Abstract
Climate change has been occurring due to global warming since the 1950s, causing impacts on natural and social systems, including health. This review article involves the One Health approach as a holistic approach that integrates environmental, human, and animal health, since there is a significant gap in knowledge about the impacts of climate change on health. The questions that guide this research are as follows: What is the state of the art in studies on climate change and One Health? What are the main topics addressed in studies on climate change and One Health at a global level? The main objective is to conduct a systematic review of studies on climate change and its relationship with One Health to assess the main topics studied, involving climate change and health at a global level, and identify the gaps and challenges of these studies. The review demonstrated the exponential growth of studies that relate climate change to One Health, especially in the last three decades, with more records of studies that address infectious diseases such as arboviruses. Furthermore, studies on climate and its impact on mental health were detected, causing depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), solastalgia, and eco-anxiety, especially in vulnerable populations such as indigenous communities, women, children, family farmers, and the elderly. The One Health approach was shown to be restricted to health-related issues. Thus, theoretical and experimental studies are still needed to assess the real impact of climate change on the various axes involving human health and its relationship with anthropogenic activities, environmental health, and animal health.
1. Introduction
Global warming has occurred since the 1950s, increasing atmospheric temperature and affecting systems such as the ocean. Likewise, it has been causing ice melt, rising sea levels, and extreme climate events such as heat waves, droughts, and storms due to increased greenhouse gases [1,2]. The impacts of climate change are direct and indirect [3], affecting the environment and human health [2]. Climate variations, such as increased precipitation and rising temperatures, alter natural patterns and cause more severe natural events, such as storms that increase the spread of viruses [4]. More vulnerable countries, mainly in tropical and subtropical regions, are more likely to suffer these impacts, increasing the mortality rate from extreme climate events [3].
It is a fact that climate effects are affecting the health of populations around the world [5], but to understand such impacts, it is necessary to differentiate three key concepts: EcoHealth, One Health, and Planetary Health [6]. EcoHealth is an older concept defined as the commitment to promoting the health of humans, animals, and ecosystems by conducting research that identifies their relationships, with a greater focus on biodiversity [7]. One Health is oriented towards biomedical issues with an emphasis on zoonoses and is defined as a holistic approach that integrates and recognizes animal, human, and environmental health [8]. Planetary Health is a more recent concept that incorporates equity into knowledge regarding health and is primarily focused on human health [7,9].
The report “The impacts of Climate Change on Human Health” defines areas of study of the relationship between climate change and health, such as (i) Foodborne Illness and Nutrition, (ii) Health Impacts of Air Quality, (iii) Health Impacts of Extreme Climate Events, (iv) Mental Health and Well-being, (v) People Who Are Vulnerable to Climate Change, (vi) Temperature-Related Death and Illness, (vii) Vector-borne Diseases, and (viii) Water-related Illnesses [10].
Thus, a holistic and multidisciplinary approach is necessary to address a complex issue such as climate change, mainly since One Health addresses issues of human health, environmental health, and animal health [11]. For example, diseases such as Zika infection, Ebola virus, Lassa fever, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), and Rift Valley Fever are related to human activities [11], as is mental health [6]. However, there is still a significant gap in knowledge about the relationship between climate change and arboviruses, vector-borne diseases, and zoonotic diseases [12] and mental health [6].
The added value of the One Health perspective is that it provides an integrative framework for analyzing these interconnected risks, allowing researchers and policymakers to move beyond siloed approaches. By explicitly linking human, animal, and environmental health, the One Health framework enables a better understanding of how climate drivers amplify existing vulnerabilities, facilitates the identification of early warning signals across sectors, and supports the design of more effective prevention and adaptation strategies [13,14]. Moreover, framing climate and health interactions through a One Health lens highlights equity concerns, since populations in close contact with animals or dependent on natural resources are often the most exposed to both environmental change and health threats [15]. In this way, One Health not only organizes the existing literature but also guides future research and public health action toward more systemic and resilient responses to climate change.
This systematic review was conducted based on two guiding questions: What is the state of the art in studies on climate change and One Health? What are the main topics addressed in studies on climate change and One Health at a global level? In addition, we present an assessment of the main issues studied, which involves reviewing climate change and its relationship with health worldwide, to identify the gaps and challenges in this subject.
2. Materials and Methods
The search and analysis of the selected material were prepared using the systematic review protocol (Supplementary Materials: Protocol and Tables S1–S6), which is based on the SODIP methodology [16]. The protocol includes inclusion and exclusion criteria, defining the search words, sections (title and keywords), and scope.
2.1. Data Collection
The keyword search was divided into four groups: (i) arboviruses, (ii) health system (disease notification, risk, emerging disease, One Health, etc.), (iii) Vector-Borne Disease, and (iv) Zoonotic Disease. These keywords were combined with “climate change”, “One health” and “health” to obtain more precise documents [17] in the title, keywords, and abstract section for greater search efficiency [18] in the Web of Science (WoS) database. The temporal range of the search is from 1991 to 2024, and the spatial scale is a global view. We limited the scope of our search to global and national scales to provide a broad and systematic overview of the literature; including subnational studies would have generated an unmanageable volume of articles and limited the feasibility of the analysis. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (Supplementary Materials see Figure S1) was used according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria.
2.2. Data Analysis
All studies were analyzed a priori through the word cloud by mining the author keywords section using Vosviewer [19]. According to PRISMA, the studies selected for full-text analysis were defined from the combination of words (Supplementary Materials see Table S1). The documents were grouped by countries and continents based on the spatial scale (global, transnational, and national) using the GeoExtract V1.2 tool [16]. These documents were analyzed quantitatively with XLStat and qualitatively with Voyant Tools [20] and Iramuteq v0.7 alpha 2 (Analyses Multidimensionelles de Textes et de Questionnaires) for data visualization and analysis [21]. The scatter map of studies addressing this research topic was created using QGIS v3.16 for spatial data visualization [22,23]. For the qualitative analysis, the title, author keyword, year, and abstract sections of each document were analyzed with similarity analysis [24], cluster analysis using the Reinert method with Descending Hierarchical Classification (DHC) to evaluate the segments of the evaluated full-text documents [21].
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Studies on Climate Change and Health
The total number of studies analyzed on climate change and health was 20,735, with 5956 documents found in all groups of words used in the search [25]. Of the total research on climate and health, 1% addresses the theme “one health”, and of the research related to climate change, less than 1% addresses the themes “epidemiological monitoring”, “data science”, and “disease notification”. Most studies were conducted globally (44%), mainly on the research group “health system”. Just over 1% of the research on climate and health addresses the theme “primary health care”, 2% on “health surveillance”, almost 3% on the themes “spillover” and “disease risk” related to health. The theme “mental health” makes up nearly 4% of the documents analyzed [25]. The group of words that presented the most studies related to climate change was “mental health” and “zoonotic diseases” (Supplementary Materials see Figure S2.2).
