Hydrological Impacts of the Changes in Simulated Rainfall Fields on Nakanbe Basin in Burkina Faso
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Description of the Watershed and Data Review
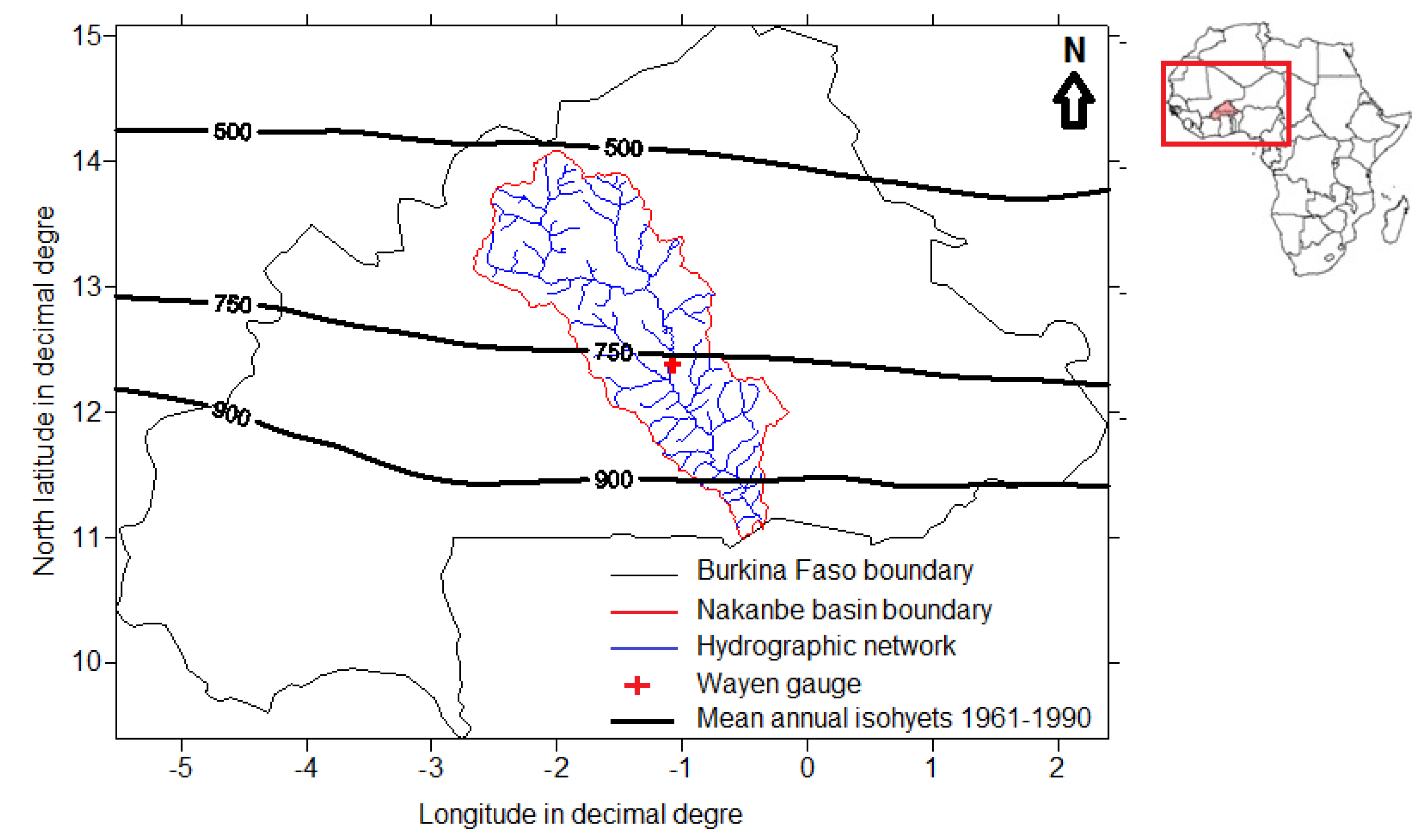
3. Hydrological Modeling of the Watershed
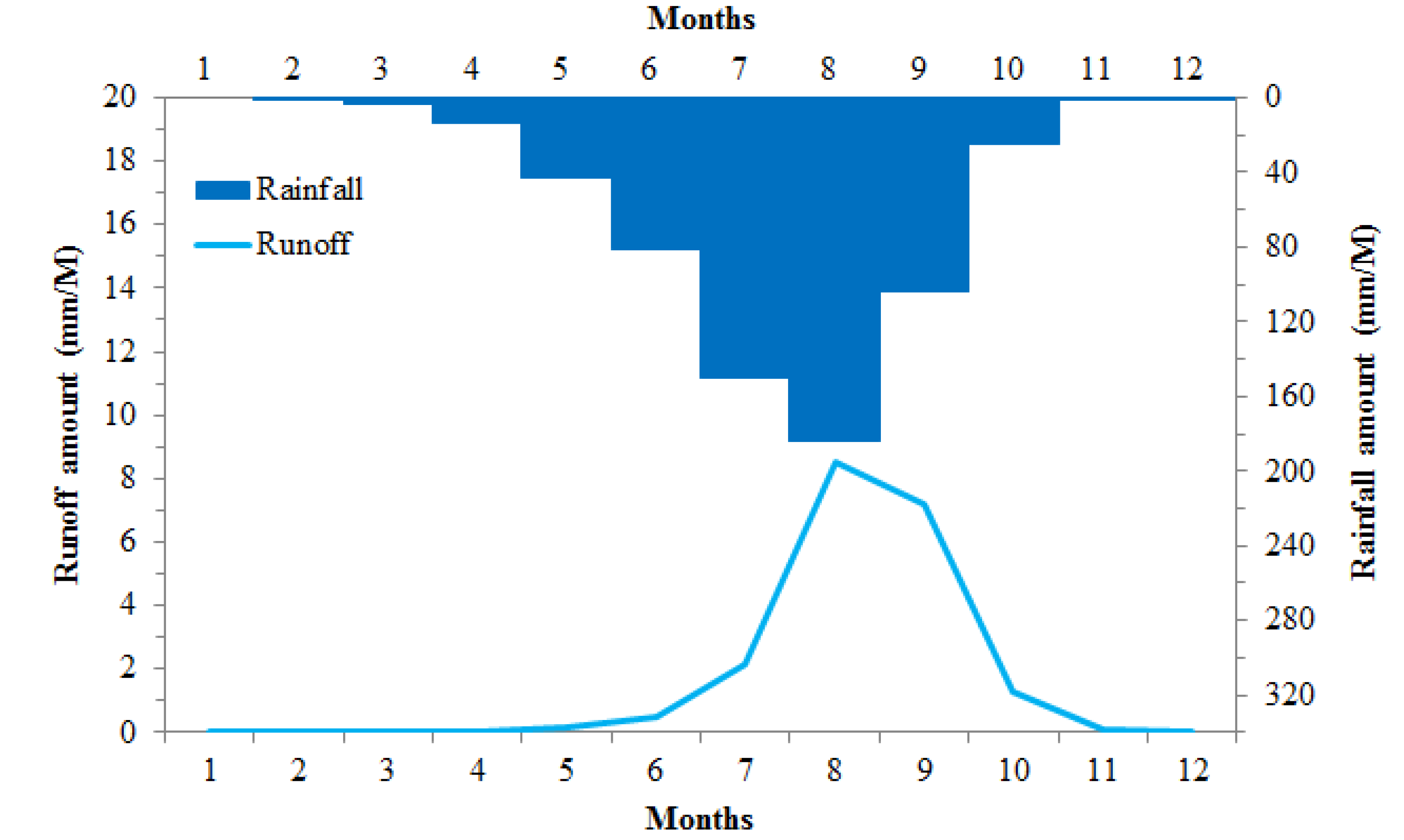
3.1. Hydrological Functioning of GR2M
3.2. Hydrological Functioning of ORCHIDEE
