An Effective Procedure to Build Space Object Datasets Based on STK
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Semantic Segmentation Network
2.2. Precision Validation Index
3. Datasets Preparation
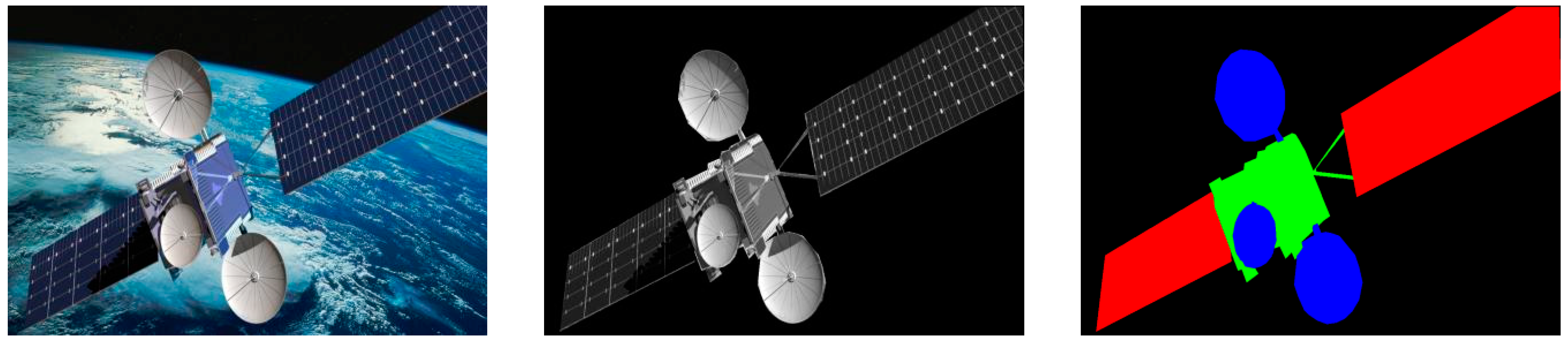
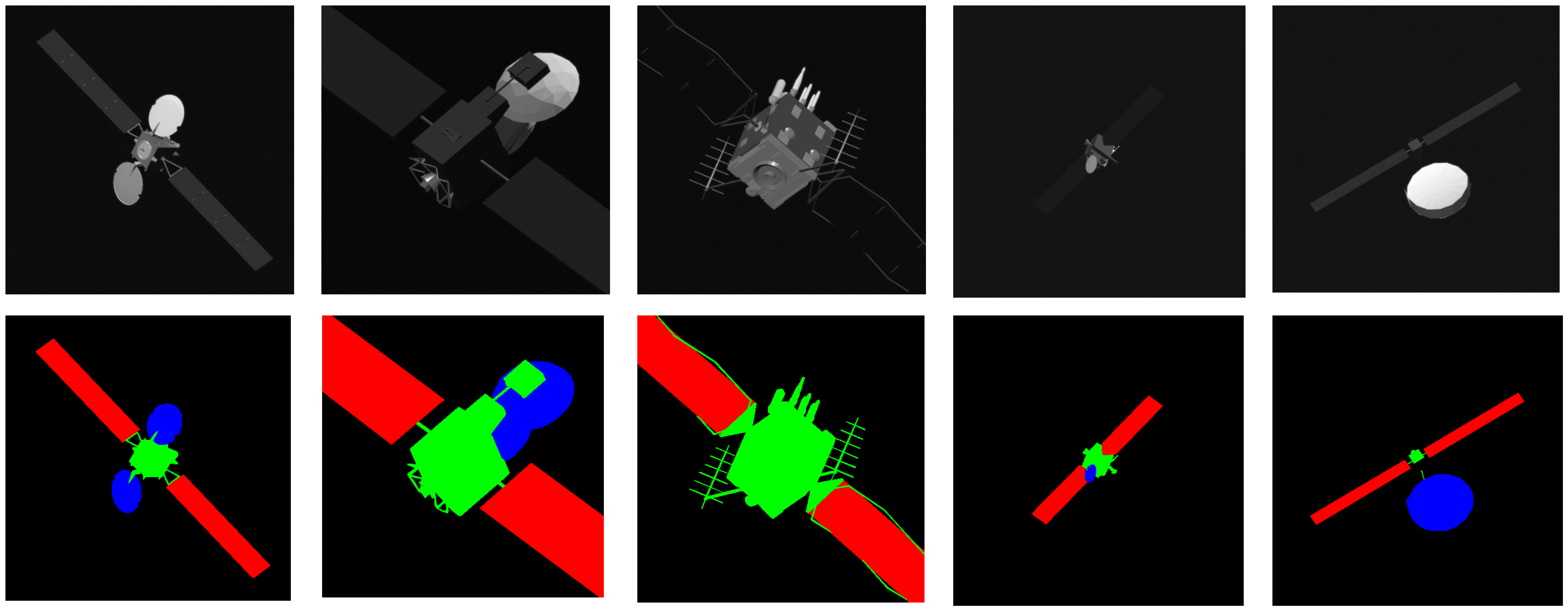
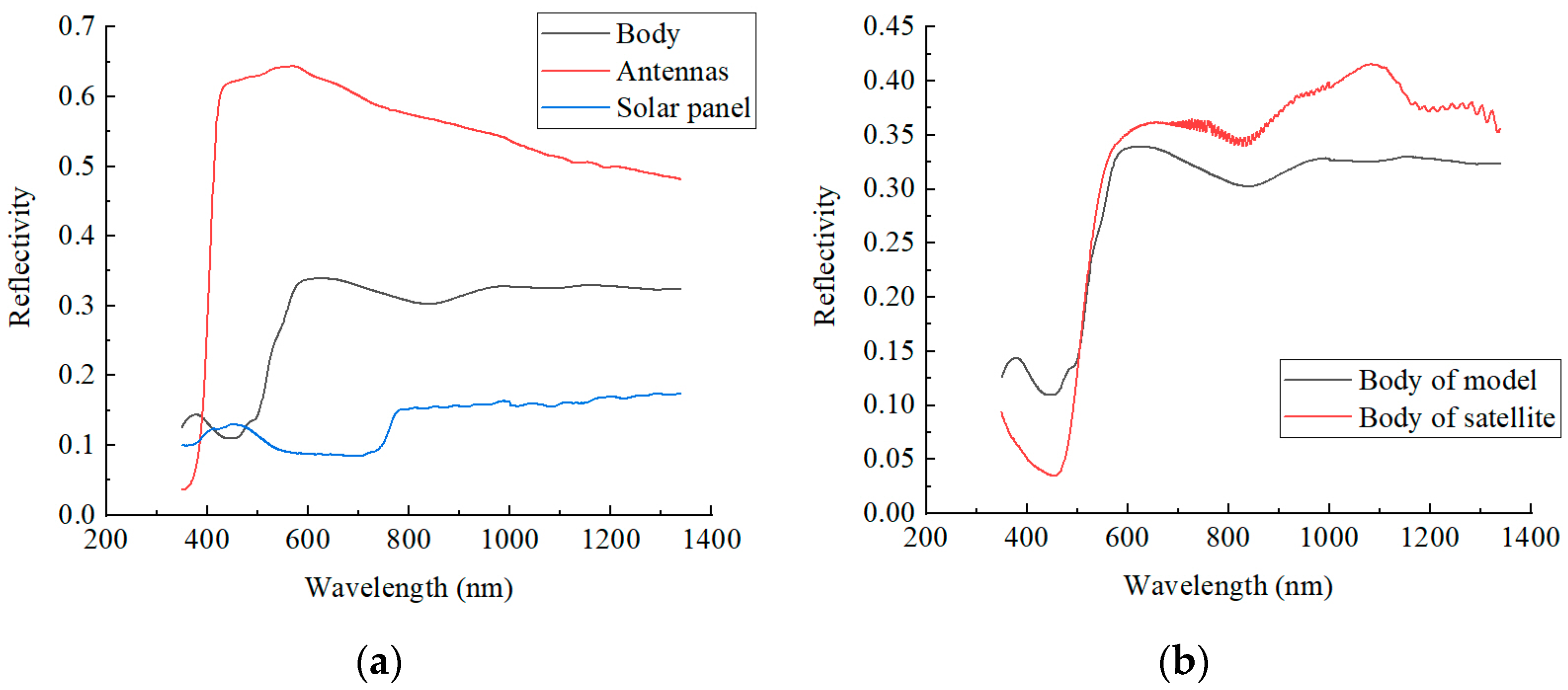
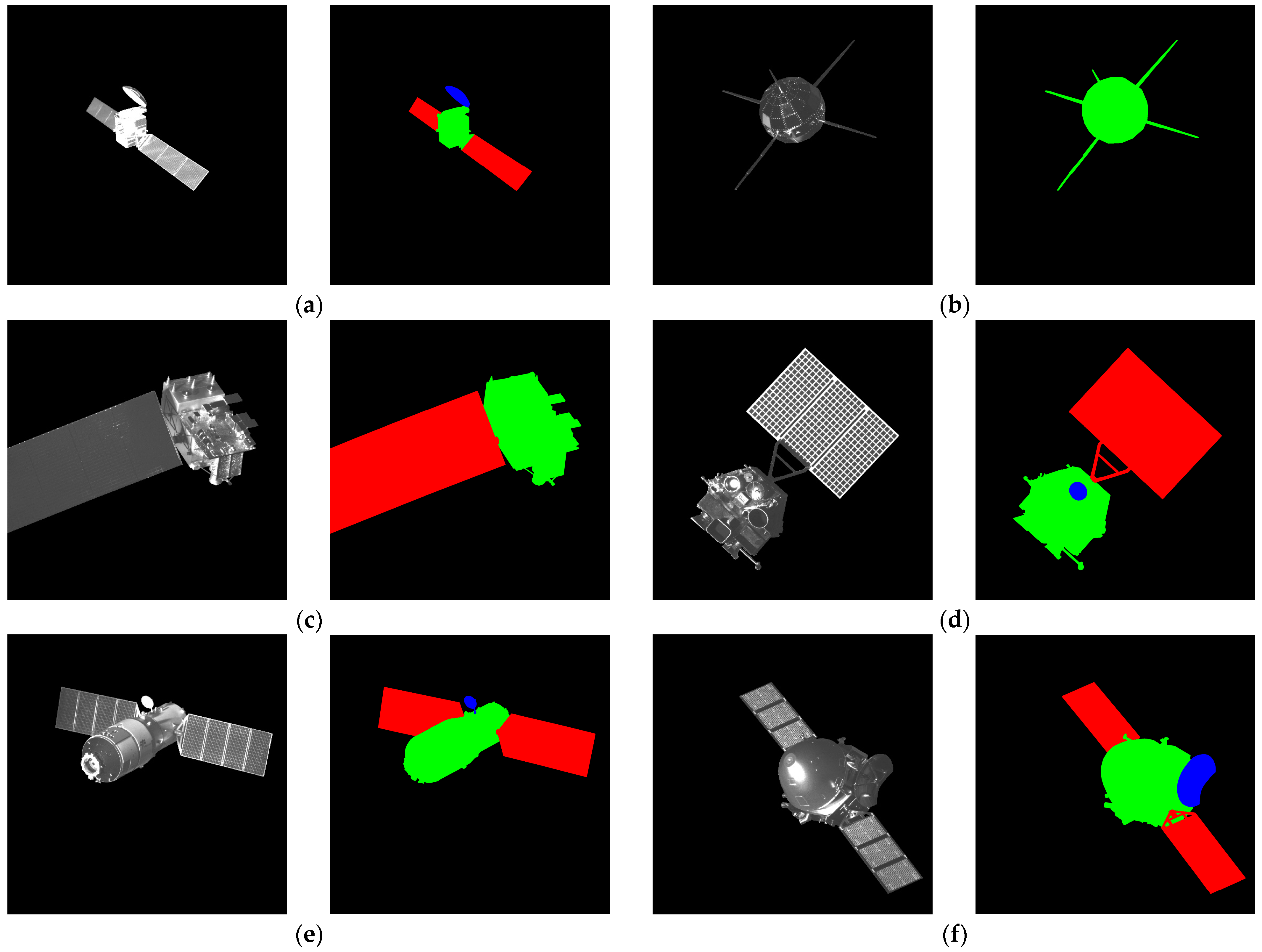
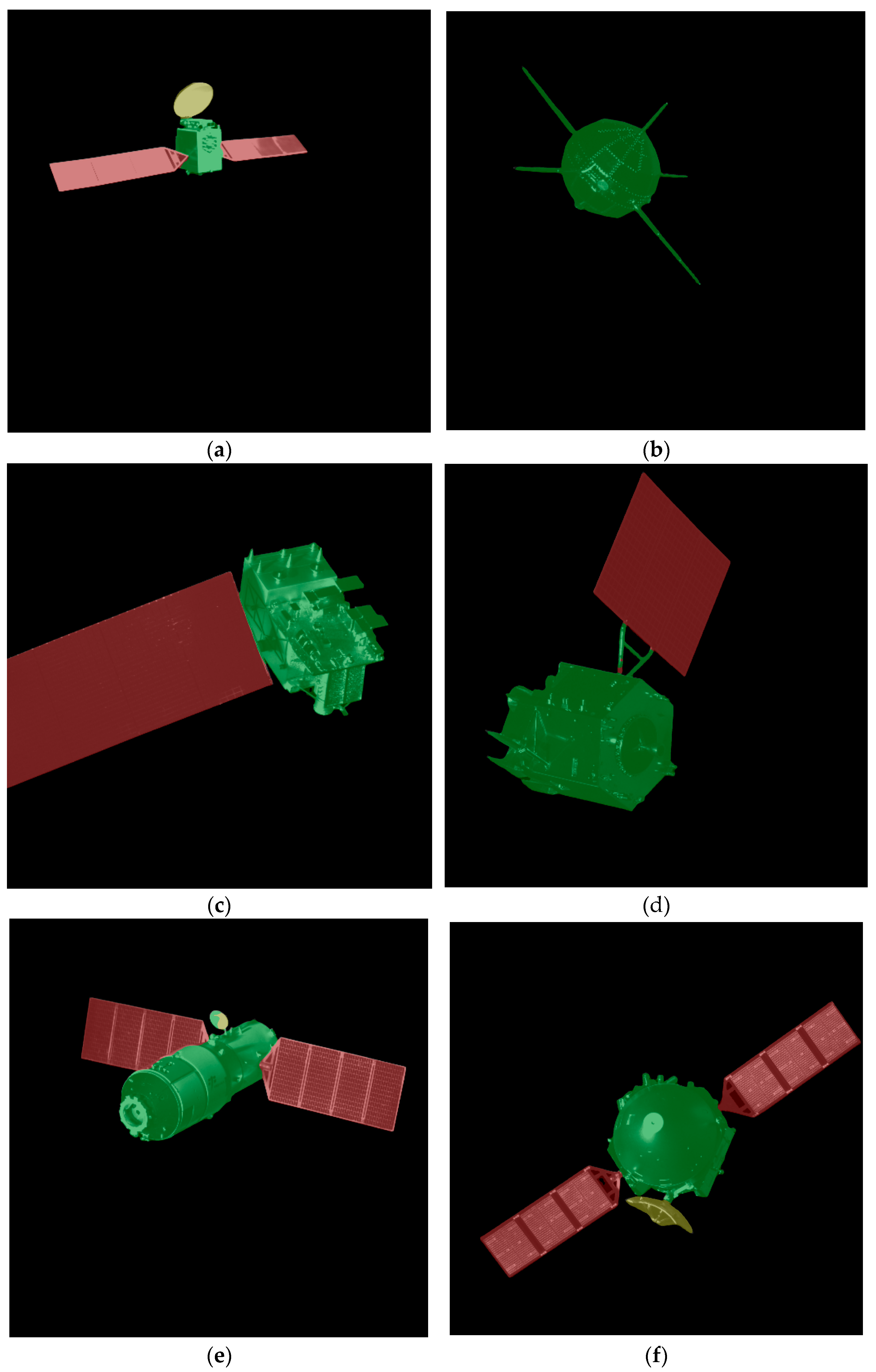
3.1. Spacecraft Dataset
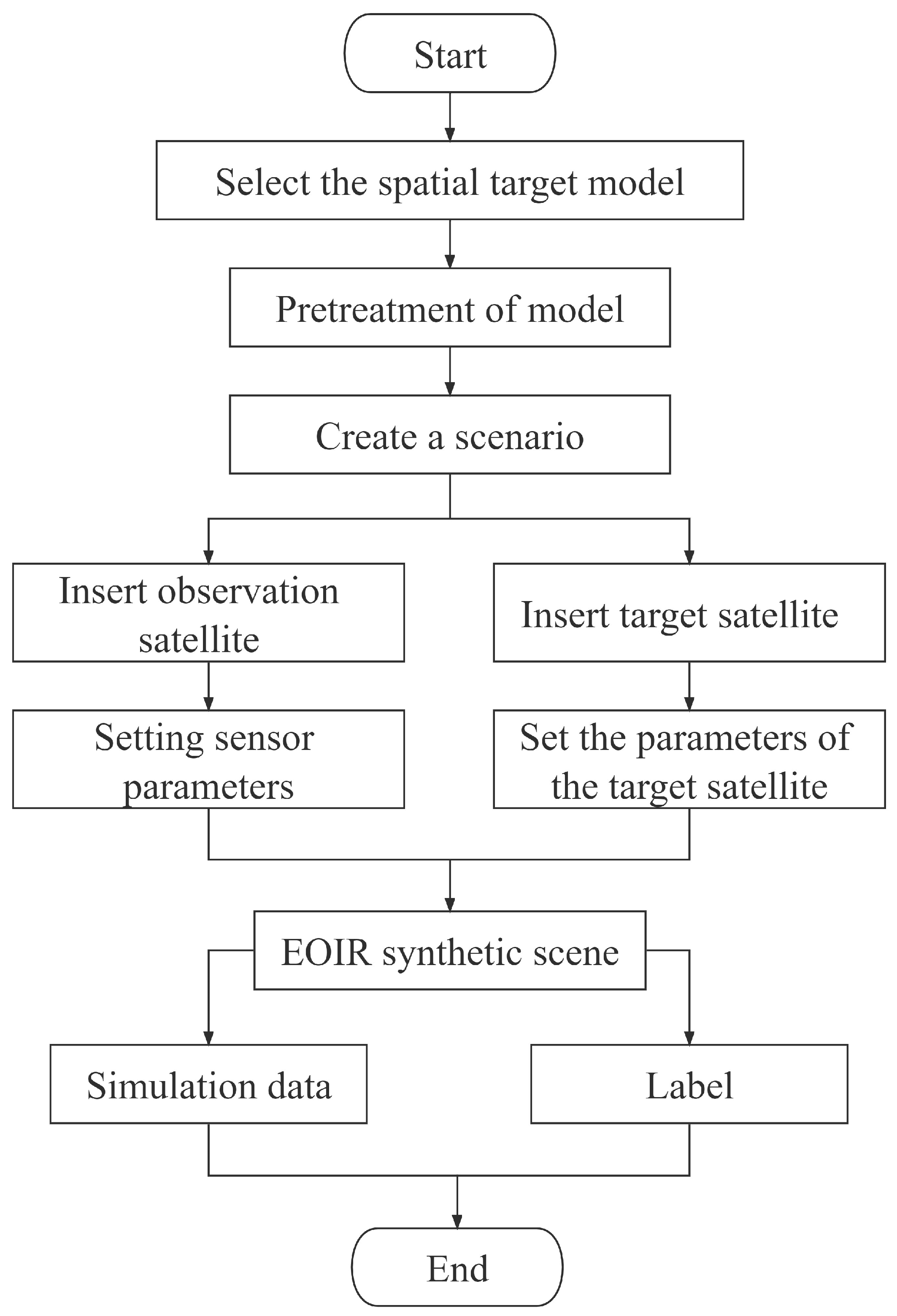
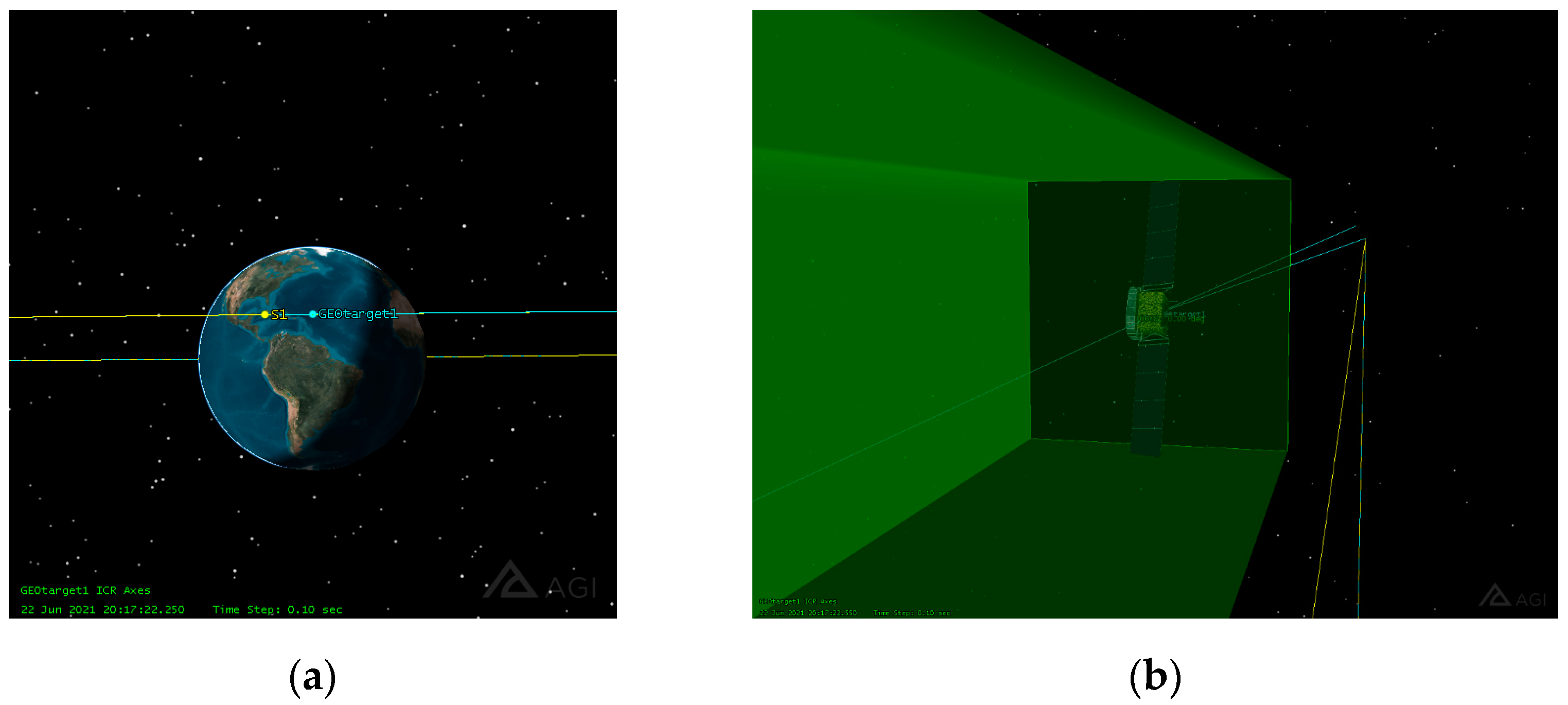
3.2. STK-Based Physical Simulation Dataset Construction
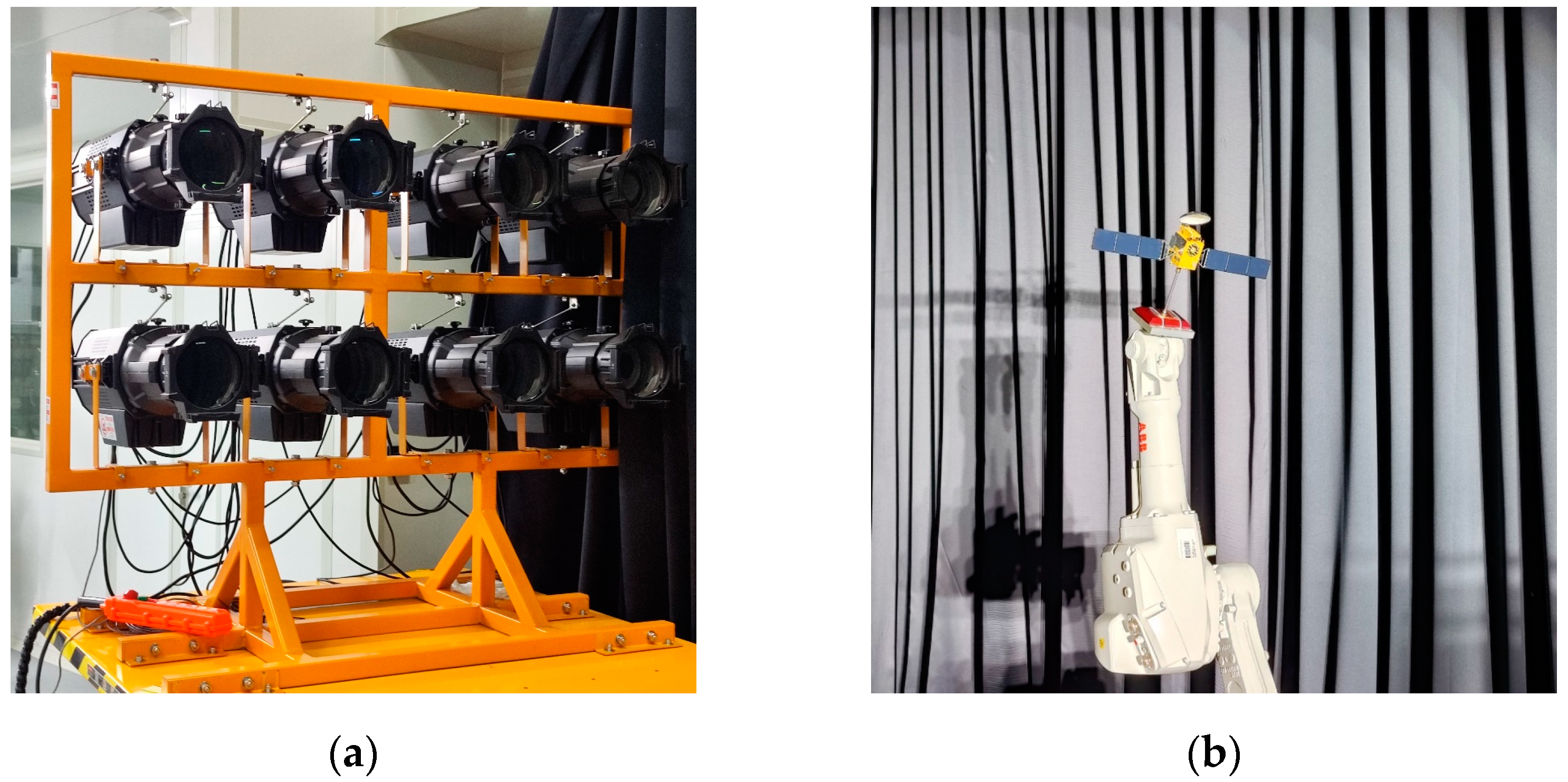
3.3. Real-Shot Validation Dataset Construction of Space Object
4. Results and Discussion
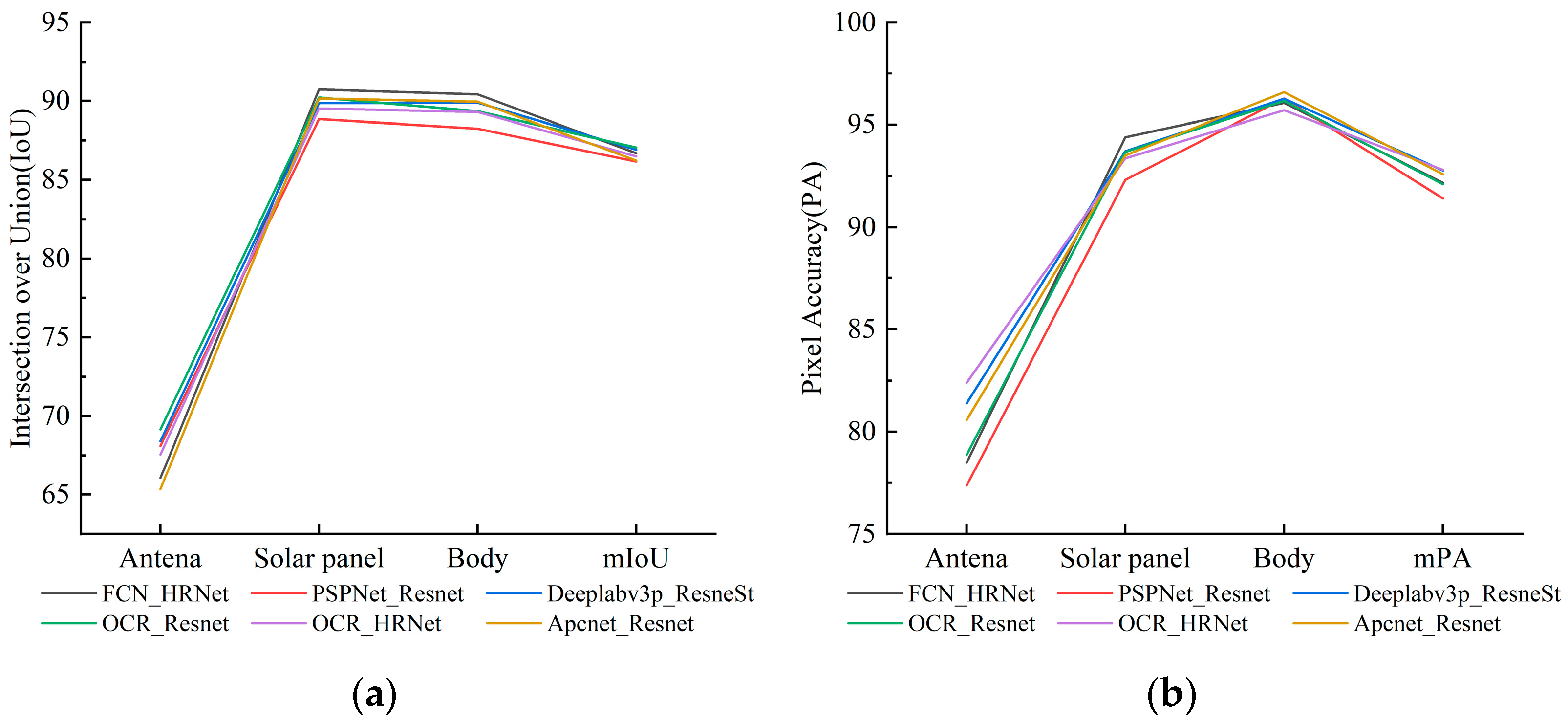
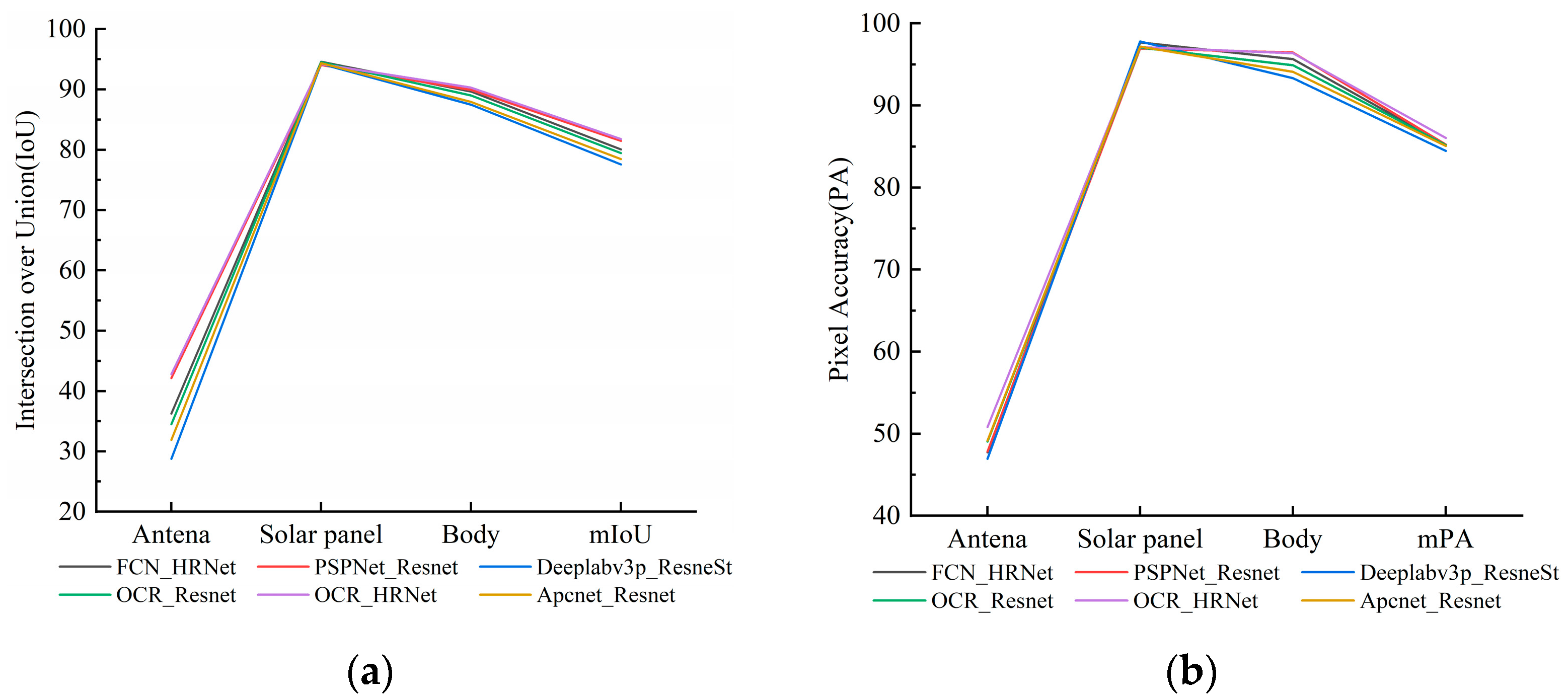
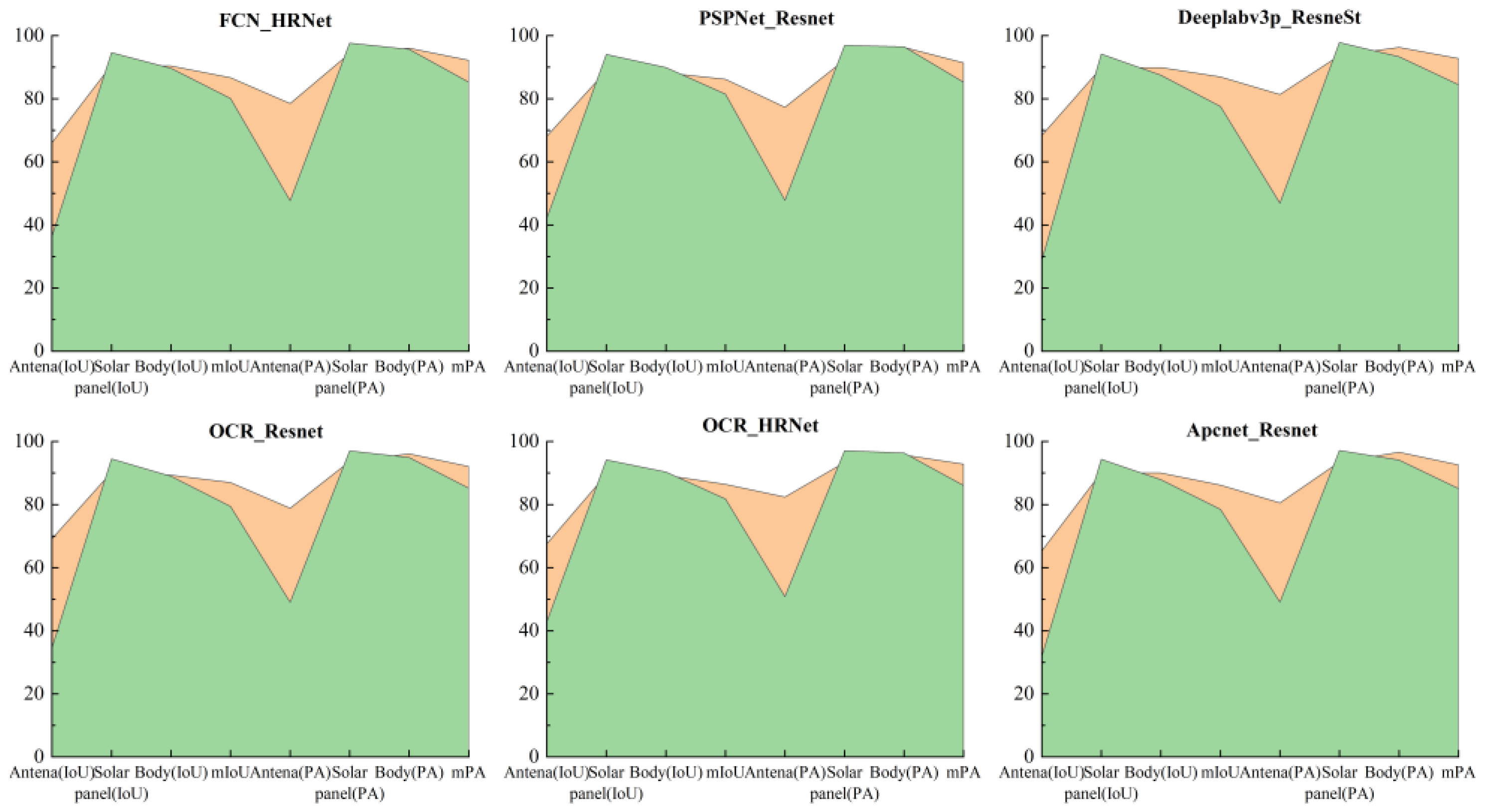
4.1. Joint Validation of Semantic Segmentation Accuracy of Spacecraft Dataset and Real-Shot Validation Dataset
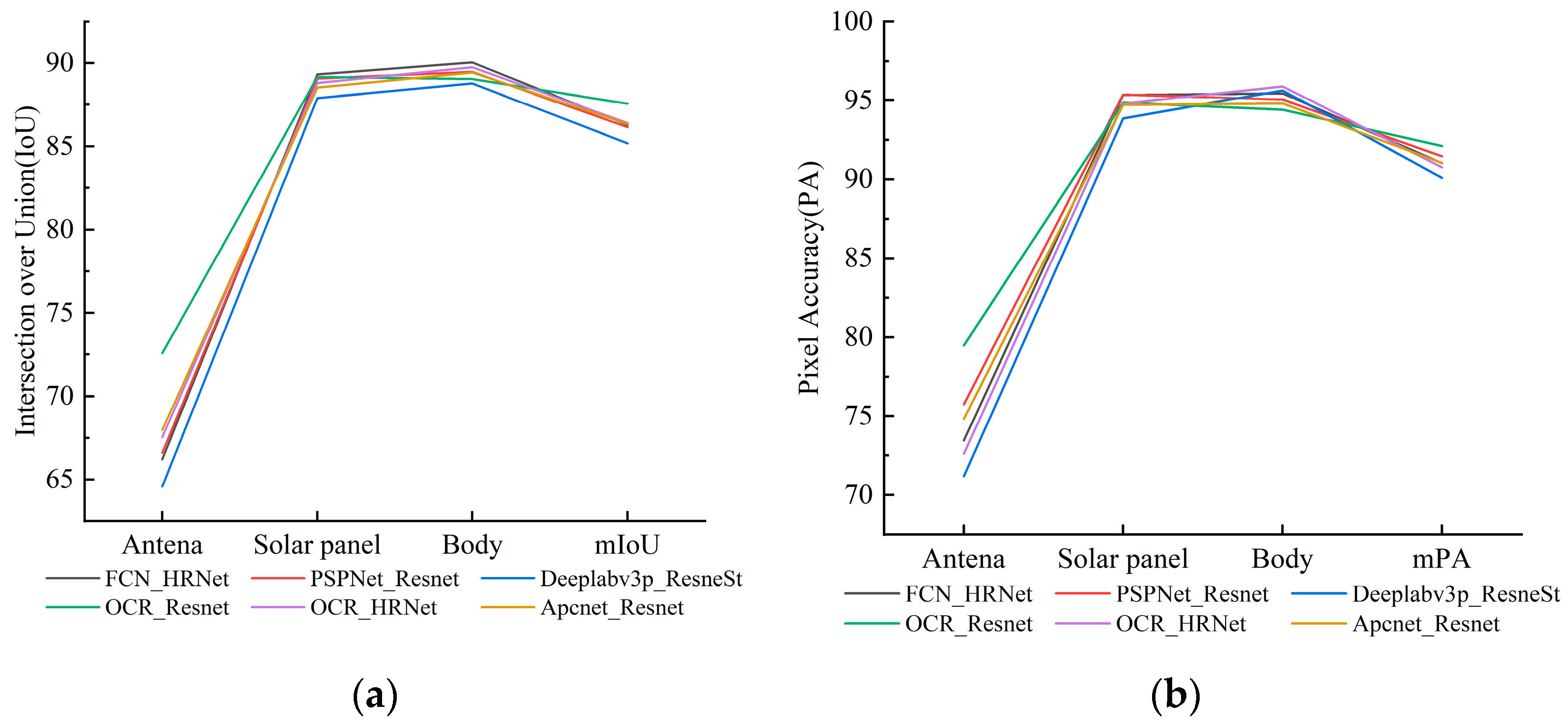
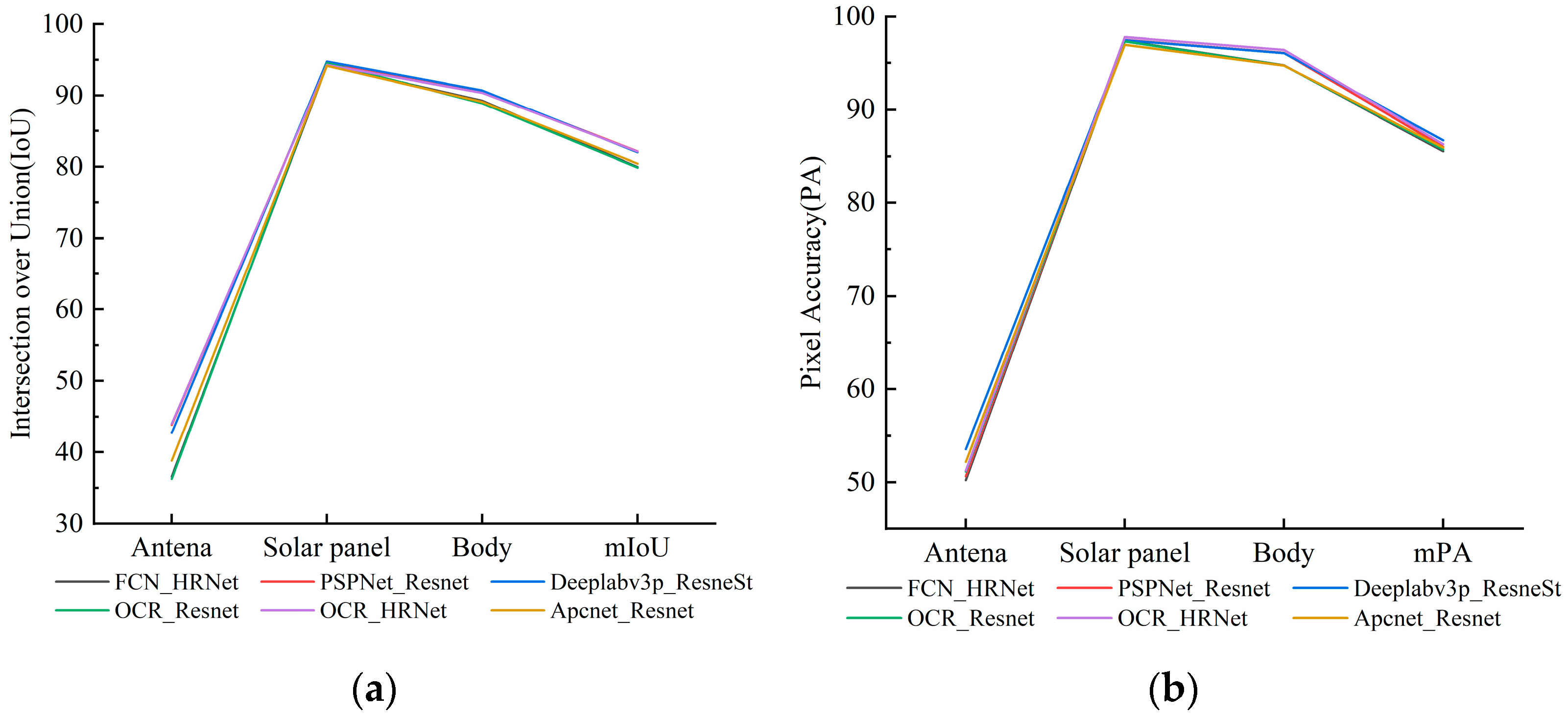
4.2. Joint Validation of Semantic Segmentation Accuracy of Mixed Dataset and Real-Shot Validation Dataset