There has been an exponential growth in studies on health related to climate change over more than three decades (Figure 1). The first study relating climate change to dengue, cholera, malaria, and yellow fever was in 1991 [26,27]. The first study relating schistosomiasis to climate change was recorded in 1995 [28], in 2001 on leishmania [29], and in 2002 on Ebola and Chagas disease [30,31]. The first study on mental health was recorded in 2008 [32], addressing the Kyoto Protocol. In the same year, a study was conducted on rabies [33]. Diseases such as Chikungunya [34], Zika [35], Mayaro [36], and COVID-19 [37] addressed the climate issue in the years 2009, 2015, 2019, and 2020, respectively. In addition, the countries with the highest CO2 emissions have the largest population, and countries in the tropical region have more records of studies on arboviruses, health systems, vector-borne diseases, and zoonotic diseases (Figure 2).
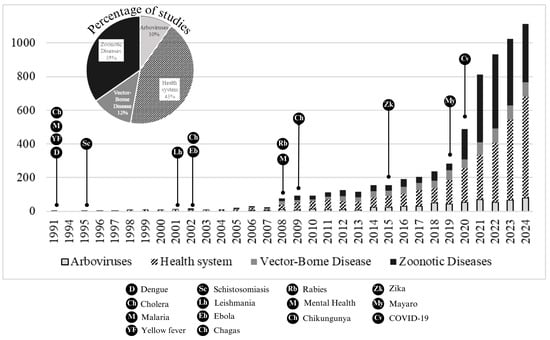
Figure 1.
Time scale of studies addressing climate change and human health.
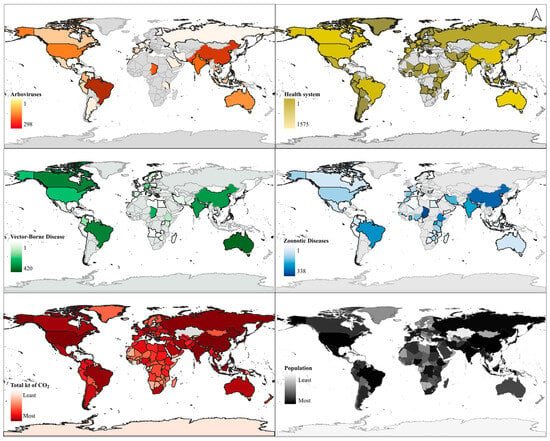
Figure 2.
Spatial scale of studies addressing the four groups.
Studies on arboviruses are in orange (298 studies), the health system is in yellow, vector-borne disease is in green, and zoonotic disease is in blue. The map was prepared based on the studies found and with climate and global population data from 2017 [8]. Information on CO2: Total greenhouse gas emissions (kt of CO2 equivalent) from 1970 to 2018 by country.
The word cloud of the authors’ keywords was created by including and excluding the terms “climate change” and “one health” to visualize better the main themes addressed in the selected studies (Figure 3 and Figure 4). In general, the studies address the themes of vulnerability, poverty, planetary health, air pollution, and antimicrobial resistance related to COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, and climate change. Themes on mental health related to public health, mental health, extreme climate events, natural disasters, and mental disorders were also recorded. On the other hand, themes on temperature were related to diseases such as malaria, vector-borne diseases, rainfall, schistosomiasis, dengue, Chikungunya, arbovirus, zika, leishmaniasis, among others. The highlighted themes were: “mental health”, “public health”, “global warming”, “epidemiology”, “dengue”, “malaria”, and “arbovirus” (Supplemental Materials: Figures S2.2 and S2.3).
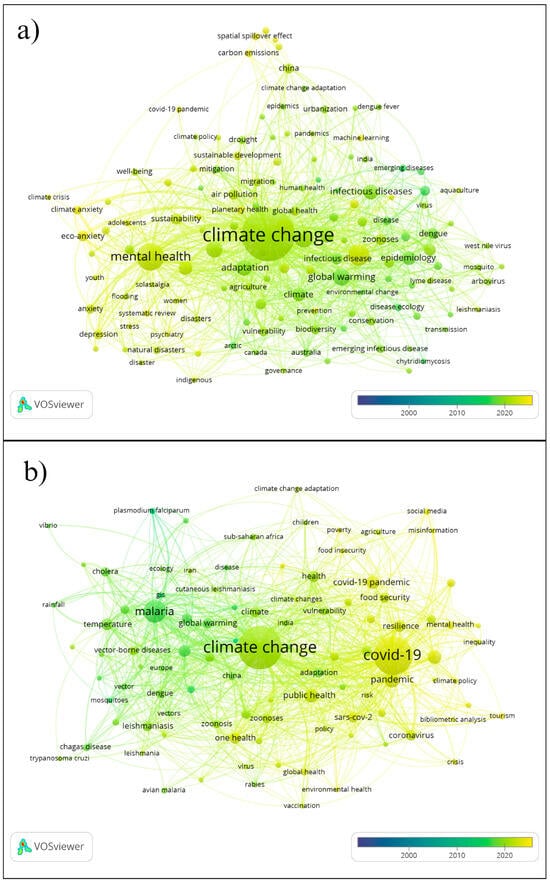
Figure 3.
Author keywords based on the searched word groups, excluding “climate change” and “one health”. (a) Health system, (b) Zoonotic diseases.
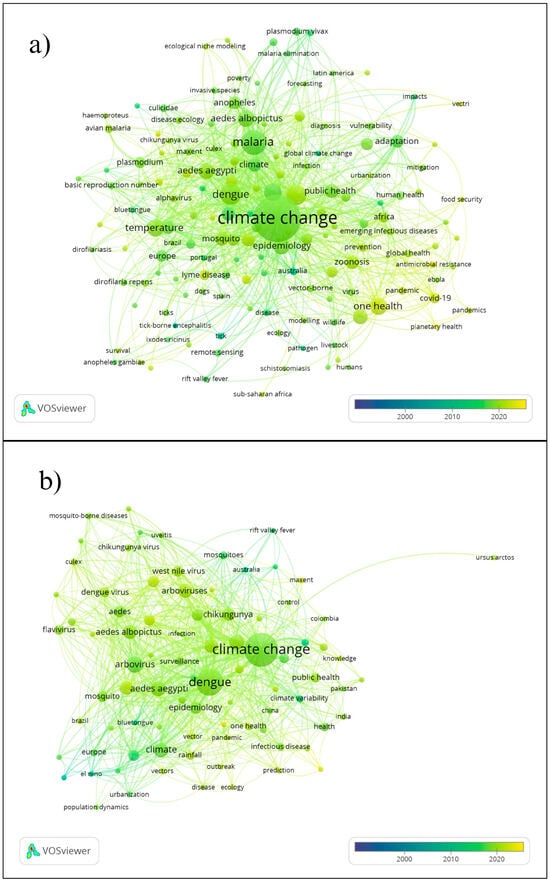
Figure 4.
