Temperature and Pressure Observations by Tommaso Temanza from 1751 to 1769 in Venice, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Observers, Instruments, Data, and Metadata
2.1. The Observers
2.2. The Instruments
2.2.1. The Barometer
2.2.2. The Amontons Thermometer
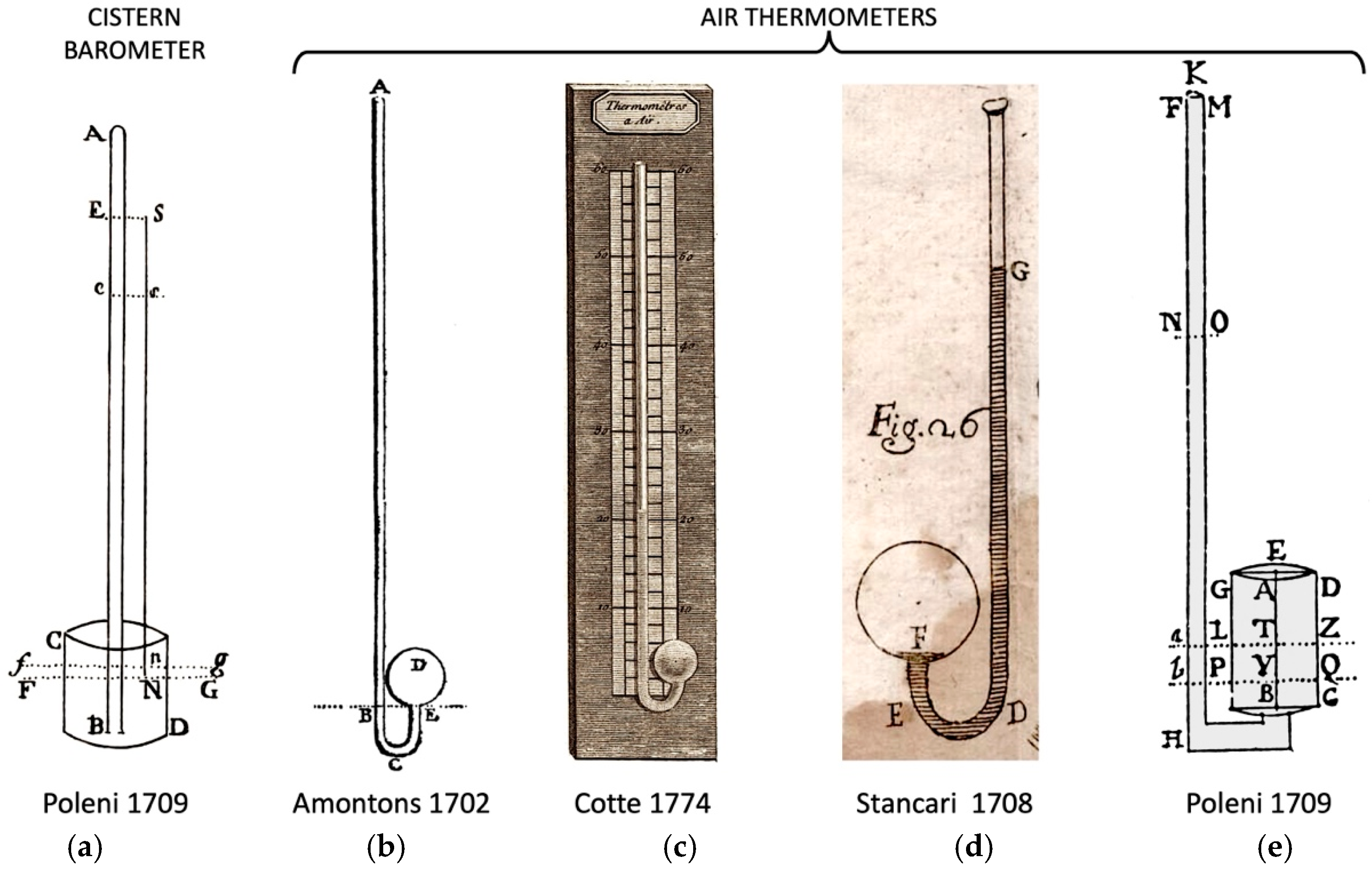
- Unknown scale.
- Missing the fixed calibration points (i.e., melting ice and boiling water).
