Study on the Dynamic Crushing Behaviors of Hourglass Honeycomb Sandwich Panels
Abstract
1. Introduction
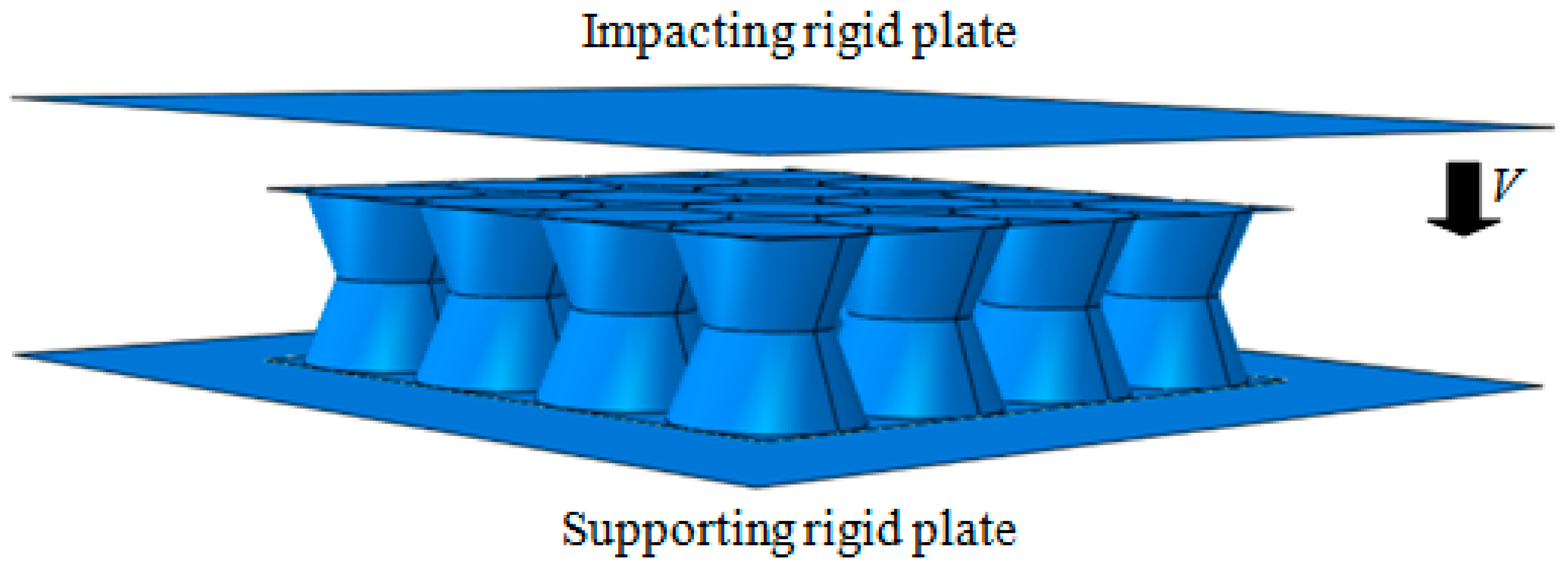
2. Computational Model
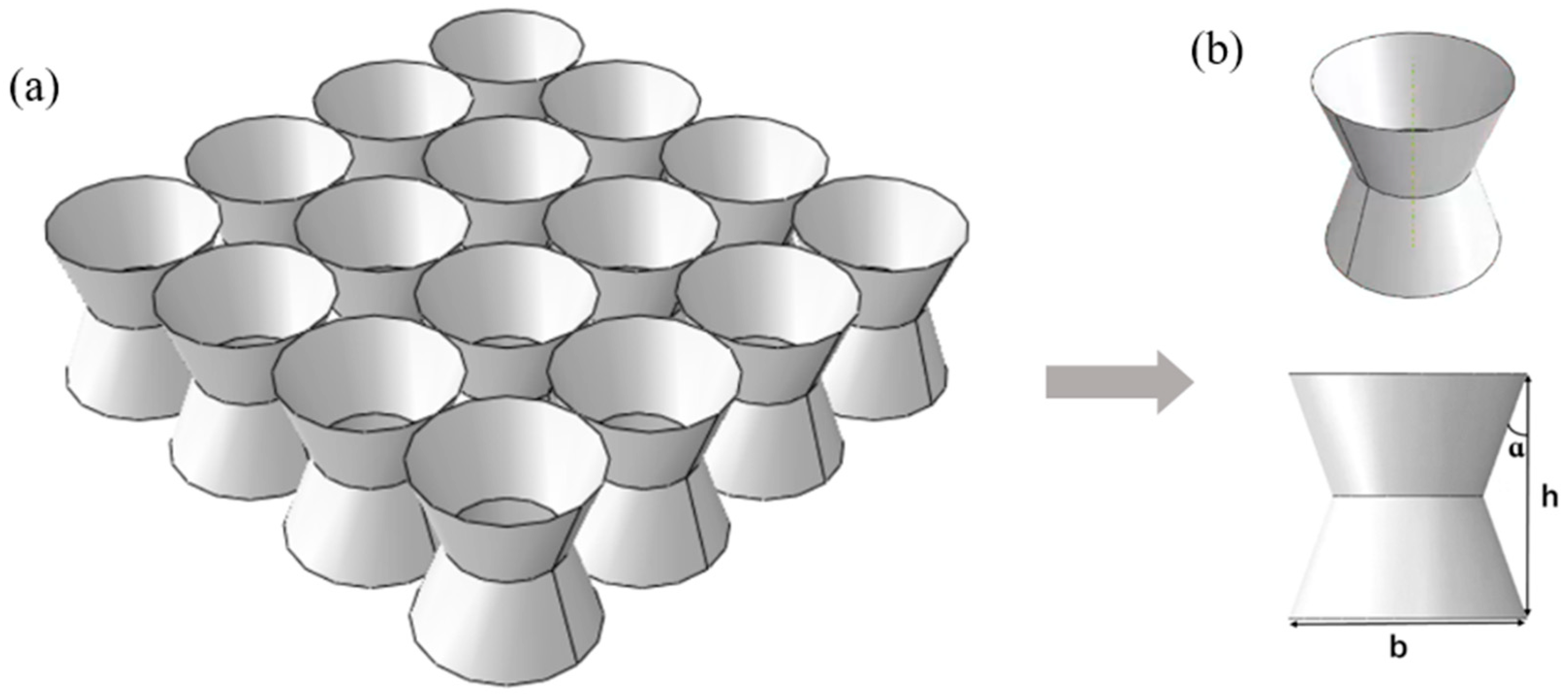
2.1. Finite Element Model
2.2. Relative Density
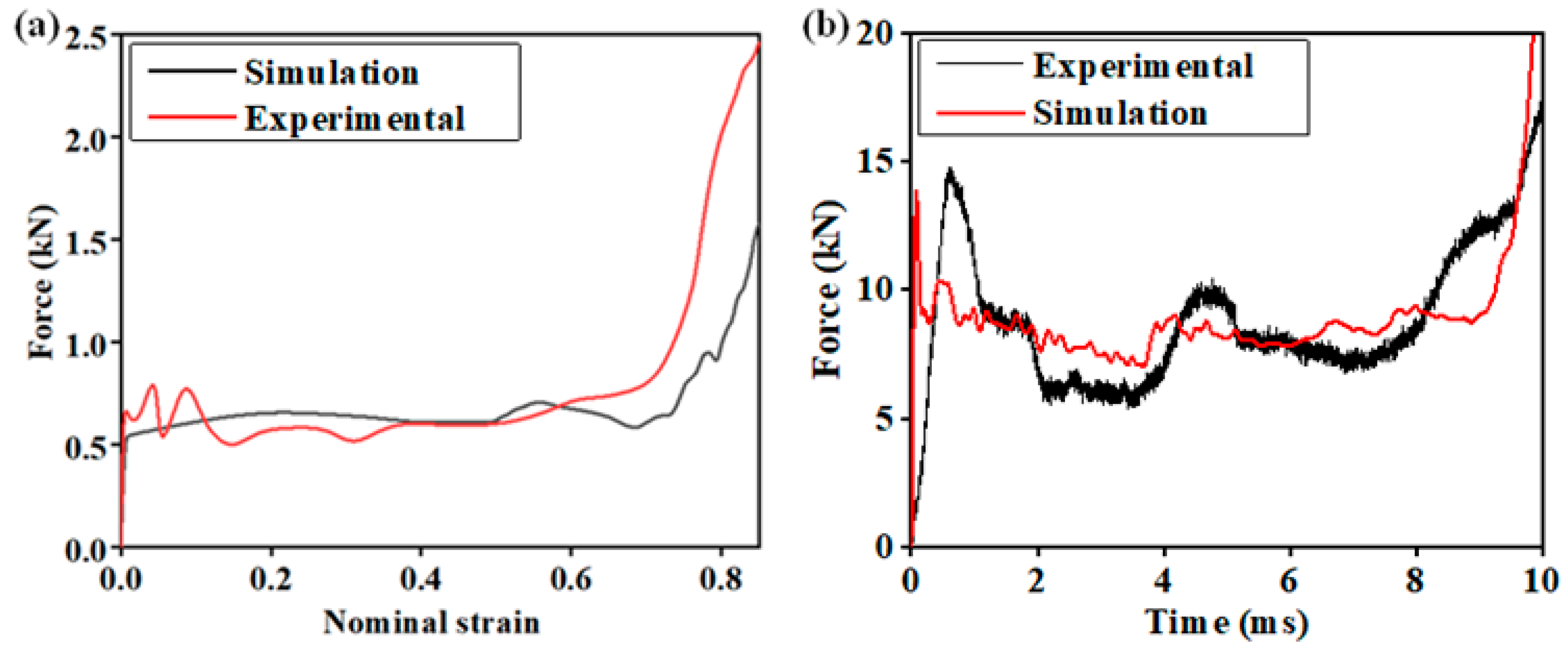
2.3. Validation of Finite Element Model
3. Results and Discussion
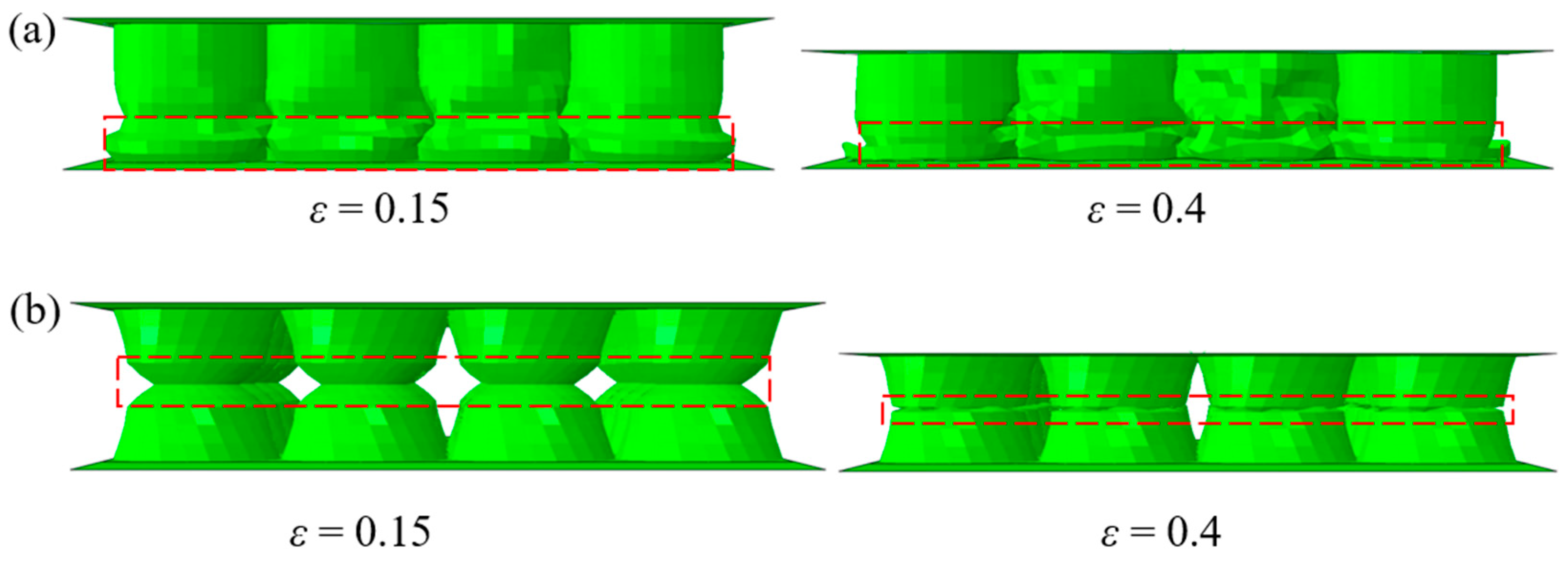
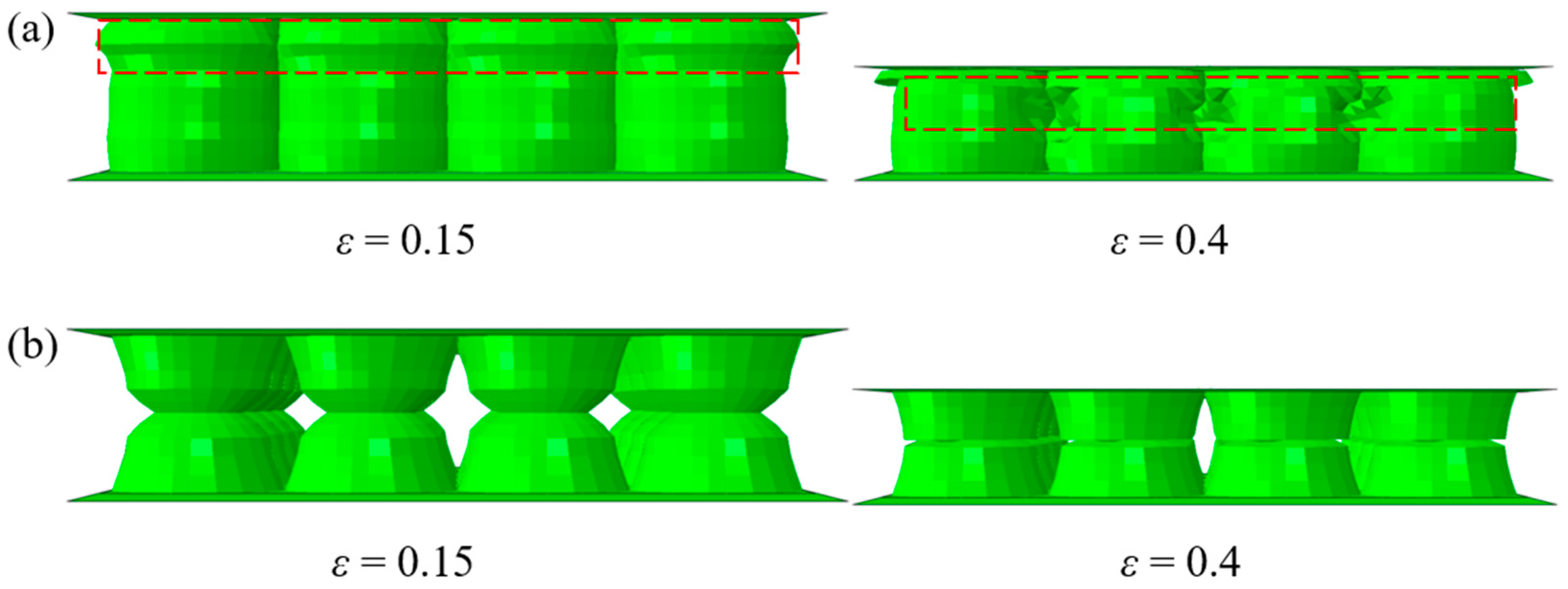
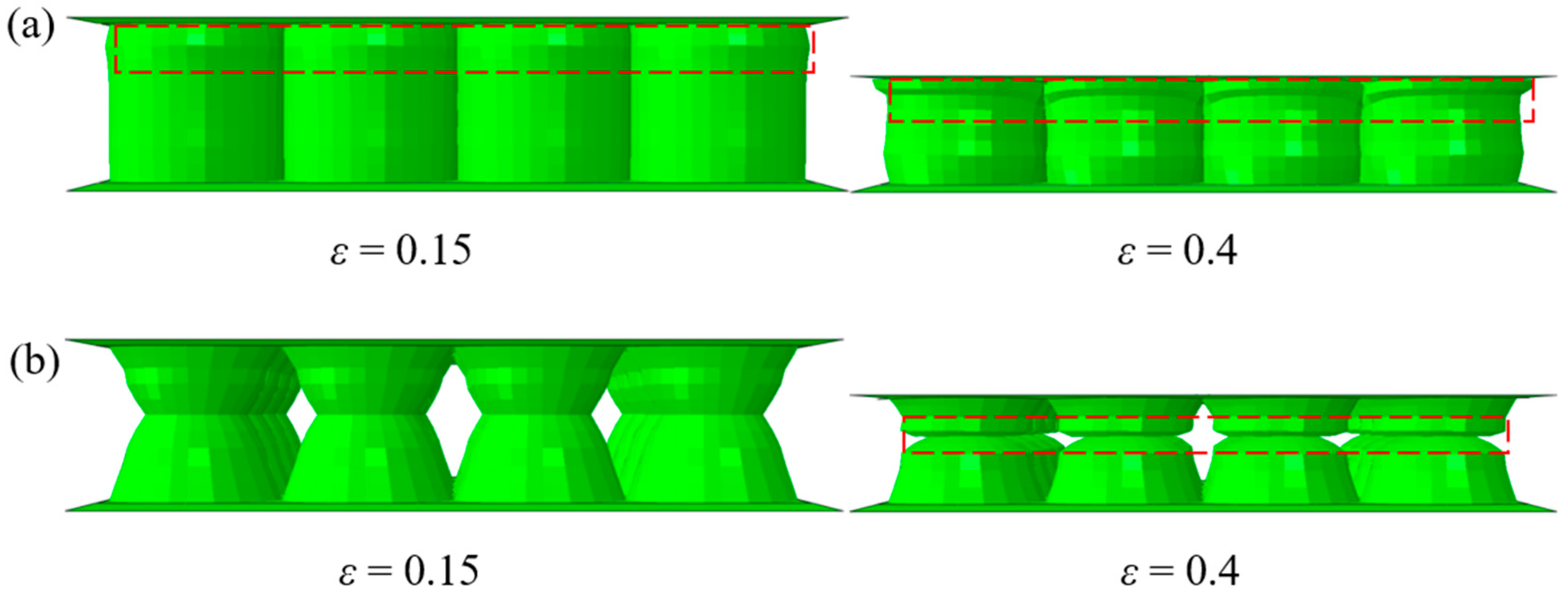
3.1. Deformation Modes
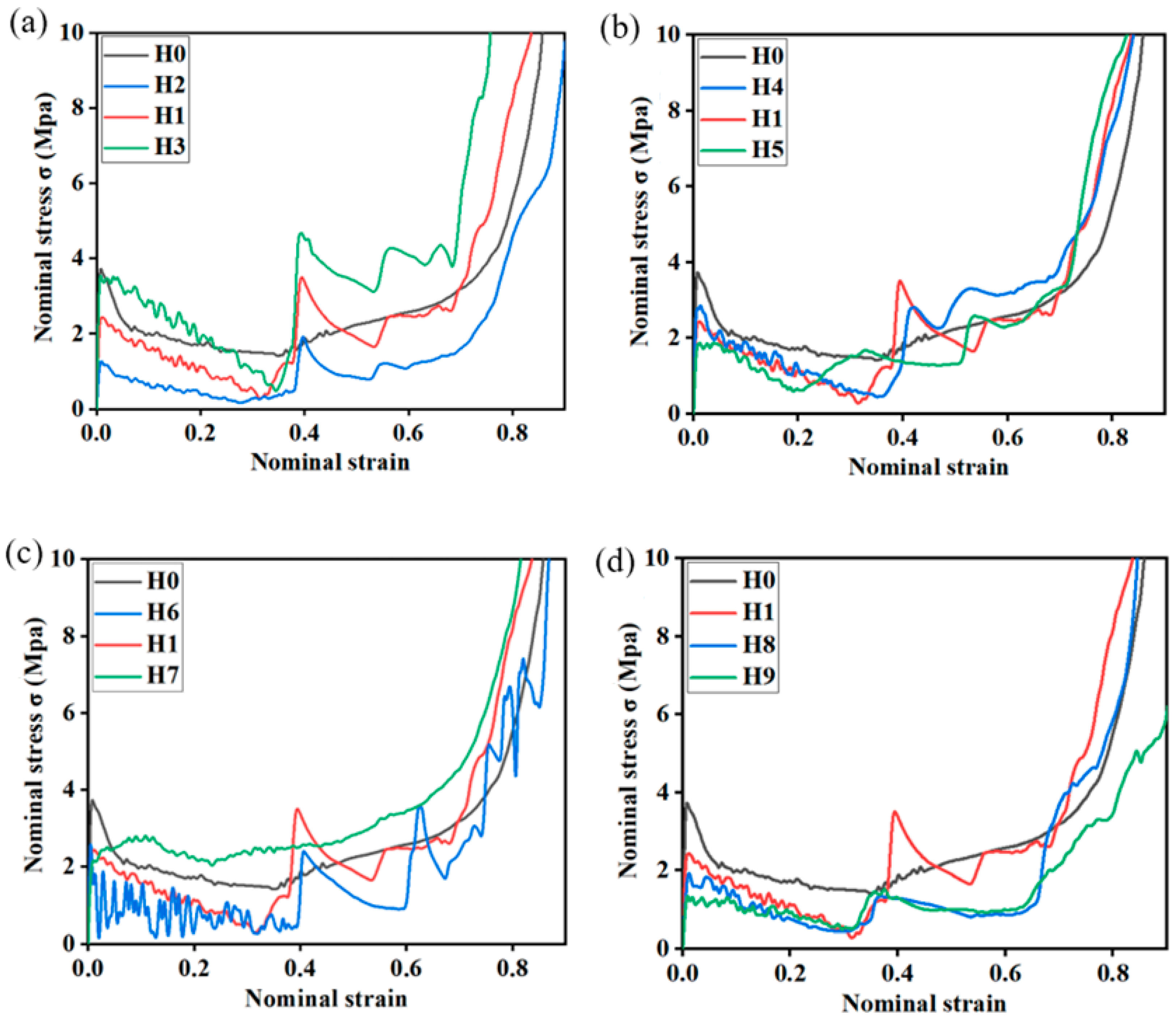
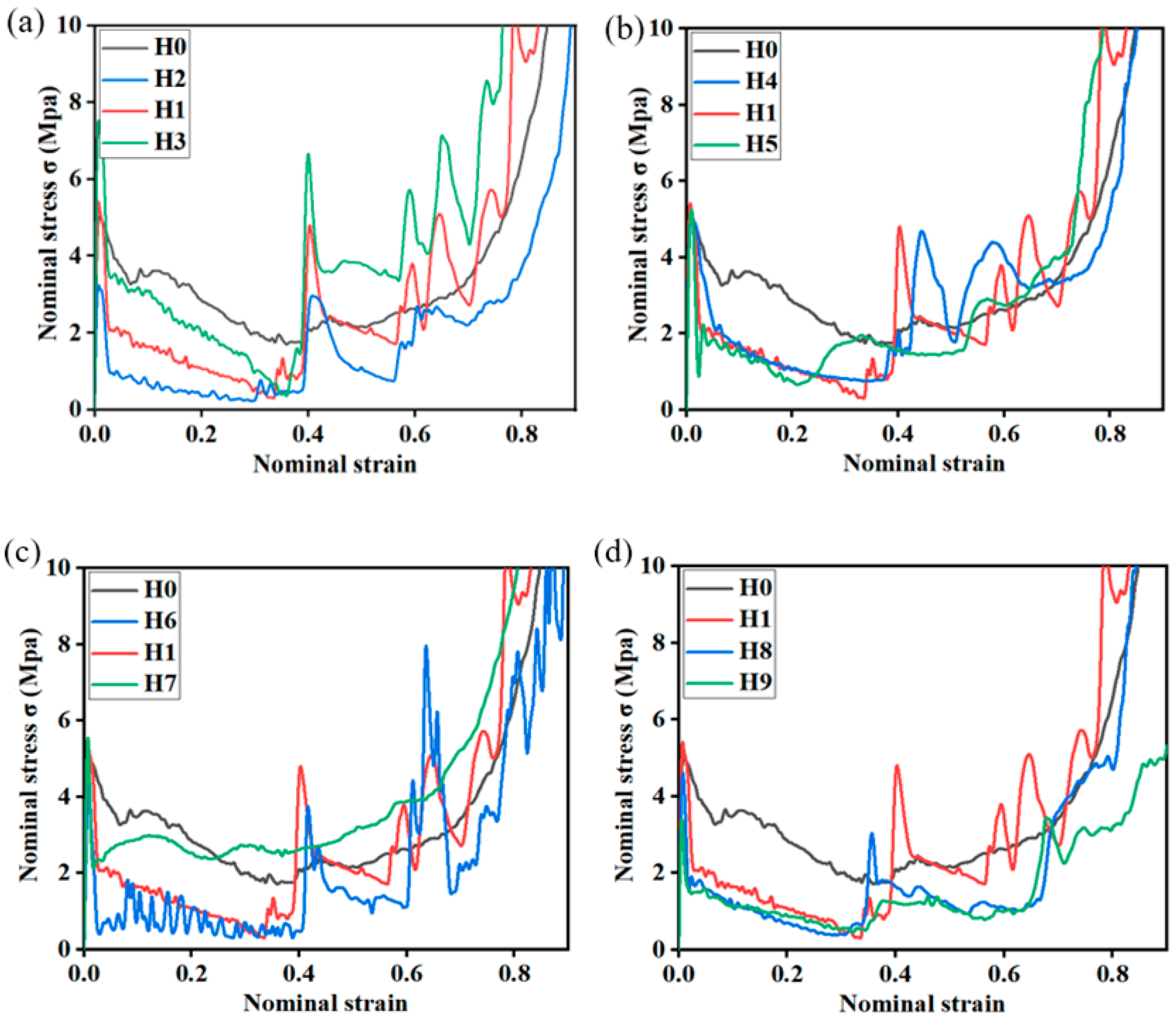
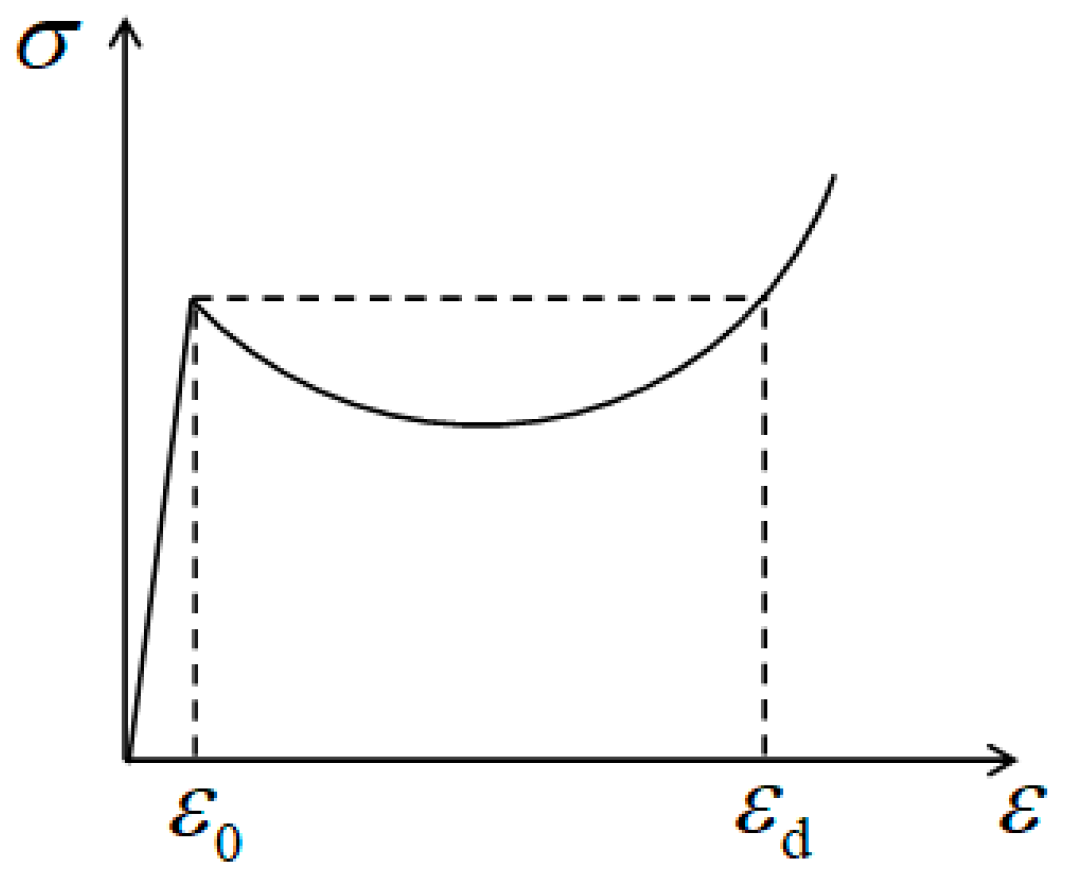
3.2. Nominal Stress–Strain Curve
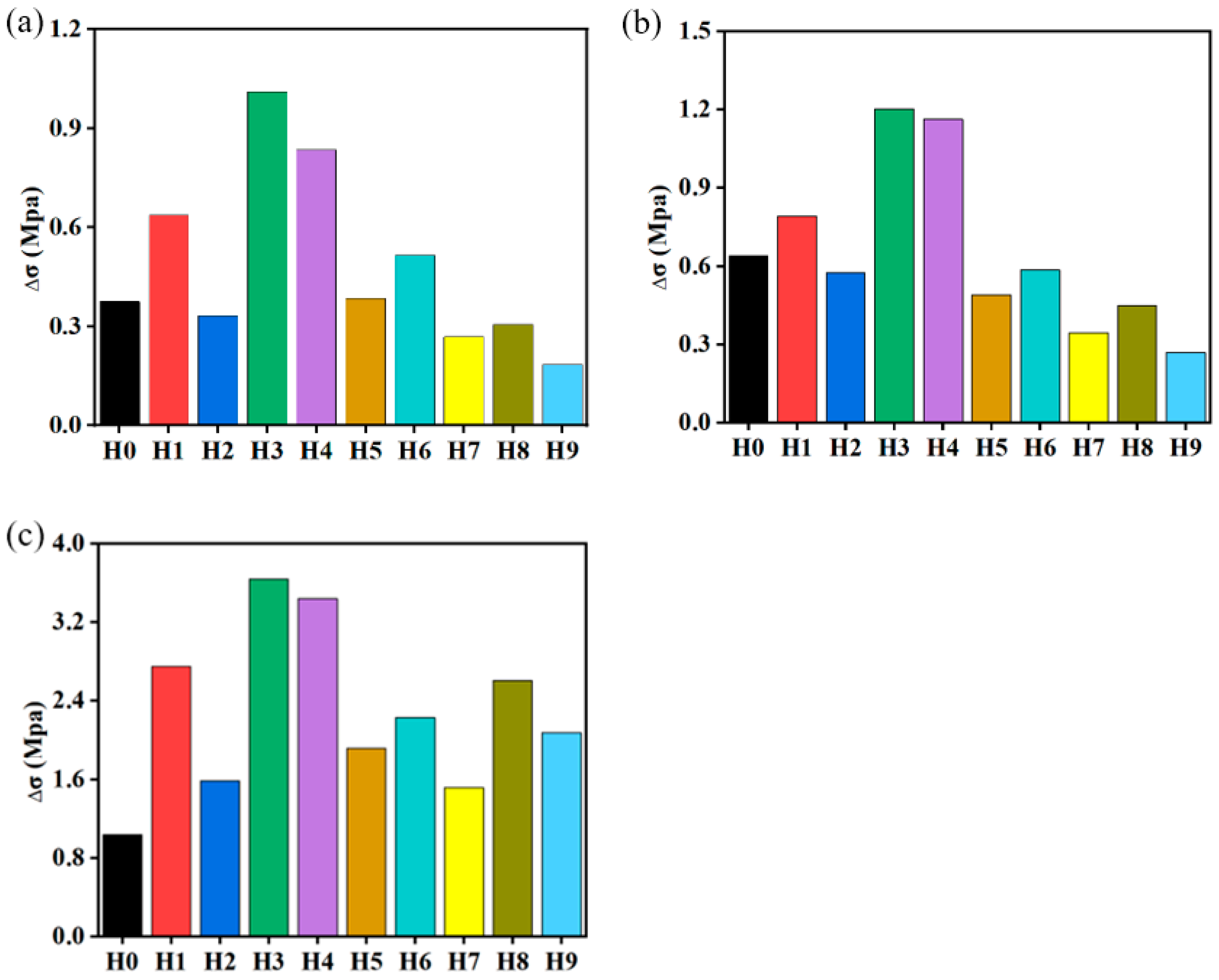
3.3. Load Uniformity
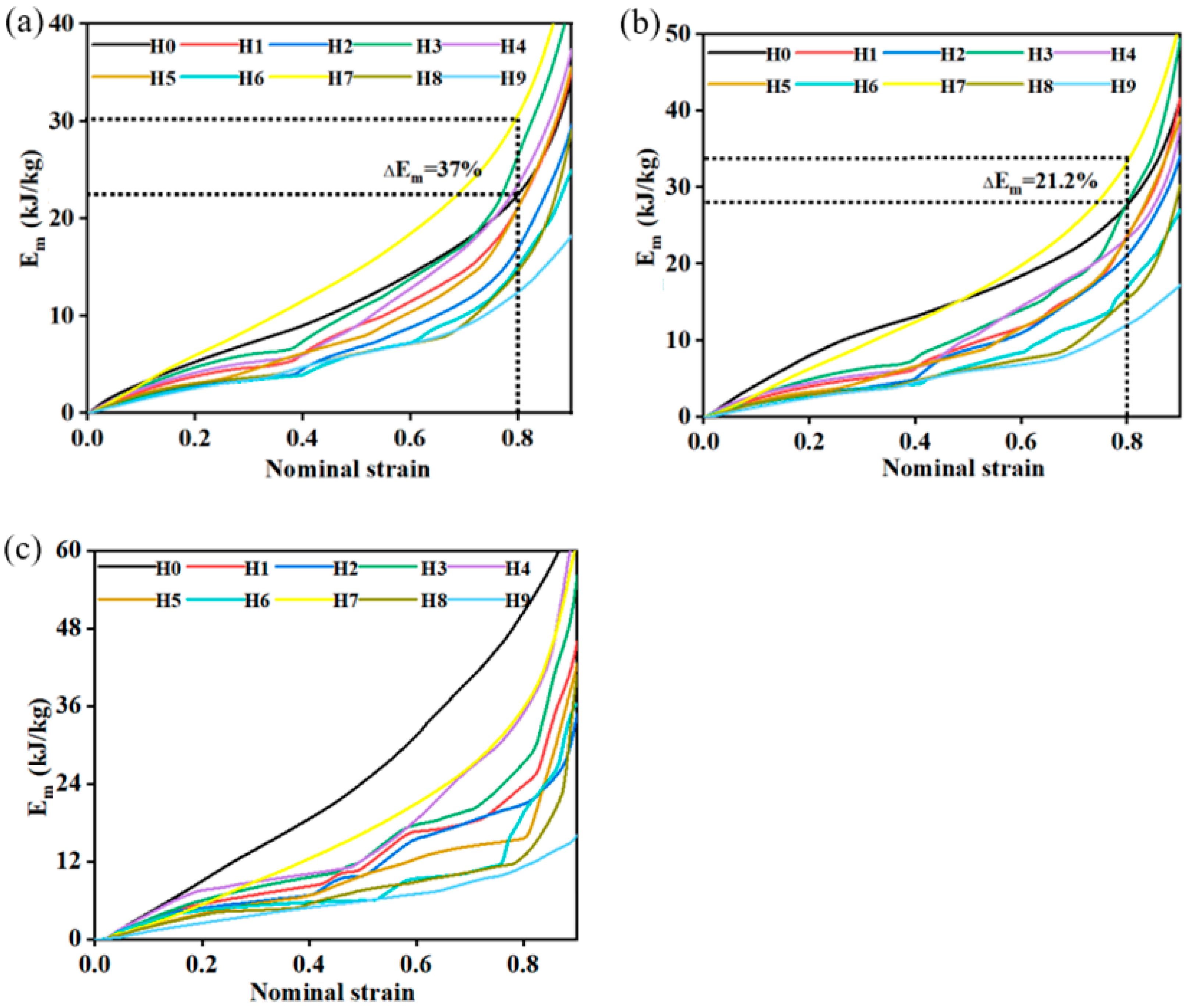
3.4. Energy Absorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.M.; Sun, Y.L. Dynamic compressive behavior of cellular materials: A review of phenomenon, mechanism and modeling. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2018, 112, 74–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Jiang, F.; Yang, S. Advanced honeycomb designs for improving mechanical properties: A review. Compos. Part B 2021, 227, 109393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, M.P.; Pitchaimani, J.; Gangadharan, K.V.; Lenin Babu, M.C. Influence of nature of core on vibro acoustic behavior of sandwich aerospace structures. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 56, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Janowski, G.M.; Vaidya, U.K.; Husman, G. Thermoplastic sandwich structure design and manufacturing for the body panel of mass transit vehicle. Compos. Struct. 