Linear Disturbance Observer-Enhanced Continuous-Time Predictive Control for Straight-Line Path-Following Control of Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The PF control scheme for the FWUAV is perfected.
- 2.
- A robust control approach is proposed for attitude control.
2. System Modeling
2.1. Command Yaw Angle
2.2. System Modeling for Latitude Movement
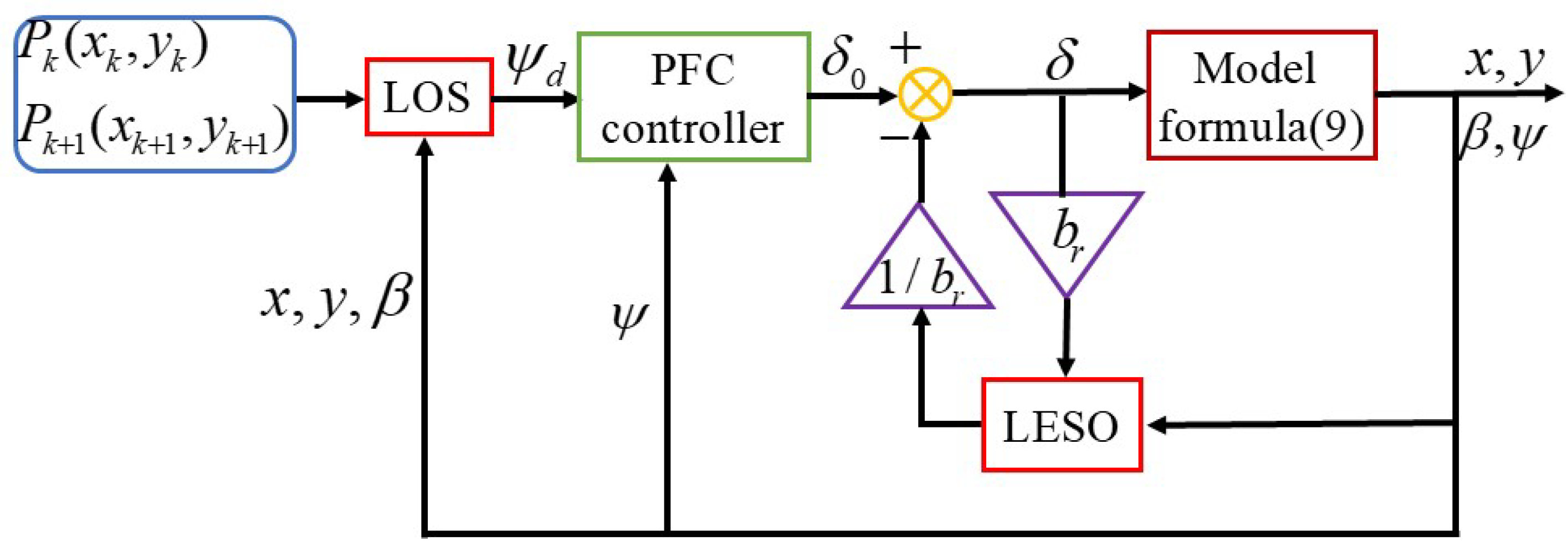
3. Design of Robust Control Scheme for Yaw System
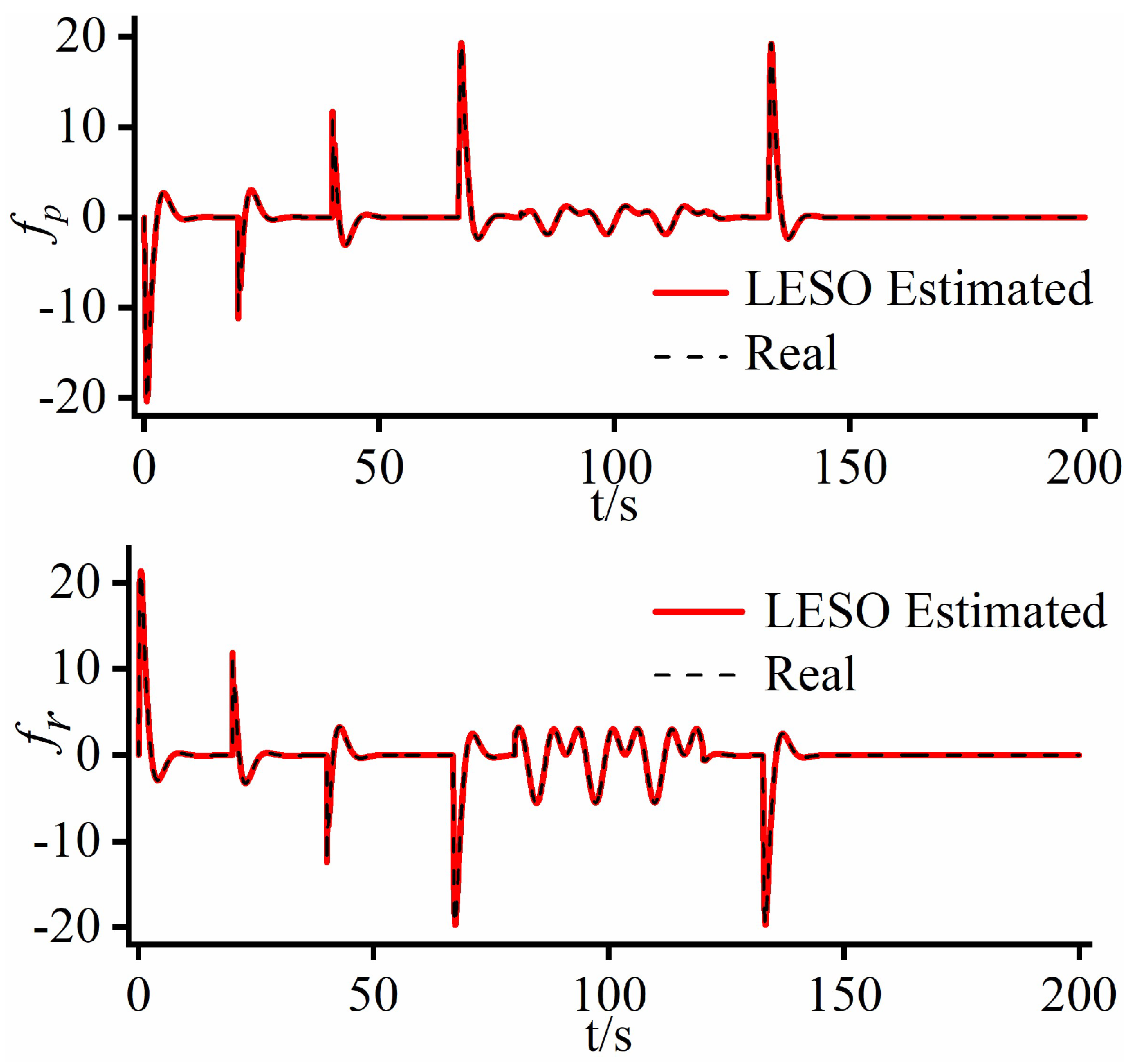
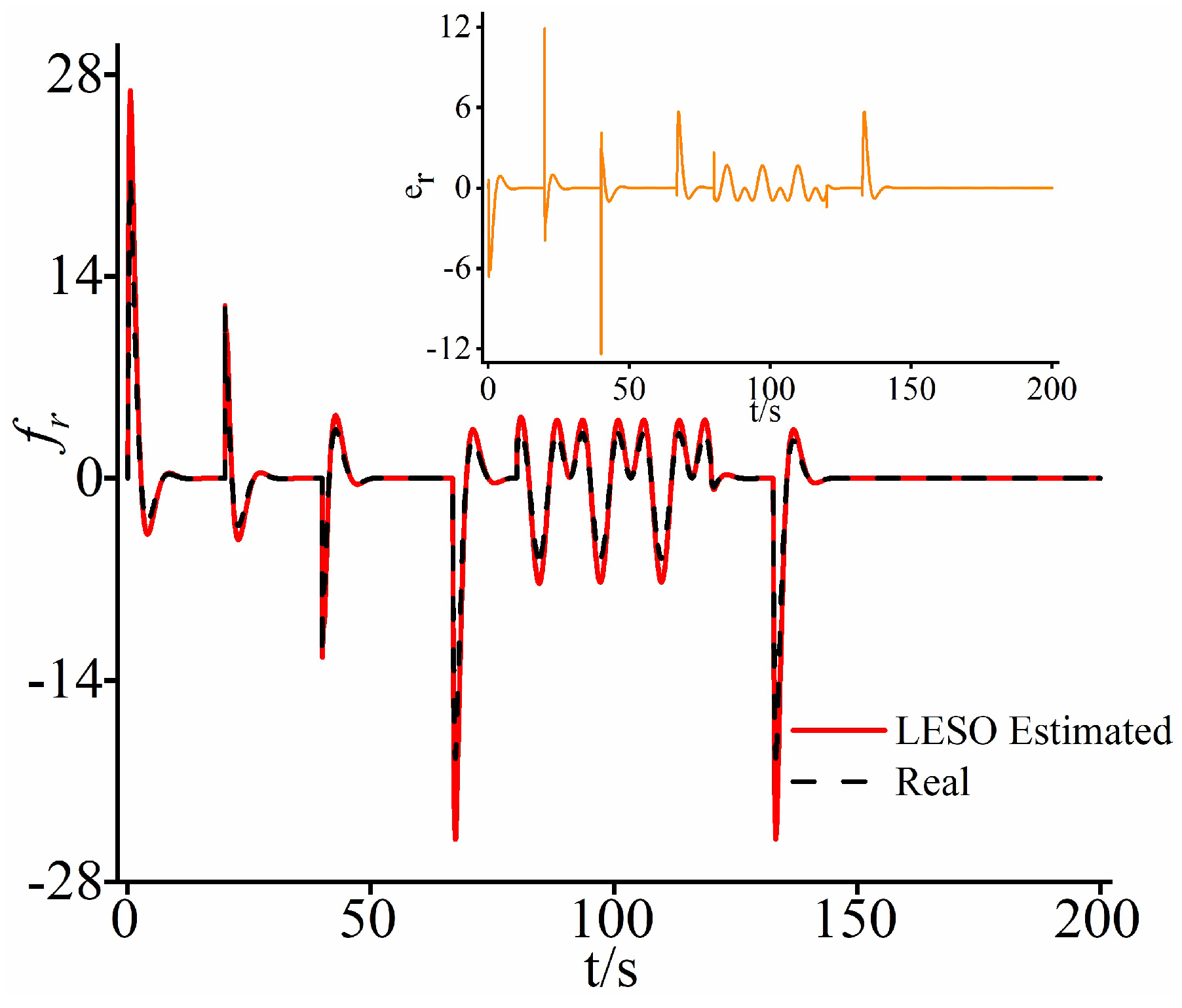
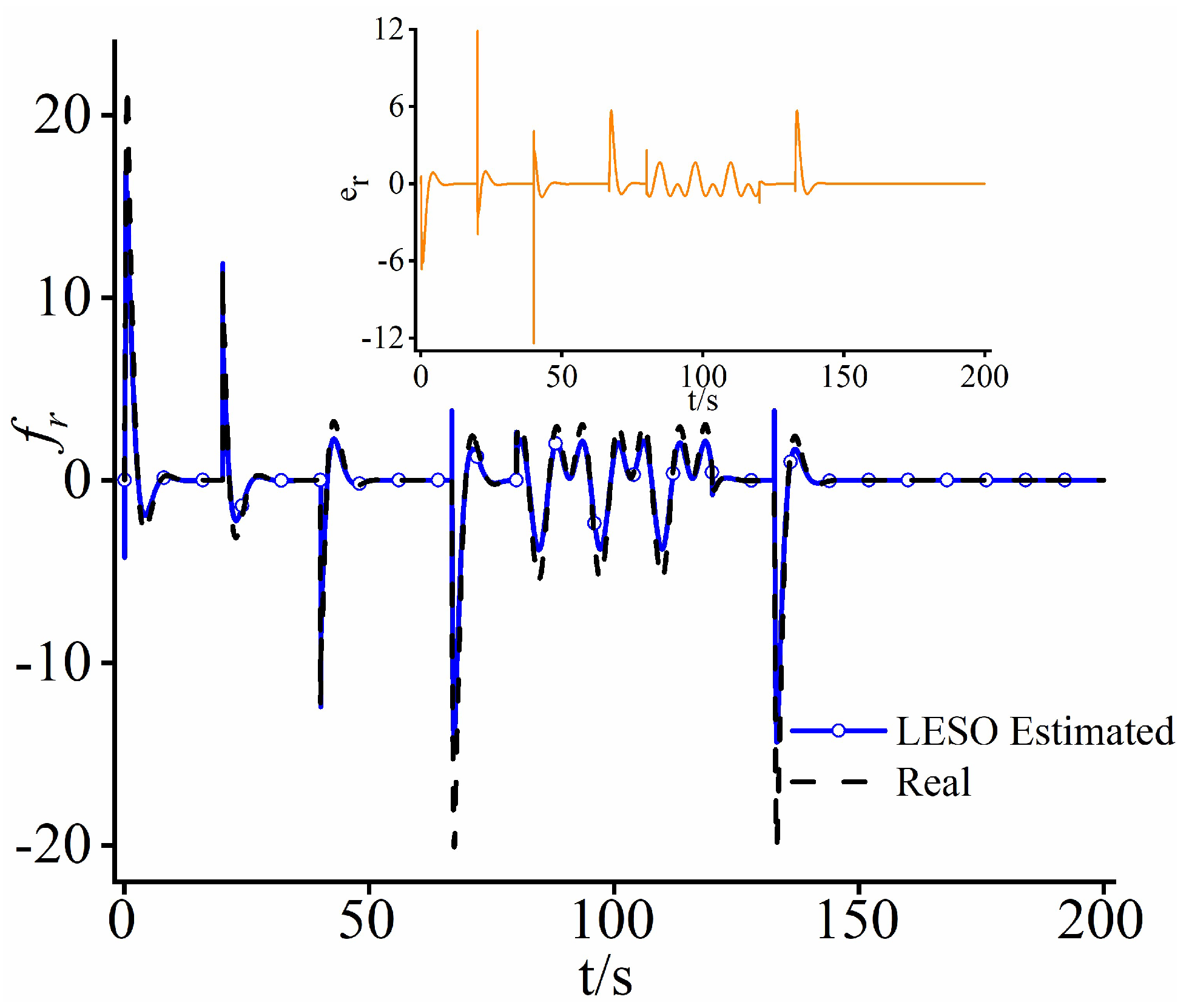
3.1. Design of the LESO
3.2. Design of the Predictive Controller
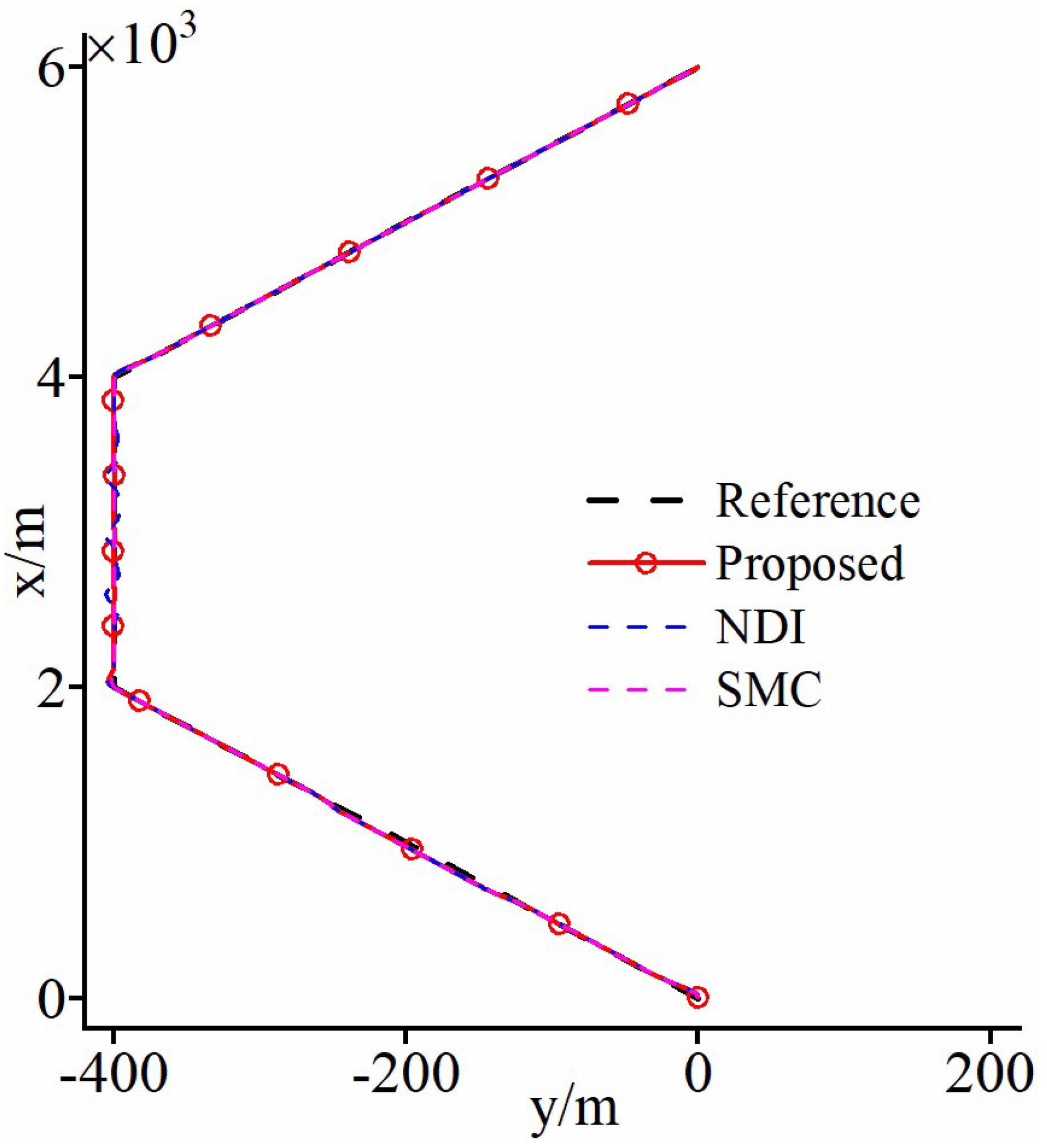
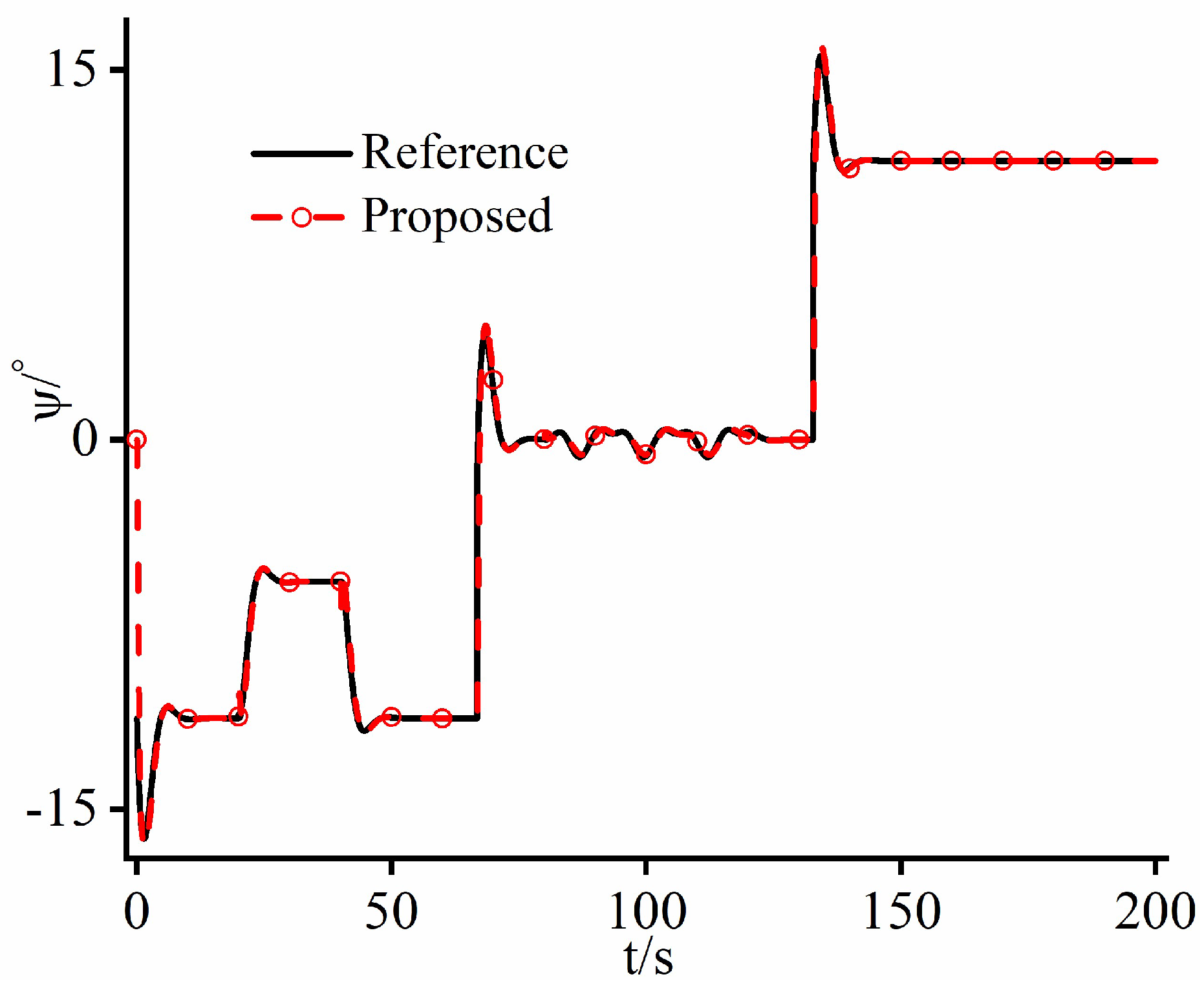
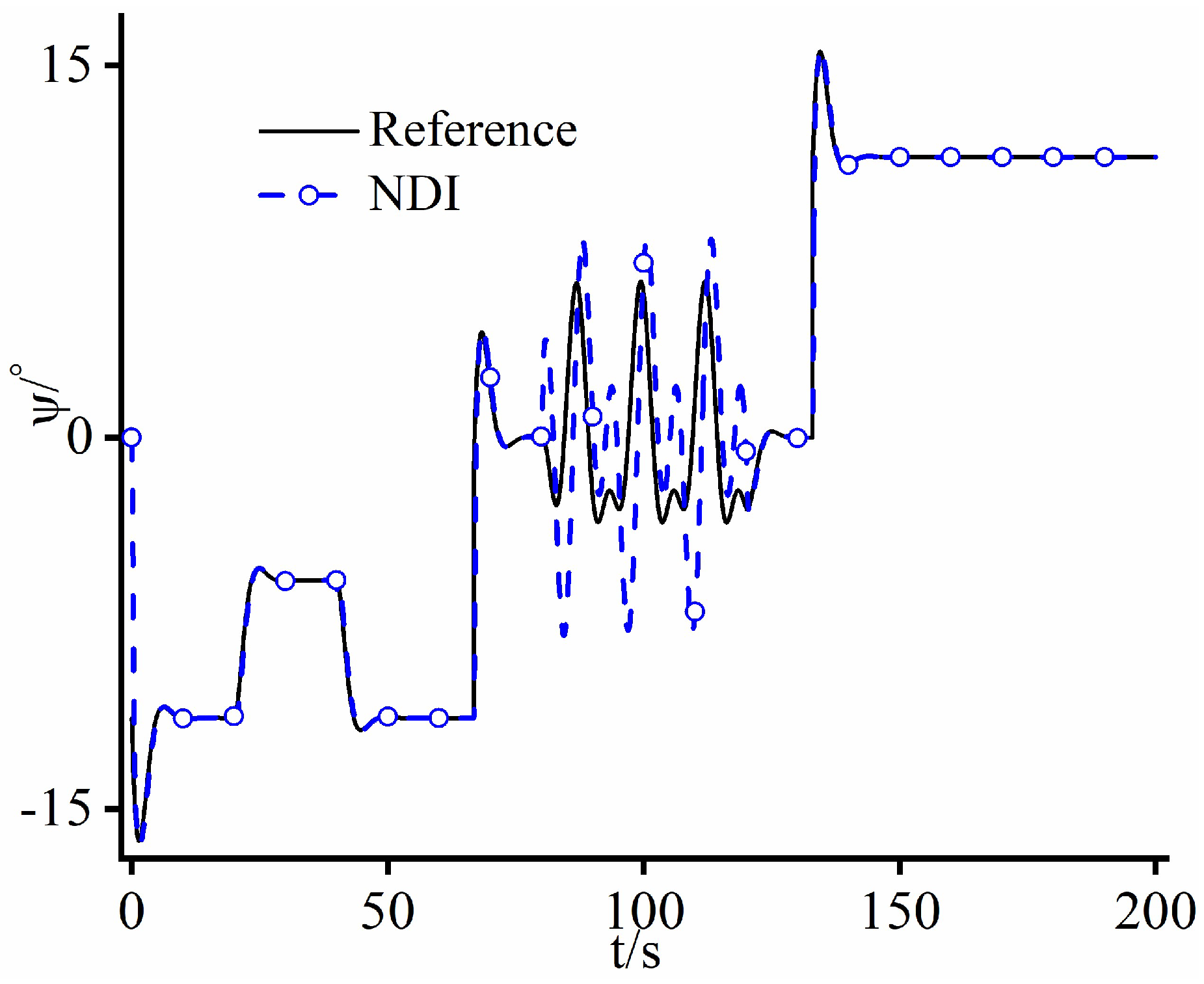
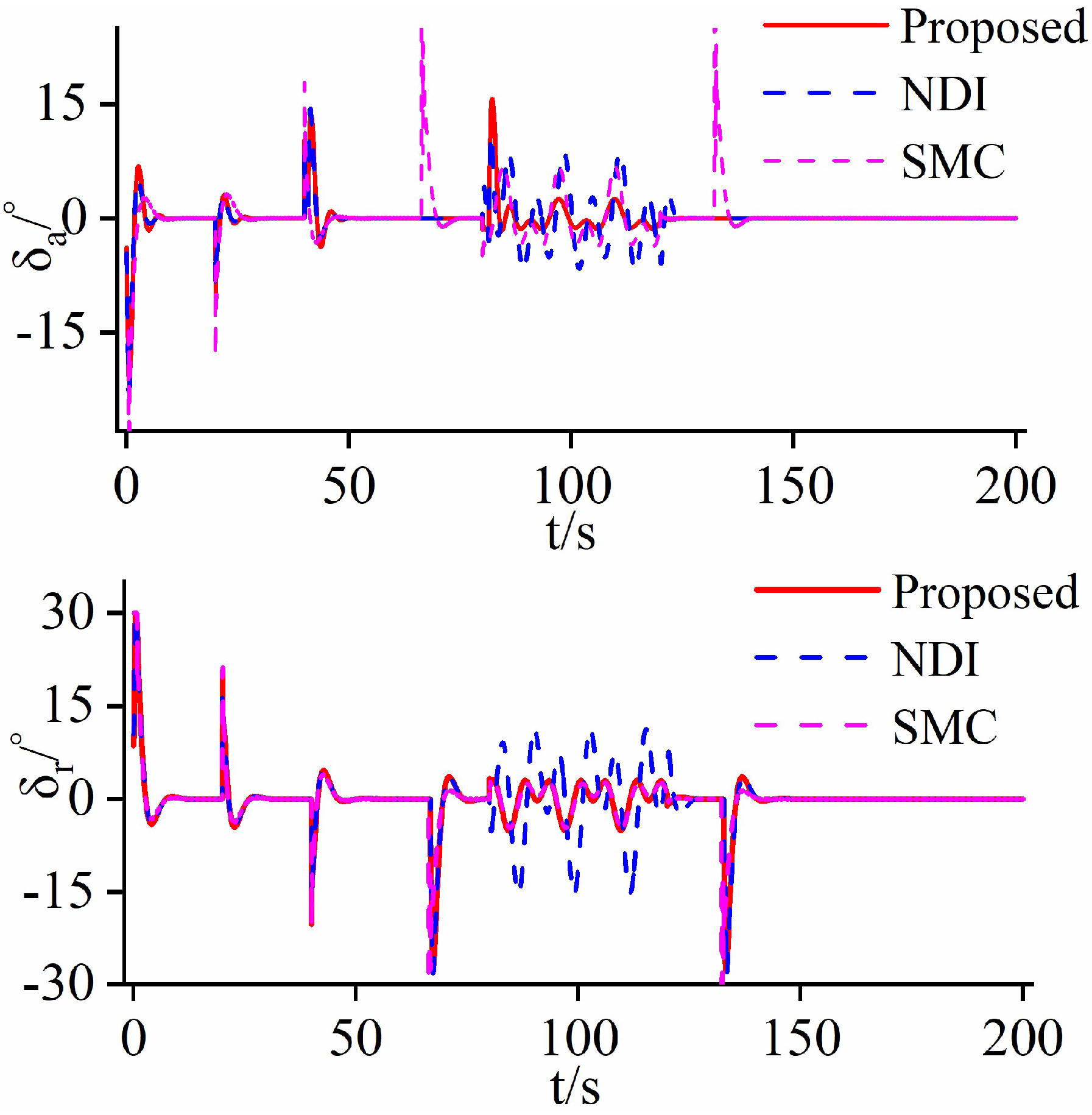
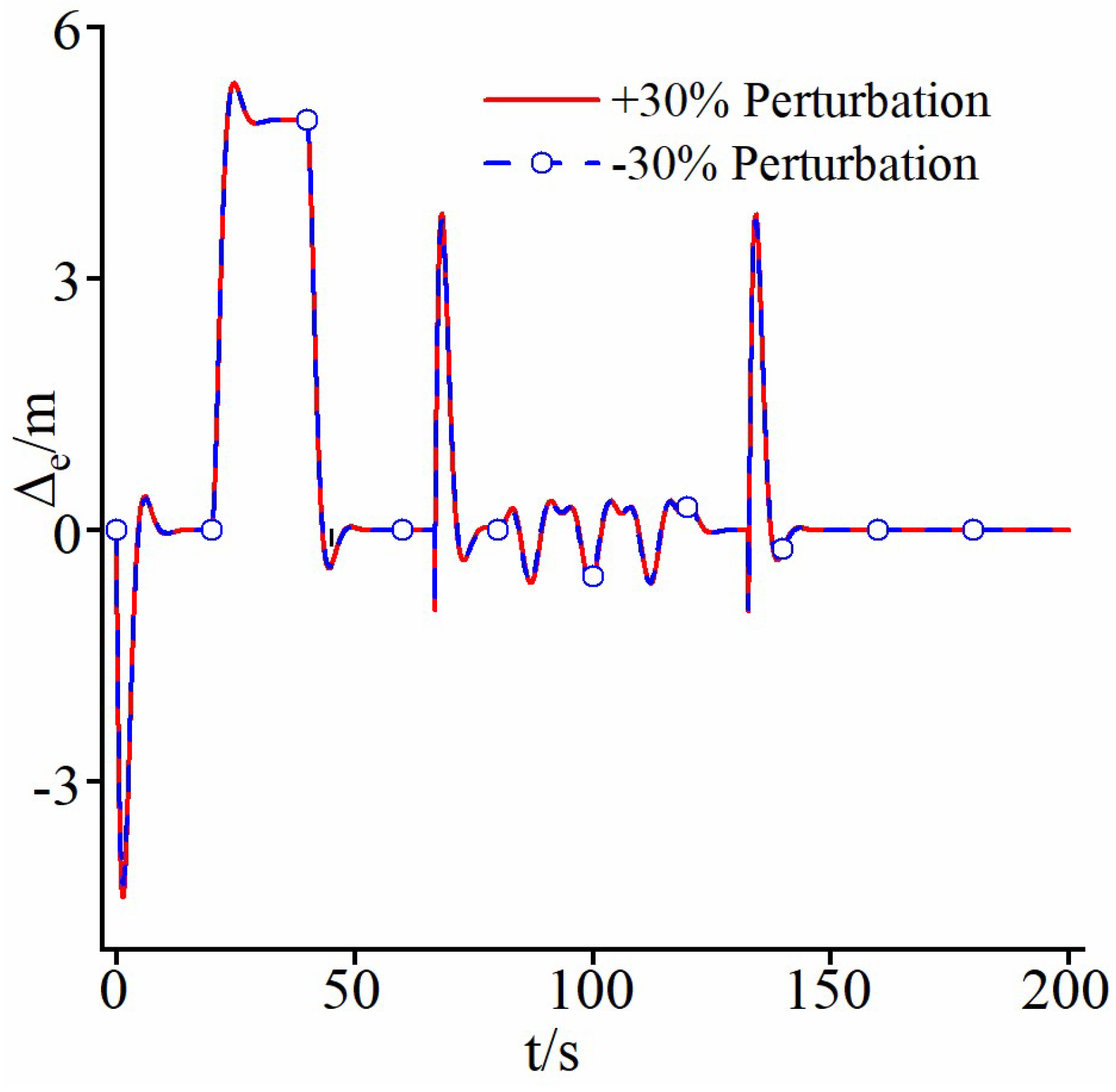
4. Numerical Simulations
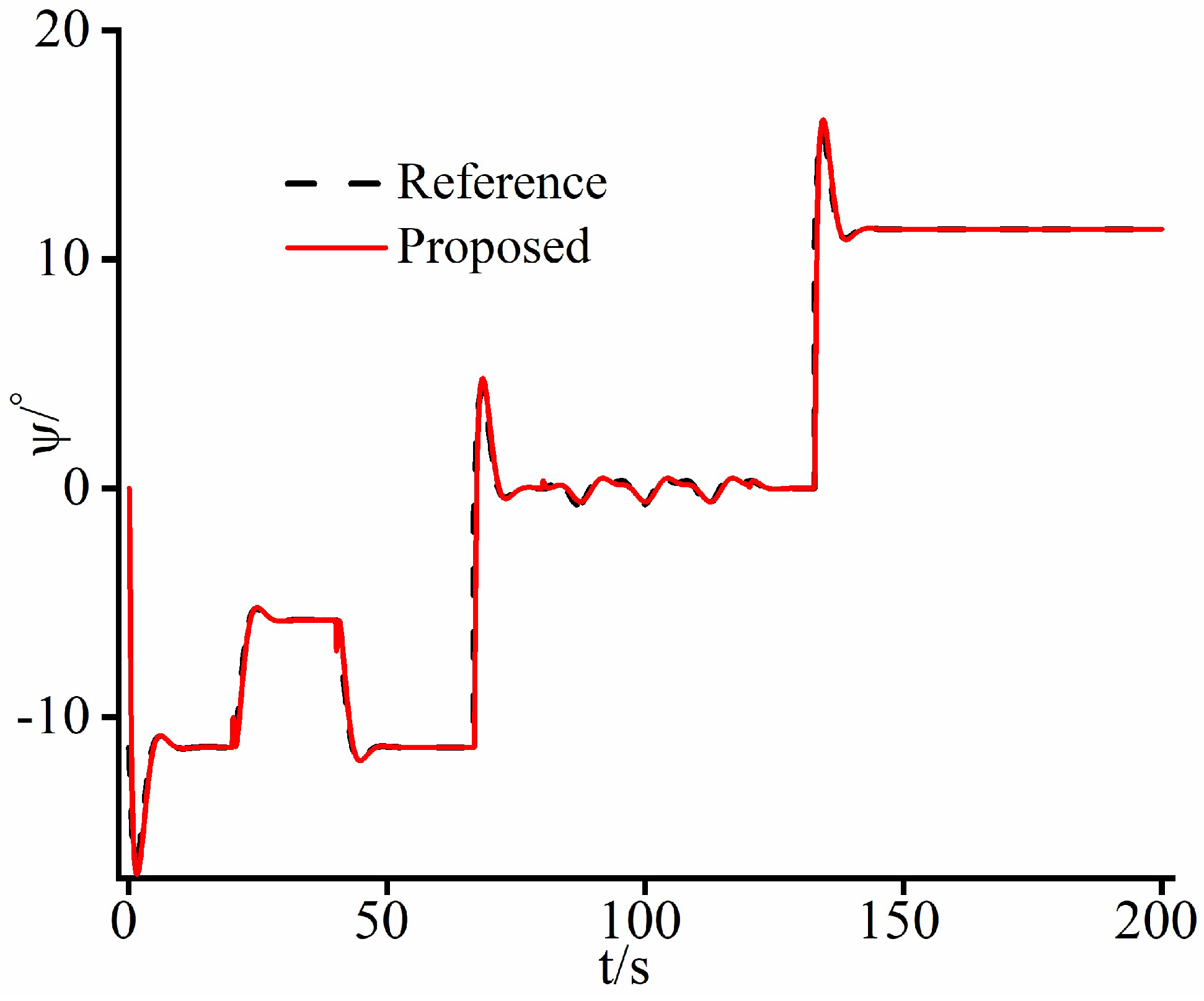
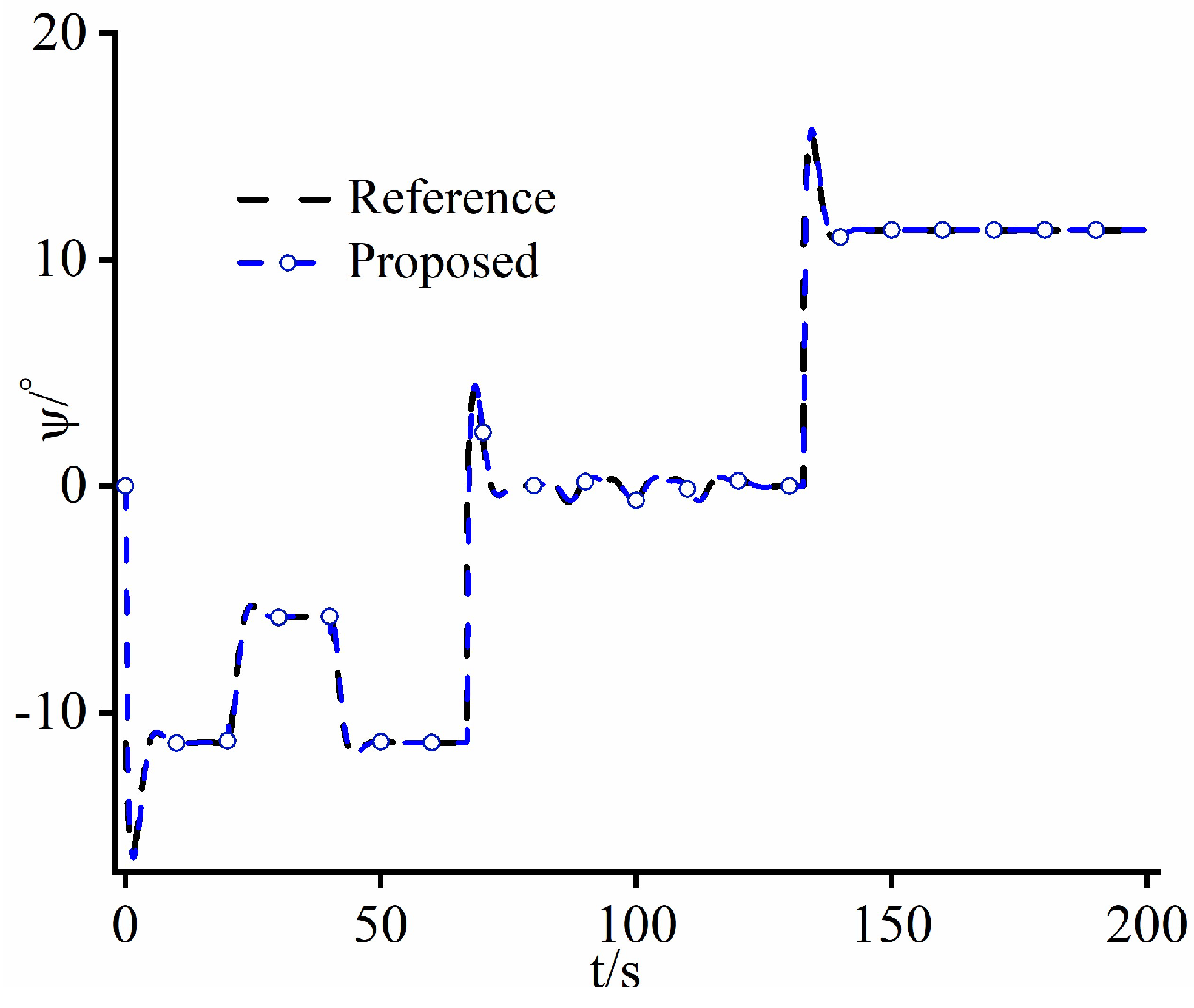
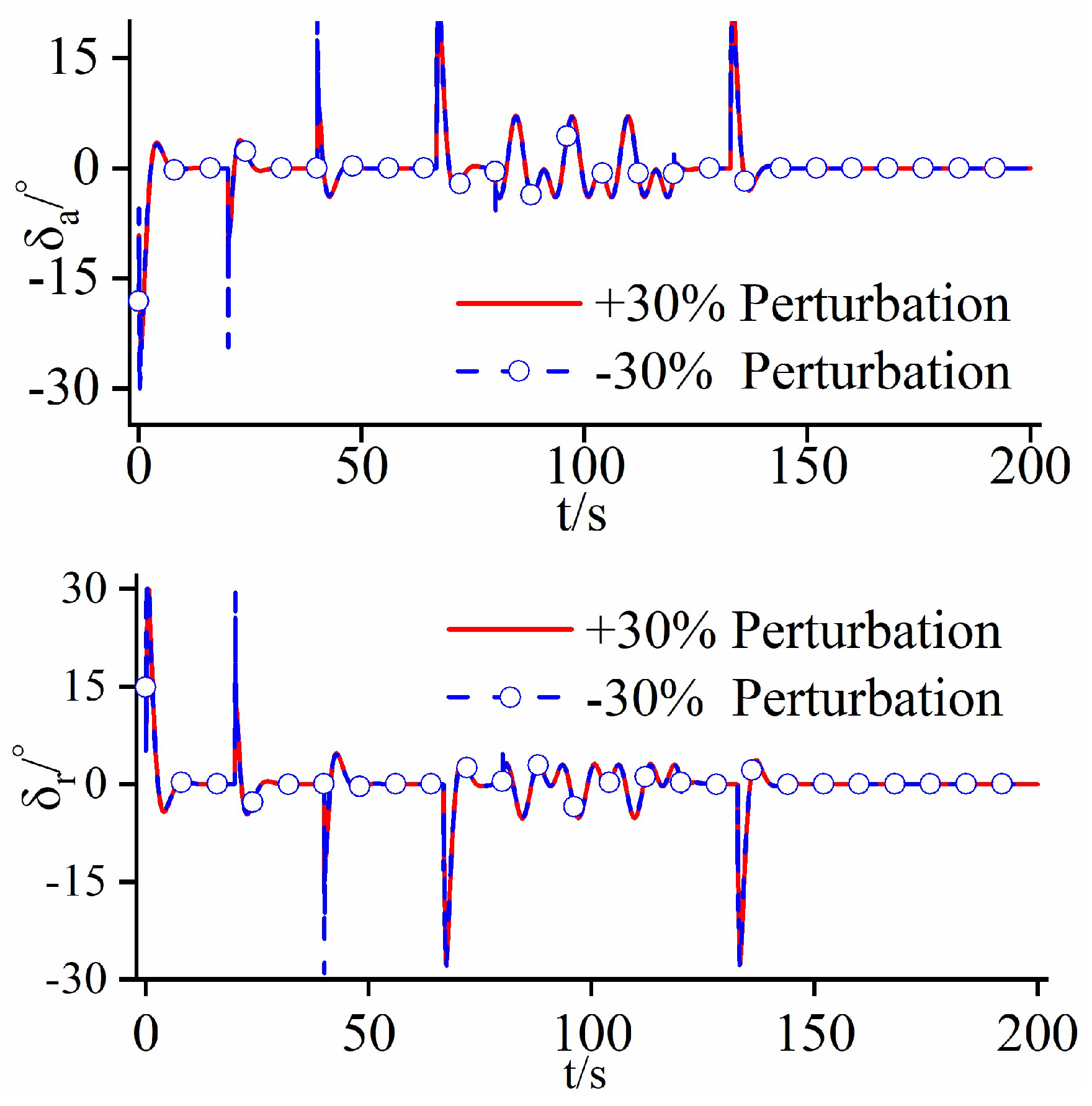
4.1. Case Study 1
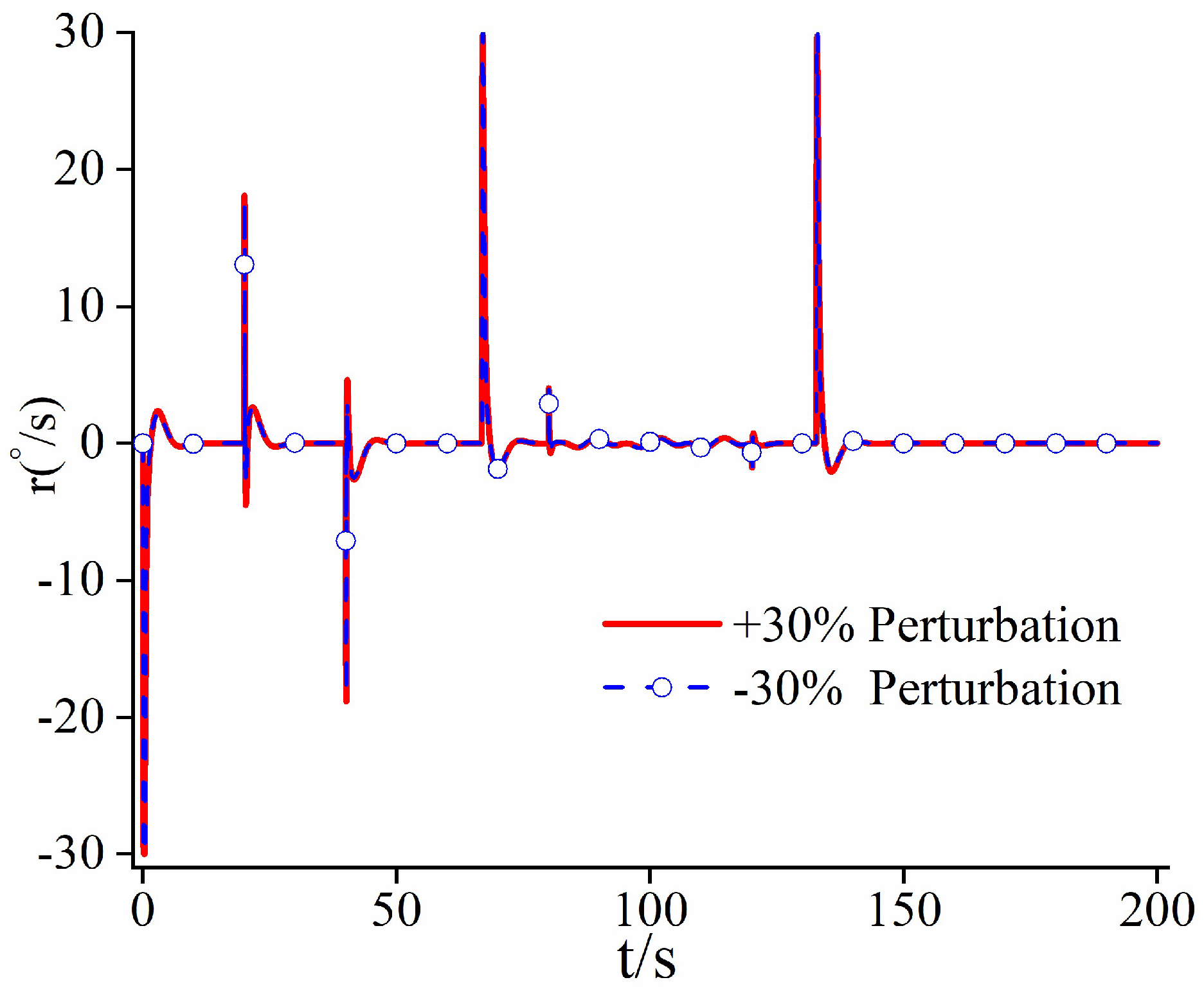
4.2. Case Study 2
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Nelson, R.C. Flight Stability and Automatic Control, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Company Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 96–130. [Google Scholar]
- Yintao, Z.; Youmin, Z.; Zhixiang, L.; Ziquan, Y.; Yaohong, Q. Line-of-Sight Path Following Control on UAV with Sideslip Estimation and Compensation. In Proceedings of the 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Wuhan, China, 25–27 July 2018; pp. 4711–4716. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Dan, W.; Peng, Z. ESO-Based Line-of-Sight Guidance Law for Path Following of Underactuated Marine Surface Vehicles with Exact Sideslip Compensation. