Extreme Coastal Water Levels Evolution at Dakar (Senegal, West Africa)
Abstract
1. Introduction
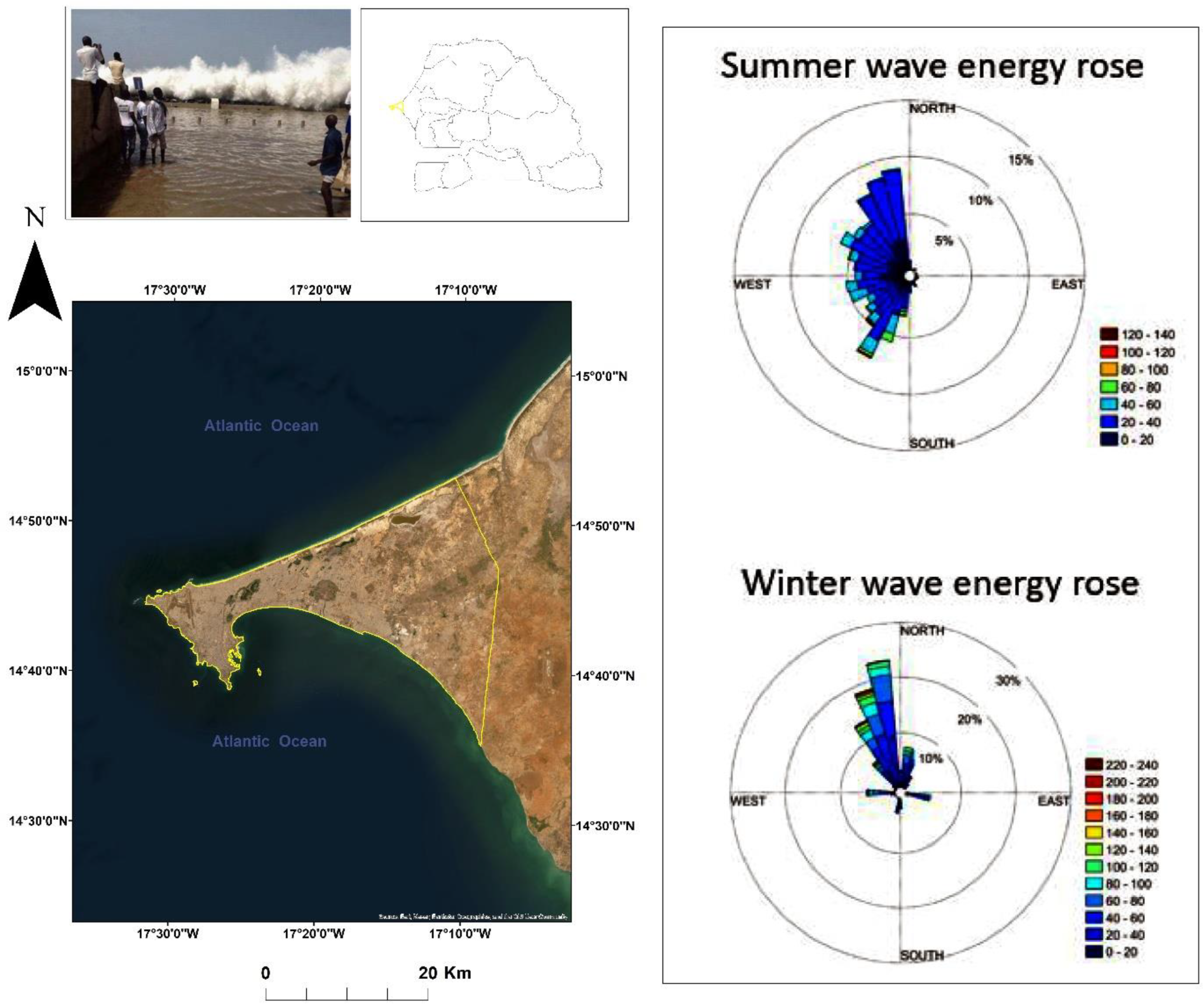
2. Presentation of the Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Hydrodynamic and Meteorological Data
3.2. Quantification of Extreme Coastal Water Level (ECWL)
4. Results
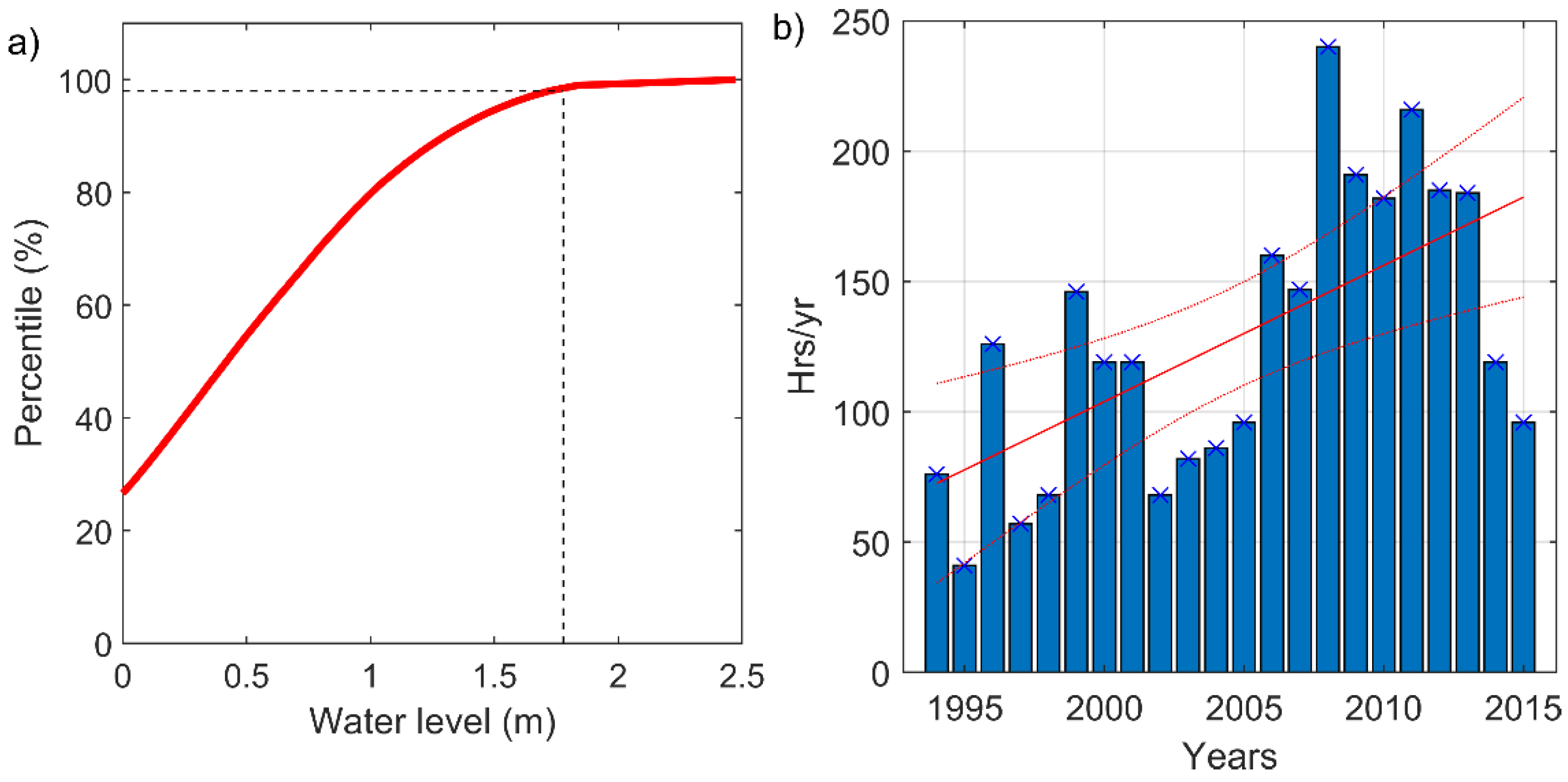
4.1. The Occurrence of Coastal Flooding
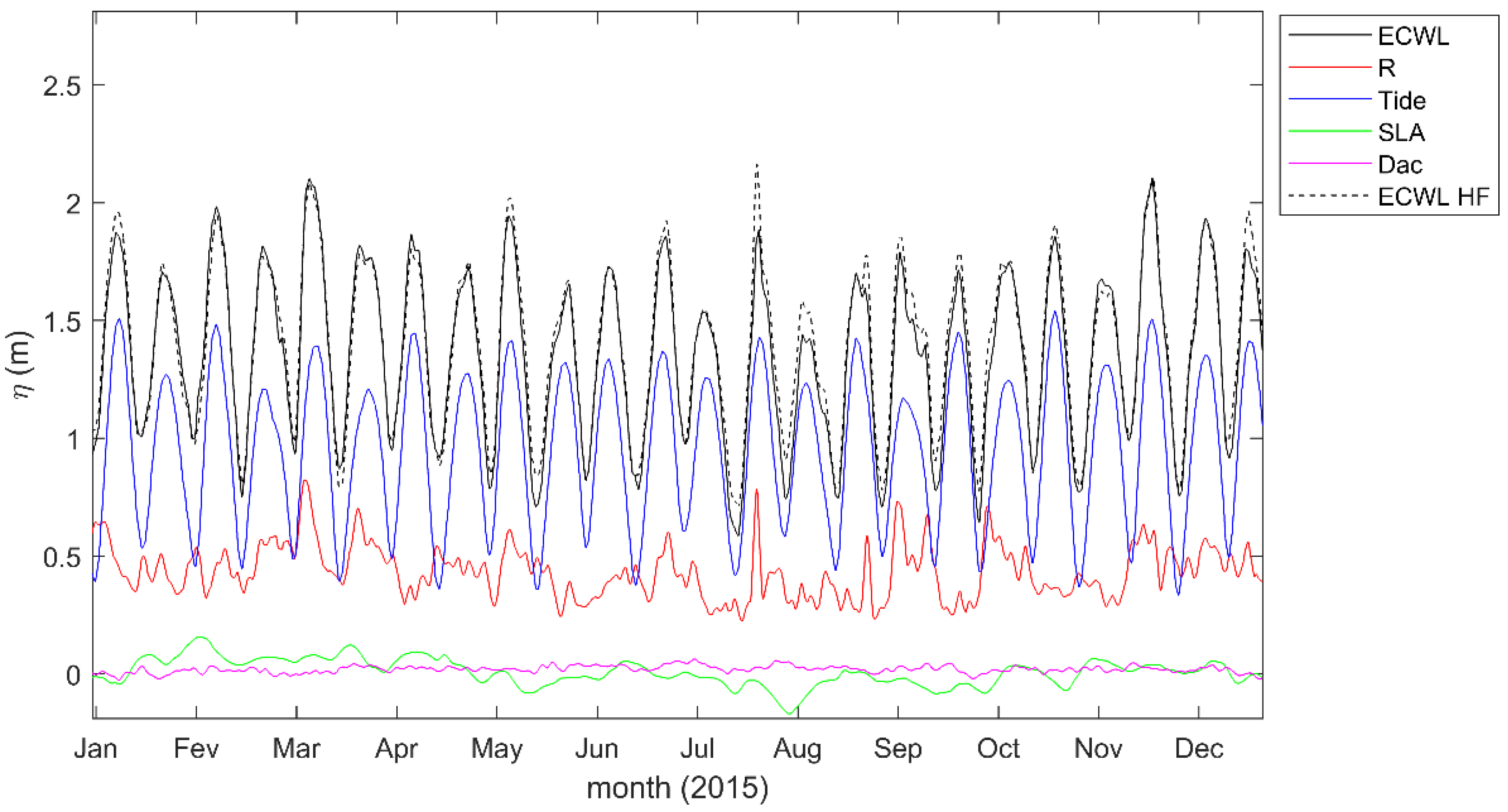
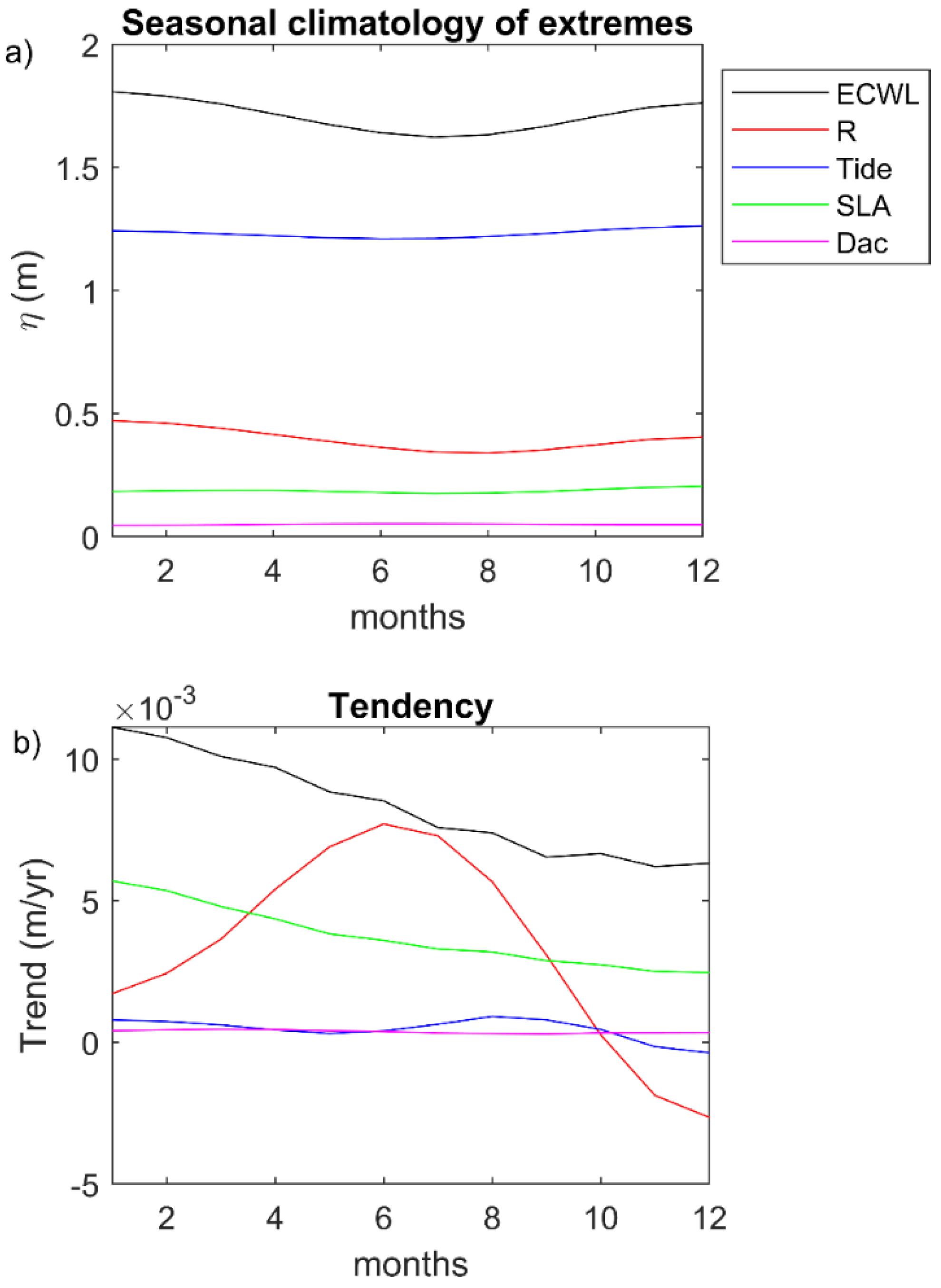
4.2. Hydrodynamic Factors Contributing to Coastal Flooding
4.3. Trend of Evolution of Extreme Coastal Water Levels in Dakar
4.4. Seasonality and Origin of Swells
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulp, S.A.; Strauss, B.H. New elevation data triple estimates of global vulnerability to sea-level rise and coastal flooding. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almar, R.; Ranasinghe, R.; Bergsma, E.W.J.; Diaz, H.; Melet, A.; Papa, F.; Vousdoukas, M.; Athanasio, P.; Dada, O.; Almeida, P.L.; et al. A global analysis of extreme coastal water levels with implications for potential coastal overtopping. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauer, M.E.; Hardy, D.; Kulp, S.A.; Mueller, V.; Wrathall, D.J.; Clark, P.U. Assessing population exposure to coastal flooding due to sea level rise. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masselink, G.; Castelle, B.; Scott, T.; Dodet, G.; Suanez, S.; Jackson, D.; Floc’h, F. Extreme wave activity during 2013/2014 winter and morphological impacts along the Atlantic coast of Europe, Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodet, G.; Melet, A.; Ardhuin, F.; Bertin, X.; Idier, D.; Almar, R. The contribution of wind-generated waves to coastal sea-level changes. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 1563–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melet, A.; Meyssignac, B.; Almar, R.; Le Cozannet, G. Under-estimated wave contribution to coastal sea-level rise. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melet, A.; Almar, R.; Hemer, M.; Le Cozannet, G.; Meyssignac, B.; Ruggiero, P. Contribution of wave setup to projected coastal sea level changes. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2020JC016078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, S.; Barnard, P.L.; Fletcher, C.H.; Frazer, N.; Erikson, L.; Storlazzi, C.D. Doubling of coastal flooding frequency within decades due to sea-level rise. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, M.; Rohmer, J.; Vousdoukas, M.I.; Mentaschi, L.; Le Gozannet, G.; Amores, A. Increased extreme coastal water levels due combined action of sturm surges and wind waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 4356–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodworth, P.L.; Melet, A.; Marcos, M.; Ray, R.D.; Wöppelmann, G.; Sasaki, Y.N.; Cirano, M.; Hibbert, A.; Huthnance, J.M.; Monserrat, S.; et al. Forcing factors affecting sea level changes at the coast. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 1351–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, O.; Almar, R.; Morand, P.; Ménard, F. Towards West African coastal social-ecosystems sustainability: Interdisciplinary approaches. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 211, 105746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, M.; Woodworth, P.L. Changes in extreme high water levels based on a quasi-global tide-gauge data set. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, C10011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousdoukas, M.I.; Almeida, L.P.; Ferreira, O. Modelling storm-induced beach morphological change in a meso-tidal, reflective beach using XBeach. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 1916–1920. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/26482510 (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Vousdoukas, M.I.; Voukouvalas, E.; Mentaschi, L.; Dottori, F.; Giardino, A.; Bouziotas, D.; Bianchi, A.; Salamon, P.; Feyen, L. Developments in large-scale coastal flood hazard mapping. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 1841–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, T.; Haigh, I.D.; Nicholls, R.J.; Arns, A.; Dangendorf, S.; Hinkel, J.; Slangen, A.B.A. Understanding extreme sea levels for broad-scale coastal impact and adaptation analysis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, S.; Aguilar, S.S.; Niekerk, L.V.; Luck-Voger, M.; Vafeidis, A.T. Investigating the interaction of waves and river discharge during compound flooding at breede estuary, South Africa. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, J.C. Inondations urbaines en Amérique Latine: Réflexions sur le rôle des facteurs de risque. Front. Flood Res. 2006, 305, 123–141. [Google Scholar]
