Fixed-Time Convergent Guidance Law with Angle Constraint and Autopilot Lag Compensation Using Partial-State Feedback
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The fixed-time convergent guidance law with AC and ALC is achieved for the first time.
- (2)
- (3)
2. Preliminaries
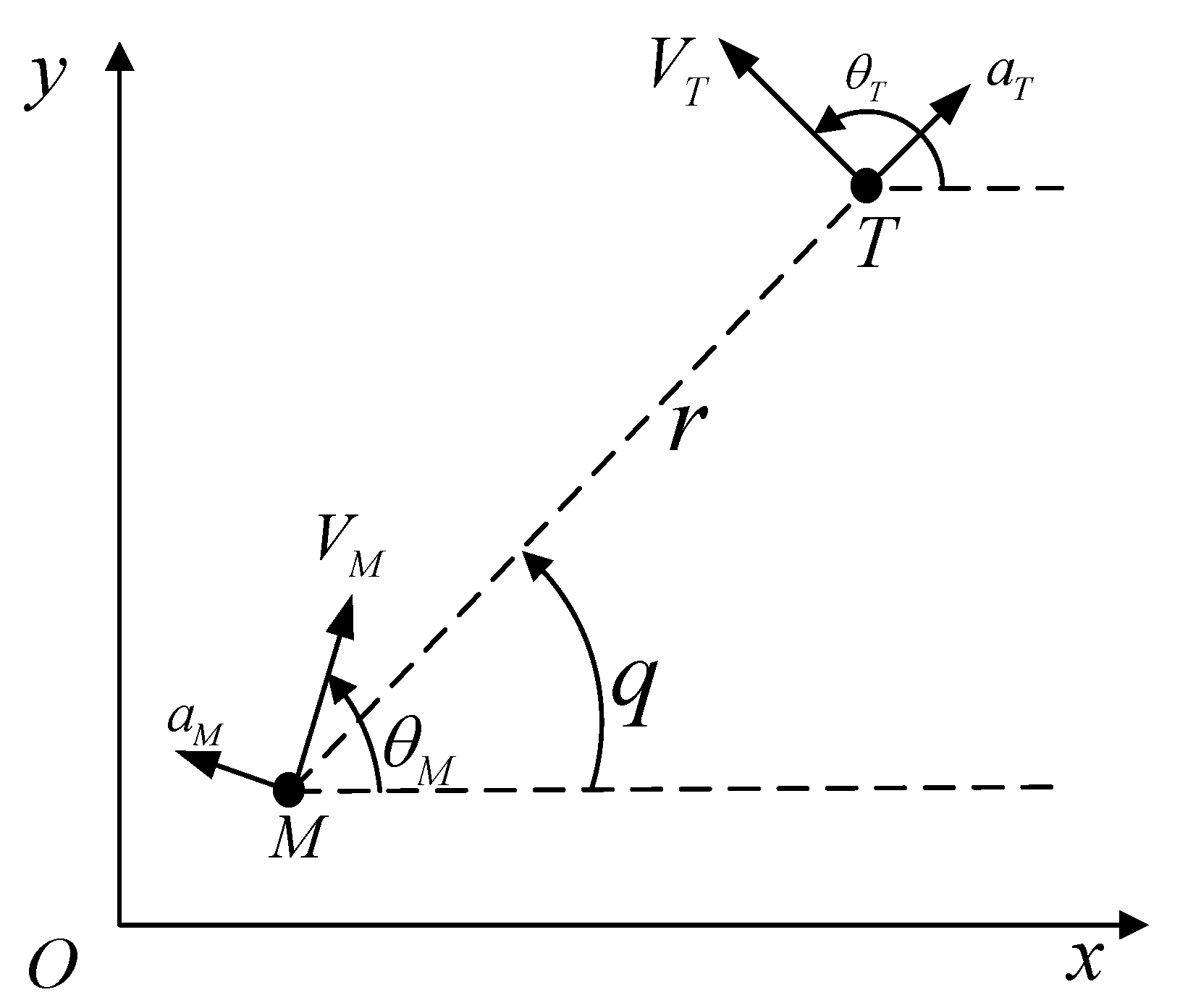
2.1. Model of Missile-Target Engagement
2.2. Design Objective and Motivation
- (1)
- The first objective is to design the command of autopilot u in such a way that the guidance errors are guaranteed in fixed-time under the disturbance . And, the convergence time is always bounded by a fixed constant. Compared with existing results, the fixed-time convergent guidance scheme with AC and ALC is achieved for the first time.