- Undefined reference value X (the “Temperate”).
- Moisture entrapped in the air pocket.
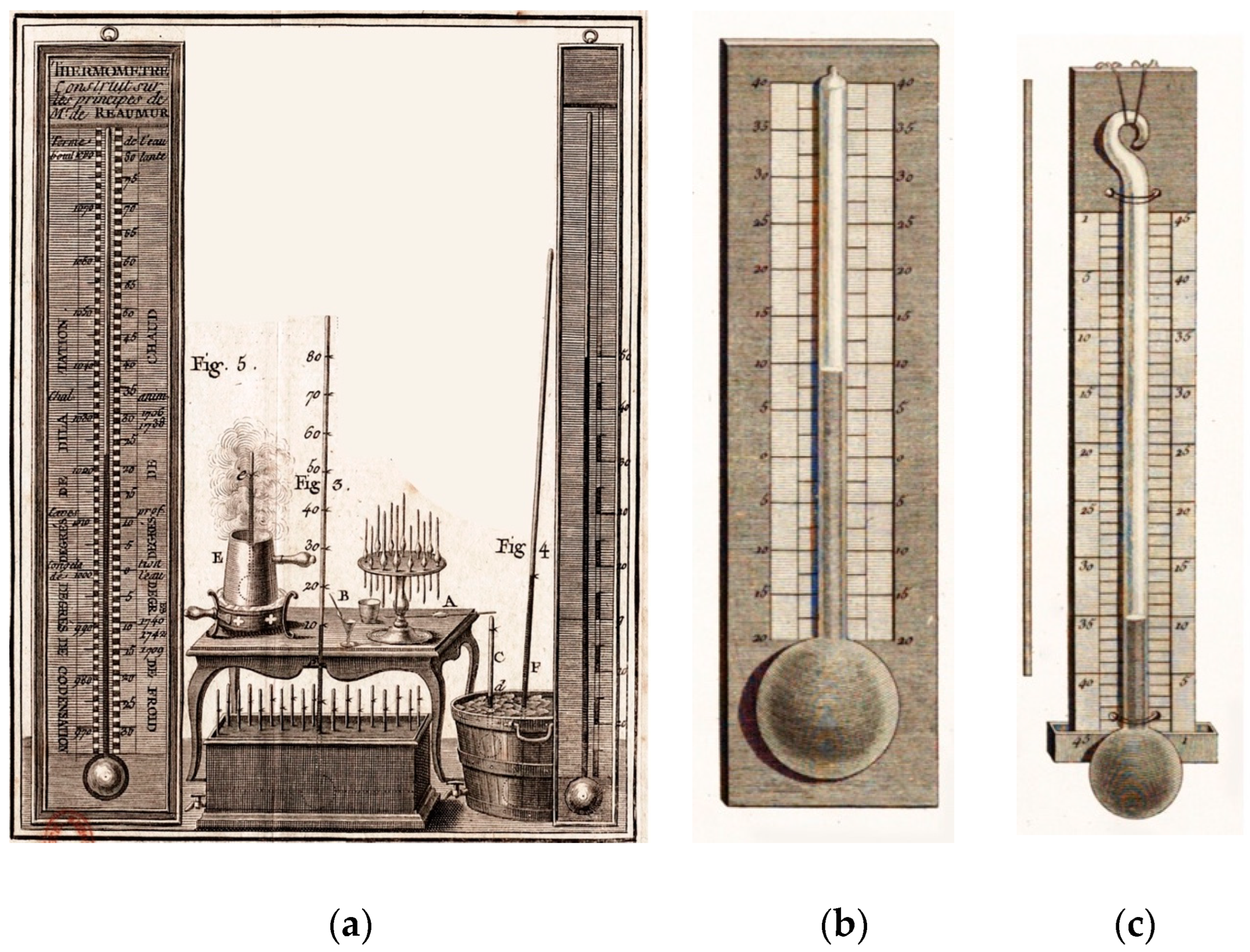
2.2.3. The Réaumur Thermometer
2.3. Handwritten Register and Metadata
2.4. Thermometer Exposure
2.5. Reading Time
2.6. The Series of Padua Used as a Reference
3. Data Recovery and Analysis: Methods and Discussions
3.1. Overview
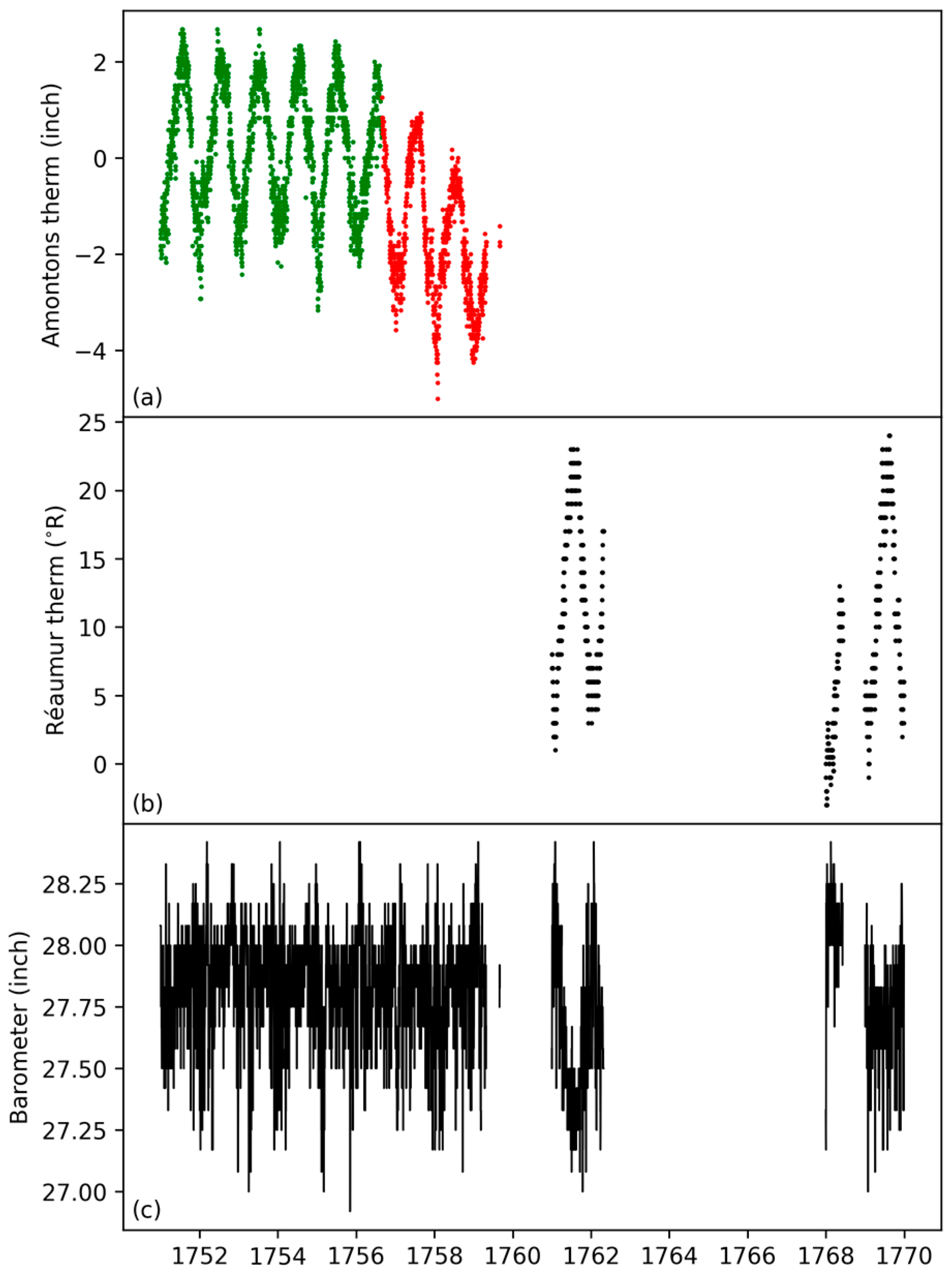
3.2. Temperature from the Amontons Thermometer
