Heatwaves and Public Health: A Bibliometric Exploration of Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We assessed the evolving body of literature on heatwaves and public health impacts and identified key thematic areas and emerging research trends.
- To identify the adaptive strategies adopted to reduce health vulnerabilities to heat events.
- Identifying critical knowledge gaps that require further investigation to enhance heatwave preparedness and public health response.
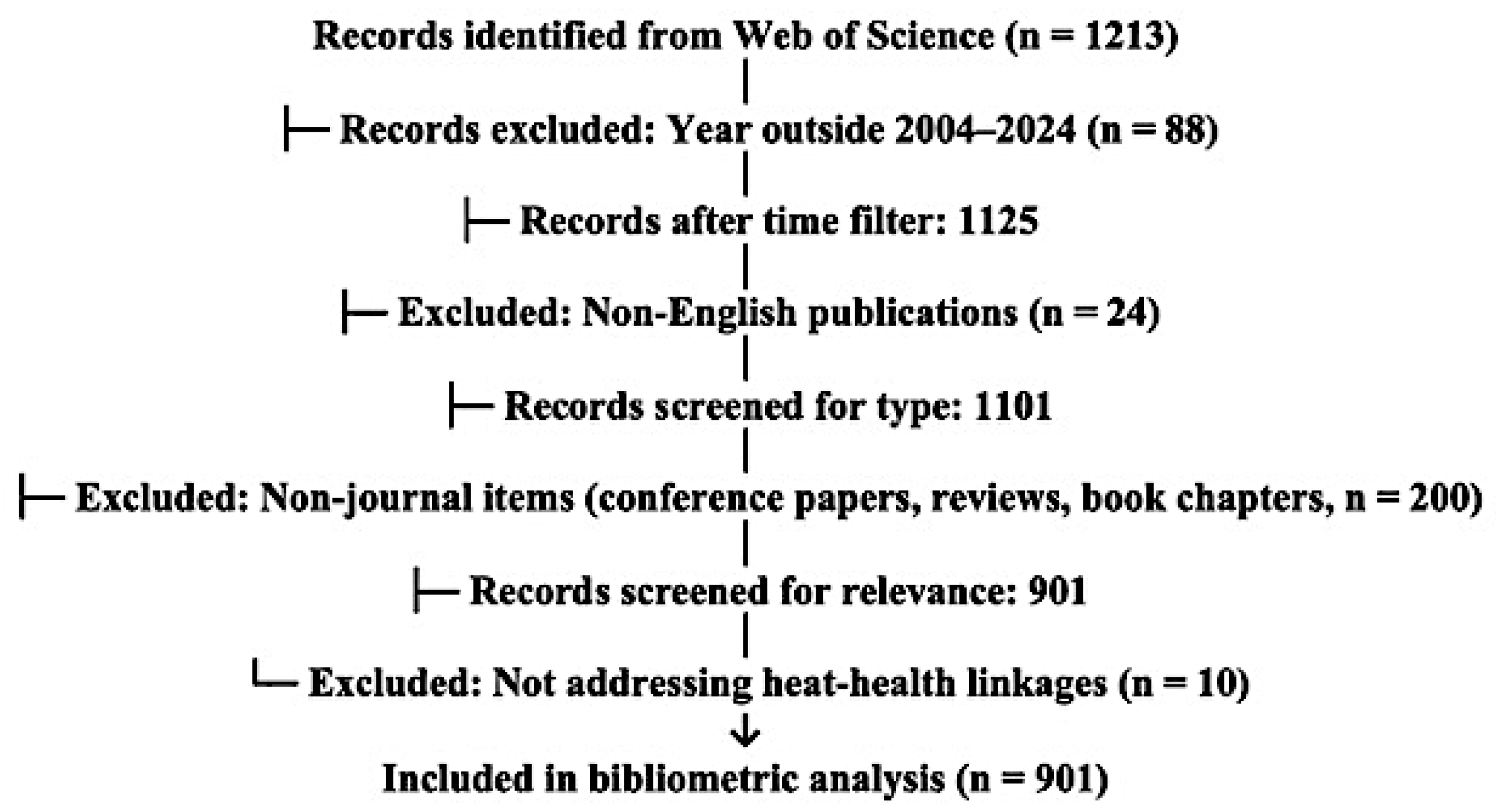
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
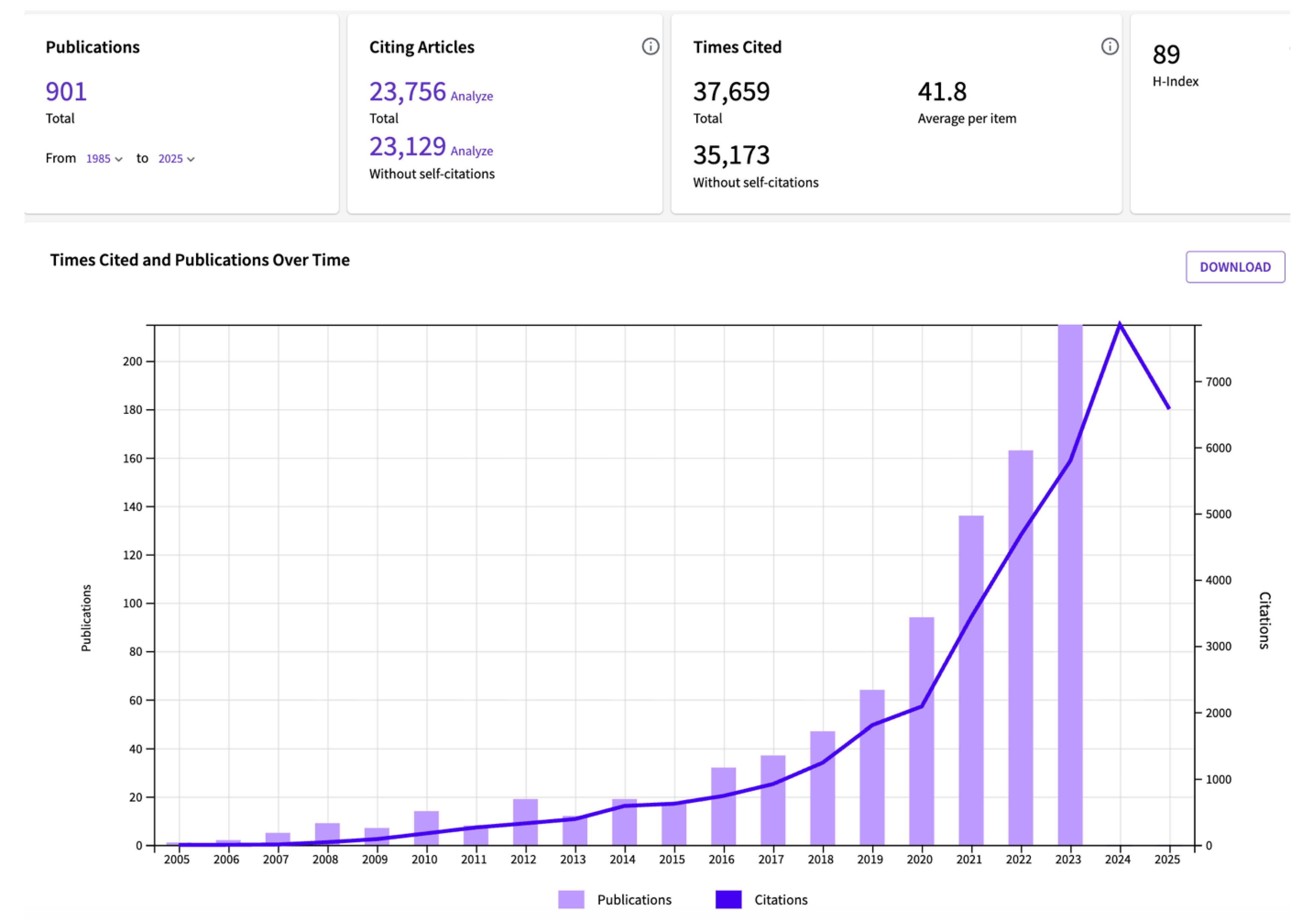
3.1. Trends and Growth in Heatwave and Health Research
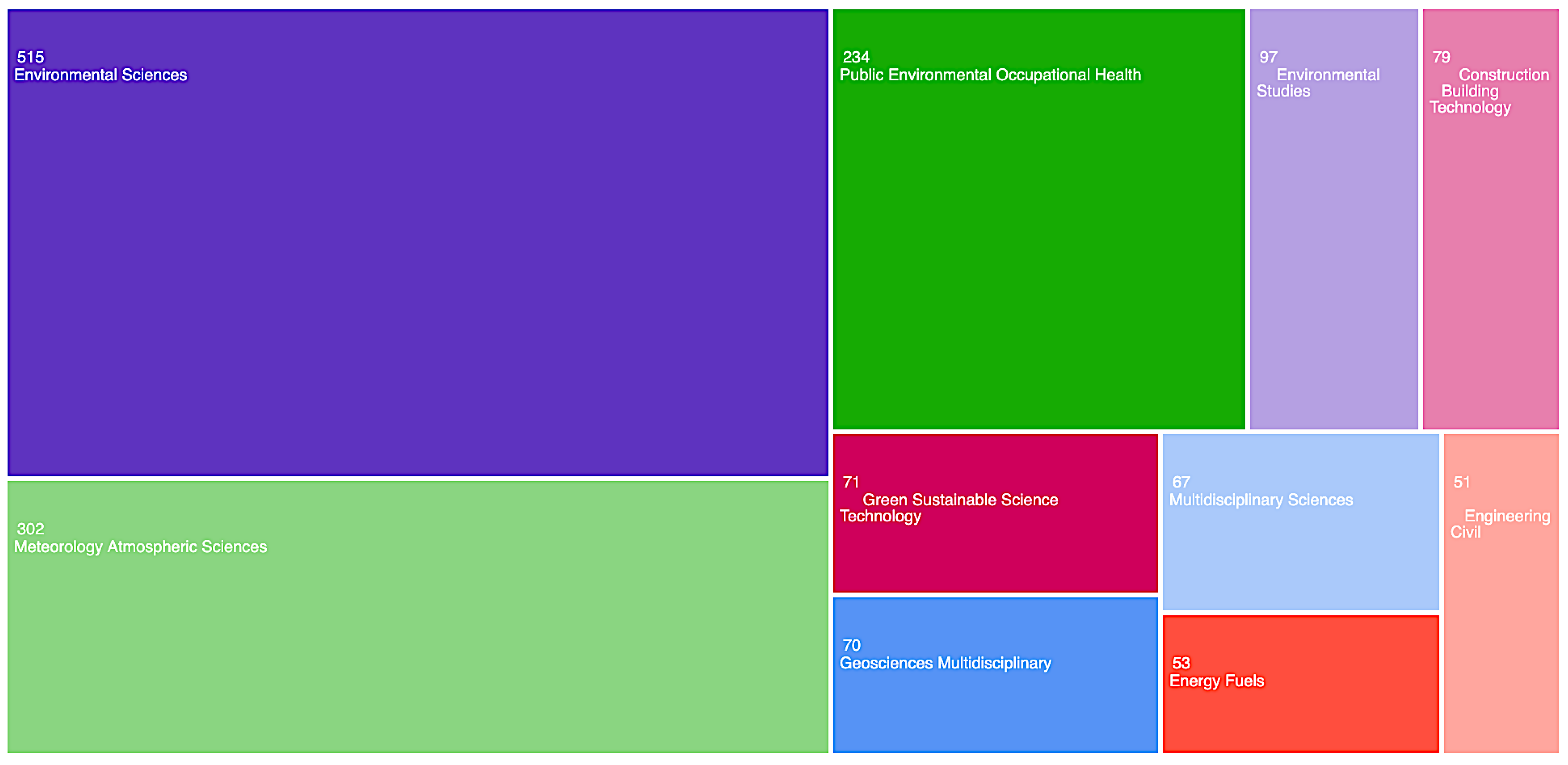
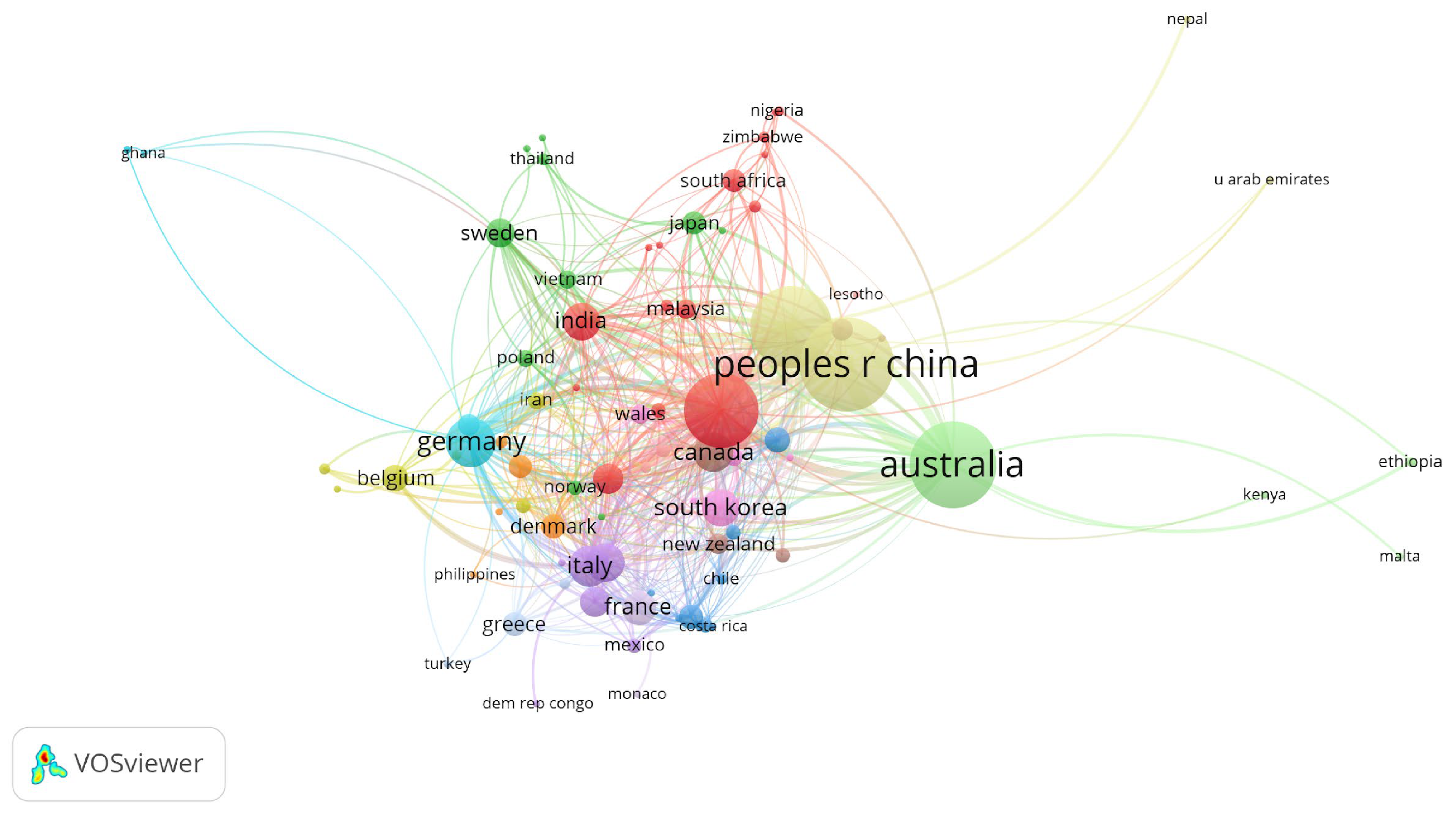
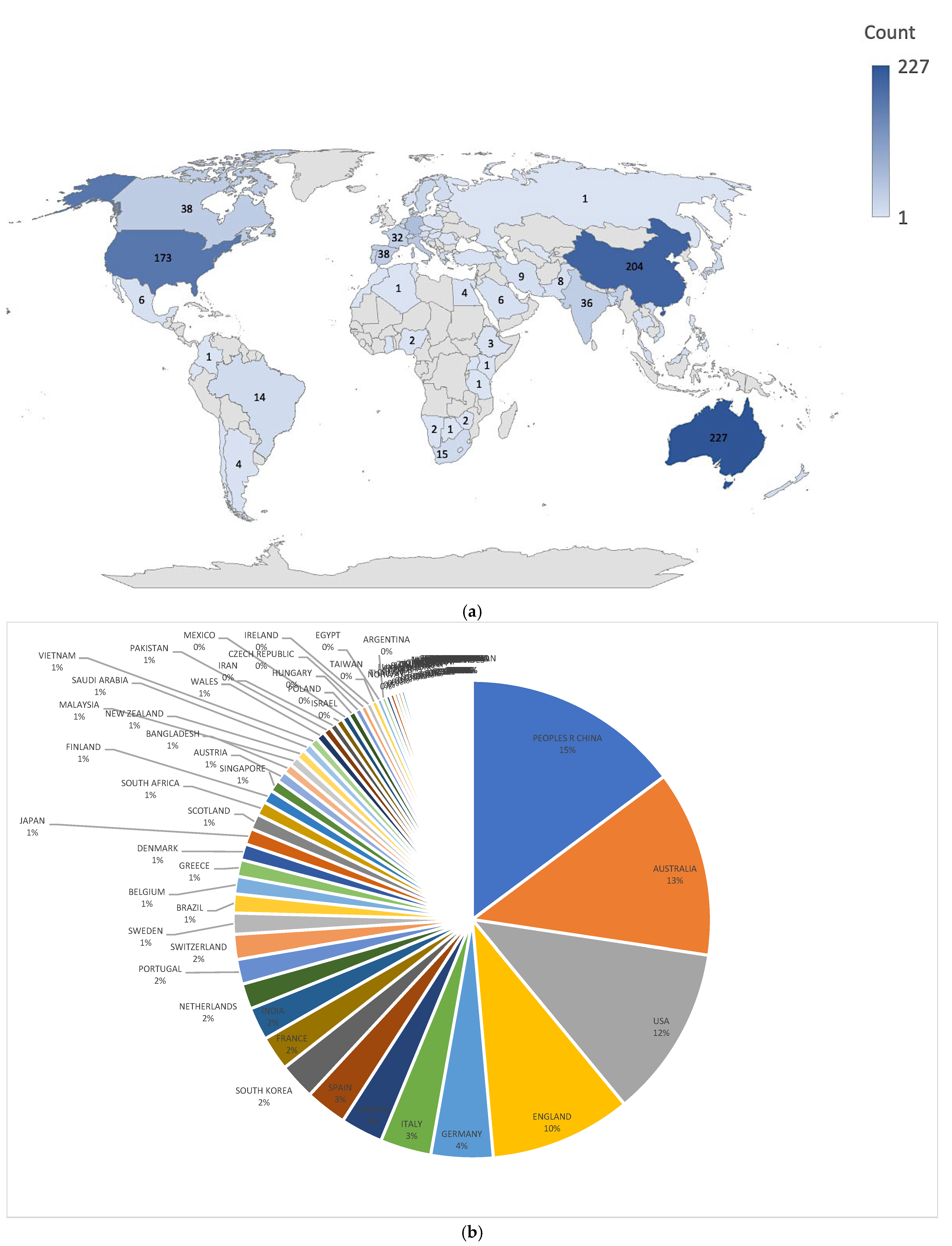
3.2. Geographic Distribution of Heatwave and Health Research
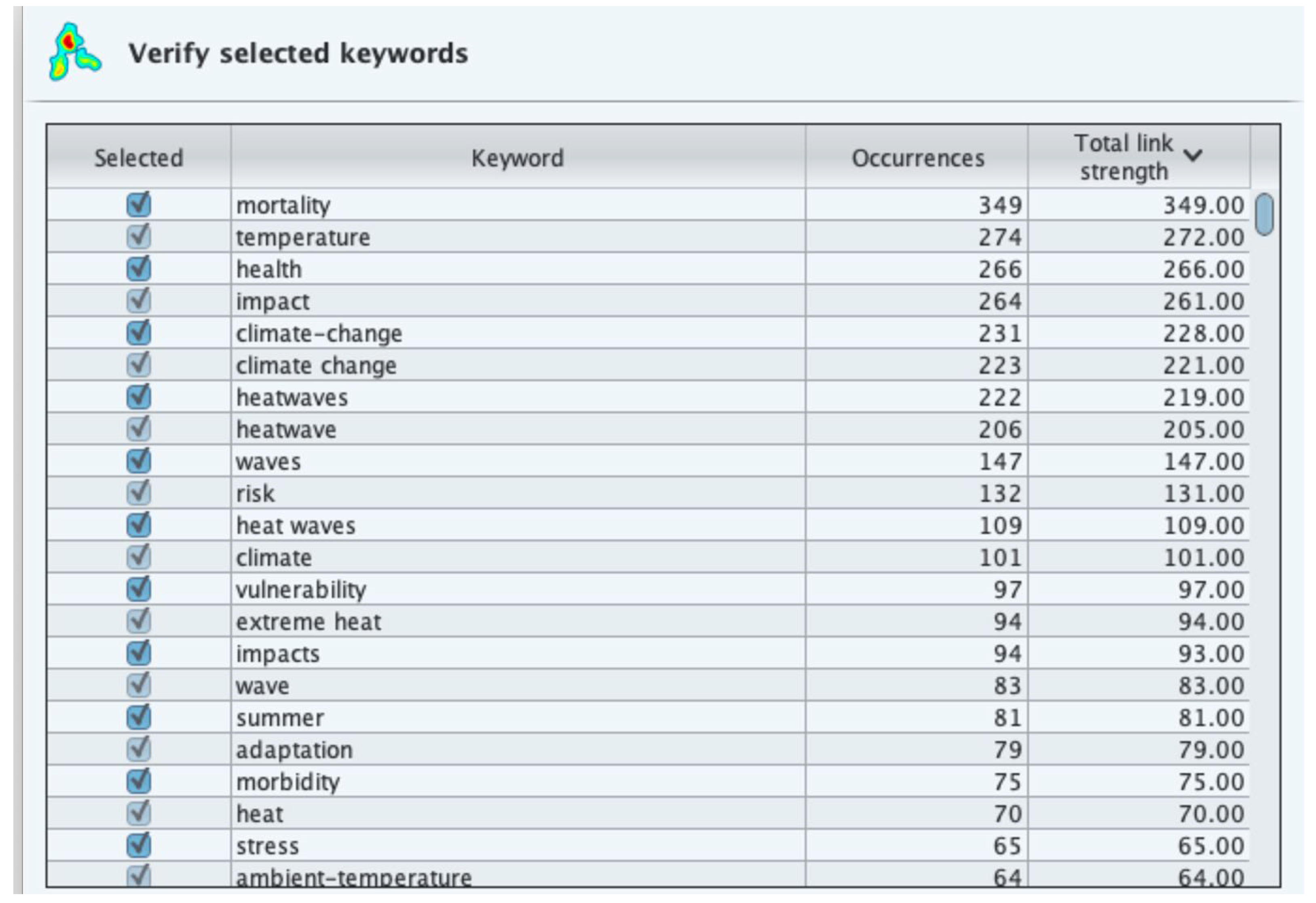
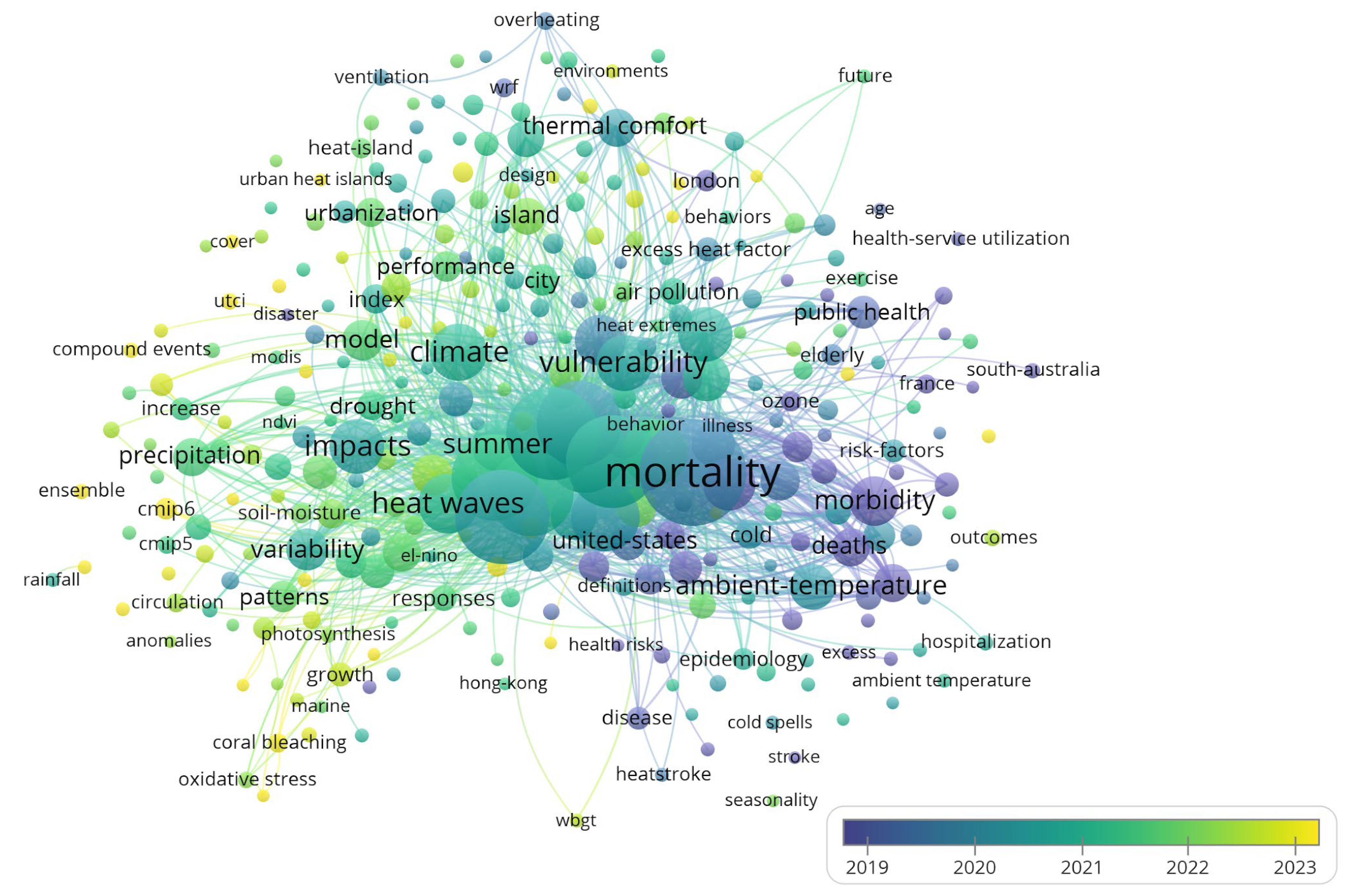
3.3. Key Terms and Evolving Themes on Heatwave and Health
3.4. Physiological and Mental Health Consequences of Heatwaves
3.5. Urban and Rural Disparities in Heatwave Exposure
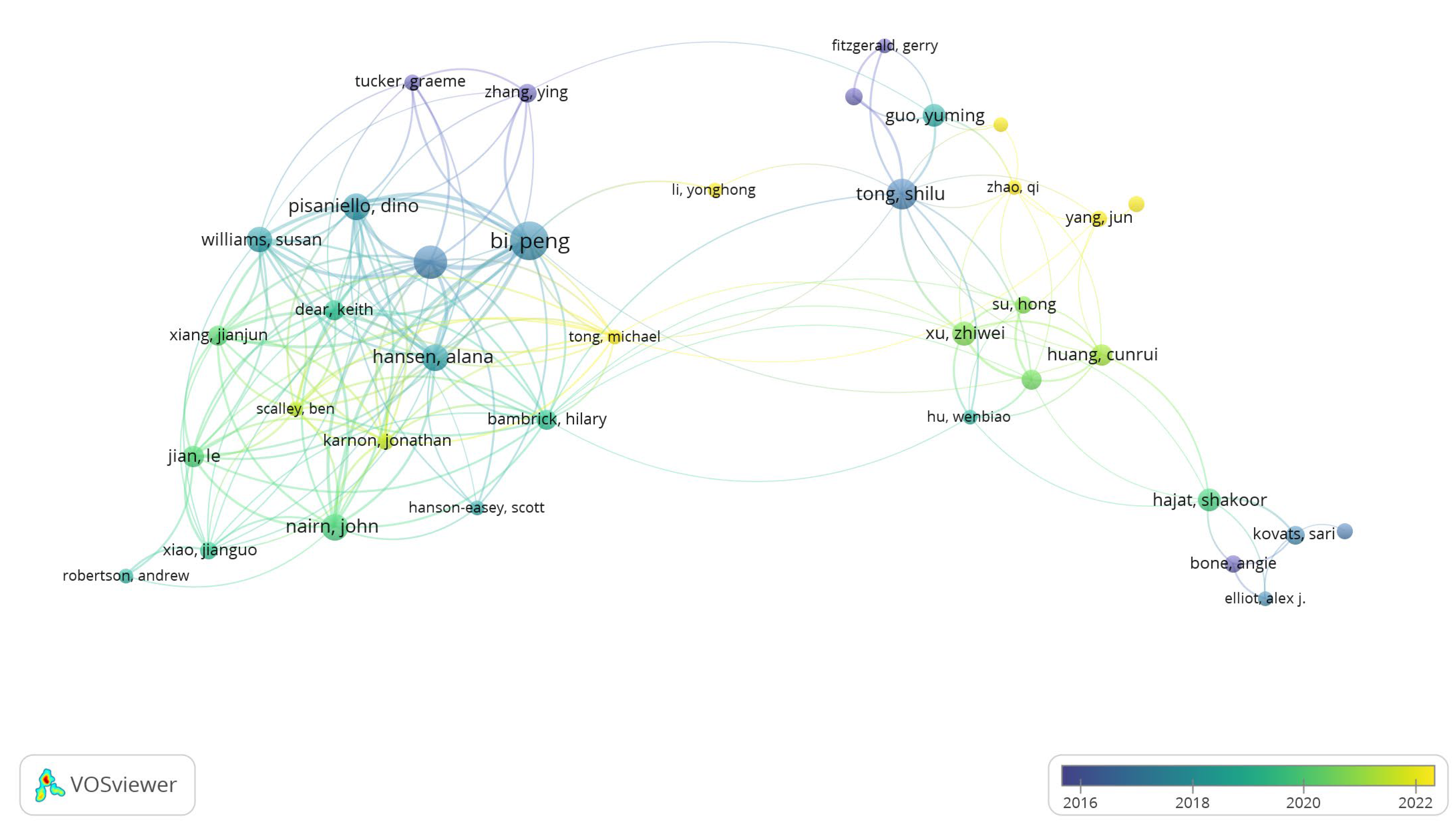
3.6. Regional and Global Perspectives on Heatwave Research
3.7. Building Resilience and Adaptation to Heatwaves
3.8. Research Gaps Future Direction and Policy Perspectives
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, R.; Noy, I. The Global Costs of Extreme Weather That Are Attributable to Climate Change. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibitane, Z.E.; Dube, K.; Lekaota, L. Global Warming and Its Implications on Nature Tourism at Phinda Private Game Reserve, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.A.; Alam, L.; Alam, M.M.; Rahman, L.F.; Pereira, J.J. Estimation of Losses and Damages Caused by Flash Floods in the Commercial Area of Kajang, Selangor, Malaysia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, K.; Nhamo, G.; Kilungu, H.; Hambira, W.L.; El-Masry, E.A.; Chikodzi, D.; Chapungu, L.; Molua, E.L. Tourism and Climate Change in Africa: Informing Sector Responses. J. Sustain. Tour. 2024, 32, 1811–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuni, S.; Adarkwah, F.; Ofori, B.D.; Purwestri, R.C.; Bernal, D.C.H.; Hajek, M. Managing the Challenges of Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies in Ghana. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, K.; Nhamo, G.; Chikodzi, D. Rising Sea Level and Its Implications on Coastal Tourism Development in Cape Town, South Africa. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2021, 33, 100346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinko, T.; Berchtold, C.; Handmer, J.; Deubelli-Hwang, T.; Preinfalk, E.; Linnerooth-Bayer, J.; Scolobig, A.; Serra, M.; Plana, E. A Framework for Considering Justice Aspects in Integrated Wildfire Risk Management. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriopedro, D.; García-Herrera, R.; Ordóñez, C.; Miralles, D.G.; Salcedo-Sanz, S. Heat Waves: Physical Understanding and Scientific Challenges. Rev. Geophys. 2023, 61, e2022RG000780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lala, B.; Hagishima, A. Impact of Escalating Heat Waves on Students’ Well-Being and Overall Health: A Survey of Primary School Teachers. Climate 2023, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Ullah, W.; Sachindra, D.A.; Ali, A.; Bhatti, A.S.; Ali, G. Climate Change Will Exacerbate Population Exposure to Future Heat Waves in the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2023, 40, 100570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Kim, E.; Kwag, Y.; An, H.; Kim, H.S.; Shah, S.; Lee, J.H.; Ha, E. Heat Wave Exposure and Increased Heat-Related Hospitalizations in Young Children in South Korea: A Time-Series Study. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Sun, H.; Zhong, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Luo, L.; Wang, S.; Lv, Z.; et al. Ozone, Heat Wave, and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality: A Population-Based Case-Crossover Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bueno, J.A.; Díaz, J.; Linares, C. Differences in the Impact of Heat Waves According to Urban and Peri-Urban Factors in Madrid. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, 63, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meade, R.D.; Akerman, A.P.; Notley, S.R.; McGinn, R.; Poirier, P.; Gosselin, P.; Kenny, G.P. Physiological Factors Characterizing Heat-Vulnerable Older Adults: A Narrative Review. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Grote, U.; Neubacher, F.; Rahut, D.B.; Do, M.H.; Paudel, G.P. Security Risks from Climate Change and Environmental Degradation: Implications for Sustainable Land Use Transformation in the Global South. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2023, 63, 101322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Vuurst, P.; Escobar, L.E. Climate Change and Infectious Disease: A Review of Evidence and Research Trends. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2023, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joakim, E.P.; Mortsch, L.; Oulahen, G. Using Vulnerability and Resilience Concepts to Advance Climate Change Adaptation. In Environmental Hazards and Resilience; Routledge: London, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-1-003-17143-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lanlan, J.; Sarker, M.N.I.; Ali, I.; Firdaus, R.B.R.; Hossin, M.A. Vulnerability and Resilience in the Context of Natural Hazards: A Critical Conceptual Analysis. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 19069–19092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echchakoui, S. Why and How to Merge Scopus and Web of Science during Bibliometric Analysis: The Case of Sales Force Literature from 1912 to 2019. J. Market. Anal. 2020, 8, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranckutė, R. Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The Titans of Bibliographic Information in Today’s Academic World. Publications 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soosaraei, M.; Khasseh, A.A.; Fakhar, M.; Hezarjaribi, H.Z. A Decade Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research on Leishmaniasis in Web of Science Database. Ann. Med. Surg. 2018, 26, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, K. A Comprehensive Review of Climatic Threats and Adaptation of Marine Biodiversity. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivertsen, G.; Rousseau, R.; Zhang, L. The Motivations for and Effects of Modified Fractional Counting. J. Informetr. 2025, 19, 101681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutz, R.; Daniel, H.-D. How to Consider Fractional Counting and Field Normalization in the Statistical Modeling of Bibliometric Data: A Multilevel Poisson Regression Approach. J. Informetr. 2019, 13, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaston, T.B.; Broome, R.A.; Cooper, N.; Duck, G.; Geromboux, C.; Guo, Y.; Ji, F.; Perkins-Kirkpatrick, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dissanayake, G.S.; et al. Mortality Burden of Heatwaves in Sydney, Australia Is Exacerbated by the Urban Heat Island and Climate Change: Can Tree Cover Help Mitigate the Health Impacts? Atmosphere 2022, 13, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Jian, L.; Xiao, J.; Jansz, J.; Yun, G.; Robertson, A. Joint Effect of Heatwaves and Air Quality on Emergency Department Attendances for Vulnerable Population in Perth, Western Australia, 2006 to 2015. Environ. Res. 2019, 174, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, J.A.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.; Holloway, T.; Foley, J.A. Impact of Regional Climate Change on Human Health. Nature 2005, 438, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins-Kirkpatrick, S.E.; Lewis, S.C. Increasing Trends in Regional Heatwaves. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lee, X.; Smith, R.B.; Oleson, K. Strong Contributions of Local Background Climate to Urban Heat Islands. Nature 2014, 511, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luber, G.; McGeehin, M. Climate Change and Extreme Heat Events. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2008, 35, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Patel, D.; Xiao, J.; Jansz, J.; Yun, G.; Lin, T.; Robertson, A. Can We Use a Machine Learning Approach to Predict the Impact of Heatwaves on Emergency Department Attendance? Environ. Res. Commun. 