- Boucharel, J.; Almar, R.; Kestenare, E.; Jin, F.F. On the influence of ENSO complexity on Pan-Pacific coastal wave extremes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2115599118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousdoukas, M.I.; Clarke, J.; Ranasinghe, R.; Reimann, L.; Khalaf, N.; Duong, T.M.; Simpson, N.P. African heritage sites threatened as sea-level rise accelerates. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijendijk, A.; Hagenaars, G.; Ranasinghe, R.; Baart, F.; Donchyts, G.; Aarninkhof, S. The state of the world’s beaches. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, B.; Angnuureng, D.B.; Morand, P.; Almar, R. A review on coastal erosion and flooding risks and best management practices in West Africa: What has been done and should be done. J. Coast. Conserv. 2020, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hzami, A.; Heggy, E.; Amrouni, O.; Mahé, G.; Maanan, M.; Abdeljaouad, S. Alarming coastal vulnerability of the deltaic and sandy beaches of North Africa. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennesser, Y.; Terrier, M.; Said, V. The large coastal cities of North Africa facing climate change and natural hazards. Geosci. BRGM Mag. A Sustain. Earth 2016, 21, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Ovono, Z.M.; Pottier, P. Flood Risk in the Small Urban Coastal Slopes of Libreville (Gabon). Example of Ogombié and Inongui. Available online: https://cahiers-nantais.fr/index.php?id=1166 (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Tchindjang, M.; Mbevo, F.; Bodpa, A. Construire Ville Portuaire de demain en Afrique Atlantique. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332371792_Construire_Ville_Portuaire_de_demain_en_Afrique_Atlantique (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Almar, R.; Kestenare, E.; Boucharel, J. On the key influence of remote climate variability from Tropical Cyclones, North and South Atlantic mid-latitude storms on the Senegalese coast (West Africa). Environ. Res. Commun. 2019, 1, 071001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, I.A.; De Murieta, E.S.; Losada, I.; Toimil, A.; Torres, S.; Markanday, A.; Briones, A. Coastal Flooding and Erosion under Climate Change: Risk Assessment Risk in Dakar. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/6035738#.Y6khYxVByUk (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Woodruff, J.D.; Irish, J.L.; Camargo, S.J. Coastal flooding by tropical cyclones and sea-level rise. Nature 2013, 504, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Z.; Vuik, V.; Wen, J.; Gao, H.; Bouma, T.J. Morphological wave attenuation of the nature-based flood defense: A case study from Chongming Dongtan Shoal. China Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diongue, M. Urban periphery and flood risks in Dakar (Senegal): The case of Yeumbeul Nord. Eso Work. Doc. 2014, 37, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ndao, M. Dynamics and Environmental Management from 1970 to 2010 of Wetlands in Senegal: Study of Land Use by Remote Sensing of the Niayes with Djiddah Thiaroye Kao (in Dakar), Mboro (in Thiès and Saint-Louis). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toulouse, Toulouse, French, 2012; 372p. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.G.; Montoliu-Munoz, M.; Gueye Nd, F.D. Preparing to manage natural hazards and climate change risks. In Dakar Senegal. A Spatial and Institutional Approach; The World Bank Géoville: Tokyo, Japan, 2009; 90p. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, S.; Rudant, J.P.; Ba, K.; Ndoye, B. Remote sensing and management of natural disasters: Application to the study of urban flooding of Saint-Louis and Gulling due to water erosion in Nioro du Rip (Senegal). Rev. Teledetect. 2009, 8, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Cisse, O. Les Inondations à Dakar; Éditions Karthala: Paris, France, 2018; 322p. [Google Scholar]
- Breilh, J.F.; Chaumillon, E.; Bertin, J. Improve of a static flooding method and application to the case of the Xynthia Storm. XIIth J. Natl. Conf. Coast. Eng.—Civ. Cherbg. 2012, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisse, C.O.T.; Sagne, P.; Ba, K.; Fall, B.; Sy, B.A.; Marone, A. Modélisation des niveaux d’eau extrêmes sur les plages sableuses de Malibu, de Gadaye et de Malika (Dakar, Sénégal) consécutive à la tempête du 19 novembre 2018. Eur. Sci. J. 2022, 18, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldi, C.; Strass, B.H.; Zervas, C.E. Modelling sea level rise impacts on storm surges along us coasts. Envr. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 014032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, D.; Mora, O.; Menthière, N.; Bethinger, A. Sea level rise: Consequences and anticipations by 2100, the light of foresight. Study Rep. Natl. Environ. Res. Alliance 2019, 51, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Ndour, A. Evolution Morpho-Sédimentaire et Impacts des Ouvrages de Protection sur le Littoral de Dakar, Petite Côte. Ph.D. Thesis, Cheikh Anta Diop University in Dakar, Dakar, Senegal, 2015; 243p. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhoum, P.W.; Niang, I.; Sambou, B.; Diaw, A.T. A peninsula in coastal erosion? Dakar, the Senegalese capital facing sea rise in the context of climate change. Environ. Water Sci. Public Health Territ. Intell. 2018, 2, 91–108. Available online: http://revues.imist.ma/?journal=ewash-ti/ (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- MOLOA (West African coastline observation mission). Reporting of Hazards Due to Extreme Coastal/Sea Weather Events. Available online: https://ocean-climate.org/en/west-african-regional-coastal-observatory-orloa/ (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Diallo, S. Geomorphological Evolution of the Coastline on the Little Coast in Dakar. Master’s Thesis, Cheikh Anta Diop University in Dakar, Dakar, Senegal, 1982; 117p. [Google Scholar]
- Guerin, K. Dynamics of the Sandy Coastline from Thiaroye to Bargny (Bay of Goree-Senegal). Master’s Thesis, University of Paris 1-Sorbonne-Panthéon, Paris, France, 2003; 198p. [Google Scholar]
- Turmine, V. Coastal Dynamics between Mbour and Joal; University of Paris VII Denis Diderot: Paris, France, 2000; 255p. [Google Scholar]
- Carrere, L.; Lyard, F.H.; Cancet, M.; Guillot, A. Finite Element Solution FES2014, a New Tidal Model–Validation Results and Perspectives for Improvements. In Proceedings of the ESA Living Planet Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Marti, F.; Cazenave, A.; Birol, F.; Passaro, M.; Léger, F.; Niño, F.; Almar, F.; Benveniste, J.; Legeais, J.F. Altimetry-based sea level trends along the coasts of western Africa. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 504–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idier, D.; Bertin, X.; Thompson, P.; Pickering, M.D. Interactions between mean sea level, tide, surge, waves and flooding: Mechanisms and contributions to sea level variations at the coast. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 1603–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsma, E.W.; Almar, R.; Anthony, E.J.; Garlan, T.; Kestenare, E. Wave variability along the world’s continental shelves and coasts: Monitoring opportunities from satellite earth observation. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 3236–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfai, M.A.; King, L. Coastal flood management in Semarang, Indonesia. Environ. Geol. 2007, 55, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Esteban, M.; Mikami, T.; Fuji, D. Projection of coastal flood in 2050 Jakarta. Urban Clim. 2016, 17, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, V.W.; Dusek, G.; Obeysekera, J.; Marra, J.J. Patterns and Projections of High Tide Flooding a Long the U.S. Coastaline Using a Common Impct Threshold; NOAA Technical Report NOS CO-OPS; NOAA, NOS Center for Operational Oceanographic Products and Services: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2018; Volume 86, 56p.
- Li, Y.; Zeng, C.; Yihan, Z.; Hu, P.; Sun, T.; Hou, Y.; Mo, D.; Wang, D. Experimental Study of Overtopping on Sea Dikes and Coastal Flooding Under the Coupled Processes of Tides and Waves. China Ocean. Eng. 2022, 36, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonte, Y. Effect of Swash on the Erosion of a High Beach Escarpment. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Caen Lower Normandy, Caen, France, 2013; 163p. [Google Scholar]
- Sergent, P.; Prevot, G.; Trmal, C. Renforcement des Ouvrages Situés en Faibles Profondeurs vis-à-vis de la Montée du Niveau des Mers. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256306084_RENFORCEMENT_DES_OUVRAGES_SITUES_EN_FAIBLES_PROFONDEURS_VIS-A-VIS_DE_LA_MONTEE_DU_NIVEAU_DES_MERS (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Costa, S. Sea level rise and response strategies: The case of the Normandy-Picardy coastline. Ann. De Géographie 1995, 107, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Zwiers, F.W.; Swail, V.R. North Atlantic Ocean wave cliamte change scenarios for the twebty first century. J. Clim. 2003, 17, 2368–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, N.; Ruggiero, P. The influence of seasonal to interannual nearshore profile variability on extreme water levels: Modeling wave runup on dissipative beaches. Coast. Eng. 2016, 115, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almar, R.; Kestenare, E.; Reyns, J.; Jouanno, J.; Anthony, E.J.; Laibi, R.; Hemer, M.; Du Penhoat, Y.; Ranasinghe, R. Response of the Bight of Benin (Gulf of Guinea, West Africa) coastline to anthropogenic and natural forcing, Part1: Wave climate variability and impacts on the longshore sediment transport. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 110, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.G.; Hemer, M.A.; Hendon, H.H.; McInnes, K.L. Southern annular mode impacts on global ocean surface waves. Ocean. Model. 2018, 129, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochet, A.; Dodet, G.; Ardhuin, F.; Hemer, M.; Young, I. Sea State Decadal Variability in the North Atlantic: A Review. Climate 2021, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemer, M.; Chruch, J.-A.; Hunter, J.-R. Variability and trends in the directional wave climate of the Southern Hemisphere. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semedo, A.; Suselj, K.; Rutgersson, A.; Sterl, A. A global view on the wind sea and swell climate and variability from ERA-40. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 1461–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.R.; Zieger, S.; Babanin, A.V. Global trends in wind speed and wave height. Science 2011, 332, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemer, M.; Fan, Y.; Mori, N.; Semedo, A.; Wang, X. Projected changes in wave climate from a multi-model ensemble. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Feng, Y.; Swail, V.R. Changes in global ocean wave heights as projected using multimodel CMIP5 simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, R. Intensification of extratropical cyclones associated with the polar jet change in the CMIP5 global warming projections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L19707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semedo, A.; Weisse, R.; Behrens, A.; Sterl, A.; Bengtsson, L.; Günther, H. Projection of global wave climat change toward the end of the twenty-firsts century. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 8269–8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa, G.; Shaffrey, L.C.; Hodges, K.I.; Sansom, P.G.; Stephenson, D.B. A multimodel assessment of future projections of North Atlantic and European extratropical cyclones in the CMIP5 climate models. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 5846–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Wong, P.P.; Burkett, V.R.; Codignotto, J.O.; Hay, J.E.; McLean, R.F.; Ragoonaden, S.; Woodroffe, C.D. Coastal Systems and Low-Lying Areas. Climate Change: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. In Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Parry, M.L., Canziani, O.F., Palutikof, J.P., van der Linden, P.J., Hanson, C.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 315–356. [Google Scholar]