3.3. Implementation of the Hydrological Models on the Watershed
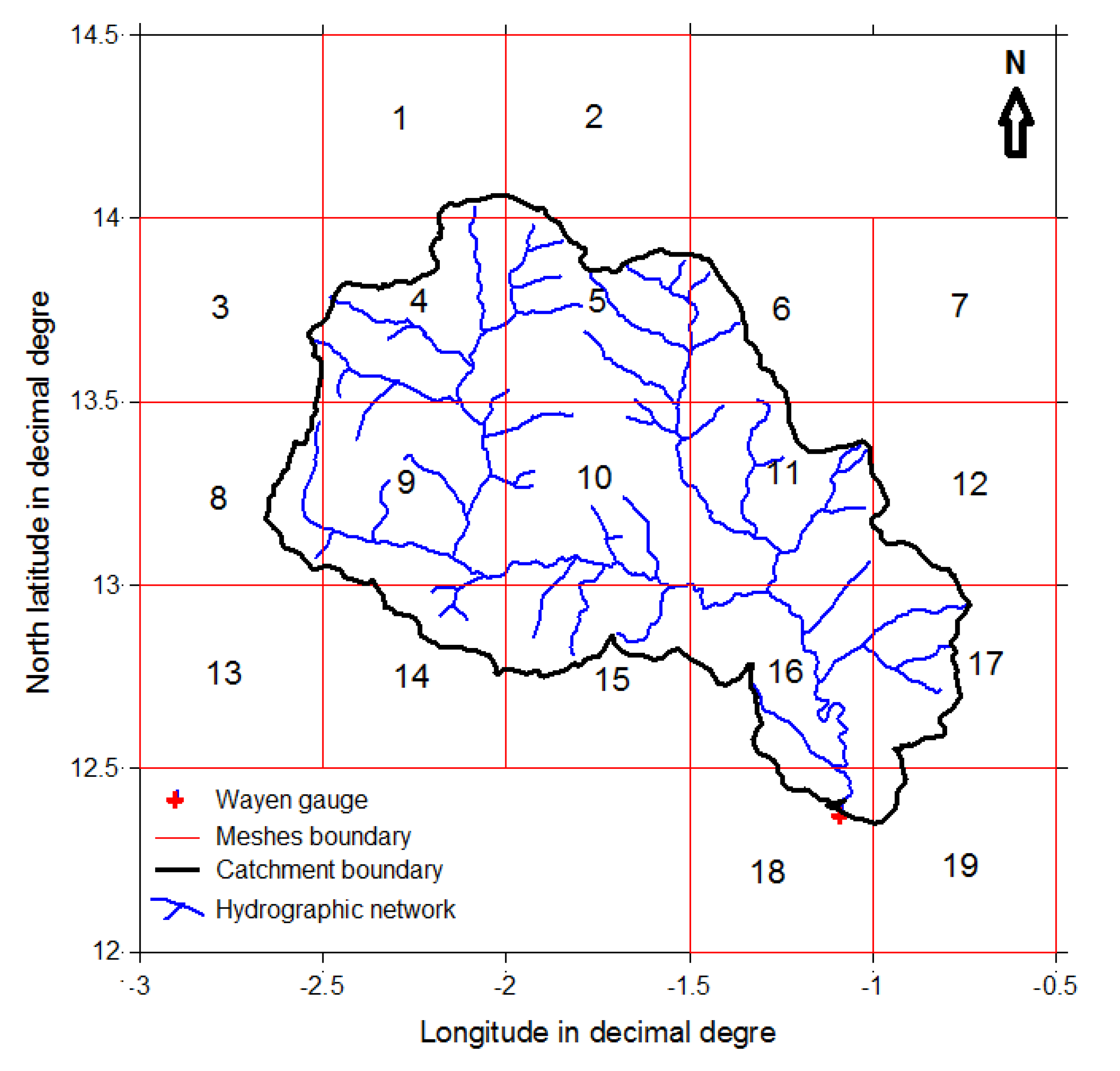
| Index | Latitude | Longitude | Fraction of the Basin (%) | Index | Latitude | Longitude | Fraction of the Basin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14.25 | −2.25 | 0.43 | 11 | 13.25 | −1.25 | 12.90 |
| 2 | 14.25 | −1.75 | 0.24 | 12 | 13.25 | −0.75 | 1.31 |