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 42, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, G.; Ariola, M.; Ciniglio, U.; Corraro, F.; de Lellis, E.; Pironti, A. Path generation and tracking in 3-D for UAVs. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2009, 17, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.Y.; Luo, H.B.; Liao, F.; Wang, X.H.; Ji, H.B. Cooperative Strategy for Aircraft Defense Line-of-Sight Guidance in Three-Dimensional Space. In Proceedings of the 2022 41st Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hefei, China, 25–27 July 2022; pp. 3398–3403. [Google Scholar]
- Balhance, N.; Martin, W.; Tal, S. Cooperative guidance law for intrasalvo tracking. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2017, 40, 1441–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.C.; Ding, G.R.; Xu, Y.T.; Wang, H.C.; Wu, Q.H. Proactive optimization of transmission power and 3D trajectory in UAV-assisted relay systems with mobile ground users. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, J.P.; Clem, G. Vector Field UAV Guidance for Path Following and Obstacle Avoidance with Minimal Deviation. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2019, 42, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fari, S.; Wang, X.; Roy, S.; Baldi, S. Addressing Unmodeled Path-Following Dynamics via Adaptive Vector Field A UAV Test Case. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R.; Barber, D.B.; McLain, T.W.; Beard, R.W. Vector field path following for miniature air vehicles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2007, 23, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, G. Vector Field Approach for Curved Path Following for Miniature Aerial Vehicles. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit, Keystone, CO, USA, 21–24 August 2006; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm, J.; Clem, G.; Casbeer, D.; Gerlach, A. Circumnavigation and obstacle avoidance guidance for UAVs using Gradient Vector Fields. In Proceedings of the AIAA Sci tech 2019 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–11 January 2019; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.R.; Blake Barber, D.; McLain, T.W.; Beard, R.W. Vector Field Path Following for Small Unmanned Air Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2006 American Control Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 14–16 June 2006; pp. 5788–5794. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, X.G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.Y. Trajectory-following guidance based on a virtual target and an angle constraint. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 87, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucco, A.; Aguiar, A.; Hauser, J. Trajectory optimization for constrained UAVs: A virtual target vehicle approach. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Denver, CO, USA, 9–12 June 2015; pp. 236–245. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.H.; Wang, L.H.; Zhao, J.; Wu, K.; Wang, Y.X. Virtual target guidance-based distributed model 4 predictive control for formation control of multiple 5 UAVs. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 33, 1037–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, X.K.; Shen, L.C.; Cong, Y.R. Formation flight of fixed-wing UAV swarms: A 4 group-based hierarchical approach. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Deyst, J.; How, J.P. Performance and Lyapunov stability and of a nonlinear path following guidance method. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2007, 30, 1718–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Y.; Tang, W.X. Guidance Strategy for UAV Tracking Target Based on Reference Point Guidance Method. J. Northwestern Polytech. Univ. 2020, 38, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.H.