Abstract
Hydrogen peroxide is a promising oxidizer and monopropellant for space propulsion, offering a green alternative to conventional propellants. In combination with microencapsulated hydrocarbon fuels, a new type of monopropellant can be formed that unites the high specific impulse of a bipropellant with the efficient hardware of a monopropellant. However, the stabilization of these microcapsule/hydrogen peroxide mixtures is problematic as they tend to separate after a short period of time. This work uses organic gelling agents to stabilize these mixtures by creating hydrogen peroxide gels. For this, the compatibility of hydrogen peroxide with several gelling agents was investigated and found to be suitable. Next, the dispersion stability of microcapsule/gel dispersions was examined and showed no sign of destabilization over four weeks or at high accelerations at 50× g in the centrifuge, even with gelling agent concentrations as low as 0.1%. A formulation with a polyacrylic acid-based gelling agent at a concentration of 0.3% showed favorable characteristics and good processability. Together with a subsequent rheological characterization of the gels, these results are critical for the further development of the fuel-filled microcapsule/hydrogen peroxide monopropellant. The hydrogen peroxide gel formulations developed in this study could also have potential applications beyond the scope of this work.
1. Introduction
1.1. Hydrogen Peroxide and Hydrogen Peroxide Gels in Space Propulsion
Hydrogen peroxide is becoming an increasingly important propellant for space propulsion systems, especially in applications where environmental considerations are critical [1]. Compared to conventional storable oxidizers, hydrogen peroxide is non-toxic and easy to handle, and is considered a highly capable green oxidizer [2,3,4]. Highly concentrated hydrogen peroxide (>80%, high test peroxide, HTP) can be either used as a monopropellant, with its decomposition products being water vapor and oxygen, or as the liquid oxidizer component for a bipropellant in combination with a suitable fuel [4,5,6,7].
To enhance the characteristics of liquid propellants, a gelling agent can be added that forms a three-dimensional network, immobilizing the liquid phase. Gelled propellants, in general, have been known for some time and are of high interest for chemical propulsion systems since they are able to combine the advantages of liquid and solid propellants [8,9]. They can be throttled and restarted similarly to liquid propellants, but have the ease of handling and storage similar to solid propellants [8]. In a low shear state, gels show a semi-solid behavior and are less susceptible to leakage or spilling during storage [10]. This also allows for the suspension of solid particles, such as metal powders, which can increase density and energetic performance [8,11]. During loading or pumping through tubes, the gel is subjected to elevated shear rates (10−2 to 103 1/s), where shear-thinning behavior is essential to facilitate flow. Even higher shear rates are expected during the injection and atomization processes (up to 106 1/s), hereby the viscosity can decrease over several orders of magnitude [10]. The type of interaction responsible for the formation of the network can vary from chemical interactions, such as covalent bonding, to physical interactions, such as the entanglement of polymer strands. Gels are a type of non-Newtonian fluid and are typically characterized by rheological properties such as shear-thinning behavior and the presence of a yield point [12]. For fuels such as hydrocarbons, a variety of gelling agents, both organic and inorganic, are known [13,14]. Also, many conventional oxidizers, such as nitric acid and even liquid oxygen, can be gelled [15,16]. Typical challenges with gelled propellants are poor pumpability, difficult atomization, injector clogging, and generally lower burning rates compared with liquid fuels [10,17].
Hydrogen peroxide gels, in general, are moderately well studied; most of the literature focuses on low-concentration hydrogen peroxide for cosmetic and dental applications [18]. For gelled high-test peroxide (GHTP), there are only a few examples described in the literature. These include silica [19,20,21,22,23], sodium alginate in combination with calcium cations [24] and cellulose [25] as gelling agents. However, most of the described procedures require a gelling agent concentration higher than 5% to achieve successful gelation. In order to affect the rheological properties and combustion efficiency of the final mixture as little as possible, it would be beneficial to utilize a minimal amount of gelling agent. Ideally, the selected gelling agent should be an organic compound that can burn without residues, reducing the risk of clogging or particle deposition on external surfaces of the spacecraft [26].
1.2. Utilization of Gelled Hydrogen Peroxide with Microencapsulated Hydrocarbon Fuels
Current research efforts in our group concern the development of a new type of high-performance monopropellant. For this, hydrocarbon-filled microcapsules as fuel are mixed with hydrogen peroxide as an oxidizer. The encapsulation keeps the fuel and oxidizer separate and allows them to be safely stored together in one tank [27,28,29]. This approach is able to combine the advantages of a mono- and bipropellant, namely a high specific impulse paired with efficient hardware [27,30,31]. In our previous research, we were already able to show that the preparation of these hydrocarbon-filled microcapsules is low in cost, easy, and reliable. The produced propellant has a high density (1.27 g/cm3) and an Isp of up to 330 s. In addition, the compatibility of the polyamide capsule membrane with hydrogen peroxide was demonstrated, with the result that neither the membrane was affected by the hydrogen peroxide, nor did the capsules enhance the hydrogen peroxide decomposition rate [27].
