A Methodological Approach (TOPSIS) to Water Management in Water-Scarce Areas Under Climate Variability Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
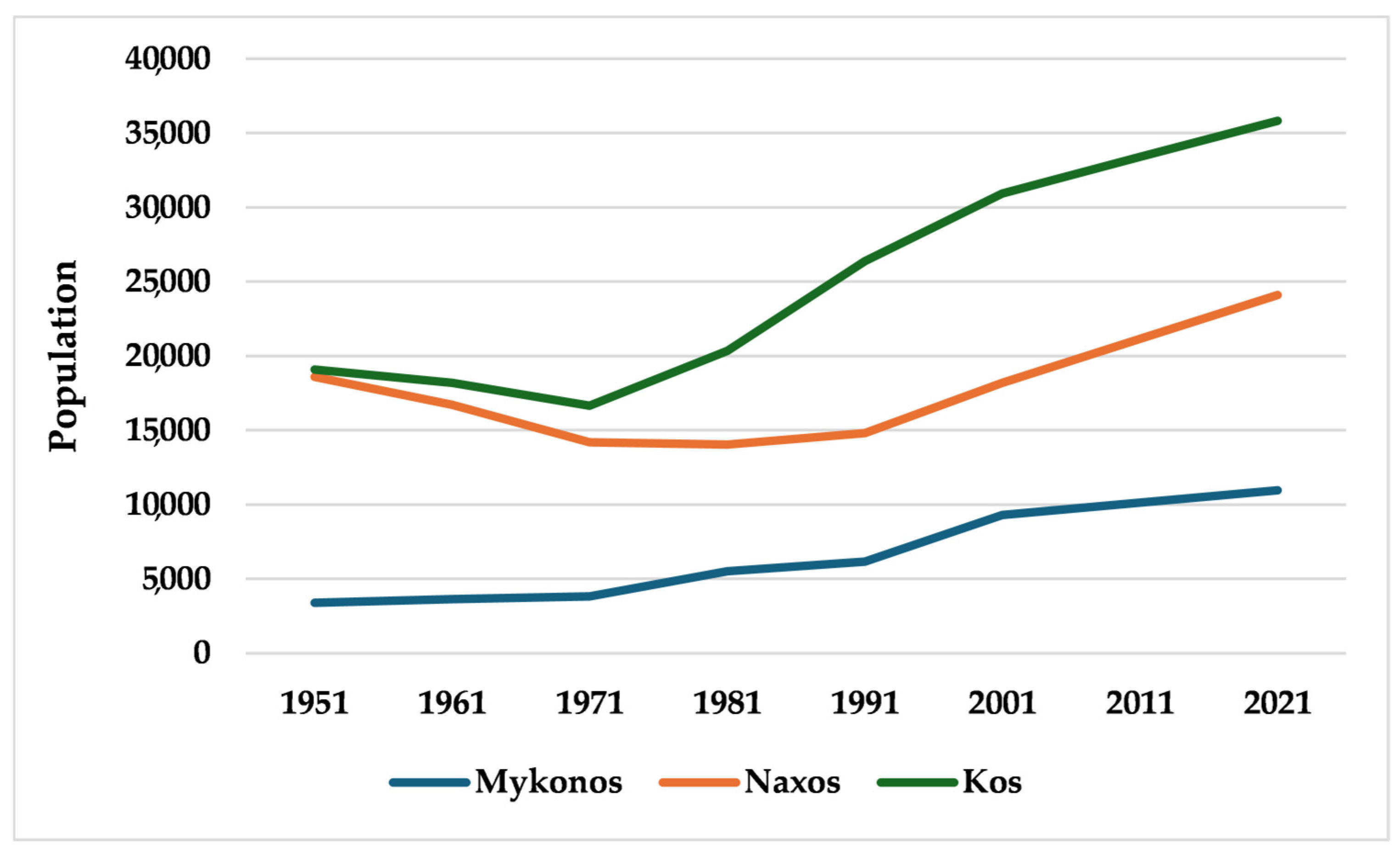
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Available Water and Water Demand—Water Deficiency Description of the Study Area
2.2.1. Island of Mykonos
2.2.2. Island of Naxos
2.2.3. Island of Kos
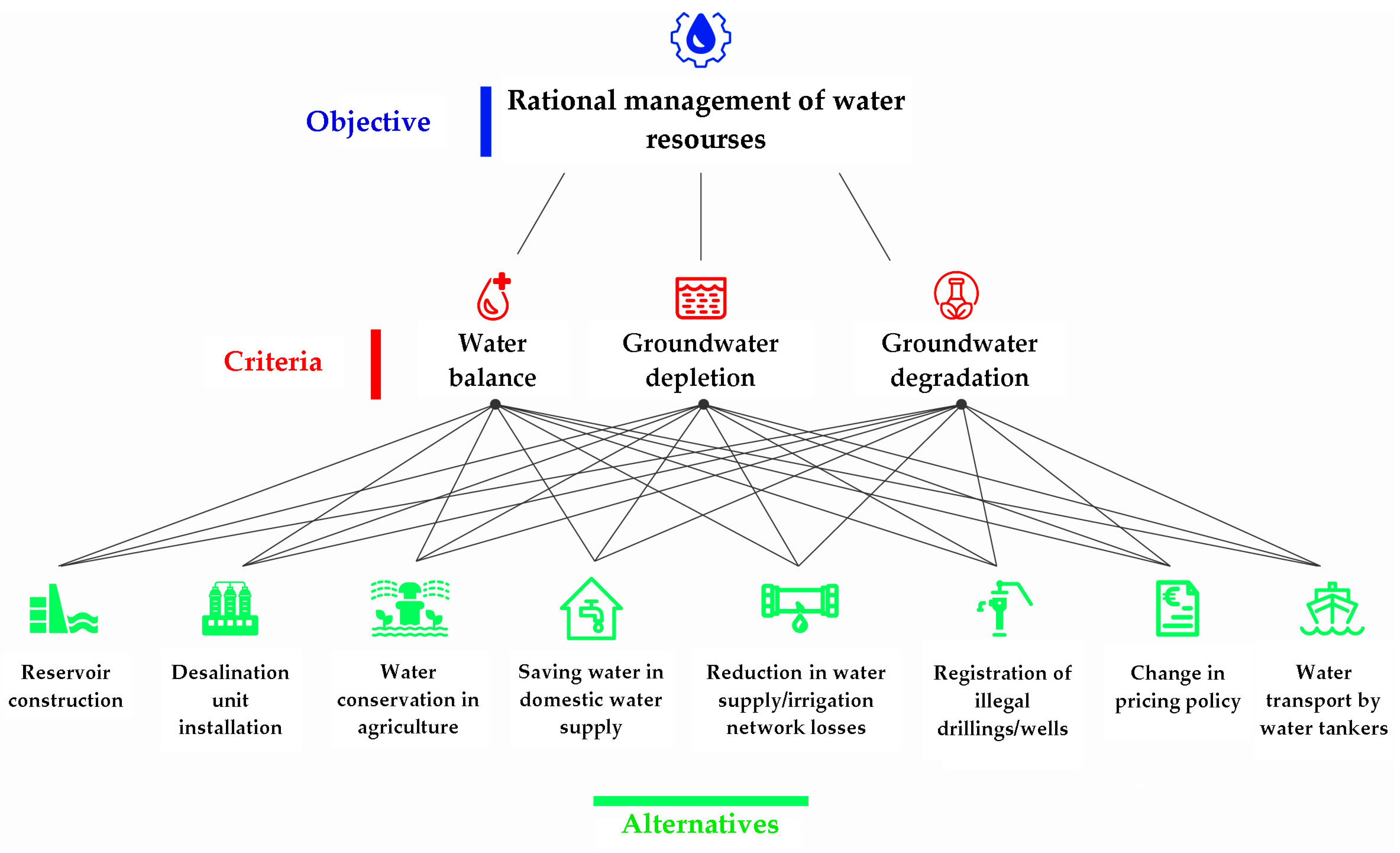
2.3. Multi-Criteria TOPSIS Analysis for Selecting the Best Water Management Practices on Each Island
- Mathematical logic that represents the logic of the individual.
- It simultaneously considers both the best and the worst alternatives.
- A systematic and easily programmable computational procedure that can be easily processed in a spreadsheet.
- The performance measures of all alternatives can be displayed on a polyhedron, at least in two dimensions.
- 1.
- Assignment of scores to the criteria and alternatives. The decision table is designed, consisting of the scores of the alternatives to the evaluation criteria.where A1, A2, …, Am, i = 1, 2, …, m are the alternatives; C1, C2, …, Cn, j = 1, 2, …, n, are the criteria; and xij is the performance of alternative Ai versus criterion Cj.
- 2.
- Calculation of the normalized decision matrix. To calculate the normalized decision matrix R, each of its elements is calculated as follows:where rij is the normalized performance of alternative Ai versus criterion Cj.
- 3.
- Calculation of the weighted normalized decision matrix. To calculate the weighted normalized decision matrix P, the normalized decision matrix R is multiplied by the weights of the criteria.
- 4.
