Abstract
The thermal decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a promising green propellant was performed over free-noble metallic-based catalysts deposited on abundant supports. A 30% (w/w) H2O2 liquid was decomposed over 1 wt.% of copper-based catalysts deposited on three different supports: γ-alumina, graphite and monocrystal clay. In this research work, the catalytic performance of the thermal decomposition of H2O2 was carried out by measuring the differential pressure (ΔP) versus time at initial constant temperatures and, for the first time, by the DTA-TG technique and by the DIP-MS technique at atmospheric pressure. The obtained preliminary results showed that copper deposited on alumina and on graphite are promising catalysts for the decomposition of the H2O2 liquid propellant. Moreover, the natural clay can be valorized on the thermal decomposition of H2O2 due to its high resistivity and high surface area. The N2-physisorption technique and scanning electron microscopy technique were used to characterize the effect of the texture properties on the decomposition and to understand the morphological characteristics of the catalyst.
1. Introduction
Hydrazine and its derivatives, namely, Unsymmetrical DiMethyl Hydrazine (UDMH) and Monomethylhydrazine (MMH) have long been utilized as conventional propellants in various aerospace applications due to their high energy density and relatively simple combustion characteristics [1,2]. However, their use comes with several inherent disadvantages, ranging from toxicity and handling hazards to environmental concerns [3,4]. As the world increasingly focuses on sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions, there is a growing interest in exploring greener alternative propellants that offer comparable performance while mitigating the drawbacks associated with hydrazine and its derivatives [5,6,7,8] such as hydroxylammonium nitrate (HAN) [9,10,11,12], ammonium dinitramide (ADN) [13,14] and hydrazinium nitrate (HNF) [15]. These alternatives offer several potential advantages: (i) Reduced toxicity: green monopropellants are designed to be less toxic than hydrazine, thereby reducing health risks to personnel involved in handling and operation [16,17]. (ii) Environmental friendliness: green monopropellants produce combustion products that are less harmful to the environment compared to hydrazine, contributing to reduced air and water pollution. (iii) Compatibility: some green monopropellants exhibit compatibility with a wider range of materials, reducing corrosion concerns and simplifying system design and maintenance. (iv) Stability: green monopropellants can offer improved stability compared to hydrazine, reducing the need for stabilizers and enhancing safety during storage and handling. (v) Cost-effectiveness: while initial development costs may be higher, green monopropellants have the potential for long-term cost savings due to reduced safety measures, disposal costs, and regulatory compliance requirements associated with hazardous materials such as hydrazine [18].
In this context and to evaluate the efficiency of various catalytic agents including ZnO, CuO, MgO, CaO, and MnO2 oxides [19], we compared their performance against a commercial catalyst comprising 5% palladium (Pd) supported on alumina pellets, sourced from Alfa Aesar. These industrial-grade, cylinder-shaped Al2O3-based pellets have a specific surface area of approximately 1.1 m2/kg [19]. For the catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), MnO2-based catalysts were utilized. A Pd/Al2O3 catalyst served as a promoter to enhance the reactivity of MnO2. Additionally, bimodal 1/8-inch alumina pellets from Alfa Aesar (Ward Hill, MA, USA) were used as the catalytic substrate, with a Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area of about 255 m2/g. This catalyst demonstrated the ability to decompose up to 90 wt% of H2O2 [19]. In a separate preparation process, cobalt nitrate, manganese nitrate, and urea were mixed with a minimal amount of distilled water under magnetic stirring within a stainless-steel reactor. The components were combined to achieve a cobalt-to-manganese molar ratio of 1:2. Two additional sets of samples with 1:1 and 2:1 ratios were also prepared. These catalysts were then applied in the decomposition of 30 wt% H2O2 [20]. For the decomposition of 98% H2O2, two catalysts were used. The first was a commercial platinum (Pt)-based catalyst, with 5 wt% Pt supported on a γ-alumina carrier [21], a commonly available formulation. The second was a MnO2 catalyst supported on silica-doped α-alumina, developed by the Łukasiewicz Institute of Aviation, with details provided in references [21,22,23]. MnO2 is a particularly effective catalyst for H2O2 decomposition, capable of breaking down 90% of the compound [24], and was therefore selected for this study, following the preparation method described by An et al. [25]. Two catalysts named MnOx/γ-Al2O3 and MnOx supported on lanthanum-doped alumina (MnOx/La-Al2O3) were tested to achieve 95 wt% H2O2 decomposition. This comparison aimed to provide deeper insights into catalyst bed design. Notably, the MnOx/La-Al2O3 catalyst exhibited nearly 57.7% higher mechanical strength than the MnOx/γ-Al2O3 variant in bulk crushing tests. The inclusion of lanthanum improved the mechanical stability of the alumina pellets, suggesting that MnOx/La-Al2O3 could help maintain consistent pellet distribution within the catalyst bed during high-temperature fire testing [26].