2023, 5, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.N.; Doan, V.Q.; Nguyen, V.T.; Khan, A.; Thai, P.K.; Cunrui, H.; Chu, C.; Schak, E.; Phung, D. Spatial Patterns of Health Vulnerability to Heatwaves in Vietnam. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trancoso, R.; Syktus, J.; Toombs, N.; Ahrens, D.; Wong, K.K.-H.; Pozza, R.D. Heatwaves Intensification in Australia: A Consistent Trajectory across Past, Present and Future. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, J.A.; Ibrahim, J.E. Minimising Harm to Older Victorians from Heatwaves: A Qualitative Study of the Role of Community-Based Health Profession and Carer Organisations. Australas. J. Ageing 2010, 29, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Bi, P.; Pisaniello, D.; Hansen, A. The Impact of Heatwaves on Workers׳ Health and Safety in Adelaide, South Australia. Environ. Res. 2014, 133, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.-O.; Wee, D. Influence of Personal Cooling at Local Body Parts on Workers’ Thermal Comfort Levels under Thermal Environments with Elevated Ambient Temperatures: A Model Study. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2023, 95, 103456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourt, D.P. Maximum Wet-Bulb Globe Temperature Mapping in Central–South Brazil: A Numerical Study. Meteorol. Appl. 2019, 26, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.M.; Schär, C. Consistent Geographical Patterns of Changes in High-Impact European Heatwaves. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Nitschke, M.; Weinstein, P.; Pisaniello, D.L.; Parton, K.A.; Bi, P. The Impact of Summer Temperatures and Heatwaves on Mortality and Morbidity in Perth, Australia 1994–2008. Environ. Int. 2012, 40, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, B.M.; Barnett, A.G.; Hansen, A.L.; Bi, P.; Nairn, J.; Rowett, S.; Nitschke, M.; Hanson-Easey, S.; Heyworth, J.S.; Sim, M.R.; et al. Characterising the Impact of Heatwaves on Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses in Three Australian Cities Using a Standard Heatwave Definition—Excess Heat Factor (EHF). J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Venugopal, K.; Nitschke, M.; Nairn, J.; Fawcett, R.; Beattie, C.; Wynwood, G.; Bi, P. Regional Morbidity and Mortality during Heatwaves in South Australia. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 1911–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, A.; Giles, L.C.; Zhang, Y.; Koehler, A.P.; Hiller, J.E.; Bi, P. Heatwaves Differentially Affect Risk of Salmonella Serotypes. J. Infect. 2016, 73, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.; Nitschke, M.; Wondmagegn, B.Y.; Tong, M.; Xiang, J.; Hansen, A.; Nairn, J.; Karnon, J.; Bi, P. Evaluating Cost Benefits from a Heat Health Warning System in Adelaide, South Australia. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2022, 46, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Yu, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Beggs, P.J.; Zhang, Y.; Boocock, J.; et al. Climate Change, Environmental Extremes, and Human Health in Australia: Challenges, Adaptation Strategies, and Policy Gaps. Lancet Reg. Health—West. Pac 2023, 40, 100936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovats, R.S.; Kristie, L.E. Heatwaves and Public Health in Europe. Eur. J. Public Health 2006, 16, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Kan, H.; Kovats, S. The Impact of the 2003 Heat Wave on Mortality in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2418–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Jin, H.; Ren, Y. Compound Daytime and Nighttime Heatwaves for Air and Surface Temperature Based on Relative and Absolute Threshold Dynamic Classified in Southwest China, 1980–2019. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, H.; Cheng, Y.; Bi, P.; Li, Y.; Yao, X. Heatwave and Urinary Hospital Admissions in China: Disease Burden and Associated Economic Loss, 2014 to 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapwata, T.; Gebreslasie, M.T.; Wright, C.Y. An Analysis of Past and Future Heatwaves Based on a Heat-Associated Mortality Threshold: Towards a Heat Health Warning System. Environ. Health 2022, 21, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapwata, T.; Abdelatif, N.; Scovronick, N.; Gebreslasie, M.T.; Acquaotta, F.; Wright, C.Y. Identifying Heat Thresholds for South Africa towards the Development of a Heat-Health Warning System. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2024, 68, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyuchi, A.E.; Vogel, C.; Wright, C.Y.; Erasmus, B. The Self-Reported Human Health Effects Associated with Heat Exposure in Agincourt Sub-District of South Africa. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2022, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Fu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, R.; Guan, X. Heat Waves Accelerate the Spread of Infectious Diseases. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becvarik, Z.A.; Smurthwaite, K.S.; Lal, A. The Effect of Temperature on the Distribution of Zoonotic Pathogens in Livestock and Wildlife Populations: A Systematic Review. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2023, 2023, 2714539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, A.J.; Bone, A.; Morbey, R.; Hughes, H.E.; Harcourt, S.; Smith, S.; Loveridge, P.; Green, H.K.; Pebody, R.; Andrews, N.; et al. Using Real-Time Syndromic Surveillance to Assess the Health Impact of the 2013 Heatwave in England. Environ. Res. 2014, 135, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Hu, W.; Tong, S. Heatwave and Health Events: A Systematic Evaluation of Different Temperature Indicators, Heatwave Intensities and Durations. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Crooks, J.L.; Black, D.; Hu, W.; Tong, S. Heatwave and Infants’ Hospital Admissions under Different Heatwave Definitions. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.A.; Reid, D.A.; Tobin, A.E. Heatwave Hyponatraemia: A Case Series at a Single Victorian Tertiary Centre during January 2014. Intern. Med. J. 2015, 45, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Wang, X.Y.; Barnett, A.G. Assessment of Heat-Related Health Impacts in Brisbane, Australia: Comparison of Different Heatwave Definitions. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Gu, K.; Bao, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; et al. Projections of Heatwave-Attributable Mortality under Climate Change and Future Population Scenarios in China. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2022, 28, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kinney, P.L.; Ma, W. Potential Impacts of Cool and Green Roofs on Temperature-Related Mortality in the Greater Boston Region. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 094042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-G.; Kim, K.R.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.-J.; Cho, C.-H.; Sheridan, S.C.; Kalkstein, L.S.; Kim, H.; Yi, S.-M. Effects of Heat Waves on Daily Excess Mortality in 14 Korean Cities during the Past 20 Years (1991–2010): An Application of the Spatial Synoptic Classification Approach. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almendra, R.; Loureiro, A.; Silva, G.; Vasconcelos, J.; Santana, P. Short-Term Impacts of Air Temperature on Hospitalizations for Mental Disorders in Lisbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noelke, C.; McGovern, M.; Corsi, D.J.; Jimenez, M.P.; Stern, A.; Wing, I.S.; Berkman, L. Increasing Ambient Temperature Reduces Emotional Well-Being. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W.; Zhang, X.; Pan, R.; Wei, Q.; Gao, J.; Xu, Z.; Duan, J.; Su, H. Quantifying the Impacts of Temperature Variability on Hospitalizations for Schizophrenia: A Time Series Analysis in Hefei, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Huang, S.; Shi, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, Z.; Wei, J.; Sun, H.; et al. Extreme Temperature Events, Fine Particulate Matter, and Myocardial Infarction Mortality. Circulation 2023, 148, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.; Martins, H.; Marta-Almeida, M.; Rocha, A.; Borrego, C. Urban Resilience to Future Urban Heat Waves Under a Climate Change Scenario: A Case Study for Porto Urban Area (Portugal); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 19, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Depietri, Y.; Renaud, F.G.; Kallis, G. Heat Waves and Floods in Urban Areas: A Policy-Oriented Review of Ecosystem Services; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7, pp. 