The preparation of the hydrocarbon-filled microcapsules is performed by interfacial polymerization with n-decane as a model substance for a hydrocarbon fuel. For this, a reactive monomer (terephthaloyl chloride, TCL) is dissolved in the hydrocarbon, which is then emulsified in water with the help of a surfactant, whereupon a second monomer (diethylenetriamine, DETA) is added to the aqueous phase. Both monomers react at once at the hydrocarbon/water interface and form a polyamide membrane, enveloping the fuel droplets [32,33]. The size of the microcapsules can hereby be influenced by the stirring speed during the emulsification, with higher stirring speeds leading to a lower average diameter of the capsules [31]. In this work, capsules with an average size of 150 µm and 25 µm with respective standard deviations of 28 µm and 6.4 µm are used [31]. A depiction of the production process and an optical microscopy image of the resulting microcapsules are shown in Figure 1. The detailed experimental procedure for the synthesis of n-decane-filled polyamide microcapsules can be found in the Supporting Information.
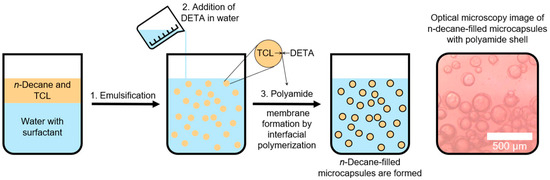
Figure 1.
Depiction of the preparation process of n-decane-filled polyamide microcapsules (left) and optical microscopy images of the capsules in water (right, 150 µm average diameter).
One of the challenges we faced when developing this propellant was to obtain a homogeneous mixture of the microcapsules in the hydrogen peroxide with sufficient resistance to segregation over long periods of time to allow for practical application [2]. This is due to the density difference between the hydrocarbon in the capsule core and the hydrogen peroxide (0.70–0.75 g/cm3 for typical hydrocarbons and up to 1.44 g/cm3 for HTP [34]). Therefore, the microcapsules tend to settle on top of the mixture after a short time, a process called creaming. The creaming velocity can be described by Stokes’ law (Equation (1)). It depends on the gravity due to acceleration , the radius of the particle , the density of the continuous and dispersed phase and and the viscosity of the continuous phase [35]. Stoke’s law suggests that creaming can be suppressed by different approaches, some of which have already been investigated in previous work by our group [31]. The majority of our previous experiments were conducted with water, which was chosen as a substitute for hydrogen peroxide because it is much cheaper, easier to handle, and has similar properties in terms of polarity, which is important for the preparation of gels [34]. This is also a common approach in the literature [36,37].
Our first approach to stabilize the dispersion of fuel-filled microcapsules in water was to decrease the size of the microcapsules, since creaming should be slower for smaller capsules. The capsule size can be varied by adjusting the stirring speed during the emulsification process. However, using microcapsules with a smaller diameter (as small as 4.6 µm on average), creaming was slower but could still be observed [31]. Another approach was the use of different surfactants (Span 80, Tween 80, Triton X-100, and polyvinyl pyrrolidine). However, neither of those surfactants showed a significant stabilizing effect on the dispersion [31].
Therefore, it is inevitable to consider other methods to stabilize the dispersion of the microcapsules in the hydrogen peroxide. This problem is analogous to the metallization of fuels, which has to overcome the same difficulties, stabilizing a dispersion of small particles in a continuous phase with a high-density difference. It has been proven that gelling the continuous phase is an effective method of stabilizing such mixtures [14].
In this work, we anticipate transforming the continuous phase (HTP) into a gel using organic gelling agents. Out of these, we selected the most promising ones for compatibility tests with HTP and characterized the rheological behavior of the gels. Furthermore, we prepared mixtures of the fuel-filled microcapsules in the gels, demonstrating that these dispersions are stable, even with low concentrations of gelling agents, which are very valuable results for further developing this hydrogen peroxide/microcapsule monopropellant.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Screening of Gelling Agents
In order to be able to identify suitable gelling agents, the gelling properties of 24 different compounds were investigated in water as a model substance for hydrogen peroxide. Some of these gelling agents were adapted from the literature examples with interest in technical applications of hydrogen peroxide gels, many of which also used water as a simulant. These included synthetic polymers, such as polyacrylic acids (trade name Carbopol, CP) [21,38,39], polysaccharides, such as Xanthan gum [40,41] and silica-based (Aerosil) gelling agents [23]. The experimental procedure for the preparation of the gels and an overview of all screened gelling agents are given in the Supporting Information (Table S1). The most favorable results were achieved with polyacrylic acid and polysaccharide-based gelling agents. In order to achieve gelation for the CP-based gels, the pH value has to be adjusted by adding a sodium hydroxide solution. A pH value of 4.5 was identified as optimum to ensure good gelation and hydrogen peroxide stability in the following experiments, since hydrogen peroxide tends to decompose faster at higher pH values [42,43].
