Abstract
The slots on a blade tip can effectively suppress the tip vortices by diffusing the core structure of a vortex and thus mitigate the adverse impacts of vortex interactions. In this paper, the effect of a slotted tip on vortex diffusion in the hovering state is investigated numerically by implementing the IDDES method using the fifth-order WENO scheme. The resulting wake flow field show that the number of secondary turbulent structures of so-called vortex worms near the slotted tip reduces significantly, indicating the weakening of vortex core rotation. It was found that the slotted tip reduced the peak value of velocity profiles in the vicinity of the vortex core by about 50%. The numerical result is close to the experimental conclusion. Correspondingly, the diameter of the vortex core is approximately doubled at each wake age relative to the baseline blade because the local flow passing through the slots will disintegrate the stable structure of the core region during the early stages of tip vortex generation. This promotes the turbulence mixture, resulting in the reduction in the vorticity value and rotating effect near the vortex core. Based on the overall results, the study of the slot parameters demonstrated that reducing the slot number or diameter will weaken the diffusing effect, causing a decrease in the flow rate.
1. Introduction
Over the past decades, considerable research has been conducted into the problem of understanding and controlling the development of blade tip vortices of helicopter rotors [1]. The vortex generated by the rotor blade during rotation will roll up and form a spiral-tip vortex system, which plays a decisive role in the aerodynamic performance of the rotor [2]. Furthermore, the rotor blade will encounter the tip vortices of other blades, leading to the phenomenon of blade–vortex interaction (BVI); the related unsteady pressure fluctuations will lead to high levels of noise and vibration [3].
Fortunately, researchers changing the structure and position of tip vortices by diffusing the vortex strength can significantly reduce the adverse aerodynamic effects of tip vortices. Many passive and active flow control methods have been considered, which aim primarily at modifying the vortex structure or affecting the stability of the vortex. Brocklehurst [4] presented a review of blade tip shapes intended to alleviate BVI noise by modifying the shape of the rotor tip, or by installing tip winglets or spoilers. Kessler [5] reviewed the active rotor control methods towards reducing the BVI phenomenon. Velez [6] realized the reduction of BVI noise based on the idea of injecting air at the leading edge of the blade. Active technologies of ONERA, aimed at reducing the vibratory loads or the noise radiation, were performed by Le Pape [7]. The effects of the blowing of a blade surface jet on the reduction of BVI noise were analyzed by Sun [8,9]. Syriac [10] developed an active control concept of air suction near the trailing edge to diffuse the vortices and hence reduce BVI noise.
Although active flow control measures can effectively diffuse vortex strength, they incur rotor performance penalties, such as an increase in the rotor power consumption for blowing/suction, or they require additional nonstructural mass for the control devices. Han [11,12] adopted a passive flow control technology called “blade tip slot” on a fixed wing and a rotating blade. These slots direct a slight amount of incident flow in the spanwise direction to diffuse the tip vortices. Relevant experimental research has been carried out, and encouraging results have been obtained. These results show that the slotted tip can diffuse the concentrated vorticity of tip vortices rapidly, while the loss of hovering power is not more than 3%.
The efficiency of tip slots in diffusing the vortex core has been confirmed by the experimental method, but the investigations are limited to the details of a local flow field near a single tip vortex and to the insight into the evolution of whole rotor vortex system, while the analysis of an overall rotor flow field is missing. In addition, manufacturing experimental models and preparing test devices of slotted blade tips are often costly and time-consuming, and the extraction of experimental information is a complicated process. To solve the problems mentioned above, the numerical investigation based on Reynolds averaged Navier−Stokes (RANS) method has been carried out. You [13] numerically analyzed the effect of tip slots on the tip−vortex formation of a rotor blade in a hovering state using unstructured meshes and the one-equation turbulence model of Spalart–Allmaras. Hu [14] evaluated the influence of slotted-blade tip shapes on flow fields, together with brownout based on the k−ω turbulence model.
Despite of the fact that the RANS method is an effective tool in the estimation of effect of slotted tips, the nature of the total-modelled turbulence of RANS means that the precise behaviors of tip vortices are averaged and ignored. Thus, the diffusion effect of tip slots on vortices will not be reflected correctly, which will confuse the validation of flow control effects. The integration of RANS and the large eddy simulation (LES) under a unified framework with the switch of branches depends on the local length scale; the DES-type RANS/LES method [15] is an available solution to the problem, which is capable of mitigating the contradiction between the simulation accuracy and the efficiency of resolving spatial turbulence. The capability of the DES-type method in the investigation of rotor flow field has been confirmed by Chaderjian [16,17] using UH−60 and V22 rotors, and by Yoon [18,19] using an XV-15 rotor.
In this paper, the diffusion effect of a slotted tip blade operating in a hovering state is investigated via IDDES [20] coupled with the fifth-order WENO scheme [21]. IDDES is a new version of the DES-type hybrid RANS/LES method, where the major part of the separated flow is resolved using LES, while RANS is applied only at the attached boundary layer region. This method can significantly resolve the spatial turbulence. Based on the numerical results of IDDES, the impacts of slotted-tip on the vortex structures are analyzed, and the mechanism of vorticity diffusion is discussed with detailed flow solution.
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2 presents the geometric model and the numerical methodologies; Section 3 provides the comparative results between RANS and IDDES, then the flow control mechanism of a slotted tip is analyzed; Section 4 studies the influences of the slot parameters, including the slot number and diameter, on diffusing effect; and finally, some conclusions are reached in Section 5.