- Sterl, A.; den Brink, V.; De Vries, H.; Haarsma, H.; van Meijgaard, R.R. An ensemble study of extreme storm surge related water levels in the North Sea in a changing climate. Ocean Sci. 2009, 5, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.; Almar, R.; Besset, M.; Reyns, J.; Laibi, R.; Ranasinghe, R.; Abessolo Ondoa, G.; Vacchi, M. Response of the Bight of Benin (Gulf of Guinea, West Africa) coastline to anthropogenic and natural forcing, Part 2: Sources and patterns of sediment supply, sediment cells, and recent shoreline change. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 173, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sea Level Component | Trend (mm/an) | Interannual Variability (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| ECWL | 8.4 * | 28.3 |
| R | 3.2 | 10.1 |
| SLA | 3.7 * | 22.3 |
| Dac | <1 | 2.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cissé, C.O.T.; Almar, R.; Youm, J.P.M.; Jolicoeur, S.; Taveneau, A.; Sy, B.A.; Sakho, I.; Sow, B.A.; Dieng, H. Extreme Coastal Water Levels Evolution at Dakar (Senegal, West Africa). Climate 2023, 11, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli11010006
Cissé COT, Almar R, Youm JPM, Jolicoeur S, Taveneau A, Sy BA, Sakho I, Sow BA, Dieng H. Extreme Coastal Water Levels Evolution at Dakar (Senegal, West Africa). Climate. 2023; 11(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli11010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleCissé, Cheikh Omar Tidjani, Rafael Almar, Jean Paul Marcel Youm, Serge Jolicoeur, Adelaide Taveneau, Boubou Aldiouma Sy, Issa Sakho, Bamol Ali Sow, and Habib Dieng. 2023. "Extreme Coastal Water Levels Evolution at Dakar (Senegal, West Africa)" Climate 11, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli11010006
APA StyleCissé, C. O. T., Almar, R., Youm, J. P. M., Jolicoeur, S., Taveneau, A., Sy, B. A., Sakho, I., Sow, B. A., & Dieng, H. (2023). Extreme Coastal Water Levels Evolution at Dakar (Senegal, West Africa). Climate, 11(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli11010006






