Integrated Guidance and Control for Collision Course Stabilization of Dual-Controlled Interceptors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Statement
2.1. Engagement Kinematics
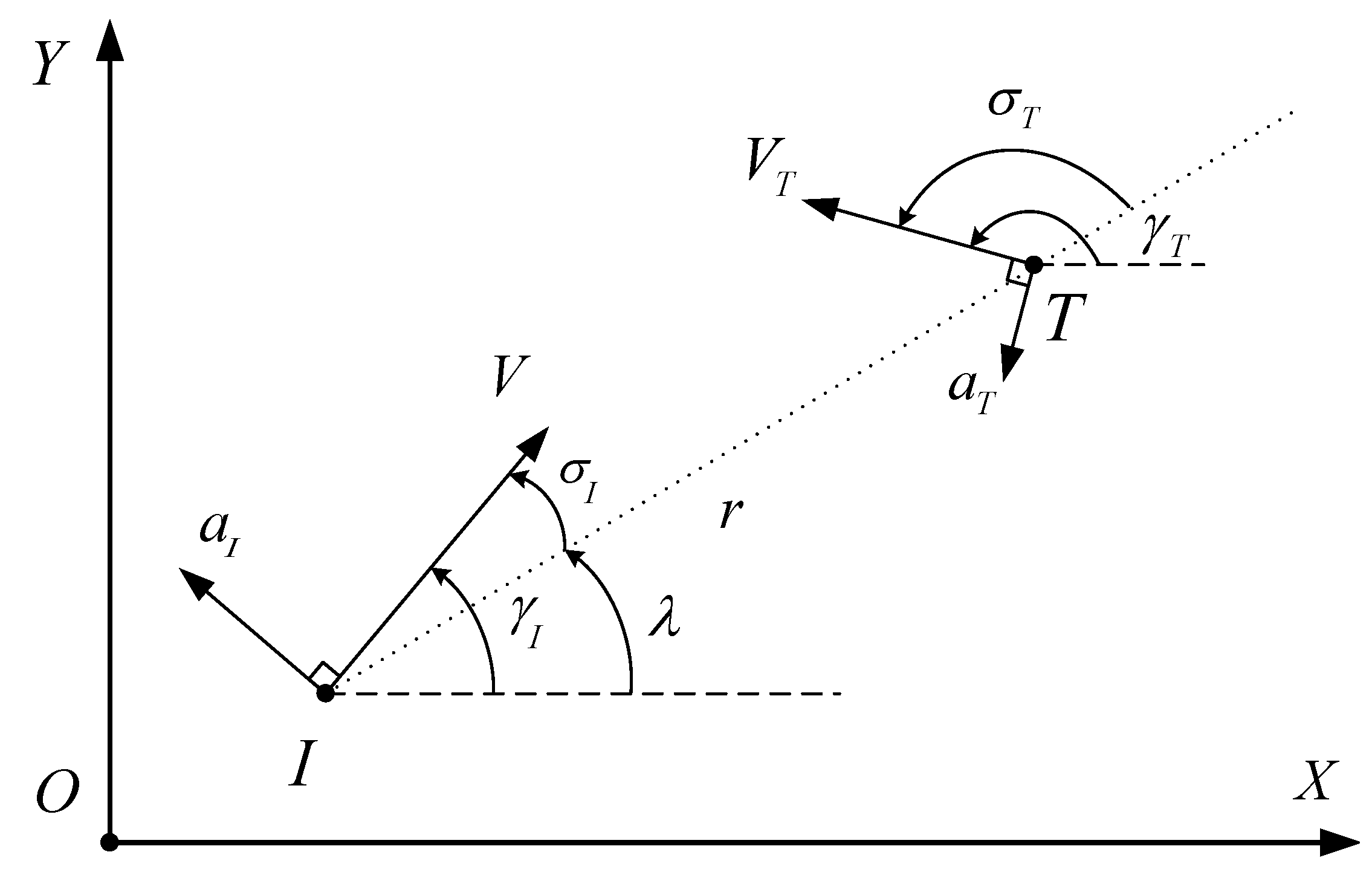
2.2. Interceptor Dynamics
2.3. Integrated Dynamics
3. Integration of Guidance and Autopilot Loops
3.1. Sliding Manifolds
3.2. Design of the Integrated Controller
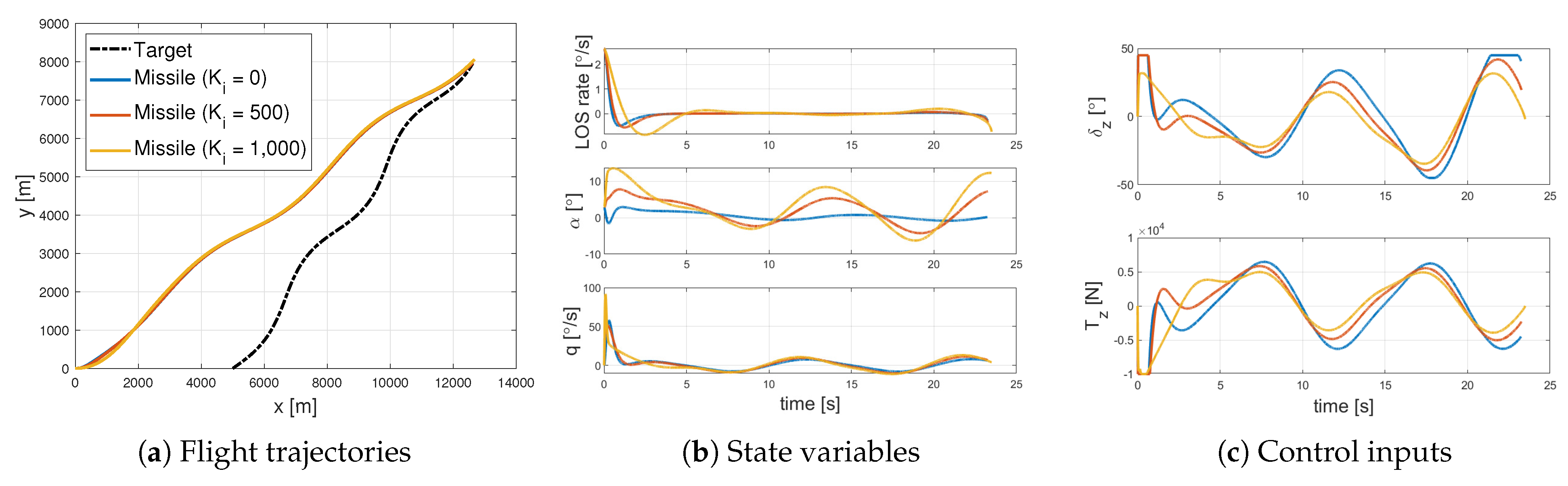
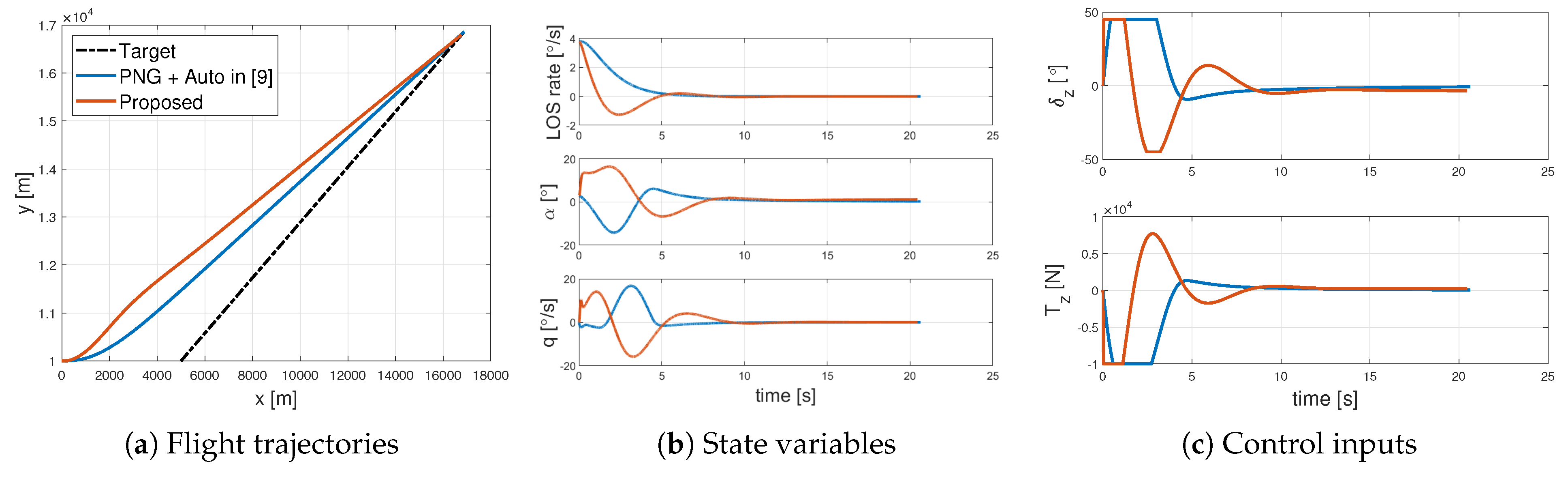
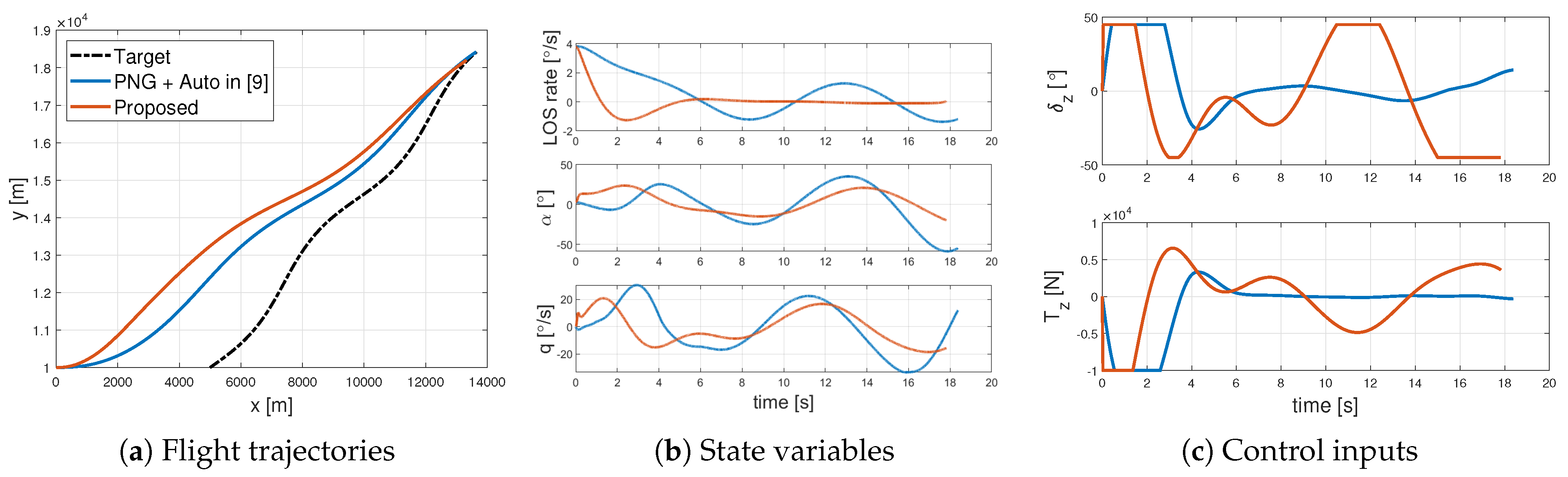
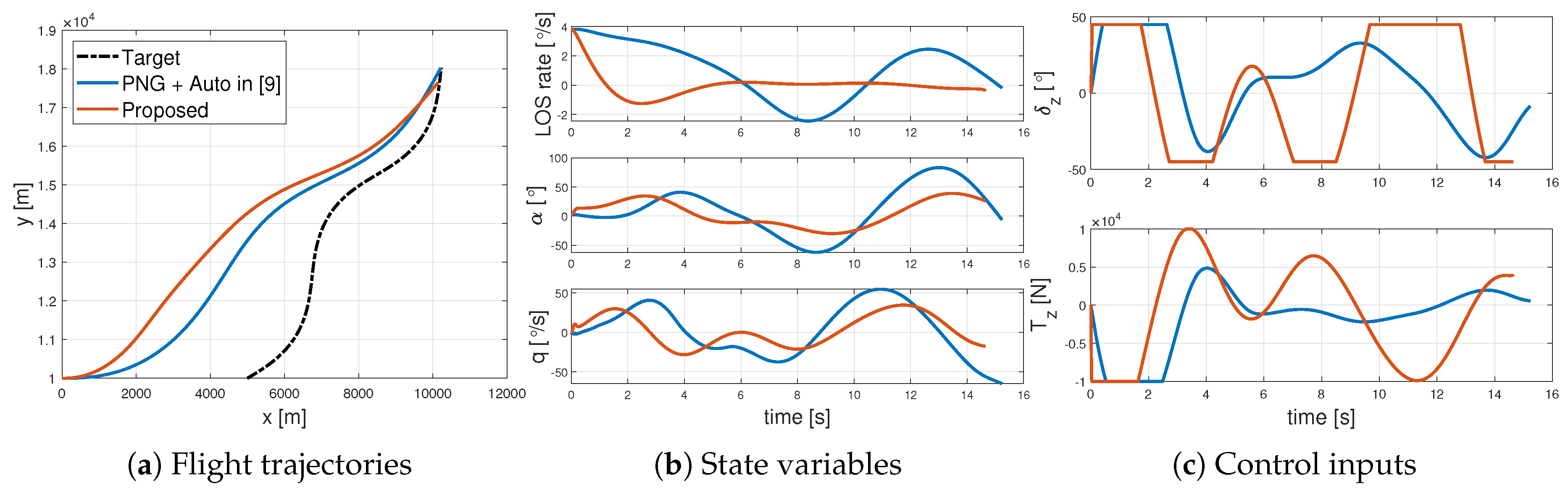
4. Numerical Simulation
4.1. Performance Analysis
4.2. Performance Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siouris, G.M. Missile Guidance and Control Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, P.; Yousefpor, M. Design of nonlinear autopilots for high angle of attack missiles. In Proceedings of the Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 29–31 July 1996; p. 3913. [Google Scholar]
- Mracek, C.; Ridgely, D. Missile longitudinal autopilots: Connections between optimal control and classical topologies. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–18 August 2005; p. 6381. [Google Scholar]
- Bruyere, L.; Tsourdos, A.; White, B. Robust augmented lateral acceleration flight control design for a quasi-linear parameter-varying missile. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2005, 219, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Jun, B.E.; Lee, J.I. Connections between linear and nonlinear missile autopilots via three-loop topology. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2016, 39, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thukral, A.; Innocenti, M. A sliding mode missile pitch autopilot synthesis for high angle of attack maneuvering. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 1998, 6, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirokawa, R.; Sato, K.; Manabe, S. Autopilot design for a missile with reaction-jet using coefficient diagram method. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit, Montreal, QC, Canada, 6–9 August 2001; p. 4162. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgely, D.; Lee, Y.; Fanciullo, T. Dual aero/propulsive missile control-optimal control and control allocation. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit, Keystone, CO, USA, 21–24 August 2006; p. 6570. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Shao, C. Dynamics and autopilot design for endoatmospheric interceptors with dual control systems. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2009, 13, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cho, D.; Kim, H.J. Force and moment blending control for fast response of agile dual missiles. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, C.K.; Cho, H.; Tahk, M.J. Optimal guidance laws with terminal impact angle constraint. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2005, 28, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.H.; Speyer, J.L.; Lianos, D. Optimal intercept missile guidance strategies with autopilot lag. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2010, 33, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, T.; Idan, M.; Golan, O.M. Sliding-mode control for integrated missile autopilot guidance. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2006, 29, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idan, M.; Shima, T.; Golan, O.M. Integrated sliding mode autopilot-guidance for dual-control missiles. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2007, 30, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaddi, S.; Menon, P.K.; Ohlmeyer, E.J. Numerical state-dependent Riccati equation approach for missile integrated guidance control. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2009, 32, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, H.M.; Abido, M. Designing integrated guidance law for aerodynamic missiles by hybrid multi-objective evolutionary algorithm and tabu search. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2010, 14, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J. Partial integrated missile guidance and control with finite time convergence. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2013, 36, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, B.; Mate, N.; Talole, S. Continuous-time predictive control-based integrated guidance and control. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2017, 40, 1579–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Shin, J. Integrated Autopilot Guidance Based on Zero-Effort-Miss Formulation for Tail-Controlled Missiles. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Kim, H.J. Integrated guidance and control of dual missiles considering trade-off between input usage and response speed. In Proceedings of the 2013 13th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS 2013), Gwangju, Republic of Korea, 20–23 October 2013; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
| Parameters | Interceptor | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Initial position (km) | ||
| Initial speed (Mach) | 2 | |
| Initial flight path angle () | 0 | 30 |
| Maneuvering acceleration (g) | - | |
| Parameters for dynamics | [9] | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-G.; Beck, D. Integrated Guidance and Control for Collision Course Stabilization of Dual-Controlled Interceptors. Aerospace 2024, 11, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11010009
Kim H-G, Beck D. Integrated Guidance and Control for Collision Course Stabilization of Dual-Controlled Interceptors. Aerospace. 2024; 11(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyeong-Geun, and Donghyun Beck. 2024. "Integrated Guidance and Control for Collision Course Stabilization of Dual-Controlled Interceptors" Aerospace 11, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11010009
APA StyleKim, H.-G., & Beck, D. (2024). Integrated Guidance and Control for Collision Course Stabilization of Dual-Controlled Interceptors. Aerospace, 11(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11010009