2. Geometric Model, Computational Grid and Numerical Methodology
2.1. Geometric Model and Computational Grid
According to reference [11], a single-bladed rotor operating in a hovering state is chosen for the numerical investigation to create a helicoidal vortex filament without interaction from vortices generated by other blades. Additionally, a single helicoidal vortex is much more spatially and temporally stable than multiple vortices, thereby allowing the tip vortex structure to be studied to much older wake ages. Figure 1 shows a model of a single-bladed rotor. The model is rectangular planform, untwisted, with a radius of 406 mm and a chord of 44.5 mm. An NACA2415 airfoil is used as the blade section, which is constant throughout the whole blade. Four slot arrays are made with the leading-edge point of the blade tip as the center of the circle. Due to the local pressure gradient between the inlet and the exit of slot, the incident flow comes through the tip and ejects through the side at the blade tip in the spanwise direction [11]. The slot system is imbedded inside the chord plane of blade at the tip region, the parameters are presented in Figure 2. The diameter of each slot is 3 mm, and the distance between the centers of adjacent slots is 7 mm.
Figure 1.
Schematic of the geometric model.
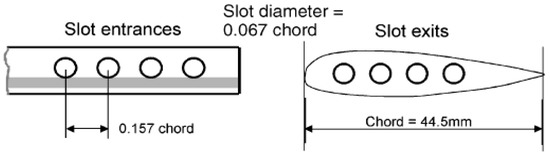
Figure 2.
Parameters of the slots [11].
ICEM-Hexa is applied in the generation of multiblock structural grid for the baseline and slotted-tip blades. The O-topology is applied to describe the rotation flow field. For the numerical simulation issues with relative motions, the dynamic patched method is used as the grid generation strategy, which has the primary advantage of handling relative motion. Fluxes are interpolated through the patched surfaces, thus enabling the coupling of the flow information of the adjacent subdomains in the process of computation. Figure 3 depicts the grid of two blades. In order to accurately predict the influence of a slotted-tip on tip vortices, the grid topology and distribution of the baseline blade and the slotted-tip blade in the region of the tip vortices must be consistent, which can be ensured via the blocks of the slot set as the inner part while the inlet and outlet of slots are set as wall surfaces when the grid of slotted-tip blade needs to be switched to baseline. The grid distribution of the blade tip region is refined to capture the evolution of the vortex system and match the application of IDDES. In order to ensure the prediction of the blade tip vortices system while reducing the numerical dissipation, the size of the cells is set as equal to 2% of the length of the blade chord. The first cell height for the normal wall grids is set to to ensure y+ ≈ 1, and the whole grid of each blade consists of nodes. The sectional grid of the wake region is shown in Figure 4.
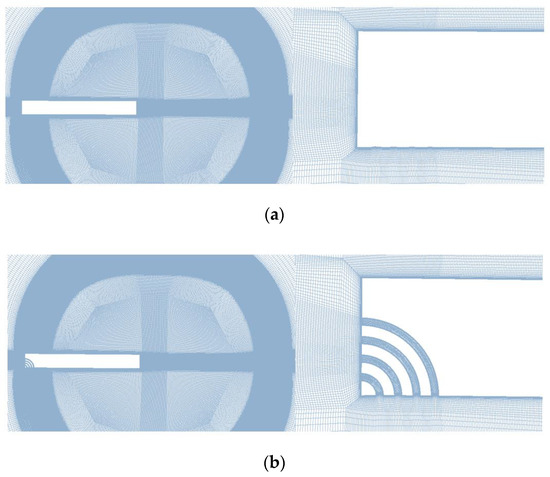
Figure 3.
Spatial grid: (a) baseline blade, (b) slotted-tip blade.
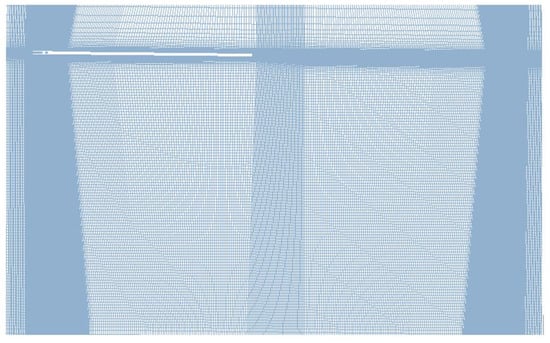
Figure 4.
Sectional grid on rotor wake region.
2.2. Numerical Methology
The RANS is initially used in the numerical investigation. Under the framework of an in-house code based on finite volume method, the third-order scheme of MUSCL-Roe [22] is implemented for the spatial discretization of the convective fluxes, and the viscous fluxes are discretized with second-order central difference scheme. The fully implicit dual-time approach is implemented as the time marching method [23]. The two-equation SST model is chosen as the base turbulence model [24].
For the IDDES simulation, the fifth-order WENO-Roe scheme is implemented for the spatial discretization of convective fluxes. Other numerical methodologies are consistent with the RANS simulation. The capability of the method has been verified via a variety of cases about helicopter fuselage and rotating blade flow fields [25,26], where how a particular numerical scheme is affected by diffusion has been discussed in detail correspondingly.
The hybrid RANS/LES length of IDDES is defined with the combination of the DDES [27] and WMLES modes. The hybrid length scale is defined in the following form:
where the modified subgrid length scale is written as follows:
When the inflow turbulence can be ignored, the hybrid length degenerates to the original DDES for :
When the turbulence content is contained in the inflow, the hybrid length will switch to the WMLES mode:
The empirical mixing function is defined as follows:
The definition of will promote the rapid switch between RANS mode and LES mode near the wall when the separation occurs:
The definition of will prevent the attenuation of Reynolds stress near the interface of RANS/LES areas:
3. Comparison of Blade Tip Vortex Characteristics
3.1. RANS Simulation
The RANS simulation is performed for the hover case, corresponding to the conditions shown in Table 1. The time step size is set as a rotor rotation at per physical time step. The unsteady calculation is carried out by 50 full revolutions firstly to ensure the convergence of flow field, then the numerical result is obtained and averaged after additional 10 full revolutions.