Author keywords based on the searched word groups, excluding “climate change” and “one health”. (a) Vector-borne disease and (b) Arboviruses.
Studies on health and climate change addressed the following main themes: studies relating to biodiversity, zoonoses, wildlife, food security, planetary health, food safety, animal health, and sustainable development goals (SDGs). Studies addressing the theme of “educational curriculum” were found, with few studies relating the themes of “one health” and “climate change” to the area of education. Studies more directly related to climate change were global health, Lyme disease, parasites, zoonotic diseases, leishmania, antibiotic resistance, and aquaculture (Supplemental Materials see Figure S2.4). Studies on climate change and mental health addressed themes such as well-being, psychiatric issues, extreme climate, psychosocial, and resilience more frequently (Supplemental Materials see Figure S2.5). At the same time, topics related to climate change and health were about the issue of gender: “women”, mental disorders, “suicide”, depression, anxiety, distress, trauma, PTSD, stress, climate anxiety, eco-anxiety, solastalgia, extreme heat, heat waves, heat, mortality, air pollution, vulnerable populations, and migration.
Studies related to the “health system” group addressed topics such as biodiversity, infectious diseases, zoonoses, pathogens, urbanization, adaptation, inequality, climate anxiety, eco-anxiety, anxiety, and depression. Terms such as environmental justice, youth, activism, indigenous health, gender, and rural health were highlighted (Figure 3). In the zoonotic diseases group, countries such as Sub-Saharan, Iran, China, Spain, Uganda, India, and the continents of Europe and Africa are mentioned most frequently.
In the keyword group “Vector-borne disease” studies, themes such as temperature, rainfall, urbanization, seasonality, infection, and forecasting related to Chikungunya stand out. In contrast, the term ecological niche was associated with Zika and Chikungunya virus. The countries most mentioned in this group of words were Portugal, Australia, Iran, Brazil, China, Africa, Latin America, and Europe. Finally, in the group of Arboviruses, the themes dengue, malaria, cholera, Chikungunya, and Zika stand out. The theme temperature is related to precipitation, transmission, surveillance, climate variability, seasonality, rainfall, and vectorial capacity. Emerging diseases are related to urbanization, bluetongue, El Niño, and rift valley fever in countries such as Australia, Brazil, and Europe. Cholera is linked to outbreaks, vulnerability in Pakistan and India, in addition to the African continent.
Undoubtedly, climate events, whether through indirect or direct drivers, cause effects that are often irreversible to most of the human population (Figure 5, Table 1, and Supplementary Material see Table S1). This study found climate events such as heat waves, drought, flood-related outbreaks, thunderstorms, ocean acidification, changes in rainfall patterns, wildfires, permafrost thawing, sea-level rise, hurricanes, wildfires, and air pollution, among others, affect not only physical but also mental health.
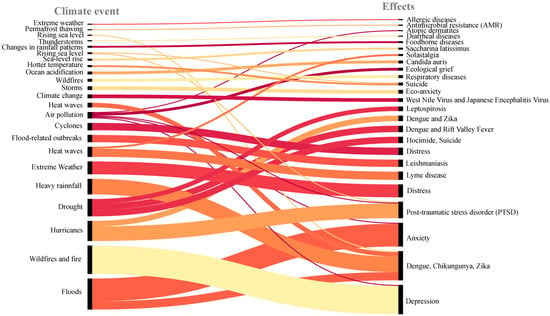
Figure 5.
Climate events and effects on climate change and health studies.

Table 1.
Climate events and their effects on health (see Supplementary Materials).
3.2. One Health and Climate Change
A total of 189 studies explored zoonoses, food security, biodiversity, and planetary health (Supplementary Materials see Figure S2.1). The first recorded study on one health and climate change addressed animal disease risk in Australia [38]. Some diseases are addressed in this topic, such as tick-borne Lyme disease in the USA and the Mediterranean region [39,40], Leishmania in Austria [41], coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 related to food security in China and Chad [42,43], dengue and climate prediction tools with machine learning under a global approach [44], West Nile virus in Singapore [45], and rabies in Uganda [46] and Brazil [47]. Some anthropogenic factors are associated with one health, such as aquaculture and the influence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the Mediterranean [48], and industrialization in agriculture [49]. The impacts on human health are via ozone depletion, which causes skin cancers, cataracts, and immunosuppression, and are direct and indirect due to climate change. Direct impacts can cause thermal stress, leading to cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. Indirect impacts can be attributed to (i) ecologically mediated impacts; (ii) vector-borne diseases that cause malaria, dengue, and schistosomiasis; (iii) marine-borne diseases that cause toxic algae and cholera; (iv) food productivity causing malnutrition; (v) air pollution that causes asthma and cardiorespiratory disorders; (vi) climate disasters; and (vii) sea-level rise that causes deaths, injuries, damage to health infrastructure, increases risk of infectious disease, and conflicts [12]. Each category has gaps in knowledge and uncertainties in the variable cause.
3.3. Vector-Borne Disease, Arboviruses, and Climate Change
There were 420 studies that relate climate change to vector-borne disease, with words that include zoonoses, mosquito-borne disease, alphavirus, Aedes, and plasmodium. Many vector-borne diseases have zoonotic origins [50]. The first record of vector-borne disease related to climate change was in the 1990s, which mentions the report entitled “The Impacts of Climate Change on Human Health: A Scientific Assessment, the Interagency Working Group on Climate Change and Health” [10]. Vector-borne disease, for example, can be influenced by the effects of socioeconomic development [12], especially when it comes to emerging vector-borne diseases [51]. Countries with larger vulnerable populations are more likely to suffer more cases of vector-borne disease; these countries are the ones that suffer most from temperature changes, as in the case of plasmodium parasites [28].
Of the 298 documents that address arboviruses, 45 mention climate change, and only 3 address climate change and health. There are 15 studies on Chikungunya, 190 on dengue, and 45 on Zika (see dataset). The first documented article on arboviruses related to climate change and health was conducted in 1998 in Australia on mosquito-borne arboviruses [52]. Most studies on Zika were conducted in Latin American countries such as Brazil [53], Colombia [54], and Ecuador [55]. Few studies related the Chikungunya virus to climate change; most of these records mentioned the word “climate change” in the abstract, theoretical framework, or conclusion, but it was not a topic directly addressed. In the records, more studies on dengue and its relationship with climate change were found in the last two decades, focusing on climate predictions [56,57], the relationship with El Niño-type phenomena [58], and migration [59], on all continents, with no record being found on the Mucambo virus related to climate change.
