Abstract
Satellites have been developed and operated for various purposes. The global satellite market is growing rapidly as the number of satellites and their mission diversity increase. Satellites revolve around the Earth to perform missions and communicate with ground stations repeatedly and sequentially. However, because satellites are orbiting the Earth, there is a limited time window for missions to a specific area and communication with ground stations. Thus, in an environment where multiple satellites and multiple ground stations (MS-MGs) are operated, scheduling missions and communications to maximize the utilization of satellites is a complex problem. For the MS-MG scheduling problem, this study proposes a mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) model to assign time windows for missions and communications with ground stations to individual satellites. The MILP model is based on the concept of a time-space network and includes constraints reflecting on the space mission environment of satellites. The objective function and constraints of the MILP model were validated through numerical experiments based on actual data from Korean satellites.
1. Introduction
Since the Soviet Union’s first satellite, Sputnik 1, in 1957, with the advancement of science and technology, satellites have been developed and operated for various purposes, such as communication, military, and science. Based on a growth factor of increasing applications for satellite data in the development of smart cities and connected vehicles, Future Market Insights [1] estimates that the commercial satellite imaging market is expected to reach USD 12.4 billion in 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.9% from 2022. Morgan Stanley [2] reported that the global space industry is currently worth USD 350 billion and is predicted to exceed >USD 1 trillion by 2040, as shown in Figure 1. The satellite communication sector is forecasted to account for 15–50% of this, i.e., >USD 0.5 trillion. While organizations project different levels of growth for the global satellite market, they all agree that the market is poised for rapid growth. An efficient satellite operation plan is needed to respond to and facilitate this growth.
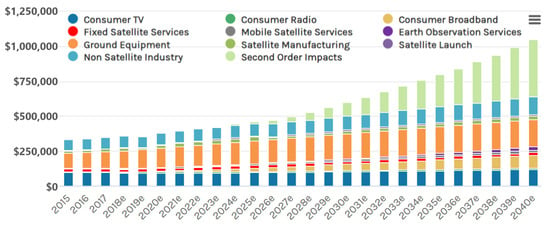
Figure 1.
Growth trends of the global space economy($t) [2].
As the number of satellites increase worldwide with the development of multipurpose satellites, next-generation medium-sized satellites, and ultra-small satellite constellations, research on mission planning systems to operate multiple satellites efficiently and effectively has been actively conducted. The satellites revolve around Earth to perform missions and communicate with ground stations repeatedly and sequentially. However, the time window when a satellite can perform missions or communicate with a specific Earth region is limited because of the revolution. Thus, for efficient mission planning, it is necessary to simultaneously plan the mission and communication schedule for satellites. However, most studies have focused on either mission or communication planning. Issues in satellite communication planning are classified as single satellite and single ground station (SS-SG), single satellite and multiple ground stations (SS-MGs), multiple satellites and single ground station (MS-SG), and multiple satellites and multiple ground stations (MS-MGs). Studies on SS-SG were extensively conducted in the early stages of satellite development and operation and are not mentioned here because they deviated from recent research trends. In the SS-MG case, Sun and Xhafa [3] solved the scheduling problem of ground stations and spacecraft using a genetic algorithm (GA). Spangelo et al. [4] studied a communication scheduling optimization model using mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) with consideration of the limited observation capability of small satellites. Extensive research has been conducted on the communication plan between satellites and ground stations, and it has developed with a focus on the MS-MG rather than the SS-SG case.
Recently, as many countries operate multiple satellites and satellite constellations, studies on the MS-MG environment have been actively conducted. In research on scheduling communications for the MS-MG, Vazquez et al. [5] have suggested the integer linear programming (ILP) model for an antenna allocation problem considering preferred assignments and priority, and Wang et al. [6] have proposed an ILP model considering the uncertainty of cloud coverage. Corrao et al. [7] have presented an optimization strategy for assigning communication opportunities by integrating GA, graph theory, and linear programming. Xhafa et al. [8] have suggested a GA for ground-station allocation problems to maximize the number of communications, communication time, and communication ground stations and minimize the number of communication collisions between satellites. When the visibilities of satellites conflict with the same ground station, Lee et al. [9] and Lee et al. [10] have introduced a GA with a greedy method that can select a satellite while considering various factors such as priority, urgency, and profit. Luo et al. [11] have suggested a heuristic algorithm combining a pre-scheduling strategy that places high-profit schedules first and a rescheduling strategy that coordinates arranged and non-placed schedules. Jeong and Kim [12] have presented an MILP model for planning communications to minimize costs, and Pachler et al. [13] have proposed a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm to determine when to start and stop serving a particular user.