2.2. Gelling Agent Compatibility with Hydrogen Peroxide
The gelling agents that showed the most promising results in the screening tests with water were investigated further, regarding their effect on the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, a process known to be accelerated by a variety of different compounds. This is a general challenge with propellants that contain hydrogen peroxide because they are sensitive to environmental factors, such as temperature, and traces of contaminants [42]. After a preliminary test round with 20% hydrogen peroxide, which already showed good compatibility, the tests were repeated with 98% hydrogen peroxide over a duration of 4 weeks. The final hydrogen peroxide concentration of each sample is listed in Table 1 and compared to a sample of the same, non-gelled hydrogen peroxide stored under the same conditions. The detailed experimental procedure and general remarks about the handling of hydrogen peroxide and thereupon based propellants are given in the Supporting Information.

Table 1.
Results of the compatibility tests of the gelling agents with highly concentrated hydrogen peroxide after 4 weeks, as described in detail in the Supporting Information, the initial concentration was 97.3%.
The hydrogen peroxide concentrations of the samples containing gelling agents were consistently higher than those of the reference sample. This supports the assumption that all the gelling agents investigated generally have good compatibility with hydrogen peroxide and do not significantly increase its decomposition rate under these conditions and time frame. A comparison between the gelling agents based on polyacrylic acid and polysaccharides shows no trends or significant differences between the two substance classes.
2.3. Centrifuge Dispersion Stability Tests
Materials used in space have to be designed to withstand the gravitational and vibrational forces to which they are exposed during liftoff. According to the Payload User’s Guide published by SpaceX, materials have to be able to withstand a continuous gravitational force of 11× g [44]. This also applies to any propellant that is transported in the spacecraft. To test the ability of the hydrogen peroxide gels to stabilize the dispersed microcapsules at elevated g-forces, tests in a centrifuge were carried out. Additionally, this accelerated creaming process can be used to simulate a longer storage time at 1× g in a shorter timeframe, since, according to Stokes’ law (Equation (1)), an increase in accelerates the creaming process.
An experimental setup was conceived that allowed the visualization and qualitative observation of the creaming process and the subsequent evaluation of dispersion stability. For this, n-decane-filled microcapsules were stirred carefully inside the gel, and the mixture was then centrifuged at 50× g for one hour. Water was used as a hydrogen peroxide simulant. The mixture was photographed before and after centrifugation in front of a black-colored background. Due to the diffuse reflection of the microcapsule surfaces, an accumulation of capsules is indicated by an increase in brightness, which is then plotted against the position in the tube. If creaming is occurring, a difference in the brightness distribution should be visible. This proved to be valuable help in addition to merely visually analyzing the pictures. The detailed procedure for the centrifuge tests and the analysis of the results is described in the Supporting Information. The mass ratio of oxidizer to fuel (ROF) for a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and the n-decane-filled capsules at Isp max has previously been calculated to be 6.1 [27]. However, initial tests conducted at this ROF showed that the concentration of the capsules had to be decreased to a ROF of 20 in order to avoid an oversaturation of the pictures. Although these are very lean mixtures, the results should be applicable to thicker mixtures with a lower ROF because of the “hindered settling” phenomenon, where particles in a dispersion typically move more slowly in the presence of other particles [45,46]. The centrifuge tests were conducted with both 150 µm and 25 µm diameter microcapsules.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show exemplary pictures of the microcapsule/water gel mixtures before and after the centrifugation, together with the corresponding brightness profile. In Figure 2, it can be seen both in the pictures and in the resulting profiles that no creaming has occurred during the centrifugation, which means the dispersion is considered stable. In contrast, Figure 3 shows the result of a centrifuge test with an unstable dispersion, which can be observed in both the brightness profile and the pictures.

Figure 2.
Centrifuge test of a dispersion which is considered stable (25 µm capsules in 0.1% Konjac gum water gel); on the left, the centrifuge tube before and after centrifugation for 60 min at 50× g, on the right is the corresponding brightness profile, the dashed lines mark the relevant part of the tube that was analyzed.