Table 1.
Conditions for calculation.
Figure 5 shows the normalized vorticity iso-surfaces at . Both of the blade tip vortex systems describe a helicoidal pattern. Based on the current spatial resolution of method, the rotor tip vortices of the baseline blade develop to the wake age of four full revolutions, which is close to the previous result [26] with the same method. Compared to the baseline blade, it is observed that the wake age of slotted blade lasted for only two revolutions, which indicates the remarkable attenuation of vorticity strength. However, for the inherent shortage of the RANS method with third-order scheme, the current effect of suppressing the tip vortices is only in a relative sense. Figure 6 compares the normalized vorticity magnitude distribution of the two blades. The slotted blade manifests a lower vorticity value at the core center, especially for the tip vortices near the rotation plane.
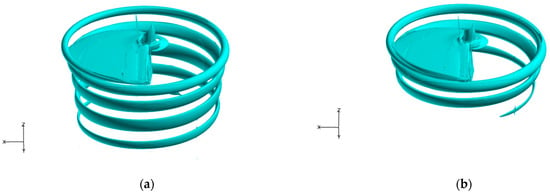
Figure 5.
Iso-surfaces of q−criterion:(a) Baseline blade. (b) Slotted-tip blade.
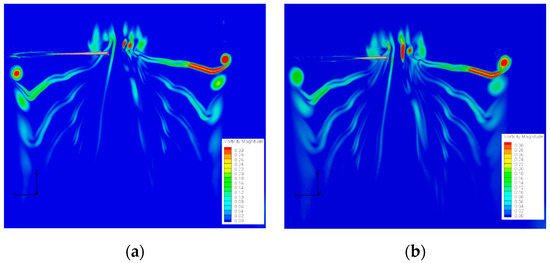
Figure 6.
Vorticity magnitude distribution: (a) baseline blade, (b) slotted-tip blade.
The diameter of vortex core and the velocity distribution can be measured with the profile through the core of the blade tip vortex. The probe line and the definition of vortex core diameter are given in Figure 7. The vortex core diameter is nominally the distance between the peaks in the swirl velocity profile. Figure 8 shows the comparison of the velocity profiles of the tip vortex in Z-direction at different wake ages of . Compared to the baseline blade, the result of the slotted-tip blade demonstrates smaller velocity peak values and increasing vortex core diameters at various wake ages, which indicates obvious diffusion effects. Figure 9 compares the diameter of the vortex core at equivalent wake ages. With the development of wake ages, the diffusion effect of the slotted-tip vortices becomes more pronounced. The vortex core diameters of the slotted blade and the baseline blade show large discrepancies at the last stage of wake evolution. The reference draws the conclusion that the peak velocity induced by the tip vortices will decrease by 20~60%, and the diameter of vortex core will increase by 2~3 times [11]. However, the result of RANS is quite different from this conclusion, which manifests the similar velocity distributions of the baseline and slotted blades. This fact indicates that the numerical dissipation of RANS has submerged the efficiency of slotted blade to some extent.
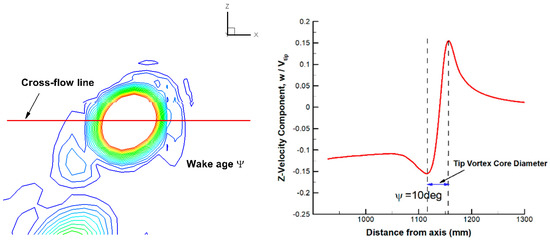
Figure 7.
Probe line of blade tip vortex core and the definition of vortex core diameter [26].
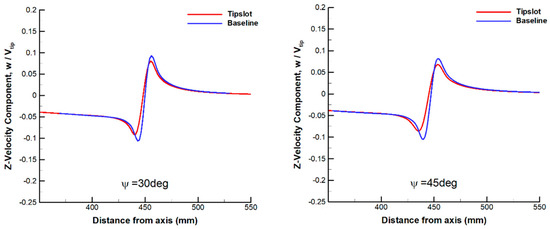
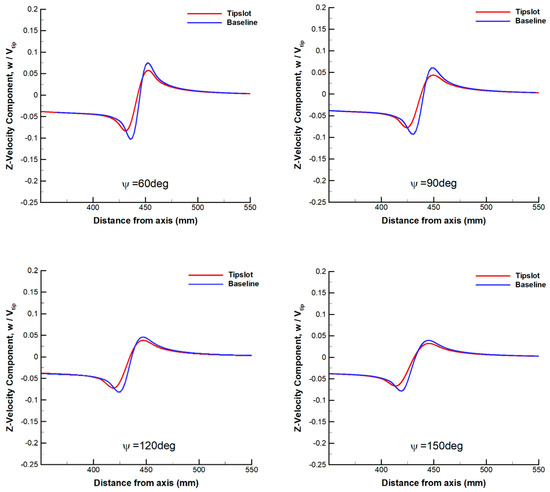
Figure 8.
Comparison of velocity profiles in Z-direction at different wake ages.