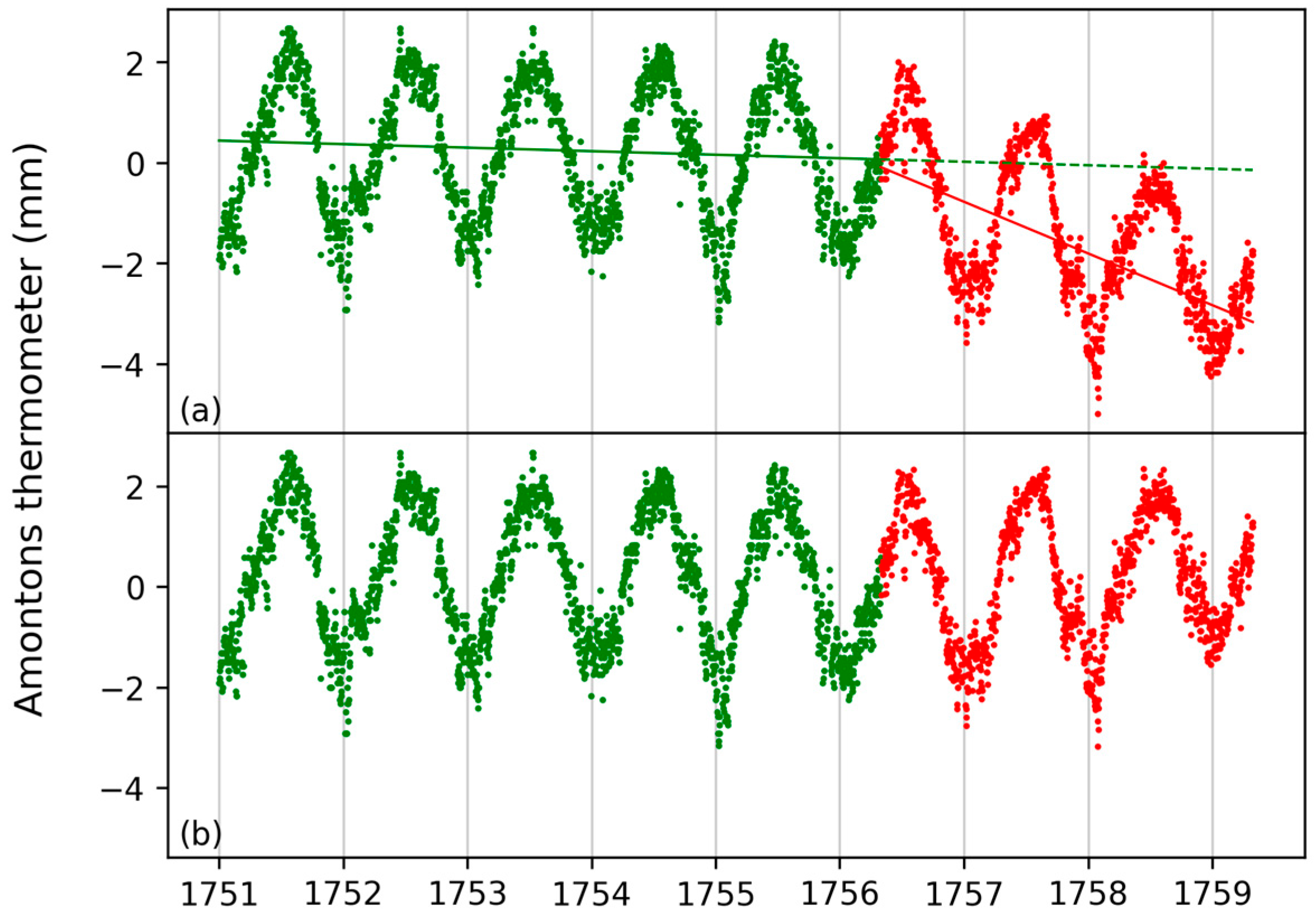
3.2.1. Reading the Scale of the Amontons Thermometer
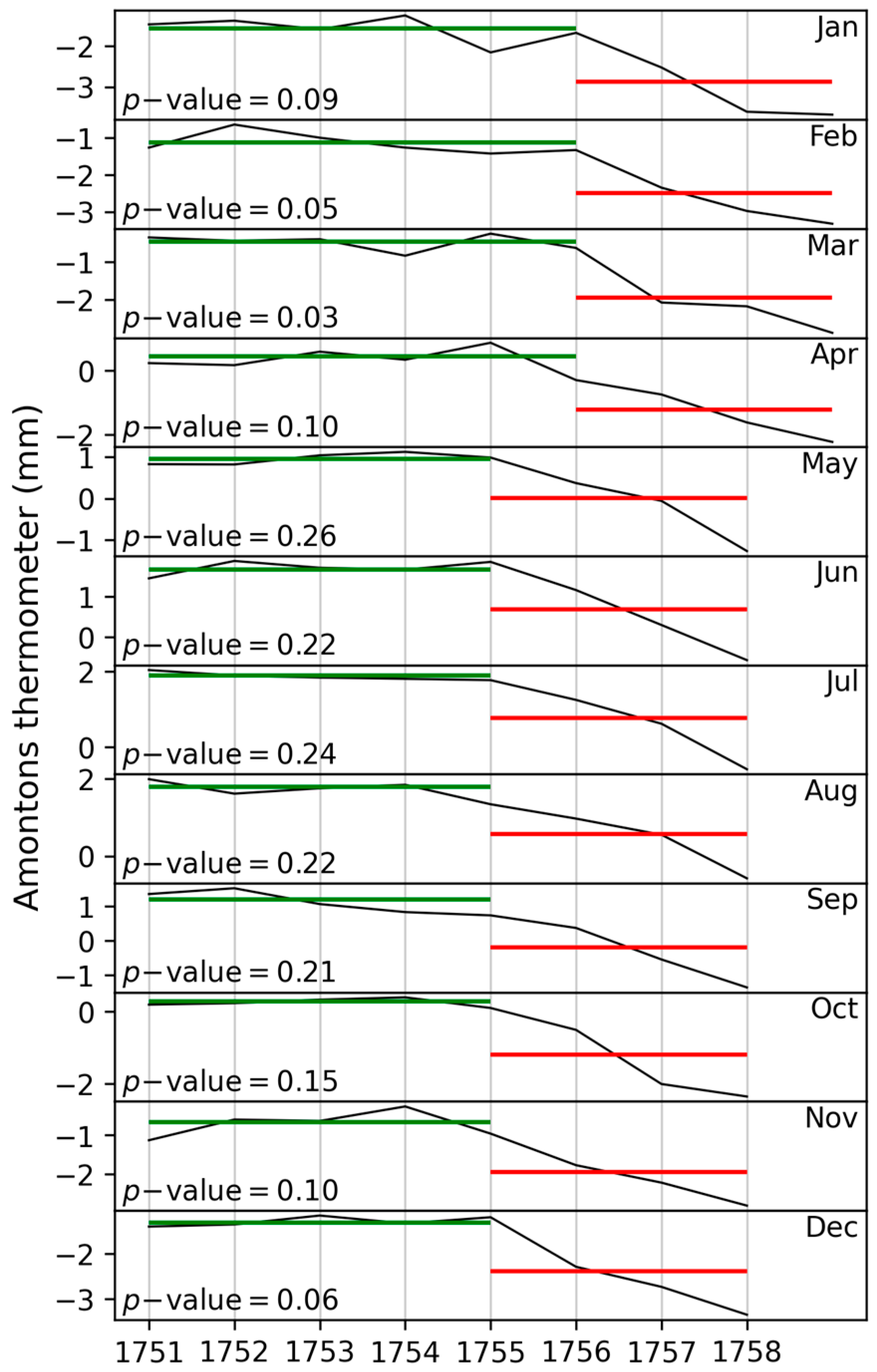
3.2.2. Correcting the Drift from 1756
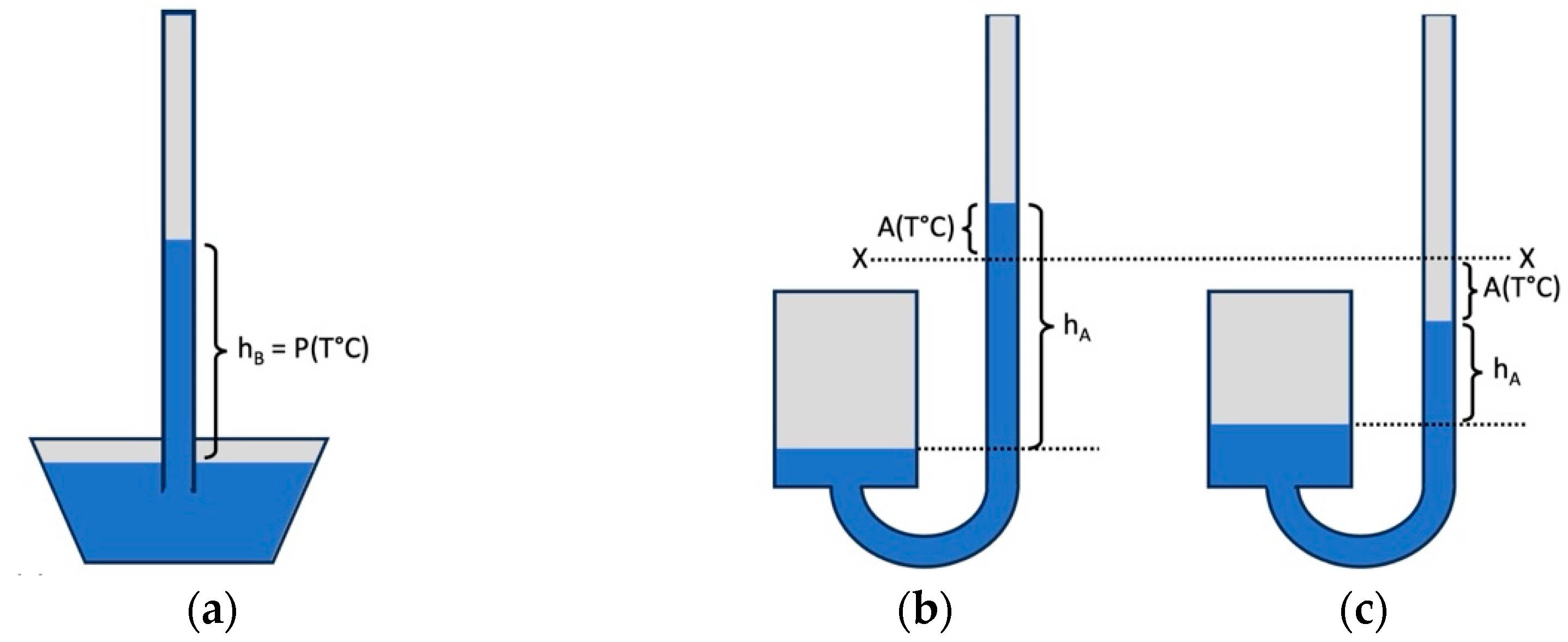
3.2.3. The Unknown Reference Named “Temperate”
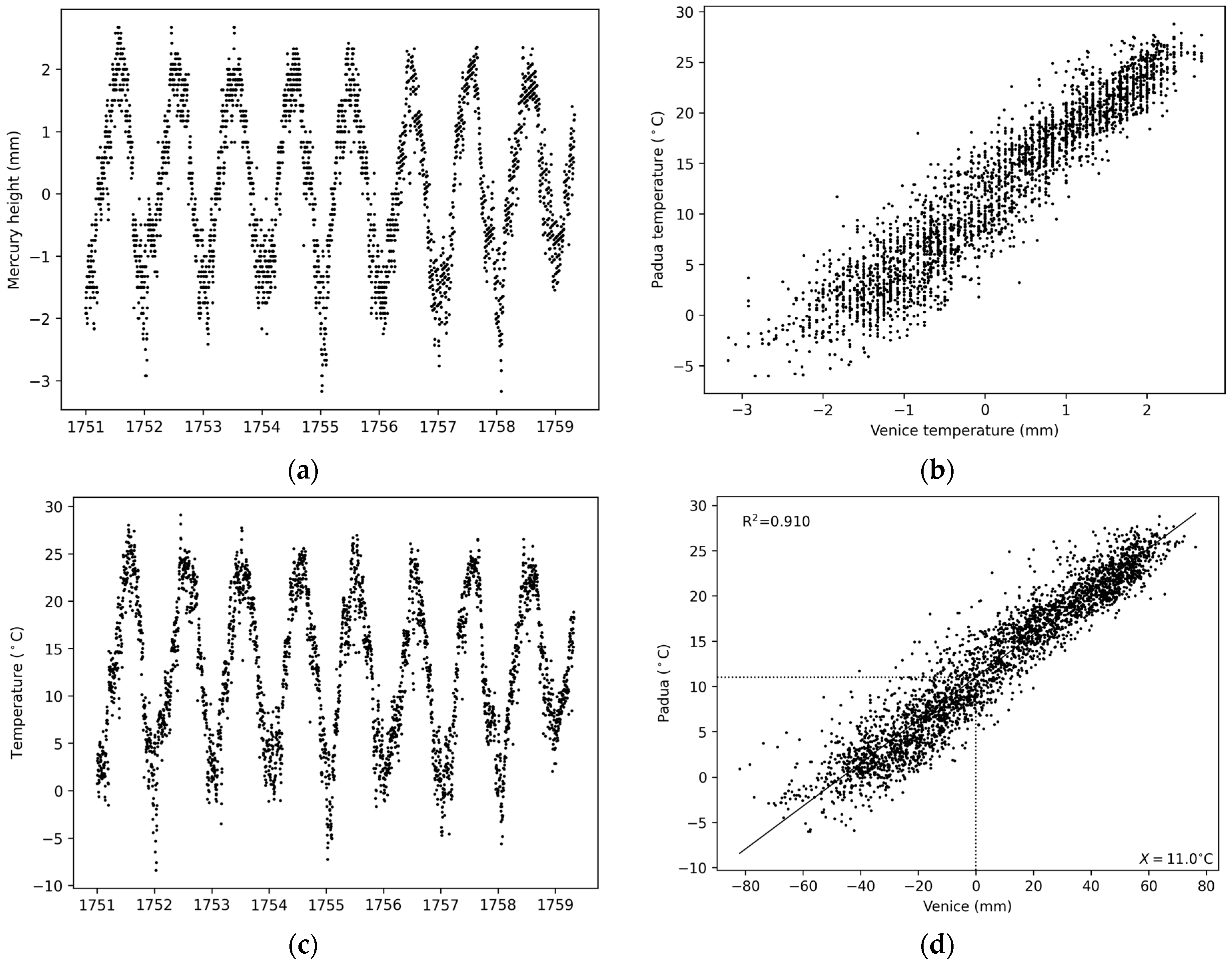
3.2.4. Amontons Scale Recognition and Readings Conversion
- Convert the temperature readings (TRs) from non-decimal inches to mm.