In research on planning missions for the MS-MG, Sarkheyli et al. [14] have modeled a scheduling problem of tasks for low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites using the graph coloring theory and suggested a tabu search (TS) algorithm for searching the solution to perform the most of the requested tasks considering the priority of each task and constraints for temporal and resource. Kim and Chang [15,16] have advanced a GA for scheduling missions of a constellation of satellites equipped with synthetic aperture radar (SAR) payload to enhance observation efficiency by minimizing the system response time. Chu et al. [17] have introduced a mission scheduling model in which low-resolution satellites recognize the following targets and assign missions to high-resolution satellites, while high-resolution satellites perform target recognition using the anytime branch and bound (B&B) algorithm. Mok et al. [18] have suggested a heuristic method that maximizes imaging ability by considering pitch maneuverability and applied reverse-order observation. He et al. [19] have proposed a hierarchical scheduling method consisting of pre-assignment, rough scheduling, and fine scheduling based on an ant colony optimization (ACO) algorithm to cope with environmental uncertainties such as cloud changes. Mitrovic-Minic et al. [20] have introduced an MILP model that applies constraints, e.g., energy, temperature, and memory storage, to multi-satellite/cluster and agile/non-agile satellites. Chen et al. [21] have suggested an MILP model to optimize mission performance by considering the types of satellite resources, such as cameras and sensors, setup time based on the swing angle, and visibility conflict. Barkaoui and Berger [22] have proposed a hybrid GA based on a vehicle routing problem with time windows (VRPTWs) to maximize the sum of mission benefits. Wang et al. [23] have employed a hybrid algorithm combining column generation (CG) and simulated annealing (SA) algorithms to maximize observational gains under cloud coverage uncertainty. Zhibo et al. [24] have introduced an individual reconfiguration-based integer-coding GA to reduce the computational cost and improve the scheduling of satellites. Lu et al. [25] have proposed a PSO algorithm to optimize the imaging sequence by clustering the mission area, considering that imaging is possible in arbitrary directions using the super-agile Earth observation satellite (SA-EOS). Ou et al. [26] have suggested a hybrid scheduling algorithm combining a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) and heuristic methods. In the algorithm, the DRL method assigns individual tasks on alternative antennas, and then the heuristic method determines the execution start and end time of assigned tasks on each antenna based on task profit sorting. This procedure is iteratively performed. Wang et al. [27] addressed an unrelated parallel machine scheduling problem with multiple time windows applied to a scheduling problem for operating Earth observation satellites. They have proposed a generic MILP model based on the non-immediate precedence of jobs and presented a bidirectional rolling horizon preprocessing algorithm for time windows to reduce the problem size.
In research on establishing the consolidated schedule of missions and communications in the MS-MG environment, Wang et al. [28] have introduced a nonlinear programming model and a heuristic algorithm for managing the schedule of a satellite constellation for disaster warning and damage environment analysis. They have prioritized observation tasks over data downloads, and the download policy for onboard memory is ‘first observed, first downloaded.’ Although this idea could simplify the computations for scheduling optimization, it could also reduce the efficiency of the schedule due to improper onboard memory capacity management and ambiguity in the reception plan for observation data. Lee et al. [29] have suggested the new problem of ensuring that satellite operations are scheduled in compliance with critical image mission sequences, command uplink → image capturing → image downlink, and proposed a GA to search the near-optimal schedule for maximizing the sum of assigned tasks’ profits. It is assumed that the profit of each requested task is pre-determined. Chen et al. [30] have proposed an ILP model for establishing the consolidated schedule of missions and a local search heuristic algorithm to solve a large-sized problem. However, the ILP model has focused on scheduling satellites and does not consider scheduling ground stations. It means that visibility conflicts between satellites for downloading data at a ground station could not confirmed. Chang et al. [31] proposed a multi-objective optimization model that minimizes data loss and energy consumption for an integrated scheduling problem involving image collection and transmission. Hu et al. [32] studied a branch and price algorithm that optimizes the imaging and downloading of Earth observation satellite constellations. Table 1 summarizes the related work. There have been many studies on single satellites, but recent studies have focused on multiple satellites and even satellite constellations. In addition, studies on consolidated scheduling that integrate mission and communication scheduling rather than focusing on either communication or missions are increasingly being conducted.