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.H.; Shen, L.C. Improving multi-target cooperative tracking guidance for UAV swarms using multi-agent reinforcement learning. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2022, 35, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Li, D.G.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.P. Adaptive Dynamic Occupancy Guidance for Air Combat of UAV. Unmanned Syst. 2024, 12, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modali, S.; Ghosh, S. Terminal-Angle-Constrained Guidance based on Sliding Mode Control for UAV Soft Landing on Ground Vehicles. Electr. Eng. Syst. Sci. 2020, 2009, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.H.; Chen, Q.Y.; Hou, Z.X.; Zheng, G. An Improved Nonlinear Guidance Law for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Path Following. In Proceedings of the 2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hangzhou, China, 28–30 July 2015; pp. 5271–5276. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminer, I.; Pascoal, A.; Xargay, E.; Hovakimyan, N.; Cao, C.Y.; Dobrokhodov, V. Path following for unmanned aerial vehicles using L1 adaptive augmentation of commercial autopilots. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2010, 33, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengyu, C.; Naira, H. Design and Analysis of a Novel L1 Adaptive Control Architecture With Guaranteed Transient Performance. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2008, 53, 586–591. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.J.; McAree, O.; Chen, W.H. Path-following control for small fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicles under wind disturbances. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2013, 23, 1682–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, R.W.; Ferrin, J.; Humpherys, J. Fixed wing UAV path following in wind with input constraints. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 2103–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.L.; Wang, X.K.; Zhang, D.B.; Shen, L.C. Curved Path Following Control for Fixed-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles with Control Constraint. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 89, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavilan, F.; Vazquez, R.; Camacho, E.F. An iterative model predictive control algorithm for UAV guidance. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 2406–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, B.; Claudio, R. Decentralized linear time-varying model predictive control of a formation of unmanned aerial vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2011 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–15 December; pp. 7488–7493.
- Yang, J.; Liu, C.J.; Coombes, M.; Yan, Y.D.; Chen, W.H. Optimal path following for small fixed-wing UAVs under wind disturbances. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2020, 29, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Zuo, Z.; Chen, W.-H. A simple optimal planer path following algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Control Conference (ECC), Limassol, Cyprus, 12–15 June 2018; pp. 1809–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Kwang, Y.; Yeonsik, K.; Salah, S. Adaptive nonlinear model predictive path-following control for a fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2013, 11, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Yeonsik, K.; Karl, J.H. Linear Tracking for a Fixed-Wing UAV Using Nonlinear Model Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2009, 17, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, M.; Postlethwaite, I.; Gu, D.W. A suboptimal path planning algorithm using rapidly-exploring random trees. Int. J. Aerosp. Innov. 