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, K.; Khan, A.; Anand, P.; Sen, J. Understanding the Synergy between Heat Waves and the Built Environment: A Three-Decade Systematic Review Informing Policies for Mitigating Urban Heat Island in Cities. Sustain. Earth Rev. 2024, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.; Lauf, S.; Kleinschmit, B.; Endlicher, W. Heat Waves and Urban Heat Islands in Europe: A Review of Relevant Drivers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 569, pp. 527–539. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdanie, M.; Dramani, J.B.; Orehounig, K. Strengthening Energy System Resilience Planning under Uncertainty by Minimizing Regret. Renew. Sustain. Energy Transit. 2025, 6, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeighami, A.; Kern, J.; Yates, A.J.; Weber, P.; Bruno, A.A. U.S. West Coast Droughts and Heat Waves Exacerbate Pollution Inequality and Can Evade Emission Control Policies. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikó, E.; Donyina, G.A.; Baccouri, W.; Tóth, V.; Flórián, K.; Gyalai, I.M.; Yüksel, G.; Köteles, D.; Srivastava, V.; Wanjala, G. One Health Agriculture: Heat Stress Mitigation Dilemma in Agriculture. One Health 2025, 20, 100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Zhao, X.; Edmonds, J.; Waldhoff, S.; Patel, P.; O’Neill, B.; Tebaldi, C.; Wise, M. Omitting Labor Responses to Heat Stress Underestimates Future Climate Impact on Agriculture. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasi, C.; Marinaccio, A.; Gariazzo, C.; Taiano, L.; Bonafede, M.; Leva, A.; Morabito, M.; Michelozzi, P.; de’ Donato, F.K.; on behalf of the Worklimate Collaborative Group. Effects of Temperatures and Heatwaves on Occupational Injuries in the Agricultural Sector in Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V.; Latha, P.K.; Shanmugam, R.; Krishnamoorthy, M. SS67-03 What Is the Health Burden of Heat Stress Combined with the Workload in India’s Informal Agriculture Sectors? Occup. Med. 2024, 74, i142–i143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierardi, A.M.; Pavilonis, B. Heat Stress Risk among New York City Public School Kitchen Workers: A Quantitative Exposure Assessment. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2020, 17, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.G.; Shrestha, S.; Kinney, P.L.; Ross, Z.; Sheridan, S.C.; Pantea, C.I.; Hsu, W.H.; Muscatiello, N.; Hwang, S.A. Development of a Heat Vulnerability Index for New York State. Public Health 2018, 161, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, K.; Lane, K.; Walters, S.; Matte, T. Heat Illness and Deaths—New York City, 2000–2011. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 617–621. [Google Scholar]
