Factors Influencing Step Ablation in the Expansion Section of a Composite Nozzle in a Solid Rocket Motor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Physical Model
2.2. Mathematical Models
2.2.1. Governing Equations for Flow and Heat Transfer
2.2.2. Gas-Phase Governing Equations and Turbulence Model
2.2.3. Heat Transfer in Nozzle Structures
2.2.4. Conservation Equations for the Fluid–Structure Coupling Boundary
2.3. Thermochemical Ablation Model
2.3.1. C/C Material Ablation Model
2.3.2. Carbon/Phenolic Material Ablation Model
2.4. Calculation Process
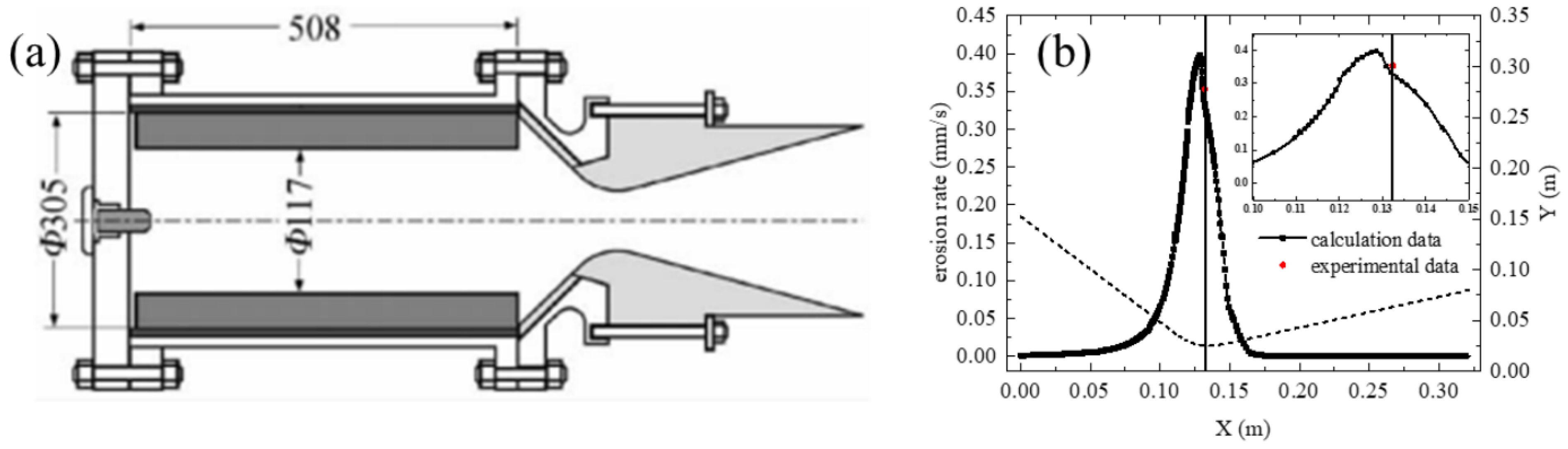
3. Model Validation
3.1. C/C Nozzle Ablation Model Validation
3.2. Carbon/Phenolic Composite Nozzle Ablation Validation
4. Analysis of Results
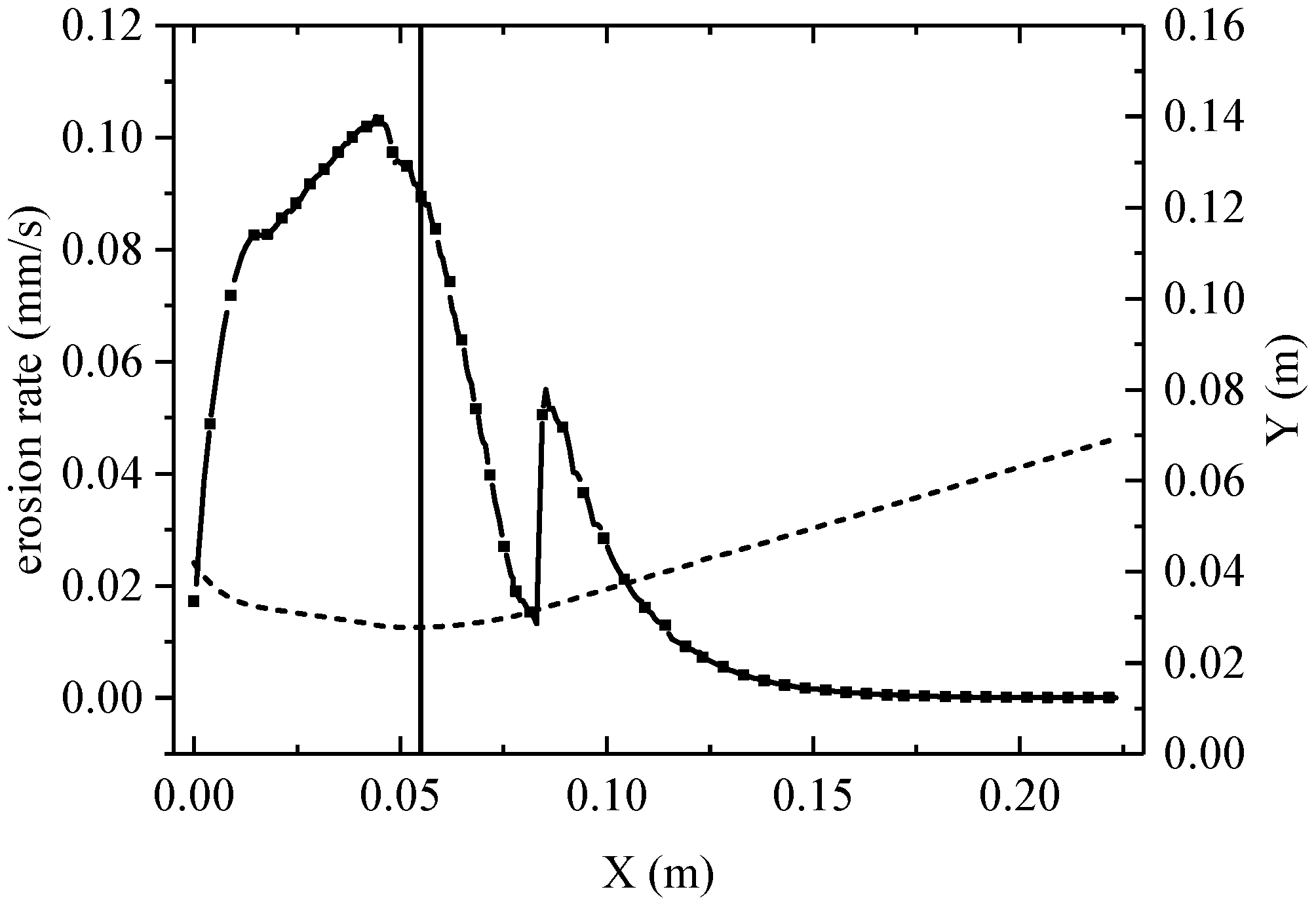
4.1. Calculation Results of Thermochemical Ablation
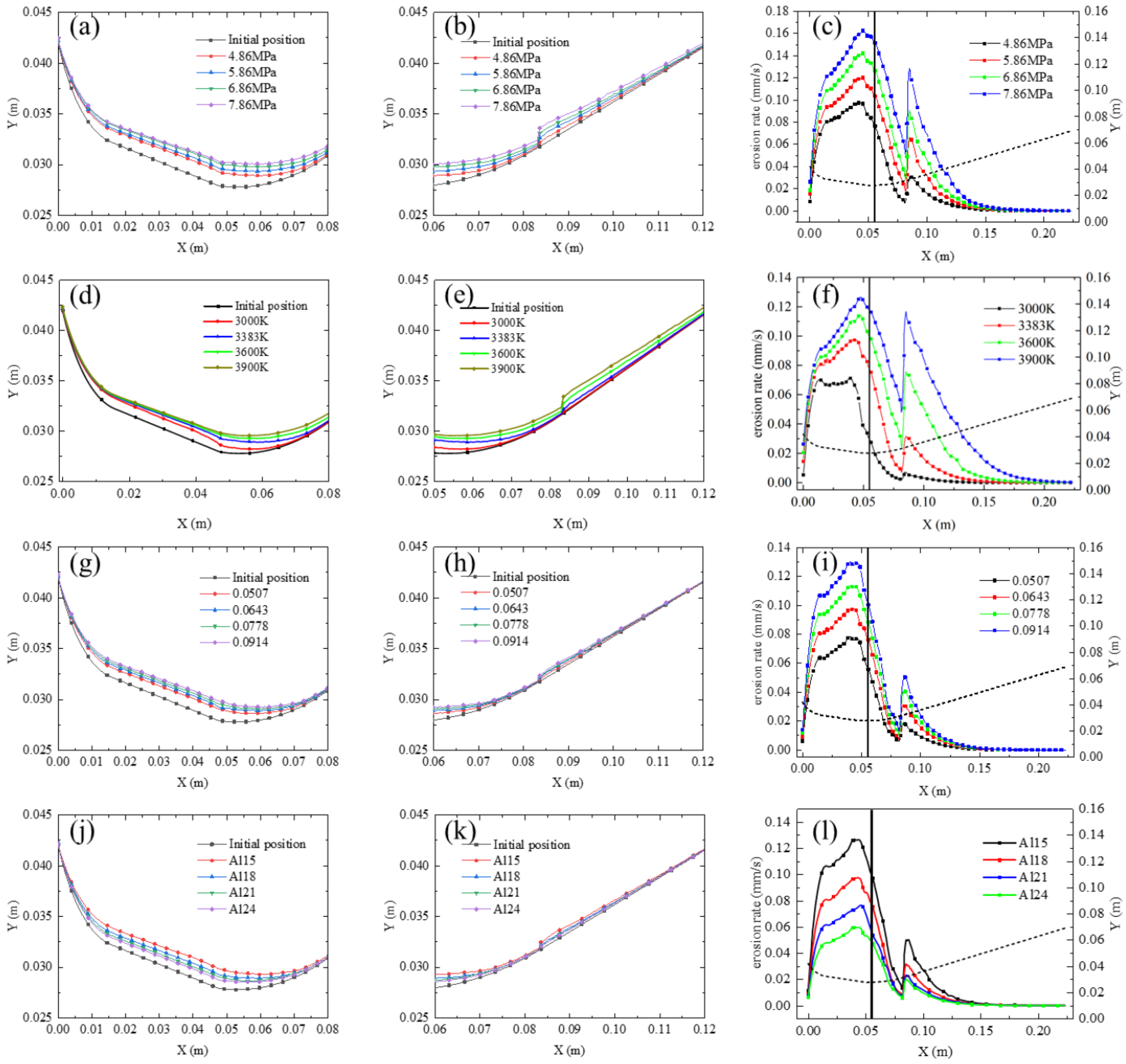
4.2. Determination of Influencing Factors and Working Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Ma, D.; Yang, B.; Qiu, C. Preliminary experimental study on combustion characteristics in a solid engine nozzle based on the TDLAS system. Energy 2023, 268, 126741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y. Effect of CNT content and size on the high-temperature particle-erosion resistance of ablative materials for thermal protection systems. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 235, 109969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Yu, K.; Yang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D. B2O3-reinforced ablative materials with superior and comprehensive ablation resistance used in aerospace propulsion TPSs. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 223, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keswani, S.; Kuo, K. An aerothermochemical model of carbon-carbon composite nozzle recession. In Proceedings of the 24th Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 2–4 May 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Natali, M.; Torre, L.; Puri, I.; Rallini, M. Thermal degradation of phenolics and their carbon fiber derived composites: A feasible protocol to assess the heat capacity as a function of temperature through the use of common DSC and TGA analysis. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 195, 109793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Zha, B.; Wang, J.; Yan, M.