2007, 80, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, J.X.; Ruan, D. Review of sandwich structures under impact loadings: Experimental, numerical and theoretical analysis. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 196, 111541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, A.G.; Langseth, M.; Hopperstad, O.S. Static and dynamic crushing of circular aluminium extrusions with aluminium foam filler. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2000, 24, 475–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, G.D.; Zhang, H. Numerical investigations on a new type of energy-absorbing structure based on free inversion of tubes. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2009, 51, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.C. In-plane crushing behavior and energy absorption design of composite honeycombs. Acta Mech. Sin. 2018, 34, 1108–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, G.J.; Townend, D.J.; Cater, S.R.; Pearce, B.P. The role of stress waves in thoracic visceral injury from blast loading: Modification of stress transmission by foams and high-density materials. J. Biomech. 1991, 24, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.P.; Poh, L.H. Auxetic hexachiral structures with wavy ligaments for large elasto-plastic deformation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 055001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, P.; Huang, G.; Feng, S.; Shen, C.; Han, B.; Zhang, X.; Jin, F.; Xu, F.; et al. Bioinspired engineering of honeycomb structure—Using nature to inspire human innovation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 74, 332–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, D.; Lu, G.; Wang, B.; Yu, T.X. In-plane dynamic crushing of honeycombs—A finite element study. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2003, 28, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.J.; Reid, S.R.; Harrigan, J.J.; Zou, Z.; Li, S. Dynamic compressive strength properties of aluminium foams. Part I—Experimental data and observations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2005, 53, 2174–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.J.; Reid, S.R.; Harrigan, J.J.; Zou, Z.; Li, S. Dynamic compressive strength properties of aluminium foams. Part II—‘Shock’ theory and comparison with experimental data and numerical models. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2005, 53, 2206–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, S.Z.; Wu, X.N.; Wang, J.Y.; Han, Y.S.; Zhang, X.C. Mechanical characteristics of a novel rotating star-rhombic auxetic structure with multi-plateau stages. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 191, 111081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.F.; Zheng, Z.J.; Yu, J.L. Dynamic crushing of 2D cellular structures: Local strain field and shock wave velocity. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2013, 57, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Zhou, Z.W.; Wang, Z.H.; Wu, G.Y.; Shu, X.F. Experimental study on the effects of specimen in-plane size on the mechanical behavior of aluminum hexagonal honeycombs. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 635, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Remennikov, A.; Pei, L.; Yang, S.; Yu, Z.; Ngo, T. Impact and close-in blast response of auxetic honeycomb-coredsandwich panels: Experimental tests and numerical simulations. Compos. Struct. 2017, 180, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapaka, S.D.; Pandey, M.; Annabattula, R.K. Dynamic compressive behaviour of auxetic and non-auxetic hexagonal honeycombs with entrapped gas. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2020, 146, 103718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Deng, J.; Liu, K.; Tao, Y. Hybrid hierarchical square honeycomb with widely tailorable effective in-plane elastic modulus. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 171, 108816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, A.H.; Dunand, D.C. Density-Graded Cellular Aluminum. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Smith, W.; Jackson, J.; Moran, B.; Cui, H.; Chen, D.; Ye, J.; Fang, N.; Rodriguez, N.; Weisgraber, T.; et al. Multiscale metallic metamaterials. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.C.; Liu, N.N.; An, C.C.; Wu, H.X.; Li, N.; Hao, K.M. Dynamic crushing behaviors and enhanced energy absorption of bio-inspired hierarchical honeycombs with different tipologies. Def. Technol. 2023, 22, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhao, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, G.H. A novel star auxetic honeycomb with enhanced in-plane crushing strength. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 149, 106623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Shim, X.P.W.