In this paper, the thermal decomposition of low-concentrated H2O2 was performed using three different methods: the technique of effective activation energy tests, the differential thermal analysis–thermogravimetry (DTA-TG) technique, and the direct insertion probe–mass spectrometry (DIP-MS) technique. Furthermore, a comparative study was conducted in terms of catalytic activities and the effect of catalyst support. In fact, we used 30 wt.% H2O2 because we are evaluating the catalytic activity on a lab scale. For safety reasons, we used diluted HP to determine which catalyst/support was suitable before progressing to high-concentration HP, such as 90%. Moreover, the aim was to evaluate the catalytic activity using low-concentrated HP in order to select the most suitable binary catalyst/support system on a lab scale. Once this selection is made, pilot-scale experiments will be initiated using a shaped copper-based catalyst using the same materials for the decomposition of highly concentrated HP. This lab-scale screening approach helps reduce costs and aligns with the paper’s objective: developing a low-cost catalyst for HP decomposition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Catalyst Preparation and Catalyst Characterization
The copper-based catalysts were prepared by the impregnation technique with an excess of water as solvent. In fact, alumina, graphite, and monocrystal clay (denoted as MNC) were used as catalyst supports and copper as the active phase. Powdered alumina and graphite with high specific surface areas (SBET) were used as catalyst carriers. MNC clay is a naturally occurring clay mineral that has attracted considerable interest in the area of catalysis owing to its unusual features. It is a member of the smectite group of phyllosilicates, which also includes montmorillonite, saponite, beidellite, nontronite, and hectorite, among others. Bentonite’s layered structure is composed of two tetrahedral sheets of silica and one octahedral sheet of alumina. This unusual structure, along with bentonite’s wide availability, large surface area, and mechanical and chemical resilience, makes it a very desirable and inexpensive catalyst support [27].
Cu(NO3)·2H2O (purity 98%, Sigma-Aldrich) was the precursor used. The determined quantity of precursor was deposited independently in three separate beakers for each support, and water was used as a solvent to dissolve it in order to achieve the desired mass percent of deposited metals, which was set at 1 weight percent of the support. To guarantee adequate metal impregnation into the support’s porous surfaces, the samples were gently mixed for approximately 24 h after maturation. The samples were then placed in a sand bath that had been preheated to 80 °C (fixed and monitored by a thermometer) until all of the water had evaporated. After that, the impregnated samples were calcined in air at 500 °C using a muffle furnace with a temperature ramp of 5 °C per minute. The finished catalysts contained one weight percent copper on each of the following materials: clay, graphite, and alumina. It should be mentioned that this study aimed to investigate the role of different catalyst supports, namely, alumina, graphite, and MNC clay, in influencing the distribution and dispersion of impregnated copper (Cu) metal on their surfaces. By comparing the surface area, morphology, and physicochemical characteristics of each support, we sought to understand how these properties affected Cu metal deposition. The resulting Cu-based catalysts were then evaluated to compare their catalytic activity, highlighting the impact of the support material on overall performance.
We could then characterize the Cu/γ-alumina catalyst by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) coupled to energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) physisorption technique.
2.2. Thermal Decomposition
2.2.1. Effective Activation Energy Tests
As previously reported by J. C. Claussen et al. [28], the effective activation energy approach was used to investigate the thermal degradation of the H2O2 green monopropellant. Three distinct catalysts—copper supported on γ-alumina, graphite, and MNC clay—were used in a series of experiments. To ensure that the results could be replicated, each catalyst was put through several tests. Two 100 mL round glass flasks made up the experimental setup, as shown in Figure 1.
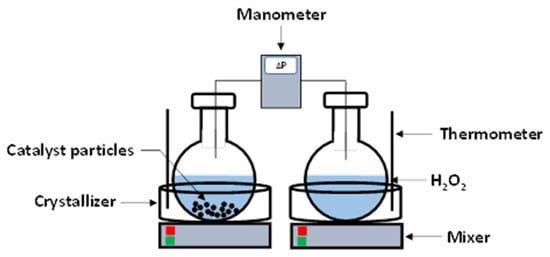
Figure 1.
Measurement of differential pressure at different initial temperatures (0 and 36 °C) using Extech HD750 (Nashua, NH, USA) differential pressure manometer [18]. Reprinted with permission from Begell House Publisher.
2.2.2. Differential Thermal Analysis–Thermogravimetric Analysis
Conversely, a LABSYS evo-gasorption apparatus (Category: DTA/TG/DSC, Model: Setaram Instrumentation) was used to perform differential thermal analysis–thermogravimetry (DTA–TG) measurements in order to investigate the thermal breakdown of H2O2 at constant atmospheric pressure (p = 1 atm). A syringe was used to inject a 30% (w/w) H2O2 microdroplet into the metallic sample cell. It was investigated how the three different catalysts affected the H2O2 thermogram. A microdroplet of liquid H2O2 was combined with a modest amount (a few micrograms) of powdered catalyst in the aluminum sample cell for each thermal study.
