, 34, 1378–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolph, C.; Logan, M.J.; Glaab, L.J.; Vranas, T.L.; McSwain, R.G.; Johns, Z. Sense and avoid for small unmanned aircraft systems. In AIAA Information Systems-AIAA Infotech@ Aerospace; AIAA: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; p. 1151. [Google Scholar]
- Dewan, A.; Caselitz, T.; Tipaldi, G.D.; Burgard, W. Motion-based detection and tracking in 3d lidar scans. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 4508–4513. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Fan, X.; Chen, H.; Lu, P. Fapp: Fast and adaptive perception and planning for uavs in dynamic cluttered environments. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2024, 41, 871–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, P.; Tan, J.; Li, F. The obstacle detection method of uav based on 2d lidar. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 163437–163448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, W.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Wang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Detrs beat yolos on real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 16965–16974. [Google Scholar]
- Airborne Object Tracking Dataset. 2021. Available online: https://registry.opendata.aws/airborne-object-tracking/ (accessed on 28 March 2025).
- Vrba, M.; Walter, V.; Pritzl, V.; Pliska, M.; Báča, T.; Spurný, V.; Heřt, D.; Saska, M. On Onboard LiDAR-Based Flying Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2025, 41, 593–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Yang, Y.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.M.; Yang, J.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Xie, L. MMAUD: A Comprehensive Multi-Modal Anti-UAV Dataset for Modern Miniature Drone Threats. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 2745–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrikar, J.; Dantas, J.; Moon, B.; Hamidi, M.; Ghosh, S.; Keetha, N.; Higgins, I.; Chandak, A.; Yoneyama, T.; Scherer, S. Image, speech, and ADS-B trajectory datasets for terminal airspace operations. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanström, F.; Englund, C.; Alonso-Fernandez, F. Real-time drone detection and tracking with visible, thermal and acoustic sensors. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 7265–7272. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H. UAVDB: Trajectory-Guided Adaptable Bounding Boxes for UAV Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.06490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhard, T.R.; Weinmann, A.; Franke, K.; Koch, T. SynDroneVision: A Synthetic Dataset for Image-Based Drone Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.05633. [Google Scholar]
- Aldao, E.; Veiga-López, F.; Miguel González-deSantos, L.; González-Jorge, H. Enhancing UAV Classification with Synthetic Data: GMM LiDAR Simulator for Aerial Surveillance Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 26960–26970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafienya, H.; Regan, A. 4D flight trajectory prediction based on ADS-B data: A comparison of CNN-GRU models. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO), Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.; Wang, B.; Tian, J. TTSAD: TCN-Transformer-SVDD Model for Anomaly Detection in air traffic ADS-B data. Comput. Secur. 2024, 141, 103840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Masood, A.; Manzoor, J.; Akleylek, S. Automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) anomalous messages and attack type detection: Deep learning-based architecture. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2025, 11, e2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamboé, M.; Marrocco, J.S.; Ouattara, J.Y.; Fernandez, J.M.; Nicolescu, G. New Machine Learning Approaches for Intrusion Detection in ADS-B. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2510.08333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, J.; Gao, M. GAN–CNN-based moving target detector for airborne radar systems. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 21614–21627. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Tian, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, X. Deep learning-based UAV detection in pulse-Doppler radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tm, D.; Verma, R.; Rajesh, R.; Varughese, S. Single shot radar target detection and localization using deep neural network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), Bangalore, India, 8–10 July 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Xie, X.; Xi, J.; Yang, X. GM-DETR: Infrared Detection of Small UAV Swarm Targets Based on Detection Transformer. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, G.; Llerena, J.P.; Usero, L.; Patricio, M.A. A comparative study of convolutional neural network and transformer architectures for drone detection in thermal images. Appl. Sci. 2024, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.W.; Chin, W.H.; Ho, H.W. Air-to-air Micro Air Vehicle interceptor with an embedded mechanism and deep learning. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 135, 108192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opromolla, R.; Fasano, G. Visual-based obstacle detection and tracking, and conflict detection for small UAS sense and avoid. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 119, 107167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenos, A.; Petrongonas, E.; Filippopoulos, O.; Skliros, C.; Kollias, D.; Kollias, S. NEFELI: A deep-learning detection and tracking pipeline for enhancing autonomy in advanced air mobility. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 155, 109613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Liang, G. YOLOv8-SMOT: An Efficient and Robust Framework for Real-Time Small Object Tracking via Slice-Assisted Training and Adaptive Association. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.12087. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Patrikar, J.; Moon, B.; Hamidi, M.M.; Scherer, S. AirTrack: Onboard deep learning framework for long-range aircraft detection and tracking. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May 2023–2 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1277–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Karampinis, V.; Arsenos, A.; Filippopoulos, O.; Petrongonas, E.; Skliros, C.; Kollias, D.; Kollias, S.; Voulodimos, A. Ensuring UAV Safety: A Vision-Only and Real-Time Framework for Collision Avoidance Through Object Detection, Tracking, and Distance Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Chania, Greece, 4–7 June 2024; pp. 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H. UAVDB: Point-Guided Masks for UAV Detection and Segmentation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2409.06490. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Pisutsin, P.; Tsao, C.W.; Feroskhan, M. Clustering-based Learning for UAV Tracking and Pose Estimation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.16867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Fang, H.; Geng, R.; Jensfelt, P. DeFlow: Decoder of Scene Flow Network in Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 2105–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Shalom, Y.; Tse, E. Tracking in a cluttered environment with probabilistic data association. Automatica 1975, 11, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D. An algorithm for tracking multiple targets. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1979, 24, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, S. Multiple hypothesis tracking for multiple target tracking. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2004, 19, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelli, R.; Graziano, A.; Farina, A. IM3HT Algorithm: A Joint Formulation of IMM and MHT for Multi-target Tracking. Eur. J. Control 1999, 5, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulampalam, M.; Maskell, S.; Gordon, N.; Clapp, T. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Shalom, Y. On the track-to-track correlation problem. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1981, 26, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant-Whyte, H.; Henderson, T.C. Multisensor Data Fusion. In Springer Handbook of Robotics; Siciliano, B., Khatib, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 867–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornic, P.; Garrec, P.; Kemkemian, S.; Ratton, L. Sense and avoid radar using data fusion with other sensors. In Proceedings of the 2011 Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalanobis, P.C. On the generalized distance in statistics. Sankhyā Indian J. Stat. Ser. A (2008-) 2018, 80, S1–S7. [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi, G.; Jestin, Y. Are You Clear About “Well Clear”? In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Dallas, TX, USA, 12–15 June 2018; pp. 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, T.; Spencer, N. Development and operation of the Traffic Alert and Collision Avoidance System (TCAS). Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, M.C.; Chamberlain, J.P.; Muñoz, C.A.; Hoffler, K.D. Concept of Integration for UAS Operations in the NAS. In Proceedings of the 28th Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences (ICAS 2012), Brisbane, Australia, 23–28 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya, S.; Khot, T. Analysis of the Tau concept used in aircraft collision avoidance through kinematic simulations. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS), Bengaluru, India, 4–8 January 2017; pp. 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, C.; Narkawicz, A.; Chamberlain, J. A TCAS-II resolution advisory detection algorithm. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control (GNC) Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 19–22 August 2013; p. 4622. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz, C.; Narkawicz, A.; Chamberlain, J.; Consiglio, M.C.; Upchurch, J.M. A family of well-clear boundary models for the integration of UAS in the NAS. In Proceedings of the 14th AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration, and Operations Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–20 June 2014; p. 2412. [Google Scholar]
- Narkawicz, A.; Mu noz, C.; Dutle, A. Sensor uncertainty mitigation and dynamic well clear volumes in DAIDALUS. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/AIAA 37th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), London, UK, 23–27 September 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Thipphavong, D.; Cone, A.; Lee, S.M.; Santiago, C. Ensuring Interoperability Between UAS Detect-and-Avoid and Manned Aircraft Collision Avoidance. In Proceedings of the Twelfth USA/Europe Air Traffic Management Research and Development Seminar (ATM2017), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dam, S.B.; Mulder, M.; Van Paassen, M. Ecological interface design of a tactical airborne separation assistance tool. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.