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Huang, W. Simulation and application of a new multiphase flow ablation test system for thermal protection materials based on liquid rocket engine. Aerospace 2022, 9, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, D.; Battista, F.; Gallo, G.; Mungiguerra, S.; Savino, R. Experimental firing test campaign and nozzle heat transfer reconstruction in a 200 N hybrid rocket engine with different paraffin-based fuel grain lengths. Aerospace 2023, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Liang, J. A model for thermal protection ablative material with local thermal non-equilibrium and thermal radiation mechanisms. Acta Astronaut. 2021, 183, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Tian, H.; Tan, G.; Zhao, S.; Cai, G. Experiments of ablation characteristics for different nozzle materials and transient simulations on thermochemical erosion in hybrid rocket motors. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 212, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; He, L.; Yu, R.; Zhao, S.; Wang, P.; Cai, G.; Zhang, Y. Transient investigation of nozzle erosion in a long-time working hybrid rocket motor. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 106978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Tian, H.; Niu, X.; Zhu, H.; Gao, J.; Cai, G. Long-duration dynamic numerical simulation of combustion and flow in hybrid rocket motors considering nozzle erosion. Aerospace 2024, 11, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciti, D.; Vinci, A.; Zoli, L.; Galizia, P.; Failla, S.; Mungiguerra, S.; Di Martino, G.D.; Cecere, A.; Savino, R. Propulsion tests on ultra-high-temperature ceramic matrix composites for reusable rocket nozzles. J. Adv. Ceram. 2023, 12, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungiguerra, S.; Di Martino, G.D.; Savino, R.; Zoli, L.; Silvestroni, L.; Sciti, D. Characterization of novel ceramic composites for rocket nozzles in high-temperature harsh environments. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 163, 120492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.T. Analysis of Ablation Step Phenomenon and Its Influence on the Performance of Nozzle. Aero Weapon. 2015, 287, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Jiang, X.; Yu, R.; Meng, X.; Niu, X.; Cai, G. Research on thermochemical erosion and thermal protection properties of multiple interface nozzles in long-time working hybrid rocket motors. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 204, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, D. Effect of operation pressure on heat release characteristics in solid rocket motor nozzle considering detailed chemical reaction mechanism. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 107794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashkovskiy, S.; Yakush, S. Numerical simulation of low-melting temperature solid fuel regression in hybrid rocket engines. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 176, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C.S.; Li, Y. Measurement of erosion morphology in a composite structure nozzle and its influence on flow field. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2015, 36, 2958–2967. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, X.; Wang, K.; Ma, G. Intentional mistuning blade dry friction model for vibration localization of the bladed disk. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 208, 112864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.E.; Burke, M.P. The discovery of non-equilibrium kinetic sequences important to ammonia/co-fuel and propellant flames. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2024, 40, 105265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Yan, Y.; Cao, T.; Li, W.; Zhang, H. Numerical prediction of the two-phase flow and radiation effects on the thermal environment and ablation of solid rocket nozzle. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2024, 197, 108794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Z.; Tian, W. Study on the Influence of Nozzle Ablation on the Performance of the Solid Rocket Motor. Aerospace 2023, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhang, W.; Yue, S.; Qiao, H.; Liu, P.; Ao, W. Mg content and AP size on the microscale flame structure of Mg-based propellant. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 150, 109213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovina, E. The gasification of carbon by carbon dioxide at high temperatures and pressures. Carbon 1980, 18, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, R.; Kuo, K.K. Effect of pressure and propellant composition on graphite rocket nozzle erosion rate. J. Propul. Power 2007, 23, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y. ZrO2-reinforced polymer-matrix composites used for thermal protection systems of ultra-high temperature aerospace propulsion. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 145, 108906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Bai, H.; Wang, Y. Excellent ablation resistance of silicone insulations reinforced with three carbon-based nano-fillers under oxygen-enriched environment. Acta Astronaut. 2025, 229, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Li, J.; Wan, L.Q.; Wang, L.; Li, K. A lightweight rubber foaming insulation reinforced by carbon nanotubes and carbon fibers for solid rocket motors. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 208, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, J.; He, Z.; Xu, Q.; Cheng, S. Study on the collision characteristics between high-temperature alumina droplets and char layer. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 225, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.A.; Blake, T.R. Theoretical Study of Burning Carbon Particles. Combust. Flame 1979, 36, 139–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, G.; Hui, S.; Liu, P. Investigation of the effects of alumina particle phase transition on internal flow field and engine performance in solid rocket motors. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 123314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.G.; Wang, C.H.; Liu, Y.; Ren, J. Coupled fluid, thermal and structural analysis of nozzle inserts in solid rocket motors. J. Solid Rocket Technol. 2011, 34, 579–583. [Google Scholar]
- Liggett, N.; Menon, S. Simulation of Nozzle Erosion Process in a Solid Propellant Rocket Motor. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z. Characterization of the nozzle ablation rate based on 3D laser scanning system. Aerospace 2023, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Lu, C.; Yu, R.; Tian, H. Numerical simulation of chemical ablation and mechanical erosion in hybrid rocket nozzle. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 192, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, D.; Nasuti, F. Thermochemical Erosion Analysis of Carbon-Carbon Nozzles in Solid-Propellant Rocket Motors. In Proceedings of the 46th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Nashville, TN, USA, 25–28 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.G.; Wang, C.H.; Liu, Y.; Ren, J. Carbon-Based Nozzle Thermochemical Erosion Characteristics in Solid Rocket Motors. J. Propuls. Technol. 2012, 33, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.P.; Zhan, H.J.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Hou, X. Fluid-Solid Coupling Simulation of Ablation Wall Recession of C/C Composite Nozzle. J. Propuls. Technol. 2022, 43, 200786. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Sun, Z.H. Ablation simulation of carbon/carbon three-dimensional nozzle based on dynamic mesh technique. J. Donghua Univ. 2022, 48, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.Q.; He, H.Q.; Mao, G.W. Calculation of ablative ‘step effect’ in nozzle divergent section. J. Propuls. Technol. 1990, 6, 19–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, T.T.; Sun, Z.H. Numerical Simulation on Heat Transfer and Ablation for the Nozzle of a Solid Rocket Motor. J. Proj. 2022, 42, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, D.; Turchi, A.; Nasuti, F. Numerical Analysis of Nozzle Flows with Finite-Rate Surface Ablation and Pyrolysis-Gas Injection. In Proceedings of the 47th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, San Diego, CA, USA, 31 July–3 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, P.; Yu, K.