| 3 | 13.75 | −2.75 | 0.14 | 13 | 12.75 | −2.75 | 0 |
| 4 | 13.75 | −2.25 | 11.37 | 14 | 12.75 | −2.25 | 0.77 |
| 5 | 13.75 | −1.75 | 12.31 | 15 | 12.75 | −1.75 | 6.17 |
| 6 | 13.75 | −1.25 | 3.92 | 16 | 12.75 | −1.25 | 11.37 |
| 7 | 13.75 | −0.75 | 0 | 17 | 12.75 | −0.75 | 6.11 |
| 8 | 13.25 | −2.75 | 2.35 | 18 | 12.25 | −1.25 | 0.99 |
| 9 | 13.25 | −2.25 | 14.18 | 19 | 12.25 | −0.75 | 0.58 |
| 10 | 13.25 | −1.75 | 14.86 |
4. Results
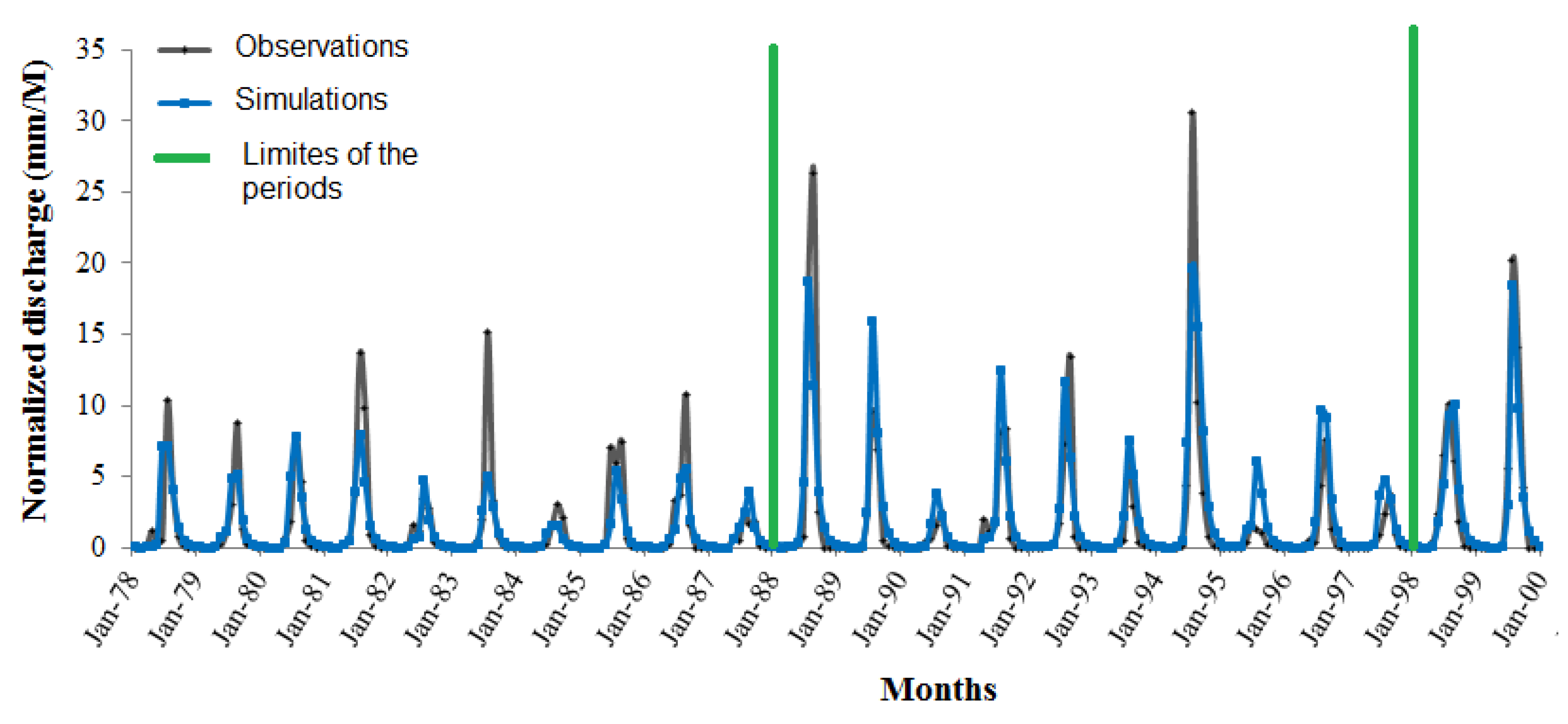
4.1. Model Settings and the Annual Hydrological Balance of the Watershed
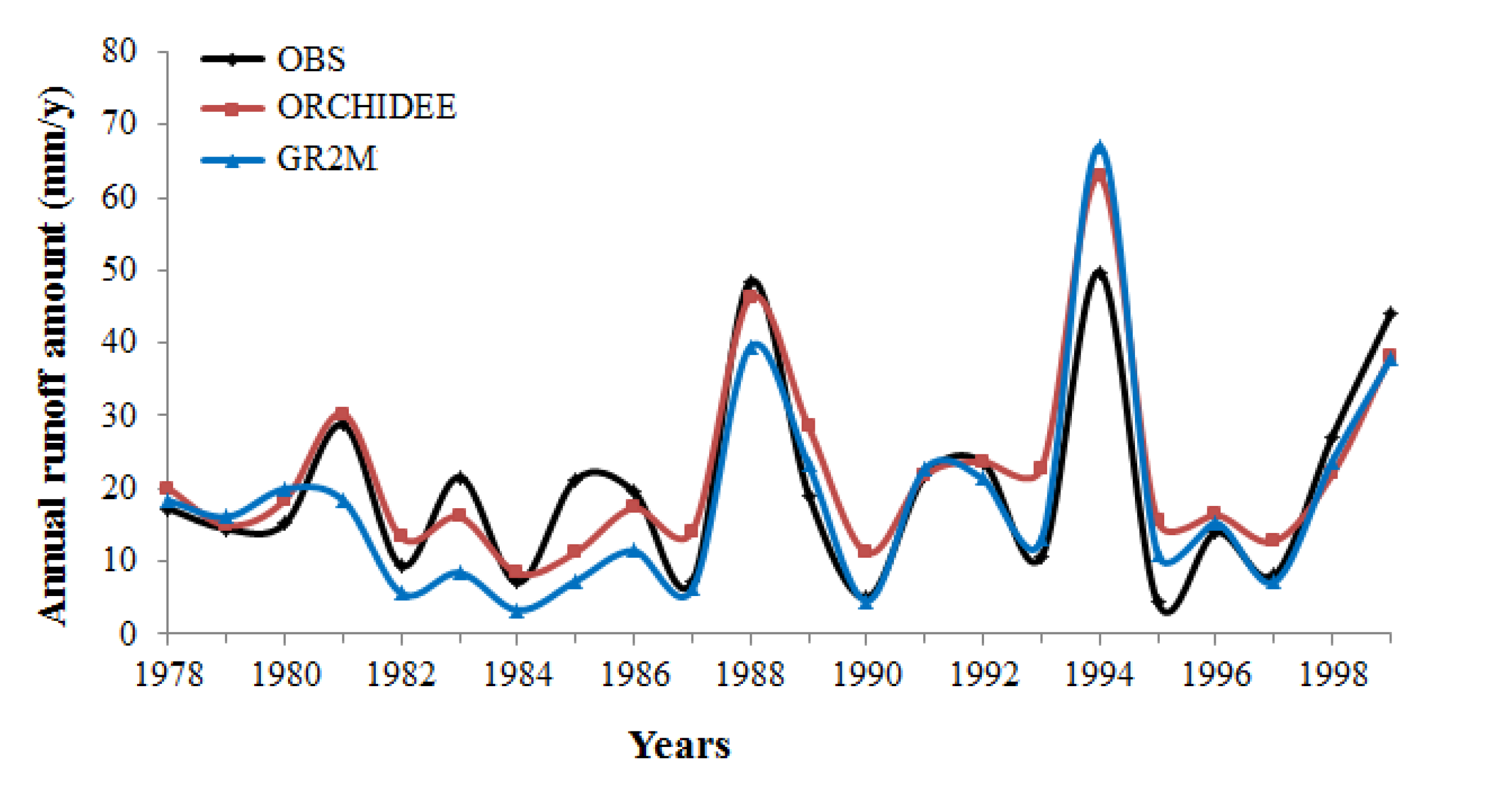
4.2. Assessment of the Changes in the Hydrological Balance of Nakanbe Watershed
4.2.1. Changes in Rainfall Field over the 2021–2050 Period from the Five RCMs
4.2.2. Hydrological Impacts of the Changes in Rainfall Field
- -
- a decrease of 10% in the number of rain days thereafter designed as Nr10%;
- -
- a decrease of 20% in the number of rain days thereafter designed as Nr20%.
- -
- a decrease of 17% in the intensity of daily rainfall thereafter designed as Hr17%;
- -
- a decrease of 30% in the intensity of daily rainfall thereafter designed as Hr30%.