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnhart, D.; Sullivan, B.; Hunter, R.; Bruhn, J.; Fowler, E.; Hoag, L.M.; Chappie, S.; Henshaw, G.; Kelm, B.E.; Kennedy, T. Phoenix program status-2013. In Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE 2013 Conference and Exposition, San Diego, CA, USA, 10–12 September 2013; p. 5341. [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker, M.A.; Vavrina, M.; Gaylor, D.E.; Mcintosh, R.; Volle, M.; Jacobsohn, J. OSAM-1 decommissioning orbit design. In Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, South Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 9–13 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, S.; Nagai, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Masuda, K.; Abe, N. Approach for on-orbit maintenance and experiment plan using 150kg-class satellites. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tarabini, L.; Gil, J.; Gandia, F.; Molina, M.Á.; Del Cura, J.M.; Ortega, G. Ground guided CX-OLEV rendez-vous with uncooperative geostationary satellite. Acta Astronaut. 2007, 61, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, B.B.; Smith, R.C.; Naasz, B.J.; Pellegrino, J.F.; Bacon, C.E. The restore-L servicing mission. In Proceedings of the AIAA Space 2016, Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2016; p. 5478. [Google Scholar]
- Aglietti, G.; Taylor, B.; Fellowes, S.; Ainley, S.; Tye, D.; Cox, C.; Zarkesh, A.; Mafficini, A.; Vinkoff, N.; Bashford, K. RemoveDEBRIS: An in-orbit demonstration of technologies for the removal of space debris. Aeronaut. J. 2020, 124, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telaar, J.; Estable, S.; De Stefano, M.; Rackl, W.; Lampariello, R.; Ankersen, F.; Fernandez, J.G. Coupled control of chaser platform and robot arm for the e. deorbit mission. In Proceedings of the 10th International ESA Conference on Guidance Navigation and Control Systems (GNC), Salzburg, Austria, 29 May–2 June 2017; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ellery, A. Tutorial Review on Space Manipulators for Space Debris Mitigation. Robotics 2019, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Assessment of Options for Extending the Life of the Hubble Space Telescope: Final Report; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrini, M.; Di Lizia, P. Guidance Strategy for Autonomous Inspection of Unknown Non-Cooperative Resident Space Objects. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2022, 45, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, P.; Meng, Z.; Liu, Z. Precise angles-only navigation for noncooperative proximity operation with application to tethered space robot. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2018, 27, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Liao, Y. Review the state-of-the-art technologies of semantic segmentation based on deep learning. Neurocomputing 2022, 493, 626–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yi, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Cao, S. Automated synthetic datasets construction for part semantic segmentation of non-cooperative satellites. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Machine Vision, Shenzhen, China, 26 February–1 March 2021; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Hu, H.; Xie, X.; He, Y. Pose Measurement Method of Non-cooperative Targets Based on Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi’an, China, 9–11 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S. Pose Estimation of Uncooperative Spacecraft Using Monocular Vision and Deep Learning; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Stathopoulou, E.K.; Remondino, F. Semantic Photogrammetry—Boosting Image-Based 3D Reconstruction with Semantic Labeling. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on 3D Virtual Reconstruction and Visualization of Complex Architectures (3D-ARCH), Bergamo, Italy, 6–8 February 2019; Copernicus Gesellschaft Mbh: Göttingen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hane, C.; Zach, C.; Cohen, A.; Pollefeys, M. Dense Semantic 3D Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1730–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, W.; Draktontaidis, S.; Lui, N. Semantic Image Segmentation of Imagery of Unmanned Spacecraft Using Synthetic Data; Technical Report; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cheplygina, V.; De Bruijne, M.; Pluim, J.P.W. Not-so-supervised: A survey of semi-supervised, multi-instance, and transfer learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 54, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang Anh, D.; Chen, B.; Chin, T.