-Part A Syst. Humans 2008, 38, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermes, P.; Mulder, M.; van Paassen, M.M.; Boering, J.H.L.; Huisman, H. Solution-Space-Based Complexity Analysis of the Difficulty of Aircraft Merging Tasks. J. Aircr. 2009, 46, 1995–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahman, S.M.; Mulder, M.; van Paassen, R. Using the solution space diagram in measuring the effect of sector complexity during merging scenarios. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 8–11 August 2011; p. 6693. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, T.; Jing, X.; Yan, Z.; Pedrycz, W. A survey on machine learning for data fusion. Inf. Fusion 2020, 57, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Liang, J.; Zhu, F. A comparative review on multi-modal sensors fusion based on deep learning. Signal Process. 2023, 213, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chao, S.; Yan, D.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, L. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Method Based on Self-Attention Mechanism. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, L.T.; Johnson, M.A. Bayesian networks for interpretable and extensible multisensor fusion. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence for Security and Defence Applications II, National Harbor, MD, USA, 22–24 April 2024; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; Volume 13206, pp. 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Luong, M.T.; Pham, H.; Manning, C.D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.04025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, M.W.; Alvarez, L.E.; Breeden, K. Improving autonomous separation assurance through distributed reinforcement learning with attention networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 22857–22863. [Google Scholar]
- Brittain, M.W.; Wei, P. One to any: Distributed conflict resolution with deep multi-agent reinforcement learning and long short-term memory. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2021 Forum, Online, 11–15 and 19–21 January 2021; p. 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Angelov, P. Sense and Avoid in UAS: Research and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ge, S.S. General fight rule-based trajectory planning for pairwise collision avoidance in a known environment. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2014, 12, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, M.P.; Faria, R.A.P.; Cunha, S.R. Visual Flight Rules-based Collision Avoidance System for VTOL UAV. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Robotics and Automation Engineering (ICRAE), Online, 20–22 November 2020; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.; Poujade, A.; Malandrakis, K.; Petrunin, I.; Panagiotakopoulos, D.; Tsourdos, A. Rule-Based Conflict Management for Unmanned Traffic Management Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2020 AIAA/IEEE 39th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 11–16 October 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, R.G.; Da Silva, R.C.; Ramos, A.C.; Mora-Camino, F. Collision avoidance based on Reynolds rules: A case study using quadrotors. In Proceedings of the Information Technology-New Generations: 14th International Conference on Information Technology, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–12 April 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 773–780. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.W. Flocks, herds and schools: A distributed behavioral model. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH ’87, Anaheim, CA, USA, 27–31 July 1987; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A. Differential Games; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub, I.E.; Pachter, M.; Garcia, E. An Introduction to Pursuit-evasion Differential Games. In Proceedings of the 2020 American Control Conference (ACC), Online, 1–3 July 2020; pp. 1049–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberkorn, T. Aircraft Separation in Uncontrolled Airspace Including Human Factors. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Graz, Graz, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Exarchos, I.; Tsiotras, P.; Pachter, M. UAV collision avoidance based on the solution of the suicidal pedestrian differential game. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–8 January 2016; p. 2100. [Google Scholar]
- D’apolito, F.; Sulzbachner, C. Collision Avoidance for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles using Simultaneous Game Theory. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/AIAA 37th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), London, UK, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, A.; Ghose, D. Obstacle avoidance in a dynamic environment: A collision cone approach. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.-Part A Syst. Humans 1998, 28, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujumdar, A.; Padhi, R. Reactive Collision Avoidance of Using Nonlinear Geometric and Differential Geometric Guidance. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2011, 34, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.C.; Bang, H.; Yoo, C.S. Proportional navigation-based collision avoidance for UAVs. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2009, 7, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Oh, H.D.; Tahk, M.J. UAV collision avoidance based on geometric approach. In Proceedings of the 2008 SICE Annual Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 20–22 August 2008; pp. 2122–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eby, M.S. A self-organizational approach for resolving air traffic conflicts. Lincoln Lab. J. 1995, 7, 239–254. [Google Scholar]