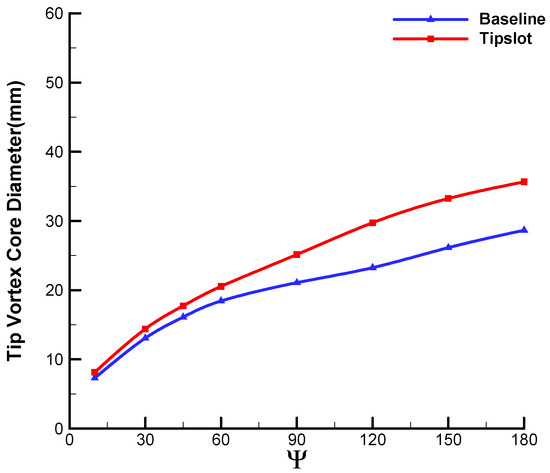
Figure 9.
Comparison of the vortex core diameters between the baseline blade and the slotted-tip blade.
Figure 10 compares the pressure distribution of the baseline and slotted blades in the radial direction. Little difference can be observed from the comparison of the two results, which proves that the slot has little impact on the rotor surface loading, thus it will not have great impacts on the aerodynamic performance of the rotor.
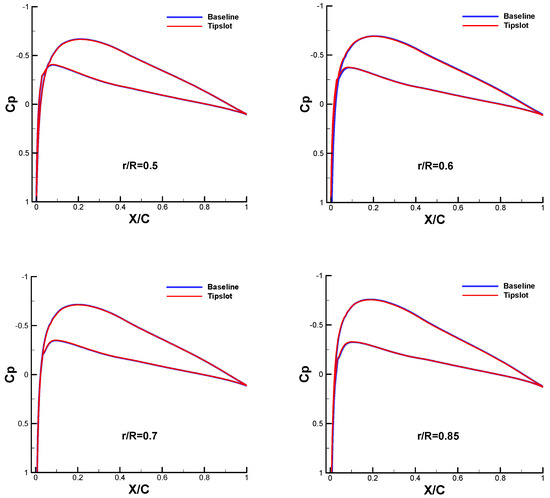
Figure 10.
Comparison of the pressure distribution at various radial positions between the baseline blade and the slotted-tip blade.
Though the basic features of the slotted-tip effects on the tip vortices can be reflected to some degree by RANS, it should be pointed out that due to the large numerical dissipation in the turbulence model, the calculated vorticity strength of the baseline blade and the slotted-tip blade are weakened numerically to a certain extent. In this case, it is not appropriate to estimate the efficiency of vortex diffusion nor to analyze the flow control mechanism with the RANS method. Therefore, the hybrid RANS/LES method of IDDES characterized by its LES-level turbulence resolving ability will be applied to further investigate the flow control effect of the slotted tip in the next section.
3.2. IDDES Simulation
The IDDES simulation is performed for the same hover case, corresponding to the conditions shown in Table 1. In this case, another 50 more revolutions are continued on the basis of the previous RANS solutions, then the numerical result is obtained after additional 10 full revolutions. The time step size is set as a rotor rotation of per physical time step with 25 subiterations, which is in consistent with Ref. [26] and is enough to fulfill the demand for convergence and robustness.
Table 2 manifests the comparison of the rotor performance of different configurations with the different methods. From the table, all the predicted thrust coefficient values are slightly higher than the experimental value of 0.002, but within the reasonable range of variation [13]. Compared with RANS, the thrust result of IDDES is closer to the measured data, while the power coefficient and figure of merit are lower. With the slotted blade tip, the thrust coefficient of the rotor slightly decreases, while the power coefficient increases, which is due to the profile drag of the blade tip increasing with the slots [11]. The power penalty of slotted-tip blade is about 3% compared with the baseline blade, which is similar with the conclusion of Refs. [11,13].

Table 2.
Comparison of rotor performance.
Figure 11 and Figure 12 compare the iso-surfaces of the normalized Q-criterion of the tip vortex system of the two blades, which is characterized by the normalized vorticity magnitude, and the cut view is provided in Figure 13. A pronounced difference can be observed in the vicinity of the tip vortices. Compared to RANS, with the rapid activation of WMLES mode in the focused region, the resolution of transient turbulent structures of blade tip vortices is significantly enhanced through IDDES. The behaviors of secondary turbulent structures of vortex worms around the blade tip vortices are successfully predicted, including the interactions and pairing of adjacent vortices [26]. IDDES successfully predicts the secondary turbulence structure near the tip vortex (the so−called “vortex worms”) [16]. The turbulence structure is characterized by the slender and curled shape in the vicinity of the tip vortices. The formation of vortex worms is closely related to the rotation and entrainment effect of tip vortices, and the abundance of these turbulent structure can be regarded as the characterization of vortex strength. However, depending on the resolution and parameters of the numerical method, these structures are not necessarily a specific feature of IDDES, as they can be also seen in some URANS simulations. It is observed that the number and the length of the vortex worms near the slotted tip are reduced significantly as seen in the second blade wake, indicating the weakening of the rotation effects of the vortex core.
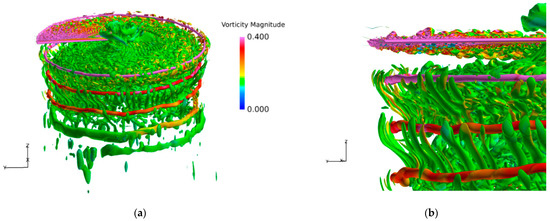
Figure 11.
Iso-surfaces of Q-criterion of the baseline blade: (a) overall view, (b) local enlarged view. (Q = 10.0.)
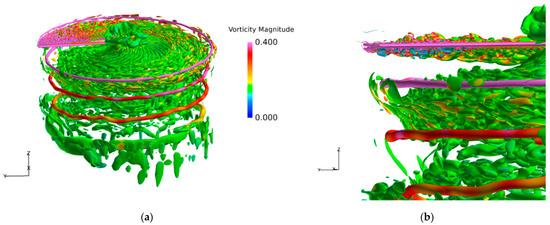
Figure 12.