Table 1.
Previous research on satellite missions and communication scheduling.
This study focuses on consolidated scheduling for mission and communication in the MS-MG problem for a constellation of Korean low-orbit satellites. We considered the communication–mission–communication sequence, the process whereby a satellite performs its mission. In addition, the operational environment generated by the satellite during various missions, such as communication–mission–mission–communication sequence, was considered too. The data storage amount of the satellite is updated every time the satellite performs mission/communication, and the mission is set such that the maximum data storage amount is not exceeded. In addition, the divided visibility was considered to maximize the opportunity for communication between the satellite and the ground station. Considering the business scale, such as the economic and time costs of developing and operating satellites, high accuracy is needed to improve satellite utilization. Therefore, considering the satellite mentioned above operation environments, this study proposes an MILP to establish consolidated scheduling for the mission and communication of a satellite constellation. The MILP model is developed based on a time-space network (TSN) that considers visibility time windows (VTWs) for missions and communications as nodes.
Section 2 defines the mission and communication system of the satellite and presents an MILP model for the effective operation of satellites. Section 3 presents the results of numerical experiments using example data and actual satellite information to validate the MILP model shown in Section 2. Section 4 presents conclusions and directions for future research.
2. Mathematical Programming Model
2.1. Problem Definition
A satellite orbiting Earth can communicate with a ground station at a specific location on Earth under particular conditions. As shown in Figure 2a, communication is possible only when the satellite is located in the cone-shaped beam range formed by the antenna of a ground station, which is referred to as “visibility.” The start of visibility is called the acquisition of signal (AOS), and the end is called the loss of signal (LOS). In this study, AOS is when a satellite rises above an observer’s horizon, and LOS is when a satellite passes below the observer’s horizon. Thus, the VTW is represented as [AOS, LOS] in this study. A limited VTW for a satellite and a specific region is formed for reconnaissance, surveillance, and observation missions. Generally, an S-band antenna with a bandwidth of 2–4 GHz in a ground station is employed to transmit a mission command (CMD) to a satellite called the “uplink”. An X-band antenna with a bandwidth of 8–12 GHz receives a satellite’s mission results, such as image and signal data, called the “downlink.” Moreover, as shown in Figure 2b, the VTWs between a ground station antenna and a satellite antenna may overlap, and a satellite may form overlapped VTWs with multiple ground stations. This situation is called “visibility conflict”. Satellites and ground station antennas cannot communicate simultaneously with multiple counterparts; i.e., only one-to-one communication is possible at a specific time. Thus, to maximize the utilization of VTWs for satellites and ground stations, we assign several schedules to a VTW to avoid visibility conflict. For example, in a ground station (G/S), when the VTWs of satellites #1 and #2 are [100, 180] and [160, 220], the time windows for satellites #1 and #2 can be assigned as [100, 150] and [170, 220], respectively. The VTW between a satellite and G/S can be utilized for several types of communication. Moreover, the satellite has a limited memory capacity for storing mission data. The remaining capacity of the memory decreases as the satellite performs missions, and the satellite can increase the remaining capacity by transmitting mission data to Earth, i.e., the G/S, and deleting them. When the remaining memory capacity is insufficient for a mission, this mission cannot be assigned to the satellite.
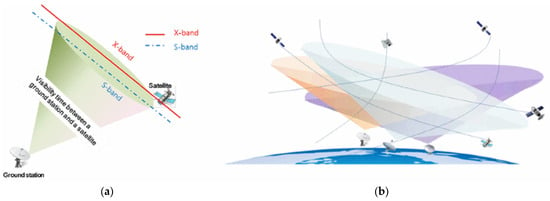
Figure 2.