- Convert the contemporary atmospheric pressure measured by Poleni in Padua from hPa to Torr (i.e., mm Hg), multiplying it by 760/1013.25 mm Hg/hPa (Figure 8a,b). Note that for this purpose it is preferable to use Torr rather than hPa because the unit of pressure (mm Hg) coincides with the unit of length (mm) of the mercury columns (either in the thermometer or barometer), making calculations easier.
- Calculate the disturbing effect of pressure ∆P (mm Hg) = P (mm Hg) − 760 (mm Hg) that causes the shift ∆hA of the column of the Amontons thermometer.
- Correct the temperature reading TR (mm) for the effect of ∆P with the formula .
- Compare with the temperature of Padua measured by Poleni to find the transfer function that allows the conversion of the Amontons readings from inches to degrees Celsius (Figure 8c,d).
3.2.5. The Snowflake Test
3.2.6. The Moist Air Bias in the Amontons Thermometer
3.3. Temperature from the Réaumur Thermometer
3.4. Atmospheric Pressure
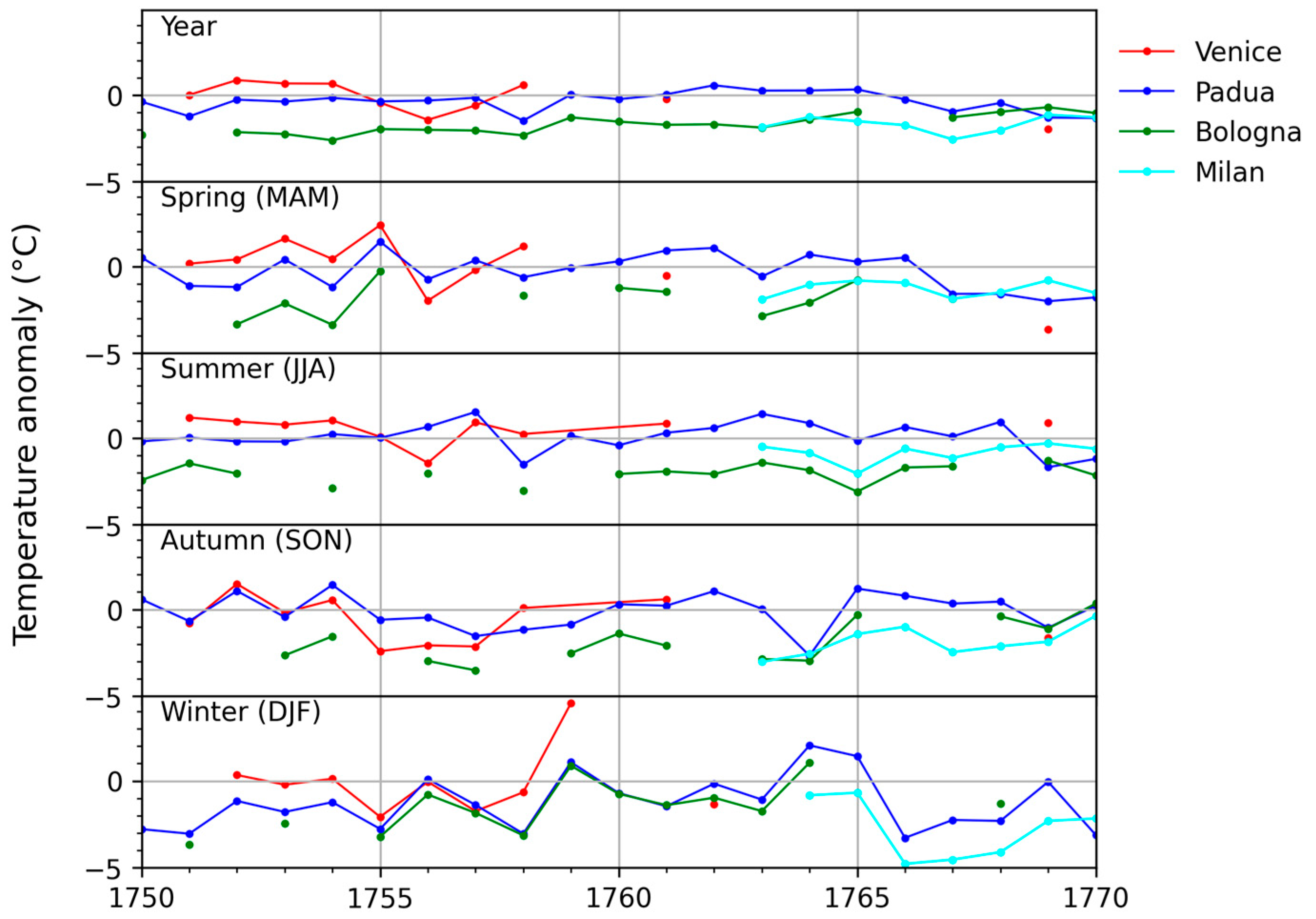
3.5. Temperature Anomaly
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BU Test | Buishand U Test |
| INAF-HA | Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica–Historical Archive (Padua) |
| MK | Mann–Kendall test |
| SNH Test | Standard Normal Homogeneity Test |
| TP | Turning Point |
| ZMPS | “Zero Mareografico Punta Salute”, i.e., the sea level reference of Venice |
Appendix A
References
- du Crest, J.B.M. Description de La Méthode d’un Thermomètre Universel; Valleyre: Paris, France, 1741. [Google Scholar]
- Talas, S. Thermometers in the Eighteenth Century: J.B. Micheli Du Crest’s Works and the Cooperation with G.F. Brander. Nuncius 2002, 17, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotte, L. Mémoires Sur La Météorologie Pour Servir de Suite et de Supplément Au Traité de Météorologie Publié En 1774; Imprimerie Royale: Paris, France, 1774. [Google Scholar]
- Martine, G. Chapter 3: Some Observations and Reflections Concerning the Construction and Graduation of Thermometer. In Essays Medical and Philosophical; Millar: London, UK, 1740. [Google Scholar]
- Martine, G. Chapter 4: The Comparison of Different Thermometers. In Essays Medical and Philosophical; Millar: London, UK, 1740. [Google Scholar]
- Camuffo, D. History of the Long Series of the Air Temperature in Padova. Clim. Change 2002, 53, 7–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; della Valle, A.; Becherini, F. Pressure and Temperature Observations in Venice by Bernardino Zendrini from 1738 to 1743. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toaldo, G. Della Vera Influenza Degli Astri, Delle Stagioni e Delle Mutazioni Di Tempo, Saggio Meteorologico, 1st ed.; Manfré: Padua, Italy, 1770. [Google Scholar]
- Temanza, T. Osservazioni del Sig. Tommaso Temanza—Tabelle manoscritte dal 1751 al 1755. 1751; Venice, Italy, 1755. manuscript.