- Rorie, R.C.; Smith, C.; Sadler, G.; Monk, K.J.; Tyson, T.L.; Keeler, J. A Human-in-the-Loop evaluation of ACAS Xu. In Proceedings of the 2020 AIAA/IEEE 39th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 11–15 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Tang, J.; Lao, S. Collision avoidance for cooperative UAVs with optimized artificial potential field algorithm. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18382–18390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchti, J.; Senkbeil, R.; Carroll, J.; Dickinson, J.; Holt, J.; Biaz, S. Unmanned Aerial System Collision Avoidance Using Artificial Potential Fields. J. Aerosp. Inf. Syst. 2014, 11, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, D.; Dissanayake, G. A Force Field Method Based Multi-Robot Collaboration. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics, Bangkok, Thailand, 1–3 June 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarm, K.; Schmidt, G. Conflict-free motion of multiple mobile robots based on decentralized motion planning and negotiation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 20–25 April 1997; Volume 4, pp. 3526–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keong, C.W.; Shin, H.S.; Tsourdos, A. Reinforcement learning for autonomous aircraft avoidance. In Proceedings of the 2019 Workshop on Research, Education and Development of Unmanned Aerial Systems (RED UAS), Cranfield, UK, 25–27 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Graves, A.; Antonoglou, I.; Wierstra, D.; Riedmiller, M. Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, Y. Physics informed deep reinforcement learning for aircraft conflict resolution. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 8288–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; Radford, A.; Klimov, O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.; Ellerbroek, J.; Hoekstra, J. Improvement of Conflict Detection and Resolution at high densities through reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the ICRAT 2020: International Conference on Research in Air Transportation, Online, 15–18 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lillicrap, T. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.02971. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.; Ellerbroek, J.; Hoekstra, J. Determining optimal conflict avoidance manoeuvres at high densities with reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the Tenth SESAR Innovation Days, Virtual, 7–10 December 2020; pp. 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou, P. Soft actor-critic for discrete action settings. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.07207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T.; Tran, N.P.; Alam, S.; Duong, V.; Delahaye, D. A machine learning approach for conflict resolution in dense traffic scenarios with uncertainties. In Proceedings of the 13th USA/Europe Air Traffic Management Research and Development Seminar, Vienne, Austria, 17–21 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, P.N.; Pham, D.T.; Goh, S.K.; Alam, S.; Duong, V. An interactive conflict solver for learning air traffic conflict resolutions. J. Aerosp. Inf. Syst. 2020, 17, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, K.D.; Lopez, J.; Brush, J.S.; Owen, M.P.; Kochenderfer, M.J. Policy compression for aircraft collision avoidance systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/AIAA 35th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), Sacramento, CA, USA, 25–29 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Julian, K.D.; Kochenderfer, M.J.; Owen, M.P. Deep neural network compression for aircraft collision avoidance systems. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2019, 42, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, K.D.; Kochenderfer, M.J. Guaranteeing safety for neural network-based aircraft collision avoidance systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/AIAA 38th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), San Diego, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, G.; Barrett, C.; Dill, D.L.; Julian, K.; Kochenderfer, M.J. Reluplex: An efficient SMT solver for verifying deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Aided Verification, Heidelberg, Germany, 24–28 July 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 97–117. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Pei, K.; Whitehouse, J.; Yang, J.; Jana, S. Formal security analysis of neural networks using symbolic intervals. In Proceedings of the 27th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 18), Baltimore, MD, USA, 15–17 August 2018; pp. 1599–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Bak, S.; Tran, H.D. Neural network compression of ACAS Xu early prototype is unsafe: Closed-loop verification through quantized state backreachability. In Proceedings of the NASA Formal Methods Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 24–27 May 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 280–298. [Google Scholar]
- European Union Aviation Safety Agency; Daedalean, A.G. Concepts of Design Assurance for Neural Networks (CoDANN) II with Appendix B; Version 1.1; Technical Report; European Union Aviation Safety Agency and Daedalean AG: 2024. Available online: https://horizoneuropencpportal.eu/sites/default/files/2024-06/easa-report-concepts-of-design-assurance-for-neural-networks-codann-ii-2024.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2025).