Before each run, the following experimental conditions were maintained:
- (i)
- Carrier gas: argon, with a flow rate of 50 mL·min−1;
- (ii)
- Heating rate: 10 °C·min−1, from room temperature up to 250 °C;
- (iii)
- The H2O2 droplet was added directly to the catalyst particles already placed in the aluminum cell.
After sealing the apparatus, a stabilization period of approximately 2 min was allowed for the system (carrier gas and sample) to equilibrate. The thermal run was then initiated to record the DTA–TG thermograms.
2.2.3. Direct Insertion Probe–Mass Spectrometry
The DIP-MS L-250G-I A system, manufactured by Canon Anelva Co., Ltd. (Kawasaki, Japan) [29], was employed for the detailed analysis and advanced thermal characterization of the H2O2 samples, specifically targeting the mass composition of hydrogen peroxide and water. In this technique, the sample is introduced into the ionization chamber, where it undergoes vaporization and subsequent ionization via electron impact.
Recognized as one of the fastest systems for the real-time identification of gaseous products during thermal decomposition, the DIP-MS instrument enables temperature ramping from 40 °C to 300 °C at a high heating rate of approximately 64 °C·min−1. This innovative method represents a novel approach, particularly within the context of H2O2-based propellants.
The probe temperature program was devised to ascend from room temperature to 300 °C at a brisk temperature ramp of 64 °C/min. Throughout the analyses, an ionization voltage of 70 eV was applied, while maintaining a source temperature of 250 °C. The examination spanned a mass range from m/z = 17 to 50, with scans conducted at a rate of 2 scans/s. To ensure optimal quality, a vacuum level exceeding 7 × 10−5 mbar was meticulously upheld. In this study, the DIP-MS technique was highly valuable for studying the thermal decomposition of low concentrated HP solution using Cu-based catalysts. It enables the real-time monitoring of volatile decomposition products with high sensitivity, providing insight into the reaction pathway. DIP-MS helps identify intermediate and final gaseous species, shedding light on the role of Cu-based catalysts in promoting or altering specific steps. This aids in understanding the catalytic mechanism, including oxidation states and surface interactions. Additionally, the rapid analysis allows for the assessment of catalyst performance under various conditions, contributing to the optimization of propulsion systems.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Decomposition
3.1.1. Effective Activation Energy Tests
Three copper-based catalysts supported on γ-alumina, graphite, and MNC clay were used to study the thermal breakdown of the H2O2 liquid propellant. Effective activation energy analysis, DTA-TG online analysis, and DIP-MS real-time analysis were the three different analytical techniques used. In the first approach, three distinct constant temperatures were used to track the difference in pressure over time. The temperature change over time at atmospheric pressure was measured using the second approach. The third method used a high temperature ramp of 64 °C min−1 to analyze the gas products generated during thermal breakdown in real time.
During the thermal breakdown of 30% w/w H2O2 liquid monopropellant, the evaluated catalysts’ differential pressure (ΔP in kPa) was observed. According to the equation in [28], the differential pressure readings correlate to the amount of oxygen gas emitted during the breakdown reaction:
2 H2O2(liq) → O2(g) + 2 H2O(liq)
Every experiment was conducted at two different temperatures: 0 °C and 36 °C.
It is evident from Figure 2a,b that the presence of copper powdered metallic particles deposited on the three supports initiated the thermal breakdown of H2O2 liquid. In fact, the decomposition of H2O2 liquid propellant over a period of approximately 20 min was caused by a significant number of active sites found in the metallic particles, as evidenced by the significant differential pressures P (kPa) versus time (min) that were recorded. In this context, for the Cu/MNC catalyst at 0 °C (Figure 2b), the copper catalytic particles were embedded within the pores of MNC bentonite. The initial interaction, occurring around 6 min, allowed the H2O2 solution to penetrate the pores and begin reacting with the catalytic particles. This reaction was evidenced by the increase in ΔP starting from 6 min. In contrast to the Cu/alumina and Cu/graphite catalysts, where the catalytic particles were deposited on the surface, the reaction with cold H2O2 began immediately upon contact due to the direct exposure of the active sites.