| Scenarios | Rainfall (%) | Runoff (%) | Groundwater Recharge (%) | AET (%) | Qmax (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nr10% | −17 | −44 | −16 | −16 | −9 |
| Nr20% | −30 | −69 | −25 | −28 | −16 |
| Hr17% | −17 | −53 | −28 | −12 | −28 |
| Hr30% | −30 | −78 | −46 | −23 | −46 |
| Hi20% | 20 | 101 | 45 | 14 | 49 |
| Scenarios | Rainfall (%) | Runoff (%) | Groundwater Recharge (%) | AET (%) | Qmax (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nr10% | −17 | −51 | −34 | −12 | −51 |
| Nr20% | −30 | −75 | −55 | −22 | −74 |
| Hr17% | −17 | −55 | −36 | −13 | −56 |
| Hr30% | −30 | −79 | −59 | −24 | −80 |
| Hi20% | 20 | 97 | 50 | 12 | 99 |
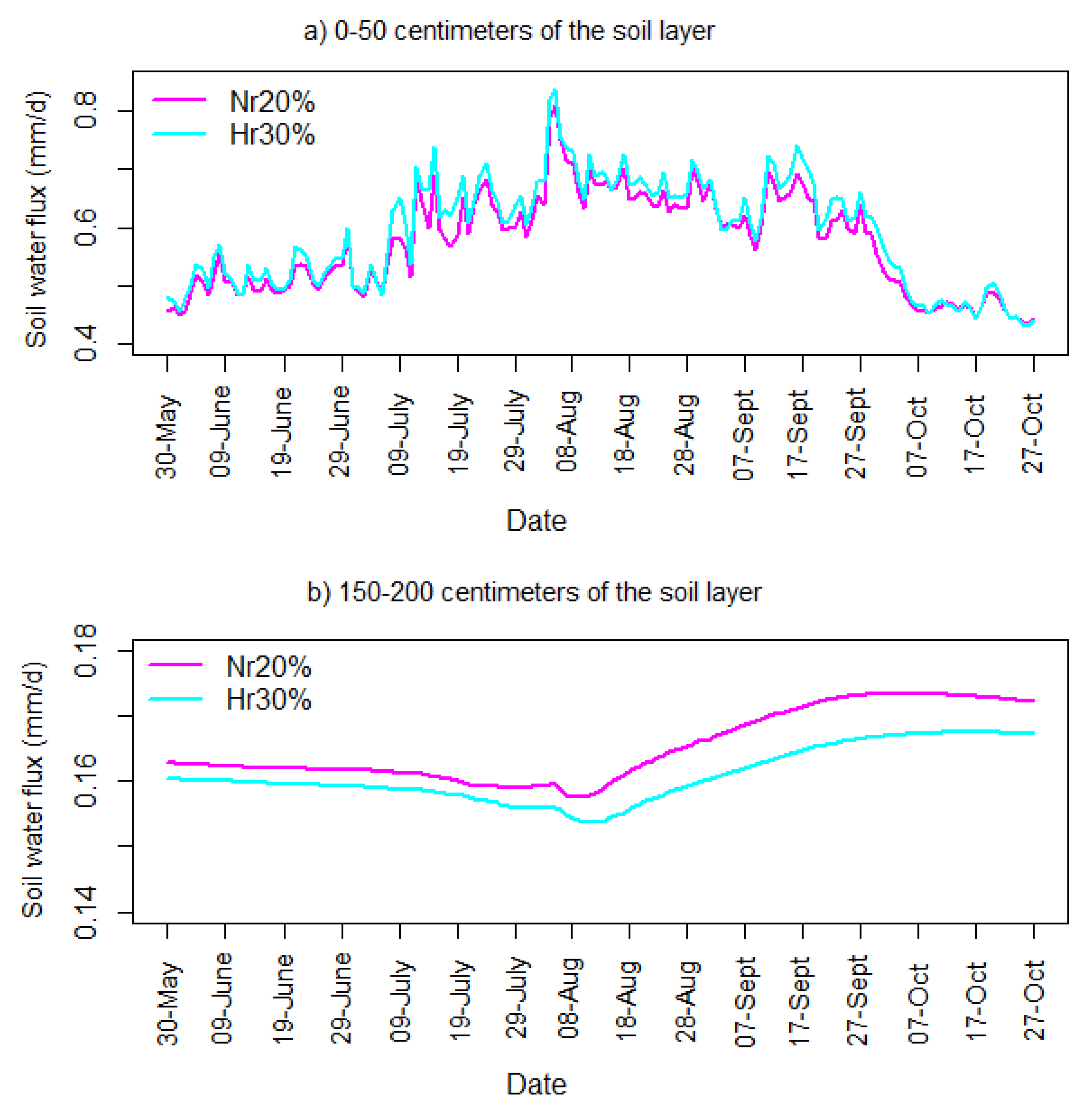
5. Discussion and Summary
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicholson, S.; Palao, I. A re-evaluation of rainfall variability in the Sahel. Part I. haracteristics of rainfall fluctuations. Int. J. Climatol. 1993, 13, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturel, J.; Boubacar, I.; L’Aour, A.; Mahé, G. Analyses de grilles pluviométriques et principaux traits des changements survenus au 20ème siècle en Afrique de l’Ouest et Centrale. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 1281–1288. (In French) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricquet, J.; Bamba, F.; Mahé, G.; Toure, M.; Olivry, J. Évolution récente des ressources en eau de l’Afrique atlantique. Rev. Sci. Eau. 1997, 3, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servat, É.; Paturel, J.; Lubes-Niel, H.; Kouame, B.; Travaglio, M.; Marieu, B. De la diminution des écoulements en Afrique de l’Ouest et centrale. C. R. Acad. Sci. Ser. IIA-Earth Planet. Sci. 1997, 325, 679–682. [Google Scholar]
- Paturel, J.; Barrau, C.; Mahé, G.; Dezetter, A.; Servat, E. Modelling the impact of climatic variability on water resources in West and Central Africa from a non-calibrated hydrological model/Modélisation d’impact de la variabilité climatique en Afrique de l’Ouest et Centrale à partir d'un modèle hydrologique non calibré. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2002, 752, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mahé, G. Surface/groundwater interactions in the Bani and Nakambe rivers, tributaries of the Niger and Volta basins, West Africa. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivry, J.; Briquet, J.; Mahé, G. de l’évolution de la puissance des crues des grands cours d'eau intertropicaux d’Afrique depuis deux décennies. Rev. Géogr. Alp. 1994, 12, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- De Vries, J.; Simmers, I. Groundwater recharge: An overview of processes and challenges. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuol, J.; Abbaspour, K.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H. Estimation of freshwater availability in the West African sub-continent using the SWAT hydrologic model. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranyossi, J.; Ndiaye, B. Etude et modélisation de la formation des dépressions piézométriques en Afrique sahélienne. Rev. Sci. Eau/J. Water Sci. 1993, 6, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwidi, J. Groundwater Potential to Supply Population Demand within the Kompienga Dam Basin in Burkina Faso. Ph.D. Thesis, Rheinischen Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität, Bonn, Allemagne, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- De Condappa, D.; Chaponnière, A.; Lemoalle, J. A decision-support tool for water allocation in the Volta Basin. Water Int. 2009, 34, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakicenovic, N.; Swart, R. Special Report on Emissions Scenarios; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, B.; Polcher, J.; Karambiri, H.; Rockel, B. Characterization of the rainy season in Burkina Faso and it’s representation by regional climate models. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hulme, M.; Doherty, R.; Ngara, T.; New, M.; Lister, D. African climate change: 1900–2100. Clim. Res. 2001, 17, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, M.; Stankiewicz, J. Changes in surface water supply across Africa with predicted climate change. Science 2006, 311, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paeth, H.; Born, K.; Girmes, R.; Podzun, R.; Jacob, D. Regional climate change in tropical and northern Africa due to greenhouse forcing and land use changes. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.; Karambiri, H.; Polcher, J.; Yacouba, H.; Ribstein, P. Changes in rainfall regime over Burkina Faso under the climate change conditions simulated by 5 regional climate models. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 1363–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karambiri, H.; García Galiano, S.; Giraldo, J.; Yacouba, H.; Ibrahim, B.; Barbier, B.; Polcher, J. Assessing the impact of climate variability and climate change on runoff in West Africa: The case of Senegal and Nakambe River basins. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2011, 12, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruelland, D.; Ardoin-Bardin, S.; Collet, L.; Roucou, P. Simulating future trends in hydrological regime of a large Sudano-Sahelian catchment under climate change. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardoin-Bardin, S.; Dezetter, A.; Servat, E.; Paturel, J.; Mahe, G.; Niel, H.; Dieulin, C. Using general circulation model outputs to assess impacts of climate change on runoff for large hydrological catchments in West Africa. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diello, P. Interrelations Climat-Homme-Environnement dans le Sahel Burkinabé: Impacts sur les états de Surface et la Modélisation Hydrologique. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Montpellier II, Sciences et Techniques du Languedoc, Hérault, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Paturel, J.; Boubacar, I.; L’Aour, A.; Mahé, G. Note de recherche: Grilles mensuelles de pluie en Afrique de l’Ouest et Centrale. Rev. Sci. Eau. 2010, 23, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weedon, G.; Gomes, S.; Viterbo, P.; Shuttleworth, W.; Blyth, E.; Österle, H.; Adam, J.; Bellouin, N.; Boucher, O.; Best, M. Creation of the WATCH Forcing Data and its use to assess global and regional reference crop evaporation over land during the twentieth century. J. Hydrometeor. 2011, 12, 823–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ENSEMBLES Project RT3. Available online: http://ensemblesrt3.dmi.dk/ (accessed on 23 June 2015).
- Beven, K. Rainfall-Runoff Modeling; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mahé, G.; Paturel, J.; Servat, E.; Conway, D.; Dezetter, A. The impact of land use change on soil water holding capacity and river flow modelling in the Nakambe River, Burkina-Faso. J. Hydrol. 2005, 300, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouelhi, S.; Michel, C.; Perrin, C.; Andreassian, V. Stepwise development of a two-parameter monthly water balance model. J. Hydrol. 2006, 318, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orgeval, T. Impact du Changement Climatique sur le Cycle de l’eau en Afrique de l’Ouest: Modelisation et Incertitude. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- IRSTEA | Irstea. Available online: http://www.irstea.fr/ (accessed on 23 June 2015).
