Method for Dynamic Load Location Identification Based on FRF Decomposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model
2.1. Phase Difference Model
2.2. Amplitude Ratio Model
2.3. FRF Reconstruction Model
2.4. Correlation Coefficient
3. The Simulation Verification
3.1. Single Source and Single Frequency
3.2. Multi-Source and Multi-Frequency Analysis
3.3. Multi-Source and Multi-Frequency Analysis for Same Frequency
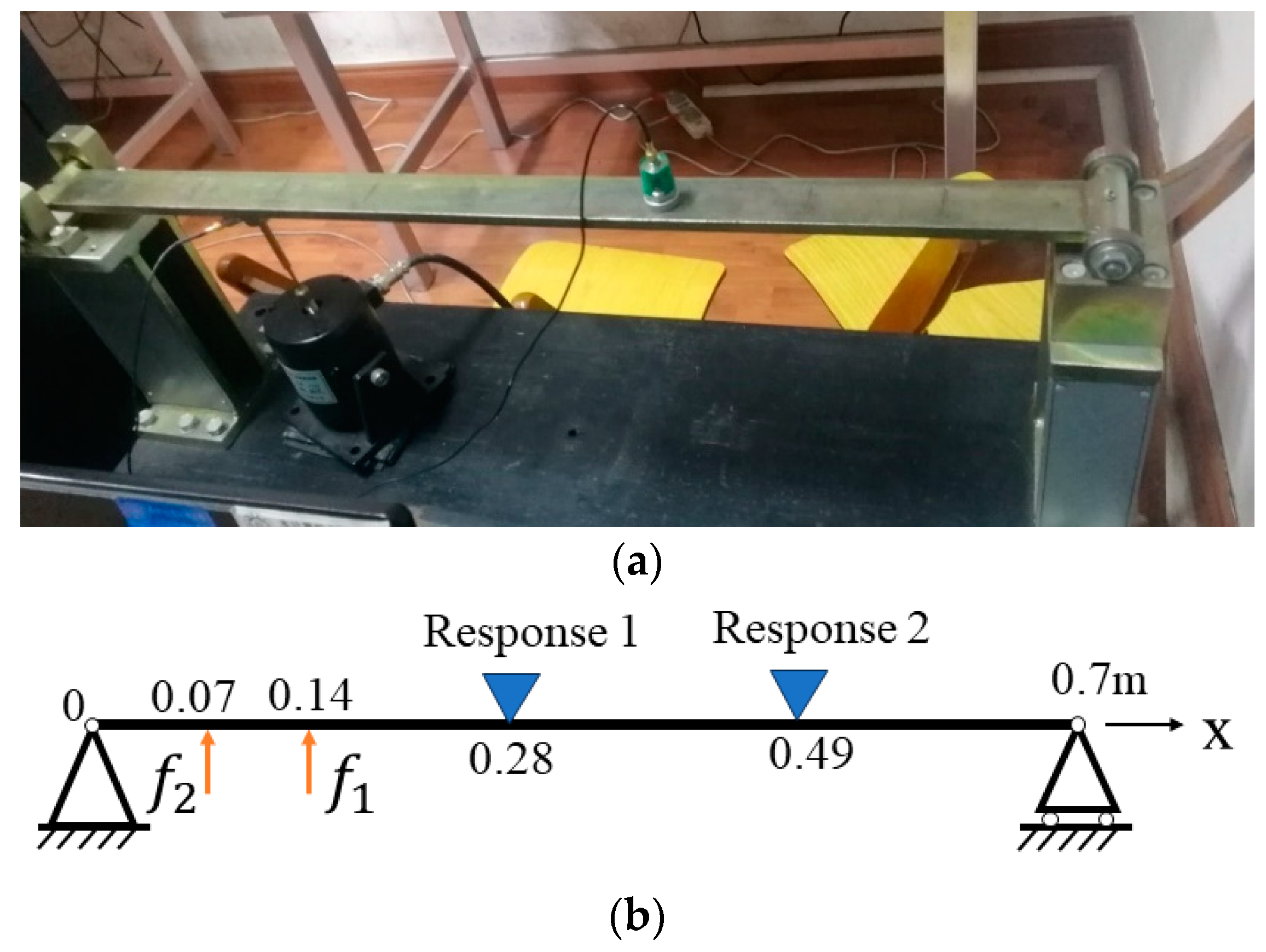
4. Experimental Verification
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- By reconstructing FRFs, the objective function containing only the excitation position variable was established and solved. After the excitation position was identified, the error was assessed by comparing the amplitude and the phase of the solution with those of the real one.