- Casanueva, A.; Burgstall, A.; Kotlarski, S.; Messeri, A.; Morabito, M.; Flouris, A.D.; Nybo, L.; Spirig, C.; Schwierz, C. Overview of Existing Heat-Health Warning Systems in Europe. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weilnhammer, V.; Schmid, J.; Mittermeier, I.; Schreiber, F.; Jiang, L.; Pastuhovic, V.; Herr, C.; Heinze, S. Extreme Weather Events in Europe and Their Health Consequences—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 233, 113688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Spicer, T.; Jian, L.; Yun, G.Y.; Shao, C.; Nairn, J.; Fawcett, R.J.B.; Robertson, A.; Weeramanthri, T.S. Variation in Population Vulnerability to Heat Wave in Western Australia. Front. Public Health 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairn, J.; Ostendorf, B.; Bi, P. Performance of Excess Heat Factor Severity as a Global Heatwave Health Impact Index. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalabajan, D.; Mayne, R.; Bobson, B.; Qazzaz, H.; Ushie, H.; Ocharan, J.; Farr, J.; Romero, J.; Priego, K.; Gomez Correa, L.V.; et al. Towards a Just Energy Transition: Implications for Communities in Lower- and Middle-Income Countries; Oxfam: Oxford, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-1-78748-993-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ustun, A.; Cizreli, B. Yeni Bir Dönemin Eşiğinde Adil Dönüşüm Yaklaşımı. İDEALKENT 2022, 13, 1913–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dube, K.; Al Ali, H.; Khan, B.; Daneshkhah, A. Heatwaves and Public Health: A Bibliometric Exploration of Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation Strategies. Climate 2025, 13, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13120249
Dube K, Al Ali H, Khan B, Daneshkhah A. Heatwaves and Public Health: A Bibliometric Exploration of Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation Strategies. Climate. 2025; 13(12):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13120249
Chicago/Turabian StyleDube, Kaitano, Hannah Al Ali, Basit Khan, and Alireza Daneshkhah. 2025. "Heatwaves and Public Health: A Bibliometric Exploration of Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation Strategies" Climate 13, no. 12: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13120249
APA StyleDube, K., Al Ali, H., Khan, B., & Daneshkhah, A. (2025). Heatwaves and Public Health: A Bibliometric Exploration of Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation Strategies. Climate, 13(12), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13120249