Figure 3.
Centrifuge test of a dispersion which is considered not stable (25 µm capsules in 0.1% CP ETD 2691 water gel); on the left, the centrifuge tube before and after centrifugation for 60 min at 50× g, on the right is the corresponding brightness profile, the dashed lines mark the relevant part of the tube that was analyzed.
In order to find the minimal concentration needed to stabilize the dispersion, the centrifugation tests were started with a concentration of 0.1%. If capsule creaming was observed, the gelling agent concentration gradually increased until a stable dispersion was obtained, which was then verified by repetition. The results are shown in Table 2; the brightness profiles of the mixtures considered stable are given in the Supporting Information.

Table 2.
Minimal gelling agent concentration needed for a stable capsule dispersion after centrifugation at 50× g for 60 min.
It can be seen that all gelling agents tested, except Guar and Tara gum, were able to stabilize the dispersion of the microcapsules. Especially the Carbopol-based gelling agents and Konjac gum stand out for requiring notably low concentrations, as low as 0.1%. These findings may also be relevant for other applications concerning GHTP that may require low organic gelling agent concentrations. Furthermore, the concentration of gelling agent required to stabilize the dispersions depends on the size of the microcapsules. Smaller capsules tend to require a lower gelling agent concentration to result in a stable dispersion, which is in accordance with Stokes’ law. To conclude these tests, an exemplary centrifugation test with a CP ETD GHTP was carried out. For water, the amount of gelling agent required is the same per mass as per volume. Due to its higher density, this is not the case for hydrogen peroxide. Therefore, hydrogen peroxide gels with 0.3% gelling agent, both mass per mass (w/w) and mass per volume (w/v), are of interest. The brightness profile of a 0.3% (w/v) hydrogen peroxide gel centrifuge test is shown in Figure 4 and suggests a similar ability to stabilize the microcapsule dispersion as the corresponding water gel.
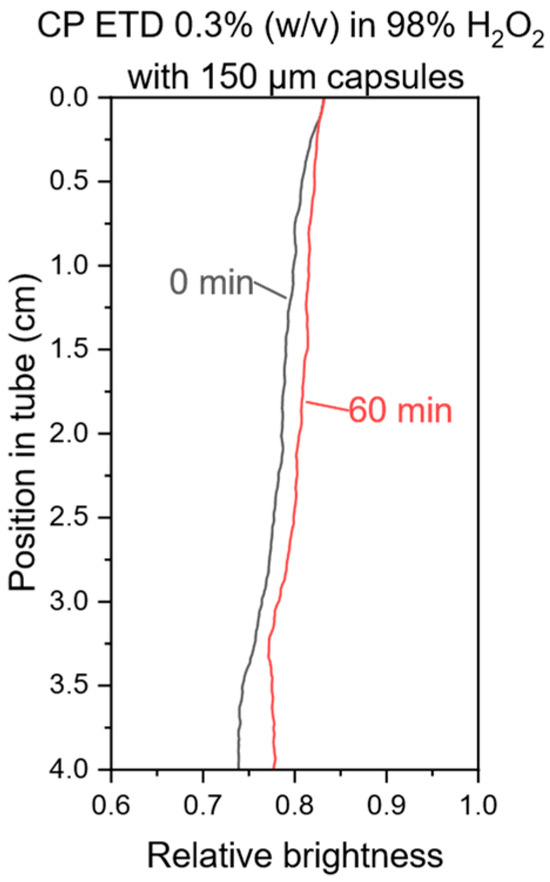
Figure 4.
Brightness profile of a centrifuge test with 150 µm capsules in 98% GHTP with 0.3% (w/v) CP ETD.
2.4. Long-Term Dispersion Stability Tests
If a dispersion shows no signs of creaming or phase separation during the centrifugation process at 50× g for 60 min, it will likely remain stable at 1× g over an extended period. However, due to the non-Newtonian nature of the gels and a potential degradation of the gelling agent or gel structure by the hydrogen peroxide, such projections remain uncertain without validation through actual long-term storage [47]. To address this, microcapsule/water gel mixtures were stored under ambient conditions for four weeks. Photographs were taken weekly, and the corresponding brightness distribution was used to identify potential destabilization. The experiments were conducted with water due to the inevitable formation of gas bubbles caused by the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide when stored at room temperature, which would interfere with the brightness distribution measurements. An example of the brightness distribution of a 0.3% CP ETD–water gel is shown in Figure 5; the data for all samples are provided in the Supporting Information. Overall, the long-term storage results regarding the minimum gelling agent concentration required for stable dispersion are consistent with the findings of the centrifugation tests and show no sign of a potential degradation of the gel network. In general, CP ETD-based gels at a concentration of 0.3% showed an excellent balance between the ease of gel preparation, their dispersion stability with both 150 µm and 25 µm microcapsules, and good hydrogen peroxide compatibility. This makes it the primary candidate for further development of this propellant system.