2010, 2, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Rucco, A.; Aguiar, A.P.; Pereira, F.L.; de Sousa, J.B. A predictive path-following approach for fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicles in presence of wind disturbances. In Proceedings of the Robot 2nd Iberian Robotics Conference, Lisbon, Portugal, 19–21 November 2015; pp. 623–634. [Google Scholar]
- Brezoescu, A.; Espinoza, T.; Castillo, P.; Lozano, R. Adaptive trajectory following for a fixed-wing UAV in presence of crosswind. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2013, 69, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qi, W.; Li, Y.; Yaowei, W.; Wenan, Z. LESO-based position synchronization control for networked multi-axis servo systems with time-varying delay. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Miao, C.; Sun, X. Model predictive current control for IPMSM drives with extended-state-observer-based sliding mode speed controller. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 38, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Gao, G.; Zhong, J. Finite-time adaptive extended state observer-based dynamic sliding mode control for hybrid robots. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Lee, C.H.T. Different active disturbance rejection controllers based on the same order GPI observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 10969–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, R.W.; Mclain, T.W. Small Unmanned Airplane: Theory and Practice, 1st ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- She, J.; Miyamoto, K.; Han, Q.L.; Wu, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Wang, Q.G. Generalized-extended-state-observer and equivalent-input-disturbance methods for active disturbance rejection: Deep observation and comparison. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 10, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.; Qiao, Q.; Deng, J.Q.; Ren, W.; Mao, Y. Model-assisted Linear Extended State Observer for Opto-Electronic Stabilized Platform. In Proceedings of the 34rd Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation (YAC), Jinzhou, China, 5 August 2019; pp. 370–374. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Baek, S.; Rawashdeh, S.; Mohammadi, A. Autonomous landing of a UAV on a moving platform using model predictive control. Drones 2018, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccani, D.; Cecchin, L.; Fagiano, L. Multitrajectory Model Predictive Control for Safe UAV Navigation in an Unknown Environment. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2022, 31, 1982–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Van Kampen, E.J.; Chu, Q.; Lu, P. Stability Analysis for Incremental Nonlinear Dynamic Inversion Control. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2019, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Nonlinear disturbance observer-enhanced dynamic inversion control of missiles. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2003, 26, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, A.; Mortazavi, M.; Talebi, H.A. UAV formation control via the virtual structure approach. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2015, 28, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Wei, X.; Wang, A. A Novel Control Method for Unmanned Agricultural Tractors: Composite Back-stepping Sliding Mode Path Tracking. Inf. Technol. Control 2023, 52, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jia, J.; Sun, X.; Xu, T. An enhanced linear ADRC strategy for a bearingless induction motor. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 8, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, M.; Jing, W.; Gao, C. Dynamics and adaptive sliding mode control of a mass-actuated fixed-wing UAV. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2021, 22, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8244 kg·m2 | 1.759 kg·m2 | ||
| S | 0.55 m2 | b | 2.8956 m |
| 0 | 0 | ||
| −0.12 | 0.25 | ||
| 0.14 | −0.35 | ||
| 0.08 | 0.06 | ||
| 0.105 | −0.032 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, W.; Tong, M.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Song, W. Linear Disturbance Observer-Enhanced Continuous-Time Predictive Control for Straight-Line Path-Following Control of Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Aerospace 2024, 11, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11110902
Qi W, Tong M, Li X, Wang Q, Song W. Linear Disturbance Observer-Enhanced Continuous-Time Predictive Control for Straight-Line Path-Following Control of Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Aerospace. 2024; 11(11):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11110902
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Weiwei, Mingbo Tong, Xubo Li, Qi Wang, and Wei Song. 2024. "Linear Disturbance Observer-Enhanced Continuous-Time Predictive Control for Straight-Line Path-Following Control of Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles" Aerospace 11, no. 11: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11110902
APA StyleQi, W., Tong, M., Li, X., Wang, Q., & Song, W. (2024). Linear Disturbance Observer-Enhanced Continuous-Time Predictive Control for Straight-Line Path-Following Control of Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Aerospace, 11(11), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11110902