In recent decades, other arboviruses associated with climate change have been mentioned, such as West Nile virus [60], Powassan virus [61], and Culex virus [62], which respond to temperature changes [63], in addition to the potential risk of zoonotic spillover from rice crops, an activity dependent on climate change [64]. Emerging arboviruses, such as Mayaro and Oropouche, have been recorded in dry and wet forest areas in Brazil [4,65]. It is important to emphasize that not only does temperature change cause adverse effects in neotropical regions, but also in “cold” regions, as happened in Canada, where there was an increase in virus transmission to polar bears due to seasonal changes [66]. Ecoclimatic differences can influence the diversity of viruses associated with invertebrates, as was recorded in a study on virome in ticks in China [67]. For example, an experimental study concluded that temperature induces transmission profiles and modifies the functioning of arboviruses [68].
3.4. Mental Health and Climate Change
The studies found on mental health related to climate change address environmental issues and how they have affected mental health (Supplemental Materials see Figure S2.5), such as, for example, the case of Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) [69] caused by wildfires. Likewise, extreme events [70,71] that caused sleep disorders, and anxiety caused by air pollution [72]. Or even, extreme climate influencing eco-anxiety, even causing eating disorders [73], as in the case of flooding [74] related to migration [75] and eco-anxiety [76]. Including cases of extreme heat that have caused an increase in suicide [77] and heat waves that have led people to depression [78]. In addition, the migration of vulnerable populations, such as women [79], indigenous people, young people, farmers, and children, has also been recorded due to the level of concern that these groups have about the effects of the climate [80].
4. Discussion
Research on the concept of One Health is growing with a holistic approach [11], and this has been evident in the results of this systematic review research, as it fills gaps in information through the systematisation of terms related to this topic. Climate change affects human, animal, and environmental health [2,81,82]. Heat stress, floods, extreme climate events, and an increase in climate-related infectious diseases, among other events caused by climate change, are potential risks to human health [83]. The inclusion of the One Health approach can help discover new results regarding mental health [6], zoonoses, and the relationship between humans and non-humans with vulnerable populations such as indigenous communities [84]. The impact of climate change varies according to the context. In neotropical regions, for example, there is potential for the expansion of viruses such as Culex (Melanoconion) and its associated arboviruses [62]. In other regions, climate variations will have different impacts, such as in Canada, where a study concluded that people living in coastal areas of the Arctic have a higher risk of exposure to arboviruses because of their proximity to polar bears, which prefer coastal regions [66].
Arboviruses are infections that are transmitted to humans and other animals through the bite of arthropods (Arthropod-borne viruses) that threaten public health, especially in tropical and subtropical countries, which are more likely to transmit viruses such as Chikungunya, Dengue, Yellow Fever, and Zika [85], as they are regions with greater socioeconomic vulnerability [86,87]. These diseases are related to environmental, human, and animal factors, such as, basic sanitation and housing conditions [11]. Brazil, China, Australia, and Canada are the countries that presented the most records of studies involving climate change related to arboviruses, vector-borne diseases, and zoonotic diseases.
A review study on climate change and arboviruses reported a strong association between global warming and the risk of new arbovirus outbreaks in endemic and non-endemic areas in countries such as Brazil, China, Australia, and the USA, which are the countries with the highest number of studies on this topic [88]. Considering that there are many vectors with the potential to expand transmission and cause future epidemics, there are still few experimental studies on the real impact of temperature changes on the biological cycle of arboviruses [89]. Furthermore, our review found few studies that relate changes in land use to zoonotic diseases, such as aquaculture, rice cultivation, and industrialization in agriculture. Our results indicate that factors such as aquaculture and industrialization of agriculture influence antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This can affect the pathogen’s prevalence, genetic transfer, and water quality distribution [90].
Diseases transmitted by vectors such as lice, insects, parasites, fleas, ticks, and mosquitoes are major public health problems [91,92]. Although there is little reliable data on zoonotic diseases and their relationship with climate change [93,94], the cycles of zoonotic diseases grouped into bacterial zoonosis, viral zoonosis, parasitic zoonoses, mycotic zoonoses, rickettsial zoonoses, protozoal zoonoses, and chlamydial zoonoses may be influenced by the global climate crisis, especially concerning temperature and precipitation [93].
There is a significant gap in knowledge about mental health and its relationship with climate change, mainly due to the challenges associated with measuring impacts [6]. We systematized publications that link climate events such as wildfires, extreme weather, and catastrophic events to mental health effects such as PTSD. More vulnerable groups are the most affected [95,96]. These groups include children, rural communities, indigenous communities, coastal communities, women, pregnant women, climate migrants, elderly populations, etc. [79,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104]. For example, countries in northern latitudes where indigenous communities are located have suffered impacts on environmental health and caused changes in daily life, affecting hunting and, consequently, the diet of these populations [84]. Similarly, smallholder farmers in countries in tropical and subtropical regions need to maintain their means of food through family farming. Still, the impacts of climate change have increased and changed their daily lives [105].
It is essential to invest in research focused on One Health to strengthen the health system [88,106] to implement surveillance systems, based on citizen science and other innovative approaches. This can be directed to prevent potential outbreaks of arboviruses, zoonotic diseases, or even effects on mental health. These actions are valuable and relevant tools to promote climate adaptation [107].
Diseases such as Zika, Ebola virus, Lassa fever, Middle East respiratory syndrome, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Nipah virus, and Rift Valley fever should be researched from the One Health approach because they have a high risk of outbreak [11]. Therefore, six global pillars have been proposed to combat arboviruses: (1) monitoring risks and anticipating them, (2) reducing local risks, (3) strengthening vector control, (4) preventing and preparing for pandemics, (5) innovating new approaches, and (6) working in partnerships [85]. Furthermore, adequate training of health personnel is a key issue in terms of the impact of climate change on human health [108].
Implementing climate and environmental change monitoring systems can help prevent the increase in vector-borne diseases, in addition to surveillance systems and the development of vaccines and diagnostic tests [91,92]. Furthermore, implementing participatory monitoring measures such as sentinel projects for surveillance [109], understanding attitudes and knowledge about diseases related to climate change [54]. An illustrative example is the recognition of the interconnection that populations (human health) have with biodiversity (animal health), as is the case with indigenous populations [110]. Knowing the cultural relationship of these communities and other traditional groups can help plan climate adaptation actions [66]. Terms such as “ecological grief” and “solastalgia” (also known as ecolalgia) refer to topics that are still little studied, but are related to the immeasurable losses caused by climate change [99,111]. Therefore, it is still imperative to implement adaptation measures so that vulnerable populations can continue their activities in an increasingly resilient way [105].