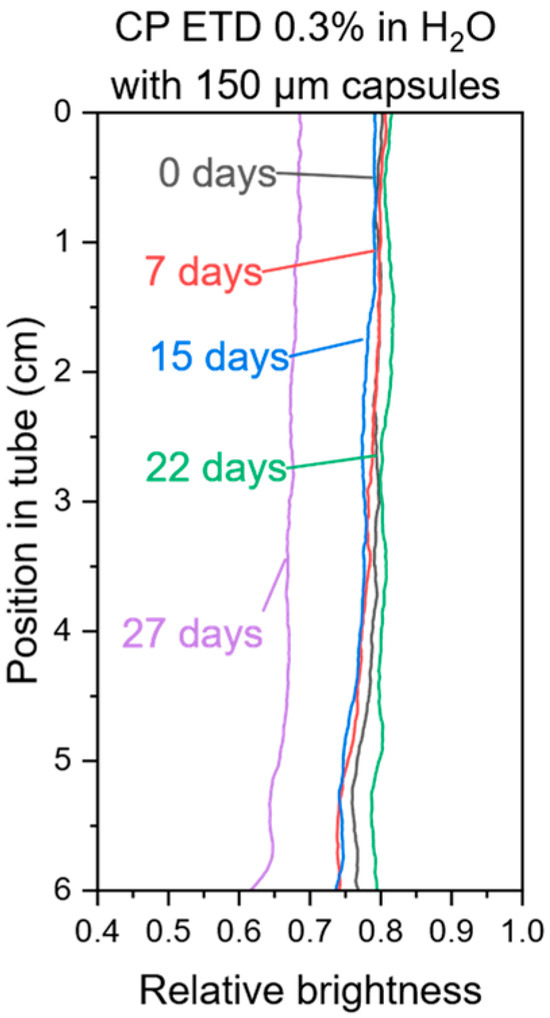
Figure 5.
Brightness distribution of a long-term storage test of a 0.3% CP ETD–water gel with 150 µm microcapsules.
2.5. Rheological Characterization
In addition to the centrifugation tests, the rheological characterization is essential for understanding the flow and deformation behavior of the gels, particularly when these materials are going to be doped with particles. They can also deliver important information on the pumpability and spray dynamics of the fuel [48,49]. In Figure 6, the viscosity curves of CP ETD–water gels, measured with an Anton Paar (Graz, Austria) MCR 102e rotational rheometer, with different concentrations of the gelling agent are shown. They show a strong shear-thinning behavior, and the viscosity can be very well regulated by the amount of gelling agent added. A detailed description of the rheological measurements can be found in the Supporting Information.

Figure 6.
Viscosity curves of CP ETD–water gels with different amounts of gelling agents.
As the gels with 0.3% CP ETD are of particular interest, measurements with a Rosand, RH2000 (Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, UK) capillary rheometer were performed up to a shear rate of 1,180,000 1/s. The viscosity curve (Figure 7) shows further shear-thinning behavior with a plateau forming at the highest shear rates at 8.9 mPa·s. This plateauing can be observed for many shear-thinning substances [50,51]. This data can be useful for designing suitable delivery and injection systems where similar high shear rates can be encountered.

Figure 7.
Viscosity curve of a 0.3% CP ETD–water gel up to a shear rate of 1,180,000 1/s, measured with a rotational and a capillary rheometer.
To measure the rheological behavior of 0.3% CP ETD GHTP samples (both w/w and w/v), a special geometry was manufactured from an aluminum alloy (AlMgSi1, plate–plate 50 mm). This was done to prevent the rapid decomposition of hydrogen peroxide that occurs when standard steel rheology materials are used. The resulting viscosity curves are shown in Figure 8. The numerical values of the viscosity measurements of Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 are shown in the Supporting Information (Tables S2 and S3) together with the corresponding derived values of kinematic viscosity. Kinematic viscosity might be relevant for the design of a delivery system for this propellant when inertia-related phenomena and turbulent flow become a factor. However, by selecting appropriate pipe diameters and pump mechanisms, predominantly laminar flow conditions can be established [10]. The apparent viscosity curve of the 0.3% (w/w) CP ETD GHTP is very similar to the curve of the 0.3% CP ETD water gel (also measured with the aluminum geometry for comparison). However, the 0.3% (w/v) gel has slightly lower viscosity over the entire shear rate area but shows similar shear-thinning properties.