- European Union Aviation Safety Agency. ToR RMT.0742: Artificial Intelligence Trustworthiness. In Terms of Reference RMT.0742 Issue 1, European Union Aviation Safety Agency; ToR Series RMT; European Union Aviation Safety Agency: Cologne, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Baheri, A.; Ren, H.; Johnson, B.; Razzaghi, P.; Wei, P. A Verification Framework for Certifying Learning-Based Safety-Critical Aviation Systems. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.04590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, M.; Alvarez, L.E.; Breeden, K.; Jessen, I. AAM-Gym: Artificial Intelligence Testbed for Advanced Air Mobility. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.04513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corso, A.; Moss, R.; Koren, M.; Lee, R.; Kochenderfer, M. A survey of algorithms for black-box safety validation of cyber-physical systems. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2021, 72, 377–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.J.; Kochenderfer, M.J.; Gariel, M.; Dubois, A. Bayesian Safety Validation for Failure Probability Estimation of Black-Box Systems. J. Aerosp. Inf. Syst. 2024, 21, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, J.G.; Dubois, A.; Moss, R.J. Formal and practical elements for the certification of machine learning systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/AIAA 42nd Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), Barcelona, Spain, 1–5 October 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, S.M.; Corso, A.L.; Yel, E.; Kochenderfer, M.J. Efficient determination of safety requirements for perception systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/AIAA 42nd Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), Barcelona, Spain, 1–5 October 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Brittain, M.; Wei, P. Safety Validation for Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Aircraft Separation Assurance with Adaptive Stress Testing. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/AIAA 42nd Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), Barcelona, Spain, 1–5 October 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lipkis, R.; Lee, R.; Silbermann, J.; Young, T. Adaptive Stress Testing of Collision Avoidance Systems for Small UASs with Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the AIAA SciTech Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 January 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ref. | CD | CR | CA | Coop. | Noncoop. | Explainability/ Certification | Decentralized Autonomy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | X | X | X | ||||
| [15] | X | X | X | ||||
| [16] | X | X | X | X | |||
| [17] | X | X | |||||
| [18] | X | X | X | X | |||
| [19] | X | X | X | ||||
| this survey | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Sensor Types | Airborne or Ground-Based | Reference | Sensor Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple sensors | Airborne sensors | [30,31] | Optical and IR cameras, Radar |
| [32] | LADAR, MMW Radar, optical and IR cameras | ||
| [33] | LiDAR, Radar | ||
| [34] | LiDAR, Stereo-cameras | ||
| Combination of airborne and ground-based sensors | [35,36] | Electro-Optical, Airborne Radar, Ground-Based Radar | |
| Ground sensors | [37] | Distributed Radars | |
| Single Sensor | Airborne sensors | [27] | LiDAR |
| [28] | X-Band Radar |
| Modality | Range/LoS/Environment Sensitivity | Update and Latency (Qualitative) | Processing Burden and False-Alarm Handling/Reporting |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADS-B | Range: comm-limited; LoS: N/A; Env: RF interference, spoofing (M–H) | Upd: H; Lat: sensor/comm-limited (L) | Comp: classical L, ML M; FAR: scenario- and detector-dependent |
| Radar | Range: H (SNR/aperture); LoS: Y; Env: clutter/multipath/weather (M) | Upd: M; Lat: sensor + processing (L–M) | Comp: classical M, ML M–H; FAR: CFAR-style control; cross-study comparability limited |
| Visual | Range: M (pixel-limited); LoS: Y; Env: illumination/haze/glare (H) | Upd: M–H; Lat: compute-limited for ML (M–H) | Comp: classical L–M, ML H; FAR: dataset-dependent (precision/recall common) |
| Thermal (IR) | Range: M (pixel/contrast-limited); LoS: Y; Env: thermal contrast/weather attenuation (M–H) | Upd: M; Lat: compute-limited for ML (M–H) | Comp: classical L–M, ML H; FAR: mixed reporting |
| LiDAR | Range: L–M (sensor/return-limited); LoS: Y; Env: fog/rain/dust (H) | Upd: M; Lat: processing-limited (M) | Comp: classical M, ML H; FAR: mixed reporting |
| Dataset | Annotations | Stationary | Moving | ADS-B | Radar | Thermal | Visual | LiDAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOT Dataset [60] | 3.3M+ | X | X | |||||
| UAV point cloud segmentation dataset [61] | 5.5 k | X | X | |||||
| MMAUD [62] | 6 drone types | X | X | X | X | |||
| TartanAviation [63] | 661 days, 3.1 M | X | X | X | ||||
| Drone detection dataset [64] | 200 k+ | X | X | X | ||||
| UAVDB [65] | 18k | X | X | |||||