5. Conclusions
This systematic review highlighted the growth of studies on One Health and climate change in recent decades. However, there is still a significant gap in knowledge regarding studies that relate climate change to arboviruses, zoonotic diseases, vector-borne diseases, and mental health from the perspective of One Health. Studies have shown that the effects of climate change such as heat waves, droughts, floods, air pollution, among others, directly and indirectly impact human, animal, and environmental health, affecting not only vulnerable groups such as women, children, and the elderly, but also more vulnerable populations such as indigenous and coastal communities. Thus, it is still necessary to develop more in-depth studies that serve as a basis for a better understanding of the groups analyzed and experimental studies that show data on the real impact of climate change on the biological cycle of disease vectors. It is also necessary to incorporate the holistic view and the complexities of systems in an interdisciplinary way to address human, environmental, and animal health issues by relating them to different variables, such as human activities.
6. Limitations
- ○
- Scale restriction: This review focused on global and national scales, which enabled a broad and systematic overview but excluded subnational studies (e.g., regional, state, and municipal).
- ○
- Loss of local detail: Excluding subnational studies means that finer-grained insights into specific vulnerabilities, exposure pathways, and adaptation strategies were not captured.
- ○
- Feasibility constraint: Including subnational studies would have produced an unmanageable number of articles, limiting the feasibility and clarity of the systematic synthesis.
- ○
- Nature of a review study: As a systematic review, this study synthesizes existing evidence without generating new primary data. While this general approach provides an organized and comprehensive mapping of the literature, it also implies inherent limitations in depth.
- ○
- Research opportunities: Precisely because of its broad and systematizing scope, this review highlights gaps and provides a foundation for more focused future studies at subnational levels, on specific populations, or on particular disease categories.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cli13100204/s1. Protocol; Figure S1. PRISMA report; Table S1: Search word groups; Table S2: Database; Table S3: Inclusion and exclusion criteria; Table S4: List of individual words; Table S5: List of words combined by group; Table S6: Climate events and their effects on health. Figure S2.1. Authors’ keywords for all categories of words searched including the words “climate change” and “one health”. Figure S2.2. Author keywords based on search terms including the words “climate change” and “one health”. (a) Health system, (b) Zoonotic diseases, (c) Vector-borne diseases, and (d) Arboviruses. Figure S2.3. Authors’ keywords for all categories of words searched excluding the words “climate change” and “one health”. Figure S2.4. Studies on one health and climate change. Figure S2.5. Studies on climate change and mental health.
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed this study: I.A.L.E. Collected and analyzed the data: I.A.L.E. Analysis and Data systematization: I.A.L.E., E.L.d.S. and Y.d.J.M. Software GeoExtract V1.2: Y.d.J.M. Wrote original draft: I.A.L.E. Wrote, reviewed & edited: I.A.L.E., M.E.B.F. and A.B.O.-F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was support by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and the Department of Science and Technology of the Secretariat of Science, Technology, Innovation and Health Complex of the Ministry of Health of Brazil (MoH) for the development of actions and the dissemination of products from the research project “IntegraClima: Integration of climate, health, and biodiversity data for disease risk zoning and participatory and integrative actions in traditional communities to raise awareness about the impacts of climate change: a Brazil-Peru-Mozambique cooperation” (grant number 444841/2023-7—A.B. Oliveira-Filho), the author Yago J. Martins received a scholarship from CNPQ (grant number 371612/2024-1).
Acknowledgments
We thank the Laboratory of Mangrove Ecology (LAMA), Institute of Coastal Studies (IECOS), and Study and Research Group on Vulnerable Populations (GEPPoV), both from the Federal University of Pará (UFPA) and Sarambuí Association, for providing logistical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- IPCC. AR5 Synthesis Report: Climate Change 2014. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/syr/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Zinsstag, J.; Crump, L.; Schelling, E.; Hattendorf, J.; Maidane, Y.O.; Ali, K.O.; Muhummed, A.; Umer, A.A.; Aliyi, F.; Nooh, F.; et al. Climate Change and One Health. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Lendrum, D.; Neville, T.; Schweizer, C.; Neira, M. Climate Change and Health: Three Grand Challenges. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciancalepore, S.; Schneider, M.C.; Kim, J.; Galan, D.I.; Riviere-Cinnamond, A. Presence and Multi-Species Spatial Distribution of Oropouche Virus in Brazil within the One Health Framework. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanello, M.; McGushin, A.; Napoli, C.D.; Drummond, P.; Hughes, N.; Jamart, L.; Kennard, H.; Lampard, P.; Rodriguez, B.S.; Arnell, N.; et al. The 2021 Report of the Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change: Code Red for a Healthy Future. Lancet 2021, 398, 1619–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weatherly, C.; Carag, J.; Zohdy, S.; Morrison, M. The Mental Health Impacts of Human-Ecosystem-Animal Relationships: A Systematic Scoping Review of Eco-, Planetary, and One Health Approaches. One Health 2023, 17, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, H.; Berg, C. A Comparison of Three Holistic Approaches to Health: One Health, EcoHealth, and Planetary Health. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO World Health Organization. Tripartite and UNEP Support OHHLEP’s Definition of “One Health”. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/01-12-2021-tripartite-and-unep-support-ohhlep-s-definition-of-one-health (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Whitmee, S.; Haines, A.; Beyrer, C.; Boltz, F.; Capon, A.G.; Dias, B.F.d.S.; Ezeh, A.; Frumkin, H.; Gong, P.; Head, P.; et al. Safeguarding Human Health in the Anthropocene Epoch: Report of The Rockefeller Foundation–Lancet Commission on Planetary Health. Lancet 2015, 386, 1973–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimmins, A.; Balbus, J.; Gamble, J.L.; Beard, C.B.; Bell, J.E.; Dodgen, D.; Eisen, R.J.; Fann, N.; Hawkins, M.D.; Herring, S.C.; et al. The Impacts of Climate Change on Human Health in the United States: A Scientific Assessment; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 1–312. [Google Scholar]
- Lebov, J.; Grieger, K.; Womack, D.; Zaccaro, D.; Whitehead, N.; Kowalcyk, B.; MacDonald, P.D.M. A Framework for One Health Research. One Health 2017, 3, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, W.J.M. Health Impacts of Climate Change and Ozone Depletion: An Ecoepidemiologic Modeling Approach. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, I.; Lemon, J.; Murnane, C.; Pet, I.; Vintila, T.; McCleery, D.; Callaway, T.; Douglas, A.; Stef, L.; Corcionivoschi, N. The One Health Aspect of Climate Events with Impact on Foodborne Pathogens Transmission. One Health 2024, 19, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.B.; Machalaba, C.; Baum, S.E.; Raufman, J.; Hill, S.E. Applying a One Health Lens to Understanding the Impact of Climate and Environmental Change on Healthcare-Associated Infections. Antimicrob. Steward. Healthc. Epidemiol. 2023, 3, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawankar, R.; Akdis, C.A.; Nadeau, K. Climate Change, Environment, and One Health. In Wellbeing, Values and Lifestyles: Towards a New Development Paradigm; Chaturvedi, S., Prabhu, K.S., Saha, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 193–205. ISBN 978-981-9747-30-6. [Google Scholar]
- Eyzaguirre, I.A.L.; Fernandes, M.E.B. Combining Methods to Conduct a Systematic Review and Propose a Conceptual and Theoretical Framework in Socio-Environmental Research. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramer, W.M.; Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kleijnen, J.; Franco, O.H. Optimal Database Combinations for Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews: A Prospective Exploratory Study. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateen, F.J.; Oh, J.; Tergas, A.I.; Bhayani, N.H.; Kamdar, B.B. Titles versus Titles and Abstracts for Initial Screening of Articles for Systematic Reviews. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 5, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukar, U.A.; Sayeed, M.S.; Razak, S.F.A.; Yogarayan, S.; Amodu, O.A.; Mahmood, R.A.R. A Method for Analyzing Text Using VOSviewer. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampsel, L.J. Voyant Tools. Music. Ref. Serv. Q. 2018, 21, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratinaud, P. IRAMUTEQ: Interface de R Pour Les Analyses Multidimensionnelles de Textes et de Questionnaires [Software]; 2009. Available online: http://www.iramuteq.org (accessed on 20 June 2025). (In French).