Iso-surfaces of Q-criterion of the slotted-tip blade: (a) overall view, (b) local enlarged view. (Q = 10.0.)
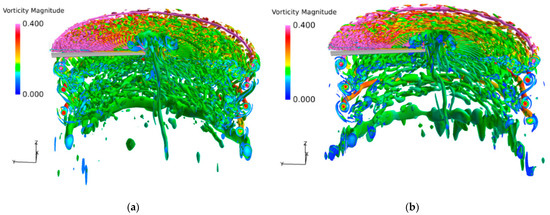
Figure 13.
Cut view of the iso-surfaces of Q-criterion: (a) baseline blade, (b) slotted-tip blade. (Q = 10.0.)
Figure 14 presents the vorticity distribution of the two blades. For the baseline blade, though the outer layer of the tip vortex manifests a certain degree of diffusion when the wake age increases, the vorticity value of the vortex core is nearly constant at each wake age. The value decreased significantly for the slotted blade and was almost indistinguishable in the outer layer of the tip vortex at old wake ages.
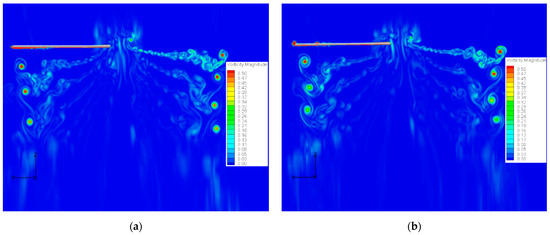
Figure 14.
Vorticity distribution of overall flow field: (a) baseline blade, (b) slotted-tip blade.
Figure 15 further presents the comparison of vorticity distribution near the blade tip, which manifests the generation of tip vortices and the interference between slot jet and newly born vortices. For the baseline blade, it is indicated that the pairing and fusion of the two vortices systems from the top and side surface of blade tip dominate the birth of tip vortices. Compared to the baseline blade, as the crossflow of the slot jet degrades the initial structure of newly born vortices, the strength of both the top vortices and side vortices has been effectively weakened, the typical diffusion features of vortices are also observed. The comparison of streamline distributions near the blade tip is shown in Figure 16 to further describe the topology of the local flow, which also demonstrates that the large-scale and concentrated vortex structures rolling-up over the tip of baseline blade are suppressed effectively with the slot and that the local flow is generally along the side of the tip except for the region near the trailing edge, where the birth of local vortex is observed.
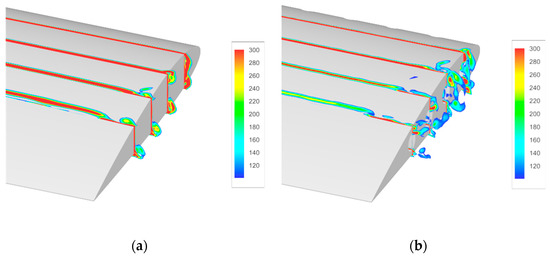
Figure 15.
Vorticity distribution near the blade tip: (a) baseline blade, (b) slotted-tip blade.
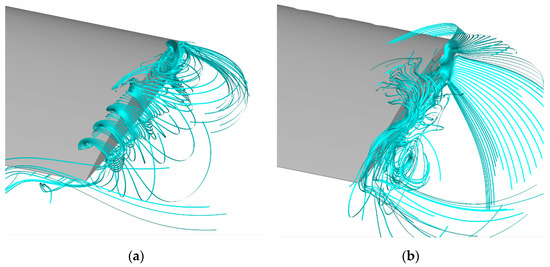
Figure 16.
Streamlines distribution near the blade tip: (a) baseline blade, (b) slotted—tip blade.
The distribution of the velocity magnitude near the slot exits is given in Figure 17, and the corresponding comparison of dimensionless mass flow rate is provided in Table 3, in which the slots are numbered from 1 to 4 from the leading edge to the trailing edge. The results indicates that the mass flow rate through slots decreases gradually from the second slot to the fourth one, which is partly consistent with the result of Ref. [13]. However, the result also manifests that the deficit of the velocity magnitude is obvious for the slots far away from the leading edge, which indicates the possibility of optimizing the layout and number of slots.
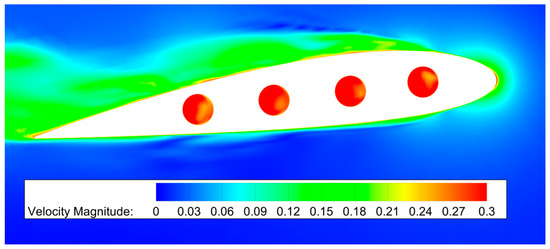
Figure 17.
The distribution of velocity magnitude near the slot exits.

Table 3.
Comparison of mass flow rate near the slot exits.
Figure 18 compares the flow visualization results captured using laser Doppler velocimetry [11] and the IDDES results of vorticity magnitude at two particular wake ages of to further discuss the flow control mechanism of the slotted blade. In general, the phenomenon of the experimentvalidates the calculation results. From Figure 18a, for the baseline blade, the tip vortex manifests a core region where the turbulent behaviors are hardly observed, which indicates weak flow mixing effects. The corresponding numerical result presents a strong vorticity value in the vicinity of the vortex core.