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. In-plane compression of 3D-printed self-similar hierarchical honeycombs—Static and dynamic analysis. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 157, 106990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.C.; Zou, M.; Liu, G.M.; Song, J.F.; Wang, H.X. Experimental study on energy absorption of bionic tubes inspired by bamboo structures under axial crushing. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2018, 115, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajdari, A.; Babaee, S.; Vaziri, A. Mechanical properties and energy absorption of heterogeneous and functionally graded cellular structures. Procedia Eng. 2011, 10, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.J.; Yu, T.X.; Lu, G. Double shock mode in graded cellular rod under impact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; An, L.Q.; Ding, H.M. Dynamic crushing behavior and energy absorption of honeycombs with density gradient. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2014, 16, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.X.; Chen, C.Q. Impact resistance of uniform and functionally graded auxetic double arrowhead honeycombs. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 83, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.Y. Predictions of Young’s modulus and negative Poisson’s ratio of auxetic foams. Phys. Status Solidi B-Basic Solid State Phys. 2011, 248, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawoto, Y. Seeing auxetic materials from the mechanics point of view: A structural review on the negative Poisson’s ratio. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 58, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.D.; Yuan, H.; Du, J.L.; Wu, X.W.; Zhang, J.X. Plastic behavior of foam-filled negative Poisson’s ratio beams. Eng. Struct. 2022, 273, 115092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Ma, L. Designing hierarchical metamaterials by topology analysis with tailored Poisson’s ratio and Young’s modulus. Compos. Struct. 2019, 214, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papka, S.D.; Kyriakides, S. Biaxial crushing of honeycombs—Part I: Experiments. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1999, 36, 4367–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papka, S.D.; Kyriakides, S. In-plane biaxial crushing of honeycombs—Part II: Analysis. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1999, 36, 4397–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Wass, A.M. Compressive response of circular cell polycarbonate honeycombs under in-plane biaxial static and dynamic loading. Part I: Experiments. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2002, 27, 729–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Wass, A.M. Compressive response of circular cell polycarbonate honeycombs under inplane biaxial static and dynamic loading—Part II: Simulations. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2002, 27, 1015–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, J.L. A novel fabrication method and mechanical behavior of all-composite tetrahedral truss core sandwich panel. Compos. Part A 2017, 102, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mines, R.A.W.; Tsopanos, S.; Shen, Y.; Hasan, R.; McKown, S.T. Drop weight impact behaviour of sandwich panels with metallic micro lattice cores. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2013, 60, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.A.A. Collapsible impact energy absorbers: An overview. Thin-Walled Struct. 2001, 39, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.W.; Lyu, M.Q.; Li, M.; Cai, J.G. In-plane dynamics crushing of a reinforced honeycomb with enhanced energy absorption. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2024, 183, 104807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wen, Z. Experimental and numerical studies on the crush resistance of aluminum honeycombs with various cell configurations. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2014, 66, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.X.; Qu, J.; Wu, L.Z. Experimental and numerical study on impact behavior of hourglass lattice sandwich structures with gradients. Materials 2023, 16, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.M.; Magkiriadis, I.; Harrigan, J.J. Compressive Strain at the Onset of Densification of Cellular Solids. J. Cell. Plast. 2006, 42, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooistra, G.W.; Deshpande, V.S.; Wadley, H.N.G. Compressive behavior of age hardenable tetrahedral lattice truss structures made from aluminum. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4229–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model | n | b (mm) | h (mm) | t (mm) | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H0 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 0.1 | 0° |
| H1 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 0.122 | 20° |
| H2 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 0.072 | 20° |
| H3 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 0.172 | 20° |
| H4 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 0.109 | 10° |
| H5 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 0.141 | 30° |
| H6 | 1 | 20 | 10 | 0.22 | 20° |
| H7 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 0.075 | 20° |
| H8 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 0.11 | 20° |
| H9 | 3 | 10 | 3.3 | 0.106 | 20° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Wang, K.; Cao, L.; Guo, P.; Qin, J.; Wu, H. Study on the Dynamic Crushing Behaviors of Hourglass Honeycomb Sandwich Panels. Aerospace 2024, 11, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11110881
Chen X, Wang K, Cao L, Guo P, Qin J, Wu H. Study on the Dynamic Crushing Behaviors of Hourglass Honeycomb Sandwich Panels. Aerospace. 2024; 11(11):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11110881
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xinhai, Kai Wang, Lu Cao, Pengyu Guo, Jiangyi Qin, and Hexiang Wu. 2024. "Study on the Dynamic Crushing Behaviors of Hourglass Honeycomb Sandwich Panels" Aerospace 11, no. 11: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11110881
APA StyleChen, X., Wang, K., Cao, L., Guo, P., Qin, J., & Wu, H. (2024). Study on the Dynamic Crushing Behaviors of Hourglass Honeycomb Sandwich Panels. Aerospace, 11(11), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11110881