- GLOBIL. Mangrove Extent Countries Giri. Available online: https://globil-panda.opendata.arcgis.com/items/c3522b68c37c41b78f4c1c48f5a37159 (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Natural Earth. Natural Earth Database 2021. Available online: https://www.naturalearthdata.com/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Alexander, A. Sacred Ecology: Traditional Ecological Knowledge and Resource Management. Organ. Environ. 2001, 14, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyzaguirre, I. Climate Change and Health, version 1; Mendeley Data: London, UK, 2025.
- Shope, R. Global Climate Change and Infectious Diseases. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 96, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.H. Ecological Consequences of Atmospheric and Climate Change. Clim. Change 1991, 18, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, W.; Jetten, T.; Rotmans, J.; Niessen, L. Climate Change and Vector-Borne Diseases: A Global Modelling Perspective. Glob. Environ. Change 1995, 5, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.E.J.; Dye, C.; Kovats, R.S.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.H.; McMichel, A.J.; Woodward, A.; Cox, J.S.H. Early Effects of Climate Change: Do They Include Changes in Vector-Borne Disease? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 356, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.; Wilson, J.; Mahoney, R.; Anyamba, A.; Linthicum, K.; Myers, M. Climatic and Ecological Context of the 1994–1996 Ebola Outbreaks. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Prokopec, G.M.; Ceballos, L.A.; Cecere, M.C.; Gürtler, R.E. Seasonal Variations of Microclimatic Conditions in Domestic and Peridomestic Habitats of Triatoma Infestans in Rural Northwest Argentina. Acta Trop. 2002, 84, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.B. Population Health Needs beyond Ratifying the Kyoto Protocol: A Look at Occupational Deprivation. Rural Remote Health 2008, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.; Kauhala, K.; Holmala, K.; Smith, G.C. Rabies Risk in Raccoon Dogs and Foxes. Dev. Biol. 2008, 131, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Vuurst, P.; Escobar, L.E. Climate Change and Infectious Disease: A Review of Evidence and Research Trends. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2023, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso, A. Zika Threatens to Become a Huge Worldwide Pandemic. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henss, L.; Yue, C.; Kandler, J.; Faddy, H.M.; Simmons, G.; Panning, M.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Baylis, S.A.; Schnierle, B.S. Establishment of an Alphavirus-Specific Neutralization Assay to Distinguish Infections with Different Members of the Semliki Forest Complex. Viruses 2019, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, K.; Nath, D.; Nath, R.; Chen, W. Impact of Extreme Hot Climate on COVID-19 Outbreak in India. Geohealth 2020, 4, e2020GH000305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, P.F.; Murray, J.G.; Nunn, M.J. Managing Animal Disease Risk in Australia: The Impact of Climate Change. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2008, 27, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, G.; Beetch, J.E.; Heller, J.G.; Naqvi, O.H.; Kuhn, K.G. Assessing the Influence of Climate Change and Environmental Factors on the Top Tick-Borne Diseases in the United States: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2023, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutantou, M.; Drancourt, M.; Angelakis, E. Prevalence of Lyme Disease and Relapsing Fever Borrelia Spp. in Vectors, Animals, and Humans within a One Health Approach in Mediterranean Countries. Pathogens 2024, 13, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riebenbauer, K.; Czerny, S.; Egg, M.; Urban, N.; Kinaciyan, T.; Hampel, A.; Fidelsberger, L.; Karlhofer, F.; Porkert, S.; Walochnik, J.; et al. The Changing Epidemiology of Human Leishmaniasis in the Non-Endemic Country of Austria between 2000 to 2021, Including a Congenital Case. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0011875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, F.O.; Rich, K.M.; Boden, L.A.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Caipo, M.L.; Zimin-Veselkoff, N.; Alateeqi, A.M.; Baltenweck, I. The COVID-19 Pandemic and Global Food Security. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 578508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. One World, One Health: Combating Infectious Diseases in the Age of Globalization. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, M.; Leake, J.; Naranjo-Torres, J.; Valero, N.; Cabrera, J.C.; Rodríguez-Morales, A.J. Dengue Prediction in Latin America Using Machine Learning and the One Health Perspective: A Literature Review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, G.; Mailepessov, D.; Lim, X.F.; Chan, S.; How, C.B.; Humaidi, M.; Yeo, G.; Chong, C.S.; Lam-Phua, S.G.; Lee, R.; et al. Detection of Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Culex Mosquitoes in Singapore. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantima, N.; Ilukor, J.; Kaboyo, W.; Ademun, A.R.O.; Muwanguzi, D.; Sekamatte, M.; Sentumbwe, J.; Monje, F.; Bwire, G. The Importance of a One Health Approach for Prioritising Zoonotic Diseases to Focus on Capacity-Building Efforts in Uganda. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2019, 38, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.C.; Min, K.-D.; Romijn, P.C.; De Morais, N.B.; Montebello, L.; Manrique Rocha, S.; Sciancalepore, S.; Hamrick, P.N.; Uieda, W.; Câmara, V. de M.; et al. Fifty Years of the National Rabies Control Program in Brazil under the One Health Perspective. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepi, M.; Focardi, S. Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Aquaculture and Climate Change: A Challenge for Health in the Mediterranean Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health. 2021, 18, 5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.J. An Ethical Investigation into the Microbiome: The Intersection of Agriculture, Genetics, and the Obesity Epidemic. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1760712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jánová, E. Emerging and Threatening Vector-Borne Zoonoses in the World and in Europe: A Brief Update. Pathog. Glob. Health 2019, 113, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winch, P. Social and Cultural Responses to Emerging Vector-Borne Diseases. J. Vector Ecol. J. Soc. Vector Ecol. 1998, 23, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.C. Mosquito-Borne Arboviruses in Australia: The Current Scene and Implications of Climate Change for Human Health. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, H.; Carpenter, D.O. Effects of Climate Change on the Spread of Zika Virus: A Public Health Threat. Rev. Environ. Health 2018, 33, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, M.R.; Casas, I.; Victoria, A.M.; Carbonell, D.; Dávalos, D.M.; Delmelle, E.M. Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Regarding Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika in Cali, Colombia. Health Place 2020, 63, 102339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, C.J.; Borbor-Cordova, M.J.; Calvello-Hynes, E.; Diaz, A.; Lemery, J.; Stewart-Ibarra, A.M. Climate Variability, Vulnerability, and Natural Disasters: A Case Study of Zika Virus in Manabi, Ecuador Following the 2016 Earthquake. Geohealth 2017, 1, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colón-González, F.J.; Harris, I.; Osborn, T.J.; Steiner São Bernardo, C.; Peres, C.A.; Hunter, P.R.; Warren, R.; van Vuurene, D.; Lake, I.R. Limiting Global-Mean Temperature Increase to 1.5–2 °C Could Reduce the Incidence and Spatial Spread of Dengue Fever in Latin America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6243–6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumharn, W.; Piwngam, W.; Pilahome, O.; Ninssawan, W.; Jankondee, Y.; Chaochaikong, S. Effects of Meteorological Factors on Dengue Incidence in Bangkok City: A Model for Dengue Prediction. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 9, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andhikaputra, G.; Lin, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-C. Effects of Temperature, Rainfall, and El Niño Southern Oscillations on Dengue-like-Illness Incidence in Solomon Islands. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Beer, J.; Charrow, A. Climate Change and the Displaced Person: How Vectors and Climate Are Changing the Landscape of Infectious Diseases among Displaced and Migrant Populations. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outammassine, A.; Zouhair, S.; Loqman, S. Rift Valley Fever and West Nile Virus Vectors in Morocco: Current Situation and Future Anticipated Scenarios. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Kim, H. Immunoinformatics and Computational Approaches Driven Designing a Novel Vaccine Candidate against Powassan Virus. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurito, M.; Arias-Alzate, A. Current and Future Potential Distribution of Culex (Melanoconion) (Diptera: Culicidae) of Public Health Interest in the Neotropics. J. Med. Entomol. 2024, 61, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, S.K.; Barnard, M.; Frantz, R.M.; Spencer, J.A.; Rodarte, K.A.; Crooker, I.K.; Bartlow, A.W.; Romero-Severson, E.; Manore, C.A. Scoping Review of Culex Mosquito Life History Trait Heterogeneity in Response to Temperature. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, B.L.; Hyder, S.; Claes, F.; Karlsson, E.A. Ingrained: Rice Farming and the Risk of Zoonotic Spillover, Examples from Cambodia. One Health 2024, 18, 100696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustolin, M.; Pujhari, S.; Terradas, G.; Werling, K.; Asad, S.; Metz, H.C.; Henderson, C.A.; Kim, D.; Rasgon, J.L. In Vitro and In Vivo Coinfection and Superinfection Dynamics of Mayaro and Zika Viruses in Mosquito and Vertebrate Backgrounds. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0177822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhler, K.J.; Dibernardo, A.; Pilfold, N.W.; Harms, N.J.; Fenton, H.; Carriere, S.; Kelly, A.; Schwantje, H.; Aguilar, X.F.; Leclerc, L.-M.; et al. Widespread Exposure to Mosquitoborne California Serogroup Viruses in Caribou, Arctic Fox, Red Fox, and Polar Bears, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.-B.; Pei, Y.; Ye, Y.-T.; Shum, M.H.-H.; Cui, X.-M.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Pierce, M.P.; Zhao, L.; Wang, G.-P.; Wei, J.-T.; et al. Ecoclimate Drivers Shape Virome Diversity in a Globally Invasive Tick Species. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellone, R.; Lechat, P.; Mousson, L.; Gilbart, V.; Piorkowski, G.; Bohers, C.; Merits, A.; Kornobis, E.; Reveillaud, J.; Paupy, C.; et al. Climate Change and Vector-Borne Diseases: A Multi-Omics Approach of Temperature-Induced Changes in the Mosquito. J. Travel Med. 2023, 30, taad062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonita, I.; Halabicky, O.M.; Liu, J. Exposure to Wildfires Exposures and Mental Health Problems among Firefighters: A Systematic Review. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Mutavi, T.; Mburu, J.M.; Mathai, M. Prevalence of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Depression Among Internally Displaced Persons in Mogadishu-Somalia. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2023, 19, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, S.; Kornbluh, M.; Withers, M.C.; Grennan, G.; Ramanathan, V.; Mishra, J. Chronic Mental Health Sequelae of Climate Change Extremes: A Case Study of the Deadliest Californian Wildfire. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayta, S. The Effect of Air Pollution and Climate Change on Sleep. Nöropsikiyatri Arşiv 2024, 61, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, R.F.; Paxton, S.J.; Nagata, J.M.; Becker, A.E. The Impact of Climate Change on Eating Disorders: An Urgent Call for Research. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 56, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieronimi, A.; Elbel, J.; Schneider, M.; Wermuth, I.; Schulte-Körne, G.; Nowak, D.; Bose-O’Reilly, S. A Qualitative Study to Explain the Factors Influencing Mental Health after a Flooding. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni, O.; Salami, B.; Oluwasina, F.; Ojo, F.; Kennedy, M. Climate Change and African Migrant Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.P.; Jamieson, J.; Gibson, K.; Duffy, M.; Williamson, M.; Parr, H. Eco-Anxiety among Regional Australian Youth with Mental Health Problems: A Qualitative Study. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2024, 18, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, L.; Cox, B.; Nemery, B.; Deboosere, P.; Nawrot, T.S. High Temperatures Trigger Suicide Mortality in Brussels, Belgium: A Case-Crossover Study (2002–2011). Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ye, Z.; Lang, H.; Fang, Y. Climate Change and Depressive Disorders in Middle-Aged and Older People in China: A Quasi-Experimental Study. J. Environ. Psychol. 2023, 92, 102162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, J.; Haase, E. Women’s Mental Health and Climate Change Part II: Socioeconomic Stresses of Climate Change and Eco-Anxiety for Women and Their Children. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2023, 160, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, S.E.L.; Sanson, A.V.; Van Hoorn, J. The Psychological Effects of Climate Change on Children. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, P.R. Climate and Health. Science 1999, 285, 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patz, J.A.; Hahn, M.B. Climate change and human health: A one health approach. In One Health: The Human-Animal-Environment Interfaces in Emerging Infectious Diseases: Food Safety and Security, and International and National Plans for Implementation of One Health Activities; Mackenzie, J.S., Jeggo, M., Daszak, P., Richt, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 141–171. ISBN 978-3-642-35846-3. [Google Scholar]
