Prospects for Erratic and Intensifying Madden-Julian Oscillations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lagrangian Coupled Model (LCM)
2.2. Model Configuration
2.3. Compositing Technique
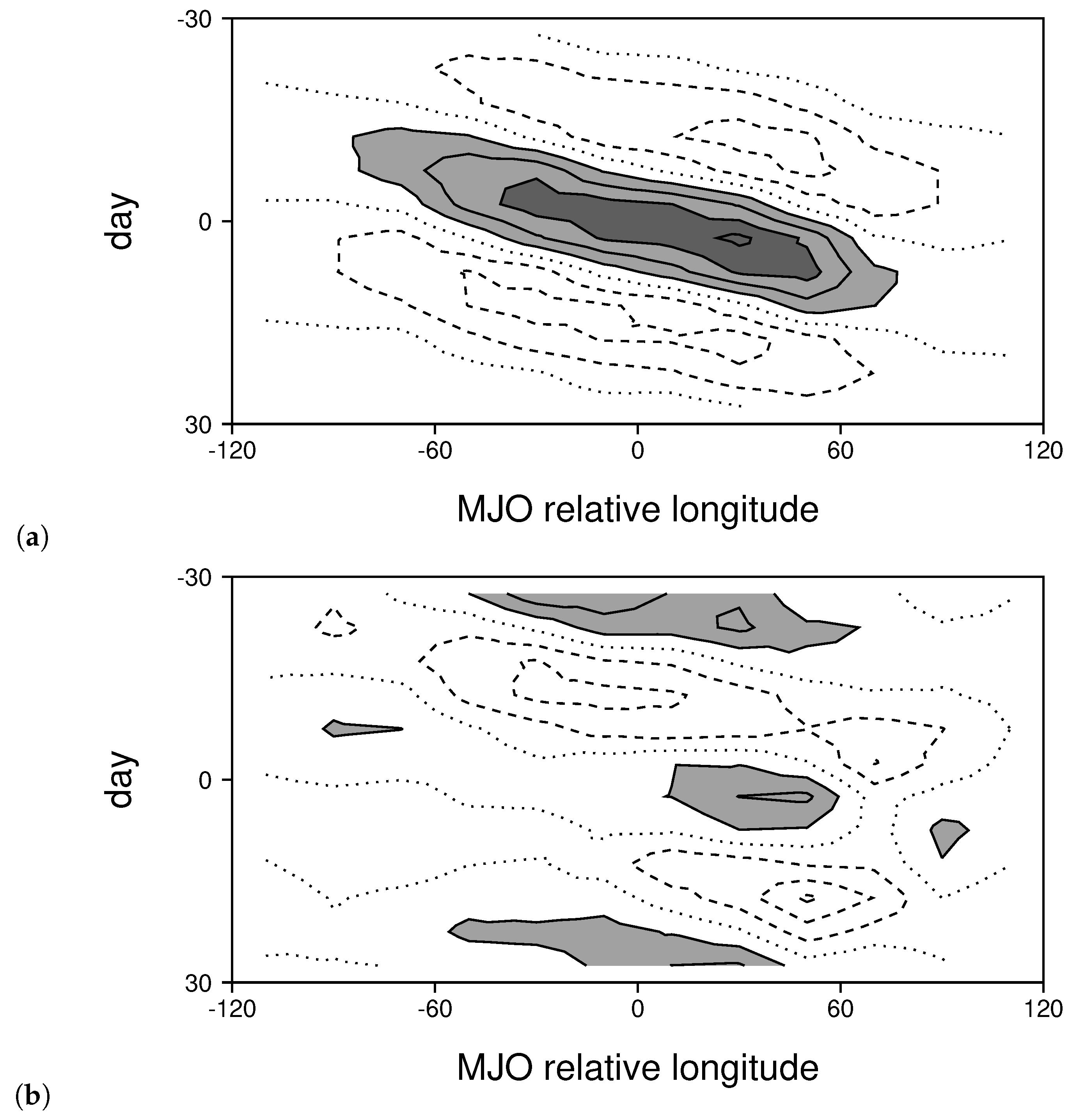
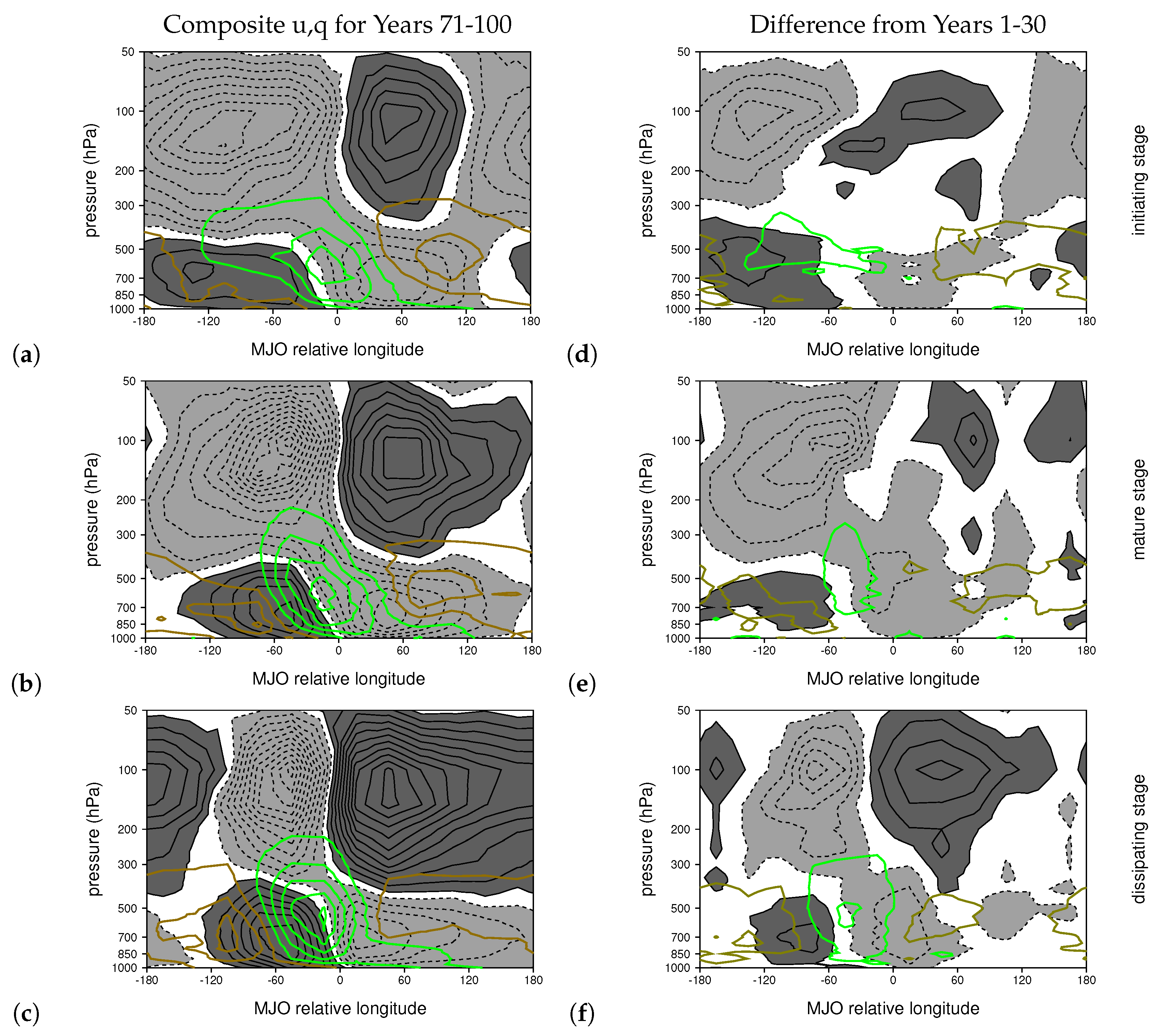
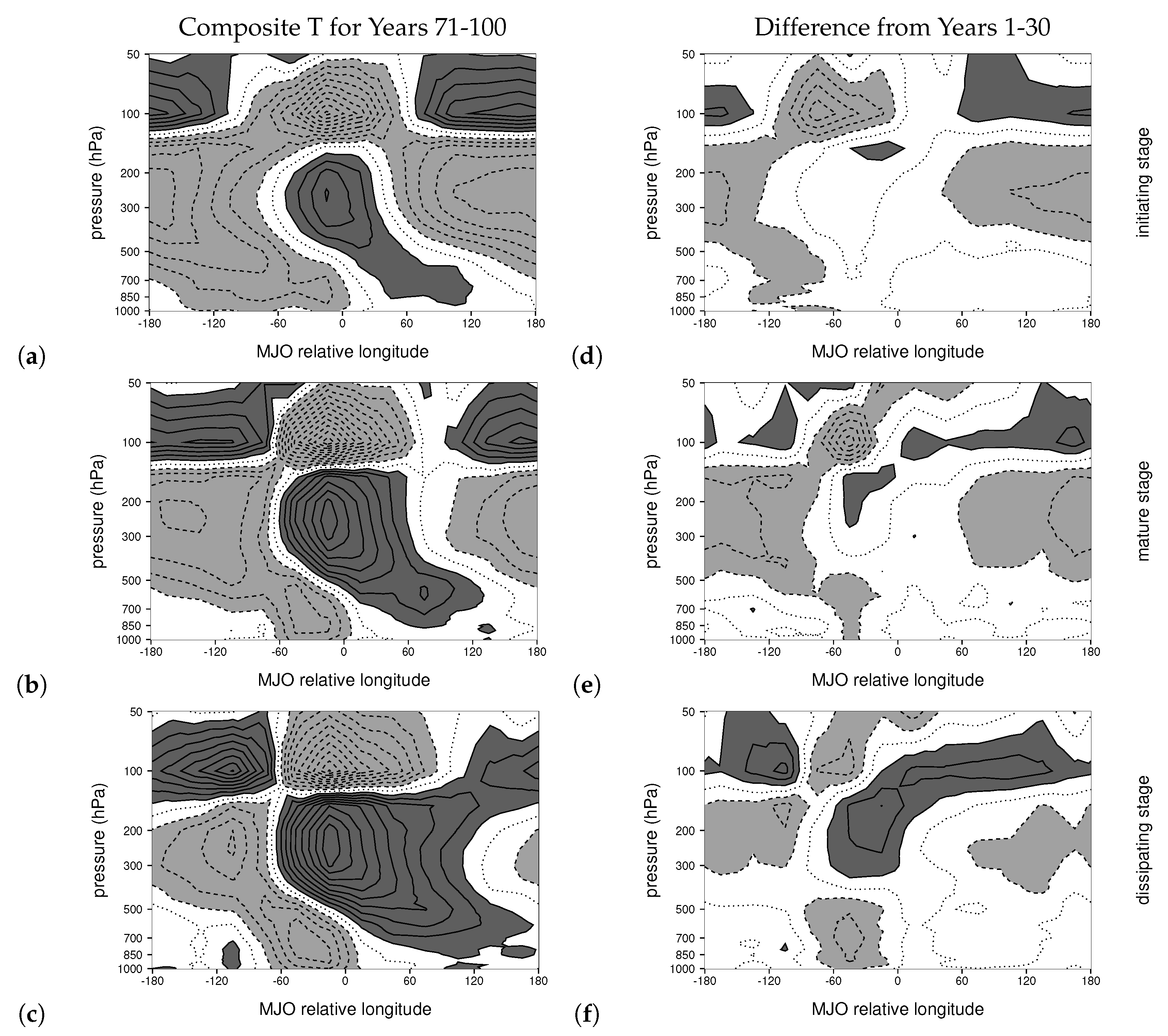
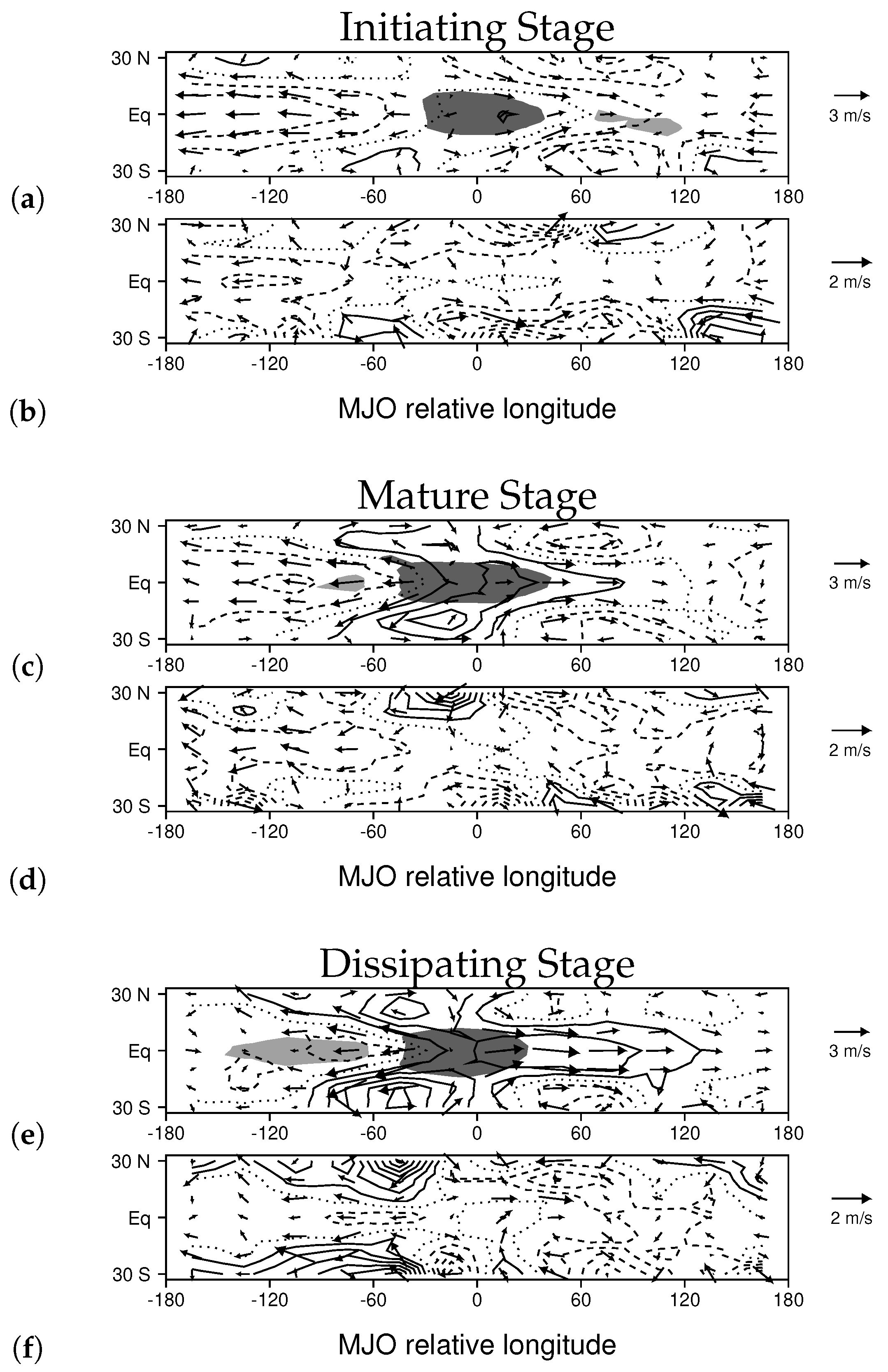
3. Results
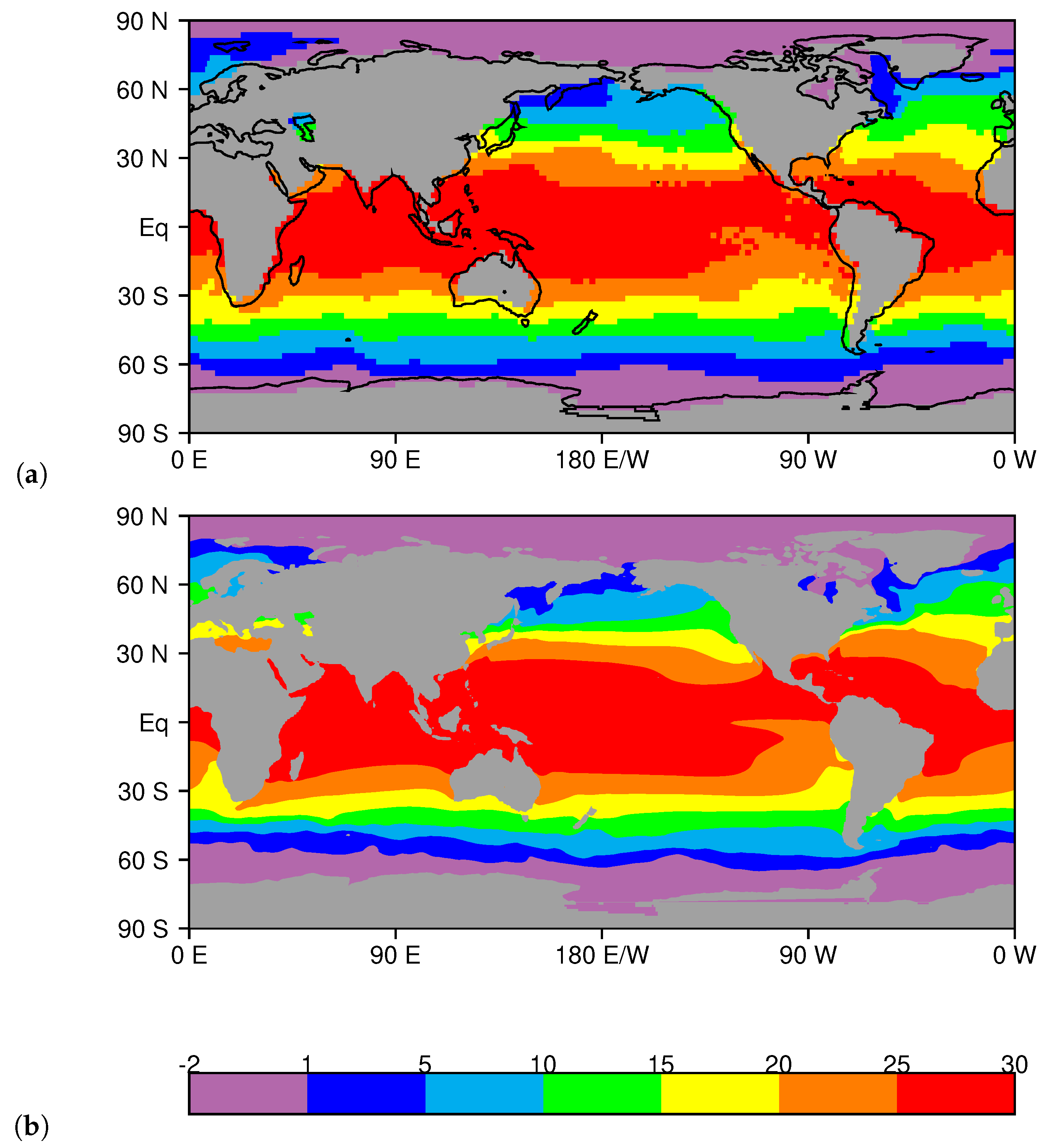
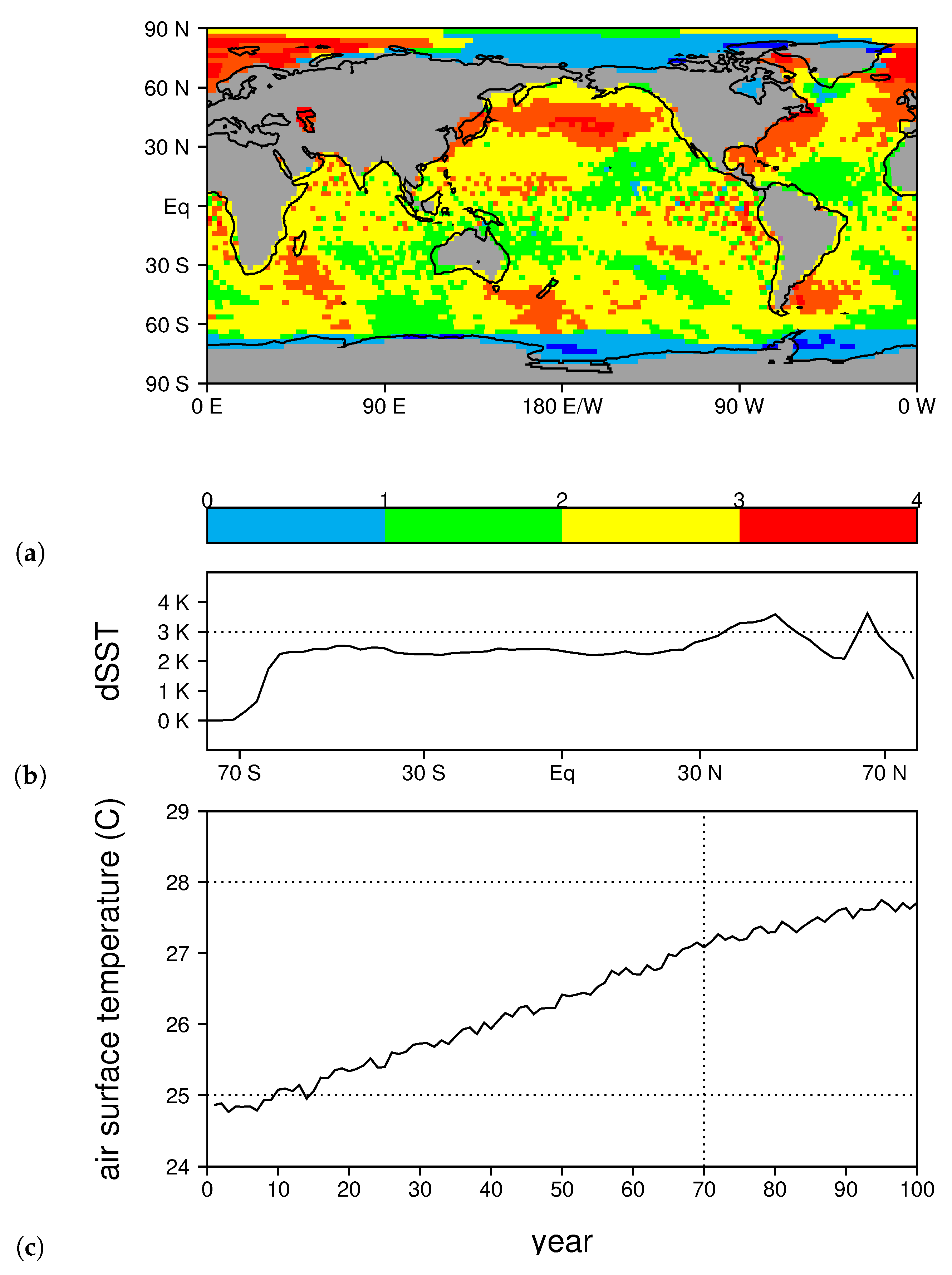
3.1. LCM Basic State and Warming Patterns
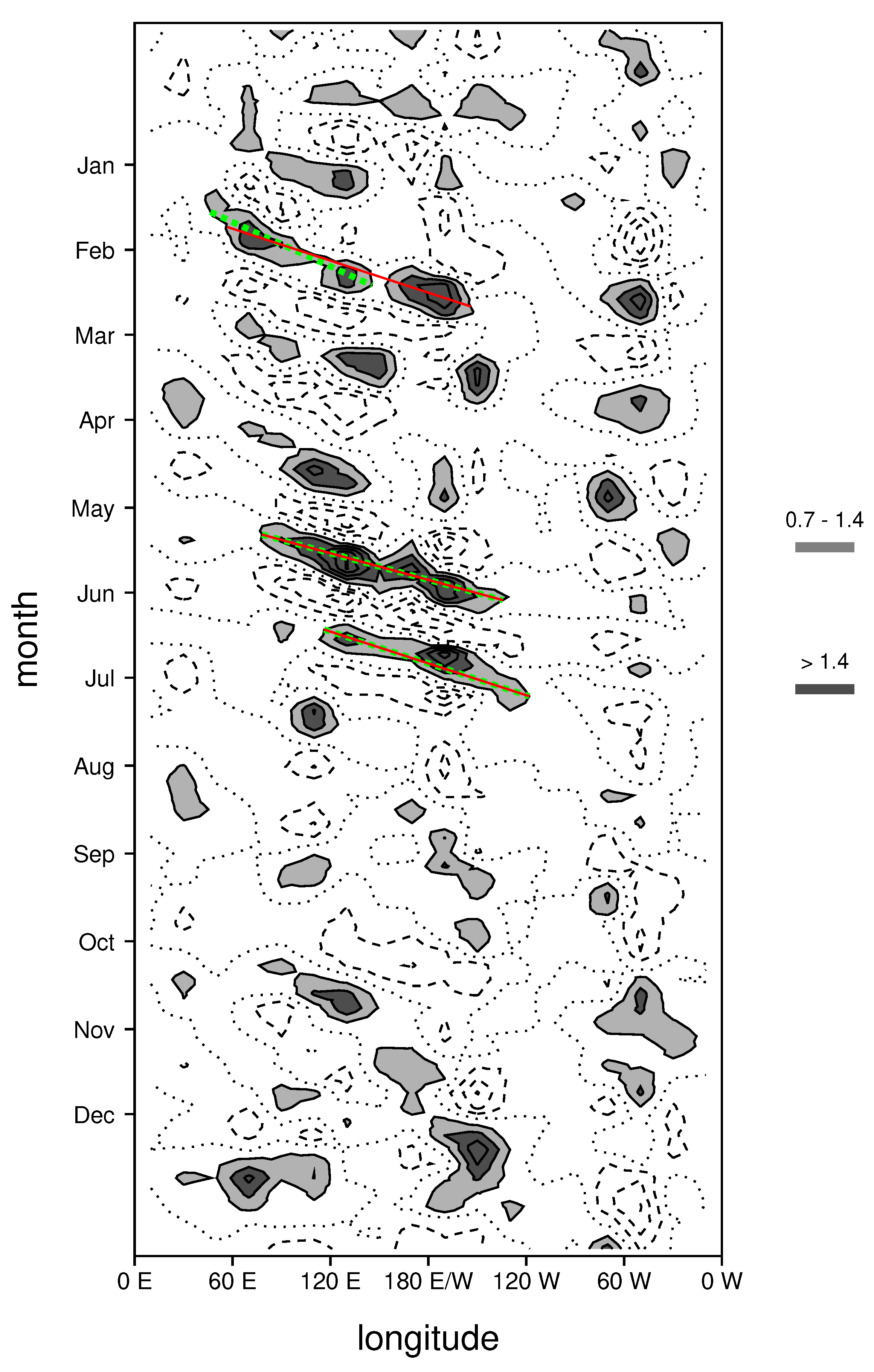
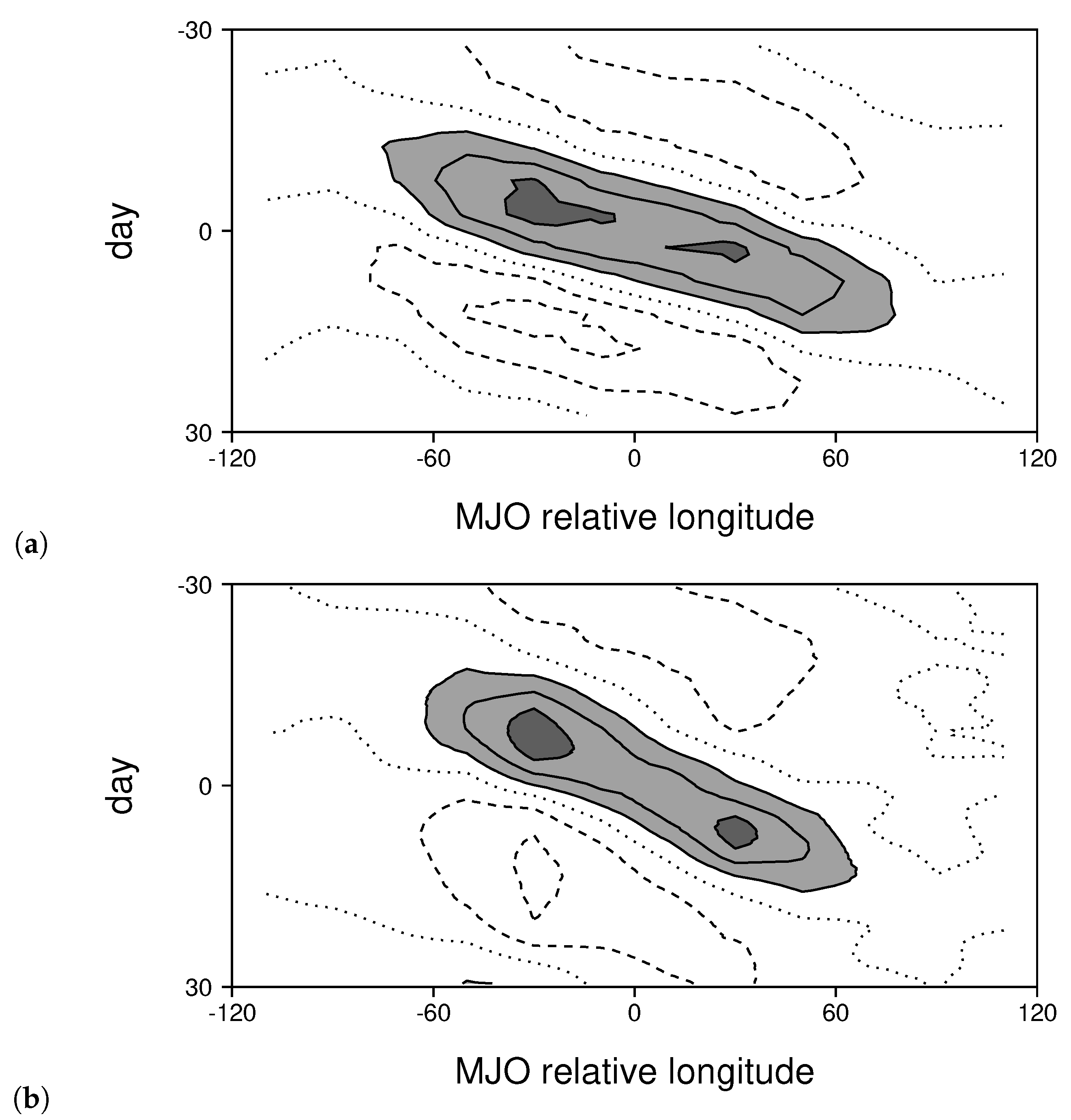
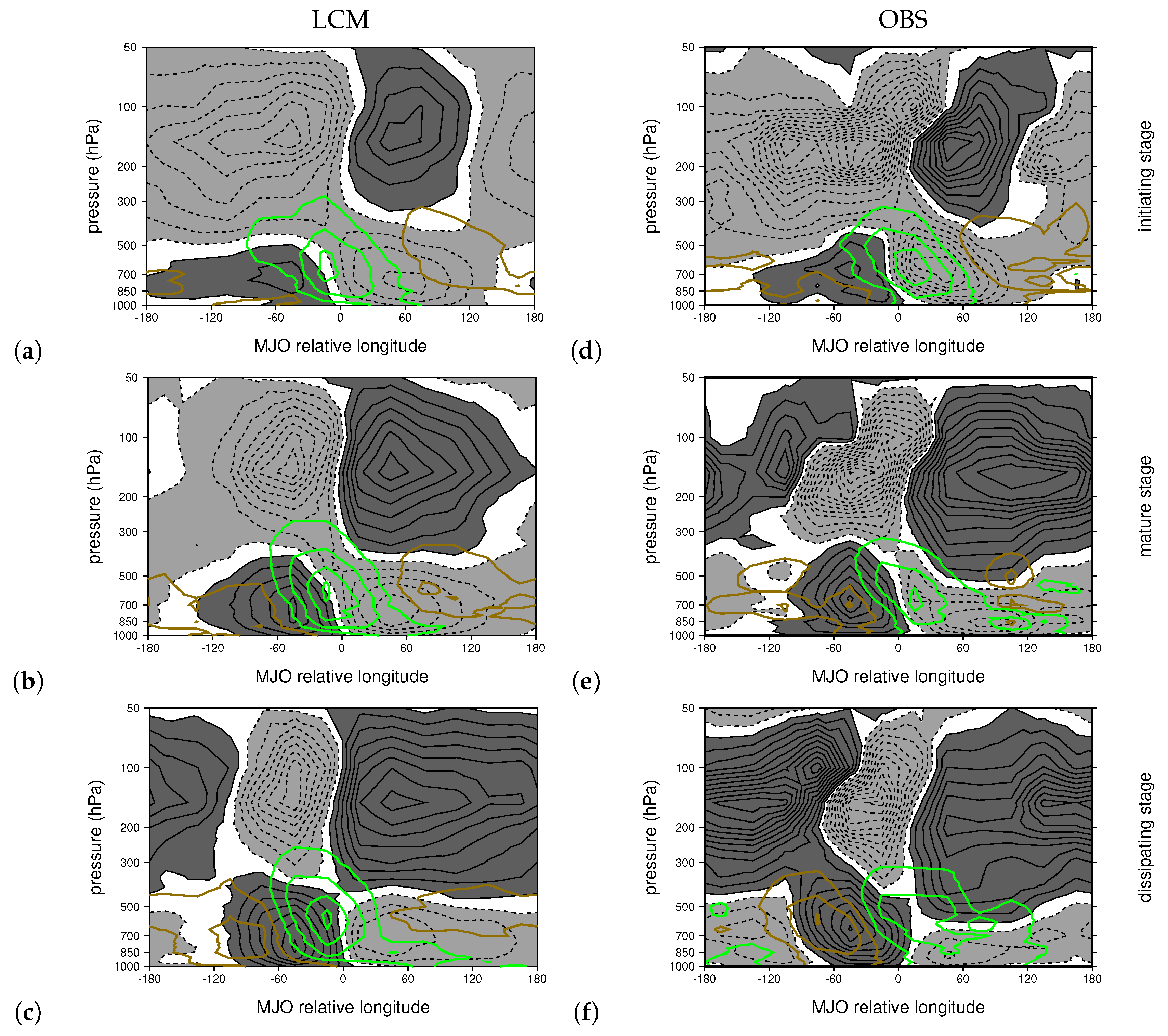
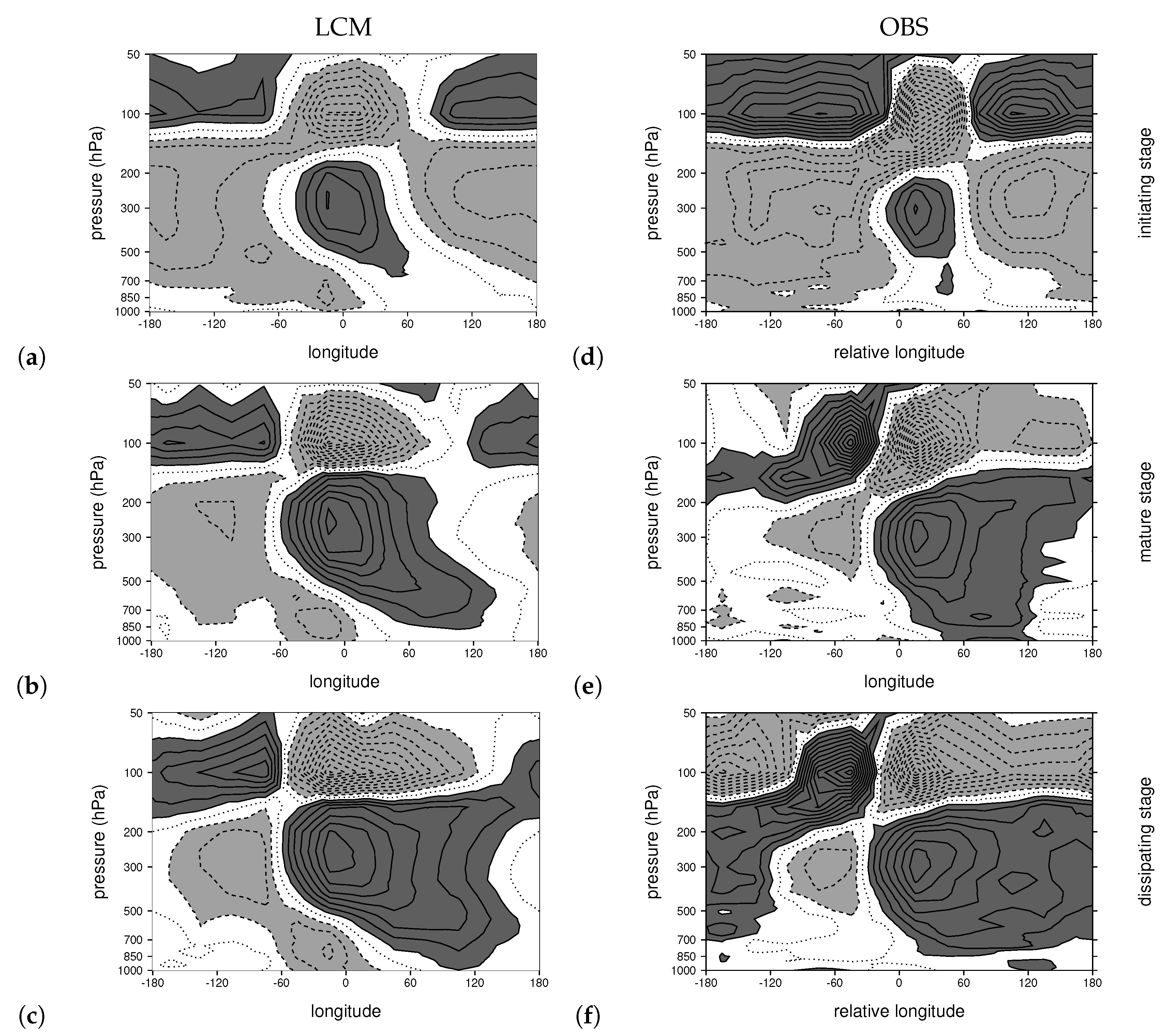
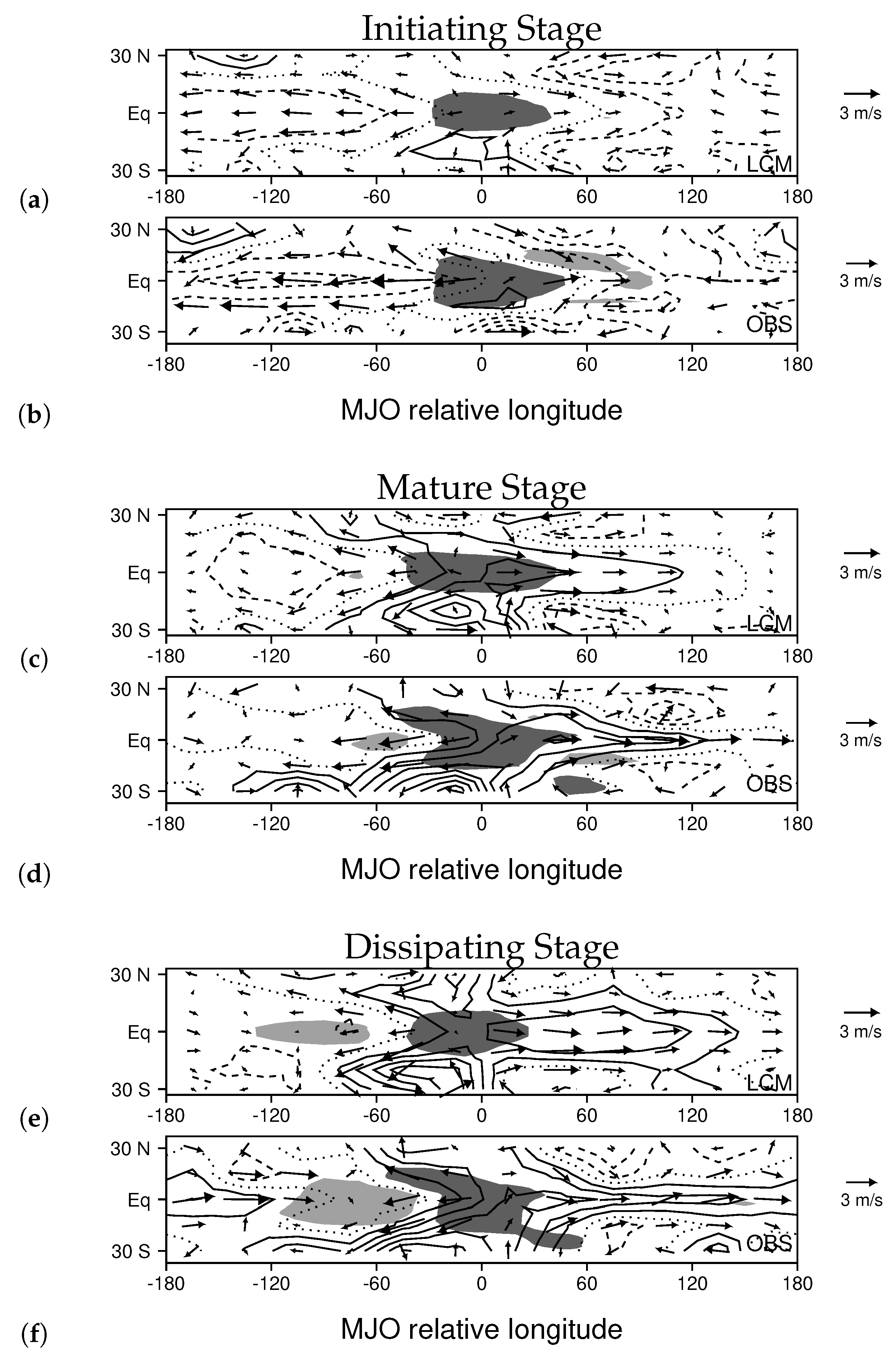
3.2. Comparing Simulated and Observed MJOs
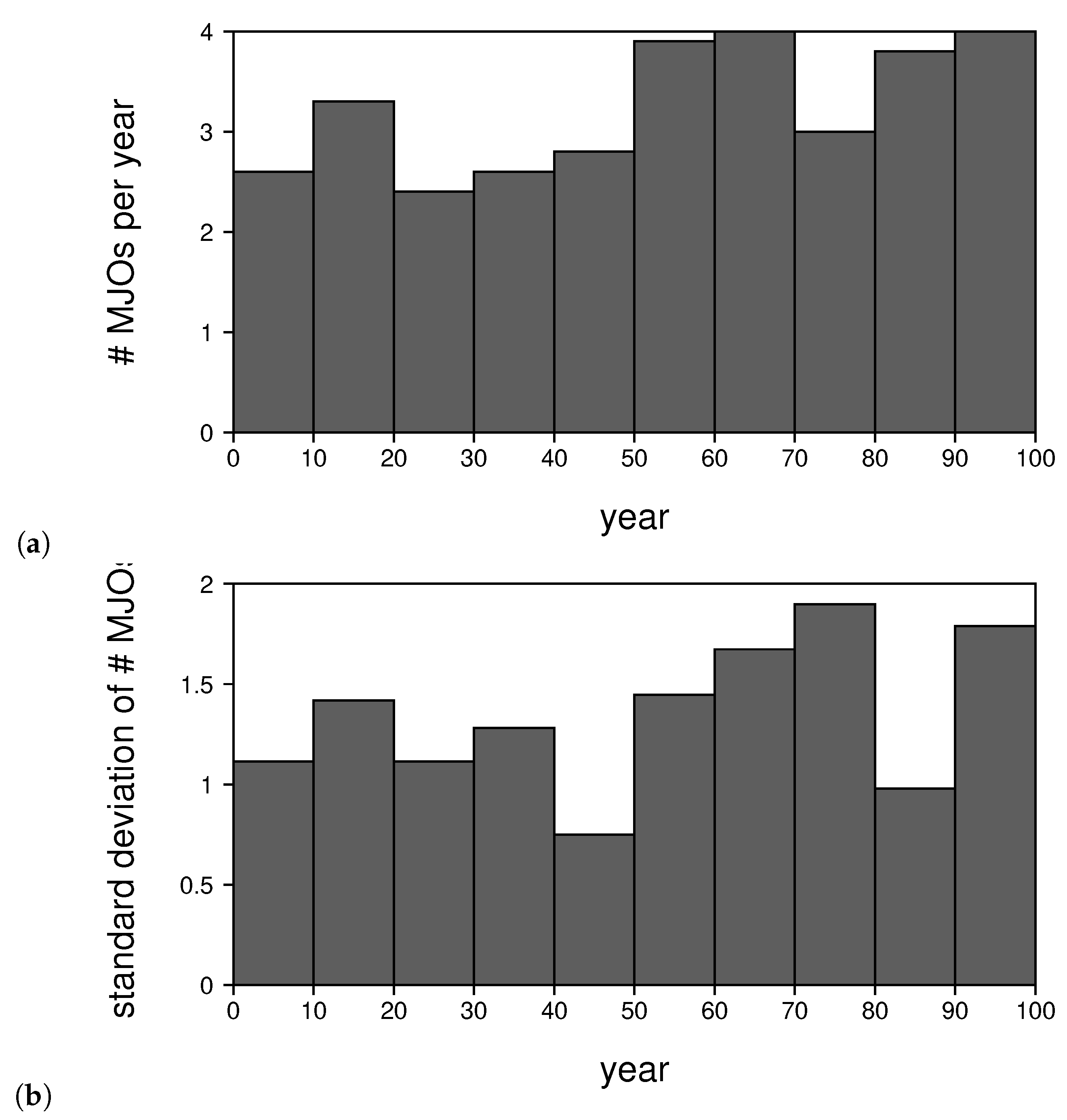
3.3. Changes to the MJO
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Observations of the 40–50-day tropical oscillation—A review. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122, 814–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Madden-julian oscillation. Rev. Geophys. 2005, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiladis, G.N.; Straub, K.H.; Haertel, P.T. Zonal and vertical structure of the Madden–Julian oscillation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 2790–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, T. Tropical super clusters within intraseasonal variations over the western Pacific. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 1988, 66, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, M.; Kiladis, G.N.; Webster, P.J. Large-scale dynamical fields associated with convectively coupled equatorial waves. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 613–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertel, P.; Straub, K.; Budsock, A. Transforming circumnavigating Kelvin waves that initiate and dissipate the Madden–Julian Oscillation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 1586–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, M.; Kiladis, G.N. Convectively coupled equatorial waves: Analysis of clouds and temperature in the wavenumber–frequency domain. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 374–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, E.D.; Hartmann, D.L. Modulation of eastern North Pacific hurricanes by the Madden–Julian oscillation. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.L.C.; Schubert, S.; Huang, N.E. The development of the South Asian summer monsoon and the intraseasonal oscillation. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2054–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, D.J.; Hartmann, D.L. The effect of the MJO on the North American monsoon. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhaden, M.J. Evolution of the 2002/03 El Niño. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 677–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Fedorov, A.V.; Lengaigne, M.; Guilyardi, E. The impact of westerly wind bursts on the diversity and predictability of El Niño events: An ocean energetics perspective. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4654–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K.A. An air-sea interaction model of intraseasonal oscillations in the tropics. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 44, 2324–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, A.; Maloney, E. Moisture modes and the eastward propagation of the MJO. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Rui, H. Dynamics of the coupled moist Kelvin–Rossby wave on an equatorial β-plane. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.J. A new model of the Madden–Julian oscillation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 2807–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biello, J.A.; Majda, A.J.; Moncrieff, M.W. Meridional momentum flux and superrotation in the multiscale IPESD MJO model. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 1636–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Straus, D.M.; Lindzen, R.S. Planetary-scale baroclinic instability and the MJO. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 3609–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.L.; Kiladis, G.N.; Mapes, B.E.; Weickmann, K.M.; Sperber, K.R.; Lin, W.; Wheeler, M.C.; Schubert, S.D.; Del Genio, A.; Donner, L.J.; et al. Tropical intraseasonal variability in 14 IPCC AR4 climate models. Part I: Convective signals. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 2665–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, M.P.; Lin, J.L.; Wang, W.; Kim, D.; Shinoda, T.; Weaver, S.J. MJO and convectively coupled equatorial waves simulated by CMIP5 climate models. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 6185–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, W.W. Coupling cloud processes with the large-scale dynamics using the cloud-resolving convection parameterization (CRCP). J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 978–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Sobel, A.H.; Maloney, E.D.; Frierson, D.M.; Kang, I.S. A systematic relationship between intraseasonal variability and mean state bias in AGCM simulations. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 5506–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiga, M.A.; Schreck, C.J., III; Ridout, J.A.; Flatau, M.; Barton, N.P.; Metzger, E.J.; Reynolds, C.A. Subseasonal forecasts of convectively coupled equatorial waves and the MJO: Activity and predictive skill. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 2337–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slingo, J.; Rowell, D.; Sperber, K.; Nortley, F. On the predictability of the interannual behaviour of the Madden-Julian Oscillation and its relationship with El Niño. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 583–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, E.C.; Thompson, K.R. A reconstruction of Madden–Julian Oscillation variability from 1905 to 2008. J. Clim. 2011, 25, 1996–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Carvalho, L.M. Changes in the activity of the Madden–Julian oscillation during 1958–2004. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 6353–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, N.P.; Branson, M.; Kuang, Z.; Randall, D.A.; Tziperman, E. MJO intensification with warming in the superparameterized CESM. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 2706–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, C.; Sato, N.; Seiki, A.; Yoneyama, K.; Shirooka, R. Projected future change of MJO and its extratropical teleconnection in east Asia during the northern winter simulated in IPCC AR4 models. Sola 2011, 7, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adames, A.F.; Kim, D.; Sobel, A.H.; Del Genio, A.; Wu, J. Changes in the structure and propagation of the MJO with increasing CO2. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 1251–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, H.; Caballero, R. Enhanced MJO and transition to superrotation in warm climates. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2016, 8, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Carvalho, L.M. Stochastic simulations of the Madden–Julian oscillation activity. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 36, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertel, P. Sensitivity of the Madden Julian Oscillation to Ocean Warming in a Lagrangian Atmospheric Model. Climate 2018, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, E.D.; Adames, Á.F.; Bui, H.X. Madden–Julian oscillation changes under anthropogenic warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, M.S.; Bretherton, C.S. Causal evidence that rotational moisture advection is critical to the superparameterized Madden–Julian oscillation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 800–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adames, Á.F.; Kim, D.; Sobel, A.H.; Del Genio, A.; Wu, J. Characterization of moist processes associated with changes in the propagation of the MJO with increasing CO2. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 2946–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haertel, P.; Straub, K.; Fedorov, A. Lagrangian overturning and the Madden–Julian Oscillation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 1344–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertel, P.; Boos, W.R.; Straub, K. Origins of Moist Air in Global Lagrangian Simulations of the Madden–Julian Oscillation. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertel, P. A Lagrangian Ocean Model for Climate Studies. Climate 2019, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Waliser, D.E.; Molotch, N.P.; Fetzer, E.J.; Neiman, P.J. Does the Madden–Julian oscillation influence wintertime atmospheric rivers and snowpack in the Sierra Nevada? Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertel, P. A Lagrangian method for simulating geophysical fluids. In Lagrangian Modeling of the Atmosphere; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuta, R.; Arakawa, O.; Ose, T.; Kusunoki, S.; Endo, H.; Kitoh, A. Classification of CMIP5 future climate responses by the tropical sea surface temperature changes. Sola 2014, 10, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, A.J. Primary and successive events in the Madden–Julian oscillation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.W.; Houze, R.A., Jr. Effect of dry large-scale vertical motions on initial MJO convective onset. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 4783–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertel, P.; Boos, W.R. Global association of the Madden-Julian Oscillation with monsoon lows and depressions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 8065–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Initiating | Mature | Dissipating | |
|---|---|---|---|
| zonal wind | 0.94, 30% | 0.95, 22% | 0.96, 25% |
| temperature | 0.93, 35% | 0.92, 18% | 0.93, 15% |
| moisture | 0.93, 33% | 0.95, 27% | 0.94, 40% |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haertel, P. Prospects for Erratic and Intensifying Madden-Julian Oscillations. Climate 2020, 8, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8020024
Haertel P. Prospects for Erratic and Intensifying Madden-Julian Oscillations. Climate. 2020; 8(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8020024
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaertel, Patrick. 2020. "Prospects for Erratic and Intensifying Madden-Julian Oscillations" Climate 8, no. 2: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8020024
APA StyleHaertel, P. (2020). Prospects for Erratic and Intensifying Madden-Julian Oscillations. Climate, 8(2), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8020024