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J.; Zhu, D. Hollow microsphere-reinforced ablative materials for thermal protection systems of solid rocket motors. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 221, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, S.; Li, H.; Song, T.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L. Epoxidized vinyl silicone rubber-based flexible ablative material with low linear ablation rate. Compos. Commun. 2023, 40, 101606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, R.; Beckman, C. The History of the BATES motors at the Air Force Rocket Propulsion Laboratory. In Proceedings of the 34th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Cleveland, OH, USA, 13–15 July 1998; p. 3981. [Google Scholar]
- Klager, K. The Interaction of the Efflux of Solid Propellants with Nozzle Materials. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1977, 2, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.Y.; Xia, Z.X.; Jiang, C.L. Engineering Calculation of C/C Throat Insert Ablation. J. Solid Rocket Technol. 2000, 2, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Ren, J. New discrimination method for ablative control mechanism in solid-propellant rocket nozzle. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakre, P.; Yang, V. Chemical Erosion of Carbon-Carbon/ Graphite Nozzles in Solid-Propellant Rocket Motors. J. Propuls. Power 2008, 24, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, J.; Zhang, C.; Yan, H.; Feng, X.; Zhu, G. Factors Influencing Step Ablation in the Expansion Section of a Composite Nozzle in a Solid Rocket Motor. Aerospace 2025, 12, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060499
Cheng J, Zhang C, Yan H, Feng X, Zhu G. Factors Influencing Step Ablation in the Expansion Section of a Composite Nozzle in a Solid Rocket Motor. Aerospace. 2025; 12(6):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060499
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Jiming, Chunyu Zhang, Hang Yan, Xiping Feng, and Guoqiang Zhu. 2025. "Factors Influencing Step Ablation in the Expansion Section of a Composite Nozzle in a Solid Rocket Motor" Aerospace 12, no. 6: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060499
APA StyleCheng, J., Zhang, C., Yan, H., Feng, X., & Zhu, G. (2025). Factors Influencing Step Ablation in the Expansion Section of a Composite Nozzle in a Solid Rocket Motor. Aerospace, 12(6), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060499