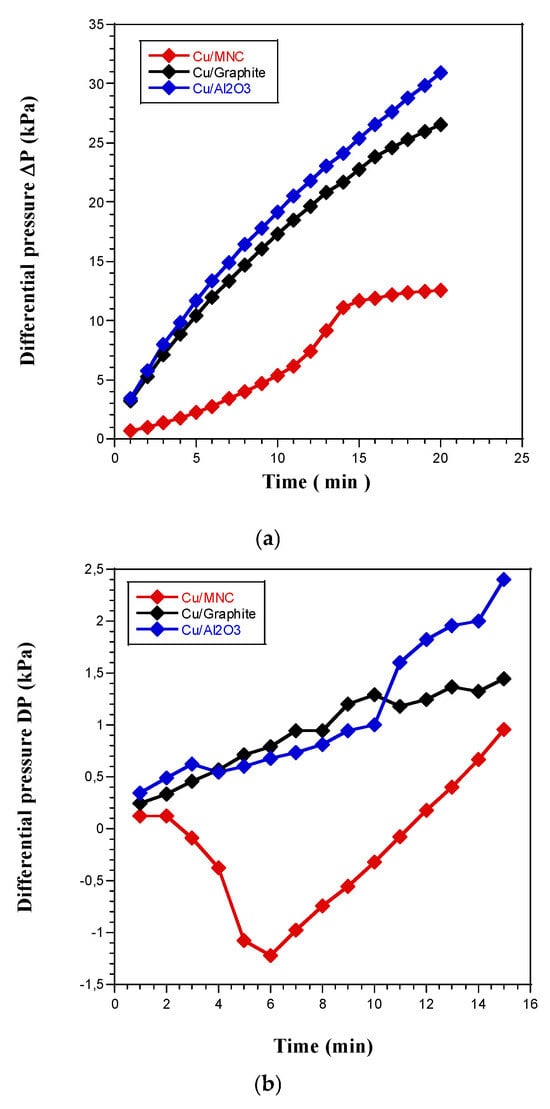
Figure 2.
In the presence of copper-based catalysts, the differential pressure versus time of the thermal breakdown of H2O2 liquid droplets was measured (a) at 36 °C and (b) at 0 °C.
The rate of H2O2 liquid decomposition can be observed converting generated moles of oxygen released to moles of H2O2 via the reaction stoichiometry, 2 moles of H2O2 consumed for every 1 mole of oxygen. The kinetics of H2O2 over the metallic particles can be described by the following first-order rate equation [28,30].
where K represents an apparent kinetic constant and ‘t’ is time. It also means the absolute value of the slope of the graph of the natural logarithm of H2O2 concentration versus time of Cu/alumina, Cu/graphite, and Cu/MNC clay catalysts.
Figure 3 shows that negative linear slopes were obtained at both temperatures: 36 and 0 °C. However, positive allure can be subsequently observed in the case of γ-alumina at 0 °C (Figure 3b). These findings can be attributed to the differing mechanisms of HP decomposition observed at 36 and 0 °C. Factors such as thermal conductivity, the extent of contact between hydrogen peroxide and the catalytic particles, and support effects undoubtedly have a significant influence on decomposition behavior. These variations contribute to the observed differences in the slopes of Ln[H2O2]t over time.
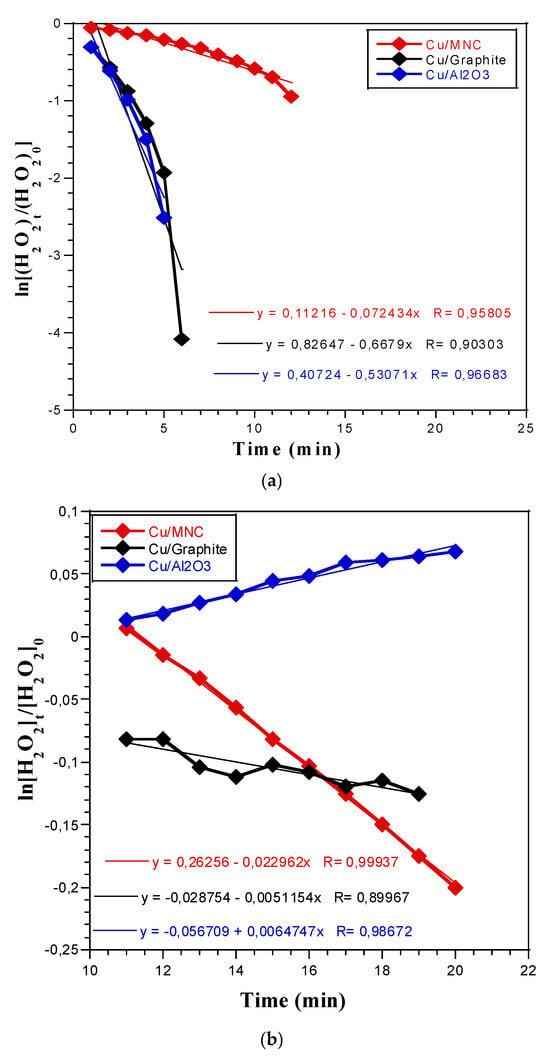
Figure 3.