Introduction to VTW and visibility conflict [27]: (a) VTW of a satellite and G/S; (b) visibility conflict.
2.2. Time-Space Network (TSN)
The TSN is one of the methods used in research related to flight and train schedule optimization and has the advantage of expressing spatial changes over time [33,34,35]. In the case of satellites, the current position changes with time, and a time window allows missions and communication to be performed at specific times in a fixed orbit. Figure 3 shows the VTW of the satellite as a two-dimensional graph of the TSN. The -axis indicates time, and the -axis indicates the set of ground stations and mission areas. The dotted line indicates the VTW, which is repeatedly generated according to the satellite’s orbital period, and the solid line indicates the assigned mission/communication time within the VTW. In Figure 3, the satellite communicates with G/S #2 and uplinks the CMD for the two missions during . Then, it moves to Mission #1 to perform this mission and to G/S #2 to downlink the results. Subsequently, it moves to Mission #2 to fulfill this mission and moves to G/S #1 to downlink the mission results.
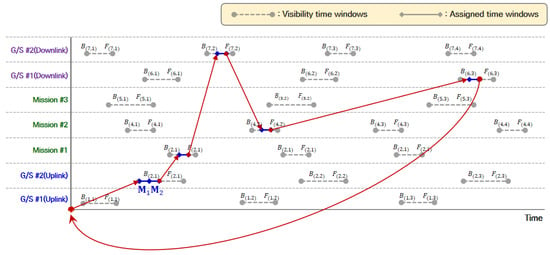
Figure 3.
Example of scheduling mission and communication on the TSN.
As mentioned, satellites and ground stations can communicate for a limited time. Modeling by the TSN, considering that a satellite moves to the mission area and then performs a mission, a conceptual transition to a vehicle routing problem with pickup and delivery (VRPPD) in industrial engineering can be made, as shown in Table 2. Virtual nodes correspond to the depots from which vehicles depart and arrive, satellites correspond to vehicles, and VTWs correspond to nodes. Image data storage fits to pick up, and image downlink is delivery. The capacity of an onboard memory is the load freight of a vehicle. Thus, the proposed MILP model for optimizing satellite mission/communication scheduling is based on the TSN concept.

Table 2.
Comparison of VRPPD and this study.
2.3. Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP) Model
The proposed MILP model for scheduling missions and communication of multiple satellites consists of Equations (1)–(42), and it is classified explicitly into five parts: (1) the objective function, (2) constraints related to the virtual node designating the start and finish of a satellite’s schedule, (3) constraints related to the generation of schedule paths for satellites, (4) constraints related to the communication time between satellite and ground stations (or mission areas), and (5) constraints for onboard memory management. The notations used for input parameters in the proposed MILP model are presented in Table 3, and the decision variables of the MILP model are shown in Table 4.

Table 3.
Notation of parameters for the proposed MILP model.

Table 4.
Notation of decision variables for the proposed MILP.
Equation (1) gives the objective function of the mathematical programming model, which maximizes the number of missions performed by the satellite.
Equations (2)–(8) are constraints related to the virtual nodes for specifying the start and end of schedule paths. Constraints (2) and (3) designate that the start node of a schedule path connects a G/S node for transmitting a CMD (uplink) but not mission nodes and G/S nodes for downloading mission data (downlink). Constraints (4)–(6) indicate that the last part of a schedule path consists of the connection of a downlink node and the virtual node (1,1). That is, the final task of a schedule path could not be uplink or mission. Constraints (7) and (8) indicate that virtual node for specifying the start and end of schedule path has only one VTW.
Equations (9)–(18) are constraints on generating the schedule path of a satellite. Constraint (9) ensures the continuity of a schedule path, and Constraint (10) means that the schedule path cannot stay at a node . Constraints (11) and (12) indicate that a node cannot be connected with multiple nodes simultaneously. Constraint (13) updates the decision variable to 1 when satellite visits to mission node , and it determines whether satellite has performed mission . Constraints (14) and (15) mean that a mission is performed no more than once. Constraints (16)–(18) indicate that a mission result should be transmitted to a G/S (downlink), and the decision variable is updated to 1. The decision variable activated as 1 indicate that the mission () data of satellite is transmitted to ground station at the VTW.
