Influence of Climatic Factors on the Occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Food Poisoning in the Republic of Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Data Analysis and Statistical Processing
3. Results
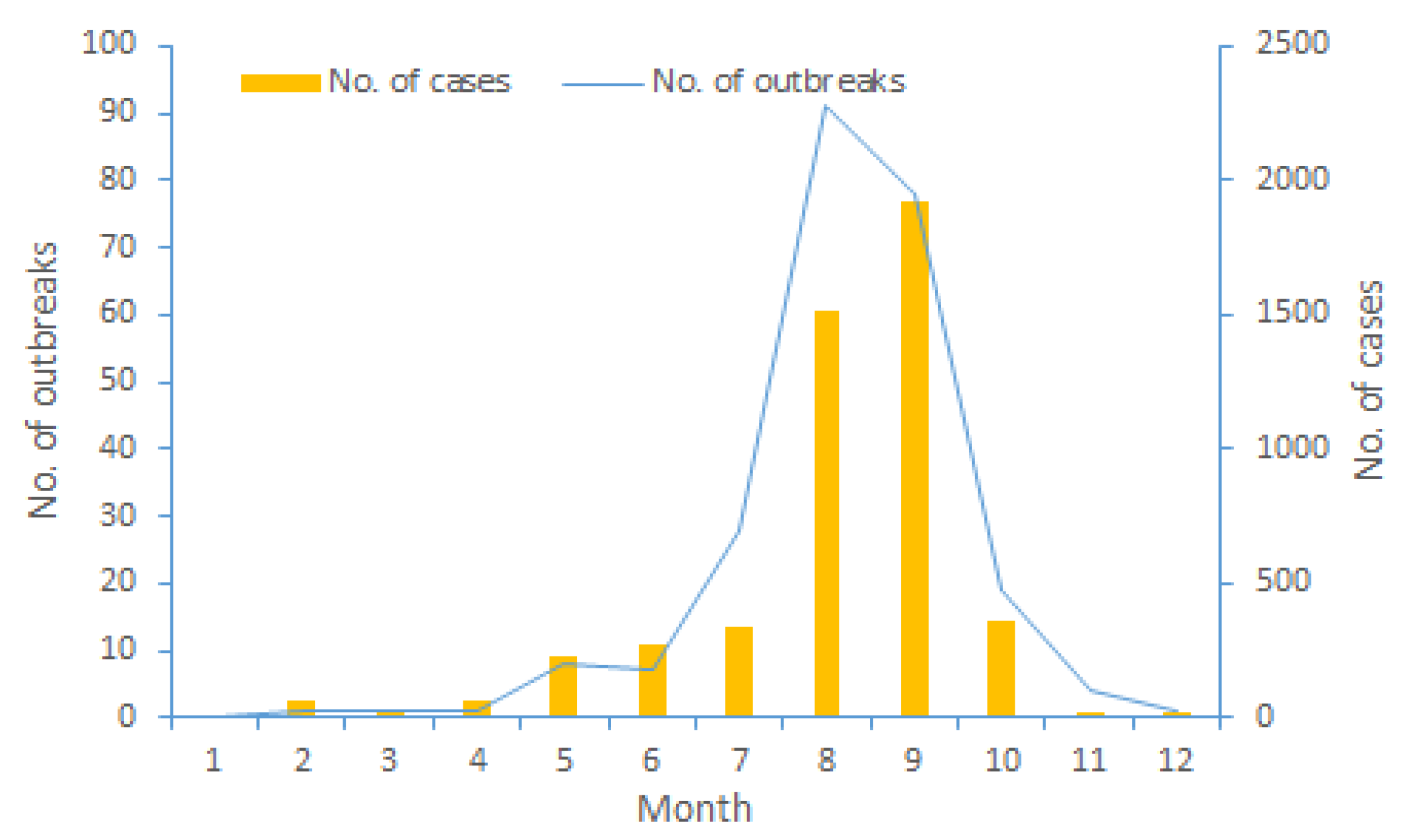
3.1. Trends in the Occurrence of V. parahaemolyticus Cases
3.2. Changes in Climatic Factors
3.3. Relationship between the Occurrence of V. parahaemolyticus Food Poisoning and Climatic Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Ket Findings
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gugliandolo, C.; Carbone, M.; Fera, M.T.; Irrera, G.P.; Maugeri, T.L. Occurrence of potentially pathogenic vibrios in the marine environment of the Straits of Messina (Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA). Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Gastroenteritis; KDCA: Osong, Republic of Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Fisheries Science of Korea. Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Available online: https://m.nifs.go.kr/sub8/sub7_1_2.jsp (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Kim, J.G. Food Hygiene and Sanitation; Shinkwang Publishing, Co.: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Letchumanan, V.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A review on the pathogenesis, prevalence, and advance molecular identification techniques. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havelaar, A.H.; Brul, S.; de Jong, A.; de Jonge, R.; Zwietering, M.H.; ter Kuile, B.H. Future challenges to microbial food safety. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, S79–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daelman, J.; Jacxsens, L.; Devlieghere, F.; Uyttendaele, M. Microbial safety and quality of various types of cooked chilled foods. Food Control 2013, 30, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Spiegel, M.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Marvin, H.J.P. Effects of climate change on food safety hazards in the dairy production chain. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.J. Current status of food poisoning in Korea and countermeasures. Ind. Hyg. 1999, 136, 4–14. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, A.; Nunes, M.L.; Moore, S.K.; Strom, M.S. Climate change and seafood safety: Human health implications. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1766–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendizabal, M.; Sepulveda, J.; Torp, P. Climate change impacts on flood events and its consequences on human in Deba River. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Parmesan, C.; Yohe, G. A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature 2003, 421, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavia, D.; Field, J.C.; Boesch, D.F.; Buddemeier, R.W.; Burkett, V.; Cayan, D.R.; Fogarty, M.; Harwell, M.A.; Howarth, R.W.; Mason, C.; et al. Climate change impacts on U.S. coastal and marine ecosystems. Estuaries 2002, 25, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.R.; Post, E.; Convey, P.; Menzel, A.; Parmesan, C.; Beebee, T.J.; Fromentin, J.M.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Bairlein, F. Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature 2002, 416, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Stockley, L.; Rangdale, R.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Environmental occurrence and clinical impact of Vibrio vulnificus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A European perspective. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, L.H.; Kang, Y.Q.; Suh, Y.S. Relationship between sea surface temperature and air temperature variation depend on time scale at coastal stations in Korea. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2000, 9, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.G. Variations in catches of fisheries according to the climate change of Korea. J. Soc. Disaster Inf. 2022, 18, 194–201. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Food Poisoning Outbreak Statistics; Ministry of Food and Drug Safety: Osong, Republic of Korea, 2002–2017. Available online: https://www.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/portal/healthyfoodlife/foodPoisoningStat.do?menu_no=4425&menu_grp=MENU_NEW02 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Statistics Korea (SK). Food Poisoning Statistics; SK: Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2018; Available online: https://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=145&tblId=DT_145012_A009&conn_path=I2 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA). Climate Perspectives on the Korean Peninsula; KMA: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2021. Available online: https://data.kma.go.kr/cmmn/main.do (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Lee, Y.W.; Kim, J.G. A study on the trend of food poisoning outbreaks, reported cases, in Korea. J. Food Hyg. Saf. 1987, 2, 215–237. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.W.; Kim, J.G. A review study of food poisoning in Korea. J. Food Hyg. Saf. 1989, 4, 199–255. [Google Scholar]
- Parveen, S.; Jacobs, J.; Ozbay, G.; Chintapenta, L.K.; Almuhaideb, E.; Meredith, J.; Ossai, S.; Abbott, A.; Grant, A.; Brohawn, K.; et al. Seasonal and geographical differences in total and pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus levels in seawater and oysters from the Delaware and Chesapeake Bays determined using several methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01581-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzulli, L.; Grande, C.; Reid, P.C.; Hélaouët, P.; Edwards, M.; Höfle, M.G.; Brettar, I.; Colweli, R.R.; Pruzzo, C. Climate influence on Vibrio and associated human diseases during the past half-century in the coastal North Atlantic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5062–E5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumfield, K.D.; Chen, A.J.; Gangwar, M.; Usmani, M.; Hasan, N.A.; Jutla, A.S.; Huq, A.; Colwell, R.R. Environmental factors influencing occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e00307-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, H.-I.; Jan, M.-S.; Chi, H.-J. Impacts of Climatic Variability on Vibrio parahaemolyticus Outbreaks in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.D. The biology of Vibrio vulnificus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetz, J.J.; Blackwood, A.D.; Fries, J.S.; Williams, Z.F.; Noble, R.T. Quantification of Vibrio vulnificus in an estuarine environment: A multi-year analysis using QPCR. Estuaries Coast 2014, 37, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, W.; Gutierrez, J.; Remmenga, M.D.; Nishiguchi, M.K. Salinity and temperature effects on physiological responses of Vibrio fischeri from diverse ecological niches. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.-I.; Myung, G.-E.; Choi, E.-J.; Soh, S.-M.; Park, G.-J.; Son, T.-J. Distribution of pathogenic Vibrios in the aquatic environment adjacent to coastal areas of South Korea and analysis of the environmental factors affecting their occurrence. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2018, 44, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA). Available online: https://vibrio.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/ (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Nam, J.H.; Lee, D.Y. Prevalence and characteristics of pathogenic Vibrio spp. in Korea, 2012. Public Health Wkly. Rep. 2013, 6, 405–410. [Google Scholar]