- Determination of positive and negative ideal solution vectors. To calculate the vectors representing the hypothetical positive ideal solution P+ (positive impact criteria) and the hypothetical negative ideal solution P− (negative impact criteria), i.e.,the positive and negative ideal solutions for each criterion are calculated aswhere J represents the positive impact (benefit) criteria and J′ the negative impact (cost) criteria.
- 5.
- Distance calculation. The distance of each alternative from the positive ideal solution is calculated asand from the negative ideal solution as
- 6.
- Calculation of relative proximity. The relative proximity Di to the positive ideal solution for each alternative Ai is calculated as
- The long-term meeting of water demand (C1);
- The management and prevention of groundwater depletion (C2);
- The management and prevention of the degradation of aquifers (C3).
- Construction of new surface water storage projects (R1);
- Installation of new plants (R2);
- Water conservation in agriculture (R3);
- Water conservation in domestic water supply (R4);
- Reduction in water supply/irrigation network losses (R5);
- Registration of illegal boreholes/wells (R6);
- Change in pricing policy (R7);
- Water transport by water tankers (R8).
3. Results
3.1. Island of Mykonos
3.2. Island of Naxos
3.3. Island of Kos
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shivakoti, B.R.; Lopez-Casero, F.; Kataoka, Y.; Shrestha, S. Methodological Framework. In An Integrated Approach for Planning Adaptation and Building Resilience of Smallholder Subsistence Livelihoods in Nepal; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Hayama, Japan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tzanakakis, V.A.; Paranychianakis, N.V.; Angelakis, A.N. Water Supply and Water Scarcity. Water 2020, 12, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetland, D. The Role of Prices in Managing Water Scarcity. Water Secur. 2021, 12, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Gosling, S.N.; Kummu, M.; Flörke, M.; Pfister, S.; Hanasaki, N.; Wada, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; et al. Water Scarcity Assessments in the Past, Present, and Future. Earths Future 2017, 5, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzioutzios, C.; Kastridis, A. Multi-Criteria Evaluation (MCE) Method for the Management of Woodland Plantations in Floodplain Areas. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2020, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, M.; Kadziński, M.; Gonzalez, M.; Słowiński, R. How to Support the Application of Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis? Let Us Start with a Comprehensive Taxonomy. Omega 2020, 96, 102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, J.; Greco, S.; Ehrogott, M. Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis: State of the Art Surveys; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 78, ISBN 978-0-387-23067-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gebre, S.L.; Cattrysse, D.; Van Orshoven, J. Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Methods to Address Water Allocation Problems: A Systematic Review. Water 2021, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cascales, M.S.; Molina-García, A.; Sánchez-Lozano, J.M.; Mateo-Aroca, A.; Munier, N. Multi-Criteria Analysis Techniques to Enhance Sustainability of Water Pumping Irrigation. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 4623–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polatidis, H.; Haralambopoulos, D.A.; Munda, G.; Vreeker, R. Selecting an Appropriate Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Technique for Renewable Energy Planning. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2006, 1, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M. The Pros and Cons of Using Pros and Cons for Multi-Criteria Evaluation and Decision Making. SSRN Electron. J. 2009, 1545189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodgson, J.S.; Spackman, M.; Pearman, A.; Phillips, L.D. Multi-Criteria Analysis: A Manual; Economic History Working Papers; London School of Economics and Political Science, Department of Economic History: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Behzadian, M.; Khanmohammadi Otaghsara, S.; Yazdani, M.; Ignatius, J. A State-of the-Art Survey of TOPSIS Applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 13051–13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyoud, S.H.; Fuchs-Hanusch, D. A Bibliometric-Based Survey on AHP and TOPSIS Techniques. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 78, 158–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, D.J.; Ross, Q.E.; Merkhofer, M.W. Multiattribute Utility Analysis for Addressing Section 316(b) of the Clean Water Act. Environ. Sci. Policy 2000, 3, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohekar, S.D.; Ramachandran, M. Application of Multi-Criteria Decision Making to Sustainable Energy Planning—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2004, 8, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.J.; Chakraborty, A.; Sehgal, R. A Systematic Review of Industrial Wastewater Management: Evaluating Challenges and Enablers. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, W.J.; Loucks, D.P. Water Management: Current and Future Challenges and Research Directions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4823–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnib, A. An Approach to Elaborate Priority Preorders of Water Resources Projects Based on Multi-Criteria Evaluation and Fuzzy Sets Analysis. Water Resour. Manag. 2004, 18, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekcioğlu, Ö.; Koc, K.; Dabanli, I.; Deniz, A. Prioritizing Urban Water Scarcity Mitigation Strategies Based on Hybrid Multi-Criteria Decision Approach under Fuzzy Environment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, A.H.A.; Magrini, A. Multi-Criteria Decision-Making to Support Sustainable Water Management in a Mining Complex in Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Del Vasto-Terrientes, L.; Valls, A.; Schuhmacher, M. Adaptation Strategies for Water Supply Management in a Drought Prone Mediterranean River Basin: Application of Outranking Method. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakis, N.; Spiliotis, M.; Voudouris, K.; Pliakas, F.-K.; Papadopoulos, B. A Fuzzy Multicriteria Categorization of the GALDIT Method to Assess Seawater Intrusion Vulnerability of Coastal Aquifers. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sinobas, L.; Zubelzu, S.; Perales-Momparler, S.; Canogar, S. Techniques and Criteria for Sustainable Urban Stormwater Management. The Case Study of Valdebebas (Madrid, Spain). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino, E.; Bottero, M.; Pomarico, S.; Rosso, M. The Combined Use of Spatial Multicriteria Evaluation and Stakeholders Analysis for Supporting the Ecological Planning of a River Basin. Land Use Policy 2016, 58, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfreda, S.; Di Leo, M.; Sole, A. Detection of Flood-Prone Areas Using Digital Elevation Models. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 16, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmehr, A.; Araghinejad, S. Flood Vulnerability Analysis by Fuzzy Spatial Multi Criteria Decision Making. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 4427–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, H.; Gu, Y.; Liu, T. Developing an Interactive Mobile Volunteered Geographic Information Platform to Integrate Environmental Big Data and Citizen Science in Urban Management. In Seeing Cities Through Big Data; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Tehrany, M.S.; Pradhan, B.; Jebur, M.N. Flood Susceptibility Mapping Using a Novel Ensemble Weights-of-Evidence and Support Vector Machine Models in GIS. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, G.; Vasiliades, L.; Loukas, A. Multi-Criteria Analysis Framework for Potential Flood Prone Areas Mapping. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, C.; Kim, B.; Kim, J. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Frequency Ratio, Analytic Hierarchy Process, Logistic Regression, and Artificial Neural Network Methods at the Inje Area, Korea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 1443–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, P.; Rezvani, A.; Wiewiora, A. The Impact of Technology on Older Adults’ Social Isolation. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubal, C.; Haase, D.; Meyer, V.; Scheuer, S. Integrated Urban Flood Risk Assessment—Adapting a Multicriteria Approach to a City. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 1881–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourgialas, N.N.; Karatzas, G.P. A National Scale Flood Hazard Mapping Methodology: The Case of Greece—Protection and Adaptation Policy Approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourgialas, N.N.; Karatzas, G.P. Flood Management and a GIS Modelling Method to Assess Flood-Hazard Areas—A Case Study. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastridis, A.; Margiorou, S.; Sapountzis, M. Check-Dams and Silt Fences: Cost-Effective Methods to Monitor Soil Erosion under Various Disturbances in Forest Ecosystems. Land 2022, 11, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajkowicz, S.; Collins, K. A Review of Multiple Criteria Analysis for Water Resource Planning and Management. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, R.E.; Na, P. Multiple Criteria Decision Making Combined with Finance: A Categorized Bibliographic Study. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 150, 496–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohon, J.L.; Marks, D.H. A Review and Evaluation of Multiobjective Programing Techniques. Water Resour. Res. 1975, 11, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, M.; Arrighi, C.; Piragino, F.; Castelli, F. Participatory Multi-Criteria Decision Making for Optimal Siting of Multipurpose Artificial Reservoirs. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamanos, A.; Mylopoulos, N.; Loukas, A.; Gaitanaros, D. An Integrated Multicriteria Analysis Tool for Evaluating Water Resource Management Strategies. Water 2018, 10, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood-Howard, I.; Thompson, J.; Shamsudduha, M.; Taylor, R.G.; Mosha, D.B.; Gebrezgi, G.; Tarimo, A.K.P.R.; Kashaigili, J.J.; Nazoumou, Y.; Tiékoura, O. A Multicriteria Analysis of Groundwater Development Pathways in Three River Basins in Sub-Saharan Africa. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 138, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastridis, A.; Stathis, D. The Effect of Small Earth Dams and Reservoirs on Water Management in North Greece (Kerkini Municipality). Silva Balc. 2015, 16, 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.-L.; Yoon, K. Methods for Multiple Attribute Decision Making. In Multiple Attribute Decision Making; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 58–191. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, H.-S.; Shyur, H.-J.; Lee, E.S. An Extension of TOPSIS for Group Decision Making. Math. Comput. Model. 2007, 45, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Park, C.S.; Yoon, K.P. Identifying Investment Opportunities for Advanced Manufacturing Systems with Comparative-Integrated Performance Measurement. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 1997, 50, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Guo, C.; Cui, J. Research on Evaluation Method of Water Resources Carrying Capacity Based on Improved TOPSIS Model. La Houille Blanche 2020, 106, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Alkhawaji, R.N.; Shafieezadeh, M.M. Evaluating Sustainable Water Management Strategies Using TOPSIS and Fuzzy TOPSIS Methods. Appl. Water Sci. 2025, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Liu, C.; Li, T.; Meng, F.; Fu, Q.; Ji, Y.; Hou, R. Evaluation of the Water Resource Carrying Capacity in Heilongjiang, Eastern China, Based on the Improved TOPSIS Model. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathi, E.; Kastridis, A.; Myronidis, D. Analysis of Hydrometeorological Trends and Drought Severity in Water-Demanding Mediterranean Islands under Climate Change Conditions. Climate 2023, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathi, E.; Kastridis, A.; Myronidis, D. Analysis of Hydrometeorological Characteristics and Water Demand in Semi-Arid Mediterranean Catchments under Water Deficit Conditions. Climate 2023, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA European Environment Agency. Corine Land Cover: Copenhagen, Denmark. 2018. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/en/products/corine-land-cover/clc2018 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Cheng, S.; Chan, C.W.; Huang, G.H. Using Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis for Supporting Decisions of Solid Waste Management. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2002, 37, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanakis, S.H.; Solomon, A.; Wishart, N.; Dublish, S. Multi-Attribute Decision Making: A Simulation Comparison of Select Methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 107, 507–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K. A Reconciliation Among Discrete Compromise Solutions. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1987, 38, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakarakos, G.; Papadakis, G.; Karavitis, C.A. Renewable Energy Desalination for Island Communities: Status and Future Prospects in Greece. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alvarez, V.; Maestre-Valero, J.F.; González-Ortega, M.J.; Gallego-Elvira, B.; Martin-Gorriz, B. Characterization of the Agricultural Supply of Desalinated Seawater in Southeastern Spain. Water 2019, 11, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentis, D.; Karalis, G.; Zervos, A.; Howells, M.; Taliotis, C.; Bazilian, M.; Rogner, H. Desalination Using Renewable Energy Sources on the Arid Islands of South Aegean Sea. Energy 2016, 94, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapanese, M.; Frazitta, V. Desalination in Small Islands: The Case Study of Lampedusa (Italy). In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2018 MTS/IEEE Charleston, Charleston, SC, USA, 22–25 October 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chartzoulakis, K.; Bertaki, M. Sustainable Water Management in Agriculture under Climate Change. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 4, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, E.; Díaz-Gaona, C.; García-Laureano, R.; Reyes-Palomo, C.; Guzmán, G.I.; Ortolani, L.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, M.; Rodríguez-Estévez, V. Agroecology for Adaptation to Climate Change and Resource Depletion in the Mediterranean Region. A Review. Agric. Syst. 2020, 181, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucaro, R.; Baralla, S.; Arzeni, A.; Bodini, A.; Ciaravino, R.; Salato, N.; Chinnici, P.; Fasolino, N.G.; Pellegrini, E.; Sarzotti, E.; et al. Integrating Irrigation Decision Support Systems for Efficient Water Use: A Case Study on Mediterranean Agriculture. Land 2024, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A. Case Studies on Water Conservation in the Mediterranean Region; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tzanakakis, V.; Angelakis, A.; Paranychianakis, N.; Dialynas, Y.; Tchobanoglous, G. Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Management of Water Resources in the Island of Crete, Greece. Water 2020, 12, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, P.; Tchobanoglous, G. Sustainable Use of Water in the Aegean Islands. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartzoulakis, K. Water Resources Management in the Island of Crete, Greece, with Emphasis on the Agricultural Use. Water Policy 2001, 3, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.; Garrote, L.; Diz, A.; Schlickenrieder, J.; Martin-Carrasco, F. Re-Thinking Water Policy Priorities in the Mediterranean Region in View of Climate Change. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 744–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donta, A.A.; Lange, M.A. Water Management on Mediterranean Islands: Pressure, Recommended Policy and Management Options. In Coping with Water Deficiency; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 11–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lebu, S.; Lee, A.; Salzberg, A.; Bauza, V. Adaptive Strategies to Enhance Water Security and Resilience in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Available Water | Amount (m3) | Demand | Amount (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dams and reservoirs | 790,000 | Settlements | 999,500 |
| 650,000 | Tourism | 522,000 | |
| Groundwater | 200,000 | Irrigation | 1,401,000 |
| Livestock | 39,000 | ||
| 5 and 2 portable desalination units | No available data | Industry | 123,000 |
| Total | 1,640,000 | Total | 3,084,500 |
| Available Water | Amount (m3) | Demand | Amount (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dams and reservoirs | 1,467,000 | Settlements | 1,600,000 |
| 570,000 | Tourism | 400,000 | |
| Springs | 3,000,000 | Irrigation | 8,000,000 |
| Groundwater | No available data | Livestock | 525,000 |
| Small industry | 150,000 | ||
| Total | 5,037,000 | 10,675,000 |
| Available Water | Amount (m3) | Demand | Amount (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dams and reservoirs | 342,000 | Settlements | 3,800,000 |
| 225,000 | Tourism | 700,000 | |
| Groundwater | – | Irrigation | 9,500,000 |
| Springs | 3,000,000 | Livestock | 520,000 |
| Small industry | 220,000 | ||
| Total | 3,567,000 | 14,740,000 |
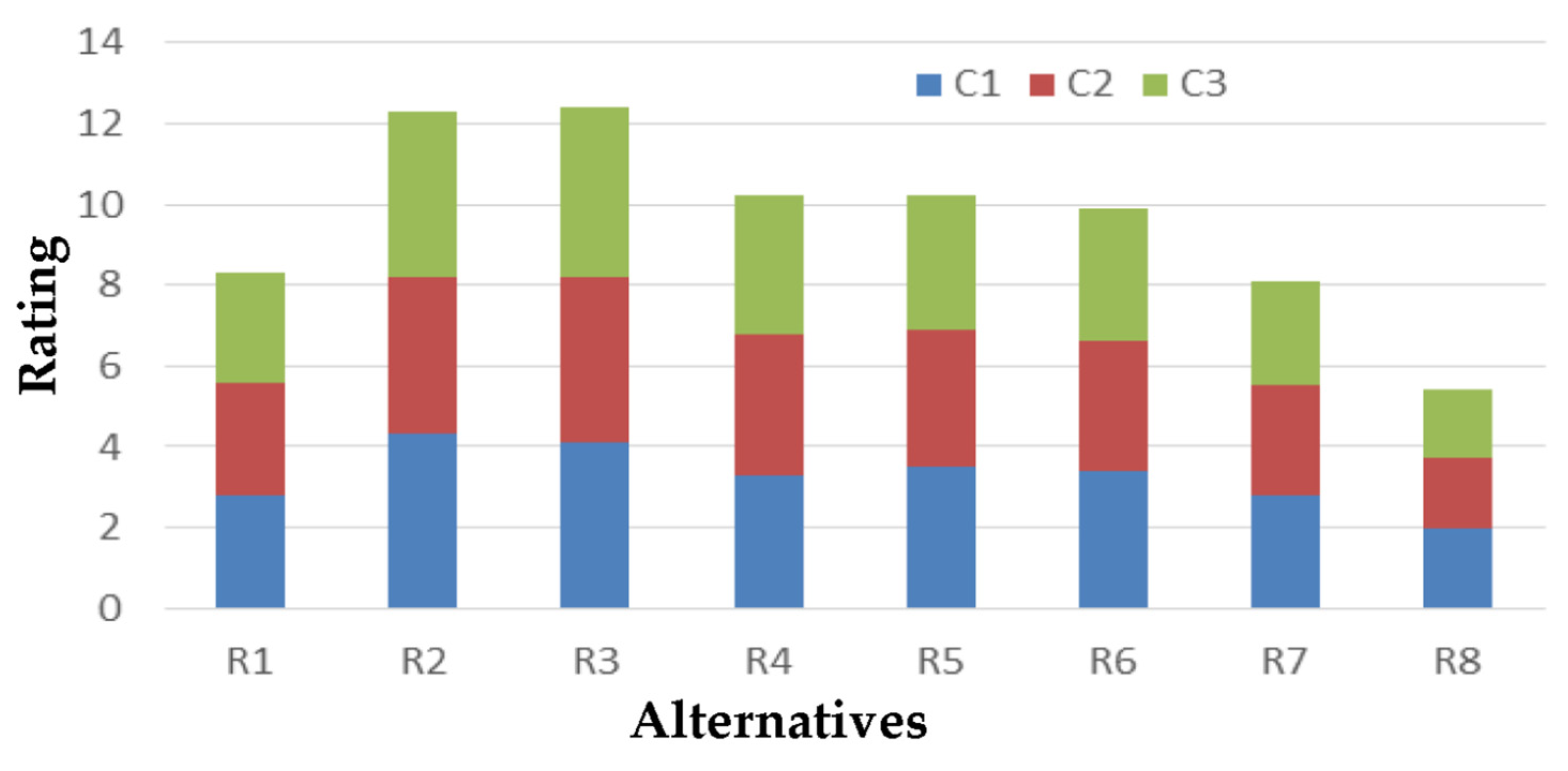
| Alternatives | Criteria | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C1. Water Balance | C2. Depletion of Aquifers | C3. Deterioration of Aquifers | |
| R1. Construction of a reservoir | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.7 |
| R2. Installation of a desalination plant | 4.3 | 3.9 | 4.1 |
| R3. Saving water in agriculture | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.2 |
| R4. Saving water in water supply | 3.3 | 3.5 | 3.4 |
| R5. Reducing network losses | 3.5 | 3.4 | 3.3 |
| R6. Recording illegal boreholes/wells | 3.4 | 3.2 | 3.3 |
| R7. Changing the pricing policy | 2.8 | 2.7 | 2.6 |
| R8. Transporting water by ship | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| Criterion weights | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.25 |
| Alternatives | Relative Proximity | Ranking | Order of Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1. Construction of a reservoir | 0.411 | 3 | 6 |
| R2. Installation of a desalination plant | 0.965 | 8 | 1 |
| R3. Saving water in agriculture | 0.938 | 7 | 2 |
| R4. Saving water in water supply | 0.669 | 5 | 4 |
| R5. Reducing network losses | 0.686 | 6 | 3 |