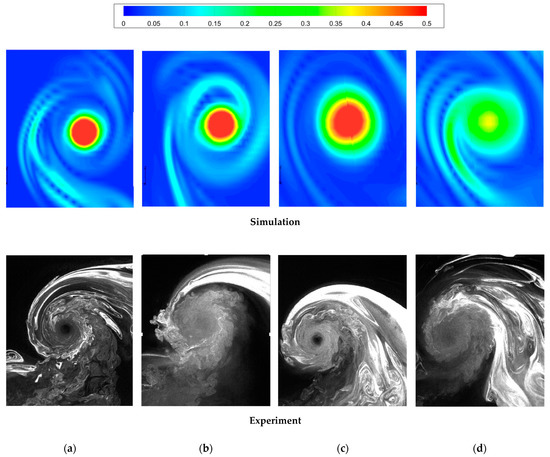
Figure 18.
Comparison between calculation and experiment [11] at two wake ages of : (a) baseline blade, ; (b) slotted-tip blade, ; (c) baseline blade, ; (d) slotted-tip blade, .
However, for the case of slotted blade, because the tip vortices are generated and roll up along the side of blade tip, the exit flow passing through the slots will break up the stable structure of core region of tip vortex at the early stage of formation, which promotes the increasing of local turbulence as well as mixture effects, thus the tip vortex generated by the slotted blade is diffused. For the baseline blade, the core region remains nearly unchanged with the increase in wake angle, while the outer layer of tip vortex continuously blends with the surrounding flow during its development. For the slotted blade, the vortex core characterized by a larger diameter and decreased vorticity magnitude is observed, which indicates that due to the attenuation of the internal stable structure of the blade tip vortex, the diffusion of the blade tip vortex is significantly and consequently accelerated. This fact indicates that when the tip vortex develops to a certain extent, the vortex strength of the core region is insufficient to maintain the stability of the entire tip vortex structure, thus the diffusion of the rotor tip vortex is promoted. Therefore, in order to strengthen the diffusion effect of rotor tip vortices, the excitation of instability in the vortex core region is necessary. This fact can explain why many flow control approaches that attempt to diffuse the tip vortex by modifying the external structure of tip vortex are not very effective [5].
Figure 19 shows the comparison of velocity profiles of a tip vortex in the Z-direction at different wake ages. The peak value of the velocity component in the vicinity of vortex core is reduced by about 50% with the slotted blade, which indicates that the result of IDDES is much closer to the experimental conclusion presented in reference [11]. Meanwhile, the predicted vortex core diameter of the slotted blade is approximately doubled at each wake age compared to the baseline blade, which is demonstrated more clearly in Figure 20.
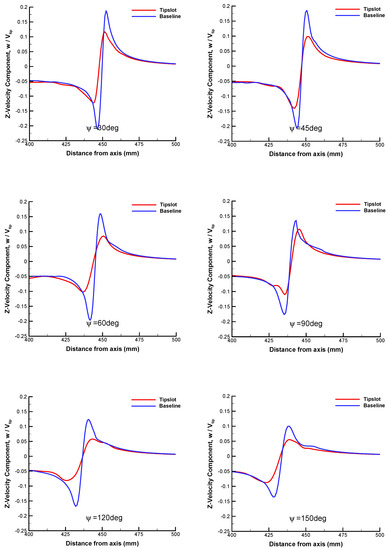
Figure 19.
Comparison of velocity profiles in the Z-direction at different wake ages between the baseline blade and the slotted-tip blade.
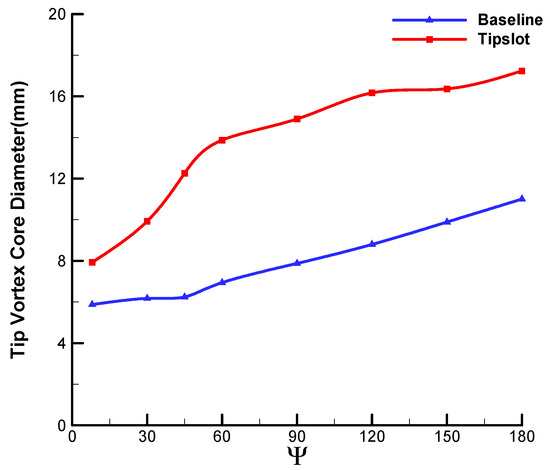
Figure 20.
Comparison of the vortex core diameters between the baseline blade and the slotted-tip blade.
In general, the IDDES result confirms the conclusion from the experiment and demonstrate the significant superiority over RANS for the capture of precise turbulence structures. The reduction of strength and rotating effect of the vortex core region are identified, which confirms that the tip slots promote the turbulent mixture inside the vortex core, thus the tip vortices can be diffused efficiently as a result. However, the noise level of specific frequency ranges might be promoted as the complexity of local flow interference increases, though the strength of tip vortices is weakened to some degree, which will be discussed in the future investigation.
4. Investigation of the Effect of Slot Parameters
4.1. Slot Number
In the above sections, all the parameters of the slots, including position, diameter and number, are set according to reference [11]. However, these parameters must be adjusted for various blades under different flight conditions. This section mainly analyzes the influence of the number of slots on the diffusion effect. The number of slots is reduced from 4 to 2, while the other parameters are kept unchanged. Figure 21 shows the sketch of the two-slot model. This blade is denoted as Tipslot–2slot. Based on the grid generation method of Section 2.1, the consistency of the grid can be ensured. IDDES simulation is implemented under the same hover condition with an identical simulation strategy.
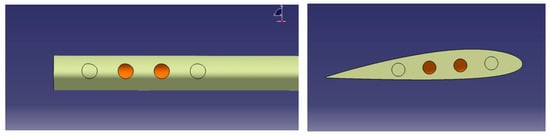
Figure 21.
Schematic of the Tipslot–2slot blade.