Equations (19)–(34) are constraints related to the mission and communication time of satellites and ground stations. Constraints (19) and (20) indicate that when a satellite communicates with a G/S, the time window for it should be sufficiently assigned considering data size and transmission speed. Constraints (19) and (20) are for uplink and downlink, respectively. Constraint (21) implies that the time window for a mission should be large enough to be at least , where is the data acquisition speed. Constraints (22) and (23) indicate that the time window for an uplink should be assigned within a VTW, i.e., . Constraints (24) and (25) indicate that the time window for a mission should be assigned within a VTW, i.e., Constraints (26) and (27) indicate that the time window for a downlink should be assigned within a VTW, i.e., Constraints (28) and (29) designate the sequence of the mission process, receiving CMD (uplink)–mission–transmitting acquired data (downlink). Constraint (30) means that the sum of the time windows for a mission should be assigned longer than the uplink and downlink times of the mission. In the case of downlink, constraint (31) implies that if the communication time at node is insufficient, additional communication is possible at other nodes . Constraint (32) means that if the satellite performs mission m, communicates (downlink) at node , and then performs mission , these tasks are performed continuously. Constraint (33) eliminates the overlapping, i.e., visibility conflict, among assigned time windows, and it is based on the logic shown in Figure 4.
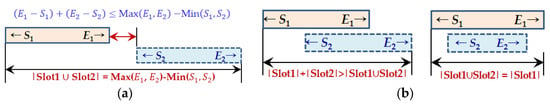
Figure 4.
Constraints for discriminating visibility conflict [12]: (a) Normal scheduling case; (b) Overlapping (visibility conflict) cases.
Constraints (34)–(41) are related to the onboard memory management of a satellite. Constraint (34) updates the amount of CMD data for mission performed by satellite at uplink node to the decision variable , and constraint (35) indicates that as the satellite receives the CMD for mission , the amount of storage in its onboard memory increases by the amount of the data. Constraint (36) indicates that the data storage of onboard memory increases by the amount of the mission data after the satellite performs mission . Constraint (37) updates to the total data storage in the mission nodes. Constraint (38) indicates that after the satellite transmits the CMD and mission data to a ground station, the data is deleted from the onboard memory. Constraint (39) updates to the total data storage in the downlink nodes Constraint (40) allocates the initial data storage of onboard memory for satellite , and constraint (41) indicates that the data storage of onboard memory should maintain less than maximum capacity.
3. Numerical Experiments and Results
Numerical experiments are performed with (1) data based on arbitrary time and (2) published information on the Korean multipurpose satellites to validate the operational concepts and MILP model presented in Section 2. The optimal solutions of experimental examples are searched by IBM’s ILOG CPLEX Optimization Studio 20.1.0.
3.1. Experiment #1
Researchers created the data for the first experimental example to include overlap between VTWs and includes the following: three satellites, two ground stations for uplink, three ground stations for downlink, and five mission types. Table 5 presents the initial storage and capacity of onboard memory and transmission speed for data for each satellite. Table 6 shows the amount of the CMD and image data for each mission.

Table 5.
Information of satellites for experiment #1.

Table 6.
Mission data (image) size for experiment #1.
Table 7 presents the VTWs for the satellites and ground stations/mission areas, which are assigned to overlap, i.e., visibility conflict, to validate the MILP model proposed in Section 2. As a result of deriving the optimal solution of the experimental example, the constraints of the MILP model were successfully validated, such as the prevention of overlapping mission/communication time windows, the schedule path for satellites, and the duplication of missions. The optimal solution for experiment #1 is presented in Table 8. Satellite #2 is assigned Missions #3, #4, and #5 and receives CMDs of the mission by communication with G/S #2 (uplink). Because Satellite #1 is assigned the VTW [552, 554], Satellite #2 is assigned split time widows [550, 552] and [554, 562], not a continuous time. After performing Missions #5, #3, and #4, a VTW from a ground station had insufficient time; the missions’ data are transmitted to G/S #1, #3, and #2 (downlink). For example, Figure 5 shows the schedule path for Satellite #2, and Figure 6 presents the changes in the data storage of onboard memories for satellites. As shown in Figure 6, the satellites did not communicate with two or more ground stations simultaneously, and the ground station did not communicate with two or more satellites simultaneously. Thus, it is confirmed that the constraints to prevent overlapping of the mission/communication time windows and mission duplication are normally operated. Moreover, it is confirmed that the onboard memory is being managed not to exceed its capacity as the satellite performs its mission and communications.