- (2)
- (3)
- The third objective is to not only guarantee the fixed-time convergence, but also to strictly guarantee the guidance error converges to zero rather than a neighborhood of zero such as in the existing fixed-time convergent guidance law in [32,33]. Thus, the proposed guidance law should avoid using the approximate method in [32,33].
2.3. Fundamental Facts
3. Main Result
3.1. Fixed-Time Convergent State Observer
3.2. Fixed-Time Convergent Guidance Law
4. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proof of Theorem 1
Appendix B. Proof of Theorem 2
References
- Ghawghawe, S.N.; Ghose, D. Pure proportional navigation against time-varying target maneuvers. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 1999, 22, 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Guoxin, S.U.N.; Qiuqiu, W.E.N.; Zhiqiang, X.U. Impact time control using biased proportional navigation for mis-siles with varying velocity. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 33, 956–964. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. A modified cooperative proportional navigation guidance law. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 5692–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, I.S.; Karpenko, M.; Lee, J.I. Connections between proportional navigation and terminal velocity maximi-zation guidance. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2020, 43, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Mu, C.; Shen, T. Robust guidance law with L2 gain performance. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2001, 44, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechevin, N.; Rabbath, C.A. Lyapunov-based nonlinear missile guidance. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2004, 27, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J. An observer-based continuous adaptive sliding mode guidance against chattering for homing missiles. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2019, 41, 3309–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denggao, J.; He, F.; Yao, Y. Approach for Missile Overload Requirement Analysis in Terminal Guidance. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2009, 22, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Niu, Y.; Zou, Y. Finite-time stabilization via sliding mode control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2016, 62, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.P.; Bernstein, D.S. Geometric homogeneity with applications to finite-time stability. Math. Control Signals Syst. 2005, 17, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Levant, A.; Li, S. Simple homogeneous slidingmode controller. Automatica 2016, 67, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, G.; Yongzhi, S.; Xiangdong, L. Finite-time sliding mode attitude control for a reentry vehicle with blended aerodynamic surfaces and a reaction control system. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 964–976. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Guangqing, X.I.A. A finite-time 3D guidance law based on fixed-time convergence disturbance observer. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 33, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Golestani, M.; Mohammadzaman, I.; Yazdanpanah, M.J.; Vali, A.R. Application of finite-time integral sliding mode to guidance law design. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2015, 137, 114501-1–114501-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Guidance law design based on non-smooth control. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2013, 35, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Lee, C.H. Optimal impact angle guidance for exoatmospheric interception utilizing gravitational effect. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 55, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.G.; Kim, T.H.; Tahk, M.J. Biased PNG with terminal-angle constraint for intercepting nonmaneuvering targets under physical constraints. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 1562–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, J. A new sliding mode control design for integrated missile guidance and control system. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yujie, S.I.; Song, S. Three-dimensional adaptive finite-time guidance law for intercepting maneuvering targets. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2017, 30, 1985–2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.R.; Rao, S.; Ghose, D. Nonsingular terminal sliding mode guidance with impact angle constraints. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2014, 37, 1114–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Song, S.; Guo, Y. Nonlinear disturbance observer-based fast terminal sliding mode guidance law with impact angle constraints. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2015, 11, 782–802. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Lan, G.; Yang, Y.; Lu, H.; Huang, X. Terminal angle constrained time-varying sliding mode guidance law with autopilot dynamics and input saturation. Asian J. Control 2023, 25, 1130–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S. Two composite guidance laws based on the backstepping control and disturbance ob-servers with autopilot lag. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 2019, 41, 2957–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.L.; Yan, H.; Ji, H.B. A guidance law with finite time convergence considering autopilot dynamics and uncertainties. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2014, 12, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Liang, X.; Duan, G. Adaptive block dynamic surface control for integrated missile guidance and autopilot. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2013, 26, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Lin, D.; Wang, J. Robust terminal angle constraint guidance law with autopilot lag for intercepting maneuvering targets. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 81, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Luo, S. Composite guidance laws based on sliding mode control with impact angle constraint and autopilot lag. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2013, 35, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, A.; Fridman, L. Stability notions and Lyapunov functions for sliding mode control systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2014, 351, 1837–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, C. Fast fixed-time nonsingular terminal sliding mode control and its application to chaos sup-pression in power system. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2016, 64, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Z. Nonsingular fixed-time consensus tracking for second-order multi-agent networks. Automatica 2015, 54, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, B. Fixed-Time Convergent Guidance Law with Impact Angle Control. Complexity 2020, 2020, 5019689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Cai, Y.; Yu, Z. Three-Dimensional Fast Fixed-time Convergence Guidance Law with Impact Angle Con-straint. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 180467–180481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shengjing, T. An adaptive fast fixed-time guidance law with an impact angle constraint for intercepting maneuvering targets. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 1327–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Vázquez, A.J. Sánchez-Torres, J.D.; Anguiano-Gijón, C.A. Single-channel predefined-time synchronization of chaotic systems. Asian J. Control 2019, 23, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Zavala, E.; Moreno, J.A.; Fridman, L.M. Uniform robust exact differentiator. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2011, 56, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Lu, H.; Zuo, Z. Fixed-time stabilization of high-order integrator systems with mismatched disturbances. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 94, 2889–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
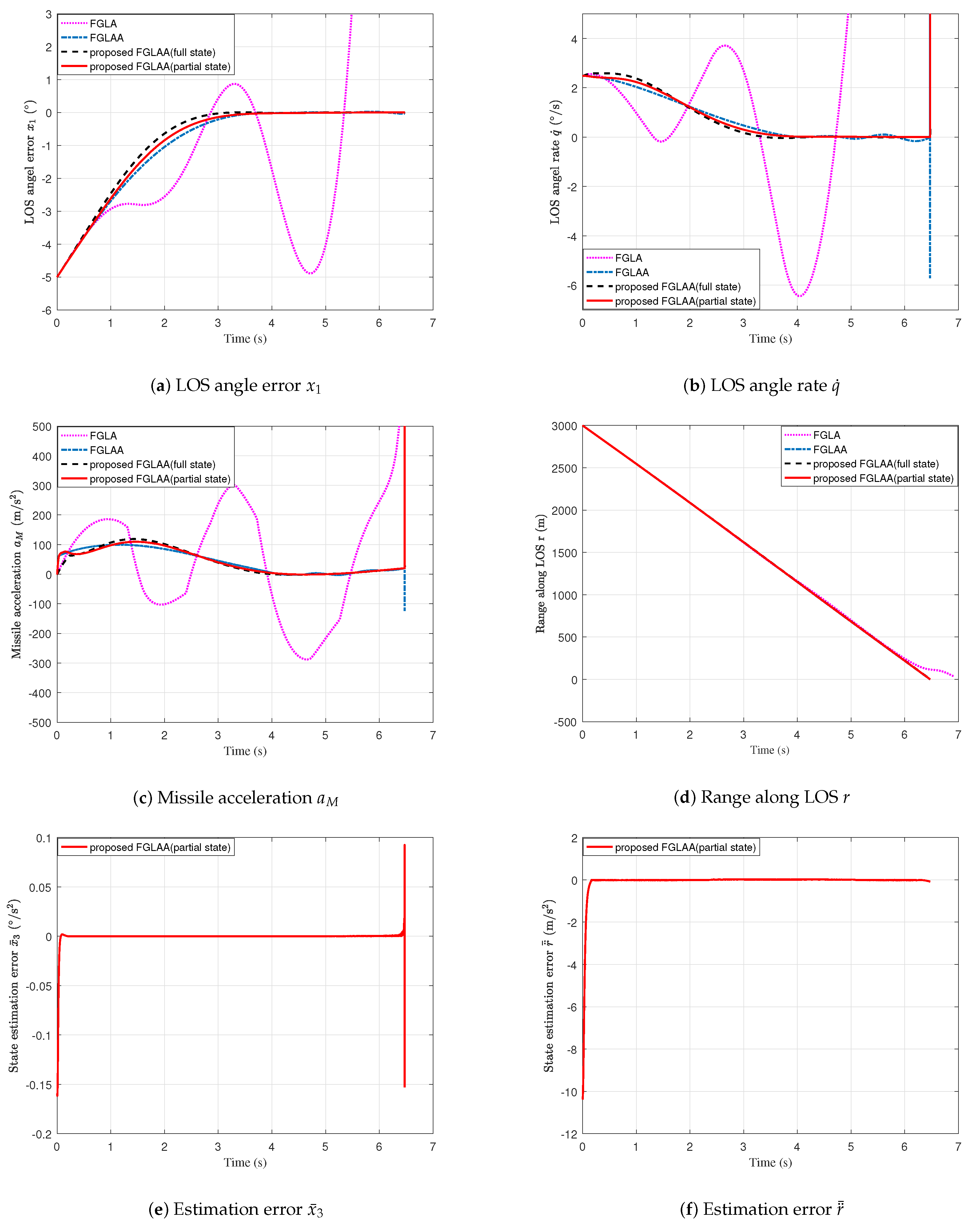
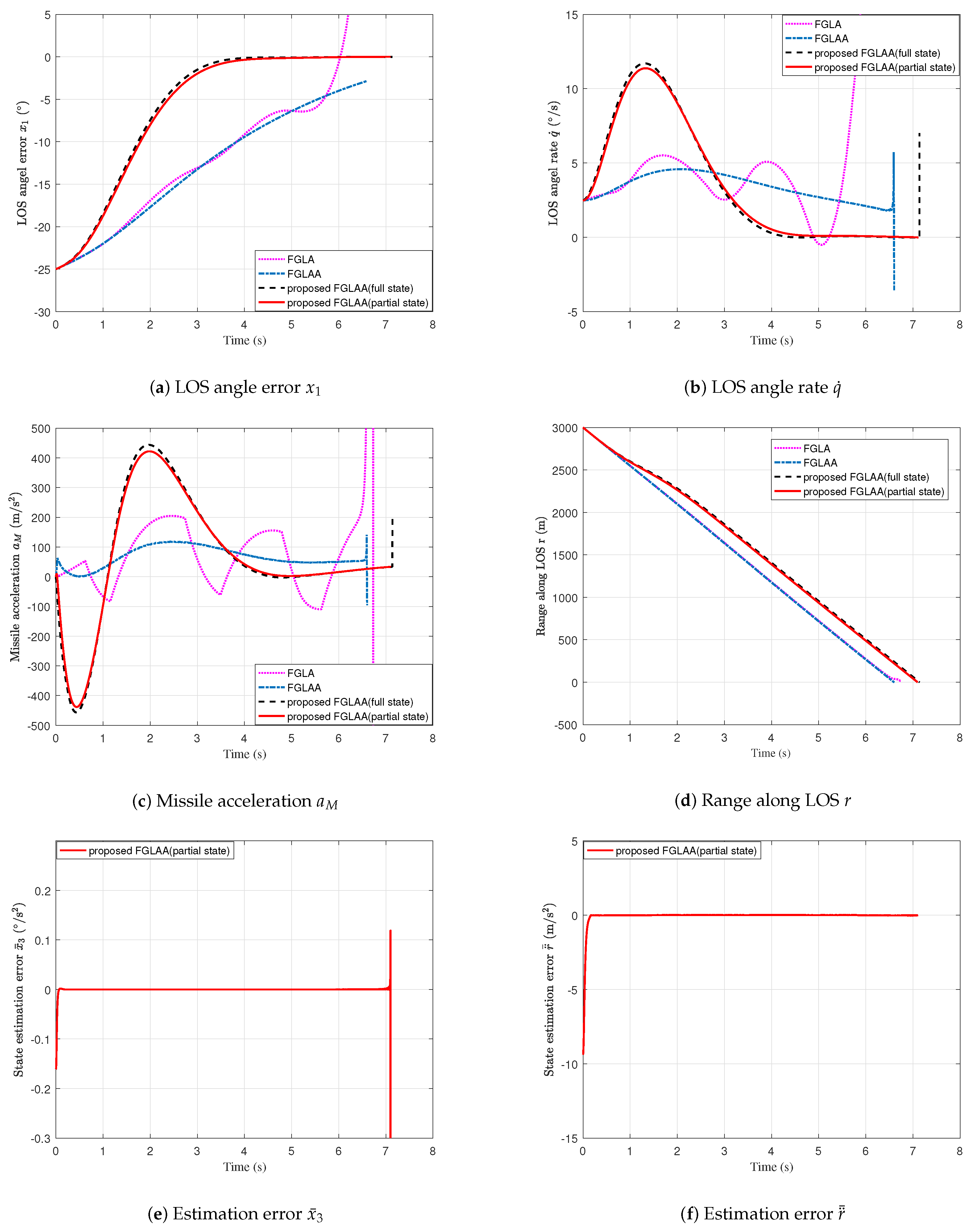
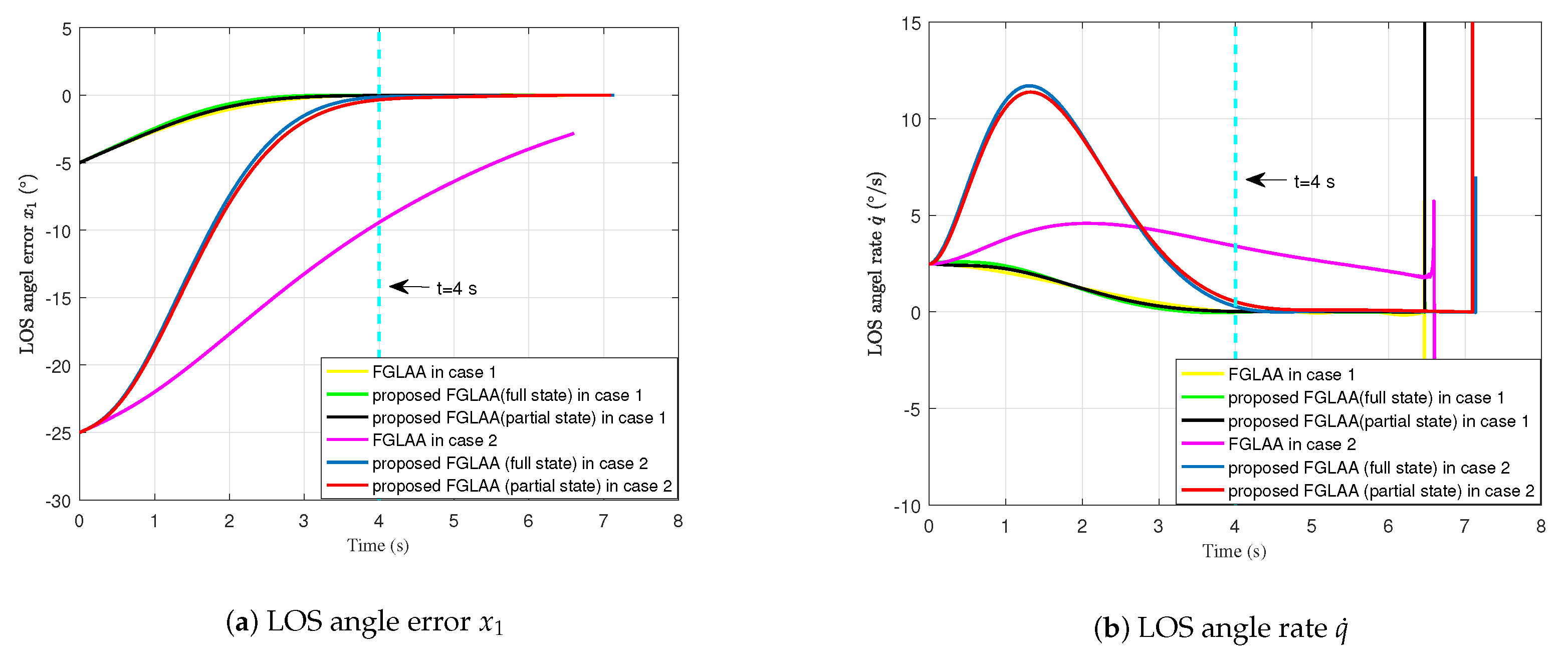
| Guidance Method | Case 1 (m) | Case 2 (m) |
|---|---|---|
| FGLA | 7.67 | 12.54 |
| FGLAA | 2.55 | |
| proposed FGLAA (full state) | ||
| proposed FGLAA (partial state) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Niu, Z.; Luo, S.; Du, F. Fixed-Time Convergent Guidance Law with Angle Constraint and Autopilot Lag Compensation Using Partial-State Feedback. Aerospace 2023, 10, 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10110964
Xu C, Wang Y, Niu Z, Luo S, Du F. Fixed-Time Convergent Guidance Law with Angle Constraint and Autopilot Lag Compensation Using Partial-State Feedback. Aerospace. 2023; 10(11):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10110964
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Chen, Yang Wang, Zhiqi Niu, Sheng Luo, and Fenghuai Du. 2023. "Fixed-Time Convergent Guidance Law with Angle Constraint and Autopilot Lag Compensation Using Partial-State Feedback" Aerospace 10, no. 11: 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10110964
APA StyleXu, C., Wang, Y., Niu, Z., Luo, S., & Du, F. (2023). Fixed-Time Convergent Guidance Law with Angle Constraint and Autopilot Lag Compensation Using Partial-State Feedback. Aerospace, 10(11), 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10110964