- McMichael, A.J.; Woodruff, R.E.; Hales, S. Climate Change and Human Health: Present and Future Risks. Lancet 2006, 367, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillier, S.A.; Taleb, A.; Chaccour, E.; Aenishaenslin, C. Examining the Concept of One Health for Indigenous Communities: A Systematic Review. One Health 2021, 12, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Global. Arbovirus Initiative: Preparing for the next Pandemic by Tackling Mosquito-Borne Viruses with Epidemic and Pandemic Potential. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240088948 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Hotez, P.J. Ten Global “Hotspots” for the Neglected Tropical Diseases. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.K.; Mawson, A.R. Neglected Tropical Diseases: Epidemiology and Global Burden. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Anna, M.W.; Ferreira, M.L.; da Silva, L.F.; Côrtes, P.L. Climate Change and Arbovirus: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Climate 2025, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delrieu, M.; Martinet, J.-P.; O’Connor, O.; Viennet, E.; Menkes, C.; Burtet-Sarramegna, V.; Frentiu, F.D.; Dupont-Rouzeyrol, M. Temperature and Transmission of Chikungunya, Dengue, and Zika Viruses: A Systematic Review of Experimental Studies on Aedes Aegypti and Aedes Albopictus. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector-Borne Dis. 2023, 4, 100139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, C.W.; Turner, R.; Salifu, E.; Khan, S.; Stillings, M.; Tonner, R. Climate Change: Any dangers from antimicrobial resistant bacteria? In Microbiomes and the Global Climate Change; Lone, S.A., Malik, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 145–171. ISBN 978-981-334-508-9. [Google Scholar]
- Caminade, C.; McIntyre, K.M.; Jones, A.E. Impact of Recent and Future Climate Change on Vector-Borne Diseases. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2019, 1436, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojahed, N.; Mohammadkhani, M.A.; Mohamadkhani, A. Climate Crises and Developing Vector-Borne Diseases: A Narrative Review. Iran. J. Public Health 2022, 51, 2664–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.N.; Gage, K.L.; Khan, A.S. Potential Influence of Climate Change on Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases: A Review and Proposed Research Plan. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal Filho, W.; Ternova, L.; Parasnis, S.A.; Kovaleva, M.; Nagy, G.J. Climate Change and Zoonoses: A Review of Concepts, Definitions, and Bibliometrics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianconi, P.; Betrò, S.; Janiri, L. The Impact of Climate Change on Mental Health: A Systematic Descriptive Review. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 490206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, A.M.H.; Ataallah, A.G. Are Climate Change and Mental Health Correlated? Gen. Psychiatry 2021, 34, e100648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombley, J.; Chalupka, S.; Anderko, L. Climate Change and Mental Health. Am. J. Nurs. 2017, 117, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wheeler, S.A.; Zuo, A. Drought and Hotter Temperature Impacts on Suicide: Evidence from the Murray–Darling Basin, Australia. Clim. Change Econ. 2024, 15, 2350024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark-Ginsberg, A.; Sprague Martinez, L.; Scaramutti, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Salas-Wright, C.P.; Schwartz, S.J. Social Vulnerability Shapes the Experiences of Climate Migrants Displaced by Hurricane Maria. Clim. Dev. 2024, 16, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, J.M.; Rechkemmer, A.; Rai, A.; McManus, K.T. Public Health and Mental Health Implications of Environmentally Induced Forced Migration. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2019, 13, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadio, K.; Filippi, V.; Congo, M.; Scorgie, F.; Roos, N.; Lusambili, A.; Nakstad, B.; Kovats, S.; Kouanda, S. Extreme Heat, Pregnancy and Women’s Well-Being in Burkina Faso: An Ethnographical Study. BMJ Glob. Health 2024, 8, e014230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, H.; Rabito, F.; Danielson, L.; Takaro, T.K. Health Effects of Flooding in Canada: A 2015 Review and Description of Gaps in Research. Can. Water Resour. J./Rev. Can. Des Ressour. Hydr. 2016, 41, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, R.; Chen, X.; Qin, X. Does Extreme Temperature Exposure Take a Toll on Mental Health? Evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2023, 28, 486–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolvir, H.R.; Madadi, A.; Safarianzengir, V.; Sobhani, B. Monitoring and Analysis of the Effects of Atmospheric Temperature and Heat Extreme of the Environment on Human Health in Central Iran, Located in Southwest Asia. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, B.; van Loon, G.W.; Hipel, K.W.; Chiotha, S.; Orbinski, J. Health Impacts of Climate Change on Smallholder Farmers. One Health 2021, 13, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima-Camara, T.N. Arboviroses emergentes e novos desafios para a saúde pública no Brasil. Rev. Saúde Pública 2016, 50, 36. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhawra, J.; Skinner, K.; Favel, D.; Green, B.; Coates, K.; Katapally, T.R. The Food Equity and Environmental Data Sovereignty (FEEDS) Project: Protocol for a Quasi-Experimental Study Evaluating a Digital Platform for Climate Change Preparedness. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2021, 10, e31389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, C.; Latkin, C. Views of Psychiatrists and Psychiatry Trainees on Climate Change: Distress, Training Needs, and Envisioned Role. Acad. Psychiatry 2024, 48, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, A.A. Wild Canids as Sentinels of Ecological Health: A Conservation Medicine Perspective. Parasites Vectors 2009, 2, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, N.; Taylor-Robinson, A.W. Confronting the Emerging Threat to Public Health in Northern Australia of Neglected Indigenous Arboviruses. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comtesse, H.; Ertl, V.; Hengst, S.M.C.; Rosner, R.; Smid, G.E. Ecological Grief as a Response to Environmental Change: A Mental Health Risk or Functional Response? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).