Table 7.
Experiment 1: VTWs between satellites and ground stations (or mission areas).

Table 8.
Results of experiment 1.
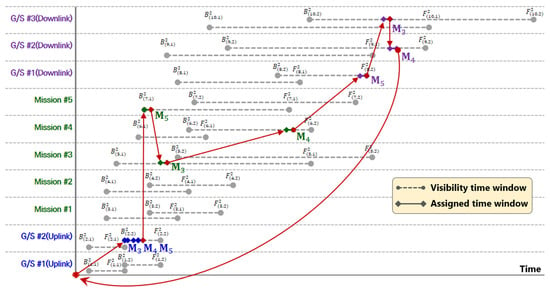
Figure 5.
Visualization of satellite #2′s schedule path on the TSN.
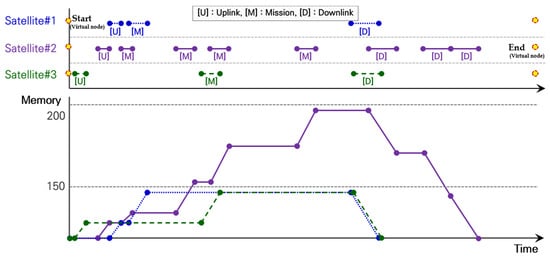
Figure 6.
Changes in the data size stored in onboard memory.
3.2. Experiment #2
Because the MILP model is validated by experiment #1 in Section 3.1, experiment #2 tests the proposed model in a real environment. The experimental data consisted of information about the Korean multipurpose satellites KOMPSAT-2, KOMPSAT-3, and KOMSAT-3A. Table 9 presents information on the satellites. The researchers arbitrarily assigned the capacity of onboard memory and data transmission speed, which are not publicly available. Information regarding the ground stations and mission areas is presented in Table 10. Weno, Jeju, and Daejeon in Republic of Korea were selected as ground stations, and Tokyo in Japan, Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, Pyeongyang in North Korea, and Tehran in Iran were selected as the mission areas. One mission was performed for each mission area; however, since the Tehran area mission will be performed twice, five missions were planned. Table 11 presents the CMD and image data sizes for each mission, along with the mission locations.

Table 9.
Information on Korean multipurpose satellites (KOMPSAT).

Table 10.
Information on ground stations and mission areas.

Table 11.
Data size and locations of the missions.
The VTW data between the satellites, ground stations, and mission areas were generated using AGI’s STK 11, a software for space flight simulation. Because the time interval of the VTW generated by the actual satellite information was large, the time units were adjusted to 10 s, and the non-VTW time not related to scheduling was reduced. The data for the numerical experiments is presented in Table 12, and the experimental results are presented in Table 13. First, KOMPSAT-2 uplinked the CMD data from at Daejeon ground station. Then, it moved to the Pyeongyang area and performed Mission #3 during , and moved to the Tehran area to perform Mission #4 during . Subsequently, it moved to the Weno ground station and downlinked the CMD and image data during . KOMPSAT-3 and KOMPSAT-3A performed Mission #1 and Mission #5, respectively, and of the five missions, all except Mission #2 (Rio) were performed. As shown in Figure 7, the satellites did not communicate with two or more ground stations simultaneously, and the ground station did not communicate with two or more satellites simultaneously. And, the mission did not exceed the maximum storage capacity of the satellite’s onboard memory.

Table 12.
Experiment 2: VTWs between satellites and ground stations (or mission areas).

Table 13.
Results of experiment 2.