- Orteschi, P. Costituzione Corrente Brevemente Considerata Dal Dott, Pietro Orteschi Medico e Filosofo Veneziano; Deregni: Venice, Italy, 1762. [Google Scholar]
- Schouw, J.F. Tableau Du Climat de La Végétation de l’Italie. Résultat de Deux Voyages En Ce Pays Dans Les Années 1817–1819 et 1829–1830. In Tableau de la Température et des Pluies de l’Italie; Luno: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1839; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cossali, P. Elogio Di Giovanni Poleni; Bettoni: Padua, Italy, 1813. [Google Scholar]
- Crestani, G. L’inizio Delle Osservazioni Meteorologiche a Padova. Il Contributo Di Giovanni Poleni Alla Meteorologia. In Memorie della R. Accademia di Scienze Lettere ed Arti; Rondi, G.B.: Padua, Italy, 1926; Volume 42, pp. 19–83. [Google Scholar]
- Poleni, G. Johannis Poleni Miscellanea Hoc Est: I Dissertatio de Barometris et Termometris; Aloysium Pavinum: Venice, Italy, 1709. [Google Scholar]
- Ongaro, G. Il Sodalizio Tra Giovanni Poleni e Giambattista Morgagni. In Giovanni Poleni Idraulico Matematico Architetto Filologo (1683–1761); Collana Accademica; Accademia Patavina di Scienze Lettere ed Arti: Padua, Italy, 1988; Volume 10, pp. 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zendrini, B. Leggi e Fenomeni, Regolazioni Ed Usi Delle Acque Correnti; Pasquali: Venice, Italy, 1741. [Google Scholar]
- Zendrini, B. Observationes Meteorologicae Venetiis Habitae Ann. MDCCXXXVIII. In Raccolta d’Opusculi Scientifici, e Filologici; Calogerà, A., Ed.; Occhi: Venice, Italy, 1741; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Zendrini, B. Fasciculus Observationum Astronomicarum & Meteorologicarum Ad Annum MDCCXXXVIII & MDCCXXXIX. In Raccolta d’Opusculi Scientifici, e Filologici; Calogerà, A., Ed.; Occhi: Venice, Italy, 1741; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Zendrini, B. Fasciculus I Observationum Astronomicarum & Meteorologicarum Annorum MDCCXL & MDCCXLI. In Raccolta d’Opusculi Scientifici, e Filologici; Calogerà, A., Ed.; Occhi: Venice, Italy, 1744; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zendrini, B. Fasciculus II Observationum Astronomicarum & Meteorologicarum Annorum MDCCXLII & MDCCXLIII. In Raccolta d’Opusculi Scientifici, e Filologici; Calogerà, A., Ed.; Occhi: Venice, Italy, 1744; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Raicich, F. Long-Term Variability of Storm Surge Frequency in the Venice Lagoon: An Update Thanks to 18th Century Sea Level Observations. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, F. Notizie Intorno Alla Persona e All’opere Di Tommaso Temanza; Fracasso: Venice, Italy, 1830. [Google Scholar]
- Corniani, G.B. I Secoli Della Letteratura Italiana Dopo Il Suo Risorgimento—Commentario; Unione Tipografico-Editrice: Turin, Italy, 1856; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Crestani, G. Le Osservazioni Meteorologiche—I Fenomeni Meteorologici. In La Laguna di Venezia; Magrini, G., Ed.; Ferrari: Venice, Italy, 1933; Volume 1, Part 2, Tomo 3; pp. 1–203. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organization. Technical Note No. 7: Reduction of Atmospheric Pressure; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1954; Volume WMO-No. 36. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organization. Technical Note No. 61: Note on the Standardization of Pressure Reduction in the International Network of Synoptic Stations; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1964; Volume WMO-No. 154. [Google Scholar]
- Venice Municipality. The Altimetry of the Historical Center: Percentage of Flooding; Venice Municipality: Venice, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Camuffo, D.; Bertolin, C.; Schenal, P. A Novel Proxy and the Sea Level Rise in Venice, Italy, from 1350 to 2014. Clim. Change 2017, 143, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D. A Discussion on Sea Level Rise, Rate Ad Acceleration. Venice as a Case Study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Guide to Instruments and Methods of Observation; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Volume WMO-No. 8, I. ISBN 978-92-63-10008-5. [Google Scholar]
- Berzelius, J.J. Trattato Di Chimica; Puzziello: Naples, Italy, 1845; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Belli, G. Corso Elementare Di Fisica Sperimentale; Società Tipografica de’ Classici Italiani: Milan, Italy, 1830. [Google Scholar]
- Amontons, G. Discours Sur Quelques Propriétés de l’Air & Le Moyen d’en Connaitre La Température Dans Tous Les Climats de La Terre. In Mémoires de Mathématique et de Physique; Coignard & Guerin: Paris, France, 1702; pp. 155–174. [Google Scholar]
- Zeno, A.; Zeno, P.C. Victorii Francisci Stancarii… Articolo VII. In Giornale de’ Letterati d’Italia; Giovanni Giacomo Hertz: Venice, Italy, 1714; Volume 17, pp. 170–202. [Google Scholar]