-J.; Soc, I.C. A Spacecraft Dataset for Detection, Segmentation and Parts Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Electr Network, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Faraco, N.; Maestrini, M.; Di Lizia, P. Instance Segmentation for Feature Recognition on Noncooperative Resident Space Objects. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2022, 59, 2160–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Object-contextual representations for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Adaptive pyramid context network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; He, T.; Mueller, J.; Manmatha, R. Resnest: Split-attention networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, X. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contributors, M. MMSegmentation: Openmmlab Semantic Segmentation Toolbox and Benchmark. Available online: https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmsegmentation (accessed on 18 May 2022).
- Everingham, M.; Winn, J. The PASCAL visual object classes challenge 2012 (VOC2012) development kit. Pattern Anal. Stat. Model. Comput. Learn. Tech. Rep. 2012, 2007, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Puig, X.; Fidler, S.; Barriuso, A.; Torralba, A. Scene parsing through ade20k dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? the kitti vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.H.; Märtens, M.; Lecuyer, G.; Izzo, D.; D’Amico, S. SPEED+: Next-generation dataset for spacecraft pose estimation across domain gap. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO), Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2022. [Google Scholar]




| Name | Configurations |
|---|---|
| Camera | Point Grey |
| Focal | 75mm |
| Resolution | 2048 × 2048 |
| Light Intensity | 0.1 Solar Constant |
| Light Condition | 0°, 30° and 60° |
| Name | Configurations |
|---|---|
| Operating system | Ubuntu 20.04 |
| GPU | NVIDIA TITAN RTX |
| CPU | Intel i9-10900k |
| CUDA | Cuda 11.3 |
| Memory | 32G |
| Deep learning framework | Pytorch 1.12 |
| Python | 3.8 |
| Method | Dataset | mIoU (%) | mPA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCN_HRNet | spacecraft dataset | 80.06 | 85.21 |
| mixed dataset | 79.96 | 85.56 | |
| PSPNet_ResNet | spacecraft dataset | 81.45 | 85.25 |
| mixed dataset | 82.14 | 86.02 | |
| Deeplabv3p_ResNeSt | spacecraft dataset | 77.56 | 84.47 |
| mixed dataset | 81.99 | 86.73 | |
| OCR_ResNet | spacecraft dataset | 79.43 | 85.2 |
| mixed dataset | 79.85 | 85.75 | |
| OCR_HRNet | spacecraft dataset | 81.77 | 86.04 |
| mixed dataset | 82.11 | 86.31 | |
| Apcnet_ResNet | spacecraft dataset | 78.46 | 85.06 |
| mixed dataset | 80.43 | 85.93 | |
| Average accuracy improvement | 1.29 | 0.85 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, R.; Song, A.; Duan, H.; Pei, H. An Effective Procedure to Build Space Object Datasets Based on STK. Aerospace 2023, 10, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10030258
Wei R, Song A, Duan H, Pei H. An Effective Procedure to Build Space Object Datasets Based on STK. Aerospace. 2023; 10(3):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10030258
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Rongke, Anyang Song, Huixian Duan, and Haodong Pei. 2023. "An Effective Procedure to Build Space Object Datasets Based on STK" Aerospace 10, no. 3: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10030258
APA StyleWei, R., Song, A., Duan, H., & Pei, H. (2023). An Effective Procedure to Build Space Object Datasets Based on STK. Aerospace, 10(3), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10030258