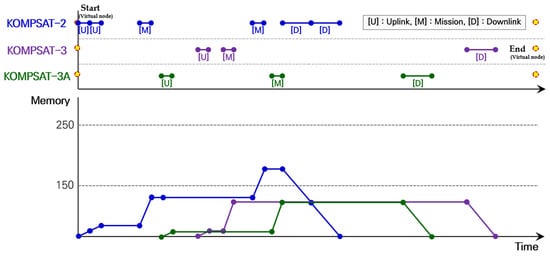
Figure 7.
Changes in onboard memory storage on KOMPSAT satellites.
4. Conclusions and Future Studies
Satellite technology advances, and the number of missions increases; the global satellite market has proliferated. In response to this growth, the mission/communication scheduling problem in MS-MG environments is becoming increasingly essential. This study proposes a TSN-based MILP model for optimizing satellite mission/communication schedules in the MS-MG environment and verifies the proposed MILP through numerical experiments based on actual data from Korean satellites. The model has been enhanced to allow partitioned use of the visibility’s time window to maximize communication opportunities between satellites and ground stations. Moreover, a satellite could perform several missions consecutively with enough residual capacity for onboard memory and visibility. Considering the practical environment of satellite control, the data acquired by a mission are transmitted to a ground station, i.e., the data for an assignment are not split and sent to multiple ground stations.
In future research, we plan to apply an index to determine whether a satellite can perform its mission and its importance. When a satellite performs a mission, it is possible to determine whether the mission can be performed with consideration of the clouds and weather in the mission area and to select a mission priority according to the mission importance, time limit, and profit. Furthermore, we will apply the energy required to operate the satellites. Satellites often use solar energy and obtain energy only from a specific location. In addition, a more realistic scheduling problem considering the orbit maintenance and energy consumption for performing missions in the ground station/mission area is recommended.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.K. and K.K.; methodology, H.K.; software, M.L. (Minkeon Lee) and S.Y.; validation, H.K., K.K., M.L. (Myungshin Lee), and J.L.; formal analysis, H.K, M.L. (Minkeon Lee), and S.Y; investigation, H.K., M.L. (Minkeon Lee) and S.Y; resources, K.K.; data curation, K.K. and M.L. (Minkeon Lee); writing—original draft preparation, H.K. and M.L. (Minkeon Lee); writing—review and editing, H.K. and M.L. (Minkeon Lee); visualization, M.L. (Minkeon Lee) and S.Y.; supervision, H.K.; project administration, K.K. and H.K.; funding acquisition, K.K., H.K., M.L. (Myungshin Lee), and J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Satellite Information Public Utilization Project (Multi-satellite Mission Management System Operation Optimization Study) of the Korea Aerospace Research Institute and the Financial Program for Self-Directed Research Capacity (2022) of the Changwon National University.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in this study were presented in this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Commercial Satellite Imaging Market. Available online: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/commercial-satellite-imaging-market (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Space: Investing in the Final Frontier. Available online: https://www.morganstanley.com/ideas/investing-in-space (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Sun, J.; Xhafa, F. A Genetic Algorithm for Ground Station Scheduling. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Complex, Intelligent and Software Intensive Systems (CISIS), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 30 June–2 July 2011; pp. 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Spangelo, S.; Cutler, J.; Gilson, K.; Cohn, A. Optimization-based scheduling for the single-satellite, multi-ground station communication problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2015, 57, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, R.; Perea, F.; Vioque, J.G. Resolution of an Antenna–Satellite assignment problem by means of Integer Linear Programming. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2014, 39, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Demeulemeester, E.; Qiu, D. A pure proactive scheduling algorithm for multiple earth observation satellites under uncertainties of clouds. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 74, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, G.; Falone, R.; Gambi, E.; Spinsante, S. Ground station activity planning through a multi-algorithm optimisation ap-proach. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE First AESS European Conference on Satellite Telecommunications (ESTEL), Rome, Italy, 2–5 October 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xhafa, F.; Sun, J.; Barolli, A.; Biberaj, A.; Barolli, L. Genetic algorithms for satellite scheduling problems. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2012, 8, 351–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Wang, S.; Chung, D.; Hyun, C.; Choi, S.; Ko, K.; Jung, O. Visibility conflict resolution for multiple antennae and multi-satellites via genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Chung, H.; Ko, K. Genetic algorithm-based scheduling for ground support of multiple satellites and antennae considering operation modes. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2016, 17, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. High-performance technique for satellite range scheduling. Comput. Oper. Res. 2017, 85, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Kim, H. A Mathematical Model for Optimal Communication Scheduling between Multiple Satellites and Multiple Ground Stations. J. Soc. Korea Ind. Syst. Eng. 2018, 41, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachler, N.; Crawley, E.F.; Cameron, B.G. Beam-to-satellite scheduling for high throughput satellite constellations using par-ticle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO), Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkheyli, A.; Bagheri, A.; Ghorbani-Vaghei, B.; Askari-Moghadam, R. Using an effective tabu search in interactive resources scheduling problem for LEO satellites missions. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Chang, Y.K. Mission scheduling optimization of SAR satellite constellation for minimizing system response time. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2015, 40, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Chang, Y.-K. Optimal mission scheduling for hybrid synthetic aperture radar satellite constellation based on weighting factors. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 107, 106287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Y. An anytime branch and bound algorithm for agile earth observation satellite onboard scheduling. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 2077–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, S.-H.; Jo, S.; Bang, H.; Leeghim, H. Heuristic-based mission planning for an agile earth observation satellite. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2019, 20, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, X.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Xing, L.N.; Liu, K. Hierarchical scheduling for real-time agile satellite task scheduling in a dy-namic environment. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic-Minic, S.; Thomson, D.; Berger, J.; Secker, J. Collection planning and scheduling for multiple heterogeneous satellite missions: Survey, optimization problem, and mathematical programming formulation. In Modeling and Optimization in Space Engineering: State of the Art and New Challenges; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 271–305. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Reinelt, G.; Dai, G.; Spitz, A. A mixed integer linear programming model for multi-satellite scheduling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 275, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkaoui, M.; Berger, J. A new hybrid genetic algorithm for the collection scheduling problem for a satellite constellation. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2020, 71, 1390–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, Y.; Wu, G.; Woodward, J.R. Robust scheduling for multiple agile Earth observation satellites under cloud cov-erage uncertainty. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 156, 107292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhibo, E.; Shi, R.; Gan, L.; Baoyin, H.; Li, J. Multi-satellites imaging scheduling using individual reconfiguration based integer coding genetic algorithm. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 178, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Shen, X.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, D. A Mission Planning Modeling Method of Multipoint Target Imaging Within a Single Pass for Super-Agile Earth Observation Satellite. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 16, 1921–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Xing, L.; Yao, F.; Li, M.; Lv, J.; He, Y.; Song, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, G. Deep reinforcement learning method for satellite range scheduling problem. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2023, 77, 101233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, G.; Liang, Z.; Demeulemeester, E.; Hu, X.; Liu, J. Unrelated parallel machine scheduling with multiple time windows: An application to earth observation satellite scheduling. Comput. Oper. Res. 2023, 149, 106010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Reinelt, G.; Gao, P.; Tan, Y.J. A Model, a heuristic and a decision support system to solve the Earth observing satellites fleet scheduling problem. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Computers & Industrial Engineering, Troyes, France, 6–9 July 2009; pp. 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Chung, H.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.; Jung, O.; Chung, D.; Ko, K. Schedule optimization of imaging missions for multiple satellites and ground stations using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2018, 19, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; He, R.; Ou, J. An Efficient Local Search Heuristic for Earth Observation Satellite Integrated Scheduling. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Xing, L.; Yao, F. Integrated scheduling problem for earth observation satellites based on three modeling frameworks: An adaptive bi-objective memetic algorithm. Memetic Comput. 2021, 13, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhu, W.; An, B.; Jin, P.; Xia, W. A branch and price algorithm for EOS constellation imaging and downloading inte-grated scheduling problem. Comput. Oper Res. 2019, 104, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliewer, N.; Mellouli, T.; Suhl, L. A time–space network based exact optimization model for multi-depot bus scheduling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 175, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Rim, S.-C. The Train Conflict Resolution Model Using Time-space Network. J. Korean Soc. Railw. 2015, 18, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liao, Z.; Li, H.; Miao, J.; Corman, F. Railway capacity estimation considering vehicle circulation: Integrated timetable and vehicles scheduling on hybrid time-space networks. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2021, 124, 102961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).