- (2)
- This method can identify the locations of multiple loads with different frequencies, avoiding the ill-posed problem formulation caused by the traditional matrix inversion, identifying the excitation position quickly and accurately with a small amount of dynamic response information, and having a strong anti-noise ability.
- (3)
- When the same frequency data at different locations were used for the FRF reconstruction model, the method failed. So the data for different frequencies from measuring dynamic response should be selected to identify the load location for the FRF reconstruction model.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, R.; Dobriban, E.; Hou, Z.; Qian, K. Dynamic load identification for mechanical systems: A review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 831–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhou, L.; Lian, X.; Li, K. Coherence analysis of the transfer function for dynamic force identification. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, E. Multi-source random excitation identification for stochastic structures based on matrix perturbation and modified regularization method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 119, 266–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, E. A strategy to identify exciting forces acting on structures. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2005, 64, 1483–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillary, B.; Ewins, D.J. The use of strain gauges in force determination and FRF measurements. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Modal Analysis Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 6–9 February 1984; pp. 627–634. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, S.E.S. Identification of external structural loads from measured harmonic responses. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 261, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkey, J.M.; Merrill, G.L. On the ill-Conditioned nature of indirect force measurements techniques. Int. J. Anal. Exp. Modal Anal. 1990, 8, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquelin, E.; Bennani, A.; Hamelin, P. Force reconstruction: Analysis and regularization of a deconvolution problem. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 265, 81–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yu, K.; Gai, X. Application of L∞ Norm fitting regularization method in dynamic load Identification of space-crafts. J. Vib. Shock 2017, 36, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Han, X.; Xie, Y. A new conjugate gradient method for solving multi-source dynamic load identification problem. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 2013, 9, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chan, T.H.; Nguyen, A. Moving force identification based on modified preconditioned conjugate gradient method. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 423, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Tang, H.; Mohamed, M.S.; Luo, S.; Chen, J. Augmented Tikhonov regularization method for dynamic load identification. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Han, X.; Jiang, C.; Yu, D. Dynamic load identification for stochastic structures based on Gegenbauer polynomial approximation and regularization method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 56, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, Z.; Chu, F. A load identification method based on wavelet multi-resolution analysis. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaul, L.; Hurlebaus, S. Identification of the impact location on a plate using wavelets. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 1998, 12, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajlouni, S.; Albakri, M.; Tarazaga, P. Impact localization in dispersive waveguides based on energy-attenuation of waves with the traveled distance. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 105, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W. Research on Load Location Identification Based on Directional Coupling; Harbin Engineering University: Harbin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, J. Identification of dynamic load location based on variable separation method. J. Vib. Eng. 2021, 34, 584–591. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J. Dynamic load identification and structural response reconstruction based on the augmented kalman filter. Appl. Math. Mech. (Chin. Ed.) 2021, 42, 665–674. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.F.; Lu, Q.H. Impact localization and identification under a constrained optimization scheme. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 366, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Hematiyan, M. An efficient inverse method for identification of the location and time history of an elastic impact load. J. Test. Eval. 2009, 37, 545–555. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Sugiyama, Y.; Mitsui, Y. Application of artificial neural networks to load identification. Comput. Struct. 