- Stancari, F. Vittorio De Thermometro Ab Amontonio Recens Inventis. Ex Epistula Ad Maraldum. In Printed Posthumous in: Schedae Mathematicae; Barbiroli Archigymnasium: Bologna, Italy, 1708; pp. 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Camuffo, D.; della Valle, A.; Bertolin, C.; Santorelli, E. The Stancari Air Thermometer and the 1715–1737 Record in Bologna, Italy. Clim. Change 2016, 139, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, G.B. Descrizione Delle Pitture, Sculture Ed Architetture Di Padova; Stamperia del Seminario: Padua, Italy, 1776. [Google Scholar]
- Brandolese, P. Pitture Sculture e Architetture Ed Altre Cose Notabili Di Padova Nuovamente Descritte; Self-Published: Padua, Italy, 1795. [Google Scholar]
- Moschini, G. Guida per La Città Di Padova All’amico Delle Belle Arti; Gamba: Venice, Italy, 1817. [Google Scholar]
- Giormani, V. L’insegnamento Della Chimica All’Università Di Padova Dal 1749 al 1808; Antenore: Padua, Italy, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Réaumur, R.A. Règles Pour Construire Des Thermomètres Dont Les Degrés Soient Comparables et Qui Donnent Des Idées d’un Chaud et d’un Froid Qui Puissent Être Rapportés à Des Mesures Connues. Mémoires De L’académie R. Des Sci. 1730, 10, 452–457. [Google Scholar]
- Réaumur, R.A. Second Mémoire Sur La Construction Des Thermomètres Dont Les Degrés Soient Compatibles. Mémoires De L’académie R. Des Sci. 1731, 4, 250–296. [Google Scholar]
- De Luc, J.A. Recherches Sur Les Modifications de l’atmosphère: Contenant l’histoire Critique Du Baromètre et Du Thermomètre; Self-Published: Geneva, Switzerland, 1772; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Réaumur, R.A. Observations Du Thermomètre Pendant l’année MDCCXXXIX Faites à Paris et En Différents Pays. Mémoires De L’académie R. Des Sci. 1740, 5, 447–468. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, W.E.K. A History of the Thermometer and Its Use in Meteorology; Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organization. International Meteorological Vocabulary; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992; Volume WMO No. 182. [Google Scholar]
- Camuffo, D. Key Problems in Early Wine-Spirit Thermometers and the “True Réaumur” Thermometer. Clim. Change 2020, 163, 1083–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D. Microclimate for Cultural Heritage, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 978-0-444-64106-9. [Google Scholar]
- Nollet, J.A. L’Art Des Experiences; Durand: Paris, France, 1770; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Jurin, J. Invitatio Ad Observationes Meteorologicas Communi Consilio Instituendas a Jacobo Jurin M. D. Soc. Reg Secr et Colleg Med Lond Socio. Philos. Trans. 1723, 379, 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmer, J.J. Descriptio Instrumentorum Meteorologicorum, Tam Eorum, Quam Societas Distribuit, Quam Quibus Praeter Haec Manheimii Utitur. In Ephem Soc Meteorol Palat; Ex Officina Novae Societatis Typographicae: Mannheim, Germany, 1783; Volume 1, pp. 57–90. [Google Scholar]
- Toaldo, G. Investigatio Caloris Plurimum Italiae Locorum. In Saggi Scientifici e Letterari dell’Accademia di Padova; Accademia di Scienze Lettere e Arti: Padua, Italy, 1788; Volume 3, Part 1; pp. 216–228. [Google Scholar]
- Camuffo, D.; della Valle, A.; Becherini, F. From Time Frames to Temperature Bias in Long Temperature Series. Clim. Change 2021, 165, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toaldo, G. Costituzione Meteorologica Del Cielo Di Venezia. In Completa Raccolta di Opuscoli, Osservazioni, e Notizie Diverse Contenute nei Giornali Astro-Meteorologici Dall’anno 1773 sino All’ anno 1798; Andreola: Venice, Italy, 1795; Volume 4, pp. 159–169. [Google Scholar]
- Cocheo, C.; Camuffo, D. Corrections of Systematic Errors and Data Homogenisation in the Padova Series (1725-Today). Clim. Change 2002, 53, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; della Valle, A.; Bertolin, C.; Santorelli, E. Temperature Observations in Bologna, Italy, from 1715 to 1815: A Comparison with Other Contemporary Series and an Overview of Three Centuries of Changing Climate. Clim. Change 2017, 142, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D. Calibration and Instrumental Errors in Early Measurements of Air Temperature. Clim. Change 2002, 53, 297–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D. Errors in Early Temperature Series Arising from Changes in Style of Measuring Time, Sampling Schedule and Number of Observations. Clim. Change 2002, 53, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; Bertolin, C. Recovery of the Early Period of Long Instrumental Time Series of Air Temperature in Padua, Italy (1716–2007). Phys. Chem. Earth 2012, 40–41, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; della Valle, A.; Becherini, F. Instrumental and Observational Problems of the