Figure 22 shows the comparative results in terms of velocity profile at different wake ages. It can be seen that the two-slot blade demonstrates a larger peak velocity value than the original slotted blade, which is closer to the baseline blade. It is indicated that decreasing the number of slots will reduce the diffusion effect on the tip vortices. Figure 23 presents the comparison of the core diameters calculated by the three blades. It is apparent that the vortex core diameter of the two-slot blade is approximately 1.5 times that of the baseline blade result. Moreover, the core diameter of two-slot blade is slightly smaller than the four-slot blade in the early stages before , while after , the core diameter of two-slot blade is about 80% of the value of the original slotted blade.
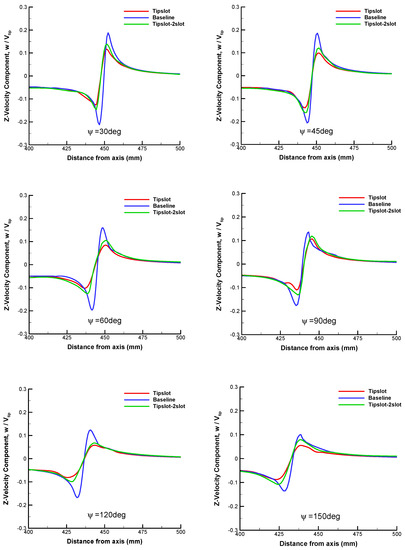
Figure 22.
Comparison of velocity profiles in the Z-direction at different wake ages among baseline, tipslot, and Tipslot–2slot blades.
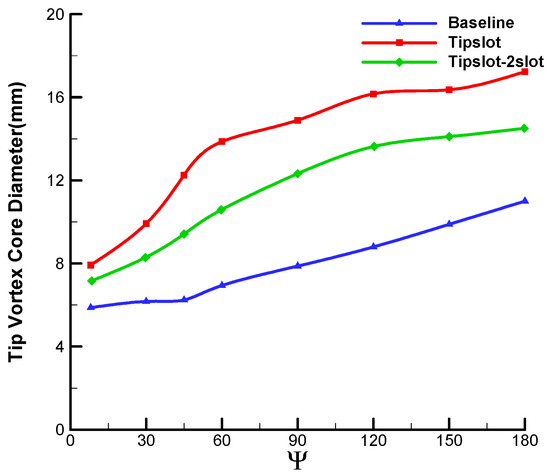
Figure 23.
Comparison of vortex core diameters among baseline, tipslot and Tipslot–2slot blades.
4.2. Slot Diameter
This section focuses on analyzing the influence of the slot diameter on the diffusion effect. The numerical configuration used in this part has four slots located on the chord plane of the blade with the slot diameter reduced to 1/2 of the original slot diameter. Figure 24 depicts the model, which is denoted as Tipslot–1/2D blade. Similarly, the simulation with IDDES is carried out in the investigation.
Figure 24.
Schematic of the Tipslot–1/2D blade.
Figure 25 shows the comparative results of the velocity profile at different wake ages. It can be seen from the figure that the velocity component of the 1/2-diameter blade is closer to the baseline blade, especially after , indicating that the diffusing effect of the slots is similarly weakened. Figure 26 shows the comparison of the vortex core diameter obtained through the three blades. It is apparent that the core diameter of 1/2-diameter blade is obviously smaller than the baseline blade while a little larger than the original slotted blade. The effect of the slot diameter reduction is not linear as is the case with the number of slots. When the total rate of flow through the slot is reduced to 1/4 of original slotted blade, the attenuation of the flow control efficiency is apparent. Hence, it is indicated that when the flow control technology is adopted for specific types of rotor blades, it is necessary to optimize the slot parameters according to specific geometry shapes and working conditions.
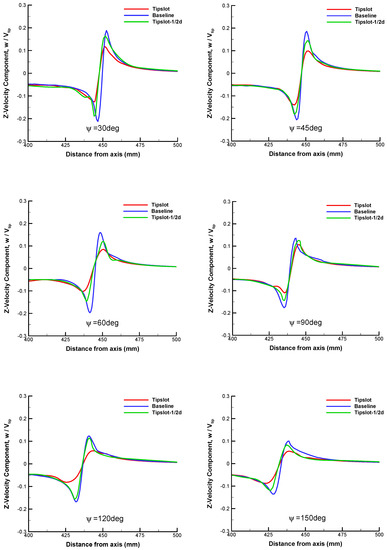
Figure 25.
Comparison of velocity profiles in Z-direction at different wake ages among baseline, tipslot and Tipslot–1/2D blades.
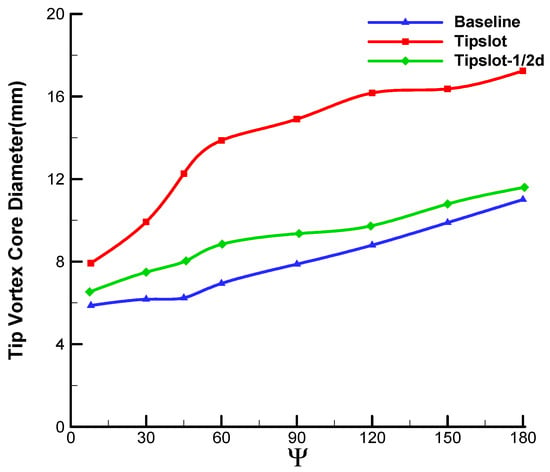
Figure 26.
Comparison of vortex core diameters among baseline, tipslot and Tipslot–1/2D blades.
5. Conclusions
The diffusing effect of the slotted–tip on a single–bladed rotor is confirmed at the hover state with numerical methods. The investigation is initiated by using RANS based on third-order MUSCL scheme. IDDES coupled with the fifth-order WENO scheme is then implemented in the investigation. Based on the results of IDDES, the diffusion mechanism of the tip vortices is analyzed, and the influence of slot number and diameter on diffusing effect is carried out.