| Year | Average Temp. (°C) | Maximum Temp. (°C) | Minimum Temp. (°C) | Precipitation (mm) | No. of Days with Rainfall | Daytime Hours | Relative Humidity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 12.6 | 18.1 | 7.8 | 1463.1 | 105.0 | 2284.3 | 66 |
| 2003 | 12.5 | 17.7 | 8.0 | 1856.1 | 120.7 | 2055.0 | 68 |
| 2004 | 13.2 | 19.0 | 8.2 | 1454.6 | 101.4 | 2336.7 | 65 |
| 2005 | 12.4 | 17.9 | 7.6 | 1285.3 | 102.5 | 2286.4 | 65 |
| 2006 | 12.9 | 18.4 | 8.3 | 1420.3 | 103.8 | 2073.3 | 67 |
| 2007 | 13.3 | 18.7 | 8.7 | 1442.1 | 113.9 | 1937.1 | 69 |
| 2008 | 13.0 | 18.5 | 8.2 | 989.7 | 101.2 | 2114.4 | 67 |
| 2009 | 13.0 | 18.6 | 8.2 | 1203.0 | 105.6 | 2121.9 | 66 |
| 2010 | 12.7 | 18.0 | 8.1 | 1442.9 | 126.1 | 1970.4 | 68 |
| 2011 | 12.4 | 17.7 | 7.8 | 1620.5 | 113.1 | 2058.8 | 66 |
| 2012 | 12.3 | 17.6 | 7.8 | 1471.9 | 115.9 | 2189.5 | 66 |
| 2013 | 12.9 | 18.4 | 8.2 | 1162.4 | 111.1 | 2335.0 | 68 |
| 2014 | 13.1 | 18.6 | 8.4 | 1158.4 | 111.7 | 2231.1 | 68 |
| 2015 | 13.5 | 18.9 | 8.7 | 939.2 | 112.9 | 2277.1 | 69 |
| 2016 | 13.6 | 18.9 | 9.0 | 1264.1 | 109.5 | 2243.5 | 69 |
| 2017 | 13.1 | 18.8 | 8.1 | 964.4 | 100.0 | 2482.0 | 66 |
| Factors | No. of Outbreaks | Average Temp. (°C) | Maximum Temp. (°C) | Minimum Temp. (°C) | Precipitation (mm) | No. of Days with Rainfall | Daytime Hours | Relative Humidity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of outbreaks | 1.000 | 0.469 *** | 0.451 *** | 0.489 *** | 0.442 *** | 0.400 *** | −0.242 ** | 0.509 *** |
| Average temp. (°C) | 0.469 *** | 1.000 | 0.996 *** | 0.996 *** | 0.679 *** | 0.602 *** | −0.041 | 0.788 *** |
| Maximum temp (°C) | 0.451 *** | 0.996 *** | 1.000 | 0.986 *** | 0.637 *** | 0.549 *** | −0.028 | 0.747 *** |
| Minimum temp. (°C) | 0.489 *** | 0.996 *** | 0.986 *** | 1.000 | 0.713 *** | 0.643 *** | −0.114 | 0.829 *** |
| Precipitation (mm) | 0.442 *** | 0.679 *** | 0.637 *** | 0.713 *** | 1.000 | 0.873 *** | −0.472 *** | 0.737 *** |
| No. of days with rainfall | 0.400 *** | 0.602 *** | 0.549 *** | 0.643 *** | 0.873 *** | 1.000 | −0.578*** | 0.725 *** |
| Daytime hours | −0.242 ** | −0.041 | 0.028 | −0.114 | −0.472 *** | −0.578 *** | 1.000 | −0.532 *** |
| Relative humidity (%) | 0.509 *** | 0.788 *** | 0.747 *** | 0.829 *** | 0.737 *** | 0.725 *** | −0.532 *** | 1.000 |
| Unstandardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | VIF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | ||||
| (Constant) | 6.822 | 1.820 | 3.748 | 0.000 | |
| Minimum temperature | 0.807 | 0.166 | 4.853 | 0.000 | 0.016 |
| Precipitation | −0.015 | 0.003 | −4.882 | 0.000 | 0.337 |
| Maximum temperature | −0.496 | 0.161 | −3.081 | 0.002 | 0.019 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-G. Influence of Climatic Factors on the Occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Food Poisoning in the Republic of Korea. Climate 2024, 12, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli12020025
Kim J-G. Influence of Climatic Factors on the Occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Food Poisoning in the Republic of Korea. Climate. 2024; 12(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli12020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jong-Gyu. 2024. "Influence of Climatic Factors on the Occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Food Poisoning in the Republic of Korea" Climate 12, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli12020025
APA StyleKim, J.-G. (2024). Influence of Climatic Factors on the Occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Food Poisoning in the Republic of Korea. Climate, 12(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli12020025