Earliest Temperature Records in Italy: A Methodology for Data Recovery and Correction. Climate 2023, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, C.; Becherini, F.; della Valle, A.; Camuffo, D. Homogenization of the Long Instrumental Daily-Temperature Series in Padua, Italy (1725–2023). Climate 2024, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; Cocheo, C.; Sturaro, G. Corrections of Systematic Errors, Data Homogenisation and Climatic Analysis of the Padova Pressure Series (1725–1999). Clim. Change 2006, 79, 493–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; della Valle, A.; Becherini, F.; Zanini, V. Three Centuries of Daily Precipitation in Padua, Italy, 1713–2018: History, Relocations, Gaps, Homogeneity and Raw Data. Clim. Change 2020, 162, 923–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- della Valle, A.; Camuffo, D.; Becherini, F.; Zanini, V. Recovering, Correcting, and Reconstructing Precipitation Data Affected by Gaps and Irregular Readings: The Padua Series from 1812 to 1864. Clim. Change 2023, 176, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; Bertolin, C.; Bergonzini, A.; Amore, C.; Cocheo, C. Early Hygrometric Observations in Padua, Italy, from 1794 to 1826: The Chiminello Goose Quill Hygrometer versus the de Saussure Hair Hygrometer. Clim. Change 2014, 122, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandersson, H. A Homogeneity Test Applied to Precipitation Data. J. Climatol. 1986, 6, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buishand, T.A. Some Methods for Testing the Homogeneity of Rainfall Records. J. Hydrol. 1982, 58, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, A.N. A Non-Parametric Approach to the Change-Point Problem. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijngaard, J.B.; Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Können, G.P. Homogeneity of 20th Century European Daily Temperature and Precipitation Series. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 23, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, B. Henry Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.M.; Mahmud, I. pyMannKendall: A Python Package for Non Parametric Mann Kendall Family of Trend Tests. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toaldo, G. Della Vera Influenza Degli Astri, Delle Stagioni e Delle Mutazioni Di Tempo, Saggio Meteorologico, 2nd ed.; Stamperia del Seminario: Padua, Italy, 1781. [Google Scholar]
- Boggs, P.T.; Rogers, J.E. Orthogonal Distance Regression. In Proceedings of the Statistical Analysis of Measurement Error Models and Applications, Humboldt State University, Arcata, CA, USA, 10–16 June 1989; American Mathematical Society: Arcata, CA, USA, 1990; Volume 112, pp. 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Camuffo, D.; Bertolin, C.; Craievich, A.; Granziero, R.; Enzi, S. When the Lagoon Was Frozen over in Venice from A.D. 604 to 2012: Evidence from Written Documentary Sources, Visual Arts and Instrumental Readings. Méditerranée 2017, 129, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; Becherini, F.; della Valle, A. Temperature Observations in Florence, Italy, after the End of the Medici Network (1654–1670): The Grifoni Record (1751–1766). Clim. Change 2020, 162, 943–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Sasyo, Y. Non-Melting Phenomena of Snowflakes Observed in Subsaturated Air below Freezing Level. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1981, 59, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masih, I. Understanding Hydrological Variability for Improved Water Management in the Semiarid Karkheh Basin, Iran. Ph.D. Thesis, Leiden University, Leiden, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- O’Gorman, P.A. Contrasting Responses of Mean and Extreme Snowfall to Climate Change. Nature 2014, 512, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; Becherini, F.; della Valle, A. Daily Temperature Observations in Florence at the Mid-Eighteenth Century: The Martini Series (1756–1775). Clim. Change 2021, 164, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeazzi, D.M.G. De Thermometris Amontonianis Conficiendis. In Commentarii de Bononiensi Scientiarum et Artium Instituto atque Academia; Della Volpe: Bologna, Italy, 1746; Volume 2, Part 1; pp. 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Parkes, E.A. A Manual of Practical Hygiene Prepared Especially for Use in the Medical Service of the Army; John Churchill & Sons: London, UK, 1866. [Google Scholar]
- JCGM. International Vocabulary of Metrology. 3rd Edition, Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology, 3rd ed.; BIPM: Sèvres Cedex, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, A. The Diurnal Cycle from Observations and ERA5 in Surface Pressure, Temperature, Humidity, and Winds. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 61, 2965–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Climate Data Management System Specifications, 2nd ed.; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025; Volume WMO-No. 1131, ISBN 978-92-63-11131-9. [Google Scholar]