The specific conclusions can be summarized as follows:
(1) For a proper resolution to the spatial turbulence with the switch to LES mode, the major improvement of IDDES compared to RANS is the resolution to the multiscale vortices, which is essential to the validation of the flow control efficiency and especially the estimation of the vortex core diameter.
(2) The IDDES result show that the number of secondary turbulent structures (the so-called vortex worms) near the slotted tip reduces significantly, which indicates the weakening of the rotation effect of the vortex core.
(3) The peak value of the velocity profiles in the vicinity of the vortex core reduced by about 50% with slotted-tip, and this result is closer to the experimental conclusion. Correspondingly, the predicted vortex core diameter of the slotted blade is approximately doubled at each wake age.
(4) For the slotted blade, because the exit flow passing through the slots will break up the stable structure of core region of the tip vortex during the early stages of vortex generation, which promotes an increase in local mixture effects, the vorticity value and rotating effect near the vortex core are greatly weakened as a result. Thus, the inner region of the tip vortex suggests a larger core diameter with decreased vorticity magnitude. With the increase in the wake age, the vortex diffusion becomes stronger, and the vorticity value and rotating effect near the vortex core are greatly weakened.
(5) As the total rate of flow through the slot is weakened, when the number or diameter of the slots is reduced, the attenuation of the diffusion efficiency is apparent. It is necessary to optimize the slot parameters according to the specific geometric shapes and working conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z.; methodology, H.Z.; software, W.S.; validation, W.S.; formal analysis, W.S.; investigation, W.S.; resources, Y.L.; data curation, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, W.S. and Y.L.; writing—review and editing, H.Z.; visualization, Y.L.; supervision, H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Scientific Research Fund of Young Teachers from Xi’an Technological University.
Data Availability Statement
Data available upon request due to privacy restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Conlisk, A.T. Modern helicopter aerodynamics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1997, 29, 515–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlisk, A.T. Modern helicopter rotor aerodynamics. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2001, 37, 419–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, H.Y. Rotor blade–vortex interaction noise. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2000, 36, 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst, A.; Barakos, G.N. A review of helicopter rotor blade tip shapes. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2013, 56, 35–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, C. Active rotor control for helicopters: Individual blade control and swashplateless rotor designs. CEAS Aeronaut. J. 2011, 1, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, C.; Ilie, M. Reduction of helicopter BVI noise using active flow control; the case of vortex street interactions. In Proceedings of the 18th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27–30 June 2012; p. 2141. [Google Scholar]
- Le Pape, A.; Lienard, C.; Bailly, J. Active flow control for helicopters. Aerosp. Lab. 2013, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, G.; Shi, Y. Numerical investigation on noise reduction of rotor blade-vortex interaction using blade surface jet blowing. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 106868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, G.; Shi, Y. Parametric effect of blade surface blowing on the reduction of rotor blade–vortex interaction noise. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2022, 35, 4021110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syriac, J.S.; Vinod, N. Numerical Analysis and Reduction of Blade-Vortex Interaction (BVI) Noise in Helicopter Using Numerical Simulation. In Machines, Mechanism and Robotics; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 547–553. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.O.; Leishman, J.G. Investigation of Helicopter Rotor-Blade-Tip-Vortex Alleviation Using a Slotted Tip. AIAA J. 2004, 42, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.O. Diffused tip vortex structure generated by a slotted tip rotor blade. In Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 10–13 January 2005; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.Y.; Kwon, O.J.; Han, Y.O. Viscous flow simulation of rotor blades with tip slots in hover. J. Am. Helicopter Soc. 2009, 54, 12006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Xu, G.; Shi, Y.; Huang, S. The influence of the blade tip shape on brownout by an approach based on computational fluid dynamics. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2021, 15, 692–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalart, P.R. Detached-eddy simulation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2009, 41, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaderjian, N.M.; Ahmad, J.U. Detached eddy simulation of the UH-60 rotor wake using adaptive mesh refinement. In Proceedings of the AHS International 68th Annual Forum, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 1–3 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chaderjian, N.M. Advances in rotor performance and turbulent wake simulation using DES and adaptive mesh refinement. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ICCFD7), Big Island, HI, USA, 9–13 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Pulliam, T.H.; Chaderjian, N.M. Simulations of XV-15 rotor flows in hover using OVERFLOW. In Proceedings of the Fifth Decennial AHS Aeromechanics Specialists’ Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–24 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Chaderjian, N.M.; Pulliam, T.H.; Holst, T.L. Effect of turbulence modeling on hovering rotor flows. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 22–26 June 2015; p. 2766. [Google Scholar]
- Shur, M.L.; Spalart, P.R.; Strelets, M.K.; Travin, A.K. A hybrid RANS-LES approach with delayed-DES and wall-modelled LES capabilities. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.S.; Shu, C.W. Efficient implementation of weighted ENO schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 1996, 126, 202–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leer, B. Towards the ultimate conservative difference scheme. V. A second-order sequel to Godunov’s method. J. Comput. Phys. 1979, 32, 101–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, A. Time dependent calculations using multigrid with applications to unsteady flows past airfoils and wings. In Proceedings of the 10th Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–26 June 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Li, J.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Numerical investigations on drag reduction of a civil light helicopter fuselage. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 106104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Enhancing the Resolution of Blade Tip Vortices in Hover with High-Order WENO Scheme and Hybrid RANS–LES Methods. Aerospace 2023, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalart, P.R.; Deck, S.; Shur, M.L.; Squires, K.; Streletsw, M.; Travin, A. A new version of detached-eddy simulation, resistant to ambiguous grid densities. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2006, 20, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).