| SynDroneVision [66] | 140 k | X |
| Sensor | Approach | Reference | Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADS-B | Classical | [38,39,40] | flight path modeling, RF fingerprinting, cosine-similarity |
| ML | [68,69,70,71] | CNN-base flight trajectory prediction, anomaly detection and intrusion detection | |
| Radar | Classical | [42,43,44,45] | CFAR probability estimation, Doppler methods |
| ML | [72,73,74] | CNN-based object detection | |
| Thermal | Classical | [46,47] | statistical sensitivity analysis, background extraction |
| ML | [75,76] | CNN- and transformer-based feature extraction and object detection | |
| Visual | Classical | [48,49,50,51,52] | optical flow, SURF feature matching, HMM filter |
| ML | [77,78,79,80,81,82,83,83] | YOLO, CNN- and transformer-based, foundation model | |
| LiDAR | Classical | [53,54,55,56] | clustering, SOCP, RANSAC, DBSCAN, CBRDD |
| ML | [84,85] | CL-Det, DeFlow |
| Reference | Data Association Algorithm | Filtering and Tracking |
|---|---|---|
| [30,31] | Ellipsoidal Gating | EKF |
| [32] | Track-toTrack | |
| [35,36] | MHT | EKF |
| [89] | MHT | IMM |
| [93] | Mahalanobis Distance | IMM |
| Category | References | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
| Rule-based | [114] | Based on the General Flight Rule |
| [115] | Based on the Visual Flight Rule | |
| [116] | Rule-based deconfliction method based on three stages | |
| [117] | Swarm CA based on the Reynolds rule | |
| Game-theoretic methods | [121] | Pursuit–evasion differential game |
| [122] | Suicidal Pedestrian (pursuit–evasion) differential game | |
| [123] | Pursuit–evasion simultaneous game | |
| Geometric | [125] | Collision cone followed by differential geometry |
| [126] | Collision cone followed by proportional guidance | |
| [127] | Cooperative geometrical approach based on missed distance | |
| [5,128] | Modified Voltage Potential | |
| Probabilistic approaches | [24] | MDP and dynamic programming |
| Potential-field-based methods | [131,132] | Artificial potential field |
| Category | References | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
| Reinforcement Learning | [134] | DQN |
| [136] | PPO from SSD-like graphical conflict representation | |
| [138] | DDPG with pre-training of the critic network using the MVP method | |
| [140] | DDPG to optimize MVP parameters | |
| [111] | Attention networks followed by SACD | |
| [112] | Multi-agent PPO for distributed conflict resolution | |
| [6] | Safe-DQN | |
| [142] | DDPG for optimal maneuver parameters and DQN for selecting the time of heading change | |
| [143] | DDPG from ATCO demonstrations | |
| value-function approximation | [144,145] | Function approximation of the large ACAS Xu score table obtained via dynamic programming |
| Classification Used in this Paper | Classical Function | Key Families (Representative) | Prereq/Failure Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensing | Detect | CFAR; classical vision/IR pipelines; LiDAR clustering; ADS-B validation/anomaly; learning-based detectors | P1, P2, P3/F1, F2, F6 |
| Reasoning and Alerting | Track | State estimation and track management; multi-sensor fusion; intent/threat inference | P2, P4/F3, F4, F5 |
| Evaluate | DAIDALUS WCV predicates; SSD; LOS-rate heuristics; uncertainty-aware variants | P4, P5, P7/F7, F8, F12 | |
| Declare | Thresholded alert logic (incl. hysteresis/persistence); multi-intruder prioritization (e.g., max-alert/min time-to-violation); learned threat ranking (attention) | P6, P7/F9, F10, F11 | |
| Avoidance | Avoid | Geometric guidance (collision cone, proportional navigation, miss-distance guidance, MVP); decision-theoretic (MDP/dynamic programming, e.g., ACAS Xu); game-theoretic (pursuit–evasion formulations); potential-field methods; learning-based policies (e.g., RL/neural controllers) | P8, P9/F13, F14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
d’Apolito, F.; Fanta-Jende, P.; Widhalm, V.; Sulzbachner, C. Conflict Detection, Resolution, and Collision Avoidance for Decentralized UAV Autonomy: Classical Methods and AI Integration. Aerospace 2026, 13, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace13020113
d’Apolito F, Fanta-Jende P, Widhalm V, Sulzbachner C. Conflict Detection, Resolution, and Collision Avoidance for Decentralized UAV Autonomy: Classical Methods and AI Integration. Aerospace. 2026; 13(2):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace13020113
Chicago/Turabian Styled’Apolito, Francesco, Phillipp Fanta-Jende, Verena Widhalm, and Christoph Sulzbachner. 2026. "Conflict Detection, Resolution, and Collision Avoidance for Decentralized UAV Autonomy: Classical Methods and AI Integration" Aerospace 13, no. 2: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace13020113
APA Styled’Apolito, F., Fanta-Jende, P., Widhalm, V., & Sulzbachner, C. (2026). Conflict Detection, Resolution, and Collision Avoidance for Decentralized UAV Autonomy: Classical Methods and AI Integration. Aerospace, 13(2), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace13020113