Reaction rate plots calculated according to the first-order rate equation: (a) at 36 °C and (b) at 0 °C.
3.1.2. DTA-TG Analysis
Subsequently, DTA-TG analysis was performed and is represented in Figure 4.
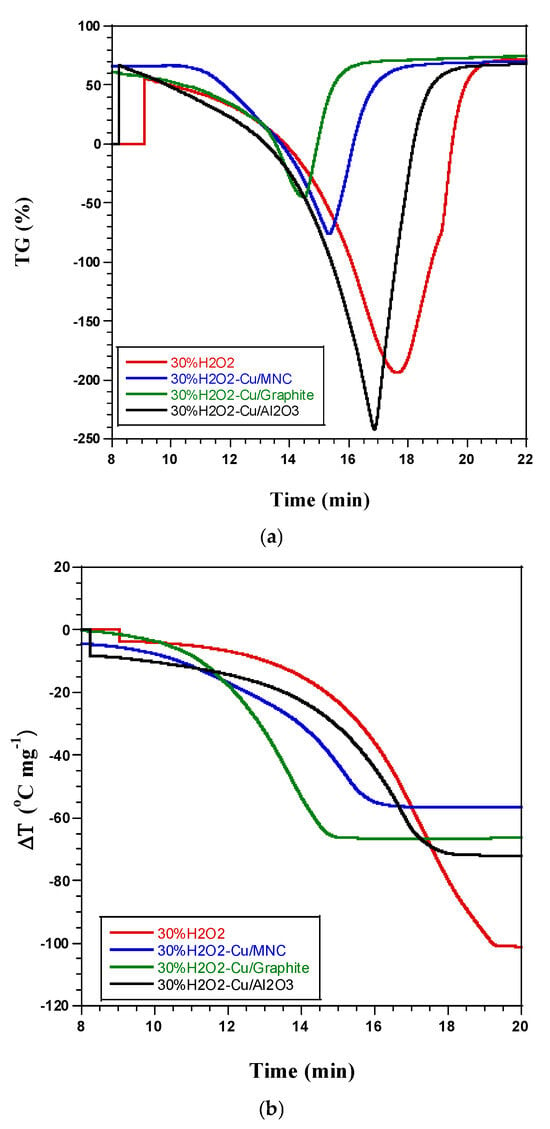
Figure 4.
Comparative data of DTA and TG thermograms of the thermal decomposition of 30% (w/w) H2O2 alone (without catalyst) and over copper-based catalysts: (a) TG versus time and (b) DTA versus time.
The HP solution used in our study was low-concentrated, consisting of approximately 70% water. Since water evaporation is an endothermic process, the catalytic effect was observed through a reduction in the intensity of the large endothermic peak and a noticeable acceleration in the evaporation duration. The increased rate at which HP decomposition takes place, that is, the reaction is proceeding more quickly than it was previously, is referred to as the acceleration of the reaction velocities. A number of variables, including temperature, pressure, and the presence of catalysts, can be responsible for this acceleration; thermal energy, or heat, and potentially catalysis are important in accelerating the process. Since endothermic reactions need heat to break bonds and start the reaction, thermal endothermic behaviors explain how the reaction absorbs heat from its surroundings during decomposition. The terms “narrowness” and “sharpness” are used to describe the reaction profile (Figure 4a). “Narrowness” implies that the energy absorption takes place within a very specific temperature range, indicating a concentrated and brief thermal behavior, while “sharpness” indicates a steep or quick onset of energy absorption, suggesting a sudden, rapid change in temperature or reaction rate. The sharp and narrow thermal profile, which indicates a more confined thermal window and greater sensitivity to temperature changes, shows that the decomposition reaction is therefore faster and more efficient. The reaction is tracked by mass losses over time, which are frequently depicted by a graph showing the mass loss of the material during decomposition. The release of gases or byproducts causes the substance to lose mass during decomposition; tracking this mass loss over time allows one to determine the rate and completeness of the reaction. Mass loss that happens faster or in less time lends credence to the notion that the decomposition is proceeding more quickly, which is consistent with the reaction velocities’ apparent acceleration (Figure 4b). Since catalysts accelerate reactions without being consumed, some catalytic particles usually remain in the Al-cell after the reaction. This implies that some catalytic particles are still active and may continue to affect subsequent reactions or the end products. Nevertheless, a tiny quantity of catalytic particles was released during the breakdown; these were probably lost because of the quick decomposition process or carried away with the gaseous byproducts. This could suggest that some catalysts were ejected due to the speed or intensity of the reaction, which could reduce efficiency if too many catalytic particles are lost. The term “quickness of thermal decomposition” suggests that the compound breaks down quickly, most likely as a result of higher temperatures or increased catalytic activity. This rapid rate may account for the observed loss of catalytic particles because the system may have been overloaded, causing some catalysts to be expelled along with the byproducts.