Figure 8.
Viscosity curves of a hydrogen peroxide gel with 0.3% (w/v and w/w) CP ETD and a comparison to the corresponding water gel.
In Figure 9, amplitude sweep measurements of the water and hydrogen peroxide CP ETD gels are shown. The yield point, defined by the intersection of the storage modulus (G′) and the loss modulus (G″), reflects the critical stress at which the gel transitions from elastic to plastic deformation. A higher yield point indicates a stronger gel network, providing greater resistance to sedimentation and creaming over time. The obtained values for viscosity and yield point are in the range of other CP-water gels reported in the literature [50,52]. Higher concentrations of the gelling agent were found to lead to a higher yield point. GHTP with 0.3% (w/w) CP ETD was found to have a very similar yield point to the corresponding water gel. This affirms the similarities between the two gels, which were also observed in the viscosity curves (Figure 8) and the centrifuge test (Figure 4). This leads to the conclusion that the ability of the water-based gel to stabilize dispersed hydrocarbon-filled microcapsules is transferable to hydrogen peroxide-based gels. The use of CP ETD as a gelling agent with a concentration of 0.3% has proven to be very promising for the further development of gelled hydrogen peroxide and thereupon based propellant formulations.


Figure 9.
Amplitude sweep measurements for determining the yield point of water and hydrogen peroxide CP ETD gels with different amounts of gelling agents.
3. Conclusions
In this work, a crucial step in the development of a new type of monopropellant that consists of fuel-filled microcapsules dispersed in hydrogen peroxide was taken by stabilizing these dispersions with organic gelling agents. For this, several gelling agents were screened for their gelling properties using water as a model substance. The most promising candidates were then selected for compatibility tests with hydrogen peroxide and showed no evidence of potential incompatibility. It has also been shown that the microcapsule/gel dispersions with gelling agent concentrations as low as 0.1% are stable over periods of four weeks and under elevated accelerations in a centrifuge. In addition, a first rheological characterization of the gels was conducted, including viscosity curves and amplitude sweeps. Together, these results can form the basis for future development of hydrogen peroxide gel-based propellant formulations. A formulation containing 0.3% polyacrylic acid-based gelling agent has proven useful for our development of a high-performance monopropellant consisting of hydrogen peroxide gel and microencapsulated hydrocarbon fuels.
Supplementary Materials
Detailed experimental procedures and additional brightness distribution diagrams can be found in the supporting information, which can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/aerospace12111002/s1, Figure S1: Calibration curve for the determination of hydrogen peroxide concentration from refractive index measurements; Figure S2: Brightness profiles of centrifuge stability tests of water gels with 150 µm capsules; Figure S3: Brightness profiles of centrifuge stability tests of water gels with 25 µm capsules; Figure S4: Brightness profiles of long-term stability tests of water gels with 150 µm capsules; Figure S5: Brightness profiles of long-term stability tests of water gels with 25 µm capsules; Table S1: List of screened gelling agents (GA) and their suppliers; Table S2: Numerical viscosity values of rheology measurements from Figure 6 and Figure 7; Table S3: Numerical viscosity values of rheology measurements from Figure 8 and the corresponding kinematic viscosity values for the hydrogen peroxide.