- Maugeri, M.; Buffoni, L.; Delmonte, B.; Fassina, A. Daily Milan Temperature and Pressure Series (1763–1998): Completing and Homogenising the Data. Clim. Change 2002, 53, 119–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Abridged Final Report of the Second Session. In Proceedings of the Commission for Weather, Climate, Water and Related Environmental Services and Applications, Geneva, Switzerland, 17–21 October 2022; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Volume WMO-No. 1307. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organization. Manual on the High-Quality Global Data Management Framework for Climate—Annex IX to the WMO Technical Regulations, 2nd ed.; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Volume WMO-No. 1238, ISBN 978-92-63-11238-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pohlert, T. Trend: The Non-Parametric Trend Tests and Change-Point Detection, version 1.1.6; R package; R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]

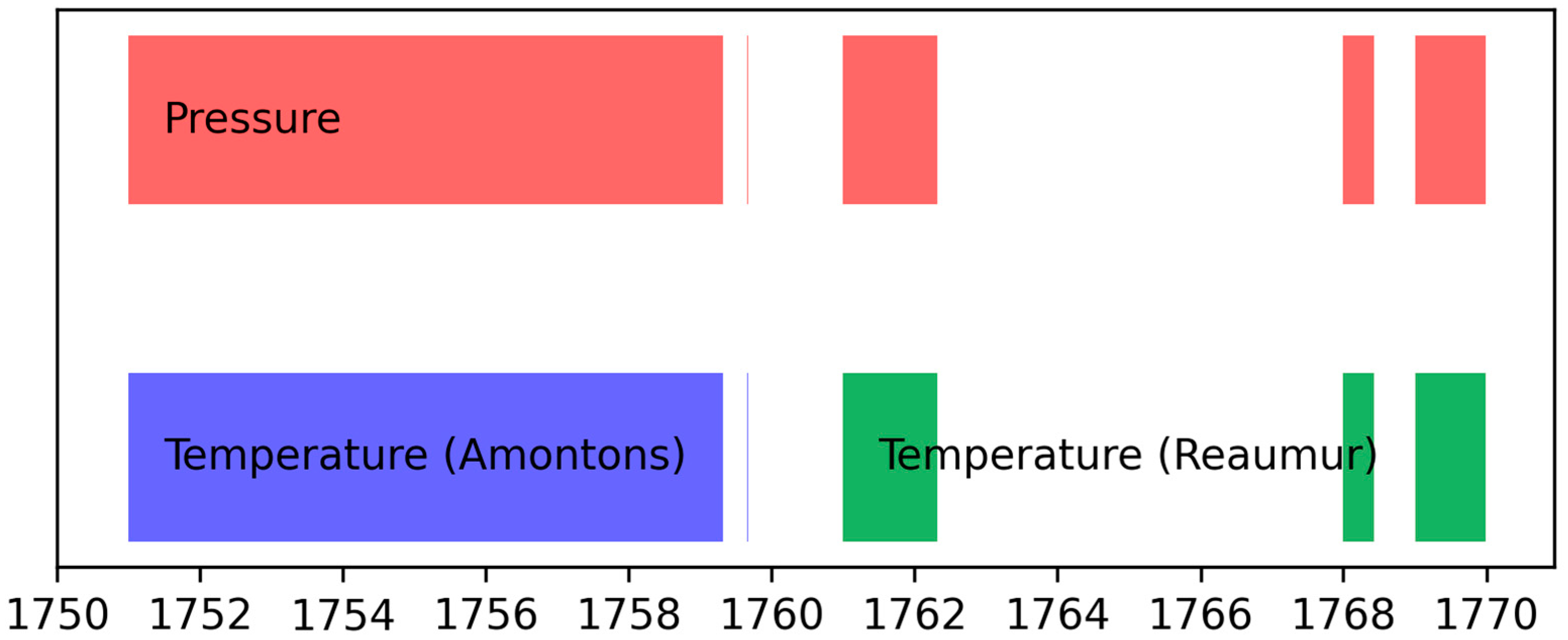

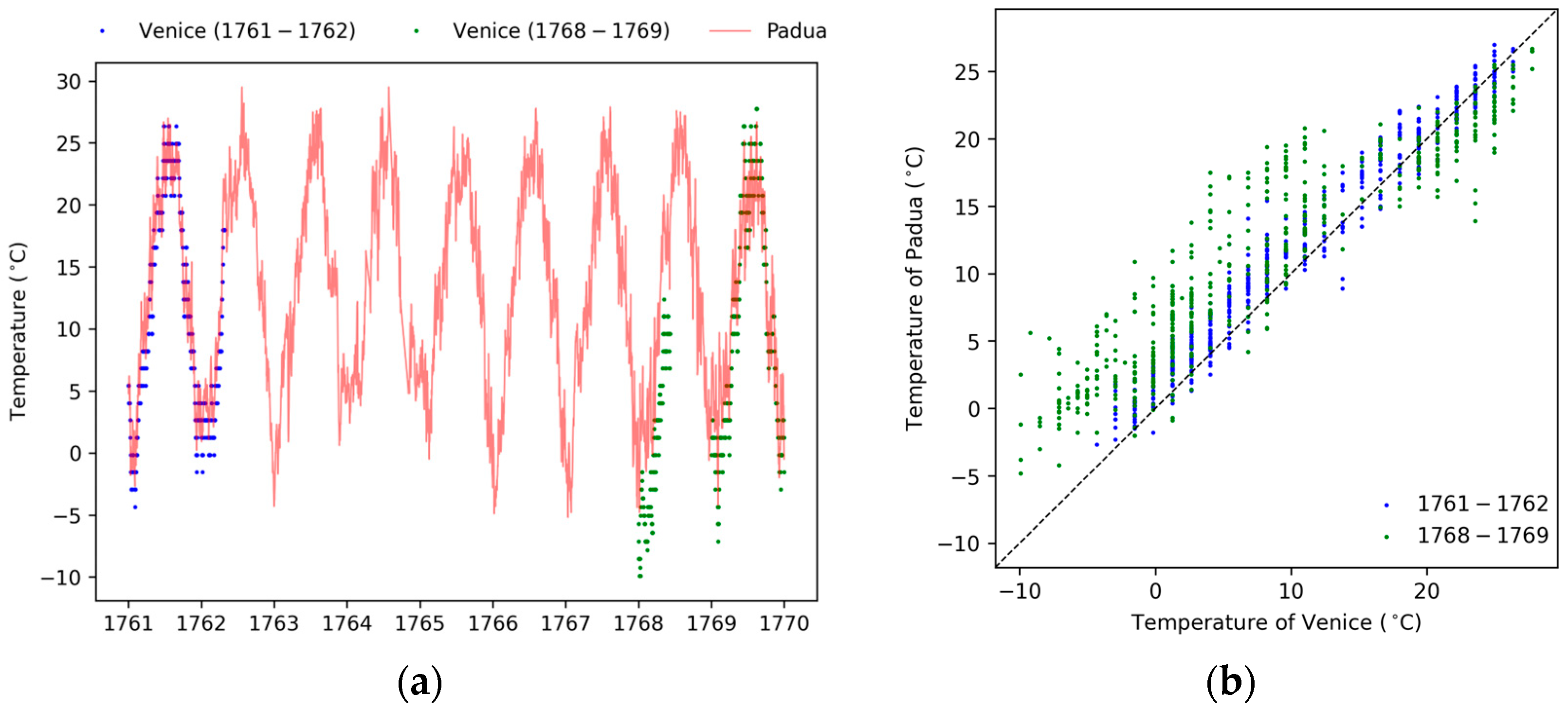
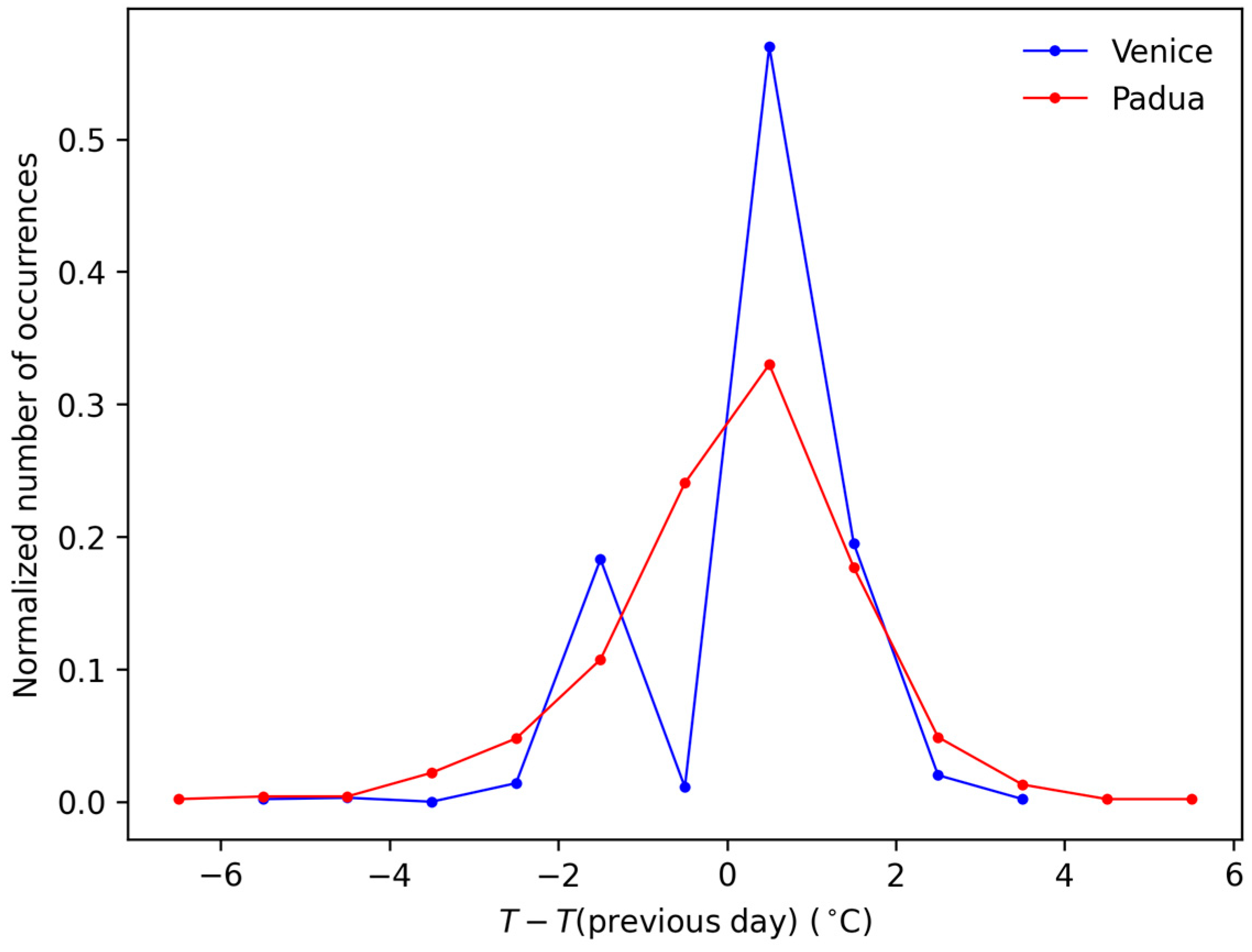

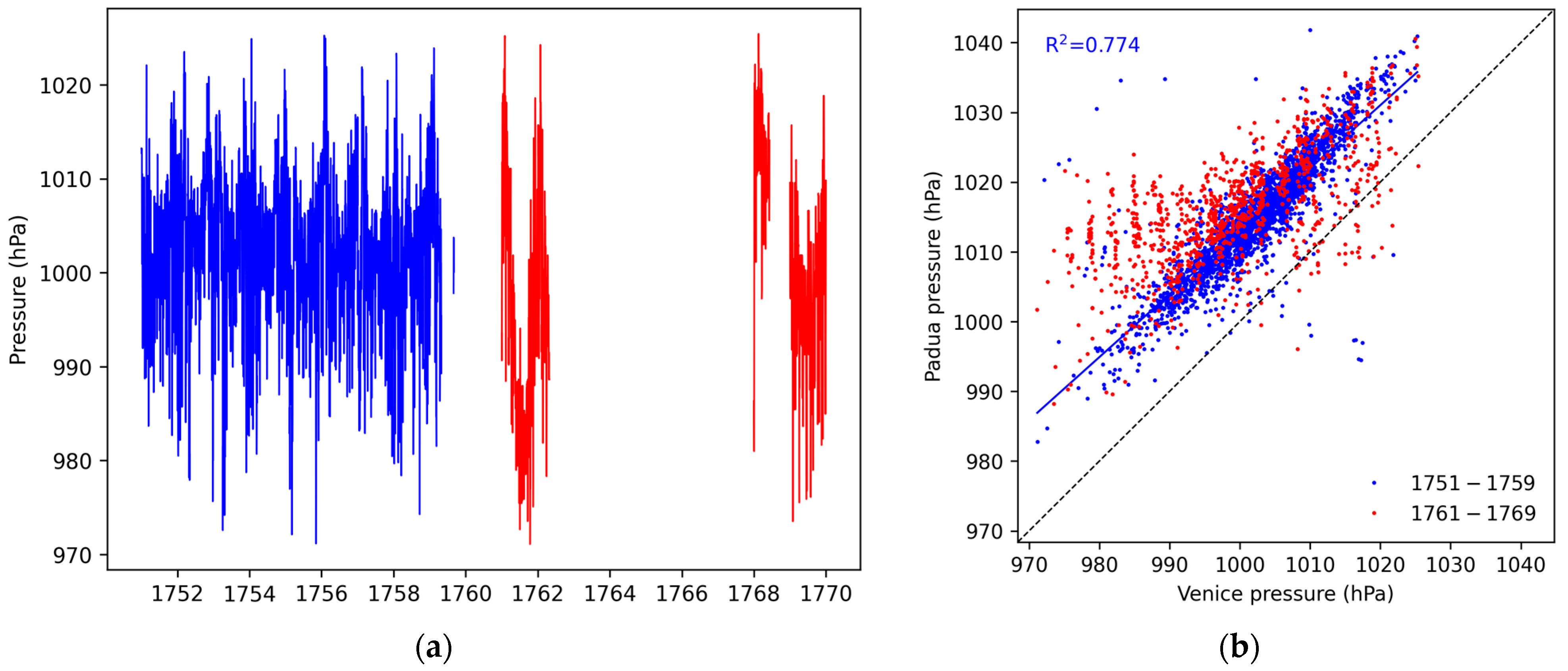
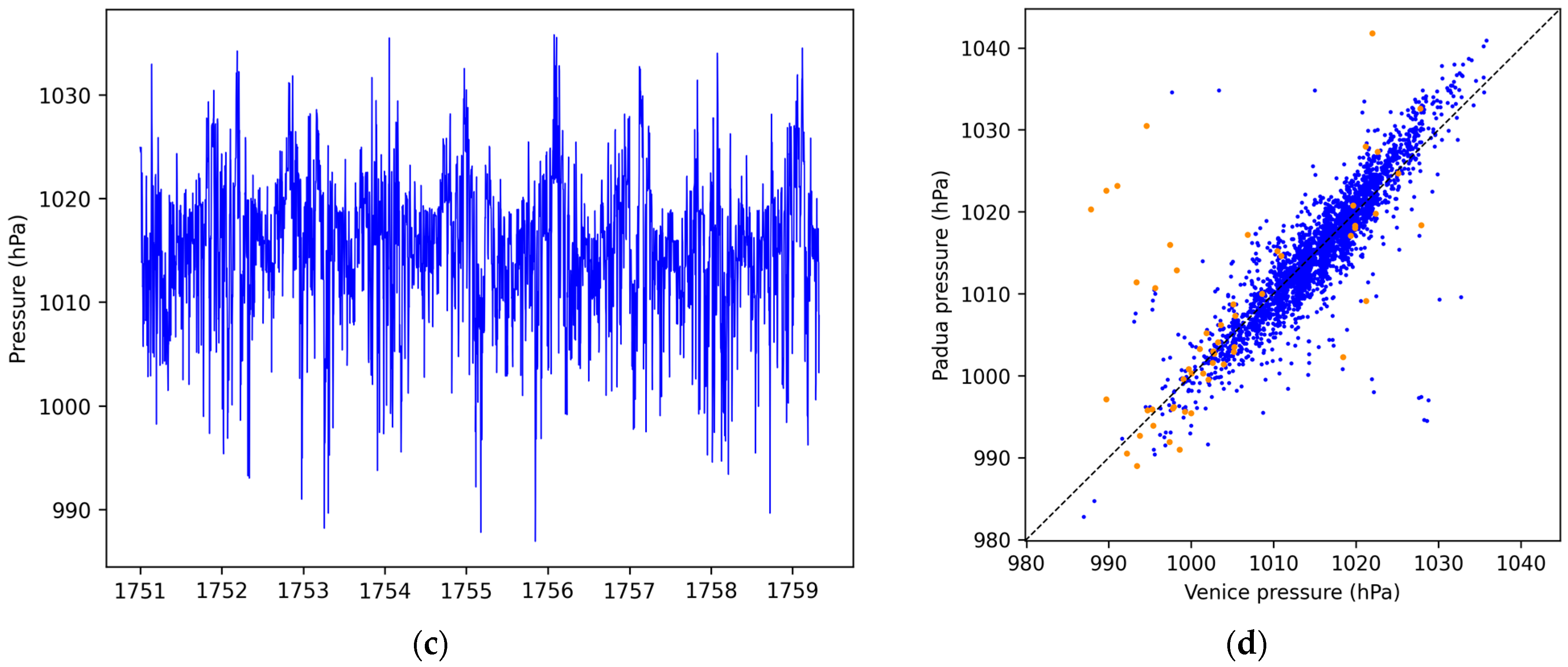
| Period | Reference | Observations |
|---|---|---|
| 1751–1755 | INAF HA | Pressure, temperature (Amontons), ebb and flow of the sea, weather note, wind, rain amount. |
| 1756–30 April 1759 | ||
| 1755 | Toaldo [8] | Pressure, temperature (Amontons), ebb and flow of the sea, weather notes, wind, rain amount. |
| 1755 | INAF HA—folii 21–25 | Description of the lagoon frozen out in 1755. |
| 1761–30 April 1762 | Orteschi [10] | Pressure, temperature (Réaumur), weather notes, wind and rain. |
| 1765–30 June 1766 | INAF HA | Ebb and flow of the sea. |
| 1 January–7 June 1768 | INAF HA | Pressure, temperature (Réaumur), weather note, wind and rain. |
| 1769 | INAF HA | Pressure, temperature (Réaumur), ebb and flow of the sea, weather notes, wind and rain. |
| Physical Variable | References |
|---|---|
| Temperature | [6,55,57,58,59,60,61] |
| Pressure | [62] |
| Precipitation | [60,63,64] |
| Humidity | [65] |
| Observing time | [53,57] |
| Error Type | Explanation | Largest Value |
|---|---|---|
| Purity of mercury | Crude mercury not purified, with inclusions of bismuth, tin, lead, iron, sulfur, calcium carbonate, and other impurities. It could be filtered from dust, rust, or other solid debris. | 5 mm |
| Glass composition and contaminants | Glass composition and impurities deposited on the tube. | 6 mm |
| Meniscus | Meniscus curvature, deformation and selected part (top, base) for reading. | 2 mm |
| Capillarity | Depression of the column for capillarity in narrow tubes. | 25 mm |
| Scale composition | Depending on the material of which the scale was made, it underwent different expansions. A wooden scale had shrinkage and swelling due to relative humidity. | 5 mm |
| Scale graduation | Irregularities from being made manually. | 1 mm |
| Fixed scale | A fixed scale had the 0 dipped into the mercury, and the dipped value had to be read (meniscus error) and subtracted. | 2 mm |
| Adjustable scale | The scale had to be adjusted manually, but the ivory point was invented by Fortin in 1805. | 2 mm |
| Imperfect vacuum | Some small bubbles of moist air or other contaminants were outgassed by mercury or introduced when the tube was filled. These depressed the mercury column. | 10–30 mm |
| Bulk instrumental errors | Any other error different from the above list. | 5 mm |
| Wind dynamic effect | Upwind overpressure or downwind low generated by strong winds interacting with the building. | 2 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camuffo, D.; della Valle, A.; Becherini, F. Temperature and Pressure Observations by Tommaso Temanza from 1751 to 1769 in Venice, Italy. Climate 2025, 13, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13100217
Camuffo D, della Valle A, Becherini F. Temperature and Pressure Observations by Tommaso Temanza from 1751 to 1769 in Venice, Italy. Climate. 2025; 13(10):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13100217
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamuffo, Dario, Antonio della Valle, and Francesca Becherini. 2025. "Temperature and Pressure Observations by Tommaso Temanza from 1751 to 1769 in Venice, Italy" Climate 13, no. 10: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13100217
APA StyleCamuffo, D., della Valle, A., & Becherini, F. (2025). Temperature and Pressure Observations by Tommaso Temanza from 1751 to 1769 in Venice, Italy. Climate, 13(10), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13100217