Based on this comparative analysis, we can conclude that the inclusion of copper particles deposited on three distinct supports can speed up the thermal breakdown of a droplet of 30% (w/w) H2O2 liquid monopropellant.
3.1.3. DIP-MS Analysis
To examine the behavior of its process, the DIP-MS technique was used to accomplish the thermal decomposition of a 30% H2O2 solution.
Figure 5a,b depict the decomposition of H2O2 both in isolation and in the presence of a Cu/γ-alumina catalyst, respectively, under a high temperature ramp of 64 °C/min. Throughout the experiment, the real-time analysis of the process revealed a significant release of gas species, particularly vapor steam, exhibiting higher intensity attributed to water evaporation from the solution, which serves as the primary product of thermal decomposition. Notably, due to the non-homogeneous nature of the decomposition process, it was observed that thermal decomposition proceeded in three distinct steps in both cases, with and without the catalyst. Additionally, the detection of oxygen and the remaining unreacted H2O2 was carried out during the experiment.
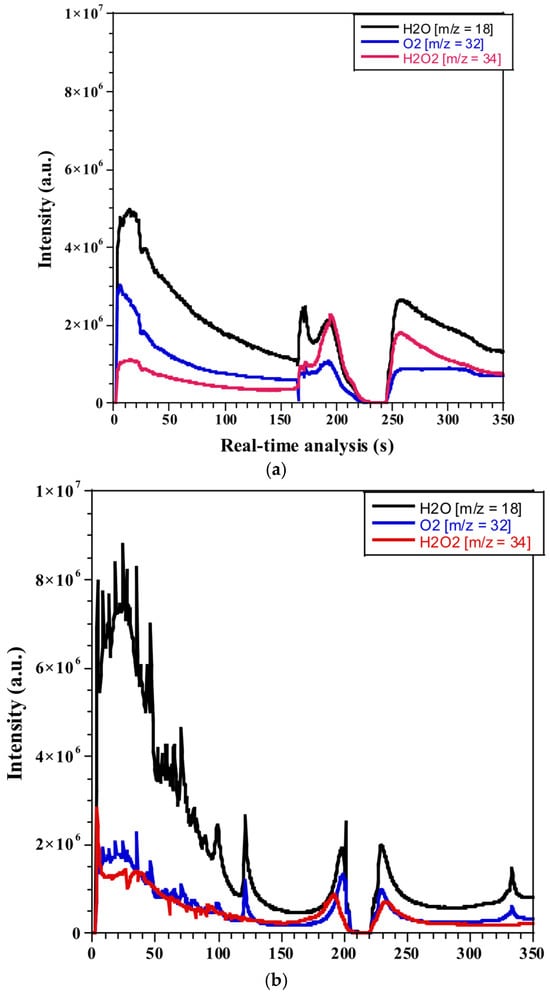
Figure 5.
Real-time analysis of the thermal decomposition of 30% H2O2 via the DIP-MS technique: (a) without a catalyst and (b) over a Cu/γ-alumina catalyst.
3.2. Catalytic Characterization
The Cu/γ-alumina catalyst was selected to be characterized by the SEM technique coupled with EDS surface analysis. Indeed, the characterization before and after testing using SEM allowed us to determine which support can withstand high temperatures when using the same catalysts under propulsion conditions.
The SEM micrograph and its corresponding EDS spectrum are presented in Figure 6.
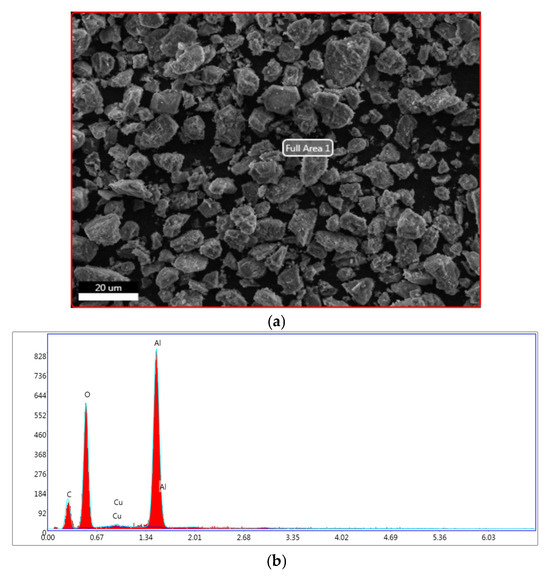
Figure 6.
(a) SEM micrograph and (b) EDS spectrum of Cu/γ-alumina catalyst.