Author Contributions
R.S.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—original draft. E.S.: Investigation, Writing—original draft. D.F.: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing—review and editing. S.S.: Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the team members of the Department for Chemical Propellant Technology at the DLR Institute of Space Propulsion for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CP | Carbopol |
| DETA | Diethylenetriamine |
| GHTP | Gelled high-test peroxide |
| HTP | High-test peroxide |
| ROF | Ratio of oxidizer to fuel |
| TCL | Terephthaloyl chloride |
References
- Sarritzu, A.; Pasini, A. Performance comparison of green propulsion systems for future Orbital Transfer Vehicles. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 217, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackheim, R.L.; Masse, R.K. Green Propulsion Advancement: Challenging the Maturity of Monopropellant Hydrazine. J. Propul. Power 2014, 30, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, S.C.; Brüggemann, D.; Freudenmann, D.; Ricker, R.; Schlechtriem, S. Protic thiocyanate ionic liquids as fuels for hypergolic bipropellants with hydrogen peroxide. Fuel 2022, 328, 125290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okninski, A.; Surmacz, P.; Bartkowiak, B.; Mayer, T.; Sobczak, K.; Pakosz, M.; Kaniewski, D.; Matyszewski, J.; Rarata, G.; Wolanski, P. Development of Green Storable Hybrid Rocket Propulsion Technology Using 98% Hydrogen Peroxide as Oxidizer. Aerospace 2021, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.D. Ignition! An Informal History of Liquid Rocket Propellants; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Dadieu, A.; Damm, R.; Schmidt, E.W. Raketentreibstoffe; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1968; ISBN 9783709171332. [Google Scholar]
- Sarritzu, A.; Pasini, A.; Merz, F.; Werling, L.; Lauck, F. Experimental investigation of combustion performance of a green hypergolic bipropellant based on hydrogen peroxide. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 219, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, M.; Ciezki, H.K. Combustion of Gelled Propellants Containing Microsized and Nanosized Aluminum Particles. J. Propul. Power 2015, 31, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaszewski, B.; Powell, R. Launch vehicle performance using metallized propellants. J. Propul. Power 1994, 10, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwal, M.B.; Natan, B.; Mishra, D.P. Gel propellants. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2021, 83, 100885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaszewski, B.; Zakandy, J. Metallized gelled propellants-Oxygen/RP-1/aluminum rocket heat transfer and combustion measurements. In Proceedings of the 32nd Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 1–3 July 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Negri, M.; Ciezki, H.K. Atomization of Viscoelastic Fluids with An Impinging Jet Injector: Morphology And Physical Mechanism of Thread Formation. At. Sprays 2017, 27, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, Y.; Natan, B. Experimental Investigation of The Combustion of Organic-Gellant-Based Gel Fuel Droplets. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2006, 178, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchberger, C.; Stiefel, A.; Kurilov, M.; Ciezki, H. An Overview on Current Gelled Propellants Activities at DLR Lampoldshausen. In Proceedings of the Space Propulsion Conference, Seville, Spain, 14–18 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Munjal, N.L.; Gupta, B.L.; Varma, M. Preparative and mechanistic studies on unsymmetrical Dimethyl Hydrazine-Red Fuming Nitric Acid Liquid Propellant Gels. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1985, 10, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickman, J.; James, E. Gelled liquid oxygen/metal powder monopropellants. In Proceedings of the 28th Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Reston, VA, USA, 6–8 July 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.; Nandagopalan, P.; John, J.; Miglani, A. The characterization of disruptive combustion of organic gellant-laden ethanol fuel droplets. Combust. Flame 2023, 257, 113018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, P.; Bousquet, C.; Lassu, N.; Maggio, A.-F.; Civade, C.; Brenier, C.; Lempereur, L. High-performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of hydrogen peroxide present or released in teeth bleaching kits and hair cosmetic products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchberger, C.; Kurilov, M.; Stiefel, A.; Freudenmann, D.; Ciezki, H. Investigations on Rheology, Spray and Combustion Processes of Gelled Propellants at DLR Lampoldshausen. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference for Aeronautics and Space Sciences, Madrid, Spain, 1–4 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jyoti, B.; Baek, S.W. Rheological Characterization of Hydrogen Peroxide Gel Propellant. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2014, 15, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Hasan, D.; Peretz, A. Development of laboratory-scale gel propulsion technology. J. Propul. Power 2004, 20, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, G.S.; Da Silva Mota, F.A.; Fei, L.; Tang, C.; de Souza Costa, F. Gelled hydrogen peroxide: Hypergolic reaction with low toxicity fuel by drop and impinging jets tests. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 222, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, G.S.; Da Silva Mota, F.A.; Fei, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, M.; Tang, C.; de Souza Costa, F. Hypergolic fuel impacting a gelled oxidizer wall: Droplet dynamics, heat release, ignition, and flame analysis. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2025, 160, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yang, J.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, J. Preparation, characterization, and thermal decomposition kinetics of high test peroxide gel. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 211, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.; Jyoti, B.V.S.; Yun, Y.; Shoaib, M.N.; Kwon, S. Preliminary Assessment of Hydrogen Peroxide Gel as an Oxidizer in a Catalyst Ignited Hybrid Thruster. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2018, 2018, 5630587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florczuk, W.; Rarata, G.P. Performance evaluation of the hypergolic green propellants based on the HTP for a future next generation spacecrafts. In Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Antlanta, Georgia, 10–12 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Scholl, R.; Freudenmann, D.; Schlechtriem, S. Microencapsulation of hydrocarbon fuels for monopropellant creation with hydrogen peroxide. Fuel 2024, 356, 129520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, A.; Knorr, A.; Wehrstedt, K.D.; Wandrey, P.A.; Gmeinwieser, T.; Steinbach, J. Investigation of the explosive hazard of mixtures containing hydrogen peroxide and different alcohols. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 108, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.D.; Dee, L.A.; Greene, B.; Hornung, S.D.; McClure, M.B.; Rathgeber, K.A. Fire, Explosion, Compatibility and Safety Hazards of Hydrogen Peroxide; NASA: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Scholl, R.; Freudenmann, D.; Schlechtriem, S. Microencapsulation of non-miscible Liquid Bipropellant Systems. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Flight Vehicles, Aerothermodynamics and Re-entry Missions Engineering (FAR), Heilbronn, Germany, 19–23 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Scholl, R.; Partsch, S.; Bühler, L.; Freudenmann, D.; Schlechtriem, S. Implementation of Microencapsulated Fuels in Combination with Hydrogen Peroxide for Creation of New Monopropellants. In Proceedings of the Aerospace Europe Conference, Lausanne, Switzerland, 9–13 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Perignon, C.; Ongmayeb, G.; Neufeld, R.; Frere, Y.; Poncelet, D. Microencapsulation by interfacial polymerisation: Membrane formation and structure. J. Microencapsul. 2015, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, R.; Freudenmann, D. Ionic Liquid-Filled Polyamide Microcapsules Obtained by Interfacial Polymerization. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 12, 2400393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chanamai, R.; McClements, D.J. Creaming Stability of Flocculated Monodisperse Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 225, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Weihs, D. Gelled Fuel Simulant Droplet Impact onto a Solid Surface. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2011, 36, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Peretz, A.; Natan, B. Rheological Matching of Gel Propellants. J. Propul. Power 2010, 26, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacki, K.; Feikema, D. Atomization studies of gelled bipropellant simulants using planar laser induced fluorescence. In Proceedings of the 31st Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Reston, VA, USA, 10–12 July 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E.; Theron, A.; Rahimi, S.; Sobe, Z.; Hasan, D. Elongational behavior of gelled propellant simulants. J. Rheol. 2004, 48, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Yang, L.; Cui, K.; Zhuang, F. Effects of Orifice Geometry on Gelled Propellants Sprayed from Impinging-Jet Injectors. J. Propul. Power 2014, 30, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Duan, R.; Cui, K.; Yang, L. Spray of gelled propellants from an impinging-jet injector under different temperatures. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2014, 39, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak, C.; Meyer, H.-J.; Gudat, D.; Alsfasser, R. Moderne Anorganische Chemie, 4th ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2012; ISBN 9783110249019. [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann, E.; Attin, T.; Mohn, D.; Zehnder, M. Hydrogen Peroxide Versus Sodium Hypochlorite: All a Matter of pH? J. Endod. 2021, 47, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SpaceX. Falcon Payload User’s Guide. Available online: https://www.spacex.com/assets/media/falcon-users-guide-2025-05-09.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Xue, J.; Herbolzheimer, E.; Rutgers, M.A.; Russel, W.B.; Chaikin, P.M. Diffusion, dispersion, and settling of hard spheres. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 69, 1715–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, H.; Peng, D.; Dou, J. Modelling the Hindered Settling Velocity of a Falling Particle in a Particle-Fluid Mixture by the Tsallis Entropy Theory. Entropy 2019, 21, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuentz, M.; Rothlisberger, D. Sedimentation analysis of aqueous microsuspensions based on near infrared transmission measurements during centrifugation Determination of a suitable amount of gelling agent to minimise settling in the gravitational field. STP Pharma Sci. 2002, 12, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Negri, M.; Ciezki, H.K. Effect of Elasticity of Boger Fluids on the Atomization Behavior of an Impinging Jet Injector. At. Sprays 2015, 25, 695–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, M.; Wilhelm, M.; Hendrich, C.; Wingborg, N.; Gediminas, L.; Adelöw, L.; Maleix, C.; Chabernaud, P.; Brahmi, R.; Beauchet, R.; et al. New technologies for ammonium dinitramide based monopropellant thrusters—The project RHEFORM. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 143, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Varges, P.; M. Costa, C.; S. Fonseca, B.; F. Naccache, M.; de Souza Mendes, P.R. Rheological Characterization of Carbopol® Dispersions in Water and in Water/Glycerol Solutions. Fluids 2019, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhil, H.; Auhl, D.; Wierschem, A. Infinite-shear viscosity plateau of salt-free aqueous xanthan solutions. J. Rheol. 2019, 63, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giuseppe, E.; Corbi, F.; Funiciello, F.; Massmeyer, A.; Santimano, T.N.; Rosenau, M.; Davaille, A. Characterization of Carbopol® hydrogel rheology for experimental tectonics and geodynamics. Tectonophysics 2015, 642, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).