- De Rosnay, P. Représentation de L’interaction Sol-Végétation-Atmosphère Dans le Modèle de Circulation Générale du Laboratoire de Meteorologie Dynamique. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.; Sutclie, J. River flow forecasting through conceptual models. Part I: A discussion of principle. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturel, J.; Ouedraogo, M.; Mahé, G.; Servat, E.; Dezetter, A.; Ardoin, S. The influence of distributed input data on the hydrological modelling of monthly river flow regimes in West Africa. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2003, 48, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahé, G.; Girard, S.; New, M.; Paturel, J.; Cres, A.; Dezetter, A.; Dieulin, C.; Boyer, J.; Rouche, N.; Servat, E. Comparing available rainfall gridded datasets for West Africa and the impact on rainfall-runoff modelling results, the case of Burkina-Faso. Water Sa 2008, 34, 529–536. [Google Scholar]
- Dakouré, D. Etude Hydrogéologique et Géochimique de la Bordure Sud-Est du Bassin Sédimentaire de Taoudéni (Burkina Faso—Mali)—Essai de modélisation. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris 6—Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dérive, G. Estimation de L’évapotranspiration en Région Sahélienne. Synthèse des Connaissances et Evaluation de Modélisations (SISVAT, RITCHIE): Appllication à la zone d’Hapex-Sahel (Niger). Ph.D. Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Grenoble, Valence, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, N. Development of a Water Balance for the Atankwidi Catchment, West Africa: A Case Study of Groundwater Recharge in a Semi-Arid Climate. Center for Development Research, University of Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Vissin, E. Impact de la Variabilité Climatique et de la Dynamique des états de Surface sur les Ecoulements du Bassin Béninois du Fleuve Niger. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Bourgogne, Dijon, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, B. Caractérisation des Saisons de Pluies au Burkina Faso Dans un contexte de Changement Climatique et Evaluation des Impacts Hydrologiques sur le Bassin du Nakanbé. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.W.; Zhan, T.L.T.; Chen, Y.M.; Fredlund, D.G. Influence of rainfall pattern on the infiltration into landfill earthen final cover. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Symposium on Geoenvironmental Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 8–10 September 2009.
- Risbey, J.S.; Entekhabi, D. Observed Sacramento Basin streamflow response to precipitation and temperature changes and its relevance to climate impact studies. J. Hydrol. 1996, 184, 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Brunel, J.; Bouron, B. Evaporation des Nappes d’eau Libres en Afrique Sahélienne et Tropicale; Publications CIEH-ORSTOM: Montpellier, France, 1992. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, J.; Holwill, C. Soil evaporation from tiger-bush in South-West Niger. J. Hydrol. 1997, 188, 426–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milville, F. Etude hydrodynamique et quantication de la recharge des aquifères en climat Soudano-Sahélien: Application a un bassin expérimental au Burkina Faso, in soil water balance in the Sudano-Sahelian zone. In Proceedings of 1991 International Workshop, Niamey, Niger, 18–23 February 1991. (In French)
- Vischel, T.; Lebel, T. Assessing the water balance in the Sahel: Impact of small scale rainfall variability on runoff. Part 2: Idealized modeling of runoff sensitivity. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 340–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruelland, D.; Levavasseur, F.; Tribotté, A. Patterns and dynamics of land-cover changes since the 1960s over three experimental areas in Mali. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12, S11–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahé, G.; Paturel, J. 1896–2006 Sahelian annual rainfall variability and runoff increase of Sahelian Rivers. C. R. Geosci. 2009, 341, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudhomme, C.; Reynard, N.; Crooks, S. Downscaling of global climate models for flood frequency analysis: where are we now? Hydrol. Proc. 2002, 16, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, B.; Karambiri, H.; Polcher, J. Hydrological Impacts of the Changes in Simulated Rainfall Fields on Nakanbe Basin in Burkina Faso. Climate 2015, 3, 442-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli3030442
Ibrahim B, Karambiri H, Polcher J. Hydrological Impacts of the Changes in Simulated Rainfall Fields on Nakanbe Basin in Burkina Faso. Climate. 2015; 3(3):442-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli3030442
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Boubacar, Harouna Karambiri, and Jan Polcher. 2015. "Hydrological Impacts of the Changes in Simulated Rainfall Fields on Nakanbe Basin in Burkina Faso" Climate 3, no. 3: 442-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli3030442