| R6. Recording illegal boreholes/wells | 0.627 | 4 | 5 |
| R7. Changing pricing policy | 0.384 | 2 | 7 |
| R8. Transporting water by ship | 0.000 | 1 | 8 |
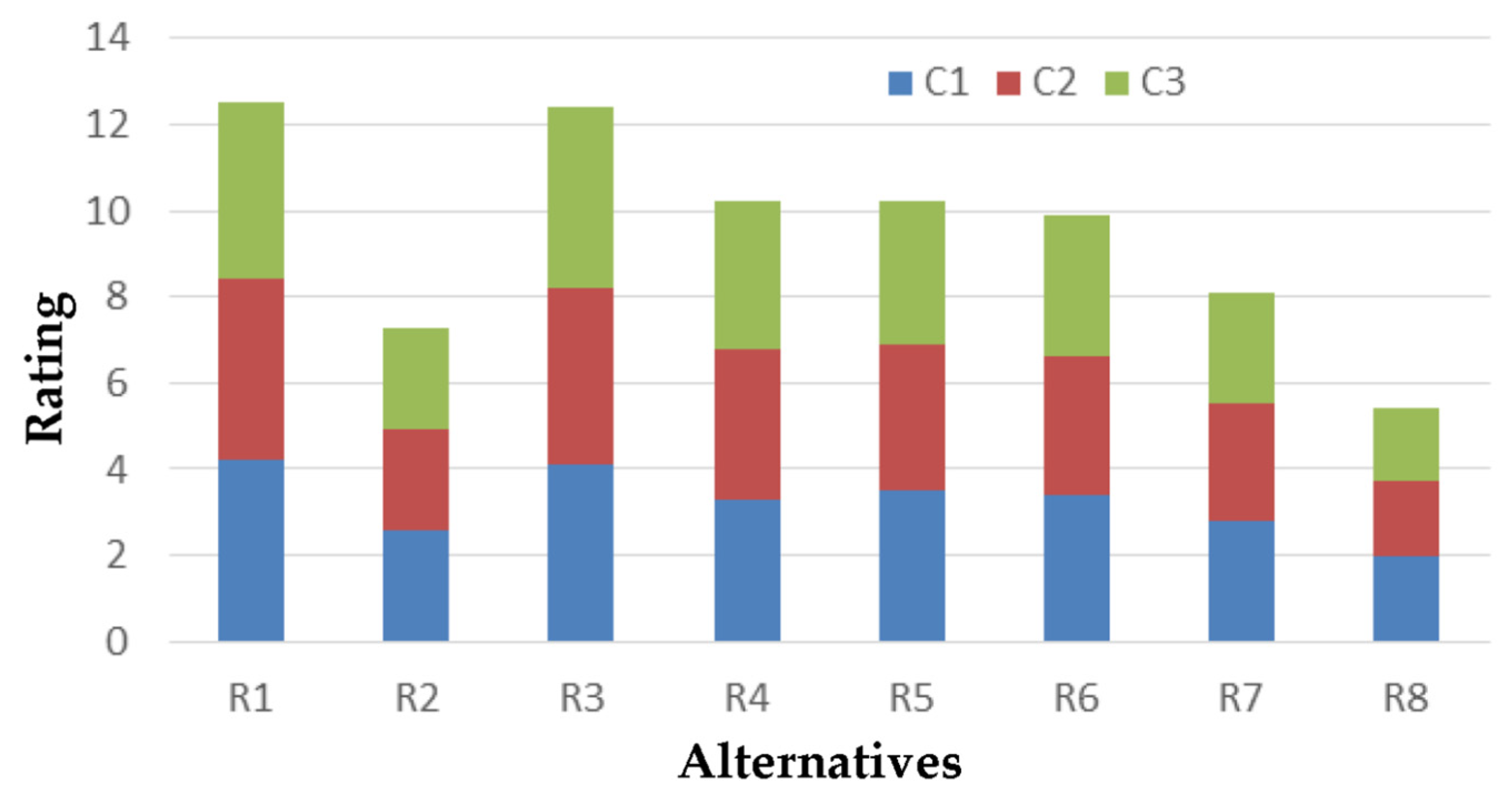
| Alternatives | Criteria | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C1. Water Balance | C2. Depletion of Aquifers | C3. Deterioration of Aquifers | |
| R1. Construction of a reservoir | 4,2 | 4.2 | 4.1 |
| R2. Installation of a desalination plant | 2.6 | 2.3 | 2.4 |
| R3. Saving water in agriculture | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.2 |
| R4. Saving water in water supply | 3.3 | 3.5 | 3.4 |
| R5. Reducing network losses | 3.5 | 3.4 | 3.3 |
| R6. Recording illegal boreholes/wells | 3.4 | 3.2 | 3.3 |
| R7. Changing the pricing policy | 2.8 | 2.7 | 2.6 |
| R8. Transporting water by ship | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| Criterion weights | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.25 |
| Alternatives | Relative Proximity | Ranking | Order of Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1. Construction of a reservoir | 0.980 | 8 | 1 |
| R2. Installation of a desalination plant | 0.256 | 2 | 7 |
| R3. Saving water in agriculture | 0.945 | 7 | 2 |
| R4. Saving water in water supply | 0.669 | 5 | 4 |
| R5. Reducing network losses | 0.683 | 6 | 3 |
| R6. Recording illegal boreholes/wells | 0.623 | 4 | 5 |
| R7. Changing the pricing policy | 0.382 | 3 | 6 |
| R8. Transporting water by ship | 0.000 | 1 | 8 |
| Alternatives | Criteria | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C1. Water Balance | C2. Depletion of Aquifers | C3. Deterioration of Aquifers | |
| R1. Construction of a reservoir | 4.2 | 4.1 | 3.9 |
| R2. Installation of a desalination plant | 2.6 | 2.3 | 2.4 |
| R3. Saving water in agriculture | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.2 |
| R4. Saving water in water supply | 3.3 | 3.5 | 3.4 |
| R5. Reducing network losses | 3.5 | 3.4 | 3.3 |
| R6. Recording illegal boreholes/wells | 3.4 | 3.2 | 3.3 |
| R7. Changing pricing policy | 2.8 | 2.7 | 2.6 |
| R8. Transporting water by ship | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| Criterion weights | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.25 |
| Alternatives | Relative Proximity | Ranking | Order of Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1. Construction of a reservoir | 0.949 | 7 | 2 |
| R2. Installation of a desalination plant | 0.251 | 2 | 7 |
| R3. Saving water in agriculture | 0.965 | 8 | 1 |
| R4. Saving water in water supply | 0.682 | 5 | 4 |
| R5. Reducing network losses | 0.696 | 6 | 3 |
| R6. Recording illegal boreholes/wells | 0.635 | 4 | 5 |
| R7. Changing the pricing policy | 0.389 | 3 | 6 |
| R8. Transporting water by ship | 0.000 | 1 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stathi, E.; Kastridis, A.; Myronidis, D. A Methodological Approach (TOPSIS) to Water Management in Water-Scarce Areas Under Climate Variability Conditions. Climate 2025, 13, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13040078
Stathi E, Kastridis A, Myronidis D. A Methodological Approach (TOPSIS) to Water Management in Water-Scarce Areas Under Climate Variability Conditions. Climate. 2025; 13(4):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13040078
Chicago/Turabian StyleStathi, Efthymia, Aristeidis Kastridis, and Dimitrios Myronidis. 2025. "A Methodological Approach (TOPSIS) to Water Management in Water-Scarce Areas Under Climate Variability Conditions" Climate 13, no. 4: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13040078
APA StyleStathi, E., Kastridis, A., & Myronidis, D. (2025). A Methodological Approach (TOPSIS) to Water Management in Water-Scarce Areas Under Climate Variability Conditions. Climate, 13(4), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13040078