1998, 69, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszewski, W.J.; Worden, K.; Wardle, R.; Tomlinson, G.R. Fail-safe sensor distributions for impact detection in composite materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2000, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihan, H. Identification on Dynamic Load Position Based on Genetic Algorithm; Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, J.; Chen, G.; Zhao, J. Dynamic load identification based on deep convolution neural network. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 185, 109757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.M.; Dong, L.L.; Guan, W.; Yan, J. Impact load identification of nonlinear structures using deep Recurrent Neural Network. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 133, 106292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.B.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Qu, X.Q.; Tong, F.S. Unknown impact force localisation and reconstruction in experimental plate structure using time-series analysis and pattern recognition. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 166, 105231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.B.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Trikha, M. Impact force identification in structures using time-domain spectral finite elements. Acta Mech. 2020, 231, 4513–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, S.; Wu, Z. Inverse load identification in stiffened plate structure based on in situ strain measurement. Struct. Durab. Health Monit. 2021, 15, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, J. Identification technology of dynamic load location. J. Vib. Shock 2012, 31, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, W. Time-domain identification technology for dynamic load locations. J. Vib. Shock 2013, 32, 74–78. [Google Scholar]






| f | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.3 | 0.5 |
| y (m) | 0.12 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| No Noise | Amplitude Noise (5%) | Phase Noise (5%) | Both Noise (5%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase difference model | Position x (m) | 0.2000 | 0.2000 | 0.0013 | 0.1676 |
| Position y (m) | 0.2000 | 0.2000 | 0.1243 | 0.0754 | |
| Calculation time (s) | 7.96 | 8.56 | 4.57 | 4.50 | |
| Amliptitude ratio model | Position x (m) | 0.2000 | 0.1991 | 0.2000 | 0.1985 |
| Position y (m) | 0.2000 | 0.2010 | 0.2000 | 0.2004 | |
| Calculating time (s) | 10.20 | 11.23 | 8.74 | 10.51 | |
| FRF model | Position x (m) | 0.2000 | 0.2005 | 0.2000 | 0.2001 |
| Position y (m) | 0.2000 | 0.2002 | 0.2000 | 0.2002 | |
| Calculating time (s) | 13.23 | 17.56 | 20.74 | 15.86 | |
| x (m) | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.3 | 0.5 |
| y (m) | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Frequency (Hz) | 45 | 40 | 35 | 25 | 20 | 15 | 10 |
| Frequency | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position (m) | no noise | 0.2000 | 0.2000 | 0.2000 | 0.4000 | 0.4000 | 0.4000 | 0.2000 | |
| 0.2000 | 0.2000 | 0.2000 | 0.4000 | 0.4000 | 0.4000 | 0.3000 | |||
| SNR 10 db | 0.2076 | 0.1918 | 0.2071 | 0.4062 | 0.4074 | 0.4067 | 0.2070 | ||
| 0.1955 | 0.2040 | 0.1910 | 0.4010 | 0.3918 | 0.3912 | 0.2915 | |||
| SNR 20 db | 0.2010 | 0.1968 | 0.1984 | 0.3998 | 0.3996 | 0.4067 | 0.1985 | ||
| 0.2005 | 0.2066 | 0.1975 | 0.3973 | 0.3961 | 0.3899 | 0.2966 | |||
| Excitation Signal | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (Hz) | 45 | 40 | 35 | 25 | 25 |
| Amplitude (N) | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| Phase (rad) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Position (m) | (0.20, 0.20) | (0.10, 0.20) | (0.18, 0.12) | (0.20, 0.20) | (0.10, 0.20) |
| Excitation Frequency | (45 Hz) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Identify position (m) | (0.2000, 0.2000) | (0.1000, 0.2000) | (0.1800, 0.1200) |
| Frequency (Hz) | Single-Source | Multi-Source | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position (m) | Error (m) | % | Position (m) | Error (m) | % | |
| 0.1394 | 0.0006 | 0.43 | 0.1394 | 0.0006 | 0.43 | |
| 0.1375 | 0.0025 | 1.79 | 0.0705 | 0.0005 | 0.36 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Silberschmidt, V.; Zhang, L. Method for Dynamic Load Location Identification Based on FRF Decomposition. Aerospace 2023, 10, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10100852
Qin Y, Zhang Y, Silberschmidt V, Zhang L. Method for Dynamic Load Location Identification Based on FRF Decomposition. Aerospace. 2023; 10(10):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10100852
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Yuantian, Yucheng Zhang, Vadim Silberschmidt, and Luping Zhang. 2023. "Method for Dynamic Load Location Identification Based on FRF Decomposition" Aerospace 10, no. 10: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10100852
APA StyleQin, Y., Zhang, Y., Silberschmidt, V., & Zhang, L. (2023). Method for Dynamic Load Location Identification Based on FRF Decomposition. Aerospace, 10(10), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10100852