The majority of the metallic particles were integrated into the porous structure of alumina, and they were evenly distributed across the alumina surface. The identification of a faint distinctive peak of copper metal (EDS spectrum) provides an explanation for this consideration.
N2-physisorption by the BET technique was performed to determine the specific surface area and the porous volume of fresh γ-alumina and the Cu/γ-alumina catalyst. The obtained data are illustrated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Textural properties of γ-alumina and Cu/γ-alumina catalyst.
The obtained data indicated that the surface area and pore volume of γ-alumina are notably high, ensuring efficient distribution and strong interaction between the support and the metallic copper active phase. The incorporation of metallic copper particles onto the support surface resulted in a slight decrease in both parameters. This minor reduction in surface area and pore volume can be attributed to the partial filling of the pores by the metal. The small change is consistent with the relatively low mass percent of copper deposited on the γ-alumina.
The next phase of this project focuses on activating natural clay to increase the number of active sites and its porosity. This activation process aims to ensure the optimal accessibility of the metal to the solid surface of the material, thereby influencing the thermal decomposition of H2O2, even at the propulsion level (high-concentration H2O2). The approach utilizes low-cost catalysts supported by abundant materials and inexpensive metals, such as copper or copper oxide. In addition, the development of test low-cost catalysts based on copper deposited onto various support materials will be performed. These catalysts will be engineered into different shapes, grain sizes, and forms to enable their integration into high-concentrated HP thruster systems for propulsion applications.
4. Conclusions
The catalytic performance in the decomposition of low-concentrated HP (H2O2, 30% (w/w)) was demonstrated by copper in its metallic state, deposited onto γ-alumina, graphite, and CMN clay supports using the impregnation method. Three experimental techniques were employed in this study: (i) effective activation energy tests, (ii) DTA-TG thermal analysis, and (iii) DIP-MS analysis. These experiments revealed that metallic copper is a promising active phase for the thermal decomposition of H2O2 monopropellant at high temperatures, specifically around 0 °C and 36 °C. Furthermore, the incorporation of metallic copper particles onto alumina was achieved homogeneously, as confirmed by SEM micrographs, and the textural properties of the support were only slightly affected by the copper deposition. Moreover, this study provides strong evidence that copper in its metallic form is an effective catalyst for the thermal decomposition of H2O2, making it a promising candidate for monopropellant applications. The deposition of copper onto various supports, particularly γ-alumina, enhances catalytic activity without significantly altering the support’s structural properties. The results from the thermal analysis and activation energy tests suggest that copper’s catalytic efficiency is maintained across the studied temperature range, offering potential for use in practical applications involving high-temperature conditions. Further investigations into the long-term stability and performance of copper-supported catalysts could provide additional insights into optimizing their effectiveness for monopropellant decomposition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.R., A.M. and A.B.; methodology, R.A.; resources, I.R. and R.A.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A.; writing—review and editing, R.A., A.T. and A.E.S.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Marshall, W.M.; Deans, M.C. Recommended figures of merit for green monopropellants. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 14–17 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Final Report Summary-GRASP (Green Advanced Space Propulsion); CORDIS EU Research Results, 18 January 2013. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/218819/reporting (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Gotzig, U. Challenges and Economic Benefits of Green Propellants for Satellite Propulsion. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference for Aeronautics and Space Sciences (EUCASS), Milan, Italy, 3–6 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.L.; Law, C.K. Aerothermochemical studies of energetic liquid materials: 1. Combustion of HAN-based liquid gun propellants under atmospheric pressure. Combust. Flame 1987, 70, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remissa, I.; Jabri, H.; Hairch, Y.; Toshtay, K.; Atamanov, M.; Azat, S.; Amrousse, R. Propulsion Systems, Propellants, Green Propulsion Subsystems and their Applications: A Review. Eurasian Chem. J. 2023, 25, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosseir, A.E.S.; Cervone, A.; Pasini, A. Review of State-of-the-Art Green Monopropellants: For Propulsion Systems Analysts and Designers. Aerospace 2021, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.S.; Cheah, K.H.; Wu, M.-H.; Koh, K.S.; Sun, D.; Meng, H. A Review on Hydroxylammonium Nitrate (HAN) Decomposition Techniques for Propulsion Application. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 196, 194–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez Valles, L.; Blondel Canepari, L.; Apel, U.; Tajmar, M.; Pasini, A. Challenges and Opportunities of Green Propellants and Electric Pump Feeding for Future European Kick Stages. Aerotec. Missili Spaz. 2022, 101, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrousse, R.; Katsumi, T.; Itouyama, N.; Azuma, N.; Kagawa, H.; Hatai, K.; Ikeda, H. New HAN-based Mixtures for Reaction Control System and Low Toxic Spacecraft Propulsion Subsystem: Thermal Decomposition and Possible Thruster Applications. Combust. Flame. 2015, 162, 2686–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrousse, R.; Hori, K.; Fetimi, W.; Farhat, K. HAN and ADN as Liquid Ionic Mono- Propellants: Thermal and Catalytic Decomposition Processes. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 127, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasbi, Y.; Remissa, I.; Toshtay, K.; Mabrouk, A.; Bachar, A.; Azat, S.; Nosseir, A.E.S.; Tiwari, A.; Sabbar, E.M.; Amrousse, R. H2O2 and HAN Green Monopropellants—A State-of-the-Art Review on Their Recent Development, Corresponding Synthesized Catalysts, and Their Possible Use as Thrusters. Catalysts 2025, 15, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrousse, R.; Katsumi, T.; Azuma, N.; Hori, K. Hydroxylammonium Nitrate (HAN)-based Green Propellant as Alternative Energy Resource for Potential Hydrazine Substitution: From Lab Scale to Pilot Plant Scale-up. Combust. Flame 2017, 176, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. An Overview on Properties, Thermal Decomposition, and Combustion Behavior of ADN and ADN based Solid Propellants. Def. Technol. 2018, 14, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenmann, D.; Ciezki, H.K. ADN and HAN-based Monopropellants—A Minireview on Compatibility and Chemical Stability in Aqueous Media. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2019, 44, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadiot, G.M.H.J.L.; Mul, J.M.; Meulenbrugge, J.J.; Korting, P.A.O.G.; Schnorkh, A.J.; Schöyer, H.F.R. New Solid Propellants Based on Energetic Binders and HNF. Acta Astronaut. 1993, 29, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kwon, S. Preparation and Performance Evaluation of Platinum Barium Hexaaluminate Catalyst for Green Propellant Hydroxylamine Nitrate Thrusters. Materials 2021, 14, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansurov, Z.A.; Amrousse, R.; Hori, K.; Atamanov, M.K. Combustion/Decomposition Behavior of HAN under the Effects of Nanoporous Activated Carbon. In Innovative Energetic Materials: Properties, Combustion Performance and Application; Pang, W., DeLuca, L., Gromov, A., Cumming, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Amrousse, R.; Katsumi, T.; Azuma, N.; Hatai, K.; Ikeda, H.; Hori, K. Development of green propellants for future space applications. Sci. Technol. Energetic Mater. 2016, 77, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Cassese, S.; Monteverde, F.; Gallo, G.; Mungiguerra, S.; Cecere, A.; Saraga, F.; Savino, R. Compositionally complex catalytic oxide beds free of noble metals for H2O2 fuelled monopropellant thrusters. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 4854–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bispo, T.S.S.C.; Assunção, V.V.; Oliveira, L.R.; Alves, K.G.B.; Kulesza, J.; Barros, B.S. Synthesis and stoichiometric optimization of cobalt-manganese oxide nanocatalysts for decomposition of the green monopropellant H2O2. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 26635–26641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzybut, A.; Surmacz, P.; Gut, Z. Impact of hydrogen peroxide concentration on manganese oxide and platinum catalyst bedperformance. Aerospace 2023, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmacz, P.; Kostecki, M.; Gut, Z.; Olszyna, A. Aluminum Oxide–Supported manganese oxide catalyst for a 98% hydrogenperoxide thruster. J. Propuls. Power 2019, 35, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rarata, G.; Rokicka, K. The manganese oxides decomposition catalysts for highly concentrated hydrogen peroxide. Trans. Inst. Aviat. 2015, 240, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Kang, S.; Kwon, S. Preheating characteristics of H2O2 monopropellant thruster using manganese oxide catalyst. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2014, 41, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Jin, J.; Lee, J.; Jo, S.; Park, D.; Kwon, S. Chugging Instability of H2O2 Monopropellant Thrusters with Reactor Aspect Ratio and Pressures. J. Propul. Power 2011, 27, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Lee, D.; Kwon, S. Manganese oxide lanthanum-doped alumina catalyst for application in 95 wt.% hydrogen peroxide thruster. CEAS Space J. 2020, 13, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srasra, E.; Bekri-Abbes, I. Bentonite Clays for Therapeutic Purposes and Biomaterial Design. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 6, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claussen, J.C.; Daniele, M.A.; Geder, J.; Pruessner, M.; Makinen, A.J.; Melde, B.J.; Twigg, M.; Verbarg, J.M.; Medintz, I.L. Platinum-paper micromotors: An urchin-like nanohybrid catalyst for green monopropellant bubble-thrusters. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 17837–17847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harimech, Z.; Toshtay, K.; Atamanov, M.; Azat, S.; Amrousse, R. Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium Dinitramide (ADN) as Green Energy Source for Space Propulsion. Aerospace 2023, 10, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, D.W. Catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by metals and alloys of the platinum group. J. Catal. 1969, 14, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).